Atrial Fibrillation in β-Thalassemia: Overview of Mechanism, Significance and Clinical Management
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
2.1. Thalassemia
2.2. Atrial Fibrillation in Thalassemia
2.3. Thromboembolism
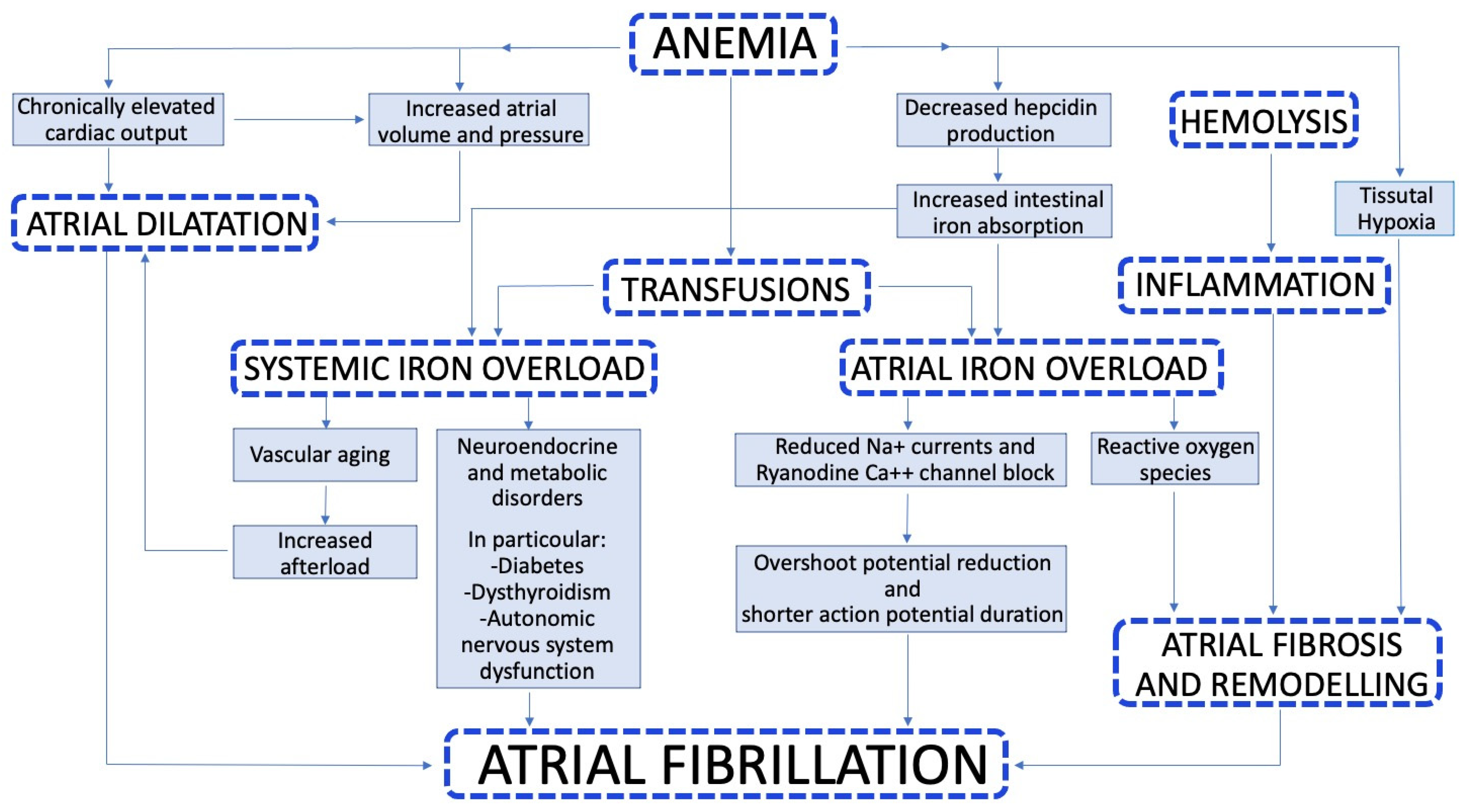
3. Pathophysiology
4. How to Identify Patients at Risk for Atrial Fibrillation
5. Clinical Features
6. Treatment Options
6.1. Rhythm Control Drugs
- -
- Deferoxamine: this was the first iron chelator introduced in clinical practice. It has a short plasma life and is not absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract, so it must be administered parenterally. Deferoxamine can also be administered in continuous intravenous infusion when intensive chelation is needed [44].
