Simple Summary
Soil quality and fertility rely on soil microorganisms which contribute to nutrient cycling and plant nutrition. Accidental or intentional fires can almost completely kill soil microbiota and cause soil sterilization. Fires can also destroy soil organic matter (OM), thus causing the release of potentially toxic elements such as Cr that can further disturb soil recolonization by surviving bacteria. The identification of species able to cope with such altered environments is highly relevant to restore soil life in degraded soils and to remediate polluted sites. In this study, we identified soil microorganisms potentially suitable to colonize fire-affected areas and tolerate high concentrations of bioavailable and toxic Cr, and which therefore could be useful for the above-mentioned purposes.
Abstract
Fire events in agricultural soils can modify not only soil properties but also the structure of soil microbial communities, especially in soils containing high concentrations of potentially toxic elements (PTEs). The recolonization of burned soils can in fact favor the proliferation of certain microorganisms, more adaptable to post-fire soil conditions and higher PTE availability, over others. In this study, we simulated with laboratory experiments the microbial recolonization of an agricultural soil containing high Cr concentrations after heating at 500 °C for 30 min, to mimic the burning of crop residues. Changes in soil properties and Cr speciation were assessed, as well as soil microbial structure by means of 16S rRNA gene sequencing. Both altered soil conditions and increased Cr availability, especially Cr(VI), appeared to be responsible for the reduction in species diversity in heated soils and the proliferation of Firmicutes. Indeed, already after 3 days from the heat treatment, Firmicutes increased from 14% to 60% relative abundance. In particular, Paenibacillus was the most abundant genus identified after the simulation, with an average relative abundance of 40%. These bacteria are known to be good fire-responders and Cr-tolerant. These results could be useful to identify bacterial strains to be used as bioindicators of altered environments and for the recovery of fire-impacted polluted sites.
1. Introduction
Fires affect large areas of land around the world, causing a temporary and localized increase in soil temperatures, often of high magnitude [1]. In the last few decades, uncontrolled fires are becoming increasingly frequent as a consequence of global warming or, in some other cases, of biomass and waste burning on the soil [2]. Additionally, controlled fires are widely used in many common agricultural practices including slash-and-burn farming, land clearing and post-harvest stubble management [3].
High temperatures occurring during (and immediately after) fire events can cause significant changes in soil properties and element biogeochemistry [4]. In particular, the effects of fire on soil properties as well as the short and/or long-term impacts on chemical and microbiological characteristics are strictly related to fire intensity and residence time, which depend on several environmental factors such as fuel distribution, soil mineral composition, climatic conditions, etc. Fire typically increases soil pH and electrical conductivity (EC), reduces the soil organic matter (OM) content, thus altering nutrient cycling (especially P and N cycles), and decreases soil permeability and porosity [4,5].
Fire can also affect the mobility and bioavailability of potentially toxic elements (PTEs), most often as a consequence of changes in soil properties (e.g., OM decomposition and mineral weathering) [6]. In agricultural soils, PTEs’ release and mobilization could represent a potential risk for crop production and consequently for human health [6]. Such a risk is higher for elements such as chromium (Cr), which, depending on the soil redox conditions and the availability of OM, can modify its oxidation state, forming highly mobile and toxic hexavalent species (Cr(VI)) [7].
Soil biological properties have been reported to significantly change after fires as well, since fires can impact (either directly or indirectly) both the composition and the activity of soil microbial communities. Microbial communities can be profoundly altered in the short term through selective heat-induced microbial mortality, whereas medium- and long-term responses are strictly related to indirect effects concerning the changes in the abiotic environment [8,9] and the consequent recolonization by different microbial groups; in fact, several studies have reported that some microbial groups may take advantage of fire-altered conditions, while others may be adversely affected [10].
Firmicutes phylum, for example, was found to be a positive fire-responder, becoming predominant in post-fire soils characterized by low organic carbon content. In the same way, an increase in other fire-responder taxa, such as the spore-forming Actinobacteria and the akinetes producing Cyanobacteria, was observed in different studies [11,12,13]. Some of the strongest fire-responder taxa have also been identified as highly PTE-resistant, such as those belonging to bacterial phyla of Proteobacteria (e.g., genera Burkholderia, Pseudomonas, Shewanella and Agrobacterium), Firmicutes (e.g., genera Serratia, Bacillus and Exiguobacterium), and Actinobacteria (e.g., genera Arthrobacter) [13].
Most of the studies on the effect of fire on soil’s physico-chemical and microbiological properties have been carried out in forest environments, where these events are more frequent and of higher intensity, while limited information on agricultural soils is available [6]. The soil microbiota plays a key role both in nutrient and PTE cycling in the rhizosphere, with relevant implications for crop productivity and production quality [13]. Fire can induce a positive or negative selective pressure on specific microbial taxa, with consequences not only on plant fitness but also on the soil’s capacity to restore its pre-fire properties [4]. Therefore, it is crucial to assess how fire can shape the composition and functioning of soil microbial communities in agricultural soils, especially in the presence of high concentrations of PTEs.
