The Reversible Methylation of m6A Is Involved in Plant Virus Infection
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. The Discovery of N6-Methyladenosine (m6A) in Viral RNAs and in Plants
2. Plant Viruses May Act as an Inducer to Disrupt m6A Methylation
3. Plant Viral RNA Can Be the Target of m6A Methylation
4. m6A Methylation Is One of the Defense Mechanisms against Plant Viral Infection
5. The Virus Encodes AlkB Protein to Promote Virus Infection
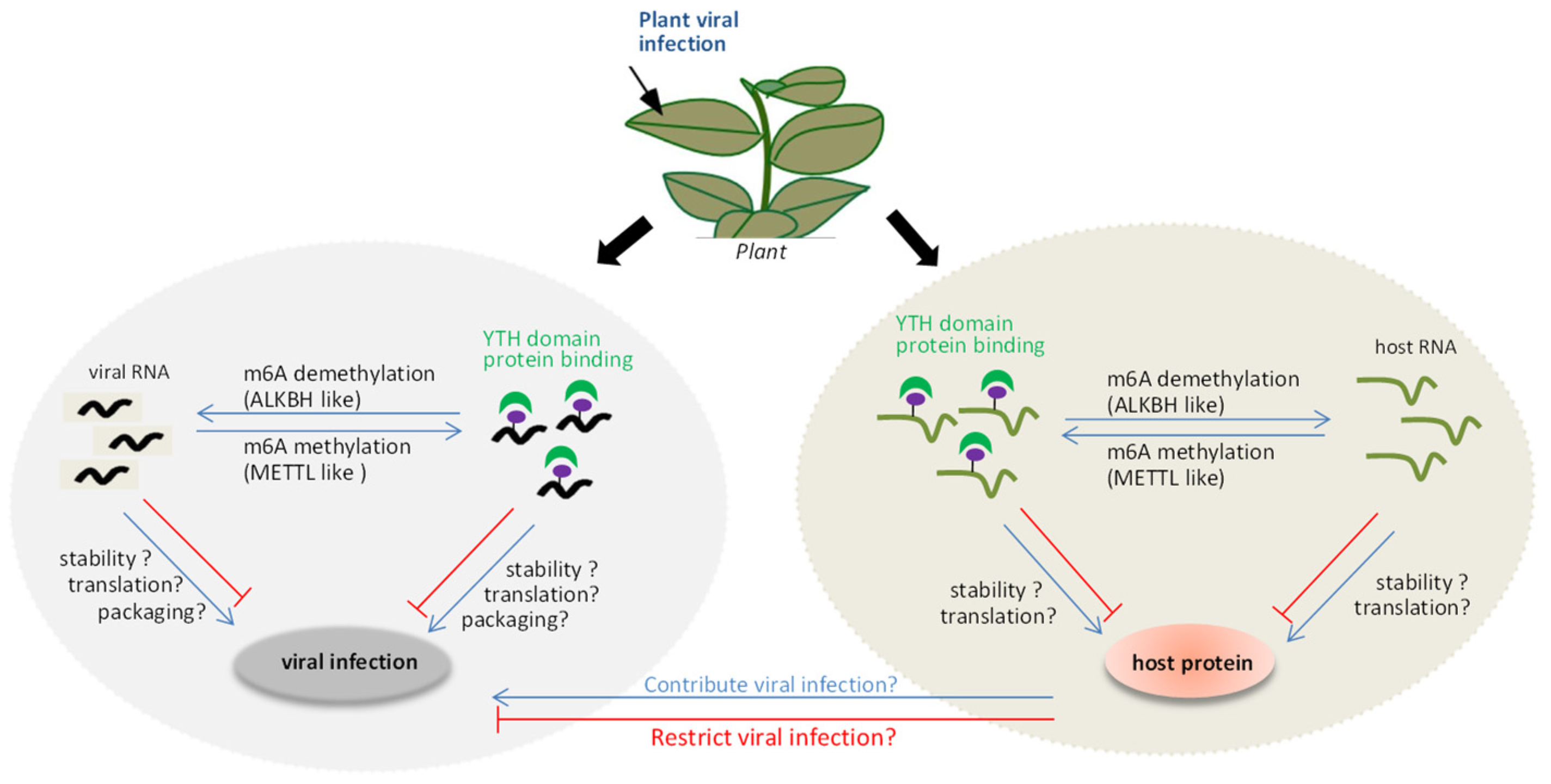
6. The Interplay between m6A Methylation and Viruses in Plant
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Desrosiers, R.; Friderici, K.; Rottman, F. Identification of Methylated Nucleosides in Messenger RNA from Novikoff Hepatoma Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 3971–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Krug, R.M.; Morgan, M.A.; Shatkin, A.J. Influenza viral mRNA contains internal N6-methyladenosine and 5’-terminal 7-methylguanosine in cap structures. J. Virol. 1976, 20, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moss, B.; Gershowitz, A.; Stringer, J.R.; Holland, L.E.; Wagner, E.K. 5’-Terminal and internal methylated nucleosides in herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA. J. Virol. 1977, 23, 234–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beemon, K.; Keith, J. Localization of N6-methyladenosine in the Rous sarcoma virus genome. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 113, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, S.E.; Beemon, K. Precise localization of m6A in Rous sarcoma virus RNA reveals clustering of methylation sites: Implications for RNA processing. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1985, 5, 2298–2306. [Google Scholar]
- Canaani, D.; Kahana, C.; Lavi, S.; Groner, Y. Identification and mapping of N6-methyladenosine containing sequences in simian virus 40 RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979, 6, 2879–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aloni, Y.; Dhar, R.; Khoury, G. Methylation of nuclear simian virus 40 RNAs. J. Virol. 1979, 32, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Finkel, D.; Groner, Y. Methylations of adenosine residues (m6A) in pre-mRNA are important for formation of late simian virus 40 mRNAs. Virology 1983, 131, 409–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen-Kiang, S.; Nevins, J.R.; Jr, J. N-6-methyl-adenosine in adenovirus type 2 nuclear RNA is conserved in the formation of messenger RNA. J. Mol. Biol. 1979, 135, 733–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.D.; Saletore, Y.; Zumbo, P.; Elemento, O.; Mason, C.E.; Jaffrey, S.R. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3’ UTRs and near stop codons. Cell 2012, 149, 1635–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dominissini, D.; Moshitch-Moshkovitz, S.; Schwartz, S.; Salmon-Divon, M.; Ungar, L.; Osenberg, S.; Cesarkas, K.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Amariglio, N.; Kupiec, M. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature 2012, 485, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Hsu, P.J.; Chen, Y.S.; Yang, Y.G. Dynamic transcriptomic m6A decoration: Writers, erasers, readers and functions in RNA metabolism. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yue, Y.; Liu, J.; He, C. RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Gene. Dev. 2015, 29, 1343–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roundtree, I.A.; Evans, M.E.; Pan, T.; He, C. Dynamic RNA Modifications in Gene Expression Regulation. Cell 2017, 169, 1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, N.; Pan, T. N6-methyladenosine-encoded epitranscriptomics. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.S.; Roundtree, I.A.; He, C. Post-transcriptional gene regulation by mRNA modifications. