Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNFα) Stimulates Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Stem Cells to Promote Intratumoral Invasion and Neovasculogenesis in the Liver of a Xenograft Model
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Line
2.2. Cell Culture and Medium
2.3. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.4. 3D Sphere Forming Assay
2.5. Reverse Transcription and Quantitative PCR
2.6. Protein Isolation
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Cell Invasion Assay
2.9. Conditioned Medium
2.10. Tube Formation Assay
2.11. Orthotopic Breast Cancer Xenografts
2.12. Immunohistochemistry
2.13. Elastica Van Gieson (EVG) Staining
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. TNFα Induces EMT, Such as Phenotype with Increasing Self-Renewal Capacity in TNBCSCs
3.2. TNFα Enhances Proliferation and Invasion in BCSCs
3.3. TNFα-Treated BCSCs Secrete Factors to Increase Network Formation of the Endothelial Cells In Vitro
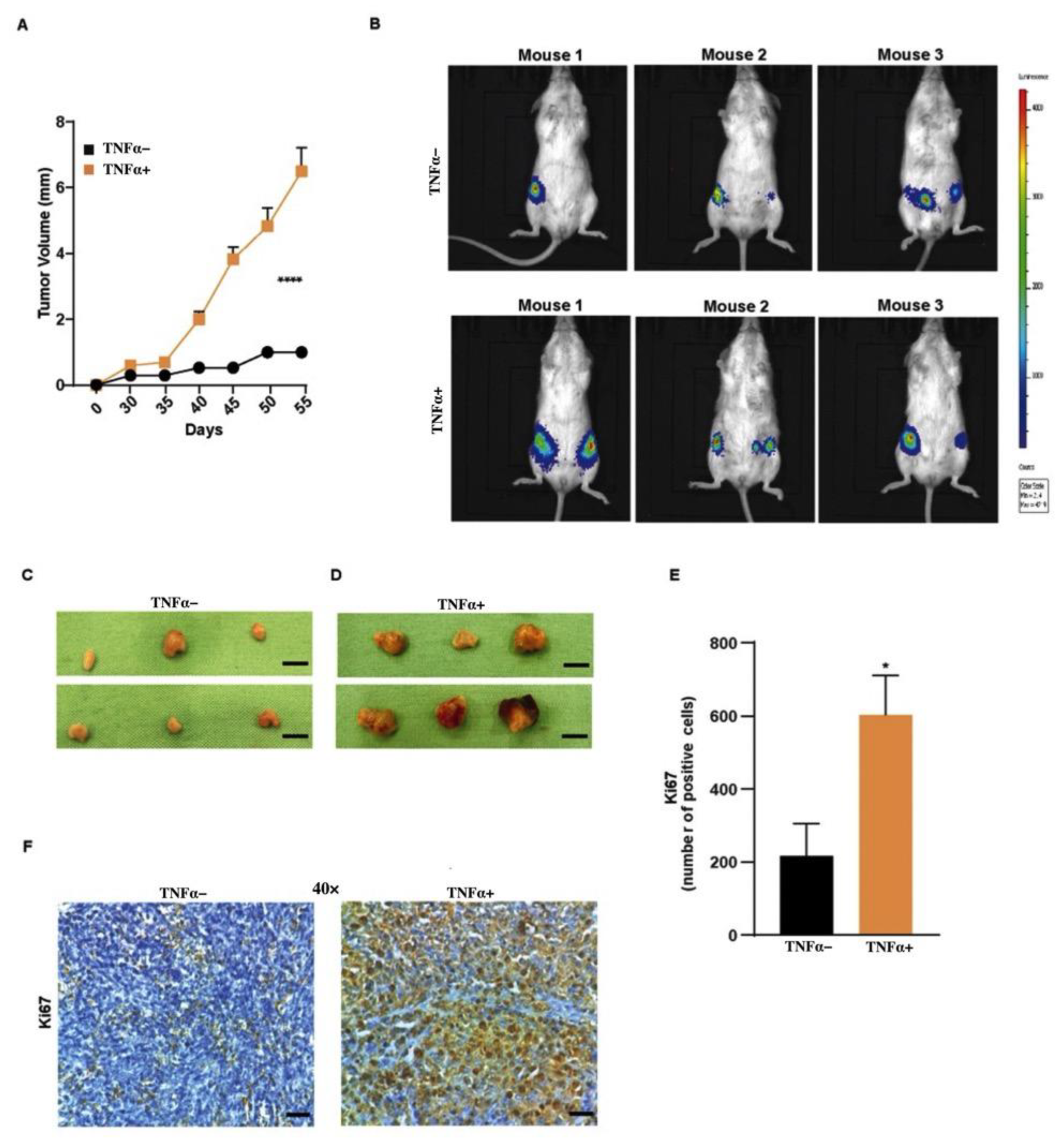
3.4. TNFα Increases Tumor Growth of BCSCs
3.5. TNFα-Treated BCSC Tumors Develop Fibrotic Septa with Increased Collagen and Elastin Fibers
3.6. TNFα-Treated BCSCs Leads to Intratumoral Vessel Formation
3.7. TNFα-Treated BCSC Show an Increase in Liver Neovasculogenesis in Mice
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TNFα | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
| TNBC | Triple-Negative Breast Cancer |
| CSCs | Cancer Stem Cells |
| BCSCs | Breast Cancer Stem Cells |
| BC | Breast Cancer |
| ER | Estrogen Receptor |
| PR | Progesterone Receptor |
| EMT | Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition |
| MEBM | Mammary Epithelial Basal Medium |
| MSC | Mammary Stem Cell |
| ACTB | Actin Beta |
| HUVECs | Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells |
| EVG | Elastic Verhoeff–Van Gieson |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 |
References
- Martinez-Reza, I.; Diaz, L.; Garcia-Becerra, R. Preclinical and clinical aspects of TNF-alpha and its receptors TNFR1 and TNFR2 in breast cancer. J. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 24, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Reilly, D.; Sendi, M.A.; Kelly, C.M. Overview of recent advances in metastatic triple negative breast cancer. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 12, 164–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collina, F.; Di Bonito, M.; Li Bergolis, V.; De Laurentiis, M.; Vitagliano, C.; Cerrone, M.; Nuzzo, F.; Cantile, M.; Botti, G. Prognostic Value of Cancer Stem Cells Markers in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 158682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fultang, N.C.M.; Peethambaran, B. Regulation of cancer stem cells in triple negative breast cancer. Cancer Drug Resist 2021, 4, 321–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strietz, J.; Stepputtis, S.S.; Follo, M.; Bronsert, P.; Stickeler, E.; Maurer, J. Human Primary Breast Cancer Stem Cells Are Characterized by Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiba, T.; Zheng, Y.W.; Kita, K.; Yokosuka, O.; Saisho, H.; Onodera, M.; Miyoshi, H.; Nakano, M.; Zen, Y.; Nakanuma, Y.; et al. Enhanced self-renewal capability in hepatic stem/progenitor cells drives cancer initiation. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, M.F. A self-renewal assay for cancer stem cells. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2005, 56 (Suppl. 1), 64–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rajaraman, R.; Guernsey, D.L.; Rajaraman, M.M.; Rajaraman, S.R. Stem cells, senescence, neosis and self-renewal in cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2006, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.S.; Paredes, J. P-cadherin linking breast cancer stem cells and invasion: A promising marker to identify an “Intermediate/Metastable” EMT state. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danforth, D.N. The role of chronic inflammation in the development of breast cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kartikasari, A.E.R.; Huertas, C.S.; Mitchell, A.; Plebanski, M. Tumor-induced inflammatory cytokines and the emerging diagnostic devices for cancer detection and prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 692142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.; Cao, C.; Li, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, X.; Ye, L. Inflammatory factor TNF-alpha promotes the growth of breast cancer via the positive feedback loop of TNFR1/NF-kappaB (and/or p38)/p-STAT3/HBXIP/TNFR1. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 58338–58352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepak, K.G.K.; Vempati, R.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Dasari, V.R.; Nagini, S.; Rao, D.N.; Malla, R.R. Tumor microenvironment: Challenges and opportunities in targeting metastasis of triple negative breast cancer. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 153, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, P.; Zhang, Z. TNF-alpha promotes colon cancer cell migration and invasion by upregulating TROP-2. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 3820–3827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Mu, Y.; Sa, N.; Wang, H.; Xu, W. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes metastasis via NF-kappaB signaling pathway-mediated TWIST expression in hypopharyngeal cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2014, 31, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makrilia, N.; Kollias, A.; Manolopoulos, L.; Syrigos, K. Cell adhesion molecules: Role and clinical significance in cancer. Cancer Invest. 2009, 27, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, D.H.; Kim, Y.K.; Kim, M.R.; Jang, J.H.; Lee, S. Emerging roles of Vascular Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (VCAM-1) in immunological disorders and cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siyasi, M.; Mahjoubi, F.; Mahjoubi, B.; Shabani, S. Study of VCAM-1 gene expression in normal and tumoral tissues in patients with colorectal cancer. J. Biotechnol. Biomed. Sci. 2017, 1, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemagno, C.; Dumas, L.; Cavailles, P.; Ahmadi, M.; Bacot, S.; Debiossat, M.; Soubies, A.; Djaileb, L.; Leenhardt, J.; Leiris, N.; et al. In vivo assessment of VCAM-1 expression by SPECT/CT imaging in mice models of human triple negative breast cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hynes, R.O. Metastatic cells will take any help they can get. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 689–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Sharma, R.; Khaket, T.P.; Dutta, C.; Chakraborty, B.; Mukherjee, T.K. Breast cancer metastasis: Putative therapeutic role of vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Cell Oncol. 2017, 40, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercogliano, M.F.; Bruni, S.; Elizalde, P.V.; Schillaci, R. Tumor necrosis factor alpha blockade: An opportunity to tackle breast cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilir, C.; Engin, H.; Can, M.; Likhan, S.; Demirtas, D.; Kuzu, F.; Bayraktaroglu, T. Increased serum tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor-6 expression in patients with non-metastatic triple-negative breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 2819–2824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, H.H.; Zhu, H.; Liu, L.S.; Huang, Y.; Guo, J.; Li, J.; Sun, X.P.; Chang, C.X.; Wang, Z.H.; Zhai, K. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha gene polymorphism is associated with metastasis in patients with triple negative breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, T.; Wakabayashi, H.; Matsumine, A.; Sudo, A.; Uchida, A. TNF inhibitor suppresses bone metastasis in a breast cancer cell line. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 407, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pileczki, V.; Braicu, C.; Gherman, C.D.