In this work, 16S rRNA gene sequencing was used for probing the possible changes in bacterial community structure as affected by laboratory-simulated fire events in an agricultural soil containing a high concentration of Cr. We hypothesize that the soil bacterial community diversity and structure change as a consequence of both altered post-fire chemical soil properties and modified speciation and availability of Cr.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Site Description
The experiment was conducted in a monoculture of durum wheat (Triticum durum Desf.) field in the south of Italy (Apulia Region) near the town of Altamura (Figure 1), amended for more than 10 years by low-quality compost derived from tannery waste sludges, as described by Gattullo et al. (2020) [14]. The soils in this area are classified as Calcaric Leptosols, according to WRB classification [15].
Figure 1.
Location of the sampling site with geographic coordinates.
As reported by Gattullo et al. (2020) [14], Cr was the most abundant PTE in the soil, with concentrations up to 5160 g kg−1. Anyway, the high OM content (about 220 g kg−1) formed strong complexes with Cr and other PTEs, thus immobilizing them and making them not available for plant uptake, and not affecting wheat production [16]. Additionally, the high OM content of soil hindered Cr oxidation; therefore, Cr was present only in the reduced and less mobile form (Cr(III)) [14].
2.2. Soil Sampling and Characterization
Three soil sub-samples were collected at 0–10 cm depth in an area of approximately 4 m2 and were carefully homogenized. A portion of soil was immediately stored at 4 °C for the subsequent microbial extraction, while the remaining part was air-dried, sieved at 2 mm, and then characterized for pH, EC, organic C content, total N content, available P, total CaCO3 and exchangeable bases, following the standard methodologies of soil analysis [17]. The total PTE content was determined by ED-XRF (NITON XL3t GOLDD with laboratory stand, Thermo Scientific) following the procedure reported in Gattullo et al. (2020) [14]. Chromium(VI) was determined after the alkaline digestion of soil samples [18], while the exchangeable Cr(VI) was extracted by shaking the soils for 30 min with a 5 mM K2HPO4/KH2PO4 buffer solution (pH 7.2) at a ratio of 1:4 (soil: buffer solution, w/v), as reported in Bartlett and James, 1996 [19]. The Cr(VI) estimation in both extracts (total Cr(VI) and exchangeable Cr(VI)) was performed by the colorimetric assay with diphenylcarbazide [20]. The detection limit of the assay is 0.0052 mg L−1 [19], corresponding to about 0.2 μg Cr(VI) g−1 of dry soil for the total Cr(VI), and 0.02 μg Cr(VI) g−1 of dry soil for the exchangeable Cr(VI).
PTE plant-available fraction (DTPA-extracts) was also determined by extracting the soil sample with a diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) solution (0.005 M DTPA, 0.01 M CaCl2, 0.1 M triethanolamine, pH = 7.3) [21] and analyzing the extracts by ICP-OES (Thermo iCAP 6000 series, Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc., Waltham, MA, USA).
2.3. Soil Thermal Treatment
Fire was simulated in the laboratory by heating the soil in a muffle furnace (Nabertherm, B180). Muffle furnace heating is one of the most common strategies to simulate fire events in the lab, as reported by Pereira et al. (2019) [22]. Two hundred grams of soil was placed in a 20 cm diameter ceramic crucible, creating a soil layer of about 0.7 cm thickness to allow a homogeneous heat transfer through the sample. Soil was heated up to 500 °C for 30 min. Such a temperature was selected after performing preliminary thermogravimetric analyses (not reported) showing that at 500 °C almost all the soil OM was lost [4]. Heating time was selected according to studies on agricultural soils where such high temperatures were recorded for about 30 min after burning crop residues on soil [23]. Three replicates were set up and, for each of them, soil characterization was carried out as described in Section 2.2.
2.4. Extraction of Bacterial Communities and Soil Inoculation
About 100 g of unheated soil was weighed and homogenized in 900 mL 25% sterile Ringer solution and 100 mL sodium pyrophosphate (Na4P2O7 1,8%). Ringer solution was prepared by solubilizing in deionized water NaCl (0.225% w/v), KCl (0.0105 % w/v), CaCl2 (0.0045% w/v), NaHCO3 (0.005% w/v) and citric acid (0.0034% w/v) at pH = 7.0 ± 0.2 [24]. The solution was autoclaved for 15 min at 121 °C before use. Microbial community desorption from soil particles was performed by sonication for 2 min and subsequent storage at 4 °C for 15 min to let soil particles sediment. Serial dilutions (10−4, 10−5 and 10−6) of the aqueous phase were performed and poured on nutrient agar plates after addition of cycloheximide (1% w/v) to determine the number of CFU. The plates were then incubated at 30 °C for 48 h. Since after 48 h the number of grown colonies for each plated dilution was very low, about 80 mL of 10−1 dilution was used for the inoculation of 100 g aliquots of the 500 °C heated soil sample. Each aliquot was then incubated in sterile glass flasks closed with a screw cap, and kept for 3, 7 and 14 days (T3, T7 and T14) in a growth chamber at 23 °C. For each incubation time, three experimental replicates were set up. Inoculation of bacterial community extracted from untreated soil was performed to simulate a recolonization of the soil after burning, since heating treatment at 500 °C causes soil sterilization.
