Effectiveness of Olympic Combat Sports on Balance, Fall Risk or Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Protocol and Registration
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Information and Database Search Process
2.4. Studies Selection and Data Collection Process
2.5. Methodological Quality Assessment
2.6. Data Synthesis
2.7. Summary Measures for Meta-Analysis
2.8. Certainty of Evidence
3. Results
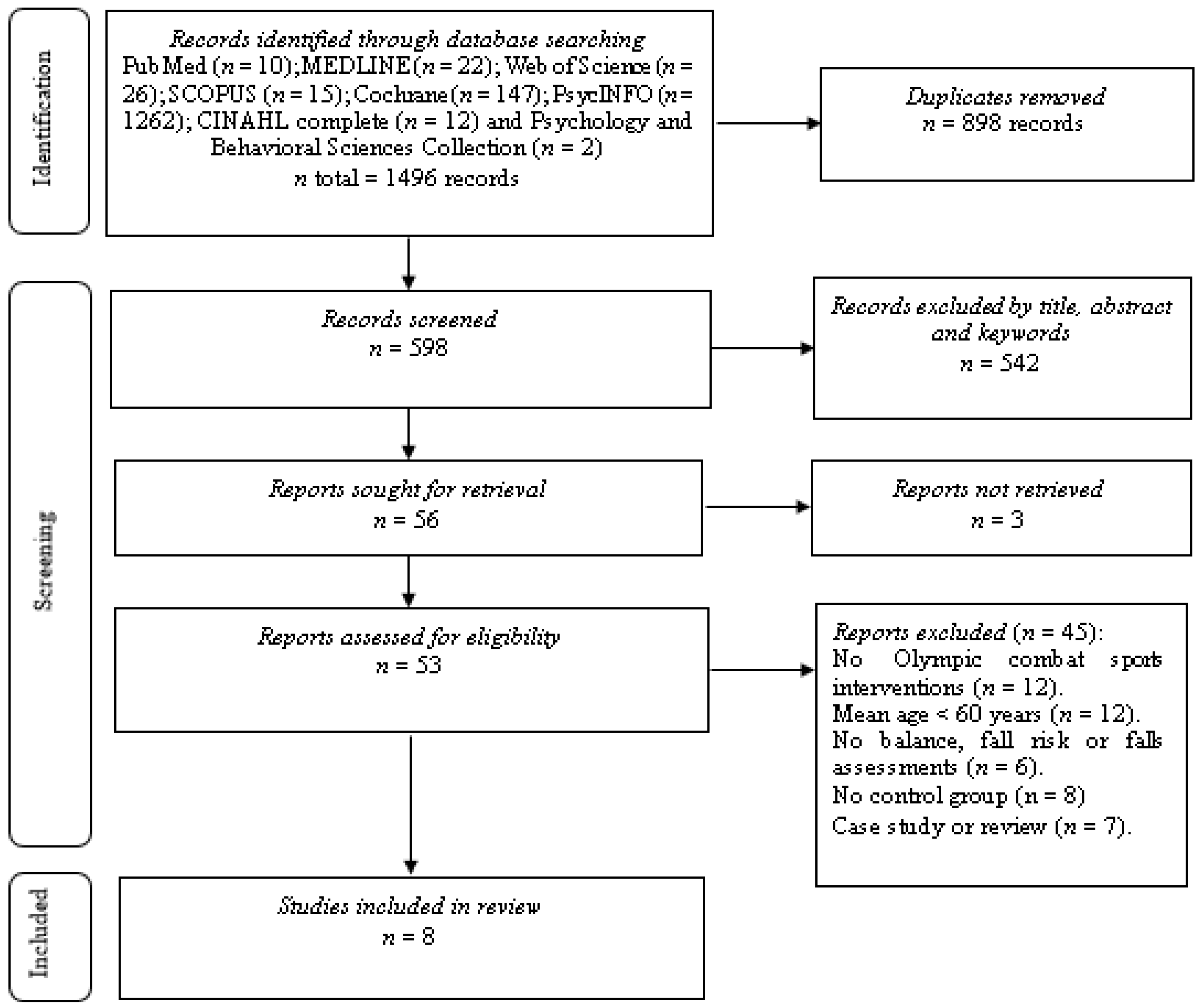
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Methodological Quality
3.3. Risk of Bias within Studies
3.4. Studies Characteristics
3.5. Sample Characteristics
3.6. Interventions Conducted and Dosing
3.7. Data Collection Instruments of Balance
3.8. Data Collection Instruments of Fall Risk or Falls
3.9. Balance
3.10. Fall Risk or Falls
3.11. Certainty of Evidence
3.12. Adverse Events and Adherence
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Falls. 2021: Geneva, Swiss. Available online: https://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/falls (accessed on 10 November 2021).
