Natural Pest Regulation and Its Compatibility with Other Crop Protection Practices in Smallholder Bean Farming Systems
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
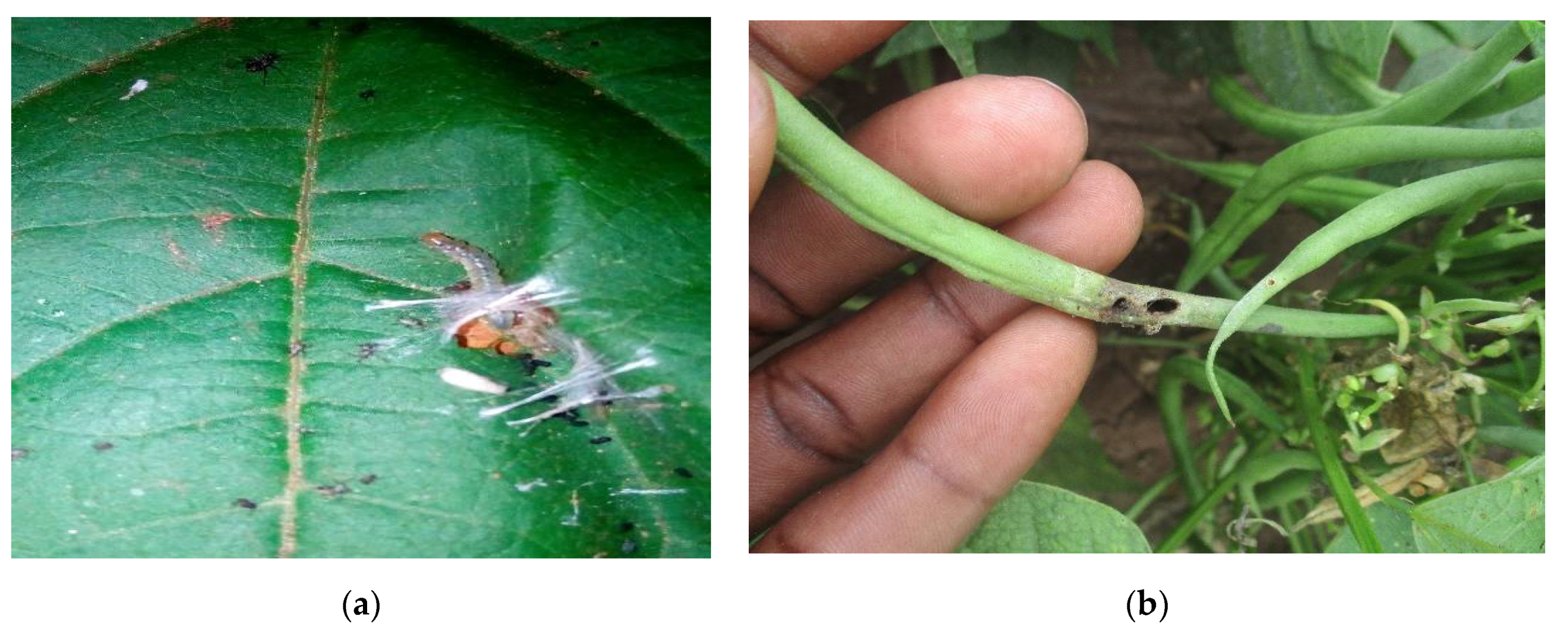
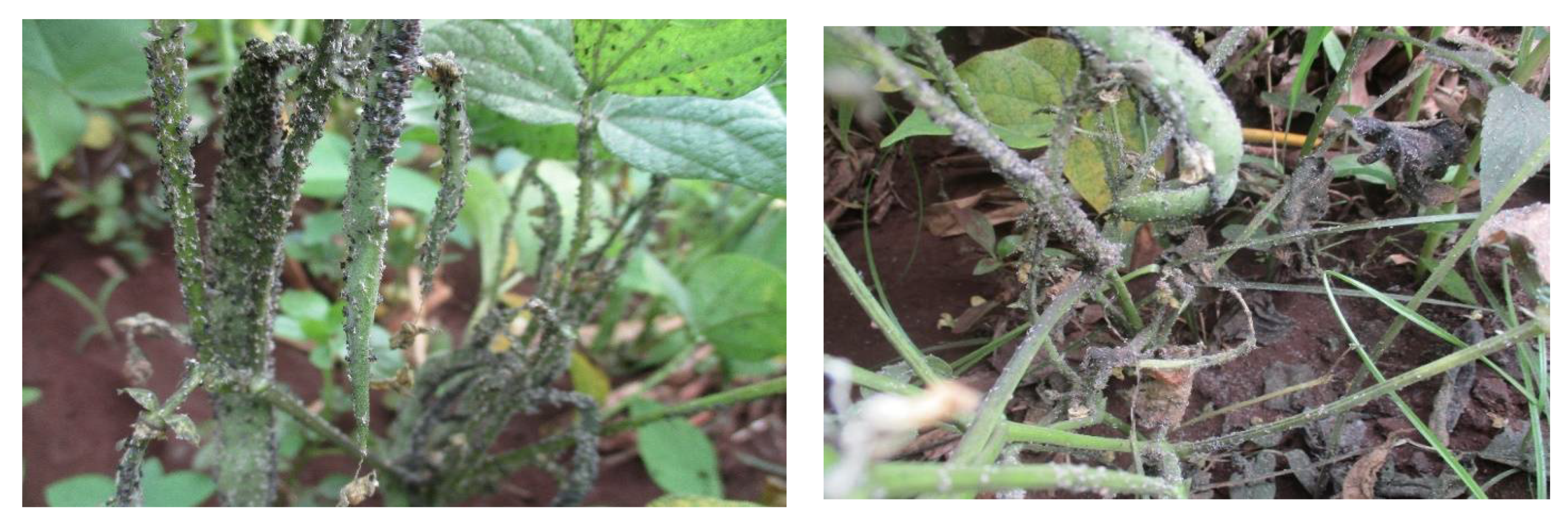
2. Selected Common Bean Pests: Bean Pod Borer (Maruca vitrata) and Black Bean Aphid (Aphis fabae)
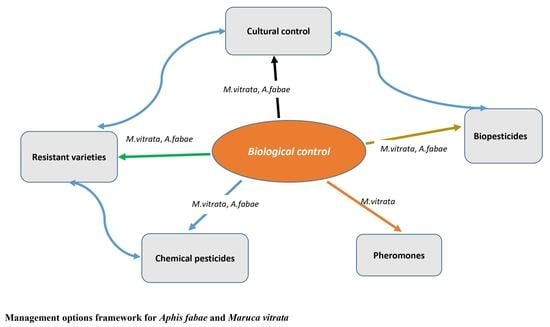
3. The Use of Biological Control as a Central Focus for Aphis fabae and Maruca vitrata Control
Ecological Manipulations for Supporting Natural Enemies
4. Synthetic Chemicals and Their Impact on Natural Enemies of Maruca vitrata and Aphis fabae
5. Other Sustainable Alternatives Compatible with Natural Enemies for Managing Maruca vitrata and Aphis fabae
5.1. Biopesticides
5.2. Use of Resistant Varieties with Natural Enemies
5.3. Cultural Control
6. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO; IFAD; UNICEF; WFP; WHO. The State of Food Security and Nutrition in the World 2020: Transforming Food Systems for Affordable Healthy Diets; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Hillocks, R.J.; Madata, C.S.; Chirwa, R.; Minja, E.M.; Msolla, S. Phaseolus bean improvement in Tanzania, 1959–2005. Euphytica 2006, 150, 215–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development); Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). OECD-FAO Agricultural Outlook 2016–2025; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi, V.; Wane, A.; Sidhu, B.S.; Godde, C.; Solomon, D.; McCullough, E.; Diekmann, F.; Porciello, J.; Jain, M.; Randall, N.; et al. A scoping review of research funding for small-scale farmers in water-scarce regions. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 836–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanlauwe, B.; Coyne, D.; Gockowski, J.; Hauser, S.; Huising, J.; Masso, C.; Nziguheba, G.; Schut, M.; Van Asten, P. Sustainable intensification and the African smallholder farmer. Curr. Opin. Environ. Sustain. 2014, 8, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.J.; Hernandez, G.; Blair, M.; Beebe, S.; Gepts, P.; Vanderleyden, J. Beans (Phaseolus spp.)–model food legumes. Plant Soil 2003, 252, 55–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedumaran, S.; Abinaya, P.; Jyosthnaa, P.; Shraavya, B.; Rao, P.P.; Bantilan, M.C.S. Grain Legumes Production, Consumption and Trade Trends in developing Countries; Markets, Institutions and Policies 64 Working Paper Series No 60. ICRISAT Research Program, Markets, Institutions and Policies; International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics: Patancheru, Telangana, India, 2015; p. 64. [Google Scholar]
- Katungi, E.; Farrow, A.; Mutuoki, T.; Gebeyehu, S.; Karanja, D.; Alamayehu, F.; Sperling, L.; Beebe, S.; Rubyogo, J.C.; Buruchara, R. Improving Common Bean Productivity: An Analysis of Socioeconomic Factors in Ethiopia and Eastern Kenya. Baseline Rep. Trop. legumes II; Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical-CIAT: Cali, Colombia, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Otieno, M.; Steffan-Dewenter, I.; Potts, S.G.; Kinuthia, W.; Kasina, M.J.; Garratt, M.P.D. Enhancing legume crop pollination and natural pest regulation for improved food security in changing African landscapes. Glob. Food Secur. 2020, 26, 100394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Loon, M.P.; Deng, N.; Grassini, P.; Rattalino Edreira, J.I.; Wolde-meskel, E.; Baijukya, F.; Marrou, H.; van Ittersum, M.K. Prospect for increasing grain legume crop production in East Africa. Eur. J. Agron. 2018, 101, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, D.J. Pests, Diseases, and Nutritional Disorders of the Common Bean in Africa: A Field Guide (No. 260); CIAT: Cali, Colombia, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- da Silva, A.G.; Junior, A.L.B.; da Silva Farias, P.R.; de Souza, B.H.S.; Rodrigues, N.E.L.; Carbonell, S.A.M. Common bean resistance expression to whitefly in winter and rainy seasons in Brazil. Sci. Agric. 2019, 76, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muimba-Kankolongo, A. Food Crop Production by Smallholder Farmers in Southern Africa: Challenges and Opportunities for Improvement; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyamwasa, I.; Li, K.; Rutikanga, A.; Rukazambuga, D.N.T.; Zhang, S.; Yin, J.; Ya-Zhong, C.; Zhang, X.X.; Sun, X. Soil insect crop pests and their integrated management in East Africa: A review. Crop. Prot. 2018, 106, 163–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmain, S.R.; Haggar, J.; Holt, J.; Stevenson, P.C. Managing Legume Pests in Sub-Saharan Africa: Challenges and Prospects for Improving Food Security and Nutrition through Agroecological Intensification; Natural Resources Institute, University of Greenwich: Chatham Maritime, UK, 2013; p. 34. [Google Scholar]
- Rice, P.J.; Arthur, E.L.; Barefoot, E.C. Advances on environmental fate and exposures assessments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 5367–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Heneidy, A.H.; Khidr, A.A.; Taman, A.A. Side-effects of insecticides on non-target organisms: 1-In Egyptian cotton fields. Int. Med. J. 2015, 25, 685–690. [Google Scholar]
- Bora, D.; Khanikor, B.; Gogoi, H. Plant-based pesticides: Green environment with special reference to silk worms. Pestic. Adv. Chem. Bot. Pestic. 2012, 8, 171–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurr, G.M.; Reynolds, O.L.; Johnson, A.C.; Desneux, N.; Zalucki, M.P.; Furlong, M.J.; Li, Z.; Akutse, K.S.; Chen, J.; Gao, X.; et al. Landscape ecology and expanding range of biocontrol agent taxa enhance prospects for diamondback moth management. A review. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2018, 38, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurr, G.M.; Wratten, S.D.; Landis, D.A.; You, M. Habitat management to suppress pest populations: Progress and prospects. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2017, 62, 91–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevenson, P.C.; Isman, M.B.; Belmain, S.R. Pesticidal plants in Africa: A global vision of new biological control products from local uses. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 110, 2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyanga, M.O.; Yada, B.; Yencho, G.C.; Ssemakula, G.N.; Alajo, A.; Farman, D.I.; Mwanga, R.O.; Stevenson, P.C. Segregation of hydroxycinnamic acid esters mediating sweet potato weevil resistance in storage roots of sweet potato. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.R.; Gut, L.J. Mating disruption for the 21st century: Matching technology with mechanism. Environ. Entomol. 2015, 44, 427–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karungi, J.; Adipala, E.; Kyamanywa, S.; Ogenga-Latigo, M.W.; Oyobo, N.; Jackai, L.E.N. Pest management in cowpea. Part 2. Integrating planting time, plant density, and insecticide application for management of cowpea field insect pests in eastern Uganda. Crop. Prot. 2000, 19, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karel, A.K.; Autrique, A. Insects and other pests in Africa. In Bean Production Problems in the Tropics, 2nd ed.; Schwarts, H.F., Pastor-Corrales, M.A., Eds.; Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical (CIAT): Cali, Colombia, 1989; pp. 455–504. [Google Scholar]
