Structure and Chemical Composition of ca. 10-Million-Year-Old (Late Miocene of Western Amazon) and Present-Day Teeth of Related Species
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
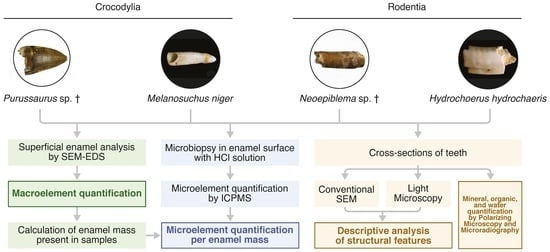
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Institutional Abbreviations
2.2. Fossil Specimens and Provenance
2.3. Modern Specimens
2.4. SEM-EDS Analysis
2.5. Preparation of Samples for Light and Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.6. Light Microscopy
2.7. Quantification of Major Enamel Biochemical Components
2.8. Superficial Enamel Sampling with Acid
2.9. Chemical Analysis by ICP-MS
3. Results
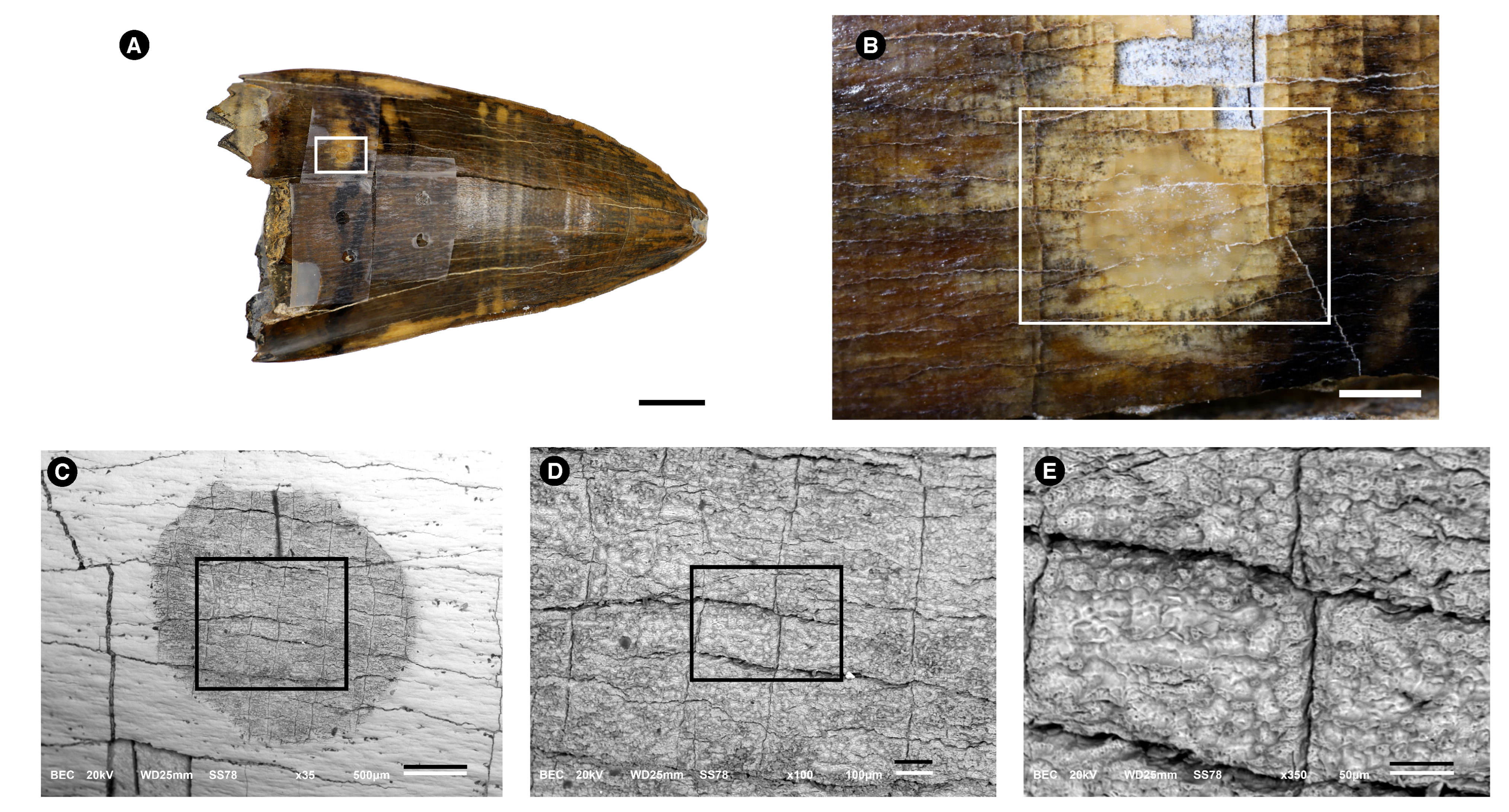
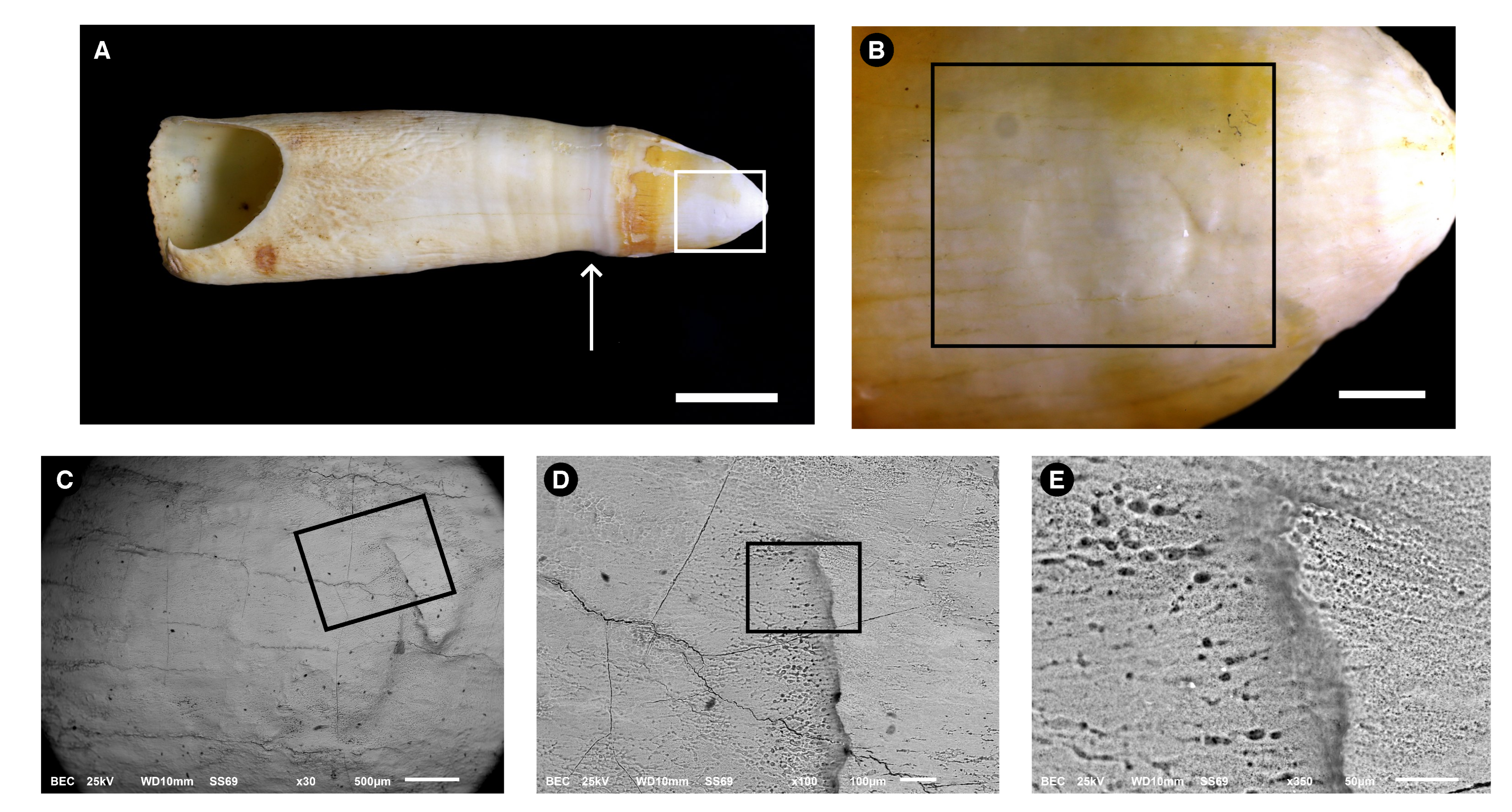
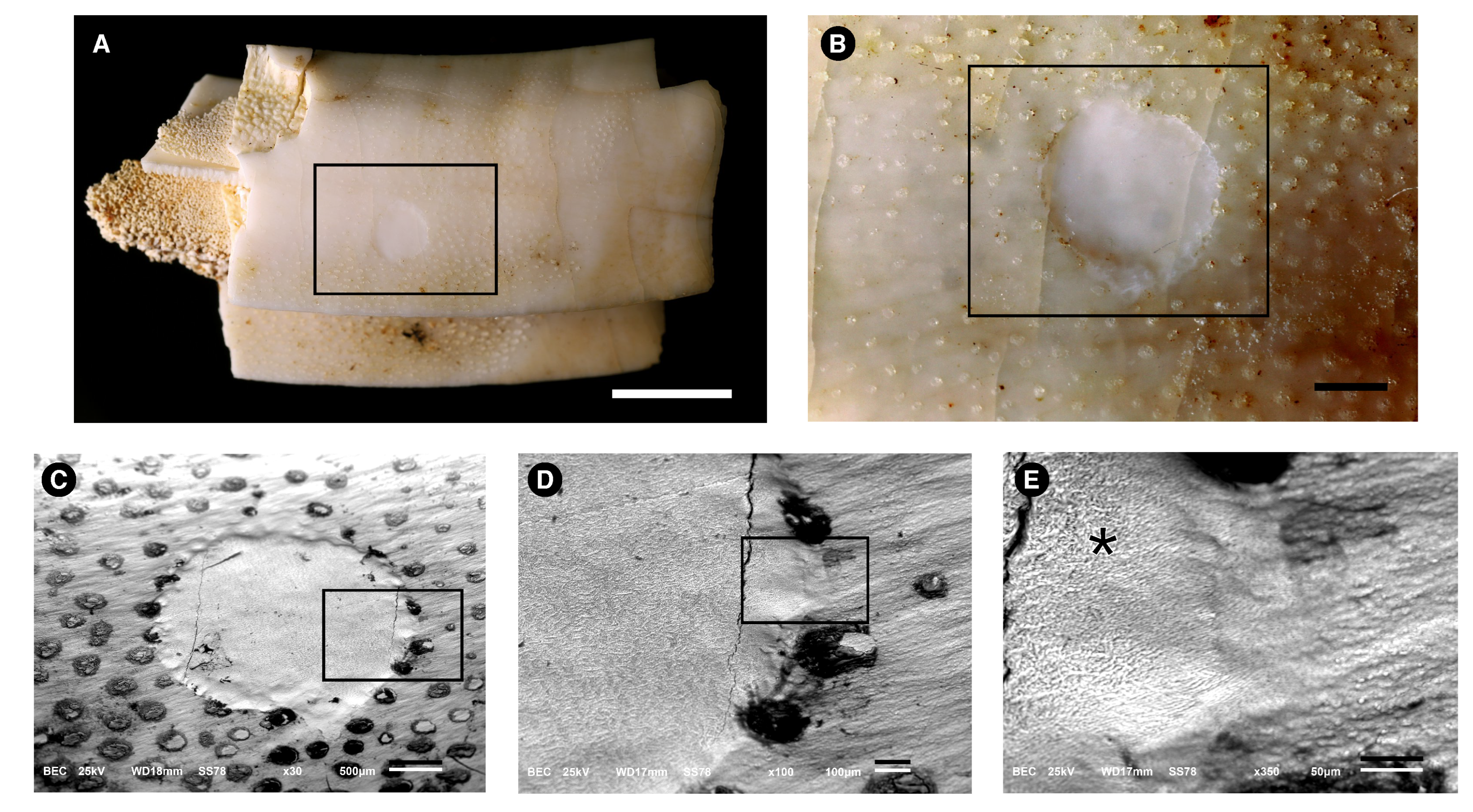
3.1. Morphological Description
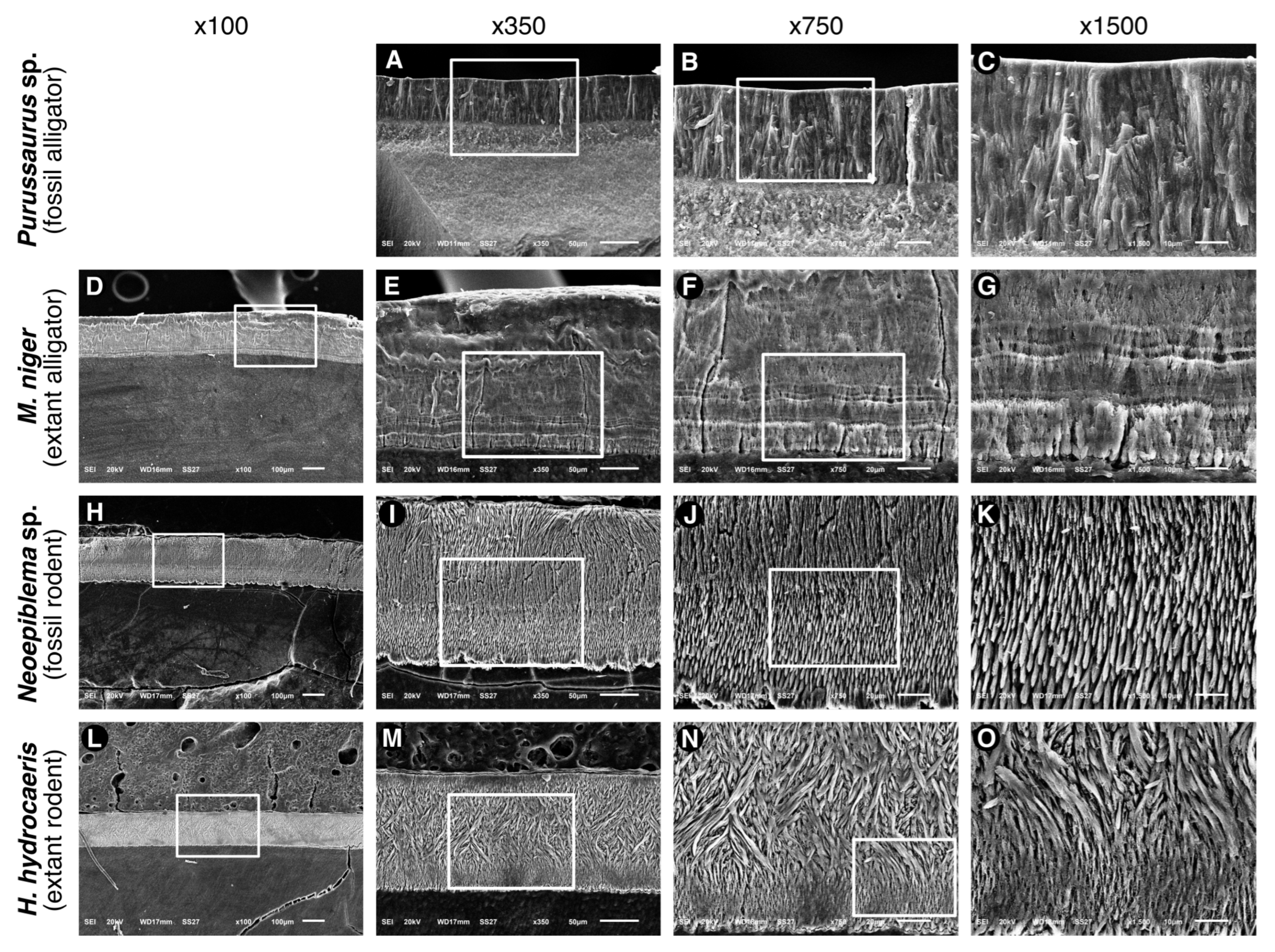
3.2. Microstructure (SEM Analysis)
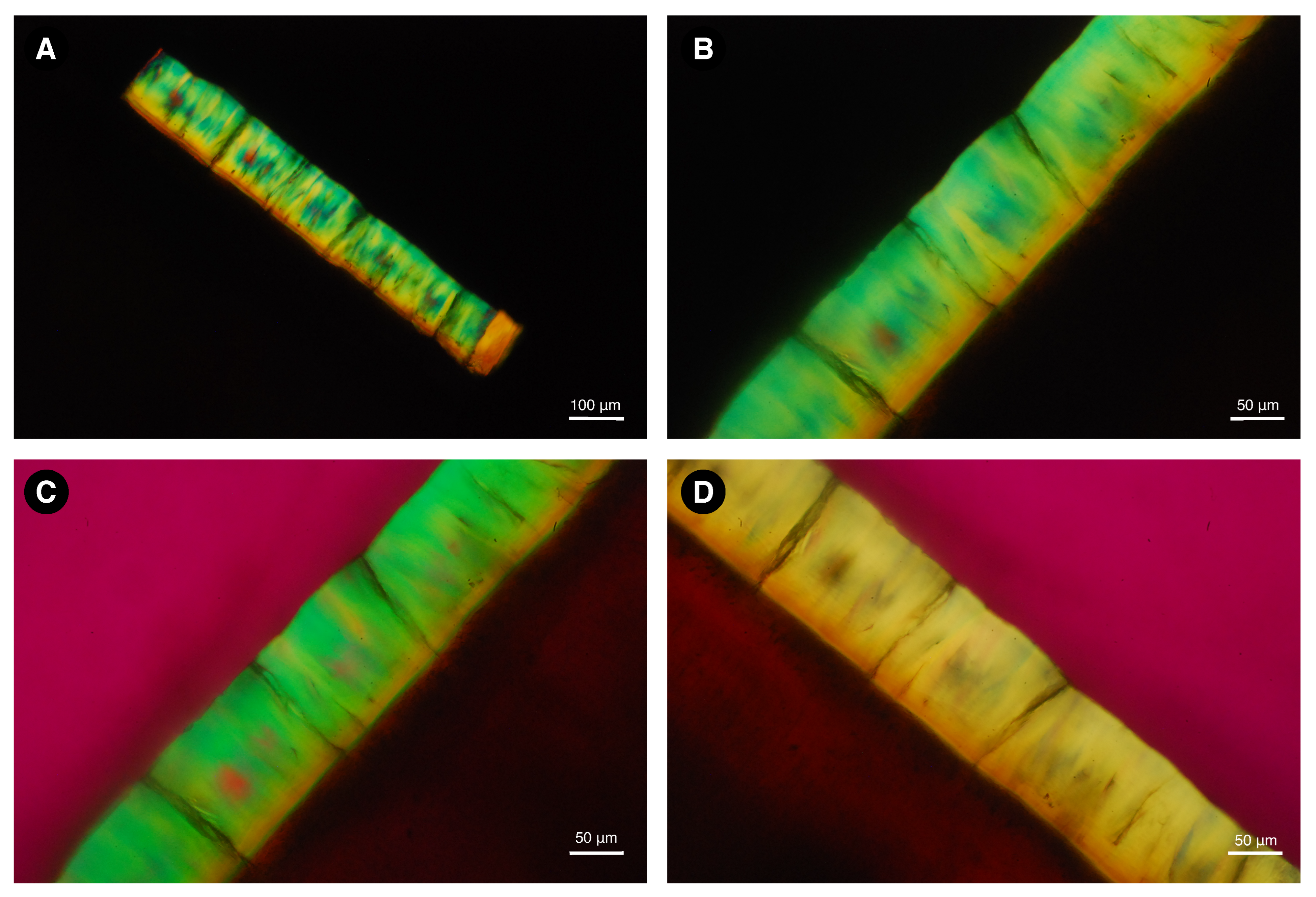
3.3. Determination of Organic, Mineral, and Water Content of Dental Enamel
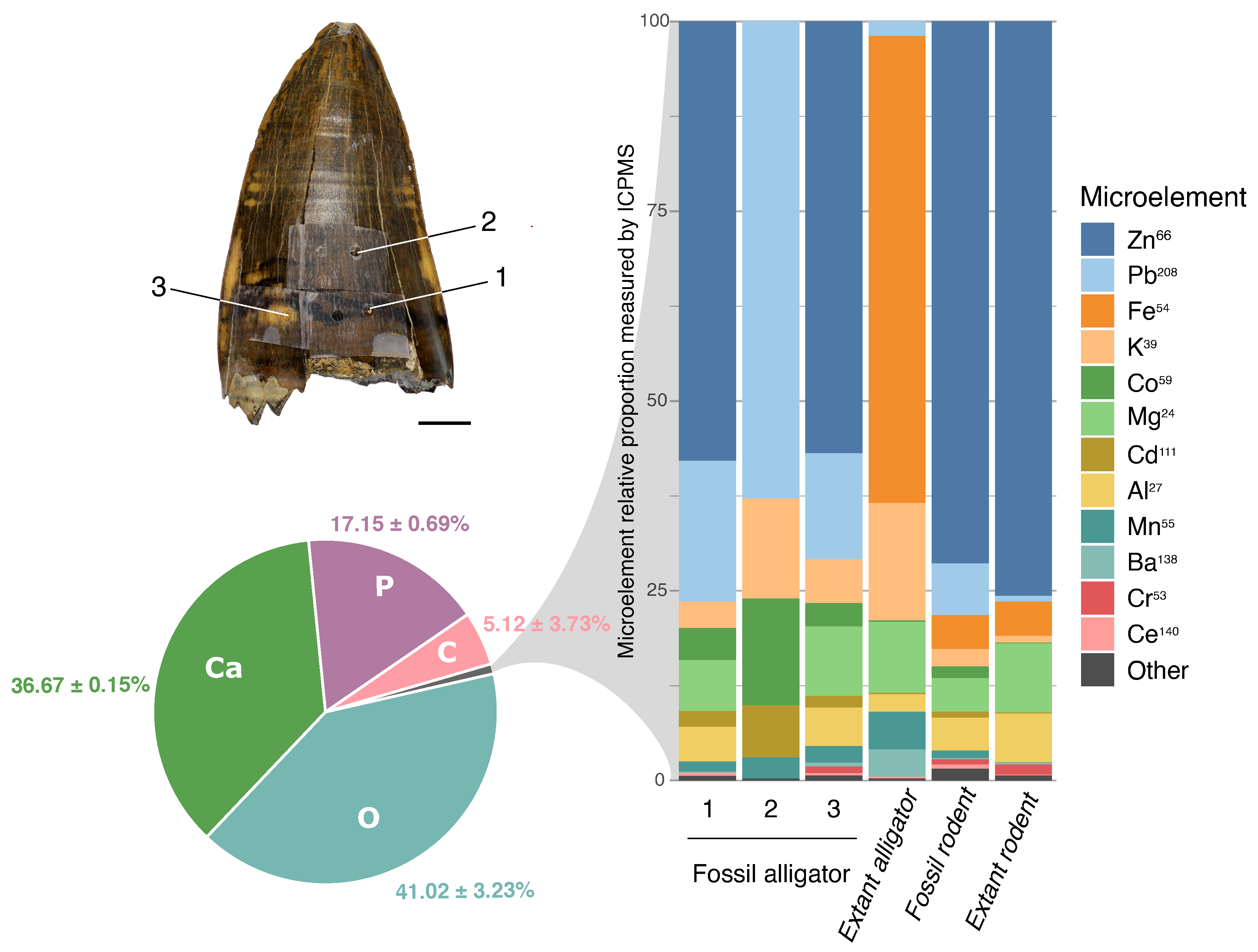
3.4. Inorganic Composition of the Superficial Enamel
3.4.1. Energy-Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS)
3.4.2. Inductively Coupled Plasma-Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wiens, J.J.; Chippindale, P.T.; Hillis, D.M. When Are Phylogenetic Analyses Misled by Convergence? A Case Study in Texas Cave Salamanders. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 501–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, I.M.; Laure, H.J.; Tykot, R.H.; de Sousa, F.B.; Rosa, J.C.; Gerlach, R.F. Recovery and identification of mature enamel proteins in ancient teeth. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 119 (Suppl. 1), 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, F.C.S.; Neves, L.X.; Pessoa-Lima, C.; Langer, M.C.; Domont, G.B.; Line, S.R.P.; Paes Leme, A.F.; Gerlach, R.F. Ancient enamel peptides recovered from the South American Pleistocene species Notiomastodon platensis and Myocastor cf. coypus. J. Proteom. 2021, 240, 104187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, I.M.; Line, S.R.P.; Laure, H.J.; Gerlach, R.F. Comparison of three methods for enamel protein extraction in different developmental phases of rat lower incisors. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2006, 114 (Suppl. 1), 272–275; discussion 285–286, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, V.E.; Rosário de Sousa, M.d.L.; Barbosa, F., Jr.; Krug, F.J.; Pereira Saraiva, M.d.C.; Cury, J.A.; Gerlach, R.F. In vivo studies on lead content of deciduous teeth superficial enamel of preschool children. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 320, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa, F.; Tanus, S.J.E.; Gerlach, R.F.; Parsons, P.J. A Critical Review of Biomarkers Used for Monitoring Human Exposure to Lead: Advantages, Limitations, and Future Needs. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 1669–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa de Almeida, G.R.; Pereira Saraiva, M.d.C.; Barbosa, F.; Krug, F.J.; Cury, J.A.; Rosário de Sousa, M.d.L.; Rabelo Buzalaf, M.A.; Gerlach, R.F. Lead contents in the surface enamel of deciduous teeth sampled in vivo from children in uncontaminated and in lead-contaminated areas. Environ. Res. 2007, 104, 337–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andre Stewart, N.; Ferian Molina, G.; Issa, J.P.M.; Andrew Yates, N.; Sosovicka, M.; Rezende Vieira, A.; Peres Line, S.R.; Montgomery, J.; Fernanda Gerlach, R. The identification of peptides by nanoLC-MS/MS from human surface tooth enamel following a simple acid etch extraction. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 61673–61679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, N.A.; Gerlach, R.F.; Gowland, R.L.; Gron, K.J.; Montgomery, J. Sex determination of human remains from peptides in tooth enamel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 13649–13654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado, S.; Vidal, N.; Veron, G.; Sire, J.Y. Amelogenin, the major protein of tooth enamel: A new phylogenetic marker for ordinal mammal relationships. Mol. Phylogenetics Evol. 2008, 47, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappellini, E.; Welker, F.; Pandolfi, L.; Ramos-Madrigal, J.; Samodova, D.; Rüther, P.L.; Fotakis, A.K.; Lyon, D.; Moreno-Mayar, J.V.; Bukhsianidze, M.; et al. Early Pleistocene enamel proteome from Dmanisi resolves Stephanorhinus phylogeny. Nature 2019, 574, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welker, F.; Ramos-Madrigal, J.; Kuhlwilm, M.; Liao, W.; Gutenbrunner, P.; de Manuel, M.; Samodova, D.; Mackie, M.; Allentoft, M.E.; Bacon, A.M.; et al. Enamel proteome shows that Gigantopithecus was an early diverging pongine. Nature 2019, 576, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Line, S.R.P. Incremental markings of enamel in ectothermal vertebrates. Arch. Oral Biol. 2000, 45, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Line, S.R.P.; Bergqvist, L.P. Enamel structure of paleocene mammals of the São José de Itaboraí basin, Brazil. ‘Condylarthra’, Litopterna, Notoungulata, Xenungulata, and Astrapotheria. J. Vertebr. Paleontol. 2005, 25, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vašinová Galiová, M.; Nývltová Fišáková, M.; Kynický, J.; Prokeš, L.; Neff, H.; Mason, A.Z.; Gadas, P.; Košler, J.; Kanický, V. Elemental mapping in fossil tooth root section of Ursus arctos by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS). Talanta 2013, 105, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, V.; Shchetnikov, A.; Semeney, E.; Filinov, I.; Simon, K. LA-ICP-MS analysis of rare earth elements in tooth enamel of fossil small mammals (Ust-Oda section, Fore-Baikal area, Siberia): Paleoenvironmental interpretation. J. Quat. Sci. 2022, 37, 1246–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demarchi, B.; Hall, S.; Roncal-Herrero, T.; Freeman, C.L.; Woolley, J.; Crisp, M.K.; Wilson, J.; Fotakis, A.; Fischer, R.; Kessler, B.M.; et al. Protein sequences bound to mineral surfaces persist into deep time. eLife 2016, 