2.5. Soil DNA Extraction, 16S rRNA Sequencing and Bioinformatics Analysis
Soil DNA was extracted from 0.5 g of both unheated soil (Control) and 500 °C-heated and inoculated soil aliquots (T3, T7 and T14) by using the soil DNA extraction kit (MP Biomedicals™ FastDNA™ SPIN Kit) and following the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and concentration of the extracted DNA were verified with the NanoDrop spectrophotometer (ND-1000, EuroClone, Italy). The DNA was then concentrated up to 20 ng µL−1 by SpeedVac concentrator (Savant DNA120, ThermoScientific) and stored at −20 °C prior to the sequencing procedure. Universal primers: 341F (5′–CCTACGGGNGGCWGCAG–3′) and 805R (5′–GACTACHVGGGTATCTAATCC–3′), based on the V3 and V4 hypervariable region of the 16S rRNA, were used for the detection of Bacteria, and the sequencing procedure was performed by using an Illumina MiSeq next-generation sequencer (Illumina, San Diego, CA, USA). The sequencing was carried out at the IGA Technology Service (Udine, Italy) (https://igatechnology.com, accessed 7 January 2020).
Raw reads produced by Illumina sequencing were processed using the Metagenomic Rast Server (MG-RAST) (http://metagenomics.anl.gov, accessed on 23 April 2020) [25]. Raw data were uploaded as FASTQ files and subjected to quality control, which includes the removal of artificial duplicate reads, quality-based read trimming, and length-based read trimming. The sequences were then clustered into operational taxonomical units (OTUs) at 97% similarity and then subjected to taxonomic assignment using the Ribosomal Database Project (RDP) Naïve Bayesian classifier.
Sequence data were deposited at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) and available under the SRA accession: PRJNA723052.
Relative abundances of each taxon were calculated as a percentage of the total number of sequences for each sample; only the relative abundances greater than 1% are shown in the text.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
The α-diversity indices were statistically analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), and means were compared by the Student–Newman–Keul (SNK) test at p ≤ 0.05 using the SPSS package (SPSS Inc., v.24, Chicago, IL, USA).
The Bray–Curtis dissimilarity matrix was used for the analysis of similarity (ANOSIM) to highlight the differences among bacterial composition in the investigated soils.
The β-diversity was evaluated by Principal Coordinate Analysis (PCoA) to compare and plot the structure of all samples. Moreover, Canonical Correspondence Analysis (CCA) was used to relate the relative abundances of the phyla (>1%) to some selected environmental variables in a two-dimension graphic. Finally, SIMilarity PERcentage (SIMPER) analysis was carried out to identify the OTUs responsible for the differences between T3, T7 and T14 samples. Multivariate statistical approach (ANOSIM, PCoA, CCA and SIMPER) and Ward’s clustering method were performed using PAST 3.17 software.
3. Results
3.1. Soil Chemical Characterization
Soil chemical analyses, performed both on unburned soil and 500 °C thermally treated soil, revealed that the heating treatment significantly altered the soil chemical properties (Table 1).

Table 1.
Chemical properties and potentially toxic element (PTE) concentrations in the unheated and heated soils (mean value ± standard deviation, n = 3). Only one determination was performed for the basic chemical properties of the unheated soil, being a composite sample.
After the thermal treatment, pH and even more EC increased compared to untreated soil. The organic C content was strongly reduced and, consequently, the value of OM content decreased from 234 g kg−1 in unburned soil to 24 g kg−1 in burned soil. The heating treatment also reduced the total N content by about 80%, while it increased the available P by more than twice and total carbonates by 18%. The concentrations of exchangeable base cations in the unburned soil followed the sequence Ca2+ > K+ > Mg2+ > Na+, while after the 500 °C thermal treatment they followed the sequence Ca2+ > Mg2+ > K+ > Na+. In particular, K+ and Ca2+ concentrations decreased in the heated soil.
The total concentrations of Cu, Pb, Zn and Cr increased after the thermal treatment by 50%, 55%, 44% and 11%, respectively. Total PTE concentration increased as a consequence of OM loss. Available Pb and Cu remained almost similar after the thermal treatment, while potentially available Zn decreased and available Cr dramatically increased. In addition, the concentration of Cr(VI), which is the most mobile and toxic form of Cr, changed from undetectable values in the untreated soil to 152 mg kg−1 in the heated soil. Moreover, about 22% of Cr(VI) was exchangeable, thus potentially available for plants and microorganisms. The soil chemical properties of burned soil did not change during the different incubation times (3, 7 and 14 days), as expected (data not shown).
3.2. Soil Bacterial Communities and Correlation with Physico-Chemical Soil Properties
Illumina sequencing produced a total of 1,144,661 raw reads, reduced to 953,904 reads after quality control. The rarefaction curves (Figure 2), drawn by plotting the number of sequences and the OTUs associated with each sample, showed that the coverage of sequencing was reasonable. Nevertheless, considering the different size of sequences among samples, a reduced dataset was built by randomly selecting 52,517 sequences for each sample, corresponding to the lowest number of sequences obtained in the sample T3_c.
