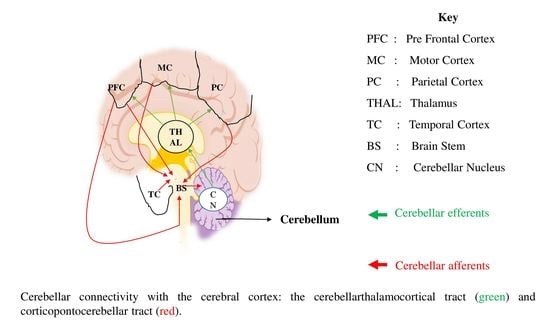
Sex Differences in Animal Models of Sodium-Valproate-Induced Autism in Postnatal BALB/c Mice: Whole-Brain Histoarchitecture and 5-HT2A Receptor Biomarker Evidence
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Animals
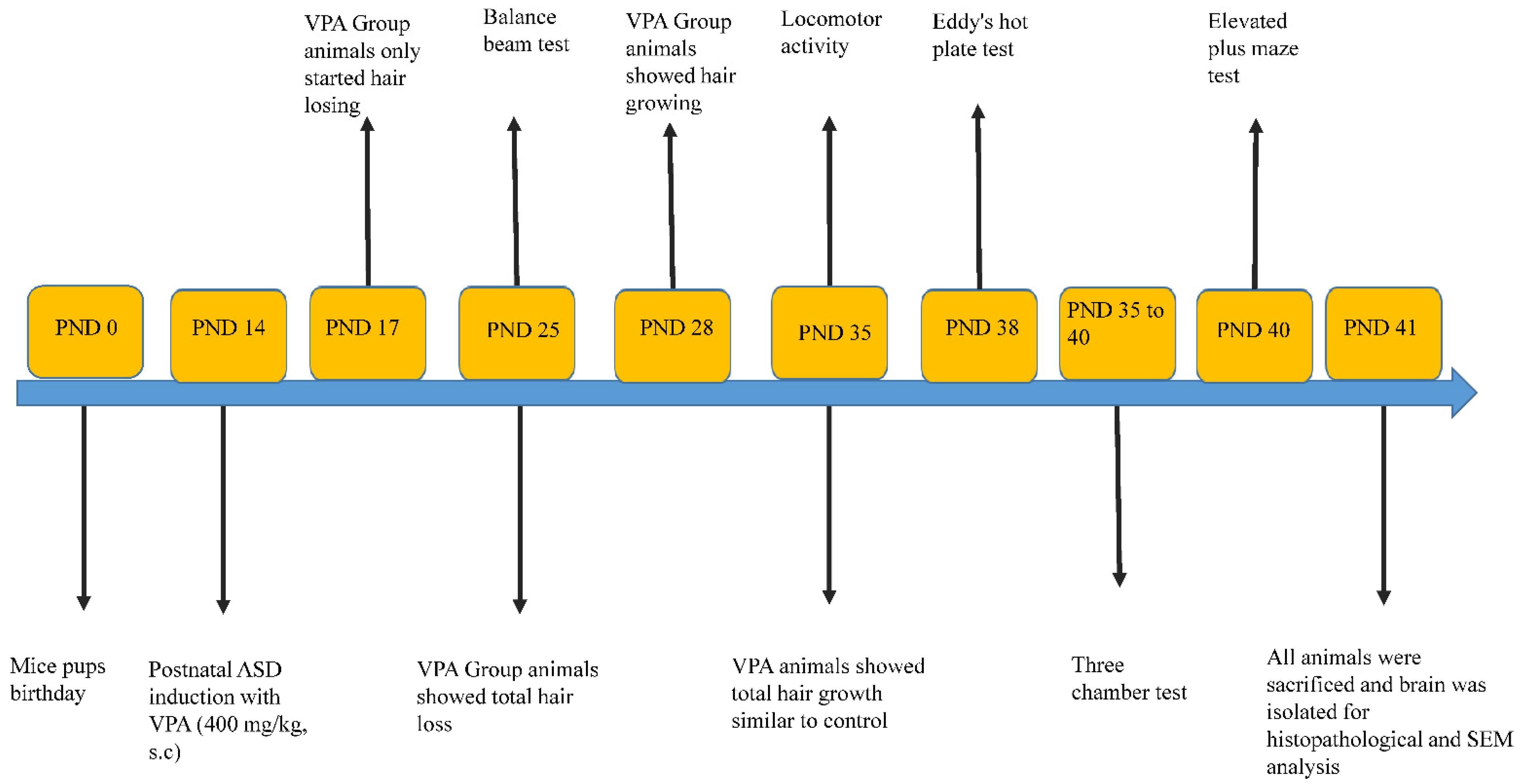
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Behavioural Analysis
2.4.1. Balance Beam
2.4.2. Nociception
2.4.3. Elevated plus Maze
2.4.4. Actophotometer for Locomotor Activity
2.4.5. Assessment of Social Interaction
2.5. Histopathology
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
2.7. Immunohistochemical Studies
2.8. Statistics
3. Results
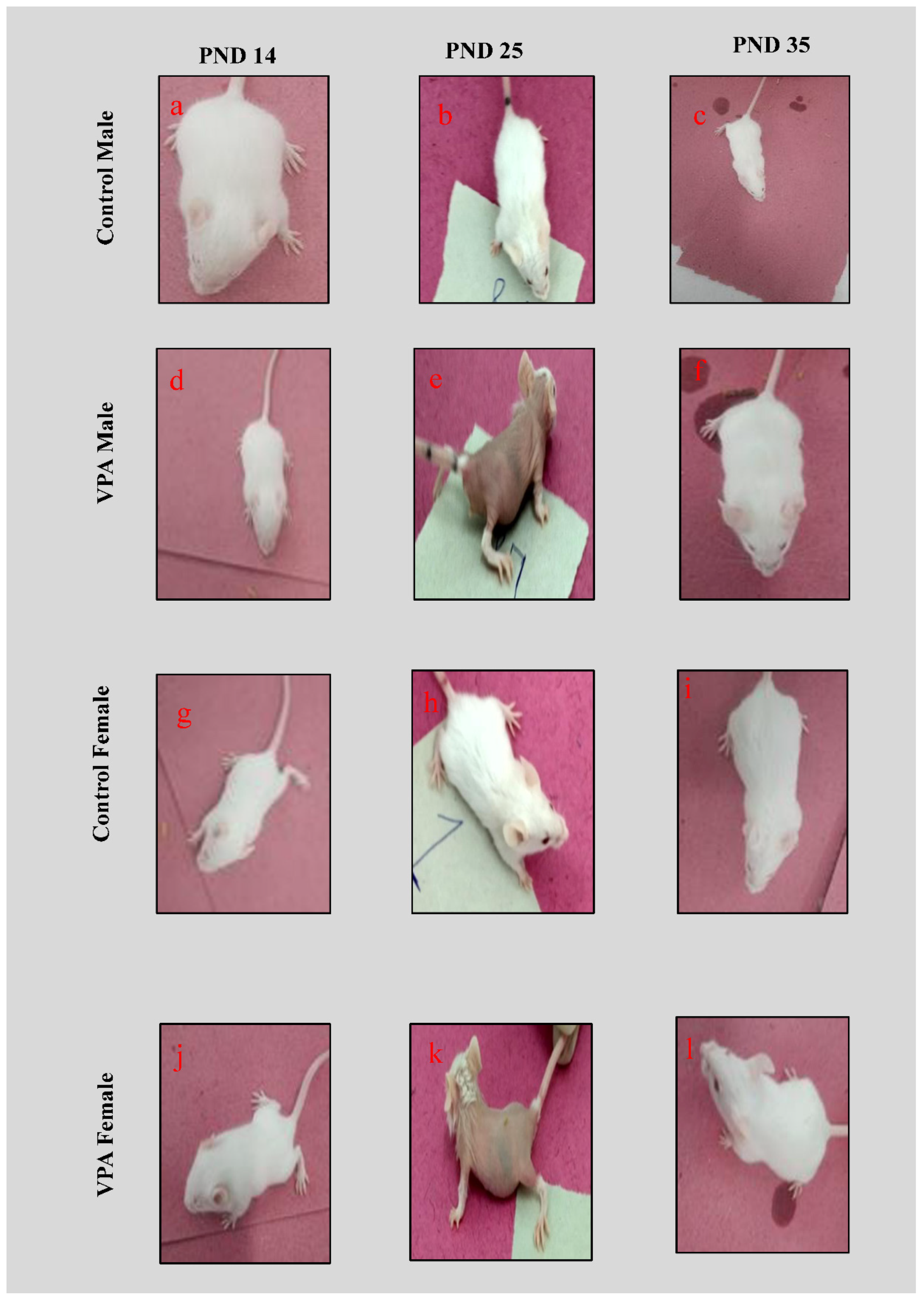
3.1. Physical Appearance
3.2. Balance Beam
3.3. Actophotometer
3.4. Hot Plate
3.5. Elevated Plus Maze Test
3.6. Effect on Social Interaction
3.6.1. Social Ability and Social Ability Index
3.6.2. Social Preference and Social Preference Index
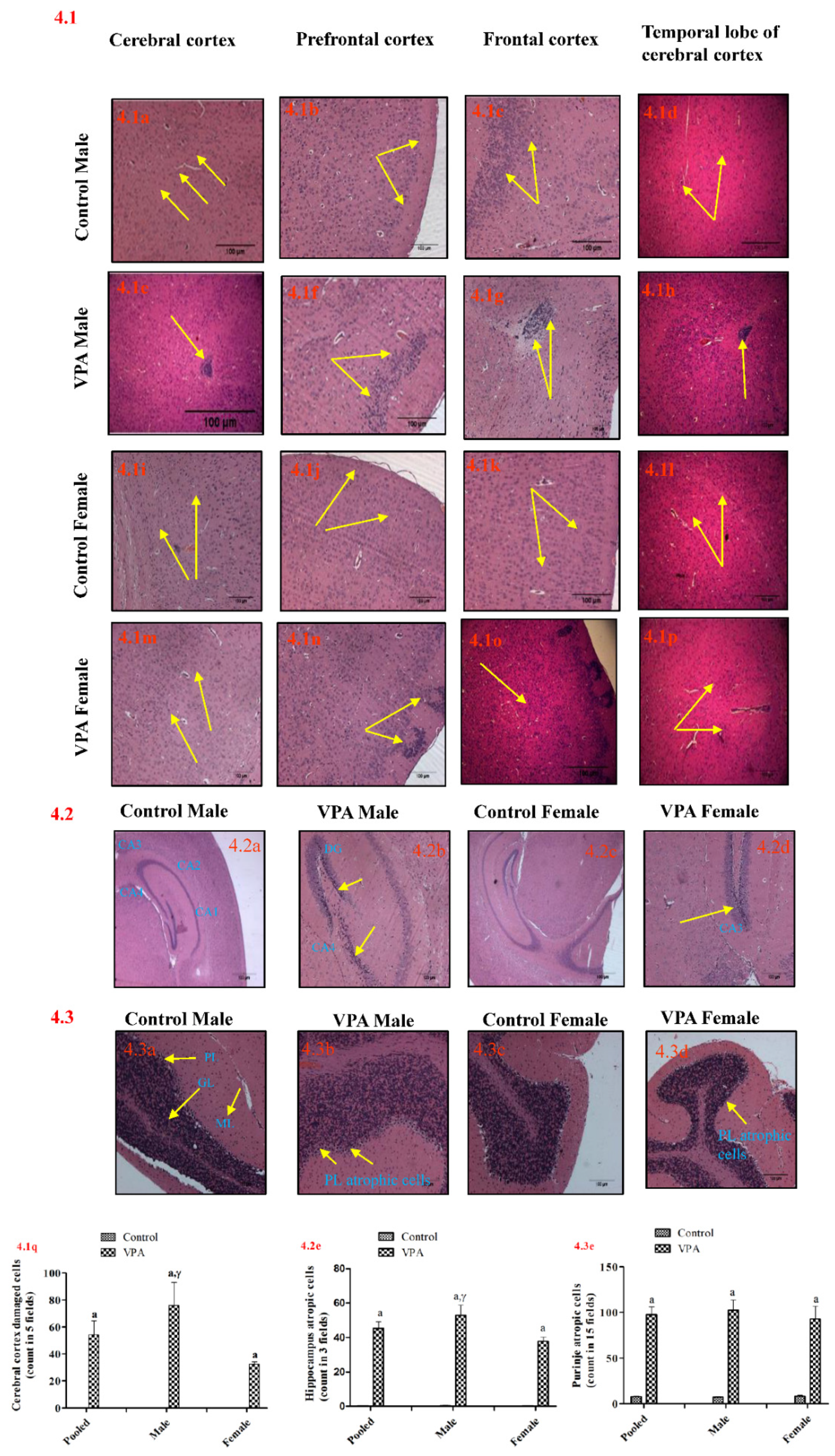
3.7. Histopathology of the Brain
3.7.1. Cerebral Cortex
3.7.2. Hippocampus
3.7.3. Cerebellum
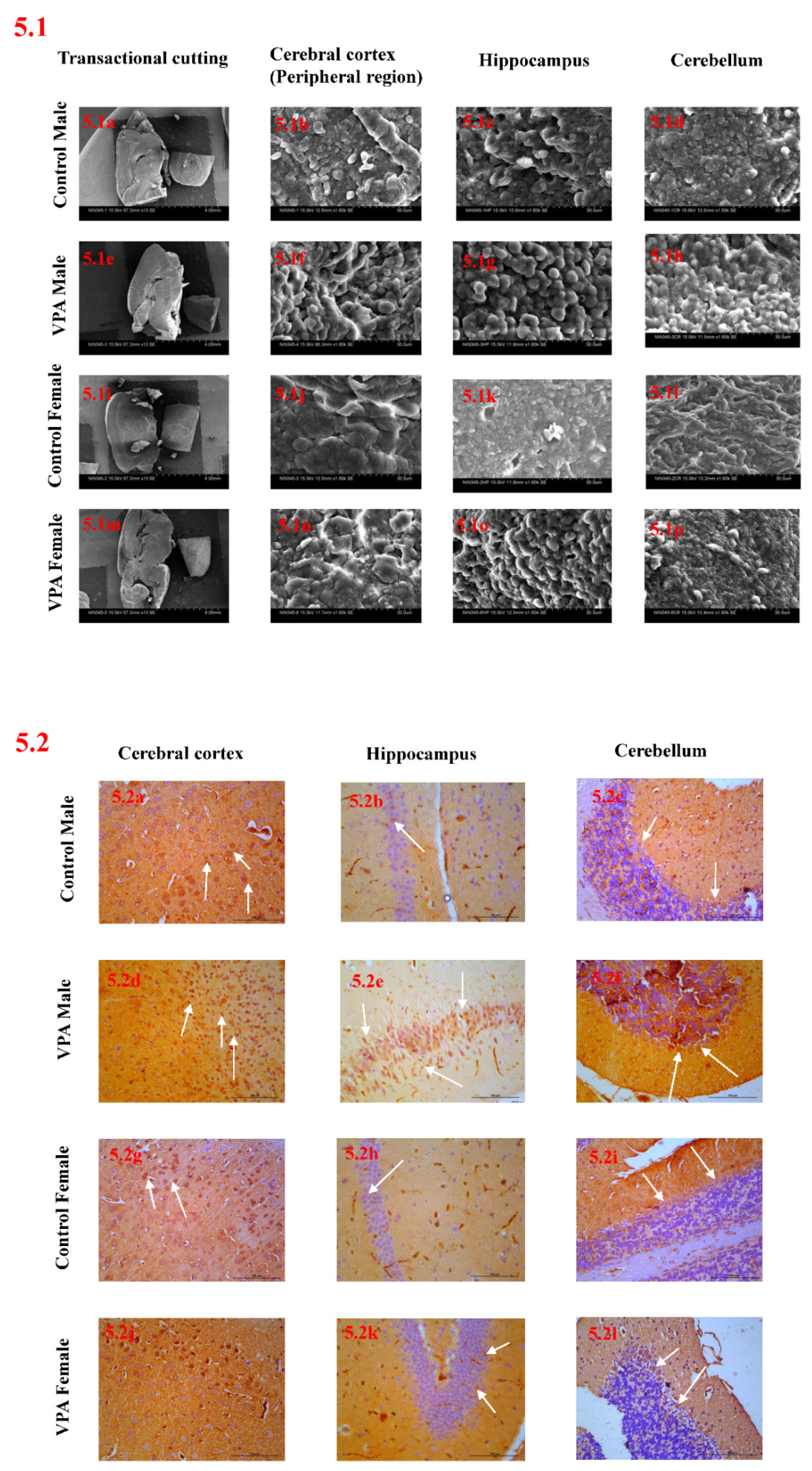
3.8. Scanning Electron Microscope Analysis
3.9. Immunohistochemical Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fakhoury, M. Imaging genetics in autism spectrum disorders: Linking genetics and brain imaging in the pursuit of the underlying neurobiological mechanisms. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 80 Pt B, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhoury, M. Autistic spectrum disorders: A review of clinical features, theories and diagnosis. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2015, 43, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arafat, E.A.; Shabaan, D.A. The possible neuroprotective role of grape seed extract on the histopathological changes of the cerebellar cortex of rats prenatally exposed to Valproic Acid: Animal model of autism. Acta Histochem. 2019, 121, 841–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, S.; Enayati, A.; Redwood, L.; Roger, H.; Binstock, T. Autism: A novel form of mercury poisoning. Med. Hypotheses 2001, 56, 462–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chaste, P.; Leboyer, M. Autism risk factors: Genes, environment, andgene–environment interactions. Dialogues. Clin. Neurosci. 2012, 14, 281–292. [Google Scholar]
- Dai, Y.C.; Zhang, H.F.; Schön, M.; Böckers, T.M.; Han, S.P.; Han, J.S.; Zhang, R. Neonatal Oxytocin Treatment Ameliorates Autistic-Like Behaviors and Oxytocin Deficiency in Valproic Acid-Induced Rat Model of Autism. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balaji, G.; Sinha, S.N. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD): A current review of assessment, risk factors and prevention. Ind. J. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 55, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Rodier, P.M.; Hyman, S.L. Early environmental factors in autism. Ment. Retard. Dev. Dis. Res. 1998, 4, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pragnya, B.; Kameshwari, J.S.L.; Veeresh, B. Ameliorating effect of piperine on behavioral abnormalities and oxidative markers in sodium valproate induced autism in BALB/c mice. Behav. Brain. Res. 2014, 270, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinaldi, T.; Kulangara, K.; Antoniello, K.; Markram, H. Elevated NMDA receptor levels and enhanced postsynaptic long-term potentiation induced by prenatal exposure to valproic acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 