Dimorphilus gyrociliatus (Annelida: Dinophiliformia) Dwarf Male Nervous System Represents a Common Pattern for Lophotrochozoa
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Handling
2.2. Fixation and Immunostaining
2.3. Microscopy and Image Processing
3. Results
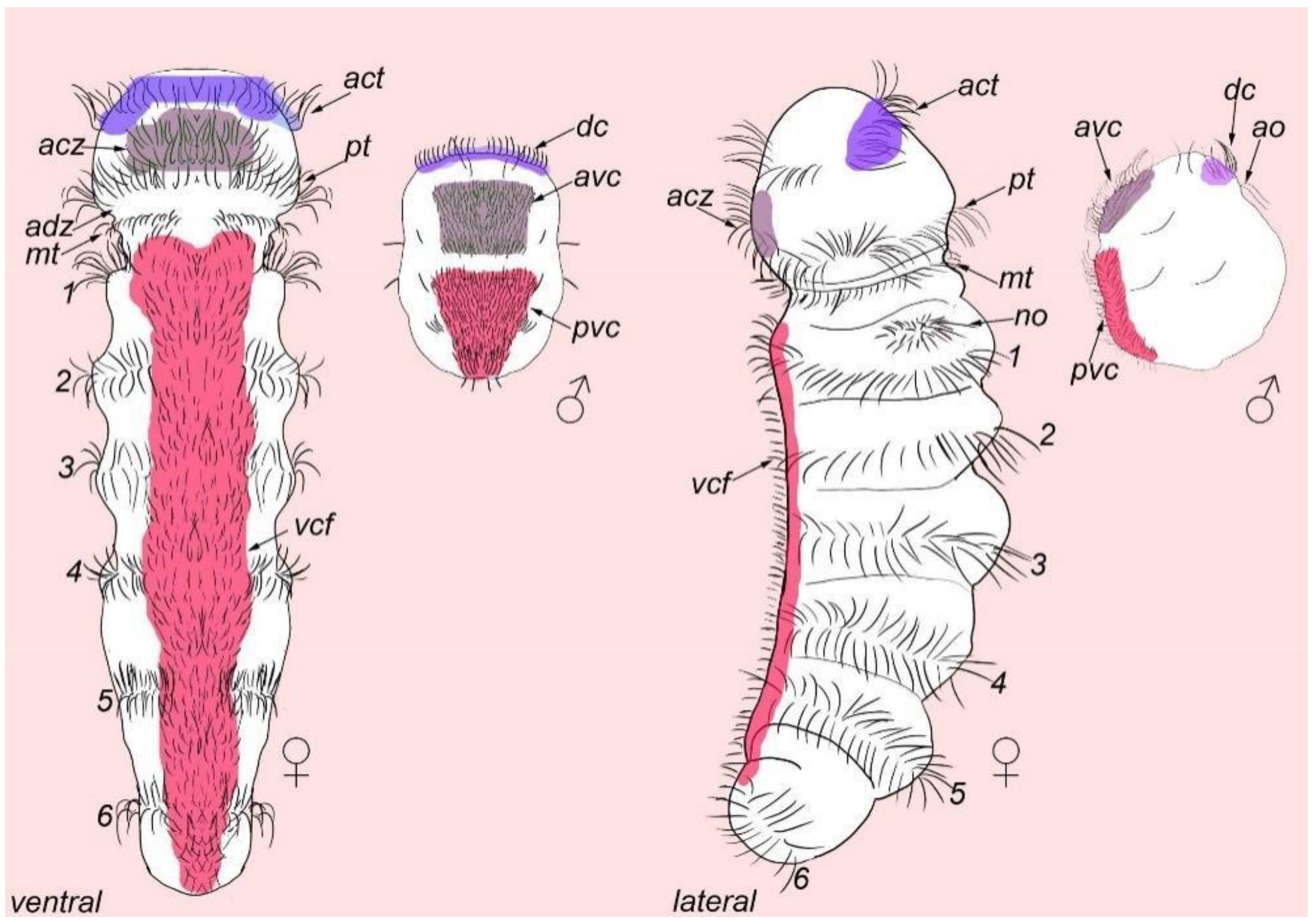
3.1. External Ciliation
3.2. Morphology
3.3. Type 1a Cells
3.4. Type 1b Cells
3.5. Type 1c Cells
3.6. Type 2 Cells
3.7. Acetylated-Tubulin Positive Nerve Elements
3.8. 5-HT-like Immunoreactive Elements
4. Discussion
4.1. Ciliary Landmark
4.2. Sensory Neurons and CNS and 5-HT-like Immunoreactive Nervous System
4.3. Apical Organ
4.4. Male Dwarfism
5. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| * | nephridia |
| act | acrotroch |
| acz | anterior ciliary field |
| adz | adoral cilary zone |
| avc | anterior ventral cilia |
| c | commissure |
| co | copulative organ |
| dc | dorsal commissure |
| dc | dorsal cilia |
| dn | dorsal nerve |
| arrowheads | indicate neuronal cell bodies |
| E10, 11 | multiciliated cells of the dorsal ciliary field |
| gl | gland cell |
| go | genital opening |
| mt | metatroch |
| pvc | posterior ventral cilia |
| sgd | stylet gland cell |
| sn1–sn23 | sensory neurons 1–23 |
| sv | seminal vesicles |
| test | testis |
| vb | ventral bundle |
| vc | ventral commissure |
References
- Martín-Durán, J.M.; Vellutini, B.C.; Marlétaz, F.; Cetrangolo, V.; Cvetesic, N.; Thiel, D.; Henriet, S.; Grau-Bové, X.; Carrillo-Baltodano, A.M.; Gu, W.; et al. Conservative route to genome compaction in a miniature annelid. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worsaae, K.; Kerbl, A.; Domenico, M.D.; Gonzalez, B.C.; Bekkouche, N.; Martínez, A. Interstitial Annelida. Diversity 2021, 13, 77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windoffer, R.; Westheide, W. The Nervous system of the male Dinophilus gyrociliatus (Polychaeta, Dinophilidae): II. electron microscopical reconstruction of nervous anatomy and effector cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 1988, 272, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windoffer, R.; Westheide, W. The nervous system of the male Dinophilus gyrociliatus (Annelida: Polychaeta). I. Number, types and distribution pattern of sensory cells. Acta Zool. 1988, 69, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Baltodano, A.M.; Seudre, O.; Guynes, K.; Martín-Durán, J.M. Early embryogenesis and organogenesis in the annelid Owenia fusiformis. EvoDevo 2021, 12, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helm, C.; Vöcking, O.; Kourtesis, I.; Hausen, H. Owenia fusiformis—A basally branching annelid suitable for studying ancestral features of annelid neural development. BMC Evol. Biol. 2016, 16, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carrillo-Baltodano, A.M.; Boyle, M.J.; Rice, M.E.; Meyer, N.P. Developmental architecture of the nervous system in Themistelageniformis (Sipuncula): New evidence from confocal laser scanning microscopy and gene expression. J. Morphol. 