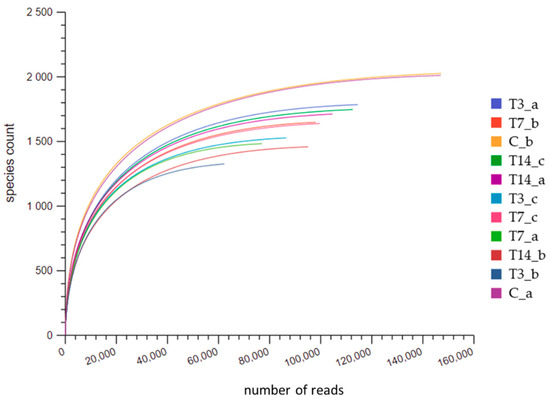
Figure 2.
Rarefaction curves relative to the number of sequences and OTUs associated with each soil sample. C are the control unheated samples; T3, T7, T14 are the thermally treated samples after 3, 7 and 14 days of incubation, respectively; a, b, c are the replicates.
The C_a and C_b samples (two replicates of the control unheated sample) had the highest number of sequences, compared to T3, T7 and T14 samples.
Consequently, the α-diversity indices (Shannon, Simpson 1-D, Evenness) (Table 2) were calculated for all the samples under investigation on the normalized dataset. The highest number of OTUs, as well as the highest values of Shannon and Evenness indices, were observed in the control sample, thus pointing out a significant difference compared to T3, T7 and T14 samples.

Table 2.
Species richness and diversity indices of bacterial communities of control (C), T3, T7 and T14 soil samples.
The taxonomic composition showed that the identified sequences were related to 25 phyla, 49 classes, 109 orders, 253 families, 793 genera and 3058 species within all the samples under investigation (C, T3, T7 and T14).
Eight phyla were considered as the most abundant, represented by more than 1% of bacterial total sequences: Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Chloroflexi, Firmicutes, Gemmatimonadetes, Planctomycetes, Proteobacteria, Verrucomicrobia, and unclassified bacteria (Figure 3).
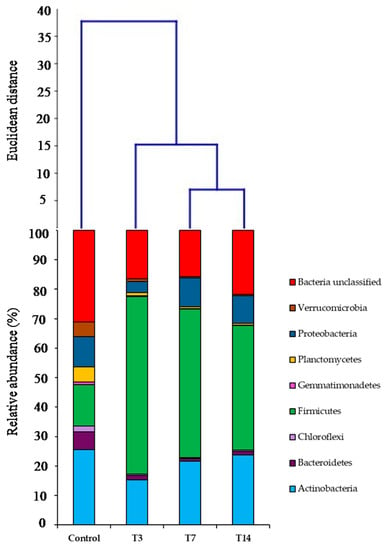
Figure 3.
Relative abundances of the dominant bacterial phyla (>1%) and cluster analysis of control, T3, T7 and T14 samples using Ward’s method.
The analysis of the taxonomic profile revealed a significant difference among the soils under investigation (Figure 3), which was considerably evident already at the phylum level. The difference among all the samples was confirmed by the ANOSIM global test of the relative abundances, by comparing group similarities (R = 0.61 and p = 0.0012). Additionally, the pairwise comparison highlighted that the control sample (C) was very different compared to T3, T7 and T14 samples (R = 1 for C vs. T3, T7, T14, each); on the other hand, no significant differences among T3, T7 and T14 samples (R = −0.03 for T3 vs. T7; R = 0.70 for T3 vs. T14; R = 0.14 for T7 vs. T14) have emerged.
Firmicutes relative abundance increased up to 60% after 3 days of incubation (T3), whereas it represented only 14% of the total sequences in the control. Moreover, Firmicutes relative abundance slightly decreased 7 and 14 days after inoculation down to percentages of 50% and 42%, respectively. On the other hand, Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria relative abundances decreased after 3 days of incubation, compared to the control, while after 7 and 14 days from the inoculation they increased, reaching approximately the initial values (about 25% for Actinobacteria and 10% for Proteobacteria). A low percentage of the sequences of the control was associated with Bacterioidetes, Planctomycetes, Verrucomicrobia, Chloroflexi, and Gemmatimonadetes; these phyla rapidly and strongly decreased after 3 days of incubation (T3) and continued to decrease after 14 days (T14), when they showed relative abundances of 1%, 0.5%, 0.4% (both Verrucomicrobia and Chloroflexi) and 0.1%, respectively. Euclidean distances among the control, T3, T7 and T14 soil samples were computed using Ward’s clustering algorithm. In this regard, treatments clustered into different groups in terms of bacterial communities at the phylum level (relative abundance > 1%), in which T3 treatment has less distance to the control compared to T7 and T14 treatments (Figure 3).
PCoA better illustrates the differences between the structure of bacterial communities associated with the control (C), T3, T7 and T14 soil samples (Figure 4). The two-dimensional plot revealed a clear segregation of C from T3, T7 and T14 samples. The first axis, accounting for about 77% of the variance, highlighted the differences between the T3, T7 and T14 and the control soil. The second axis (~14%) separated C from T14 well.