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Bio. 2017, 18, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtergaele, S.; He, C. The emerging biology of RNA post-transcriptional modifications. RNA Biol. 2016, 14, 156–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Feng, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, K.; Huang, X.; Pan, L.; Su, J.; Zheng, Y.; Li, R.; Deng, S.; et al. Genome-wide identification and characterization of circular RNA m6A modification in pancreatic cancer. Genome Med. 2021, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, W.; Adhikari, S.; Dahal, U.; Chen, Y.S.; Hao, Y.J.; Sun, B.F.; Sun, H.Y.; Li, A.; Ping, X.L.; Lai, W.Y. Nuclear m(6)A Reader YTHDC1 Regulates mRNA Splicing. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.; Yang, Y.; Sun, B.F.; Chen, Y.S.; Xu, J.W.; Lai, W.Y.; Li, A.; Wang, X.; Bhattarai, D.P.; Xiao, W.; et al. 5-methylcytosine promotes mRNA export -NSUN2 as the methyltransferase and ALYREF as an m5C reader. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 606–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roundtree, I.A.; Luo, G.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Xiao, W.; He, C. YTHDC1 mediates nuclear export of N-methyladenosine methylated mRNAs. eLife Sci. 2017, 6, e31311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishima, Y.; Tomari, Y. Codon Usage and 3’UTR Length Determine Maternal mRNA Stability in Zebrafish. Mol. Cell 2016, 61, 874–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Du, H.; Zhao, Y.; He, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xi, H.; Liu, M.; Ma, J.; Wu, L. YTHDF2 destabilizes m6A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Z.; Gomez, A.; Hon, G.C.; Yue, Y.; Han, D.; Fu, Y.; Parisien, M.; Dai, Q.; Jia, G. N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 2014, 505, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, H.; Xiao, W.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, B.S.; Ma, H.; Hsu, P.J.; Chang, L.; He, C. YTHDF3 facilitates translation and decay of N6-methyladenosine-modified RNA. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 315–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, A.; Chen, Y.S.; Ping, X.L.; Yang, X.; Xiao, W.; Yang, Y.; Sun, H.Y.; Zhu, Q.; Baidya, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Cytoplasmic m6A reader YTHDF3 promotes mRNA translation. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alarcon, C.R.; Lee, H.; Goodarzi, H.; Halberg, N.; Tavazoie, S.F. N6-methyladenosine marks primary microRNAs for processing. Nature 2015, 519, 482–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy, M.J.; Eileen, S.M.; Timpte, C.S.; Bokar, J.A. Induction of sporulation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae leads to the formation of N6-methyladenosine in mRNA: A potential mechanism for the activity of the IME4 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 4509–4518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shah, J.C.; Clancy, M.J. IME4, a gene that mediates MAT and nutritional control of meiosis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1992, 12, 1078–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Bodi, Z.; Button, J.D.; Grierson, D.; Fray, R.G. Yeast targets for mRNA methylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 5327–5335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, C.; Hu, S.; Yu, J.; Song, S. Transcriptome-wide N6-methyladenosine profiling of rice callus and leaf reveals the presence of tissue-specific competitors involved in selective mRNA modification. RNA Biol. 2014, 11, 1180–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luo, G.Z.; Macqueen, A.; Zheng, G.; Duan, H.; Dore, L.C.; Lu, Z.; Liu, J.; Chen, K.; Jia, G.; Bergelson, J. Unique features of the m6A methylome in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat. Commun. 