13501–13506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morakotsriwan, N.; Wattanathorn, J.; Kirisattayakul, W.; Chaisiwamongkol, K. Autistic-Like Behaviors, Oxidative Stress Status, and Histopathological Changes in Cerebellum of Valproic Acid Rat Model of Autism Are Improved by the Combined Extract of Purple Rice and Silkworm Pupae. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 3206561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bertolino, B.; Crupi, R.; Impellizzeri, D.; Bruschetta, G.; Cordaro, M.; Siracusa, R.; Esposito, E.; Cuzzocrea, S. Beneficial Effects of Co-Ultramicronized Palmitoylethanolamide/Luteolin in a Mouse Model of Autism and in a Case Report of Autism. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 23, 87–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirza, R.; Sharma, B. Benefits of Fenofibrate in prenatal valproic acid-induced autism spectrum disorder related phenotype in rats. Brain Res. Bull. 2019, 147, 36–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, C.G.; Reuhl, K.R.; Cheh, M.; McRae, P.; Halladay, A.K. A new neurobehavioral model of autism in mice: Pre- and postnatal exposure to sodium valproate. J. Autism. Dev. Dis. 2006, 36, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yochum, C.L.; Dowling, P.; Reuhl, K.R.; Wagner, G.C.; Ming, X. VPA-induced apoptosis and behavioral deficits in neonatal mice. Brain Res. 2008, 1203, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, T.; Przewlocki, R. Behavioral alterations in rats prenatally exposedto valproic acid: Animal model of autism. Neuropsychopharmacology 2005, 30, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rice, D.; Barone, S. Critical periods of vulnerability for the developing nervous system: Evidence from human and animal models. Environ. Health Perspect. 2000, 108, 511–533. [Google Scholar]