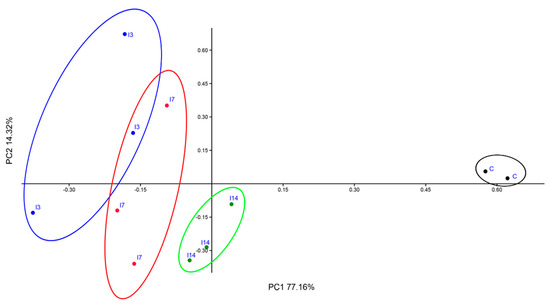
Figure 4.
PCoA plot of control (C), T3, T7 and T14 soil bacterial communities.
Canonical correspondence analysis (CCA) aimed at explaining the relationships between the most abundant phyla (relative abundance ≥ 1%) and selected environmental variables (soil parameters) of the T3, T7 and T14 samples. The selected soil parameters were: pH, EC, base cations, organic C, total N, available P, total Cr, DTPA-extractable Cr, total Cr(VI), and exchangeable Cr(VI). Most of the total variance (95%) was accounted by seven axes and explained by the first two components (Figure 5). The first axis, accounting for about 75% of variance, clearly discriminated T3 from T7 and T14. A further division within these three main clusters accounted for about 20% of variance by the second axis.
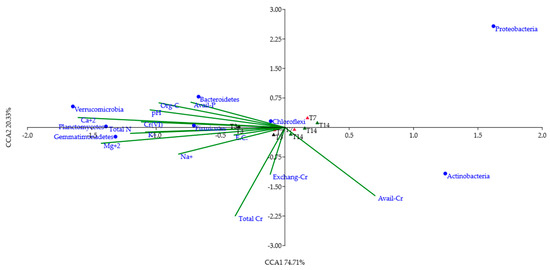
Figure 5.
CCA biplot showing the relationships between the most abundant phyla (>1%) and selected chemical properties of T3, T7 and T14 samples.
With the exception of Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria, all other phyla were strictly correlated to most of the considered environmental parameters, Cr(VI) included. According to CCA (Figure 5), Firmicutes was highly related to Cr(VI) content and other soil chemical properties such as pH, organic C, total N, available P, Ca2+. On the other hand, Bacteroidetes, Verrucomicrobia, Gemmatimonadetes, Chloroflexi and Planctomycetes were less influenced by these soil properties, while Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria were not influenced by any variable. Looking at the soil microbiota at the three different times of incubation, T3 samples appeared related to Cr(VI) concentration, soil pH, organic C, total N, available P, Ca2+, Mg2+ and K+, whereas T7 and T14 samples were mainly related to total Cr, available Cr and exchangeable Cr(VI).
The SIMPER analysis (Table 3) on the relative abundance of OTUs (genus level) revealed that OTUs belonging to Firmicutes, Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria phyla were those mainly responsible for differences between T3, T7 and T14. Particularly, OTU belonging to Paenibacillus genus contributed to ~40% of differences.

Table 3.
Similarity percentage analysis (SIMPER) showing (i) the relative abundance of each identified genus and the corresponding phylum, (ii) the contribution to the total diversity and, (iii) the cumulative contribution to the average similarity. Contributions below 3% are not shown.
4. Discussion
Chemical analyses performed on both unheated and heated soil revealed that heating treatment significantly altered most of the soil properties (Table 1). The increase in pH observed in burned soil was ascribable to the loss of organic acids, the release of oxides, hydroxides, carbonates and cations through ash particles, and the displacement of H+ from the exchange sites of clay minerals [26,27]. The soil EC considerably increased after heating because of the release of soluble inorganic ions deriving mainly from the combustion of OM, but also from the exchange complexes [28]. The increase in soil salinity can enhance the PTEs’ mobility due to the competition between salt-derived ions and PTE ions for the adsorption sites, as well as to PTE complexation by salt-derived anions [29]. The organic C content, as well as the total N concentration, decreased after thermal treatment by about 90% and 80%, respectively. This was due to the mineralization of the OM, which is almost total at 460 °C [30]. Furthermore, the OM combustion released inorganic P, as proved by the doubling of the available P concentration in heated soil compared to unheated soil. All these modifications reveal the positive effects of fire in regard to the nutrient release, at least in the short term (14 days).
The PTE total concentrations after the thermal treatment increased by a minimum of 11% (for Cr) to a maximum of 55% (for Pb). However, the hazardousness of PTEs is correlated more to their mobility and bioavailability, rather than to their total concentrations. Therefore, the quantification of the PTE plant-available fraction (estimated through DTPA-extraction) is a better index of potential risk for microorganisms and crops and, via the food chain, for human health. Zinc DTPA-extractable fraction decreased after the thermal treatment, Cu and Pb remained almost unchanged, while the DTPA-extractable fraction of Cr increased from 0.3 to 105 mg kg−1. Indeed, in the unheated soil, Cr was almost completely immobilized by OM, as reported by Gattullo et al. (2020) [14]. After soil burning, part of the Cr complexed or entrapped by OM was released, thus explaining the sharp increase in its available fraction. Another dangerous transformation caused by fire in soil was the oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI), in agreement with other pieces of evidence reported in the literature [7,31]. As suggested by Panichev et al. (2008) [7], Cr oxidation might have been favored by the presence of carbonates released by fuel combustion. In the soil under investigation, the concentration of total carbonates was very high already before the fire, then it further increased after the laboratory fire simulation (Table 1). Additionally, Fe and Mn oxyhydroxides’ transformation might have also contributed to the Cr oxidation process [31]. The Cr (VI) concentration after the thermal treatment was 152 mg kg−1, a level considerably higher than the safety threshold established for agricultural sites in Italy (2 mg kg−1; Italian Legislative Decree n. 152/2006) [32]. About 20% of the total concentration of Cr(VI) was exchangeable and therefore potentially available for plant and microbe uptake.