2013, 5, 293–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Duan, H.C.; Wei, L.H.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Chen, L.; Lu, Z.; Chen, P.R.; He, C.; Jia, G. ALKBH10B is An RNA N6-Methyladenosine Demethylase Affecting Arabidopsis Floral Transition. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 2995–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, L.H.; Song, P.; Wang, Y.; Lu, Z.; Tang, Q.; Yu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Duan, H.C.; Jia, G. The m6A Reader ECT2 Controls Trichome Morphology by Affecting mRNA Stability in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 968–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scutenaire, J.; Deragon, J.M.; Jean, V.; Benhamed, M.; Bousquet-Antonelli, C. The YTH Domain Protein ECT2 is an m6A Reader Required for Normal Trichome Branching in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 986–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Arribas-Hernández, L.; Bressendorff, S.; Hansen, M.H.; Poulsen, C.; Erdmann, S.; Brodersen, P. An m6A-YTH Module Controls Developmental Timing and Morphogenesis in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 952–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reichel, M.; Kster, T.; Staiger, D. Marking RNA: m6A writers, readers and functions in Arabidopsis. J. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2019, 11, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Murik, O.; Chandran, S.A.; Nevo Dinur, K.; Sultan, L.D.; Best, C.; Stein, Y.; Hazan, C.; Ostersetzer Biran, O. Topologies of N6-adenosine methylation (m6A) in land plant mitochondria and their putative effects on organellar gene expression. Plant J. 2020, 101, 1269–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongay, C.F.; Orr-Weaver, T.L. Drosophila Inducer of MEiosis 4 (IME4) is required for Notch signaling during oogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 14855–14860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, J.; Tang, H.W.; Li, J.; Perrimon, N.; Yan, D. Xio is a component of the Drosophila sex determination pathway and RNA N6-methyladenosine methyltransferase complex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3674–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yoon, K.J.; Ringeling, F.R.; Vissers, C.; Jacob, F.; Pokrass, M.; Jimenez-Cyrus, D.; Su, Y.; Kim, N.S.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, L. Temporal Control of Mammalian Cortical Neurogenesis by m6A Methylation. Cell 2017, 171, 877–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bansal, H.; Yihua, Q.; Iyer, S.P.; Ganapathy, S.; Proia, D.; Penalva, L.O.; Uren, P.J.; Suresh, U.; Carew, J.S.; Karnad, A.B. WTAP is a novel oncogenic protein in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1171–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, K.; Yang, Y.; Feng, G.H.; Sun, B.F.; Chen, J.Q.; Li, Y.F.; Chen, Y.S.; Zhang, X.X.; Wang, C.X.; Jiang, L.Y. Mettl3-mediated m6A regulates spermatogonial differentiation and meiosis initiation. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 1100–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wan, Y.; Tang, K.; Zhang, D.; Xie, S.; Zhu, X.; Wang, Z.; Lang, Z. Transcriptome-wide high-throughput deep m6A-seq reveals unique differential m6A methylation patterns between three organs in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.; Kai, T.; Zhang, D.; Wan, Y.; Lei, W. High-throughput m6A-seq reveals RNA m6A methylation patterns in the chloroplast and mitochondria transcriptomes of Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e185612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Lv, Z.; Diao, S.; Liu, H.; Duan, A.; He, C.; Zhang, J. Unique features of the m6A methylome and its response to drought stress in sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides Linn.). RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Xu, Y.P.; Li, K.