- Eissa, N.; Azimullah, S.; Jayaprakash, P.; Jayaraj, R.L.; Reiner, D.; Ojha, S.K.; Beiram, R.; Stark, H.; Łażewska, D.; Kieć-Kononowicz, K.; et al. The dual-active histamine H3 receptor antagonist and acetylcholine esterase inhibitor E100 ameliorates stereotyped repetitive behavior and neuroinflammmation in sodium valproate induced autism in mice. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2019, 312, 108775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazlauskas, N.; Campolongo, M.; Lucchina, L.; Zappala, C.; Depino, A.M. Postnatal behavioral and inflammatory alterations in female pupsprenatally exposed to valproic acid. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2016, 72, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Mello, A.M.; Stoodley, C.J. Cerebro-cerebellar circuits in autism spectrum disorder. Front. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ellegood, J.; Anagnostou, E.; Babineau, B.A.; Crawley, J.N.; Lin, L.; Genestine, M. Clustering autism: Using neuroanatomical differences in 26 mouse models to gain insight into the heterogeneity. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ingram, J.L.; Peckham, S.M.; Tisdale, B.; Rodier, P.M. Prenatal exposure of rats to valproic acid reproduces the cerebellar anomalies associated with autism. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2000, 22, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougherty, J.P.; Aloyo, V.J. Pharmacological and behavioral characterization of the 5-HT2A receptor in C57BL/6N mice. Psychopharmacology 2011, 215, 581–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hensler, G.J. Serotonin. Basic Neurochemistry, 8th ed.; American Society for Neurochemistry: Houston, TX, USA, 2012; pp. 300–322. [Google Scholar]