5, e17092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, Y.H.P.; Lu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Krebsbach, P.H.; Yamada, Y.; Hu, J.C.C.; Simmer, J.P. Transgenic rescue of enamel phenotype in Ambn null mice. J. Dent. Res. 2010, 89, 1414–1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, C.E.; Hu, Y.; Richardson, A.S.; Bartlett, J.D.; Hu, J.C.C.; Simmer, J.P. Relationships between protein and mineral during enamel development in normal and genetically altered mice. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 119, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatakeyama, J.; Fukumoto, S.; Nakamura, T.; Haruyama, N.; Suzuki, S.; Hatakeyama, Y.; Shum, L.; Gibson, C.W.; Yamada, Y.; Kulkarni, A.B. Synergistic roles of amelogenin and ameloblastin. J. Dent. Res. 2009, 88, 318–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, J.D.; Smith, C.E.; Hu, Y.; Ikeda, A.; Strauss, M.; Liang, T.; Hsu, Y.H.; Trout, A.H.; McComb, D.W.; Freeman, R.C.; et al. MMP20-generated amelogenin cleavage products prevent formation of fan-shaped enamel malformations. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 10570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saiani, R.A.; Porto, I.M.; Marcantonio Junior, E.; Cury, J.A.; de Sousa, F.B.; Gerlach, R.F. Morphological characterization of rat incisor fluorotic lesions. Arch. Oral Biol. 2009, 54, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, I.M.; Merzel, J.; de Sousa, F.B.; Bachmann, L.; Cury, J.A.; Line, S.R.P.; Gerlach, R.F. Enamel mineralization in the absence of maturation stage ameloblasts. Arch. Oral Biol. 2009, 54, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, I.M.; Saiani, R.A.; Chan, K.L.A.; Kazarian, S.G.; Gerlach, R.F.; Bachmann, L. Organic and inorganic content of fluorotic rat incisors measured by FTIR spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta. Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2010, 77, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, F.B.; Vianna, S.S.; Santos-Magalhães, N.S. A new approach for improving the birefringence analysis of dental enamel mineral content using polarizing microscopy. J. Microsc. 2006, 221, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Souza-Guerra, C.; Barroso, R.C.; de Almeida, A.P.; Peixoto, I.T.A.; Moreira, S.; de Sousa, F.B.; Gerlach, R.F. Anatomical variations in primary teeth microelements with known differences in lead content by micro-Synchrotron Radiation X-Ray Fluorescence (μ-SRXRF)—A preliminary study. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2014, 28, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, T.E. Retroarc foreland and related basins. In Tectonics of Sedimentary Basins; Blackwell Scientific Publications: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1995; pp. 331–391. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, A.J.P.; Lopes, R.C.L.; Vasconcelos, A.M. Bacias sedimentares paleozoicas e meso-cenozoicas interiores. In Geologia, Tectonica e Recursos Minerais do Brasil: Texto, Mapas & SIG; CPRM: Brasilia, Brazil, 2003; p. 55. [Google Scholar]