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, H.Y.; Sun, H.; Li, X.; Yu, L.; Deng, Y.Q.; Li, R.T. The methylome of SARS-CoV-2 in host cells. Cell Res. 2021, 31, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirumuru, N.; Wu, L. HIV-1 envelope proteins up-regulate N6 -methyladenosine levels of cellular RNA independently of viral replication. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 3249–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Ran, L.; Hu, D.; Song, B. N6 -methyl-adenosine level in Nicotiana tabacum is associated with tobacco mosaic virus. Virol. J. 2018, 15, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martínez-Pérez, M.; Aparicio, F.; MP, L.; Bellés, J.M.; JA, S.; Pallás, V. Arabidopsis m6A demethylase activity modulates viral infection of a plant virus and the m6A abundance in its genomic RNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10755–10760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichinchi, G.; Gao, S.; Saletore, Y.; Gonzalez, G.M.; Bansal, V.; Wang, Y.; Mason, C.E.; Rana, T.M. Dynamics of the human and viral m6A RNA methylomes during HIV-1 infection of T cells. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lichinchi, G.; Zhao, B.S.; Wu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Qin, Y.; He, C.; Rana, T. Dynamics of Human and Viral RNA Methylation during Zika Virus Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 666–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kennedy, E.M.; Bogerd, H.P.; Kornepati, A.V.R.; Kang, D.; Ghoshal, D.; Marshall, J.B.; Poling, B.C.; Tsai, K.; Gokhale, N.S.; Horner, S.M. Posttranscriptional m(6)A Editing of HIV-1 mRNAs Enhances Viral Gene Expression. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 19, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, B.; Gao, S.J. The RNA Epitranscriptome of DNA Viruses. J. Virol. 2018, 92, e00696-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hesser, C.R.; Karijolich, J.; Dominissini, D.; He, C.; Glaunsinger, B.A. N6-methyladenosine modification and the YTHDF2 reader protein play cell type specific roles in lytic viral gene expression during Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus infection. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwartz, S.; Mumbach, M.; Jovanovic, M.; Wang, T.; Maciag, K.; Bushkin, G.G.; Mertins, P.; Ter-Ovanesyan, D.; Habib, N.; Cacchiarelli, D. Perturbation of m6A Writers Reveals Two Distinct Classes of mRNA Methylation at Internal and 5’Sites. Cell Rep. 2014, 8, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Duan, H.C.; Wang, Y.; Jia, G. Dynamic and reversible RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2019, 10, e1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, W.; Qian, Y.; Jia, G. The detection and functions of RNA modification m6A based on m6A writers and erasers. J. Biol. Chem. 2021, 297, 100973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhale, N.; Mcintyre, A.R.; Mcfadden, M.; Roder, A.; Horner, S. N6-Methyladenosine in Flaviviridae Viral RNA Genomes Regulates Infection. Cell Host Microbe 2016, 20, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, S.; Li, H.; Bodi, Z.; Button, J.; Vespa, L.; Herzog, M.; Fray, R.G. MTA is an Arabidopsis messenger RNA adenosine methylase and interacts with a homolog of a sex-specific splicing factor. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bodi, Z.; Zhong, S.; Mehra, S.; Song, J.; Graham, N.; Li, H.; May, S.; Fray, R.G. Adenosine Methylation in Arabidopsis mRNA is Associated with the 3’End and Reduced Levels Cause Developmental Defects. Front. Plant 2012, 3, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, L.; Liang, Z.; Gu, X.; Chen, Y.; Teo, Z.W.; Hou, X.; Cai, W.M.; Dedon, P.C.; Liu, L.; Yu, H. N6-Methyladenosine RNA Modification Regulates Shoot Stem Cell Fate in Arabidopsis. Dev. Cell 2016, 38, 186–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Růžička, K.; Zhang, M.; Campilho, A.; Bodi, Z.; Kashif, M.; Saleh, M.; Eeckhout, D.; El-Showk, S.; Li, H.; Zhong, S.; et al. Identification of factors required for m(6)A mRNA methylation in Arabidopsis reveals a role for the conserved E3 ubiquitin ligase HAKAI. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Balacco, D.L.; Soller, M. The m(6)A Writer: Rise of a Machine for Growing Tasks. Biochemistry 2019, 58, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeurle, I.; Smith, L.; Baulcombe, D.C.; Dean, C. Widespread Role for the Flowering-Time Regulators FCA and FPA in RNA-Mediated Chromatin Silencing. Science 2007, 318, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hornyik, C.; Duc, C.; Rataj, K.; Terzi, L.C.; Simpson, G.G. Alternative polyadenylation of antisense RNAs and flowering time control. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 38, 1077–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Ji, W.; Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Qian, S.B. Dynamic m(6)A mRNA methylation directs translational control of heat shock response. Nature 2015, 526, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.Y.; Wang, Z.Q.; Hu, H.C.; Chen, Z.Q.; Liu, P.; Gao, S.Q.; Zhang, F.; He, L.; Jin, P.; Xu, M.Z.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide N(6)-Methyladenosine (m6A) Profiling of Susceptible and Resistant Wheat Varieties Reveals the Involvement of Variety-Specific m6A Modification Involved in Virus-Host Interaction Pathways. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 656302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Pérez, M.; Gómez-Mena, C.; Alvarado-Marchena, L.; Nadi, R.; Micol, J.L.; Pallas, V.; Aparicio, F. The m(6)A RNA Demethylase ALKBH9B Plays a Critical Role for Vascular Movement of Alfalfa Mosaic Virus in Arabidopsis. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 745576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielecki, D.; Zugaj, D.Ł.; Muszewska, A.; Piwowarski, J.; Chojnacka, A.; Mielecki, M.; Nieminuszczy, J.; Grynberg, M.; Grzesiuk, E. Novel AlkB dioxygenases-alternative models for in silico and in vivo studies. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aravind, L.; Koonin, E.V. The DNA-repair protein AlkB, EGL-9, and leprecan define new families of 2-oxoglutarate- and iron-dependent dioxygenases. Genome Biol. 2001, 2, 849–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falnes, P.; Johansen, R.F.; Seeberg, E. AlkB-mediated oxidative demethylation reverses DNA damage in Escherichia coli. Nature 2002, 419, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trewick, S.C.; Henshaw, T.F.; Hausinger, R.P.; Lindahl, T.; Sedgwick, B. Oxidative demethylation by Escherichia coli AlkB directly reverts DNA base damage. Nature 2002, 419, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erwin, V.D.B.; Omelchenko, M.V.; Anders, B.; Vibeke, L.; Koonin, E.V.; Dolja, V.V.; Falnes, P.Ø. Viral AlkB proteins repair RNA damage by oxidative demethylation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 5451–5461. [Google Scholar]