- Guiard, B.P.; Di Giovanni, G. Central serotonin-2A (5-HT2A) receptor dysfunction in depression and epilepsy: The missing link? Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Banji, D.; Banjia, O.; Abbagonia, S.; Hayathb, S.; Kambama, S.; Chiluka, V. Amelioration of behavioral aberrations and oxidative markers by green tea extract in valproate induced autism in animals. Brain Res. 2011, 1410, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, T.; Bando, Y.; Nakazawa, H.; Kanemoto, S.; Yoshida, S. Pathological changes in mice with long term cuprizone administration. Neurochem. Int. 2019, 126, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, Y.A.; Chalamaiah, M.; Ramesh, B.; Balaji, G.; Indira, P. Ameliorating activity of ginger (Zingiber officinale) extract against lead induced renal toxicity in male rats. J. Food. Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 908–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karnovsky, M.J. A Formaldehyde-Glutaraldehyde Fixative of High Osmolarity for Use Electron Microscopy. Cell Biol. 1965, 27, 1A–149A. [Google Scholar]
- Gluert, A.M. Fixation, Dehydration and Embedding of Biological Specimens in Practical Methods in Electron Microscopy; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1984; Volume 3. [Google Scholar]
- Gąssowska-Dobrowolska, M.; Kolasa-Wołosiuk, A.; Cieślik, M.; Dominiak, A.; Friedland, K.; Adamczyk, A. Alterations in Tau Protein Level and Phosphorylation State in the Brain of the Autistic-Like Rats Induced by Prenatal Exposure to Valproic Acid. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilbey, Y.O.; Ozbek, E.; Simşek, A.; Cekmen, M.; Somay, A.; Tasci, A.I. Pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate treatment prevents ethylene glycol-induced urolithiasis through inhibition of NF-kappaB and p38-MAPK signaling pathways in rat kidney. Arch. Ital. Urol. Androl. 2010, 82, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yochum, C.L.; Bhattacharya, P.; Patti, L.; Mirochnitchenko, O.; Wagnera, G.C. Animal model of autism using GSTM1 knockout mice and early post-natal. Behavio. Brain Res. 2010, 210, 202–210. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Beste, B. Valproate-induced hair loss: What to tell patients. Curr. Psychiatry 2011, 10, 62. [Google Scholar]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Tasdemir, H.A.; Paksu, M.S. The influence of valproic acid treatment on hair and serum zinc levels and serum biotinidase activity. Eur. J. Paediatr. Neurol. 2009, 13, 439–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, F.H.; Tunca, H.; Güney, E.; Iseri, E. Neurotransmitter Systems in Autism Spectrum Disorder. In Autism Spectrum Disorder—Recent Advances; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2015; pp. 15–30. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.T.; Yang, K.C.; Lin, W.C. Glutamatergic Dysfunction and Glutamatergic Compounds for Major Psychiatric Disorders: Evidence From Clinical Neuroimaging Studies. Front. Psychiatry 2019, 9, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tamminga, C.A.; Stan, A.D.; Wagner, A.D. The hippocampal formation in schizophrenia. Am. J. Psychiatry 2010, 167, 1178–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thau, L.; Reddy, V.; Singh, P. Anatomy, Central Nervous System. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542179/ (accessed on 14 June 2019).