- Abate, T.; Ampofo, J.K.O. Insect pests of beans in Africa: Their ecology and management. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1996, 41, 45–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaine, G. Studies on the biology and control of pests of seed beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) in northern Tanzania. Bull. Entomol. Res. 1969, 59, 323–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyiira, Z.M. Pests of grain legumes and their control in Uganda: In Pest. of Grain Legumes: Ecology and Control; Taylor, T.A., Singh, S.R., van Emden, H.F., Eds.; Academic Press: London, UK, 1978; pp. 118–121. [Google Scholar]
- Karel, A.K. Yield losses from and control of bean pod borers, Maruca testulalis (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) and Heliothis armigera (Lepidoptera: Noctuidae). J. Econ. Entomol. 1985, 78, 1323–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima, C.P.F. Management of pests of subsistence crops. In Pest and Vector Management in the Tropics; Youdowei, A., Service, M.W., Eds.; Longman: London, UK, 1983. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.C. Bionomics, host plant resistance, and management of the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata—A review. Crop. Prot. 1998, 73, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, R.C.; Premachandra, W.D.; Neilson, R. A study on Maruca vitrata infestation of Yard-long beans (Vigna unguiculata subspecies sesquipedalis). Heliyon 2015, 1, e00014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.T.; Lin, C.S. Occurrence of the legume pod borer, Maruca testulalis Geyer (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on cowpea (Vigna unguiculata Walp) and its insecticides application trial. Plant Prot. Bull. 2000, 42, 213–222. [Google Scholar]
- Margam, V.; Coates, B.; Bayles, D.; Hellmich, R.; Agunbiade, T.; Seufferheld, M.; Sun, W.; Kroemer, J.; Ba, M.; Binso-Dabiré, C.; et al. Transcriptome sequencing, and rapid development and application of snp markers for the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e21388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Wamonje, F.O.; Donnelly, R.; Tungadi, T.D.; Murphy, A.M.; Pate, A.E.; Woodcock, C.; Caulfield, J.; Mutuku, J.M.; Bruce, T.J.A.; Gilligan, C.A.; et al. Different plant viruses induce changes in feeding behavior of specialist and generalist aphids on common bean that are likely to enhance virus transmission. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackai LE, N. Integrated pest management of borers of cowpea and beans. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 1995, 16, 237–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abate, T.; Van Huis, A.; Ampofo, J.K.O. Pest management strategies in traditional agriculture: An African perspective. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 631–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atachi, P.; Djihou, Z. Record of host-plants of Maruca testulalis (Geyer) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in the Republic of Benin. Ann. Soc. Entomol. Fr. 1994, 30, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Capinera, J.L. Order Homoptera–aphids, leaf-and planthoppers, psyllids and whiteflies. In Handbook of Vegetable Pests, 1st ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001; pp. 279–282. [Google Scholar]
- Margam, V.M.; Baoua, I.; Ba, N.M.; Ishiyaku, M.F.; Huesing, J.E.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Murdock, L.L. Wild host plants of legume pod borer Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Pyraloidea: Crambidae) in southern Niger and northern Nigeria. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2010, 30, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackai, L.E.N. Efficacy of insecticide applications at different times of day against the legume pod-borer, Maruca testulalis (Geyer) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), on cowpea in Nigeria. Prot. Ecol. 1983, 5, 245–251. [Google Scholar]
- Baoua, I.; Ba, N.M.; Agunbiade, T.A.; Margam, V.; Binso-Dabiré, C.L.; Antoine, S.; Pittendrigh, B.R. Potential use of Sesbania pachycarpa (Fabaceae: Papilionoideae) as refugia for the legume pod borer Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2011, 31, 12–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larocca, A.; Fanti, P.; Molinaro, A.; Mattia, M.F.; Battaglia, D. Aphid performance on Vicia faba and two southern Italy Phaseolus vulgaris landraces. Bull. Insectology 2011, 64, 101–106. [Google Scholar]
- Adabi, S.T.; Talebi, A.A.; Fathipour, Y.; Zamani, A.A. Life history and demographic parameters of Aphis fabae (Hemiptera: Aphididae) and its parasitoid, Aphidius matricariae (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) on four sugar beet cultivars. Acta Entomol. Serbica 2010, 15, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Ehler, L.E.; Long, R.F.; Kinsey, M.G.; Kelley, S.K. Potential for augmentative biological control of black bean aphid in California sugarbeet. Entomophaga 1997, 42, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Crops: An Identification and Information Guide, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Abtew, A.; Niassy, S.; Affognon, H.; Subramanian, S.; Kreiter, S.; Garzia, G.T.; Martin, T. Farmers’ knowledge and perception of grain legume pests and their management in the Eastern province of Kenya. Crop. Prot. 2016, 87, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, M.V.; Bueno VH, P.; Silveira LC, P.; Auad, A.M. Biological control of insect pests in the tropics. In Tropical Biology and Conservation Management; Del Claro, K., Oliveira, P.S., Rico-Gray, V., Eds.; Eolss Publishers: Oxford, UK, 2009; pp. 28–70. [Google Scholar]
- Ehler, L.E. Integrated pest management (IPM): Definition, historical development and implementation, and the other IPM. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2006, 62, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowder, D.W.; Jabbour, R. Relationships between biodiversity and biological control in agroecosystems: Current status and future challenges. Biol. Control 2014, 75, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, U.; Porcel, M.; Świergiel, W.; Wivstad, M. Habitat Manipulation–As a Pest. Management Tool in Vegetable and Fruit Cropping Systems, with the Focus on Insects and Mites; SLU, EPOK—Centre for Organic Food & Farming: Uppsala, Sweden, 2016; p. 52. [Google Scholar]
