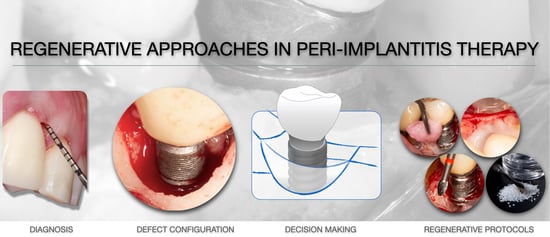
Peri-Implantitis Regenerative Therapy: A Review
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Osseointegration and Re-Osseointegration
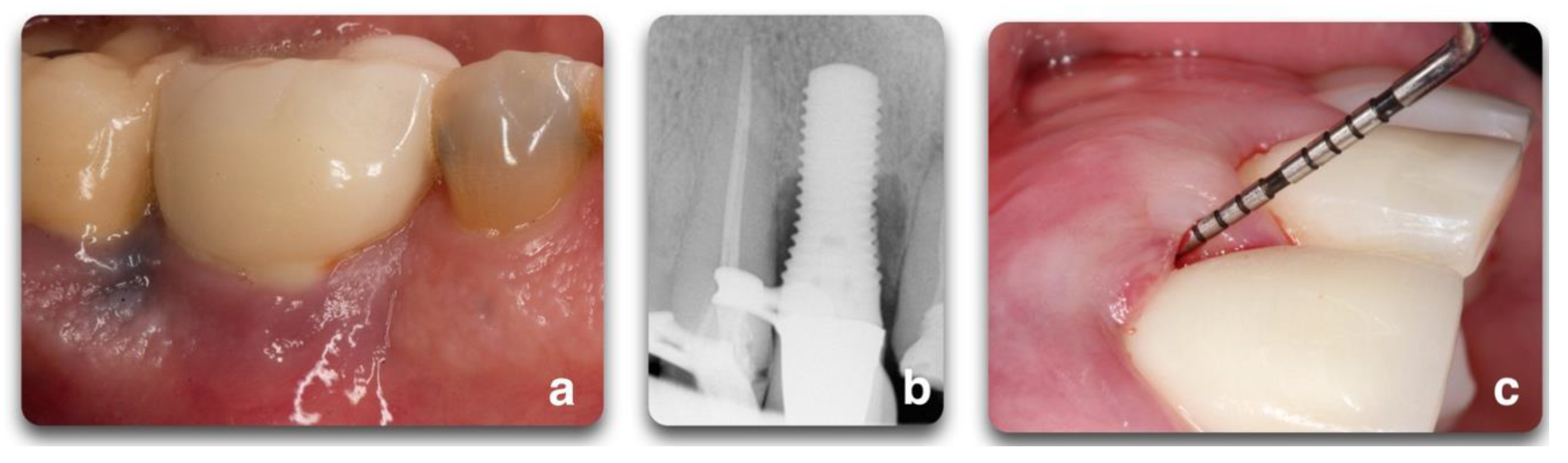
3. Peri Implant Diseases
4. Peri-Implantitis Treatment Factors
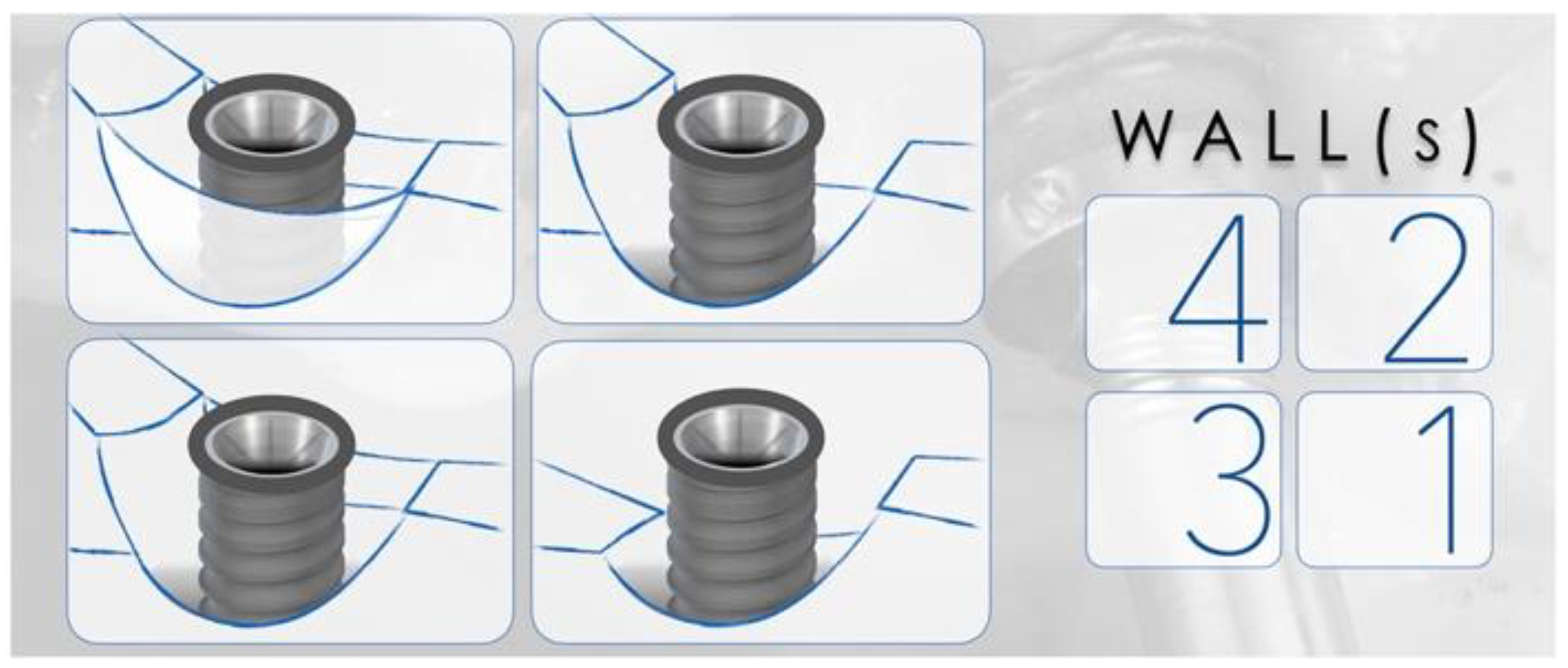
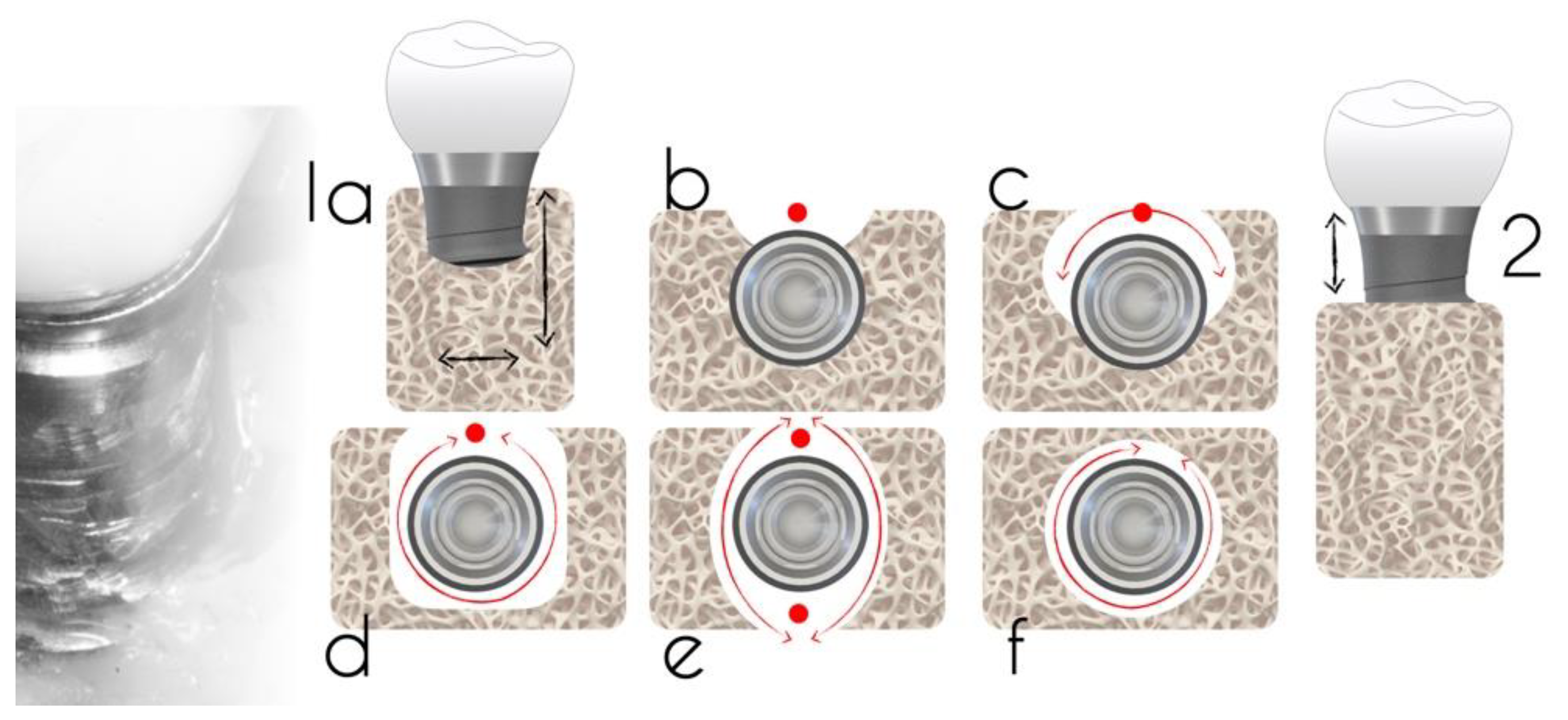
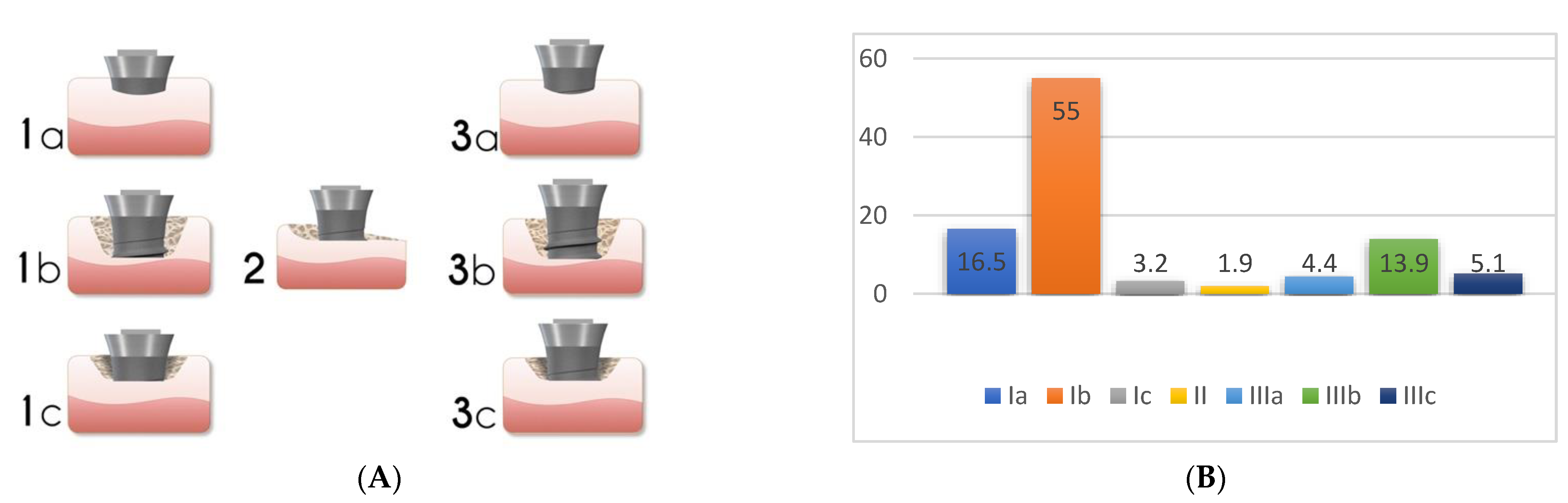
4.1. Peri-Implant Defect Configuration
4.2. Surface Decontamination
4.2.1. Pre-Clinical Studies
4.2.2. Human Clinical Studies
5. Regeneration Techniques & Materials
5.1. Animal Studies
5.2. Adjunctive Therapies
5.3. Studies on Humans
6. Treatment Outcomes
6.1. Success of Regenerative Therapy
6.2. Time Stability of Therapy
7. Discussion
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L. Peri-implantitis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S267–S290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Polyzois, I.; Maguire, R. Re-osseointegration on previously contaminated surfaces: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2009, 20 (Suppl. 4), 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Brånemark, P.-I.; Hansson, H.-A.; Lindström, J. Osseointegrated titanium implants: Requirements for ensuring a long-lasting, direct bone-to-implant anchorage in man. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1981, 52, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Branemark, P.-I. Osseointegrated implants in the treatment of the edentulous jaw. Experience from a 10-year period. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Suppl. 1977, 16, 1–132. [Google Scholar]
- Brånemark, P.-I.; Breine, U.; Adell, R.; Hansson, B.; Lindström, J.; Ohlsson, Å. Intra-osseous anchorage of dental prostheses: I. Experimental studies. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1969, 3, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brånemark, P.I.; Zarb, G.; Albrektsson, T. Introduction to osseointegration. In Tissue-Integrated Prosthesis; Osseointegration in Clinical Dentistry; Quintessence Publishing Co.: Chicago, IL, USA, 1985; pp. 11–76. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmotti, M.B.; Guerrero, C.; Cabrini, R.L. Chronodynamic evaluation of the stages of osseointegration in zirconium laminar implants. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 1997, 10, 11–23. [Google Scholar]
- Guglielmotti, M.B.; Olmedo, D.G.; Cabrini, R.L. Research on implants and osseointegration. Periodontol. 2000 2019, 79, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, S.B.; Tessler, J.; Guglielmotti, M.B.; Cabrini, R.L. Effect of dexamethasone on osseointegration: A preliminary experimental study. J. Oral Implantol. 1996, 22, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Renou, S.J.; Guglielmotti, M.B.; de la Torre, A.; Cabrini, R.L. Effect of total body irradiation on peri-implant tissue reaction: An experimental study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pien, D.M.; Olmedo, D.G.; Guglielmotti, M.B. Influence of age and gender on peri-implant osteogenesis. Age and gender on peri-implant osteogenesis. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 2001, 14, 9–13. [Google Scholar]