- Kokras, N.; Dalla, C. Sex differences in animal models of psychiatric disorders. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2014, 171, 4595–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, T.; Roman, A.; Basta-Kaim, A.; Kubera, M.; Budziszewska, B.; Schneider, K.; Przewlocki, R. Gender-specific behavioral and immunological alterations in an animal model of autism induced by prenatal exposure to valproic acid. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33, 728–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, S.A.; Gifford, J.J.; Pawlak, A.P.; Derbaly, A.; Sherman, S.L.; Zhang, H.; Wagner, G.C.; Kusnecov, A.W. Long-lasting Behavioral and Neuroanatomical Effects of Postnatal Valproic Acid Treatment. Neuroscience 2020, 434, 8–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, A.; Luthert, P.; Dean, A.; Harding, B.; Janota, I.; Montgomery, M.; Rutter, M.; Lantos, P. A clinicopathological study of autism. Brain 1998, 121, 889–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guerin, P.; Lyon, G.; Barthelemy, C.; Sostak, E.; Chevrollier, V.; Garreau, B. Neuropathological study of a case of autistic syndrome with severe mental retardation. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 1996, 38, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edalatmanesh, M.A.; Nikfarjam, H.; Vafaee, F.; Moghadas, M. Increased hippocampal cell density and enhanced spatial memory in the valproic acid rat model of autism. Brain Res. 2013, 1526, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, G. Cerebellar contributions to autism spectrum disorders. Clin. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 6, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, D.L.; Nascimbene, C.; Krishnan, C.; Zimmerman, A.W.; Pardo, C.A. Neuroglial activation and neuroinflammation in the brain of patients with autism. Ann. Neurol. 2005, 57, 67–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubenstein, J.L. Annual Research Review: Development of the cerebral cortex: Implications for neurodevelopmental disorders. J. Child. Psychol. Psychiatry 2011, 52, 339–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halberstadt, A.L. Recent advances in the neuropsychopharmacology of serotonergic hallucinogens. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 277C, 99–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Amodeo, D.A.; Jones, J.H.; Sweeney, J.A.; Ragozzino, M.E. Risperidone and the 5-HT2A receptor antagonist M100907 improve probabilistic reversal learning in BTBR T + tf/J mice. Autism Res. 2014, 7, 555–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oblak, A.; Gibbs, T.T.; Blatt, G.J. Reduced serotonin receptor subtypes in a limbic and a neocortical region in autism. Autism Res. 2013, 6, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]

| Male | Female | Pooled | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Control | VPA | p-Value | Control | VPA | p-Value | Control | VPA | p-Value |
| No. of entries in open arms | 10.17 (2.02) | 3.17 (0.91) b | 0.01 | 6.67 (0.95) | 2.00 (0.58) b | 0.002 | 8.42 (1.19) | 2.58 (0.54) a | 0.001 |
| Time spent in open arms (s) | 97.17 (9.25) | 46.17 (12.08) c | 0.007 | 77.17 (10.42) | 25.83 (7.39) b | 0.002 | 87.17 (7.29) | 36.00 (7.41) a | 0.001 |