- Cock, M.; Lenteren, J.C.; Brodeur, J.; Barratt, B.; Bigler, F.; Bolckmans, K.; Cônsoli, F.L.; Haas, F.; Mason, P.; Parra, J. Do new access, and benefit-sharing procedures under the convention on biological diversity threaten the future of biological control? BioControl 2009, 55, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacas, J.A.; Urbaneja, A. Biological control in citrus in Spain: From classical to conservation biological control. In Integrated Management of Arthropod Pests and Insect-Borne Diseases; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lenteren, J.C. The state of commercial augmentative biological control: Plenty of natural enemies, but a frustrating lack of uptake. Biol. Control 2012, 57, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Lenteren, J.C.; Bolckmans, K.; Köhl, J.; Ravensberg, W.J.; Urbaneja, A. Biological control using invertebrates and microorganisms: Plenty of new opportunities. BioControl 2018, 63, 39–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girma, H.; Rao, M.R.; Sithanantham, S. Insect pests and beneficial hedgerow intercropping systems in semiarid Kenya. Agrofor. Syst. 2000, 50, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkenda, P.A.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Mbega, E.; Stevenson, P.C.; Arnold SE, J.; Gurr, G.M.; Belmain, S.R. Multiple ecosystem services from field margin vegetation for ecological sustainability in agriculture: Scientific evidence and knowledge gaps. PeerJ 2019, 11, 1–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkenda, P.A.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Stevenson, P.C.; Sarah, S.E.; Belmain, S.R.; Chidege, M.; Gurr, G.M. Field margin vegetation in tropical African bean systems harbours diverse natural enemies for biological pest control in adjacent crops. Sustainability 2019, 11, 6399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, S.; Saeed, S. Floral host plant range of syrphid flies (Syrphidae: Diptera) under natural conditions in southern Punjab, Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2010, 42, 1187–1200. [Google Scholar]
- Colley, M.R.; Luna, J.M. The relative attractiveness of potential beneficial insectary plants to aphidophagous hoverflies (Diptera: Syrphidae). Environ. Entomol. 2000, 29, 1054–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, S.; Lopes, T.; Boeraeve, F.; Chen, J.; Francis, F. Pest regulation and support of natural enemies in agriculture: Experimental evidence of within field wildflower strips. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 98, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatt, S.; Mouchon, P.; Lopes, T.; Francis, F. Effects of wildflower strips and an adjacent forest on aphids and their natural enemies in a pea field. Insects 2017, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martini, X.; Pelz-Stelinski, K.S.; Stelinski, L.L. Plant pathogen-induced volatiles attracts parasitoids to increase the parasitism of an insect vector. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2014, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkenda, P.A.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Stevenson, P.C.; Arnold SE, J.; Darbyshire, I.; Belmain, S.R.; Priebe, J.; Johnson, A.C.; Tumbo, J.; Gurr, G.M. Knowledge gaps among smallholder farmers hinder the adoption of conservation biological control. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2020, 30, 256–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkenda, P.; Mwanauta, R.; Stevenson, P.C.; Ndakidemi, P.; Mtei, K.; Belmain, S.R. Extracts from field margin weeds provide economically viable and environmentally benign pest control compared to synthetic pesticides. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeyo-Owuor, J.B.; Oloo, G.W.; Agwaro, P.O. Natural enemies of the legume pod borer, Maruca testulalis Geyer (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in small-scale farming systems of Western Kenya. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 1991, 12, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arodokoun, D.Y. Importance of Plants-Alternative Hosts and Indigenous Natural Enemies in the Biological Control of Maruca testulalis Geyer (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), a Pest of Vigna Unguiculata Walp. Ph.D. Thesis, Laval University, Quebec, QC, Canada, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Arodokoun, D.Y.; Tamo, M.; Cloutier, C.; Brodeur, J. Larval parasitoids occurring on Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) in Benin, West Africa. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2006, 113, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dannon, E.A.; Tamò, M.; Agboton, C.; van Huis, A.; Dicke, M. Effect of Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) host plants on life-history parameters of the parasitoid Apanteles taragamae (Hymenoptera). Insect Sci. 2012, 19, 518–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.C.; Peng, W.K.; Talekar, N.S. Parasitoids and other natural enemies of Maruca vitrata feeding on Sesbania cannabina in Taiwan. Biol. Control. 2003, 48, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Halteren, P. A code of conduct for the import and release of exotic biological control agents for Europe? EPPO Bull. 1997, 27, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yule, S.; Srinivasan, R. Combining bio-pesticides with chemical pesticides to manage legume pod borer (Maruca vitrata) on yard-long bean in Thailand. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2014, 60, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souna, D.A.; Bokonon-Ganta, A.H.; Dannon, E.A.; Imorou, N.; Agui, B.; Cusumano, A.; Srinivasan, R.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Volkoff, A.N.; Tamò, M. Volatiles from Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera, Crambidae) host plants influence olfactory responses of the parasitoid, Therophilus javanus (Hymenoptera: Hymenoptera). Biol. Control 2019, 130, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza AR de Giustolin, T.A.; Querino, R.B.; Alvarenga, C.D. Natural parasitism of Lepidopteran eggs by Trichogramma species (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae) in agricultural crops in Minas Gerais, Brazil. Fla. Entomol. 2016, 99, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huis, A.V.a.n.; Dicke, M. Functional response and life history parameters of Apanteles taragamae, a larval parasitoid of Maruca vitrata. Biol. Control 2010, 55, 363–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Albajes, R.; Gullino, M.L.; van Lenteren, J.C.; Elad, Y. (Eds.) Integrated Pest and Disease Management in Greenhouse Crops; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Farhadi, R.; Allahyari, H.; Chi, H. Life table and predation capacity of Hippodamia variegata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) feeding on Aphis fabae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Biol. Control 2011, 59, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, R.; Allahyari, H.; Juliano, S.A. The functional response of larval and adult stages of Hippodamia variegata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) to different densities of Aphis fabae (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Environ. Entomol. 