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. TNF-alpha gene knockout in triple negative breast cancer cell line induces apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 14, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Strietz, J.; Bleilevens, A.; Stickeler, E.; Maurer, J. Chemotherapeutic stress influences epithelial-mesenchymal transition and stemness in cancer stem cells of triple-negative breast cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metzger, E.; Stepputtis, S.S.; Strietz, J.; Preca, B.T.; Urban, S.; Willmann, D.; Allen, A.; Zenk, F.; Iovino, N.; Bronsert, P.; et al. KDM4 inhibition targets breast cancer stem-like cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5900–5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.N.; Gao, H.; Anfossi, S.; Mego, M.; Reddy, N.G.; Debeb, B.; Giordano, A.; Tin, S.; Wu, Q.; Garza, R.J.; et al. Inflammation mediated metastasis: Immune induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in inflammatory breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0132710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josephs, S.F.; Ichim, T.E.; Prince, S.M.; Kesari, S.; Marincola, F.M.; Escobedo, A.R.; Jafri, A. Unleashing endogenous TNF-alpha as a cancer immunotherapeutic. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryugina, E.I.; Kiosses, W.B. Intratumoral cancer cell intravasation can occur independent of invasion into the adjacent stroma. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 601–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Cao, X. Characteristics and significance of the pre-metastatic niche. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 668–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Massague, J. Molecular pathways: VCAM-1 as a potential therapeutic target in metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 5520–5525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candido, J.; Hagemann, T. Cancer-related inflammation. J. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 33 (Suppl. 1), S79–S84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruceriu, D.; Baldasici, O.; Balacescu, O.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. The dual role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) in breast cancer: Molecular insights and therapeutic approaches. Cell. Oncol. 2020, 43, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landskron, G.; De la Fuente, M.; Thuwajit, P.; Thuwajit, C.; Hermoso, M.A. Chronic inflammation and cytokines in the tumor microenvironment. J. Immunol. Res. 2014, 2014, 149185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, X.; Zhang, H.; Cao, A.; Cao, L.; Hu, X. Cytokine TNF-alpha promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by down-regulating Pentraxin3. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1800–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.W.; Xia, W.; Huo, L.; Lim, S.O.; Wu, Y.; Hsu, J.L.; Chao, C.H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yang, N.K.; Ding, Q.; et al. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by TNF-alpha requires NF-kappaB-mediated transcriptional upregulation of Twist1. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Lu, X.; Shi, P.; Yang, G.; Zhou, Z.; Li, W.; Mao, X.; Jiang, D.; Chen, C. TNF-alpha increases breast cancer stem-like cells through up-regulating TAZ expression via the non-canonical NF-kappaB pathway. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Ma, L.; Dai, L.; Zuo, D.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; Xu, F. TNFalpha promotes the malignant transformation of intestinal stem cells through the NFkappaB and Wnt/betacatenin signaling pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 44, 577–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Du, Q.; Wang, X.; Tang, N.; She, F.; Chen, Y. TNF-alpha promotes gallbladder cancer cell growth and invasion through autocrine mechanisms. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 33, 1431–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leppkes, M.; Roulis, M.; Neurath, M.F.; Kollias, G.; Becker, C. Pleiotropic functions of TNF-alpha in the regulation of the intestinal epithelial response to inflammation. Int. Immunol. 2014, 26, 509–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bussard, K.M.; Mutkus, L.; Stumpf, K.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Marini, F.C. Tumor-associated stromal cells as key contributors to the tumor microenvironment. Breast Cancer Res. 2016, 18, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.H.; Massague, J. Macrophage binding to receptor VCAM-1 transmits survival signals in breast cancer cells that invade the lungs. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 538–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coussens, L.M.; Werb, Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature 2002, 420, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Khachfe, H.H.; Salhab, H.A.; Fares, Y. Molecular principles of metastasis: A hallmark of cancer revisited. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.N.; Riba, R.D.; Zacharoulis, S.; Bramley, A.H.; Vincent, L.; Costa, C.; MacDonald, D.D.; Jin, D.K.; Shido, K.; Kerns, S.A.; et al. VEGFR1-positive haematopoietic bone marrow progenitors initiate the pre-metastatic niche. Nature 2005, 438, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, M.; Haider, A.; Rashid, S.; Al-Nabet, A. Paget’s “Seed and Soil” theory of cancer metastasis: An idea whose time has come. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2019, 26, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, R.N.; Rafii, S.; Lyden, D. Preparing the “soil”: The premetastatic niche. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11089–11093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, X.; Qian, C.; Liu, Z.; Luo, D. Factors involved in cancer metastasis: A better understanding to "seed and soil" hypothesis. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribatti, D.; Mangialardi, G.; Vacca, A. Stephen Paget and the ‘seed and soil’ theory of metastatic dissemination. Clin. Exp. Med. 2006, 6, 145–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zijl, F.; Krupitza, G.; Mikulits, W. Initial steps of metastasis: Cell invasion and endothelial transmigration. Mutat. Res. 2011, 728, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Shen, S.; Verma, I.M. NF-kappaB, an active player in human cancers. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 823–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.Y.; Wolchok, J.D.; Bass, A.R. TNF in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors: Friend or foe? Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Hashemi, F.; Zabolian, A.; Saleki, H.; Ranjbar, A.; Seyed Saleh, S.H.; Bagherian, M.; Sharifzadeh, S.O.; Hushmandi, K.; et al. Regulation of Nuclear Factor-KappaB (NF-kappaB) signaling pathway by non-coding RNAs in cancer: Inhibiting or promoting carcinogenesis? Cancer Lett. 2021, 509, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alzubi, M.A.; Turner, T.H.; Olex, A.L.; Sohal, S.S.; Tobin, N.P.; Recio, S.G.; Bergh, J.; Hatschek, T.; Parker, J.S.; Sartorius, C.A.; et al. Separation of breast cancer and organ microenvironment transcriptomes in metastases. Breast Cancer Res. 2019, 21, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Narasimhan, H.; Ferraro, F.; Bleilevens, A.; Weiskirchen, R.; Stickeler, E.; Maurer, J. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNFα) Stimulates Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Stem Cells to Promote Intratumoral Invasion and Neovasculogenesis in the Liver of a Xenograft Model. Biology 2022, 11, 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101481
Narasimhan H, Ferraro F, Bleilevens A, Weiskirchen R, Stickeler E, Maurer J. Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNFα) Stimulates Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Stem Cells to Promote Intratumoral Invasion and Neovasculogenesis in the Liver of a Xenograft Model. Biology. 2022; 11(10):1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101481
Chicago/Turabian StyleNarasimhan, Harini, Francesca Ferraro, Andreas Bleilevens, Ralf Weiskirchen, Elmar Stickeler, and Jochen Maurer. 2022. "Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNFα) Stimulates Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Stem Cells to Promote Intratumoral Invasion and Neovasculogenesis in the Liver of a Xenograft Model" Biology 11, no. 10: 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101481
APA StyleNarasimhan, H., Ferraro, F., Bleilevens, A., Weiskirchen, R., Stickeler, E., & Maurer, J. (2022). Tumor Necrosis Factor-α (TNFα) Stimulates Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Stem Cells to Promote Intratumoral Invasion and Neovasculogenesis in the Liver of a Xenograft Model. Biology, 11(10), 1481. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11101481