The soil chemical properties did not change during the incubation period after bacteria inoculation (data not shown), in agreement with evidence reported in the literature. Indeed, the restoration of physico-chemical soil characteristics after a fire requires from a few months to several years, at least in an open system [4,11,33]. In the present study, the soil was incubated for 14 days in a closed system, thus the occurrence of chemical modifications was scarcely probable.
Heat can directly affect the survival and the recolonization of soil microbial communities since the temperatures occurring during a fire event often considerably exceed those for killing most of the living organisms [4]. Previous field-scale experiments have revealed that high temperatures (≥500 °C), reached during high-severity fires, are generally restricted to a soil depth of no more than 1 cm, with a residence time from some minutes up to several hours, depending on fuel density and distribution [4,13,34]. Fires are often extremely heterogeneous, depending on localized fuel loads and wind strength and direction, which result in large patches of unburned and moderately burned areas. Consequently, the microbial recolonization processes are generally driven by the bacterial communities of the unburned areas or of the deeper horizons/layers, in the case of post-fire plowing [35].
Indirect effects on microbial phylogenetic and taxonomic composition are related to different soil properties such as soil moisture, quantity and quality of organic carbon and nutrient cycling [9,36,37]. Moreover, fire severity could lead to different recolonization pathways, thus favoring the growth of some bacterial taxa rather than others. Among the factors influencing the bacterial recolonization processes, PTEs’ concentration and speciation can also play a crucial role in selecting specific taxa able to survive and promote environmental restoration.
Alpha diversity indices (i.e., species richness and evenness within a sample) are generally related to the ecosystem stability and functionality [38]; in particular, the Simpson 1-D index is weighted towards the abundances of the most common species, whereas the Shannon index is more influenced by species richness [39]. In the present study, the total species richness was significantly altered by post-fire changes in the abiotic environment. The higher diversity was found in the control (microbiota extracted from the unheated soil) compared to T3, T7 and T14 samples (microbiota extracted from heated soil inoculated and incubated for 3, 7 and 14 days) (Table 2). The reduction in diversity in T3, T7 and T14 samples was probably due to some taxa’s inability to physiologically cope with abiotic stressors. In T3, T7 and T14 samples, in fact, the combination of high Cr(VI) content (152 mg kg−1, with about 20% in the exchangeable form) and fire-altered soil chemical properties probably induced a negative selective pressure on a number of taxa, thus reducing the microbial diversity. This evidence matched with the findings reported in other studies, where both the contribution of wildfires and soil pollution on bacterial group selection are widely discussed [12,13,38,40].
Cluster analysis showed more shifts in the structure of bacterial communities in T7 and T14 treatments than in T3 samples, indicating that they were more sensitive to these variations. In this regard, taxonomic composition revealed a significant shift from Actinobacteria in the control to Firmicutes in T3, T7 and T14 samples (Figure 3). However, Actinobacteria relative abundances increased again after 14 days of incubation. A similar trend was observed for Proteobacteria. The shift at phylum-level suggests that Firmicutes can immediately (after 3 days incubation) deal with post-fire changes, including Cr oxidation and increasing bioavailability, as well as alterations in soil chemical properties (i.e., pH, EC, organic C, total N, available P, etc.). Indeed, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria and Proteobacteria were detected in different investigations where both PTE pollution and wildfire severity were considered as drivers of soil microbial diversity [12]. Miranda et al. (2018) [40] focused on responses of soil microbial communities after the application of tannery sludge for seven years. They found that Cr content in association with increased pH and organic C were the key variables that influenced the soil microbial structure. In particular, the amendment of soil with 10 and 20 Mg ha−1 of composted tannery sludge promoted a shift in bacterial community composition compared to the control unamended soil. The analysis of sequences revealed that Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria and Firmicutes were the most abundant phyla in amended soils, suggesting that these bacterial groups have a great tolerance to altered soil conditions and Cr contamination [40]. Noteworthy, it should be remembered that Firmicutes and Actinobacteria include endospore-forming bacteria, which are able to survive under environmental stresses. These groups were also found in different studies focusing on high-severity fire occurrence [13], thus confirming their ability to survive and colonize extremely altered environments.
The Planctomycetes, Chloroflexi and Verrucomicrobia relative abundances decreased after 3, 7 and 14 days of incubation compared to the control. In accordance with Miranda et al. (2018) [40], Planctomycetes relative abundance probably decreased as a consequence of the increase in soil pH and total Cr concentration, whereas the decrease in Chloroflexi and Verrucomicrobia was probably due to the selected temperature (500 °C) and residence time (30 min), as these parameters are generally ascribed to high-severity fires [12].