- Giglio, M.J.; Gorustovich, A.; Guglielmotti, M.B. Bone healing under experimental anemia in rats. Acta Odontol. Latinoam. 2000, 13, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Insua, A.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L.; Miron, R.J. Basis of bone metabolism around dental implants during osseointegration and peri-implant bone loss. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda, T.; Yliheikkilä, P.K.; Felton, D.A.; Cooper, L.F. Generalizations regarding the process and phenomenon of osseointegration. Part I. In vivo studies. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 1998, 13, 17–29. [Google Scholar]
- Parfitt, A.M. Stereologic Basis of Bone Histomorphometry: Theory of Quantitative Microscopy and Reconstruction of the Third Dimension; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1983; pp. 53–85. [Google Scholar]
- Pazzaglia, U.E.; Bernini, F.; Zatti, G.; Di Nucci, A. Histology of the metal-bone interface: Interpretation of plastic embedded slides. Biomaterials 1994, 15, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priyanka, V.; Ramamoorthy, J. Osseointegration and re-osseointegration. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2014, 5, 508–512. [Google Scholar]
- Subramani, K.; Wismeijer, D. Decontamination of titanium implant surface and re-osseointegration to treat peri-implantitis: A literature review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2012, 27, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Madi, M.; Htet, M.; Zakaria, O.; Alagl, A.; Kasugai, S. Re-osseointegration of Dental Implants After Periimplantitis Treatments: A Systematic Review. Implant Dent. 2018, 27, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, M.G.; Lindhe, J. Peri-implant health. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S249–S256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renvert, S.; Persson, G.R.; Pirih, F.Q.; Camargo, P.M. Peri-implant health, peri-implant mucositis, and peri-implantitis: Case definitions and diagnostic considerations. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S304–S312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almohandes, A.; Carcuac, O.; Abrahamsson, I.; Lund, H.; Berglundh, T. Re-osseointegration following reconstructive surgical therapy of experimental peri-implantitis. A pre-clinical in vivo study. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, A.; Pons, R.; Insua, A.; Nart, J.; Wang, H.-L.; Schwarz, F. Morphology and severity of peri-implantitis bone defects. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2019, 21, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykaras, N.; Iacopino, A.M.; Triplett, R.G.; Marker, V.A. Effect of Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein-2 on the Osseointegration of Dental Implants: A Biomechanics Study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2004, 8, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazadeh, A.; Persson, R.G.; Renvert, S. Impact of bone defect morphology on the outcome of reconstructive treatment of peri-implantitis. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2020, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Sahm, N.; Mihatovic, I.; Golubovic, V.; Becker, J. Surgical therapy of advanced ligature-induced peri-implantitis defects: Cone-beam computed tomographic and histological analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Herten, M.; Sager, M.; Bieling, K.; Sculean, A.; Becker, J. Comparison of naturally occurring and ligature-induced peri-implantitis bone defects in humans and dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2007, 18, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-García, M.; Mir-Mari, J.; Benic, G.I.; Figueiredo, R.; Valmaseda-Castellón, E. Accuracy of periapical radiography in assessing bone level in implants affected by peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Pittoni, D.; Roccuzzo, A.; Charrier, L.; Dalmasso, P. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis intrabony lesions by means of deproteinized bovine bone mineral with 10% collagen: 7-Year-results. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 1577–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshardt, D.D.; Chappuis, V.; Buser, D. Osseointegration of titanium, titanium alloy and zirconia dental implants: Current knowledge and open questions. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, F.; Keeve, P.L.; Ramanauskaite, A.; Schwarz, F.; Koo, K.T.; Sculean, A.; Romanos, G. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis-Consensus report of working group 4. Int. Dent. J. 2019, 69 (Suppl. 2), 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanz, M.; Chapple, I.L. Clinical research on peri-implant diseases: Consensus report of Working Group 4. J. Clin. Periodontol 2012, 39 (Suppl. 12), 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, K.T.; Khoury, F.; Keeve, P.L.; Schwarz, F.; Ramanauskaite, A.; Sculean, A.; Romanos, G. Implant Surface Decontamination by Surgical Treatment of Periimplantitis: A Literature Review. Implant Dent. 2019, 28, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Obreja, K.; Sader, R.; Khoury, F.; Romanos, G.; Koo, K.T.; Keeve, P.L.; Sculean, A.; Schwarz, F. Surgical Treatment of Periimplantitis With Augmentative Techniques. Implant Dent. 2019, 28, 187–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.; Mombelli, A. The therapy of peri-implantitis: A systematic review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2014, 29, 325–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renvert, S.; Polyzois, I.N. Clinical approaches to treat peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis. Periodontol. 2000 2015, 68, 369–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetzel, A.C.; Vlassis, J.; Caffesse, R.G.; Hämmerle, C.H.; Lang, N.P. Attempts to obtain re-osseointegration following experimental peri-implantitis in dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1999, 10, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, L.G.; Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J.; Sennerby, L. Re-osseointegration after treatment of peri-implantitis at different implant surfaces: An experimental study in the dog. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2001, 12, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namgoong, H.; Kim, M.D.; Ku, Y.; Rhyu, I.C.; Lee, Y.M.; Seol, Y.J.; Gu, H.J.; Susin, C.; Wikesjö, U.M.; Koo, K.T. Bone reconstruction after surgical treatment of experimental peri-implantitis defects at a sandblasted/acid-etched hydroxyapatite-coated implant: An experimental study in the dog. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Bonino, F.; Bonino, L.; Dalmasso, P. Surgical therapy of peri-implantitis lesions by means of a bovine-derived xenograft: Comparative results of a prospective study on two different implant surfaces. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 738–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Isehed, C.; Holmlund, A.; Renvert, S.; Svenson, B.; Johansson, I.; Lundberg, P. Effectiveness of enamel matrix derivative on the clinical and microbiological outcomes following surgical regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis. A randomized controlled trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 863–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jepsen, K.; Jepsen, S.; Laine, M.L.; Anssari Moin, D.; Pilloni, A.; Zeza, B.; Sanz, M.; Ortiz-Vigon, A.; Roos-Jansåker, A.M.; Renvert, S. Reconstruction of Peri-implant Osseous Defects: A Multicenter Randomized Trial. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roccuzzo, M.; Gaudioso, L.; Lungo, M.; Dalmasso, P. Surgical therapy of single peri-implantitis intrabony defects, by means of deproteinized bovine bone mineral with 10% collagen. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, F.; Hegewald, A.; John, G.; Sahm, N.; Becker, J. Four-year follow-up of combined surgical therapy of advanced peri-implantitis evaluating two methods of surface decontamination. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; John, G.; Schmucker, A.; Sahm, N.; Becker, J. Combined surgical therapy of advanced peri-implantitis evaluating two methods of surface decontamination: A 7-year follow-up observation. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nart, J.; de Tapia, B.; Pujol, À.; Pascual, A.; Valles, C. Vancomycin and tobramycin impregnated mineralized allograft for the surgical regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis: A 1-year follow-up case series. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 2199–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-López Del Amo, F.; Garaicoa-Pazmiño, C.; Fretwurst, T.; Castilho, R.M.; Squarize, C.H. Dental implants-associated release of titanium particles: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2018, 29, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stavropoulos, A.; Bertl, K.; Eren, S.; Gotfredsen, K. Mechanical and biological complications after implantoplasty—A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2019, 30, 833–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roos-Jansåker, A.M.; Persson, G.R.; Lindahl, C.; Renvert, S. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis using a bone substitute with or without a resorbable membrane: A 5-year follow-up. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2014, 41, 1108–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roos-Jansaker, A.M.; Renvert, H.; Lindahl, C.; Renvert, S. Submerged healing following surgical treatment of peri-implantitis: A case series. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2007, 34, 723–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schou, S.; Holmstrup, P.; Jørgensen, T.; Skovgaard, L.T.; Stoltze, K.; Hjørting-Hansen, E.; Wenzel, A. Anorganic porous bovine-derived bone mineral (Bio-Oss) and ePTFE membrane in the treatment of peri-implantitis in cynomolgus monkeys. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 535–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schou, S.; Holmstrup, P.; Jørgensen, T.; Skovgaard, L.T.; Stoltze, K.; Hjørting-Hansen, E.; Wenzel, A. Implant surface preparation in the surgical treatment of experimental peri-implantitis with autogenous bone graft and ePTFE membrane in cynomolgus monkeys. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 412–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schou, S.; Holmstrup, P.; Skovgaard, L.T.; Stoltze, K.; Hjørting-Hansen, E.; Gundersen, H.J. Autogenous bone graft and ePTFE membrane in the treatment of peri-implantitis. II. Stereologic and histologic observations in cynomolgus monkeys. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2003, 14, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, U.D.; Suaid, F.A.; Wikesjö, U.M.E.; Susin, C.; Taba, M., Jr.; Novaes, A.B., Jr. Comparison between two antimicrobial protocols with or without guided bone regeneration in the treatment of peri-implantitis. A histomorphometric study in dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2017, 28, 1388–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, T.M.; Choi, B.H.; Zhu, S.J.; Jung, J.H.; Lee, S.H.; Huh, J.Y.; Lee, H.J.; Li, J. Treatment of experimental peri-implantitis using autogenous bone grafts and platelet-enriched fibrin glue in dogs. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. Endod. 2007, 103, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, K.H.; Gwak, E.H.; Rhee, S.H.; Lee, J.C.; Shin, S.Y.; Koo, K.T.; Lee, Y.M.; Seol, Y.J. Ex vivo bone morphogenetic protein 2 gene delivery using periodontal ligament stem cells for enhanced re-osseointegration in the regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2015, 103, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibli, J.A.; Martins, M.C.; Nociti, F.H., Jr.; Garcia, V.G.; Marcantonio, E., Jr. Treatment of ligature-induced peri-implantitis by lethal photosensitization and guided bone regeneration: A preliminary histologic study in dogs. J. Periodontol. 2003, 74, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Machtei, E.E.; Kim, D.M.; Karimbux, N.; Zigdon-Giladi, H. The use of endothelial progenitor cells combined with barrier membrane for the reconstruction of peri-implant osseous defects: An animal experimental study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glossary of Periodontal Terms, 4th ed.; The American Academy of Periodontology: Chicago, IL, USA, 2001.