| Male | Female | Pooled | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Control | VPA | p-Value | Control | VPA | p-Value | Control | VPA | p-Value |
| Time spent in stranger chamber | 313.67 (17.03) | 276.83 (27.80) | 0.285 | 300.83 (35.19) | 236.67 (54.31) | 0.345 | 307.25 (18.7) | 256.75 (29.71) | 0.165 |
| Time spent in empty chamber | 166.67 (12.82) | 236.83 (19.38) b | 0.013 | 207.83 (26.75) | 311.33 (40.28) | 0.058 | 187.25 (15.45) | 274.08 (24.09) b | 0.006 |
| Social ability index | 1.93 (0.16) | 1.24 (0.21) c | 0.026 | 1.70 (0.44) | 1.08 (0.51) | 0.379 | 1.82 (0.23) | 1.16 (0.27) | 0.074 |
| Time spent in novel animal | 280.00 (17.83) | 258.00 (17.28) | 0.396 | 305.50 (35.25) | 288.83 (47.61) | 0.784 | 292.75 (19.22) | 273.42 (24.59) | 0.542 |
| Time spent in familiar animal | 218.17 (22.82) | 247.83 (16.42) | 0.316 | 220.17 (29.61) | 237.50 (46.05) | 0.758 | 219.17 (17.82) | 242.67 (23.36) | 0.432 |
| Social preference index | 1.38 (0.20) | 1.07 (0.11) | 0.215 | 1.64 (0.42) | 1.66 (0.53) | 0.98 | 1.51 (0.23) | 1.37 (0.27) | 0.687 |
| Male | Female | Pooled | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | Control | VPA | p-Value | Control | VPA | p-Value | Control | VPA | p-Value |
| Cerebral cortex | 2.33 (0.33) | 4.00 (0.00) c,γ | 0.03 | 2.00 (0.00) | 2.67 (0.33) | 0.11 | 2.17 (0.17) | 3.33 (0.33) c | 0.02 |
| Hippocampus | 1.00 (0.00) | 3.67 (0.3) c,γ | 0.03 | 1.00 (0.00) | 1.00 (0.00) | 1.00 | 1.00 (0.00) | 2.33 (0.61) | 0.06 |
| Purkinje cells | 2.00 (0.00) | 4.67 (0.33) c,γ | 0.03 | 2.00 (0.00) | 3.00 (0.00) c | 0.02 | 2.00 (0.00) | 3.83 (0.40) b | 0.002 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gouda, B.; Sinha, S.N.; Chalamaiah, M.; Vakdevi, V.; Shashikala, P.; Veeresh, B.; Surekha, V.M.; Kasturi, V.; Boiroju, N.K. Sex Differences in Animal Models of Sodium-Valproate-Induced Autism in Postnatal BALB/c Mice: Whole-Brain Histoarchitecture and 5-HT2A Receptor Biomarker Evidence. Biology 2022, 11, 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010079
Gouda B, Sinha SN, Chalamaiah M, Vakdevi V, Shashikala P, Veeresh B, Surekha VM, Kasturi V, Boiroju NK. Sex Differences in Animal Models of Sodium-Valproate-Induced Autism in Postnatal BALB/c Mice: Whole-Brain Histoarchitecture and 5-HT2A Receptor Biomarker Evidence. Biology. 2022; 11(1):79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010079
Chicago/Turabian StyleGouda, Balaji, Sukesh Narayan Sinha, Meram Chalamaiah, Validandi Vakdevi, Patangay Shashikala, Bantal Veeresh, Venkata Mullapudi Surekha, Vasudev Kasturi, and Naveen Kumar Boiroju. 2022. "Sex Differences in Animal Models of Sodium-Valproate-Induced Autism in Postnatal BALB/c Mice: Whole-Brain Histoarchitecture and 5-HT2A Receptor Biomarker Evidence" Biology 11, no. 1: 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010079
APA StyleGouda, B., Sinha, S. N., Chalamaiah, M., Vakdevi, V., Shashikala, P., Veeresh, B., Surekha, V. M., Kasturi, V., & Boiroju, N. K. (2022). Sex Differences in Animal Models of Sodium-Valproate-Induced Autism in Postnatal BALB/c Mice: Whole-Brain Histoarchitecture and 5-HT2A Receptor Biomarker Evidence. Biology, 11(1), 79. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010079