- Park, S.-H. Tools for assessing fall risk in the elderly: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 30, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfortmueller, C.; Lindner, G.; Exadaktylos, A. Reducing fall risk in the elderly: Risk factors and fall prevention, a systematic review. Minerva Med. 2014, 105, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fragala, M.S.; Cadore, E.L.; Dorgo, S.; Izquierdo, M.; Kraemer, W.J.; Peterson, M.D.; Ryan, E.D. Resistance training for older adults: Position statement from the national strength and conditioning association. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2019–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jehu, D.; Davis, J.; Falck, R.; Bennett, K.; Tai, D.; Souza, M.; Cavalcante, B.; Zhao, M.; Liu-Ambrose, T. Risk factors for recurrent falls in older adults: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Maturitas 2020, 144, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horak, F.B. Postural orientation and equilibrium: What do we need to know about neural control of balance to prevent falls? Age Ageing 2006, 35 (Suppl. 2), ii7–ii11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesinski, M.; Hortobágyi, T.; Muehlbauer, T.; Gollhofer, A.; Granacher, U. Effects of balance training on balance performance in healthy older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015, 45, 1721–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPhee, J.S.; French, D.P.; Jackson, D.; Nazroo, J.; Pendleton, N.; Degens, H. Physical activity in older age: Perspectives for healthy ageing and frailty. Biogerontology 2016, 17, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, C.; O’Sullivan, R.; Caserotti, P.; Tully, M.A. Consequences of physical inactivity in older adults: A systematic review of reviews and meta-analyses. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2020, 30, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.; Battaglia, G.; Patti, A.; Brusa, J.; Leonardi, V.; Palma, A.; Bellafiore, M. Physical activity programs for balance and fall prevention in elderly: A systematic review. Medicine 2019, 98, e16218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadore, E.L.; Rodríguez-Mañas, L.; Sinclair, A.; Izquierdo, M. Effects of different exercise interventions on risk of falls, gait ability, and balance in physically frail older adults: A systematic review. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudino, J.; Afonso, J.; Sarvestan, J.; Lanza, M.; Pennone, J.; Filho, C.; Serrão, J.; Espregueira-Mendes, J.; Vasconcelos, A.; de Andrade, M.; et al. Strength training to prevent falls in older adults: A systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, C.; Nguyen, H.; Ross, K.; Wingood, M.; Peterson, E.W.; DeWitt, J.E.; Moore, J.; King, M.J.; Atanelov, L.; White, J.; et al. Lower-limb factors associated with balance and falls in older adults: A systematic review and clinical synthesis. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2020, 110, Article_4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klima, D.W.; Rabel, M.; Mandelblatt, A.; Miklosovich, M.; Putman, T.; Smith, A. Community-based fall prevention and exercise programs for older adults. Curr. Geriatr. Rep. 2021, 10, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Badilla, P.; Gutiérrez-García, C.; Pérez-Gutiérrez, M.; Vargas-Vitoria, R.; López-Fuenzalida, A. Effects of physical activity governmental programs on health status in independent older adults: A systematic review. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2019, 27, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, A.; Câmara, G.; Arriaga, M.; Nogueira, P.; Miguel, J.P. Active and healthy aging after COVID-19 pandemic in Portugal and other European countries: Time to rethink strategies and foster action. Front. Public Health 2021, 9, 700279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaabene, H.; Prieske, O.; Herz, M.; Moran, J.; Höhne, J.; Kliegl, R.