All the above-discussed results were supported by the PCoA plot showing a clear separation between the bacterial communities of the control and those of T3, T7 and T14 samples (Figure 4). Furthermore, CCA (Figure 5) showed the associations between the most abundant phyla (with relative abundances > 1%) detected in T3, T7 and T14 samples and the chemical variables which were considered relevant for taxa selection.
At first glance, a correlation between T3 samples, Cr(VI) content and some of the main soil chemical parameters (pH, EC, organic C, available P, total N and base cations) was observed. This could be explained by considering that 3 days after the microbial inoculation, bacterial groups, able to grow in extreme environmental conditions, started to colonize the heated soil. Generally, as reported by Saenz de Miera et al. (2020) [12], taxa with oligotrophic strategies as well as spore-forming species are good fire-responders. Among these taxa, Firmicutes are spore-forming bacteria and have been noted to grow after high-severity fire disturbance [13]. These findings confirm the idea that nutrient deficiencies and low organic C content in soil lead to an increase in the relative abundance of oligotrophs. Previous studies have revealed that, in the case of environmental stress due to and/or resulting in low-resource concentrations in soils, the oligotrophs prevail over the copiotrophs [41,42]. Wang et al. (2019) [43] and Yaghoubi et al. (2020) [44] also reported a negative relationship between the relative abundance of oligotrophic taxa and C substrates in soil. The Firmicutes phylum was also identified as PTE-resistant; in particular, total Cr concentration has been shown to affect the relative abundances of different genera belonging to Firmicutes [40]. A positive correlation among some altered soil chemical properties, Cr(VI) and Firmicutes was also evident in CCA (Figure 5), especially in T3 soil, and is in line with the above-mentioned studies.
The CCA (Figure 5) evidenced that after 7 and 14 days of incubation, soil samples are more influenced by the total Cr content, the exchangeable Cr(VI) (Exchang-Cr) and the DTPA-extractable Cr (Avail-Cr). The differences observed in CCA among the T3, T7 and T14 soil samples suggest that, after 14 days of incubation, the highly PTE-tolerant microbial groups colonizing the soil samples may have promoted the soil recovery to pre-fire conditions.
Bacteroidetes, Verrucomicrobia, Gemmatimonadetes and Chloroflexi were less influenced by the selected chemical variables, while Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria were not influenced by such environmental parameters. In this regard, no matches were found in literature studies. Finally, the SIMPER analysis (Table 3) identified the genus Paenibacillus, belonging to the phylum Firmicutes, as the main factor responsible for the dissimilarity between T3, T7 and T14. In particular, Paenibacillus contributed to the community dissimilarity with a percentage of about 40%. This result is in line with the work of Miranda et al. (2018) [40], as Paenibacillus was found to be highly resistant to high Cr concentrations and is considered a good bioindicator of Cr pollution.
5. Conclusions
In this work, a laboratory-scale approach was used to study the effects of high temperatures on the chemical and microbiological properties of a Cr-polluted agricultural soil.
Despite the high Cr total concentration, previous studies [12,13,45,46] have shown limited environmental risks in the investigated soils because of the huge OM content that does not allow Cr mobilization and the oxidation of Cr(III) to more toxic Cr(VI). Fire occurrence (accidental or intentional) might pose a serious risk for the environment and human health since high temperatures could cause OM depletion, leading to Cr(III) oxidation and mobilization. Such remobilization could negatively affect not only crops but also soil microorganisms and therefore soil quality.
Heating treatment considerably altered soil physico-chemical properties (pH, EC, total N, organic C, available P, base cations) and changed Cr speciation into more mobile and potentially available chemical forms, including the formation of significant amounts of Cr(VI), as well as a different colonization capacity of microbial communities. Soil microbial analyses revealed, in fact, a predominance of Firmicutes (Paenibacillus genus) in response to altered soil conditions. Specifically, 3, 7 and 14 days after the inoculation of autochthonous bacterial communities, Firmicutes relative abundances were about 60%, 50% and 42%, respectively. This phylum is known to include good fire-responder species as well as PTE-resistant microorganisms. In particular, Cr concentration appeared to affect the relative abundance of the genus Paenibacillus, which is considered a good bioindicator of Cr contamination. Indeed, SIMPER analysis performed on T3, T7 and T14 samples revealed that Paenibacillus made the greatest contribution to the community dissimilarity with a percentage of about 40%.