2019, 280, 1628–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanninger, A.; Koop, D.; Bromham, L.; Noonan, E.; Degnan, B.M. Nervous and muscle system development in Phascolionstrombus (Sipuncula). Dev. Genes Evol. 2005, 215, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristof, A.; Wollesen, T.; Maiorova, A.S.; Wanninger, A. Cellular and muscular growth patterns during sipunculan development. J. Exp. Zool. 2011, 316B, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starunov, V.V.; Voronezhskaya, E.E.; Nezlin, L.P. Development of the nervous system in Platynereis dumerilii (Nereididae, Annelida). Front. Zool. 2017, 14, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Tumu, S.C.; Helm, C.; Hausen, H. The Development of early pioneer neurons in the annelid Malacoceros fuliginosus. BMC Evol. Biol. 2020, 20, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fofanova, E.; Mayorova, T.D.; Voronezhskaya, E.E. Dinophiliformia early neurogenesis suggests the evolution of conservative neural structures across the Annelida phylogenetic tree. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerbl, A.; Winther Tolstrup, E.; Worsaae, K. Nerves innervating copulatory organs show common FMRFamide, FVRIamide, MIP and serotonin immunoreactivity patterns across Dinophilidae (Annelida) indicating their conserved role in copulatory behaviour. BMC Zool. 2019, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, C.; Beckers, P.; Bartolomaeus, T.; Drukewitz, S.H.; Kourtesis, I.; Weigert, A.; Purschke, G.; Worsaae, K.; Struck, T.H.; Bleidorn, C. Convergent evolution of the ladder-like ventral nerve cord in Annelida. Front. Zool. 2018, 15, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerbl, A.; Fofanova, E.G.; Mayorova, T.D.; Voronezhskaya, E.E.; Worsaae, K. Comparison of neuromuscular development in two dinophilid species (Annelida) suggests progenetic origin of Dinophilus gyrociliatus. Front. Zool. 2016, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voronezhskaya, E.E.; Tsitrin, E.B.; Nezlin, L.P. Neuronal development in larval polychaete Phyllodoce maculata (Phyllodocidae). J. Comp. Neurol. 2003, 455, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, C. Larval and Adult Brains. Evol. Dev. 2005, 7, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanninger, A. Comparative lophotrochozoan neurogenesis and larval neuroanatomy: Recent advances from previously neglected taxa. Acta Biol. Hung. 2008, 59 (Suppl. 21), 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marlow, H.; Tosches, M.A.; Tomer, R.; Steinmetz, P.R.; Lauri, A.; Larsson, T.; Arendt, D. Larval body patterning and apical organs are conserved in animal evolution. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McDougall, C.; Chen, W.-C.; Shimeld, S.M.; Ferrier, D.E.K. The development of the larval nervous system, musculature and ciliary bands of Pomatoceros lamarckii (Annelida): Heterochrony in Polychaetes. Front. Zool. 2006, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, N.P.; Seaver, E.C. Neurogenesis in an annelid: Characterization of brain neural precursors in the polychaete Capitella sp. I. Dev. Biol. 2009, 335, 237–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meyer, N.P.; Carrillo-Baltodano, A.; Moore, R.E.; Seaver, E.C. Nervous system development in lecithotrophic larval and juvenile stages of