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Behm, D.; Hortobágyi, T.; Granacher, U. Home-based exercise programs improve physical fitness of healthy older adults: A PRISMA-compliant systematic review and meta-analysis with relevance for COVID-19. Ageing Res. Rev. 2021, 67, 101265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakicevic, N.; Moro, T.; Paoli, A.; Roklicer, R.; Trivic, T.; Cassar, S.; Drid, P. Stay fit, don’t quit: Geriatric Exercise Prescription in COVID-19 Pandemic. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2020, 32, 1209–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Badilla, P.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Aedo-Muñoz, E.; Martín, E.B.-S.; Ojeda-Aravena, A.; Branco, B. Effects of Olympic combat sports on older adults’ health status: A systematic review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Origua Rios, S.; Marks, J.; Estevan, I.; Barnett, L.M. Health benefits of hard martial arts in adults: A systematic review. J. Sports Sci. 2018, 36, 1614–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobosz, D.; Barczyński, B.J.; Kalina, A.; Kalina, R.M. The most effective and economic method of reducing death and disability associated with falls. Arch. Budo 2018, 14, 239–246. [Google Scholar]
- Murad, M.H.; Asi, N.; Alsawas, M.; Alahdab, F. New evidence pyramid. Evid. Based Med. 2016, 21, 125–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. World Report on Ageing and Health. 2015: Geneva, Swiss. Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/186463 (accessed on 27 December 2021).
- Smart, N.; Waldron, M.; Ismail, H.; Giallauria, F.; Vigorito, C.; Cornelissen, V.; Dieberg, G. Validation of a new tool for the assessment of study quality and reporting in exercise training studies: TESTEX. Int. J. Evid.-Based Healthc. 2015, 13, 9–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyatt, G.; Oxman, A.D.; Akl, E.A.; Kunz, R.; Vist, G.; Brozek, J.; Norris, S.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Glasziou, P.; DeBeer, H.; et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction—GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Sutton, A.J.; Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Terrin, N.; Jones, D.R.; Lau, J.; Carpenter, J.; Rucker, G.; Harbord, R.M.; Schmid, C.H.; et al. Recommendations for examining and interpreting funnel plot asymmetry in meta-analyses of randomized controlled trials. BMJ 2011, 343, d4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, S.H.; Hong, G.R.; Min, D.K.; Kim, E.H.; Park, S.K. Effects of functional fitness enhancement through taekwondo training on physical characteristics and risk factors of dementia in elderly women with depression. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 7961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Mesa, M.C.; DelCastillo-Andrés, O.; Toronjo-Hornillo, L.; Castañeda-Vázquez, C. The effect of adapted utilitarian Judo, as an educational innovation, on fear-of-falling syndrome. Sustainability 2020, 12, 4096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-Y.; Roh, H.-T. Taekwondo enhances cognitive function as a result of increased neurotrophic growth factors in elderly women. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciaccioni, S.; Capranica, L.; Forte, R.; Chaabene, H.; Pesce, C.; Condello, G. Effects of judo training on functional fitness, anthropometric, and psychological variables in old novice practitioners. J. Aging Phys. Act. 2019, 27, 831–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, S.A.; Diehl, M.D.; Chrzastowski, C.; Didrick, N.; McCoin, B.; Mox, N.; Staples, W.H.; Wayman, J. Community-based group exercise for persons with Parkinson disease: A randomized controlled trial. NeuroRehabilitation 2013, 32, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cromwell, R.L.; Meyers, P.M.; Meyers, P.E.; Newton, R.A. Tae Kwon Do: An effective exercise for improving balance and walking ability in older adults. J. Gerontol. Ser. A Boil. Sci. Med Sci. 2007, 62, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, K.; Emmermacher, P.; Pliske, G. Improvement of balance and general physical fitness in older adults by Karate: A randomized controlled trial. Complement. Med. Res. 2017, 24, 390–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youm, C.; Lee, J.