- Daugela, P.; Cicciù, M.; Saulacic, N. Surgical Regenerative Treatments for Peri-Implantitis: Meta-analysis of Recent Findings in a Systematic Literature Review. J. Oral Maxillofac. Res. 2016, 7, e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chan, H.L.; Lin, G.H.; Suarez, F.; MacEachern, M.; Wang, H.L. Surgical management of peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of treatment outcomes. J. Periodontol. 2014, 85, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aljohani, M.; Yong, S.L.; Bin Rahmah, A. The effect of surgical regenerative treatment for peri-implantitis: A systematic review. Saudi Dent. J. 2020, 32, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahrmann, P.; Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R. Regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis using bone substitutes and membrane: A systematic review. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2011, 13, 46–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Renvert, S.; Roos-Jansåker, A.M.; Persson, G.R. Surgical treatment of peri-implantitis lesions with or without the use of a bone substitute-a randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiltfang, J.; Zernial, O.; Behrens, E.; Schlegel, A.; Warnke, P.H.; Becker, S.T. Regenerative treatment of peri-implantitis bone defects with a combination of autologous bone and a demineralized xenogenic bone graft: A series of 36 defects. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2012, 14, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Froum, S.J.; Froum, S.H.; Rosen, P.S. Successful management of peri-implantitis with a regenerative approach: A consecutive series of 51 treated implants with 3- to 7.5-year follow-up. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2012, 32, 11–20. [Google Scholar]
- Haas, R.; Baron, M.; Dörtbudak, O.; Watzek, G. Lethal photosensitization, autogenous bone, and e-PTFE membrane for the treatment of peri-implantitis: Preliminary results. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2000, 15, 374–382. [Google Scholar]
- Behneke, A.; Behneke, N.; d’Hoedt, B. Treatment of peri-implantitis defects with autogenous bone grafts: Six-month to 3-year results of a prospective study in 17 patients. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac Implant. 2000, 15, 125–138. [Google Scholar]
- Shibli, J.A.; Martins, M.C.; Ribeiro, F.S.; Garcia, V.G.; Nociti, F.H., Jr.; Marcantonio, E., Jr. Lethal Photosensitization and Guided Bone Regeneration in Treatment of Peri-Implantitis: An Experimental Study in Dogs. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2006, 17, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.S.; Pabst, A.M.; Ackermann, M.; Moergel, M.; Jung, J.; Kasaj, A. Biofunctionalization of porcine-derived collagen matrix using enamel matrix derivative and platelet-rich fibrin: Influence on mature endothelial cell characteristics in vitro. Clin. Oral Investig. 