2010, 39, 1586–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franzman, B.A. Hippodamia variegata, a predacious ladybird new in Australia. Aust. J. Entomol. 2002, 41, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontodimas, D.C.; Stathas, G.J. Phenology fecundity and life table parameters of the predator Hippodamia vagriegata reared on Dyaphis crataegi. Biol. Control 2005, 50, 223–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balog, A.; Mehrparvar, M.; Weisser, W.W. Polyphagous predatory rove beetles (Coleoptera: Staphylinidae) induce winged: Morphs in the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Eur. J. Entomol. 2013, 110, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, C.J. Effects of insect predators on small populations of Aphis fabae in the field. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 1968, 11, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nordey, T.; Boni, S.B.; Agbodzavu, M.K.; Mwashimaha, R.; Mlowe, N.; Ramasamy, S.; Deletre, E. Comparison of biological methods to control Aphis fabae Scopoli (Hemiptera: Aphididae) on kalanchoe crops in East Africa. Crop. Prot. 2021, 142, 105520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, M.G.; Cross, J.V.; Fitzgerald, J.D.; Campbell CA, M.; Jolly, R.L.; Olszak, R.W.; Niemczyk, E.; Vogt, H. Biocontrol of pests of apples and pears in northern and central Europe-3. Predators. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 91–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, R.; Ramirez, R. Aphid Natural Enemies and Biological Control. Utah State University Extension. Available online: https://digitalcommons.usu.edu/extension_curall/814 (accessed on 22 June 2020).
- Nyukuri, R.W.; Kirui, S.C.; Wanjala FM, E.; Odhiambo, J.O.; Cheramgoi, E. The effectiveness of coccinellids as natural enemies of aphids in maize, beans and cowpeas intercrop. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2012, 2, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar]
- Twardowski, J.P.; Hurej, M.; Klukowski, Z. The effect of the strip-management on reduction of Aphis fabae (Homoptera: Aphididae) populations by predators on sugar beet crop. J. Plant. Prot. Res. 2005, 45, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Mkenda, P.A.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Stevenson, P.C.; Arnold, S.E.; Belmain, S.R.; Chidege, M.; Gurr, G.M.; Woolley, V.C. Characterization of hymenopteran parasitoids of Aphis fabae in an African smallholder bean farming system through sequencing of COI ‘Mini-barcodes’. Insects 2019, 10, 331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Völkl, W.; Stechmann, D.H. Parasitism of the black bean aphid (Aphis fabae) by Lysiphlebus fabarum (Hym., Aphidiidae): The influence of host plant and habitat. J. Appl. Entomol 1998, 122, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamani, A.; Talebi, A.; Fathipour, Y.; Baniameri, V. The temperature-dependent functional response of two aphid parasitoids, Aphidius colemani and Aphidius matricariae (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae), on the cotton aphid. J. Pest. Sci. 2006, 79, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, M.V.; Bueno VH, P.; da Conceicao de Menezes Soglia, M.; De Conti, B.F.; Rodrigues, S.M.M. Larval competition between Aphidius colemani and Lysiphlebus testaceipes after multiparasitism of the host Aphis gossypii. Bull. Insectology 2006, 59, 147. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, D.A.; Wratten, S.D.; Gurr, G.M. Habitat management to conserve natural enemies of arthropod pests in agriculture. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2000, 45, 175–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundgren, J.G. Relationships of Natural Enemies and Non-Prey Foods; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Gurr, G.M.; Wratten, S.D.; Altieri, M.A. Ecological engineering: A new direction for agricultural pest management. AFBM J. 2004, 1, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wäckers, F.L.; van Rijn, P.C.J. Food for protection: An introduction. In Plant-Provided Food for Carnivorous Insects: A Protective Mutualism and Its Applications; Wäckers, F.L., van Rijn, P.C.J., Bruin, J., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2005; pp. 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Wäckers, F.L.; Van Rijn, P.C.J. Pick and mix: Selecting flowering plants to meet the requirements of target biological control insects. In Biodiversity and Insect Pests: Key Issues for Sustainable Management; Gurr, G.M., Wratten, S.D., Snyder, W.E., Read, D.M.Y., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2012; pp. 139–165. [Google Scholar]
- Philips, C.R.; Rogers, M.A.; Kuhar, T.P. Understanding farmscapes and their potential for improving IPM programs. J. Integr. Pest Manag. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- FAO. Organic Agriculture: Glossary on Organic Agriculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2009; pp. 1–173. [Google Scholar]
- Rahat, S.; Gurr, G.M.; Wratten, S.D.; Mo, J.; Neeson, R. Effect of plant nectars on adult longevity of the stinkbug parasitoid, Trissolcus basalis. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2005, 51, 321–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saidov, N.S.; Douglas, L.A. Evaluation of flowering plants to attract natural enemies in Tajikistan. In Proceedings of the Conference Devoted to 50 Years Kazakh Research Institute of Plant Protection and Quarantine, Almaty, Kazakhstan, November 2008; Volume 1, pp. 127–132. [Google Scholar]
- Albrecht, M.; Kleijn, D.; Williams, N.; Tschumi, M.; Blaauw, B.; Bommarco, R.; Campbell, A.J.; Dainese, M.; Drummond, F.; Entling, M.; et al. The effectiveness of flower strips and hedgerows on pest control, pollination services and crop yield: A quantitative synthesis. Ecol. Lett. 2020, 23, 1488–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wäckers, F.L.; Romeis, J.; van Rijn, P. Nectar and pollen feeding by insect herbivores and implications for multitrophic interactions. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2007, 52, 301–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winkler, K.; Wäckers, F.L.; Termorshuizen, A.J.; van Lenteren, J.C. Assessing risks and benefits of floral supplements in conservation biological control. Biol. Control. 2010, 55, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karp, D.S.; Chaplin-Kramer, R.; Meehan, T.D.; Martin, E.A.; DeClerck, F.; Grab, H.; Gratton, C.; Hunt, L.; Larsen, A.E.; Martínez-Salinas, A.; et al. Crop pests and predators exhibit inconsistent responses to surrounding landscape composition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E7863–E7870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, P.A.D.S.; Sousa e Silva, C.R. Efeito de espécies vegetais em bordadura em cebola sobre a densidade populacional de tripes e sirfídeos predadores. Hortic. Bras. 2003, 21, 731–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Jado, R.H.; Araj, S.E.; Abu-Irmaileh, B.; Shields, M.W.; Wratten, S.D. Floral resources to enhance the potential of the parasitoid, Aphidius colemani for biological control of the aphid, Myzus persicae. J. Appl. Entomol. 