the annelid Capitella teleta. Front. Zool. 2015, 12, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carrillo-Baltodano, A.M.; Meyer, N.P. Decoupling brain from nerve cord development in the annelid Capitella teleta: Insights into the evolution of nervous systems. Dev. Biol. 2017, 431, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerbl, A.; Conzelmann, M.; Jékely, G.; Worsaae, K. High diversity in neuropeptide immunoreactivity patterns among three closely related species of Dinophilidae (Annelida). J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 3596–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Worsaae, K.; Rouse, G.W. The simplicity of males: Dwarf males of four species of Osedax (Siboglinidae; Annelida) investigated by confocal laser scanning microscopy. J. Morphol. 2010, 271, 127–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouse, G.W.; Wilson, N.G.; Worsaae, K.; Vrijenhoek, R.C. A dwarf male reversal in bone-eating worms. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vortsepneva, E.; Tzetlin, A.; Tsitrin, E. Nervous system of the dwarf ectoparasitic male of Scolelepis laonicola (Polychaeta, Spionidae). Zoosymposia 2009, 2, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hessling, R. Novel Aspects of the nervous system of Bonellia viridis(Echiura) Revealed by the combination of immunohistochemistry, confocal laser-scanning microscopy and three-dimensional reconstruction. Hydrobiologia 2003, 496, 225–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuchert, P.; Rieger, R.M. Ultrastructural observations on the dwarf male of Bonellia viridis (Echiura). Acta Zool. 1990, 71, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gąsiorowski, L.; Furu, A.; Hejnol, A. Morphology of the nervous system of monogonont rotifer Epiphanes senta with a focus on sexual dimorphism between feeding females and dwarf males. Front. Zool. 2019, 16, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neves, R.C.; da Cunha, M.R.; Funch, P.; Wanninger, A.; Kristensen, R.M. External morphology of the cycliophoran dwarf male: A comparative study of Symbion pandora and S. americanus. Helgol. Mar. Res. 2010, 64, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]














Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fofanova, E. Dimorphilus gyrociliatus (Annelida: Dinophiliformia) Dwarf Male Nervous System Represents a Common Pattern for Lophotrochozoa. Biology 2022, 11, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111674
Fofanova E. Dimorphilus gyrociliatus (Annelida: Dinophiliformia) Dwarf Male Nervous System Represents a Common Pattern for Lophotrochozoa. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111674
Chicago/Turabian StyleFofanova, Elizaveta. 2022. "Dimorphilus gyrociliatus (Annelida: Dinophiliformia) Dwarf Male Nervous System Represents a Common Pattern for Lophotrochozoa" Biology 11, no. 11: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111674
APA StyleFofanova, E. (2022). Dimorphilus gyrociliatus (Annelida: Dinophiliformia) Dwarf Male Nervous System Represents a Common Pattern for Lophotrochozoa. Biology, 11(11), 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111674