- -
- Deferiprone: is absorbed by the upper gastrointestinal tract so it can be given orally. It may lead to several adverse effects such as gastrointestinal symptoms, arthropathy and agranulocytosis [45].
- -
- Deferasirox: can be given orally once a day. It has a good safety profile, and the main adverse effects are gastrointestinal and renal, which are multiple though rare [46].
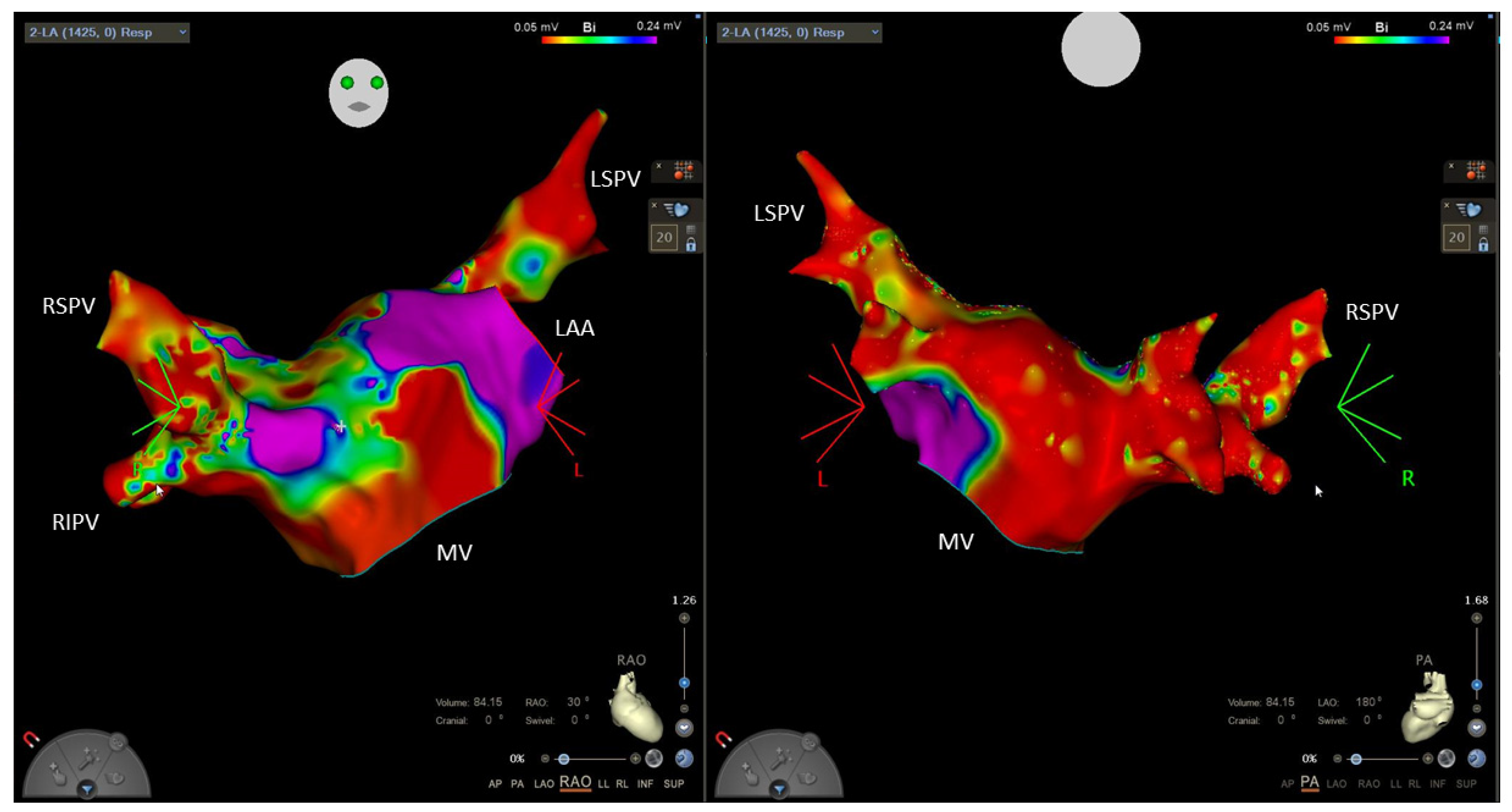
6.2. Ablation
6.3. Rate Control
6.4. Anticoagulation
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Taher, A.T.; Musallam, K.M.; Cappellini, M.D. β-Thalassemias. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 727–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kattamis, A.; Forni, G.L.; Aydinok, Y.; Viprakasit, V. Changing patterns in the epidemiology of β-thalassemia. Eur. J. Haematol. 2020, 105, 692–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colah, R.; Gorakshakar, A.; Nadkarni, A. Global burden, distribution and prevention of β-thalassemias and hemoglobin E disorders. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2010, 3, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sanctis, V.; Kattamis, C.; Canatan, D.; Soliman, A.T.; Elsedfy, H.; Karimi, M.; Daar, S.; Wali, Y.; Yassin, M.; Soliman, N.; et al. β-Thalassemia Distribution in the Old World: An Ancient Disease Seen from a Historical Standpoint. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, e2017018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modell, B.; Darlison, M. Global epidemiology of haemoglobin disorders and derived service indicators. Bull. World Health Organ. 2008, 86, 480–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Rago, A.; Papa, A.A.; Nigro, G. Electrocardiographic Presentation, Cardiac Arrhythmias, and Their Management in β-Thalassemia Major Patients. Ann. Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2016, 21, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuret, I.; Pondarré, C.; Loundou, A.; Steschenko, D.; Girot, R.; Bachir, D.; Rose, C.; Barlogis, V.; Bonadieu, J.; de Montalembert, M.; et al. Complications and treatment of patients with β-thalassemia in France: Results of the National Registry. Haematologica 2010, 95, 724–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canatan, D. Haemoglobinopathy prevention program in Turkey. Thalass. Rep. 2011, 1, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Barry, R.M.; Chretien, C.; Kirby, M.; Gallant, G.; Leppington, S.; Robitaille, N.; Corriveau-Bourque, C.; Stoffman, J.; Wu, J.; Leaker, M.; et al. Syrian Refugees and Their Impact on Health Service Delivery in the Pediatric Hematology/Oncology Clinics Across Canada. J. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 42, e107–e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vichinsky, E.; Cohen, A.; Thompson, A.A.; Giardina, P.J.; Lal, A.; Paley, C.; Cheng, W.Y.; McCormick, N.; Sasane, M.; Qiu, Y.; et al. Epidemiologic and clinical characteristics of nontransfusion-dependent thalassemia in the United States. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e27067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jobanputra, M.; Paramore, C.; Laird, S.G.; McGahan, M.; Telfer, P. Co-morbidities and mortality associated with transfusion-dependent beta-thalassaemia in patients in England: A 10-year retrospective cohort analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 191, 897–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaeefard, A.; Hajipour, M.; Tabatabaee, H.R.; Hassanzadeh, J.; Rezaeian, S.; Moradi, Z.; Sharafi, M.; Shafiee, M.; Semati, A.; Safaei, S.; et al. Analysis of survival data in thalassemia patients in Shiraz, Iran. Epidemiol. Health 2015, 37, e2015031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Borgna-Pignatti, C.; Rugolotto, S.; De Stefano, P.; Piga, A.; Di Gregorio, F.; Gamberini, M.R.; Sabato, V.; Melevendi, C.; Cappellini, M.D.; Verlato, G. Survival and disease complications in thalassemia major. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998, 850, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgna-Pignatti, C.; Cappellini, M.D.; De Stefano, P.; Del Vecchio, G.C.; Forni, G.L.; Gamberini, M.R.; Ghilardi, R.; Origa, R.; Piga, A.; Romeo, M.A.; et al. Survival and complications in thalassemia. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005, 1054, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomani, H.; Bayat, G.; Sahebkar, A.; Fazelifar, A.F.; Vakilian, F.; Jomehzadeh, V.; Johnston, T.P.; Mohammadpour, A.H. Atrial fibrillation in β-thalassemia patients with a focus on the role of iron-overload and oxidative stress: A review. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 12249–12266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbero, U.; Fornari, F.; Guarguagli, S.; Gaglioti, C.M.; Longo, F.; Doronzo, B.; Anselmino, M.; Piga, A. Atrial fibrillation in β-thalassemia Major Patients: Diagnosis, Management and Therapeutic Options. Hemoglobin 2018, 42, 189–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ako, E.; Rob, B.; Malcolm, W.; Porter, J. The prevalence and risk factors for atrial fibrillation in beta-thalassemia major: A cross-sectional study in a UK specialist cardio-haematology clinic. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 916. [Google Scholar]
- Hindricks, G.; Potpara, T.; Dagres, N.; Arbelo, E.; Bax, J.J.; Blomström-Lundqvist, C.; Boriani, G.; Castella, M.; Dan, G.-A.; Dilaveris, P.E.; et al. 2020 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation developed in collaboration with the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS): The Task Force for the diagnosis and management of atrial fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Developed with the special contribution of the European Heart Rhythm Association (EHRA) of the ESC. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 373–498. [Google Scholar]