- Cunha, P.d.C. Bacia do Acre. Bol. De Geociências Da Petrobras 2007, 15, 207–215. [Google Scholar]
- Bissaro-Júnior, M.C.; Kerber, L.; Crowley, J.L.; Ribeiro, A.M.; Ghilardi, R.P.; Guilherme, E.; Negri, F.R.; Souza Filho, J.P.; Hsiou, A.S. Detrital zircon U–Pb geochronology constrains the age of Brazilian Neogene deposits from Western Amazonia. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2019, 516, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latrubesse, E.; Bocquentin, J.; Santos, J.C.R.; Ramonell, C.G. Paleoenvironmental model for the late cenozoic of southwestern Amazonia: Paleontology and geology. Acta Amaz. 1997, 27, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latrubesse, E.M.; Cozzuol, M.; da Silva-Caminha, S.A.F.; Rigsby, C.A.; Absy, M.L.; Jaramillo, C. The Late Miocene paleogeography of the Amazon Basin and the evolution of the Amazon River system. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010, 99, 99–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cozzuol, M.A. The Acre vertebrate fauna: Age, diversity, and geography. J. South Am. Earth Sci. 2006, 21, 185–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, J.G.; Sabaj Pérez, M.H.; Dahdul, W.M.; Aguilera, O.A. The Amazonian neogene fish fauna. In Amazonia: Landscape and Species Evolution: A Look into the Past; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2009; pp. 281–301. [Google Scholar]
- Riff, D.; Romano, P.S.R.; Oliveira, G.R.; Aguilera, O.A.; Hoorn, C. Neogene crocodile and turtle fauna in northern South America. In Amazonia. Landscapes and Species Evolution: A Look Into the Past; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2010; pp. 259–280. [Google Scholar]
- Negri, F.R.; Bocquentin-Villanueva, J.; Ferigolo, J.; Antoine, P.O. A review of Tertiary mammal faunas and birds from western Amazonia. In Amazonia: Landscape and Species Evolution: A Look into the Past; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2009; pp. 243–258. [Google Scholar]
- Hsiou, A.S. Lagartos e Serpentes (Lepidosauria, Squamata) do Mioceno Médio-Superior da Região Norte da América do Sul; IGEO/UFRGS; Porto Alegre, RS, Brazil. 2010. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/10183/23712 (accessed on 6 June 2022).
- Aureliano, T.; Ghilardi, A.M.; Guilherme, E.; Souza-Filho, J.P.; Cavalcanti, M.; Riff, D. Morphometry, Bite-Force, and Paleobiology of the Late Miocene Caiman Purussaurus brasiliensis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rio, J.P.; Mannion, P.D. Phylogenetic analysis of a new morphological dataset elucidates the evolutionary history of Crocodylia and resolves the long-standing gharial problem. PeerJ 2021, 9, e12094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerber, L.; Candela, A.M.; Ferreira, J.D.; Pretto, F.A.; Bubadué, J.; Negri, F.R. Postcranial Morphology of the Extinct Rodent Neoepiblema (Rodentia: Chinchilloidea): Insights Into the Paleobiology of Neoepiblemids. J. Mamm. Evol. 2022, 29, 207–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Figueiredo, F.A.T.; Ramos, J.; Kawakita, E.R.H.; Bilal, A.S.; de Sousa, F.B.; Swaim, W.D.; Issa, J.P.M.; Gerlach, R.F. Lead line in rodents: An old sign of lead intoxication turned into a new method for environmental surveillance. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 21475–21484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meisnar, M.; Lozano-Perez, S.; Moody, M.; Holland, J. Low-energy EDX – A novel approach to study stress corrosion cracking in SUS304 stainless steel via scanning electron microscopy. Micron 2014, 66, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade Dantas, E.L.; de Figueiredo, J.T.; Macedo-Ribeiro, N.; Oliezer, R.S.; Gerlach, R.F.; de Sousa, F.B. Variation in mineral, organic, and water volumes at the neonatal line and in pre- and postnatal enamel. Arch. Oral Biol. 2020, 118, 104850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Medeiros, R.; Soares, J.; De Sousa, F. Natural enamel caries in polarized light microscopy: Differences in histopathological features derived from a qualitative versus a quantitative approach to interpret enamel birefringence. J. Microsc. 2012, 246, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Little, M.F.; Casciani, F.S. The nature of water in sound human enamel: A preliminary study. Arch. Oral Biol. 1966, 11, 565–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angmar, B.; Carlström, D.; Glas, J.E. Studies on the ultrastructure of dental enamel: IV. The mineralization of normal human enamel. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 1963, 8, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arends, J.; ten Bosch, J.J. Demineralization and remineralization evaluation techniques. J. Dent. Res. 1992, 71, 924–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, J.C. Structure, Crystal Chemistry and Density of Enamel Apatites. In Ciba Foundation Symposium 205-Dental Enamel; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007; pp. 54–72. [Google Scholar]
- de Almeida, G.R.C.; de Souza Guerra, C.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Barbosa, F.; Gerlach, R.F. A plateau detected in lead accumulation in subsurface deciduous enamel from individuals exposed to lead may be useful to identify children and regions exposed to higher levels of lead. Environ. Res. 2008, 107, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudevold, F.; Reda, A.; Aasenden, R.; Bakhos, Y. Determination of trace elements in surface enamel of human teeth by a new biopsy procedure. Arch. Oral Biol. 1975, 20, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa de Almeida, G.R.; Molina, G.F.; Meschiari, C.A.; Barbosa de Sousa, F.; Gerlach, R.F. Analysis of enamel microbiopsies in shed primary teeth by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) and Polarizing Microscopy (PM). Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5169–5175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, I.M.; Laure, H.J.; de Sousa, F.B.; Rosa, J.C.; Gerlach, R.F. New techniques for the recovery of small amounts of mature enamel proteins. J. Archaeol. Sci. 2011, 38, 3596–3604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, E.A. Crystals and Light: An Introduction to Optical Crystallography; Courier Corporation: North Chelmsford, MA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Ericson, J.E.; Shirahata, H.; Patterson, C.C. Skeletal Concentrations of Lead in Ancient Peruvians. N. Engl. J. Med. 1979, 300, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacques, L.; Ogle, N.; Moussa, I.; Kalin, R.; Vignaud, P.; Brunet, M.; Bocherens, H. Implications of diagenesis for the isotopic analysis of Upper Miocene large mammalian herbivore tooth enamel from Chad. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2008, 266, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kocsis, L.; Trueman, C.N.; Palmer, M.R. Protracted diagenetic alteration of REE contents in fossil bioapatites: Direct evidence from Lu–Hf isotope systematics. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 2010, 74, 6077–6092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohn, M.J.; Schoeninger, M.J.; Barker, W.W. Altered states: Effects of diagenesis on fossil tooth chemistry. Geochim. Et Cosmochim. Acta 1999, 63, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoeninger, M.J.; Hallin, K.; Reeser, H.; Valley, J.W.; Fournelle, J. Isotopic alteration of mammalian tooth enamel. Int. J. Osteoarchaeol. 2003, 13, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingo, L.; Cuevas-González, J.; Grimes, S.T.; Hernández Fernández, M.; López-Martínez, N. Multiproxy reconstruction of the palaeoclimate and palaeoenvironment of the Middle Miocene Somosaguas site (Madrid, Spain) using herbivore dental enamel. Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 2009, 272, 53–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeGeros, R.Z.; Bonel, G.; Legros, R. Types of “H2O” in human enamel and in precipitated apatites. Calcif. Tissue Res. 1978, 26, 111–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theuns, H.M.; van Dijk, J.W.E.; Jongebloed, W.L.; Groeneveld, A. The mineral content of human enamel studied by polarizing microscopy, microradiography and scanning electron microscopy. Arch. Oral Biol. 1983, 28, 797–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setally Azevedo Macena, M.; de Alencar e Silva Leite, M.L.; de Lima Gouveia, C.; de Lima, T.A.S.; Athayde, P.A.A.; de Sousa, F.B. A comparative study on component volumes from outer to inner dental enamel in relation to enamel tufts. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porto, I.M.; Rocha, L.B.; Rossi, M.A.; Gerlach, R.F. In situ zymography and immunolabeling in fixed and decalcified craniofacial tissues. J. Histochem. Cytochem. Off. J. Histochem. Soc. 2009, 57, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoba, T. Recent observations on enamel crystal formation during mammalian amelogenesis. Anat. Rec. 1996, 245, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, C.; Hudson, J. Tuft protein: Protein cross-linking in enamel development. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 119, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delgado, S.; Casane, D.; Bonnaud, L.; Laurin, M.; Sire, J.Y.; Girondot, M. Molecular Evidence for Precambrian Origin of Amelogenin, the Major Protein of Vertebrate Enamel. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2001, 18, 2146–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, K.; Weiss, K.M. Mineralized tissue and vertebrate evolution: The secretory calcium-binding phosphoprotein gene cluster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 4060–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Ito, Y.; Kulkarni, A.; Gibson, C.; Luan, X.; Diekwisch, T.G.H. Ameloblastin-rich enamel matrix favors short and randomly oriented apatite crystals. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2011, 119, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, G.F.; Costa de Almeida, G.R.; de Souza Guerra, C.; Cury, J.A.; de Almeida, A.P.; Barroso, R.C.; Gerlach, R.F. Lead deposition in bovine enamel during a pH-cycling regimen simulating the caries process. Caries Res. 2011, 45, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brudevold, F.; Aasenden, R.; Srinivasian, B.N.; Bakhos, Y. Lead in enamel and saliva, dental caries and the use of enamel biopsies for measuring past exposure to lead. J. Dent. Res. 1977, 56, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleymaet, R.; Retief, D.H.; Quartier, E.; Slop, D.; Coomans, D.; Michotte, Y. A comparative study of the lead and cadmium content of surface enamel of Belgian and Kenyan children. Sci. Total Environ. 1991, 104, 175–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleymaet, R.; Bottenberg, P.; Slop, D.; Clara, R.; Coomans, D. Study of lead and cadmium content of surface enamel of schoolchildren from an industrial area in Belgium. Community Dent. Oral Epidemiol. 1991, 19, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa de Almeida, G.R.; de Sousa Guerra, C.; de Angelo Souza Leite, G.; Antonio, R.C.; Barbosa, F.; Tanus-Santos, J.E.; Gerlach, R.F. Lead contents in the surface enamel of primary and permanent teeth, whole blood, serum, and saliva of 6- to 8-year-old children. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1799–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherell, J.A.; Robinson, C.; Hallsworth, A.S. Variations in the chemical composition of human enamel. J. Dent. Res. 1974, 53, 180–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Sample | Ca (wt%) | P (wt%) | Ratio Ca/P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fossil alligator | 36.8 ± 24.4 | 16.5 ± 0.2 | 2.2 ± 0.03 |
| Extant alligator | 33.3 ± 0.4 | 16.6 ± 0.1 | 2.0 ± 0.03 |
| Fossil rodent | 38.6 ± 0.3 | 17.8 ± 0.1 | 2.2 ± 0.02 |
| Extant rodent | 36.8 ± 1.5 | 17.7 ± 1.3 | 2.1 ± 0.12 |
| Distance from Enamel Surface (m) | Mineral | Organic 1 | Water | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| vol (%) | wt (%) | vol (%) | wt (%) | vol (%) | wt (%) | ||
| 15 | 85.3 | 93.1 | 8.2 | 4.5 | 6.6 | 2.4 | |
| 35 | 83.8 | 92.3 | 9.8 | 5.4 | 6.4 | 2.4 | |
| 55 | 83.3 | 92.0 | 10.3 | 5.7 | 6.3 | 2.3 | |