2019, 143, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfiffner, L.; Luka, H.; Schlatter, C.; Juen, A.; Traugott, M. Impact of wildflower strips on biological control of cabbage lepidopterans. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2009, 129, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfiffner, L.; Luka, H.; Schlatter, M.; Lichtenhahn, M. Wildflower strips to reduce lepidopteran pests in cabbage crops. In Landscape management for functional biodiversity. IOBC/WPRS Bull. 2006, 29, 97–99. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, P.; Wang, G.; Zheng, X.; Tian, J.; Lu, Z.; Heong, K.L.; Xu, H.; Chen, G.; Yang, Y.; Gurr, G.M. Selective enhancement of parasitoids of rice Lepidoptera pests by sesame (Sesamum indicum) flowers. Biol. Control. 2014, 60, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sujayanand, G.K.; Chandra, A.; Pandey, S.; Bhatt, S. Seasonal abundance of spotted pod borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius in early pigeon pea [Cajanus cajan (L.) millsp.] and its management through farmscaping in Uttar Pradesh. Legume Res. 2021, 44, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allmann, S.; Späthe, A.; Bisch-Knaden, S.; Kallenbach, M.; Reinecke, A.; Sachse, S.; Baldwin, I.T.; Hansson, B.S. Feeding-induced rearrangement of green leaf volatiles reduces moth oviposition. eLife 2013, 2, e00421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichersky, E.; Gershenzon, J. The formation and function of plant volatiles: Perfumes for pollinator attraction and defense. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2002, 5, 237–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudareva, N.; Negre, F.; Nagegowda, D.A.; Orlova, I. Plant volatiles: Recent advances and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2006, 25, 417–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, Z.R.; James, D.G.; Midega CA, O.; Pickett, J.A. Chemical ecology and conservation biological control. Biol. Control. 2008, 45, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaplan, I. Attracting carnivorous arthropods with plant volatiles: The future of biocontrol or playing with fire? Biol. Control. 2012, 60, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agbessenou, A.; Tounou, A.K.; Dannon, E.A.; Datinon, B.; Agboton, C.; Ramasamy, S.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Tamò, M. The parasitic fly Nemorilla maculosa exploits host-plant volatiles to locate the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2018, 166, 673–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashedi, A.; Rajabpour, A.; Rasekh, A.; Zandi-Sohani, N. Interactions between host plant, Aphis fabae, and its natural enemies, Orius albidipennis and Lysiphlebus fabarum in a tri-trophic system. J. Asia-Pac. Entomol. 2019, 22, 847–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Owusu, J.; Vuts, J.; Caulfield, J.C.; Woodcock, C.M.; Withall, D.M.; Hooper, A.M.; Osafo-Acquaah, S.; Birkett, M.A. Identification of Semiochemicals from cowpea, Vigna unguiculata, for low-input management of the legume pod borer, Maruca vitrata. J. Chem. Ecol. 2020, 46, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajayi, C.O.; Aknnifesi, K.F. Farmers’ understanding of pesticide safety labels and field spraying practices: A case study of cotton farmers. Sci. Res. Essay 2007, 2, 204–210. [Google Scholar]
- Nonga, H.E.; Mdegela, R.H.; Lie, E.; Sandvik, M. Assessment of farming practices and uses of agrochemicals in Lake Manyara basin, Tanzania. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2011, 6, 2216–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abeeluck, D.; Benimadhu, S.P.; Rajkomar, B.; Ramnauth, R.K. Pesticide use in Mauritius. A report of a survey. Agric. Res. Ext. Unit Réduit Maurit. 1997, 22. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.C.; Saxena, K.B.; Bhagwat, V.R. The Legume Pod Borer, Maruca vitrata: Bionomics and Management. Bulletin 1999, 55, 42. Available online: http://oar.icrisat.org/id/eprint/6608 (accessed on 5 August 2020).
- Ekesi, S. Insecticide resistance in field populations of the legume pod-borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae), on cowpea, Vigna unguiculata (L.), Walp in Nigeria. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 1999, 45, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mkindi, A.; Mpumi, N.; Tembo, Y.; Stevenson, P.C.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Mtei, K.; Machunda, R.; Belmain, S.R. Invasive weeds with pesticidal properties as potential new crops. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 110, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tembo, Y.; Mkindi, A.G.; Mkenda, P.A.; Mpumi, N.; Mwanauta, R.; Stevenson, P.C.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Belmain, S.R. Pesticidal plant extracts improve yield and reduce insect pests on legume crops without harming beneficial arthropods. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araya, J.E.; Araya, M.; Guerrero, M.A. Effects of some insecticides applied in sublethal concentrations on the survival and longevity of Aphidius ervi (Haliday) (Hymenoptera: Aphidiidae) adults. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2010, 70, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.-X.; Chen, T.-Y. Effects of the insect growth regulator fenoxycarb on immature Chrysoperla rufilabris (Neuroptera: Chrysopidae). Fla. Entomol. 2001, 84, 628–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, M.; Smagghe, G.; Pineda, S.; Vinuela, E. Action of insect growth regulator insecticides and spinosad on life-history parameters and absorption in third-instar larvae of the endoparasitoid Hyposoter didymator. Biol. Control 2004, 31, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoeb, M.A. Effect of some insecticides on the immature stages of the egg parasitoid Trichogramma evanescens. Egypt. Acad. J. Biol. Sci. 2010, 3, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, L.; Glenn, D.; Hoffmann, A. Effects of Sulfur on Trichogramma egg parasitoids in vineyards: Measuring toxic effects and establishing release windows. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2001, 40, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munyuli MB, T.; Luther, G.C.; Kyamanywa, S. Effects of cowpea cropping systems and insecticides on arthropod predators in Uganda and the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Crop. Prot. 2007, 26, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, R. A Guide to the Development of Regulatory Frameworks for Microbial Biopesticides in Sub-Saharan Africa; African Agricultural Technology Foundation: Nairobi, Kenya, 2013; Available online: https://bit.ly/2TGOwFA (accessed on 19 October 2020).