-S.; Seo, K.E. Effects of Taekwondo and walking exercises on the double-leg balance control of elderly females. Korean J. Sport Biomech. 2011, 21, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, S.A.; Diehl, M.D.; Staples, W.H.; Conn, L.; Davis, K.; Lewis, N.; Schaneman, K. Boxing training for patients with Parkinson disease: A case series. Phys. Ther. 2011, 91, 132–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, R.A.; Contreras-Vidal, J.L.; Paloski, W.H. Cortical control of upright stance in elderly. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2018, 169, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, D.; Xiao, Q.; Xiao, X.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Xia, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, J.; Zheng, H.; Jin, R. Tai Chi for improving balance and reducing falls: An overview of 14 systematic reviews. Ann. Phys. Rehabil. Med. 2020, 63, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, B.; Dudley, D.; Woodcock, S. The effect of martial arts training on mental health outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Bodyw. Mov. Ther. 2020, 24, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peset Mancebo, M.F.; Ferrer Sapena, A.; Villamón Herrera, M.; González Moreno, L.M.; Toca Herrera, J.-L.; Aleixandre Benavent, R. Scientific literature analysis of Judo in Web of Science. Arch. Budo 2013, 9, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez Gutiérrez, M.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; Gutiérrez-García, C.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T. Taekwondo scientific production published on the web of science (1988-2016): Collaboration and topics. Movimento 2017, 23, 1325–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bull, F.C.; Al-Ansari, S.S.; Biddle, S.; Borodulin, K.; Willumsen, J.F. World Health Organization 2020 guidelines on physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Br. J. Sports Med. 2020, 54, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromley, S.J.; Drew, M.K.; Talpey, S.; McIntosh, A.S.; Finch, C.F. A systematic review of prospective epidemiological research into injury and illness in Olympic combat sport. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 52, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bujak, Z.; Gierczuk, D.; Litwiniuk, S. Professional activities of a coach of martial arts and combat sports. J. Combat. Sports Martial Arts 2013, 4, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Category | Inclusion Criteria | Exclusion Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Population | Older adults, considered as older adult participants with an average age of 60 years or more according to the World Health Organization [24], and without distinction of sex. | People under 60 years of age. |
| Intervention | Interventions with Olympic combat sports (boxing, fencing, judo, karate, taekwondo, wrestling) lasting four weeks or more. | Exercise interventions not involving Olympic combat sports. |
| Comparator | Interventions that had a control group with or without supervised physical activity. | Absence of control group. |
| Outcome | At least one balance assessment (e.g., force platform, timed up-and-go test), fall risk, or falls assessment (e.g., Falls Efficacy Scale-International, Berg Balance Scale) before and after the intervention. | Lack of baseline and/or follow-up data. |