- Mcgavin, W.J.; Mcmenemy, L.S.; Macfarlane, S.A. The complete sequence of a UK strain of black raspberry necrosis virus. Arch. Virol. 2010, 155, 1897–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, H.; Hirano, S.; Chiba, S.; Andika, I.B.; Hirai, M.; Maeda, T.; Tamada, T. Characterization of burdock mottle virus, a novel member of the genus Benyvirus, and the identification of benyvirus-related sequences in the plant and insect genomes. Virus Res. 2013, 177, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bratlie, M.S.; Drabl, S.F. Bioinformatic mapping of AlkB homology domains in viruses. BMC Genom. 2005, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Virus. | M6A-Related Proteins | Summary of Knowledge | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aalfalfa mosaic virus (AMV) | ALKBH9B (At2g17970) | The demethylation activity of atALKBH9B affected the infectivity of AMV by interacting with CP of AMV. Suppression of atALKBH9B increased the relative abundance of m6A in the AMVgenome, impairing the systemic invasion of the plant. | Martinez-Perez et al., 2017 |
| Cucumber mosaic virus (CMV) | ALKBH9B (At2g17970) | atALKBH9B does not have any effect on CMV infection. atALKBH9B does not interact with CP of CMV. | Martinez-Perez et al., 2017 |
| Tobacco mosaic virus (TMV) | The potential demethylase XM_009801708 in Nicotiana tabacum. | The overall level of m6A decreases after (TMV) infection in Nicotiana tabacum. The expression level of XM_009801708 is increased upon TMV infection. | Zhurui et al., 2018 |
| Grapevine virus A (GVA) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Maintaining the integrity of the viral RNA genome through removal of deleterious RNA damage. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Blueberry scorch virus (BlScV) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Maintaining the integrity of the viral RNA genome through removal of deleterious RNA damage. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Blackberry virusY (BVY) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Maintaining the integrity of the viral RNA genome through removal of deleterious RNA damage. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Little cherry virus (LChV-2) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Not tested. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Citric leave blotch virus (CLBV) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Not tested. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Chrysanthemum virus B (CVB) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Not tested. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Lily symptomless virus (LSV) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Not tested. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Apple stem pitting virus (ASPV) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Not tested. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Garlic latent virus (GLV) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Not tested. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Zygocactus virusX (ZVX) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Not tested. | Van den Born et al., 2008 |
| Burdock mottle virus (BdMoV) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Not tested. | Kondo et al., 2013 |
| Black raspberry necrosis virus (BRNV) | Containing ALKB domain in viral genome | Not tested. | McGavin et al., 2010 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yue, J.; Wei, Y.; Zhao, M. The Reversible Methylation of m6A Is Involved in Plant Virus Infection. Biology 2022, 11, 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020271
Yue J, Wei Y, Zhao M. The Reversible Methylation of m6A Is Involved in Plant Virus Infection. Biology. 2022; 11(2):271. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020271
Chicago/Turabian StyleYue, Jianying, Yao Wei, and Mingmin Zhao. 2022. "The Reversible Methylation of m6A Is Involved in Plant Virus Infection" Biology 11, no. 2: 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020271
APA StyleYue, J., Wei, Y., & Zhao, M. (2022). The Reversible Methylation of m6A Is Involved in Plant Virus Infection. Biology, 11(2), 271. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11020271