- Macías, F.A.; Castellano, D.; Molinillo, J.M.G. Search for a standard phytotoxic bioassay for allelochemicals. Selection of standard target species. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 2512–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isman, M.B. Botanical insecticides: For richer, for poorer. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2008, 64, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshi, A.P.; Matoju, I. The status of research on and application of biopesticides in Tanzania. Review. Crop. Prot. 2017, 92, 16–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leahy, J.; Mendelsohn, M.; Kough, J.; Jones, R.; Berckes, N. Biopesticide oversight and registration at the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency. ACS Symp. Ser. 2014, 1172, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R. Integrating biopesticides in pest management strategies for tropical vegetable production. J. Biopestic. 2012, 5, 36–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bravo, A.; Likitvivatanavong, S.; Gill, S.S.; Soberón, M. Bacillus thuringiensis: A story of a successful bioinsecticide. Insect Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 41, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Addae, P.C.; Ishiyaku, M.F.; Tignegre, J.B.; Ba, M.N.; Bationo, J.B.; Atokple, I.D.; Abudulai, M.; Dabiré-Binso, C.L.; Traore, F.; Saba, M.; et al. Efficacy of a cry1Ab Gene for control of Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in Cowpea (Fabaceae). J. Econ. Entomol. 2020, 113, 974–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Huang, L.Z.; Srinivasan, R. Effect of three commercial biopesticides of neem (Azadirachta indica) and Bacillus thuringiensis on legume pod borer (Maruca vitrata) (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) in Thailand. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2014, 34, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Yule, S.; Lin, M.Y.; Khumsuwan, C. Recent developments in the biological control of legume pod borer (Maruca vitrata) on the yard-long bean. Acta Hortic. 2015, 1102, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traoré, F. Effects of Maruca vitrata multi-nucleopolyhedrovirus and neem oil, Azadirachta indica Juss on the eggs of the cowpea pod borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2019, 39, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehinto, J.T.; Loko, Y.L.E.; Kpindou, O.K.D.; Dannon, E.A.; Zanzana, K.; Kassa, P.; Adandonon, A.; Tamò, M. Management of the legume pod borer Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Crambidae) with field applications of the entomopathogenic fungus, Beauveria bassiana and a mixed formulation of the baculovirus MaviMNPV with emulsifiable neem oil. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2020, 15, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sokame, B.M.; Tounou, A.K.; Datinon, B.; Dannon, E.A.; Agboton, C.; Srinivasan, R.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Tamo, M. Combined activity of Maruca vitrata multi-nucleopolyhedrovirus, MaviMNPV and oil from neem, Azadirachta indica Juss and Jatropha curcas L., for the control of cowpea pests. Crop. Prot. 2015, 72, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, R.; Tamo, M.; Lee, S.T.; Lin, M.Y.; Huang, C.C.; Hsu, Y.C. Towards developing a biological control program for legume pod borer (Maruca vitrata). In International Conference on Grain Legumes: Quality Improvement, Value Addition and Trade (No. RESEARCH); Indian Institute of Pulses Research: Kanpur, India, 2009; pp. 183–196. [Google Scholar]
- Srinivasan, R.; Sevgan, S.; Tamò, M. Biopesticide-based sustainable pest management for safer production of vegetable legumes and brassicas in Asia and Africa. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2019, 75, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akmal, M.; Freed, S.; Malik, M.N.; Gul, H.T. Efficacy of Beauveria bassiana (deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) against different aphid species under laboratory conditions. Pak. J. Zool. 2013, 45, 71–78. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, S.; Elarrnaouty, S.A.; Alotaibi, S.; Salah, M. Pathogenicity and side effect of indigenous Beauveria bassiana on Coccinella undecimpunctata and Hippodamia variegata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Insects 2021, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammed, A.A. Lecanicillium muscarium and Adalia bipunctata combination for the control of black bean aphid, Aphis fabae. Biol. Control 2018, 63, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Grandon, G.M.; Harte, S.J.; Ewany, J.; Bray, D.; Stevenson, P.C. Additive effect of botanical insecticide and entomopathogenic fungi on pest mortality and the behavioral response of its natural enemy. Plants 2020, 9, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tumuhaise, V.; Ekesi, S.; Mohamed, S.A.; Ndegwa, P.N.; Irungu, L.W.; Srinivasan, R.; Maniania, N.K. Pathogenicity and performance of two candidate isolates of Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana (Hypocreales: Clavicipitaceae) in four liquid culture media for the management of the legume pod borer Maruca vitrata (Lepidoptera: Crambidae). Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2015, 35, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekesi, S.; Maniania, N.K.; Lux, S.A. Mortality in three African tephritid fruit fly puparia and adults caused by the entomopathogenic fungi, Metarhizium anisopliae and Beauveria bassiana. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2002, 12, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saruhan, I. Efficacy of some entomopathogenic fungi against Aphis fabae Scopoli (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Egypt. J. Biol. Pest. Control 2018, 28, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saruhan, I.; Erper, I.; Tuncer, C.; Akca, I. Efficiency of some entomopathogenic fungi as biocontrol agents against Aphis fabae scopoli (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Pak. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 52, 273–278. [Google Scholar]
- Boni, S.B.; Mwashimaha, R.A.; Mlowe, N.; Sotelo-Cardona, P.; Nordey, T. Efficacy of indigenous entomopathogenic fungi against the black aphid, Aphis fabae Scopoli under controlled conditions in Tanzania. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2020, 2009, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervez, R.; Rao, U. Infectivity of entomopathogenic nematodes against the legume pod-borer, Maruca vitrata Fabricius, infesting pigeon pea. J. Helminthol. 2021, 95, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbro, J.M.; Thomas, M.B. Spore persistence and likelihood of aeroallergenicity of entomopathogenic fungi used for mosquito control. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 80, 992–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaronski, S.T. Ecological factors in the inundative use of fungal entomopathogens. BioControl 2010, 55, 159–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacey, L.A.; Mesquita, A.L.; Mercadier, G.; Debire, R.; Kazmer, D.J.; Leclant, F. Acute and sublethal activity of the entomopathogenic fungus Paecilomyces fumosoroseus (Deuteromycotina: Hyphomycetes) on adult Aphelinus asychis (Hymenoptera: Aphelinidae). Environ. Entomol. 1997, 26, 1452–1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, H.E.; Pell, J.K. Interactions between entomopathogenic fungi and other natural enemies: Implications for biological control. Biocontrol Sci. Technol. 2000, 10, 737–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shipp, J.L.; Zhang, Y.; Hunt, D.W.A.; Ferguson, G. Influence of humidity and greenhouse microclimate on the efficacy of Beauveria bassiana (Balsamo) for control of greenhouse arthropod pests. Environ. Entomol. 2003, 32, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rattan, R.S. Mechanism of action of insecticidal secondary metabolites of plant origin. Crop. Prot. 2010, 29, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzywacz, D.; Stevenson, P.C.; Mushobozi, W.L.; Belmain, S.; Wilson, K. The use of indigenous ecological resources for pest control in Africa. Food Secur. 2014, 6, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonsignore, C.; Vacante, V. Influences of botanical pesticides and biological agents on Orius laevigatus- Frankliniella occidentalis dynamics under greenhouse conditions. J. Plant Prot. Res. 2012, 52, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tunca, H.; Kilinçer, N.; Özkan, C. Side-effects of some botanical insecticides and extracts on the parasitoid, Venturia canescens (Grav.) (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae). Turk. J. Entomol. 2012, 36, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmonds, M.; Manlove, J.; Blaney, W.; Khambay, B. Effects of selected botanical insecticides on the behaviour and mortality of the glasshouse whitefly Trialeurodes vaporariorum and the parasitoid Encarsia formosa. Entomol. Exp. Appl. 2002, 102, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaminathan, R.; Jat, H.; Hussain, T. Side effects of a few botanicals on the aphidophagous Coccinellids. J. Biopestic. 2010, 3, 81–84. [Google Scholar]