| Study design | Studies with experimental design (randomized controlled trial and non-randomized controlled trial) with pre- and post-assessment. | Cross-sectional, retrospective, and prospective studies. |
| Study | Eligibility Criteria Specified | Randomly Allocated Participants | Allocation Concealed | Groups Similar at Baseline | Assessors Blinded | Outcome Measures Assessed >85% of Participants * | Intention to Treat Analysis | Reporting of between Group Statistical Comparisons | Point Measures and Measures of Variability Reported ** | Activity Monitoring in the Control Group | Relative Exercise Intensity Reviewed | Exercise Volume and Energy Expended | Overall TESTEX # |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baek et al. [28] | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Yes (2) | Yes | Yes | Yes (2) | No | No | Yes | 10/15 |
| Campos-Mesa et al. [29] | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Yes (1) | Yes | Yes | Yes (2) | Yes | No | Yes | 9/15 |
| Cho & Roh [30] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes (2) | Yes | Yes | Yes (1) | No | Yes | Yes | 11/15 |
| Ciaccioni et al. [31] | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes (3) | Yes | Yes | Yes (2) | No | Yes | Yes | 12/15 |
| Combs et al. [32] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (3) | Yes | Yes | Yes (2) | Yes | No | Yes | 13/15 |
| Cromwell et al. [33] | Yes | No | Unclear | Yes | Yes | Yes (2) | Yes | Yes | Yes (1) | No | No | Yes | 9/15 |
| Witte et al. [34] | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes (3) | Yes | Yes | Yes (2) | No | No | Yes | 12/15 |
| Youm et al. [35] | Yes | Yes | Unclear | Yes | Unclear | Yes (1) | Yes | Yes | Yes (2) | No | Yes | Yes | 10/15 |
| Study | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | Overall GRADE |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baek et al. [28] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Campos-Mesa et al. [29] | High risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Cho & Roh [30] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Ciaccioni et al. [31] | High risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Combs et al. [32] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Cromwell et al. [33] | High risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Low risk | Some concerns | High risk |
| Witte et al. [34] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Youm et al. [35] | Some concerns | Low risk | Low risk | Low risk | Some concerns | Some concerns |
| Study | Country | Study Design | Sample’s Initial Health | Groups | Mean Age (Year) | Activities in the Intervention and Control Groups | Training Volume | Training Intensity | DCI of Balance | DCI of Fall Risk or Falls | Main Outcomes | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (n) | TD (Weeks) | Fr | TPS (min) | ||||||||||
| (Weekly) | |||||||||||||
| Baek et al. [28] | South Korea | RCT | Apparently healthy | TUG | None | EG vs. CG: ↓ TUG (in favour EG). | |||||||
| EG: 12 | 72.6 | EG: taekwondo | 12 | 3 | 60 | NA | |||||||
| CG: 12 | 72.4 | CG: usual activities | NA | NA | NA | ||||||||
| Campos-Mesa et al. [29] | Spain | NRCT | Apparently healthy | None | FES-I | EG vs. CG: ↓ FES-I π (in favour EG). | |||||||
| EG: 19 | 74.3 | EG: judo | 6 | 2 | 60 | NA | WHO Questionnaire | WHO Questionnaire was not reported post-intervention. | |||||
| CG: 11 | 77.8 | CG: physical fitness | 2 | 60 | NA | ||||||||
| Cho & Roh [30] | South Korea | RCT | Apparently healthy | 50–80%HRmax | TUG | None | |||||||
| EG: 19 | 68.9 | EG: taekwondo | 16 | 5 | 60 | ||||||||
| EG vs. CG: ↔ TUG. | |||||||||||||
| CG: 18 | 69 | CG: usual activities | NA | NA | |||||||||
| Ciaccioni et al. [31] | Italy | NRCT | Apparently healthy | Moderate to vigorous | None | FES-I | EG vs. CG: ↔ FES-I π. | ||||||