2018, 22, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, L.G.; Araújo, M.G.; Berglundh, T.; Gröndahl, K.; Lindhe, J. Resolution of peri-implantitis following treatment. An experimental study in the dog. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1999, 10, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, A.; Wang, H.L.; Nart, J. Association of Preventive Maintenance Therapy Compliance and Peri-Implant Diseases: A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1030–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
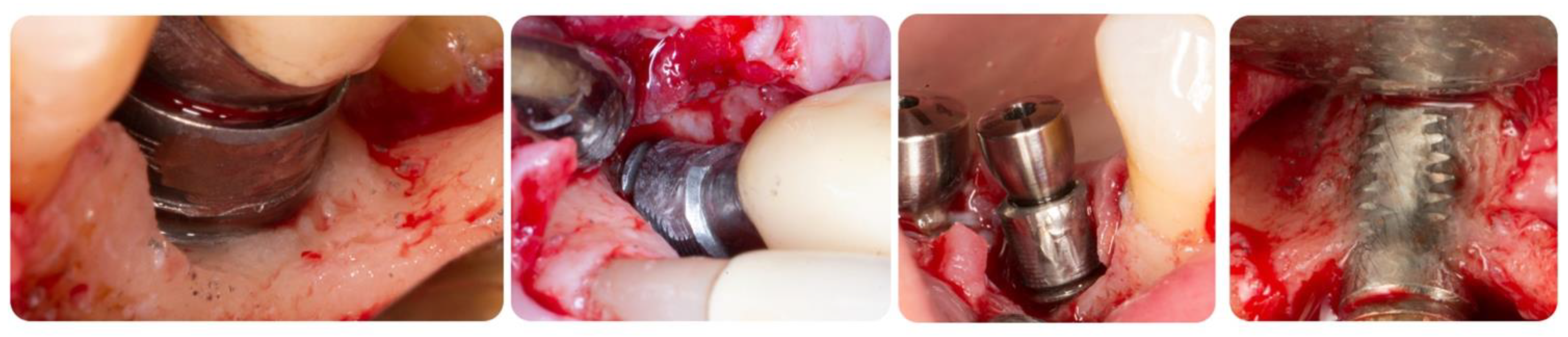

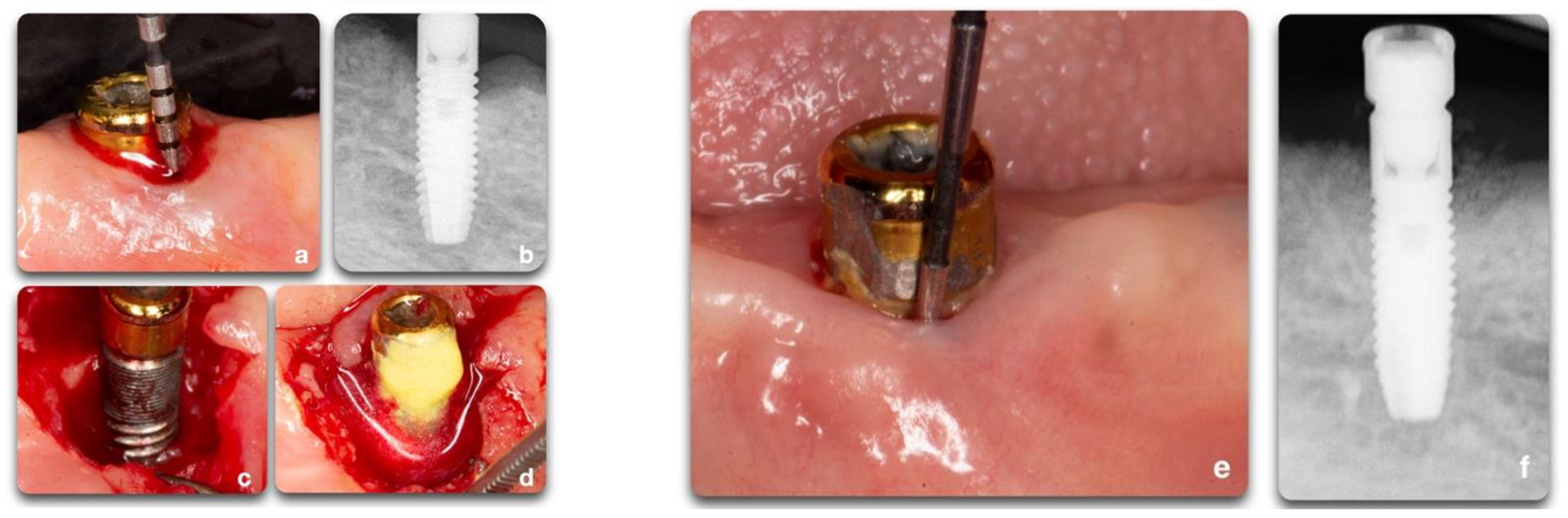
| Author | Pre-Surgical Therapy | Implant Decontamination | Grafting Material | Membrane | Healing | Systemic Antibiotics |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Roos-Jansaker et al. [49,50], 2007, 2014 | NR | T: H2O2 (3 min) | Algae-derived XENO | Resorbable synthetic membrane | NS | Amoxicillin 375 mg × 3/d + metronidazole 400 mg × 2/d, 10 d after the surgery |
| Aghazadeh et al., 2012 [25] | OHI | T & C: MD + H2O2 (1 min) | XENO | RM | NS | Post-operative ABX Azithromycin 2 × 250 mg 1/d, 1 × 250 mg 2–4/d |
| AB | ||||||
| Isehed et al., 2016 [41] | OHI | T: US + Ti Instruments + Cotton Gauze (NaCl) | EMD (0.3 mL) | No M | NS | No |
| C: US + Ti instruments + Cotton Gauze (NaCl) | OFS | |||||
| Schwartz et al., 2011, 2013, 2017 [47,48] | NST + OHI | T: Er:YAG Laser + IP | XENO | RM | NS | No |
| C: OFS + PC + Cotton Pellets & NaCl + IP | ||||||
| Roccuzzo et al., 2011, 2017 [29,40] | ID + OHI | T (SLA): PC + 24% EDTA + 1% CHX gel | XENO | No M | NS | 1g of Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid BID, 6 d |
| C (TPS): PC + 24% EDTA + 1% CHX Gel | ||||||
| Roccuzzo et al., 2016 [43] | OHI + SCRP (Teeth) + NC (Implant) | Ti Curettes + Ti Brush + 24% EDTA + 1% CHX Gel | XENO + 10% Collagen | If no KT: Tuberosity CTG | NS | 1 g of Amoxicillin + Clavulanic Acid × 2, 1 h before Surgery × 6 d |
| Nart et al., 2018 [46] | OHI + Supra- & Sub-GD (6 wk before Surgery) | SS Curette + IP + US Intrabony Debridement + 3% H2O2 (1 min) + NaCl | 50% Allograft & Vancomycin + 50% Allograft Tobramycin | RM | NS | No |
| Success of Peri-Implantitis Regenerative Treatments | ||
|---|---|---|
| Author | Success Definition | Success Outcome |
| Jepsen et al., 2016 [42] | PD ≤ 4 mm, no BOP at 6 implant sites, no further BL | 30% of implants |
| Schwarz et al., 2017 [45] | No BOP | Test: 4/6 patients Control: 5/9 patients Total: 9/15 patients (60%) |
| Roccuzzo et al., 2017 [29] | PD < 5 mm, no BOP or SUP, no further BL | Test: 7/12 (58.3%) implants Control: 2/14 (14.3%) implants |
| Aghazadeh et al., 2012 [25] | PD ≤ 5 mm, max 1 site with BOP, no SUP, no BL PD ≤ 5 mm, no BOP, no SUP, no BL | Test: 38.5% implants Control: 13.9% implants Test: 8 implants (20.5%) Control: 4 implants (11.1%) |