- Belmain, S.; Stevenson, P. Ethnobotanicals in Ghana: Reviving and modernizing age-old farmer practice. Pestic. Outlook 2001, 12, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahar, H.; Islam, A.; Mannan, A.; Uddin, J. Effectiveness of some botanical extracts on bean aphids attacking yard-long beans. J. Entomol. 2007, 4, 136–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kayange, C.D.M.; Njera, D.; Nyirenda, S.P.; Mwamlima, L. Effectiveness of Tephrosia vogelii and Tephrosia candida extracts against common bean aphid (Aphis fabae) in Malawi. Adv. Agric. 2019, 2019, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biniaś, B.; Gospodarek, J. Effect of water extract from Chamomile on black bean aphid and Colorado potato beetle. J. Ecol. Eng. 2017, 18, 118–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ugwu, J.A. Insecticidal activity of some botanical extracts against legume flower thrips and legume pod borer on cowpea Vigna unguiculata L. Walp. J. Basic Appl. Zool. 2020, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Prakash, B.; Dubey, N.K. Insecticidal activity of Ageratum conyzoides L., Coleus aromaticus Benth. and Hyptis suaveolens (L.) Poit essential oils as fumigant against storage grain insect Tribolium castaneum Herbst. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 2210–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniz, J.F.S.; da Silva, P.R.; dos Reis, M.R.; Endo, R.T.; Ramos, R.S.; Fernandes, F.L.; da Silva, Í.W. Insecticide activity of weeds to pests of stored products and crops. J. Agric. Sci. 2014, 6, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, I.L.; Tomazella, V.B.; Santos, A.J.N.; Moraes, T.; Silveira, L.C.P. Parasitoids diversity in organic Sweet pepper (Capsicum annuum) associated with Basil (Ocimum basilicum) and Marigold (Tagetes erecta). Braz. J. Biol. 2019, 79, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, S.E.; Dolma, S.K.; Verma, P.K.; Singh, B. Insecticidal activities of Parthenium hysterophorus L. extract and parthenin against diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella (L.) and aphid, Aphis craccivora Koch. Toxin Rev. 2018, 37, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahayaraj, K.; Kombiah, P.; Dikshit, A.K. Chemical constituents of the essential oils of Tephrosia purpurea and Ipomoea carnea and their repellent activity against Odoiporus longicollis. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2015, 80, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.S.; Ward, J.M.; Levine, S.L.; Baum, J.A.; Vicini, J.L.; Hammond, B.G. The food and environmental safety of Bt crops. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ba, M.N.; Huesing, J.E.; Tamò, M.; Higgins, T.J.V.; Pittendrigh, B.R.; Murdock, L.L. An assessment of the risk of Bt-cowpea to non-target organisms in West Africa. J. Pest. Sci. 2018, 91, 1165–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyangau, P.; Muriithi, B.; Diiro, G.; Akutse, K.S.; Subramanian, S. Farmers’ knowledge and management practices of cereal, legume and vegetable insect pests, and willingness to pay for biopesticides. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 2020, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constantine, K.L.; Kansiime, M.K.; Mugambi, I.; Nunda, W.; Chacha, D.; Rware, H.; Makale, F.; Mulema, J.; Lamontagne-Godwin, J.; Williams, F.; et al. Why don’t smallholder farmers in Kenya use more biopesticides? Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 3615–3625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiales, D.; Fondevilla, S.; Chen, W.; Gentzbittel, L.; Thomas, J.V. Achievements and challenges in legume breeding for pest and disease resistance. Crit. Rev. Plant Sci. 2015, 34, 195–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adati, T.; Tamò, M.; Yusuf, S.R.; Downham, M.C.A.; Singh, B.B.; Hammond, W. Integrated pest management for cowpea-cereal cropping systems in the West African savannah. Int. J. Trop. Insect Sci. 2007, 27, 123–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, J.; Srinivasan, S. Varietal screening and role of morphological factors on distribution and abundance of spotted pod borer, Maruca vitrata (Geyer) on cowpea. Ann. Plant Prot. Sci. 2011, 19, 71–74. [Google Scholar]
- Yusuf, S.R. Infestation and Damage by Maruca vitrata Fabricius (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on Some Cowpea Lines under Different Cropping Systems in Kano, Nigeria. Ph.D. Thesis, Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University, Bauchi, Nigeria, 2007; 155p. [Google Scholar]
- Huesing, J.; Romeis, J.; Ellstrand, N.; Raybould, A.; Hellmich, R.; Wolt, J.; Ehlers, J.; Dabiré, C.; Fatokun, C.; Hokanson, K.; et al. Regulatory considerations surrounding the deployment of Bt-expressing cowpea in Africa: Report of the deliberations of an expert panel. GM Crop. 2011, 2, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwangi, S.N.; Deng, A.L.; Kamau, A.W. Response of Kenyan varieties of common bean, Phaseolus vulgaris L., to infestation by Aphis fabae Scopoli. Afr. Entomol. 2008, 16, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili-Vardanjani, M.; Askarianzadeh, A.; Saeidi, Z.; Hasanshahi, G.H.; Karimi, J.; Nourbakhsh, S.H. A study on common bean cultivars to identify sources of resistance against the black bean aphid, Aphis fabae Scopoli (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Arch. Phytopathol. Plant Prot. 2013, 46, 1598–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannag, H.K.; Obeidat, W.M. Interaction between plant resistance and predation of Aphis fabae (Homoptera: Aphididae) by Coccinella septempunctata (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae). Ann. Appl. Biol. 2008, 152, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razmjou, J.; Fallahi, A. Effects of sugar beet cultivar on development and reproductive capacity of Aphis fabae. Bull. Insectology 2009, 62, 197–201. [Google Scholar]
- Adipala, E.; Nampala, P.; Karungi, J.; Isubikalu, P. A review on options for management of cowpea pests: Experiences from Uganda. Integr. Pest. Manag. Rev. 2000, 5, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nampala, P.; Kyamanywa, S.; Ogenga-Latigo, M.W.; Adipala, E.; Karungi, J.; Oyobo, N.; Jackai, L.E.N. Integrated management of major field pests of cowpea in eastern Uganda. Afr. Crop. Sci. J. 1999, 7, 479–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karel, A.K. Effects of intercropping with maize on the incidence and damage caused by pod borers of common beans. Environ. Entomol. 1993, 22, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omolo, E.O.; Nyambo, B.; Simbi CO, J.; Ollimo, P. The role of host plant resistance and intercropping in integrated pest management (IPM) with specific reference to the Oyugis project. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 1993, 39, 265–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottenberg, H.; Tamo, M.; Singh, B.B. Occurrence of phytophagous insects on wild Vigna sp. and cultivated cowpea: Comparing the relative importance of host-plant resistance and millet intercropping. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 1998, 70, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emeasor, K.C.; Ezueh, M.I. The influence of companion crops in the control of insect pests of cowpea in intercropping systems. Trop. Agric. 1997, 74, 285–289. [Google Scholar]