| 75 | 89.2 | 95.3 | 4.6 | 2.5 | 6.3 | 2.2 | |
| fossil alligator | 95 | 87.7 | 94.5 | 5.8 | 3.1 | 6.5 | 2.3 |
| Mean | 85.3 | 93.1 | 8.2 | 4.5 | 6.4 | 2.3 | |
| SD | 2.5 | 1.5 | 2.5 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 0.1 | |
| 15 | 47.7 | 65.0 | 49.0 | 33.5 | 3.3 | 1.5 | |
| 55 | 62.9 | 77.7 | 33.9 | 21.0 | 3.3 | 1.4 | |
| 95 | 59.5 | 75.3 | 35.4 | 22.5 | 5.2 | 2.2 | |
| 135 | 59.8 | 75.2 | 37.6 | 23.7 | 2.7 | 1.1 | |
| extant alligator | 175 | 59.2 | 74.5 | 39.7 | 25.1 | 1.2 | 0.5 |
| Mean | 59.5 | 75.2 | 37.6 | 23.7 | 3.3 | 1.4 | |
| SD | 5.8 | 4.9 | 6.0 | 4.9 | 1.4 | 0.6 | |
| 40 | 42.8 | 61.3 | 47.1 | 33.8 | 10.1 | 4.9 | |
| 70 | 53.2 | 70.8 | 37.3 | 24.9 | 9.5 | 4.2 | |
| 100 | 52.0 | 69.7 | 38.8 | 26.1 | 9.2 | 4.1 | |
| 130 | 52.3 | 69.9 | 39.7 | 26.6 | 8.0 | 3.6 | |
| fossil rodent | 160 | 52.3 | 69.9 | 39.2 | 26.3 | 8.5 | 3.8 |
| Mean | 52.3 | 69.9 | 39.2 | 26.3 | 9.2 | 4.1 | |
| SD | 4.3 | 3.9 | 3.8 | 3.6 | 0.8 | 0.5 | |
| 20 | 71.7 | 85.4 | 16.9 | 10.1 | 11.5 | 4.6 | |
| 45 | 69.9 | 84.2 | 18.5 | 11.2 | 11.6 | 4.7 | |
| 70 | 69.4 | 83.9 | 18.4 | 11.2 | 12.3 | 5.0 | |
| 95 | 68.4 | 83.2 | 19.2 | 11.7 | 12.5 | 5.1 | |
| extant rodent | 120 | 68.1 | 82.9 | 20.2 | 12.4 | 11.7 | 4.8 |
| Mean | 69.4 | 83.9 | 18.5 | 11.2 | 11.7 | 4.8 | |
| SD | 1.4 | 1.0 | 1.2 | 0.8 | 0.4 | 0.2 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pessoa-Lima, C.; Tostes-Figueiredo, J.; Macedo-Ribeiro, N.; Hsiou, A.S.; Muniz, F.P.; Maulin, J.A.; Franceschini-Santos, V.H.; de Sousa, F.B.; Barbosa, F., Jr.; Line, S.R.P.; et al. Structure and Chemical Composition of ca. 10-Million-Year-Old (Late Miocene of Western Amazon) and Present-Day Teeth of Related Species. Biology 2022, 11, 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111636
Pessoa-Lima C, Tostes-Figueiredo J, Macedo-Ribeiro N, Hsiou AS, Muniz FP, Maulin JA, Franceschini-Santos VH, de Sousa FB, Barbosa F Jr., Line SRP, et al. Structure and Chemical Composition of ca. 10-Million-Year-Old (Late Miocene of Western Amazon) and Present-Day Teeth of Related Species. Biology. 2022; 11(11):1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111636
Chicago/Turabian StylePessoa-Lima, Caroline, Jonas Tostes-Figueiredo, Natalia Macedo-Ribeiro, Annie Schmaltz Hsiou, Fellipe Pereira Muniz, José Augusto Maulin, Vinícius H. Franceschini-Santos, Frederico Barbosa de Sousa, Fernando Barbosa, Jr., Sergio Roberto Peres Line, and et al. 2022. "Structure and Chemical Composition of ca. 10-Million-Year-Old (Late Miocene of Western Amazon) and Present-Day Teeth of Related Species" Biology 11, no. 11: 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111636
APA StylePessoa-Lima, C., Tostes-Figueiredo, J., Macedo-Ribeiro, N., Hsiou, A. S., Muniz, F. P., Maulin, J. A., Franceschini-Santos, V. H., de Sousa, F. B., Barbosa, F., Jr., Line, S. R. P., Gerlach, R. F., & Langer, M. C. (2022). Structure and Chemical Composition of ca. 10-Million-Year-Old (Late Miocene of Western Amazon) and Present-Day Teeth of Related Species. Biology, 11(11), 1636. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11111636