| Roos-Jansaker et al., 2014 [49] | RF ≥ 25%, independent of PD or BOP; RF ≥ 25%, PD ≤ 5 mm, independent of BOP RF ≥ 25%, PD ≤ 5 mm, BOP ≤ 1 | 66.7% (30/45) implants 62.2% (28/45) implants 51.1% (23/45) implants |
| Renvert et al., 2018 [64] | DF ≥ 1.0 mm, PD ≤ 5 mm, no BOP, no SUP | Control: 1/20 (5.0%) Test: 9/21 (42.9%) |
| Authors | Study | Pt | % Success Outcome | % Sites BoP | 12 m Mean PD | Baseline PD | Bone Change (Radiographic) | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haas 2000 [67] | Clinical study | 17 (24 im) | - | - | - | - | 2 ± 1.9 mm (36.4%) (9.5 m) |
|
| Bennhke 2000 [68] | Prospective (AB graft) | 17 (25 im) | - | - | 3.3 mm (median reduction 3 y) | - |
| im lost in 6 patients |
| Roos-Jaskaren et al., 2007 [50] | Comparative trial: bone + membrane | 17 | 93 im | 22 | 2.5 mm | 5.4 mm |
2 im lost, 1 thread bone | - |
| Bone | 19 | 89 im | 25 | 2.2 mm | 5.6 mm |
1 im lost 2 threads, 3 im lost 1 thread | - | |
| Roccuzzo 2011 | Case series | 26 | 85 Pt | 36 | 4.3 mm | 7.0 mm | 1.7 mm mean bone gain (12 m) | 4 Pt with TPS-im SUP |
| Wiltfang 2010 | Case series | 22 | 75 im | 25 | 3.5 mm | 7.5 mm | 3.5 mm mean bone gain (12 m) | SUP 8% im, 1 patient lost 1 implant |
| Froum et al., 2012 [66] | Case series | 38 | 84 Pt | 18 | 3.0 mm * | 8.3 mm * | 3.4 mm mean bone gain (12 m) | 6 Pt required 2–3 surgeries no im lost bone |
| Nart et al., 2018 [46] | Case series | 13 | - | 70.6 | 4.23 ± 1.62 mm (mean reduction) | 7.88 ± 1.22 mm | Intrabony defect: T0 (mm): 4.33 ± 1.62 mm, after 12 m: 0.56 ± 0.88 mm Bone defect fill: 86.99 ± 18.2% | - |
| Renvert et al., 2018 [21] | RCT; surgical debridement | 20 | 5.0 | 65 Control | 3.9 | 6.0 | 0.2 mm (12 m) | 32.8% risk reduction in benefit of test |
| Surgical debridement + bone substitute | 21 | 42.9 | 52.4 Test | 2.6 | 6.6 | 0.7 mm (12 m) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mordini, L.; Sun, N.; Chang, N.; De Guzman, J.-P.; Generali, L.; Consolo, U. Peri-Implantitis Regenerative Therapy: A Review. Biology 2021, 10, 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080773
Mordini L, Sun N, Chang N, De Guzman J-P, Generali L, Consolo U. Peri-Implantitis Regenerative Therapy: A Review. Biology. 2021; 10(8):773. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080773
Chicago/Turabian StyleMordini, Lorenzo, Ningyuan Sun, Naiwen Chang, John-Paul De Guzman, Luigi Generali, and Ugo Consolo. 2021. "Peri-Implantitis Regenerative Therapy: A Review" Biology 10, no. 8: 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080773
APA StyleMordini, L., Sun, N., Chang, N., De Guzman, J.-P., Generali, L., & Consolo, U. (2021). Peri-Implantitis Regenerative Therapy: A Review. Biology, 10(8), 773. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10080773