- Asiwe, J.A.N.; Nokoe, S.; Jackai, L.E.N.; Ewete, F.K. Does varying cowpea spacing provide better protection against cowpea pests? Crop. Prot. 2005, 24, 465–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekesi, S.; Dike, M.C.; Ogunlana, M.O. Relationship between planting dates and damage by the legume pod-borer, Maruca testulalis (Geyer) (Lepidoptera: Pyralidae) on cowpea, Vigna unguiculata (L) Walp in Nigeria. Int. J. Pest. Manag. 1996, 42, 315–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latigo-Ogenga, M.W.; Baliddawa, C.W.; Ampofo, J.K.O. Factors influencing the incidence of the black bean aphid, Aphis fabae Scop., on common beans intercropped with maize. Afr. Crop. Sci. J. 1993, 1, 49–58. [Google Scholar]
- Azimi, S.; Amini, R. Population density of Aphis fabae Scopoli (Hemiptera, Aphididae) and its natural enemies in intercropping of faba bean (Vicia faba L.) and dragonhead (Dracocephalum moldavica L.). J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. 2015, 6, 380–388. [Google Scholar]
- Agunbiade, T.A.; Sun, W.; Coates, B.S.; Traore, F.; Ojo, J.A.; Lutomia, A.N.; Bello-Bravo, J.; Miresmailli, S.; Huesing, J.E.; Agyekum, M.; et al. Insect pests and integrated pest management techniques in grain legume cultivation. In Achieving Ustainable Cultivation of Grain Legumes, Vol. 1: Advances in Breeding and Cultivation Techniques; Sivasankar, S., Bergvinson, D., Gaur, P., Agrawal, S., Beebe, S., Tamò, M., Eds.; Burleigh Dodds: Cambridge, UK, 2018; pp. 297–320. [Google Scholar]
- Singh, S.R.; Jackai, L.E.N.; Dos Santos, J.H.R.; Adalla, C.B. Insect pests of Cowpea. In Insect Pests of Tropical Food Legumes; Singh, S.R., Ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 1990; pp. 43–89. [Google Scholar]
- Ajeigbe, H.A.; Singh, B.B. Integrated pest management in cowpea: Effect of time and frequency of insecticide application on productivity. Crop. Prot. 2006, 25, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabirye, J.; Nampala, P.; Ogenga-Latigo, M.W.; Kyamanywa, S.; Wilson, H.; Odeke, V.; Iceduna, C.; Adipala, E. Farmer-participatory evaluation of cowpea integrated pest management (IPM) technologies in Eastern Uganda. Crop. Prot. 2003, 22, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elisante, F.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Arnold, S.E.J.; Belmain, S.R.; Gurr, G.M.; Darbyshire, I.; Xie, G.; Tumbo, J.; Stevenson, P.C. Enhancing knowledge among smallholders on pollinators and supporting field margins for sustainable food security. J. Rural. Stud. 2019, 70, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Bean Pest | Country | Yield Loss% | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. fabae | Burundi | 50 | [25] |
| A. fabae | Kenya | 37–90 | [26] |
| A. fabae | Tanzania | 37 | [27] |
| A. fabae | Uganda | 90 | [28] |
| M. vitrata | Tanzania | 33–53 | [29] |
| M. vitrata | Kenya | 15–25 | [30] |
| Bean Pest | Plant Species | Family | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| M. vitrata | Vigna unguiculata | Fabaceae | [36,37] |
| M. vitrata, A fabae | Phaseolus vulgaris | Fabaceae | [36] |
| M. vitrata | Cajanus cajan | Fabaceae | [31] |
| M. vitrata, A. fabae | Phaseolus lunatus | Fabaceae | [31,38,39] |
| M. vitrata | Sesbania sp. | Fabaceae | [40] |
| M. vitrata | Crotalaria sp. | Fabaceae | [41] |
| M. vitrata | Sesbania pachycarpa | Fabaceae | [42] |
| M. vitrata, A. fabae | Vicia faba | Fabaceae | [31,43] |
| A. fabae | Beta vulgaris | Amaranthaceae | [44,45] |
| A. fabae | Solanum tuberosum | Solanaceae | [46] |
| A. fabae | Allium cepa | Amaryllidaceae | [39] |
| A. fabae | Lycopersicon esculentum | Solanaceae | [46] |
| A. fabae | Dahlia pinnata, Lactuca sativa | Asteraceae | [39,46] |
| Parasitoid Species | Family | Host Stage Parasitized | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Apanteles taragamae | Braconidae | Larva | [75] |
| Bassus bruesi, Bracon sp. | Braconidae | Larva | [68] |
| Braunsia kriegeri | Braconidae | Larva | [67,68] |
| Cadurcia sp. | Tachinidae | Larva | [68] |
| Dolichogenidea sp. | Braconidae | Larva | [68,70] |
| Phanerotoma leucobasis | Braconidae | Larva | [58] |
| Natural Enemy | Family | References |
|---|---|---|
| Aphidius colemani | Aphididae | [83,88] |
| Cheilomenes sp. | Coccinellidae | [86] |
| Exochomus spp. | Coccinellidae | [86] |
| Henosepichna spp. | Coccinellidae | [86] |
| Hippodamia variegata | Coccinellidae | [86,89] |
| Bean Pest | Biopesticide Used | References |
|---|---|---|
| M. vitrata | Bacillus thuringiensis | [140] |
| M. vitrata | Beauveria bassiana | [141,145,151] |
| M. vitrata | Mavi multi-nucleopolyhedrovirus | [141,142] |
| M. vitrata | Metarhizium anisopliae | [151,152] |
| A. fabae | Lecanicillium muscarium | [153,154] |
| A. fabae | Simplicillium lamellicola | [153,154] |
| A. fabae | Aspergillus flavus | [155] |
| M. vitrata | Heterorhabditis sp., Oscheius sp. | [156] |
| Pesticidal Plant | Family | Family | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ageratum conyzoides | Asteraceae | Tribolium castaneum | [173] |
| Allium sativum | Amaryllidaceae | Aphis fabae | [169] |
| Annona muricata | Annonaceae | Maruca vitrata | [172] |
| Azadirachta indica | Meliaceae | Aphis fabae | [169] |
| Eucalyptus sp. | Myrtaceae | Aphis fabae | [169] |
| Euphorbia heterophylla | Euphorbiaceae | Sitophilus zeamais | [174] |
| Matricaria chamomilla | Asteraceae | Aphis fabae | [172] |
| Ocimum sp. | Lamiaceae | Didyctium sp. | [175] |
| Parthenium hysterophorus | Asteraceae | Aphis craccivora | [176] |
| Piper guineense | Piperaceae | Maruca vitrata | [172] |
| Swietenia sp. | Meliaceae | Aphis fabae | [169] |
| Tephrosia purpurea | Fabaceae | Odoiporus longicollis | [177] |
| Tephrosia vogelii | Fabaceae | Aphis fabae | [124,170] |
| Biological Control Agent | Control Method | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biopesticides | Resistant Varieties | Cultural Control | Synthetic Pesticides | |||||||||||
| (−) | ||||||||||||||
| EPF | Bacteria | Viruses | Botanical | |||||||||||
| Pesticides | ||||||||||||||
| AF | MV | AF | MV | AF | MV | AF | MV | AF | MV | AF | MV | AF | MV | |
| Predators | (+) | (*) | (*) | (*) | (*) | (*) | (+) | (*) | (+) | (*) | (+) | (+) | (−) | (*) |
| [145,148,149] | [21,65,124,125] | [189] | [131,200] | [131] | [65,124,125] | |||||||||
| (+) | (*) | (*) | (*) | (*) | (+) | (+) | (*) | (*) | (*) | (*) | (+) | (*) | (*) | |
| Parasitoids | [150] | [145] | [150] | [185] | ||||||||||
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ndakidemi, B.J.; Mbega, E.R.; Ndakidemi, P.A.; Stevenson, P.C.; Belmain, S.R.; Arnold, S.E.J.; Woolley, V.C. Natural Pest Regulation and Its Compatibility with Other Crop Protection Practices in Smallholder Bean Farming Systems. Biology 2021, 10, 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080805
Ndakidemi BJ, Mbega ER, Ndakidemi PA, Stevenson PC, Belmain SR, Arnold SEJ, Woolley VC. Natural Pest Regulation and Its Compatibility with Other Crop Protection Practices in Smallholder Bean Farming Systems. Biology. 2021; 10(8):805. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080805
Chicago/Turabian StyleNdakidemi, Baltazar J., Ernest R. Mbega, Patrick A. Ndakidemi, Philip C. Stevenson, Steven R. Belmain, Sarah E. J. Arnold, and Victoria C. Woolley. 2021. "Natural Pest Regulation and Its Compatibility with Other Crop Protection Practices in Smallholder Bean Farming Systems" Biology 10, no. 8: 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080805
APA StyleNdakidemi, B. J., Mbega, E. R., Ndakidemi, P. A., Stevenson, P. C., Belmain, S. R., Arnold, S. E. J., & Woolley, V. C. (2021). Natural Pest Regulation and Its Compatibility with Other Crop Protection Practices in Smallholder Bean Farming Systems. Biology, 10(8), 805. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080805