- Meloni, A.; Restaino, G.; Borsellino, Z.; Caruso, V.; Spasiano, A.; Zuccarelli, A.; Valeri, G.; Toia, P.; Salvatori, C.; Positano, V.; et al. Different patterns of myocardial iron distribution by whole-heart T2* magnetic resonance as risk markers for heart complications in thalassemia major. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 177, 1012–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsella, M.; Borgna-Pignatti, C.; Meloni, A.; Caldarelli, V.; Dell’Amico, M.C.; Spasiano, A.; Pitrolo, L.; Cracolici, E.; Valeri, G.; Positano, V.; et al. Cardiac iron and cardiac disease in males and females with transfusion-dependent thalassemia major: A T2* magnetic resonance imaging study. Haematologica 2011, 96, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirk, P.; Roughton, M.; Porter, J.B.; Walker, J.M.; Tanner, M.A.; Patel, J.; Wu, D.; Taylor, J.; Westwood, M.; Anderson, L.; et al. Cardiac T2* magnetic resonance for prediction of cardiac complications in thalassemia major. Circulation 2009, 120, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostopoulou, A.G.; Tsiapras, D.P.; Chaidaroglou, A.S.; De Giannis, D.E.; Farmakis, D.; Kremastinos, D.T. The pathophysiological relationship and clinical significance of left atrial function and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in β-thalassemia major. Am. J. Hematol. 2014, 89, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, M.; Khanlari, M.; Rachmilewitz, E.A. Cerebrovascular accident in β-thalassemia major (β-TM) and β-thalassemia intermedia (β-TI). Am. J. Hematol. 2008, 83, 77–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taher, A.; Isma’eel, H.; Mehio, G.; Bignamini, D.; Kattamis, A.; Rachmilewitz, E.A.; Cappellini, M.D. Prevalence of thromboembolic events among 8860 patients with thalassaemia major and intermedia in the Mediterranean area and Iran. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 96, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vassilopoulou, S.; Anagnostou, E.; Paraskevas, G.; Spengos, K. Etiology and treatment of ischaemic stroke in patients with β-thalassemia major. Eur. J. Neurol. 2011, 18, 1426–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremastinos, D.T.; Farmakis, D. Iron overload cardiomyopathy in clinical practice. Circulation 2011, 124, 2253–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berdoukas, V.; Coates, T.D.; Cabantchik, Z.I. Cabantchik ZI. Iron and oxidative stress in cardiomyopathy in thalassemia. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.-F.; Lian, W.-S. Prooxidant mechanisms in iron overload cardiomyopathy. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 740573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, C.; Islam, S.; Jarosch, S.; Zhou, J.; Hoskin, D.; Greenshields, A.; Al-Banna, N.; Sharawy, N.; Sczcesniak, A.; Kelly, M.; et al. The utility of iron chelators in the management of inflammatory disorders. Mediat. Inflamm. 2015, 2015, 516740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Choi, E.; Cha, M.-J.; Hwang, K.-C. Looking into a conceptual framework of ROS-miRNA-atrial fibrillation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 21754–21776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartfay, W.J.; Bartfay, E. Iron-overload cardiomyopathy: Evidence for a free radical--mediated mechanism of injury and dysfunction in a murine model. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2000, 2, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Melillo, E.; Papa, A.A.; Rago, A.; Chamberland, C.; Nigro, G. Arrhythmias and Sudden Cardiac Death in Beta-Thalassemia Major Patients: Noninvasive Diagnostic Tools and Early Markers. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2019, 2019, 9319832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Origa, R.; Danjou, F.; Cossa, S.; Matta, G.; Bina, P.; Dessì, C.; DeFraia, E.; Foschini, M.L.; Leoni, G.; Morittu, M.; et al. Impact of heart magnetic resonance imaging on chelation choices, compliance with treatment and risk of heart disease in patients with thalassaemia major. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 163, 400–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monte, I.; Capodanno, D.; Nicolosi, E.; Licciardi, S.; Talini, E.; Di Bello, V. Atrial and ventricular function in thalassemic patients with supra-ventricular arrhythmias. Heart Int. 2009, 4, e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calık, A.N.; Ozcan, K.S.; Cağdaş, M.; Güngör, B.; Karaca, G.; Gürkan, U.; Yılmaz, H.; Bolca, O. Electromechanical delay detected by tissue Doppler echocardiography is associated with the frequency of attacks in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Cardiol. J. 2014, 21, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rago, A.; Russo, V.; Papa, A.A.; Ciardiello, C.; Pannone, B.; Mayer, M.C.; Cimmino, G.; Nigro, G. The role of the atrial electromechanical delay in predicting atrial fibrillation in beta-thalassemia major patients. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2017, 48, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yetimakman, A.F.; Oztarhan, K.; Aydogan, G. Comparison of tissue Doppler imaging with MRI t2* and 24-hour rhythm holter heart rate variability for diagnosing early cardiac impairment in thalassemia major patients. Pediatr. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 31, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzoni, F.; Galetta, F.; Di Muro, C.; Buti, G.; Pentimone, F.; Santoro, G. Heart rate variability and ventricular late potentials in beta-thalassemia major. Haematologica 2004, 89, 233–234. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pepe, A.; Meloni, A.; Rossi, G.; Midiri, M.; Missere, M.; Valeri, G.; Sorrentino, F.; D’Ascola, D.G.; Spasiano, A.; Filosa, A.; et al. Prediction of cardiac complications for thalassemia major in the widespread cardiac magnetic resonance era: A prospective multicentre study by a multi-parametric approach. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2018, 19, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, V.; Rago, A.; Pannone, B.; Mayer, M.C.; Spasiano, A.; Calabro, R.; Russo, M.G.; Gerardo, N.; Papa, A.A. Atrial Fibrillation and Beta Thalassemia Major: The Predictive Role of the 12-lead Electrocardiogram Analysis. Indian Pacing Electrophysiol. J. 2014, 14, 121–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoozgar, H.; Zeighami, S.; Haghpanah, S.; Karimi, M. A comparison of heart function and arrhythmia in clinically asymptomatic patients with beta thalassemia intermedia and beta thalassemia major. Hematology 2017, 22, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolios, M.; Korantzopoulos, P.; Vlahos, A.P.; Kapsali, E.; Briasoulis, E.; Goudevenos, J.A. Electrocardiographic abnormalities and arrhythmic risk markers in adult patients with beta thalassemia major. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 221, 932–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachou, M.; Kamperidis, V.; Vlachaki, E.; Tziatzios, G.; Pantelidou, D.; Boutou, A.; Apostolou, C.; Papadopoulou, D.; Giannakoulas, G.; Karvounis, H. Left Atrial Strain Identifies Increased Atrial Ectopy in Patients with Beta-Thalassemia Major. Diagnostics 2020, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.; Mohammed, N.; Marshall, L.; Abeysinghe, R.D.; Hider, R.C.; Porter, J.B.; Singh, S. Intravenous infusion pharmacokinetics of desferrioxamine in thalassaemic patients. Drug Metab. Dispos. 1993, 21, 640–644. [Google Scholar]
- Galanello, R.; Campus, S. Deferiprone chelation therapy for thalassemia major. Acta Haematol. 2009, 122, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galanello, R.; Campus, S.; Origa, R. Deferasirox: Pharmacokinetics and clinical experience. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2012, 8, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, B.A.; Porter, J.B. Long-term outcome of continuous 24-hour deferoxamine infusion via indwelling intravenous catheters in high-risk beta-thalassemia. Blood 2000, 95, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydinok, Y.; Kattamis, A.; Cappellini, M.D.; El-Beshlawy, A.; Origa, R.; Elalfy, M.; Kilinç, Y.; Perrotta, S.; Karakas, Z.; Viprakasit, V.; et al. Effects of deferasirox-deferoxamine on myocardial and liver iron in patients with severe transfusional iron overload. Blood 2015, 125, 3868–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miskin, H.; Yaniv, I.; Berant, M.; Hershko, C.; Tamary, H. Reversal of cardiac complications in thalassemia major by long-term intermittent daily intensive iron chelation. Eur. J. Haematol. 2003, 70, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabio, G.; Minonzio, F.; Delbini, P.; Bianchi, A.; Cappellini, M.D. Reversal of cardiac complications by deferiprone and deferoxamine combination therapy in a patient affected by a severe type of juvenile hemochromatosis (JH). Blood 2007, 109, 362–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumfu, S.; Khamseekaew, J.; Palee, S.; Srichairatanakool, S.; Fucharoen, S.; Chattipakorn, S.C.; Chattipakorn, N. A combination of an iron chelator with an antioxidant exerts greater efficacy on cardioprotection than monotherapy in iron-overload thalassemic mice. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiappa, E.; Cinque, C.; Derchi, G.; Mayer, M.; Mancuso, L.; Manfredini, R.; Sau, F.; Sernesi, L. Linee Guida per la Prevenzione ed il Trattamento Delle Complicanze Della Talassemia, a Cura Della Commissione di Studio per la Prevenzione e la Terapia Delle Complicanze Della Talassemia. 1999. Available online: https://www.osservatoriomalattierare.it/documenti/category/2-linee-guida-sulle-malattie-rare?download=122:linee-guida-talassemia-2010 (accessed on 20 December 2021).