| EG: 19 | 69.3 | EG: judo | 16 | 2 | 60 | ||||||||
| BBS | BBS was not reported post-intervention. | ||||||||||||
| CG: 21 | 70.2 | CG: usual activities | NA | NA | |||||||||
| Combs et al. [32] | United States of America | RCT | Parkinson’ ‘s disease | BBS | |||||||||
| EG: 17 | 66.5 | EG: boxing | 12 | 2–3 | 90 | NA | ABC TUG | EG vs. CG: ↑ ABC (in favour CG), ↔ BBS, ↔ TUG, ↔ DTUG. | |||||
| DTUG | |||||||||||||
| CG: 14 | 68 | CG: physical fitness | 2–3 | 90 | NA | ||||||||
| Cromwell et al. [33] | United States of America | NRCT | Apparently healthy | One question | |||||||||
| EG: 20 | 72.7 | EG: taekwondo | 11 | 2 | 60 | NA | TUG | EG vs. CG: ↓ TUG, ↑ MDRT, ↓ GSR, ↔ SLS (in favour EG). | |||||
| MDRT | |||||||||||||
| CG: 20 | 73.8 | CG: usual activities | NA | NA | NA | GSR | One question was not reported post-intervention. | ||||||
| SLS | |||||||||||||
| Witte et al. [34] | Germany | RCT | Apparently healthy | MBT (static and dynamic balance) | None | EG vs. FG vs. CG: ↔ Static balance, ↔ Dynamic balance. | |||||||
| EG: 30 | EG: karate | 2 | 60 | NA | |||||||||
| FG: 30 | 69.3 | FG: physical fitness | 20 | 2 | 60 | NA | |||||||
| CG: 30 | CG: usual activities | NA | NA | NA | |||||||||
| Youm et al. [35] | South Korea | RCT | Apparently healthy | 12 | None | EG vs. WG vs. CG: ↔ AP RMS distance, ↔ AP velocity, ↔ AP total power frequency, ↓ ML RMS distance, ↓ ML velocity, ↔ ML total power frequency (in favour EG and WG regarding CG). | |||||||
| EG: 10 | 69.4 | EG: taekwondo | 3 | 60 | |||||||||
| WG: 10 | 71.4 | WG: walking exercise | 3 | 60 | 40–60%HRmax | Force Platform (COP) | |||||||
| CG: 10 | 70.6 | CG: usual activities | NA | NA | |||||||||
| Outcomes | Study Design | Risk of Bias in Individuals Studies | Risk of Publication Bias | Inconsistency | Indirectness | Imprecision | Certainty of Evidence | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Balance | 5 RCTs and 1 NRCTs with a 9 trials and 252 participants | Moderate to High 1 | Not assessed 3 | Moderate 4 | Low 5 | High 6 | Very low 7 | The OCS does not show superior effects in the older adults compared to control groups (active/passive) on balance, fall risk, or falls. |
| Fall risk or falls | 1RCT and 2 NRCTs with a 5 trials and 91 participants | Moderate to High 2 | Not assessed 3 | Moderate 4 | Low 5 | High 6 | Very low 7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valdés-Badilla, P.; Ramirez-Campillo, R.; Herrera-Valenzuela, T.; Branco, B.H.M.; Guzmán-Muñoz, E.; Mendez-Rebolledo, G.; Concha-Cisternas, Y.; Hernandez-Martínez, J. Effectiveness of Olympic Combat Sports on Balance, Fall Risk or Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Biology 2022, 11, 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010074
Valdés-Badilla P, Ramirez-Campillo R, Herrera-Valenzuela T, Branco BHM, Guzmán-Muñoz E, Mendez-Rebolledo G, Concha-Cisternas Y, Hernandez-Martínez J. Effectiveness of Olympic Combat Sports on Balance, Fall Risk or Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Biology. 2022; 11(1):74. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010074
Chicago/Turabian StyleValdés-Badilla, Pablo, Rodrigo Ramirez-Campillo, Tomás Herrera-Valenzuela, Braulio Henrique Magnani Branco, Eduardo Guzmán-Muñoz, Guillermo Mendez-Rebolledo, Yeny Concha-Cisternas, and Jordan Hernandez-Martínez. 2022. "Effectiveness of Olympic Combat Sports on Balance, Fall Risk or Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review" Biology 11, no. 1: 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010074
APA StyleValdés-Badilla, P., Ramirez-Campillo, R., Herrera-Valenzuela, T., Branco, B. H. M., Guzmán-Muñoz, E., Mendez-Rebolledo, G., Concha-Cisternas, Y., & Hernandez-Martínez, J. (2022). Effectiveness of Olympic Combat Sports on Balance, Fall Risk or Falls in Older Adults: A Systematic Review. Biology, 11(1), 74. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010074