- Cogliandro, T.; Derchi, G.; Mancuso, L.; Mayer, M.C.; Pannone, B.; Pepe, A.; Pili, M.; Bina, P.; Cianciulli, P.; De Sanctis, V.; et al. Guideline recommendations for heart complications in thalassemia major. J. Cardiovasc. Med. 2008, 9, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nault, I.; Miyazaki, S.; Forclaz, A.; Wright, M.; Jadidi, A.; Jaïs, P.; Hocini, M.; Haïssaguerre, M. Drugs vs. ablation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation: The evidence supporting catheter ablation. Eur. Heart J. 2010, 31, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pappone, C.; Santinelli, V. Atrial fibrillation ablation: State of the art. Am. J. Cardiol. 2005, 96, 59L–64L. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennell, D.J.; Udelson, J.E.; Arai, A.E.; Bozkurt, B.; Cohen, A.R.; Galanello, R.; Hoffman, T.M.; Kiernan, M.S.; Lerakis, S.; Piga, A.; et al. Cardiovascular function and treatment in β-thalassemia major: A consensus statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2013, 128, 281–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taher, A.; Mehio, G.; Isma’eel, H.; Cappellini, M.D. Stroke in thalassemia: A dilemma. Am. J. Hematol. 2008, 83, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Corrado, E.; Luparelli, M.; Manno, G.; Mignano, A.; Ciaramitaro, G.; Boveda, S. Direct oral anticoagulants in the setting of catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: State of art. Curr. Prob. Cardiol. 2021, 46, 100622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppola, G.; Manno, G.; Mignano, A.; Luparelli, M.; Zarcone, A.; Novo, G.; Corrado, E. Management of direct oral anticoagulants in patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing cardioversion. Medicina 2019, 55, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apostolou, C.; Klonizakis, P.; Mainou, M.; Kapsali, E.; Kafantari, K.; Kotsiafti, A.; Vetsiou, E.; Vakalopoulou, S.; Vlachaki, E. Rivaroxaban Use in Patients with Hemoglobinopathies. Hemoglobin 2017, 41, 223–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Option | Pros | Cons | Caution in Thalassemia | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rhythm control strategy | Chelation therapy | Effective in preventing both arrhythmic recurrences and iron overload | First line therapy in transfusion-dependent patients | |
| Amiodarone | Effective Safe in the short term | Multiple adverse effects in the long term | Frequent coexistence of organ damage (thyroid, liver, skin) | |
| Other antiarrhythmic drugs (flecainide, propafenone, sotalol) | Less side effects in the long term | Drug interactions Contraindicated if underlying HF | Possible proarrhythmic effect in patients with iron overload cardiopathy | |
| Catheter ablation | Avoiding side effects of antiarrhythmic drugs | Invasive procedure | Atrial structural cardiopathy limiting efficacy | |
| Rate control strategy | β-blockers | Effective in reducing symptoms when rhythm control is not possible Indicated also for HF | Negative chronotropic and inotropic effect | Bradycardia may be poorly tolerated |
| Calcium channel blockers (verapamil, diltiazem) | Effective in reducing symptoms when rhythm control is not possible | Contraindicated in HF with reduced ejection fraction | Possible coexistence of HF Bradycardia may be poorly tolerated | |
| Digoxin | Second line therapy when β-blockers or calcium channel blockers are not tolerated | Small therapeutic window Possibility of overdose | Multiple drug interactions | |
| Anticoagulation | Warfarin | Frequent monitoring of coagulation state (INR) | Frequent blood test Labile INR values Less manageable and safe than DOACs | Higher hemorrhagic risk |
| DOACs (apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban, rivaroxaban) | More manageable and safe than warfarin | Higher hemorrhagic risk |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Malagù, M.; Marchini, F.; Fiorio, A.; Sirugo, P.; Clò, S.; Mari, E.; Gamberini, M.R.; Rapezzi, C.; Bertini, M. Atrial Fibrillation in β-Thalassemia: Overview of Mechanism, Significance and Clinical Management. Biology 2022, 11, 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010148
Malagù M, Marchini F, Fiorio A, Sirugo P, Clò S, Mari E, Gamberini MR, Rapezzi C, Bertini M. Atrial Fibrillation in β-Thalassemia: Overview of Mechanism, Significance and Clinical Management. Biology. 2022; 11(1):148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010148
Chicago/Turabian StyleMalagù, Michele, Federico Marchini, Alessio Fiorio, Paolo Sirugo, Stefano Clò, Elisa Mari, Maria Rita Gamberini, Claudio Rapezzi, and Matteo Bertini. 2022. "Atrial Fibrillation in β-Thalassemia: Overview of Mechanism, Significance and Clinical Management" Biology 11, no. 1: 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010148
APA StyleMalagù, M., Marchini, F., Fiorio, A., Sirugo, P., Clò, S., Mari, E., Gamberini, M. R., Rapezzi, C., & Bertini, M. (2022). Atrial Fibrillation in β-Thalassemia: Overview of Mechanism, Significance and Clinical Management. Biology, 11(1), 148. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology11010148