The results reported here could constitute a starting point for the identification of biological indicators of Cr pollution in soils after fire events and their isolation both for bioremediation purposes and post-fire recovery of fire-impacted polluted sites.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.T. and C.C.; methodology, C.C., M.Y.K., M.C., I.R.; software, M.C. and A.L.; investigation, I.R., M.Y.K., C.E.G.; resources, R.T. and C.C.; data curation, I.R., M.C., A.L.; writing—original draft preparation, I.R. and M.C.; writing—review and editing, R.T., C.C., C.E.G., M.Y.K.; visualization, M.C. and A.L.; supervision, R.T. and C.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Sequence data were deposited at the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) and available under the SRA accession: PRJNA723052.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Vega, J.A.; Fontúrbel, T.; Merino, A.; Fernández, C.; Ferreiro, A.; Jiménez, E. Testing the ability of visual indicators of soil burn severity to reflect changes in soil chemical and microbial properties in pine forests and shrubland. Plant Soil 2013, 369, 73–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santín, C.; Doerr, S.H. Fire effects on soils: The human dimension. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2016, 371, 20150171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Kumar, S.; Joshi, L. Socioeconomic and Environmental Implications of Agricultural Residue Burning; SpringerBriefs in Environmental Science; Kumar, P., Kumar, S., Laxmi, J., Eds.; Springer: New Delhi, India, 2015; ISBN 978-81-322-2146-3. [Google Scholar]
- Certini, G. Effects of fire on properties of forest soils: A review. Oecologia 2005, 143, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Jayakumar, S. Impact of forest fire on physical, chemical and biological properties of soil: A review. Proc. Int. Acad. Ecol. Environ. Sci. 2012, 2, 168–176. [Google Scholar]
- Terzano, R.; Rascio, I.; Allegretta, I.; Porfido, C.; Spagnuolo, M.; Yaghoubi Khanghahi, M.; Crecchio, C.; Sakellariadou, F.; Gattullo, C.E. Fire effects on the distribution and bioavailability of potentially toxic elements (PTEs) in agricultural soils. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panichev, N.; Mabasa, W.; Ngobeni, P.; Mandiwana, K.; Panicheva, S. The oxidation of Cr(III) to Cr(VI) in the environment by atmospheric oxygen during the bush fires. J. Hazard. Mater. 2008, 153, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontúrbel, M.T.; Barreiro, A.; Vega, J.A.; Martín, A.; Jiménez, E.; Carballas, T.; Fernández, C.; Díaz-Raviña, M. Effects of an experimental fire and post-fire stabilization treatments on soil microbial communities. Geoderma 2012, 191, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Valera, E.; Verdú, M.; Navarro-Cano, J.A.; Goberna, M. Resilience to fire of phylogenetic diversity across biological domains. Mol. Ecol. 2018, 27, 2896–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Valera, E.; Goberna, M.; Faust, K.; Raes, J.; García, C.; Verdú, M. Fire modifies the phylogenetic structure of soil bacterial co-occurrence networks. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiménez-Morillo, N.T.; Almendros, G.; De la Rosa, J.M.; Jordán, A.; Zavala, L.M.; Granged, A.J.P.; González-Pérez, J.A. Effect of a wildfire and of post-fire restoration actions in the organic matter structure in soil fractions. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 728, 138715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sáenz de Miera, L.E.; Pinto, R.; Gutierrez-Gonzalez, J.J.; Calvo, L.; Ansola, G. Wildfire effects on diversity and composition in soil bacterial communities. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 726, 138636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucas-Borja, M.E.; Miralles, I.; Ortega, R.; Plaza-Álvarez, P.A.; Gonzalez-Romero, J.; Sagra, J.; Soriano-Rodríguez, M.; Certini, G.; Moya, D.; Heras, J. Immediate fire-induced changes in soil microbial community composition in an outdoor experimental controlled system. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 696, 134033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattullo, C.E.; Allegretta, I.; Porfido, C.; Rascio, I.; Spagnuolo, M.; Terzano, R. Assessing chromium pollution and natural stabilization processes in agricultural soils by bulk and micro X-ray analyses. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 22967–22979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IUSS Working Group. WRB. World Reference Base for Soil Resources; World Soil Resources Reports No. 10; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Brunetti, G.; Farrag, K.; Soler-Rovira, P.; Ferrara, M.; Nigro, F.; Senesi, N. Heavy metals accumulation and distribution in durum wheat and barley grown in contaminated soils under Mediterranean field conditions. J. Plant Interact. 2012, 7, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sparks, D.L. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3, Chemical Methods; Soil Science Society of America Book Series No 5; ASA/SSSA Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; ISBN 9780891188254. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Method 3060a Alkaline Digestion for Hexavalent Chromium 1996; U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1996.
- Bartlett, R.J.; James, B.R. Chromium. In Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 3: Chemical Methods; ASA/SSSA Press: Madison, WI, USA, 1996; pp. 683–701. ISBN 9780891188667. [Google Scholar]
- USEPA. Method 7196a Chromium, Hexavalent (Colorimetric); U.S. Government Printing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 1992.
- Lindsay, W.L.; Norvell, W.A. Development of a DTPA Soil Test for Zinc, Iron, Manganese, and Copper. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1978, 42, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Úbeda, X.; Francos, M. Laboratory fire simulations: Plant litter and soils. In Fire Effects on Soil Properties; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 15–38. ISBN 978-1-4863-0815-6. [Google Scholar]
- Li, L.; Ishikawa, Y.; Mihara, M. Effects of Burning Crop Residues on Soil Quality in Wenshui, Shanxi of China. Int. J. Environ. Rural Dev. 2012, 30–35. [Google Scholar]
- Finegold, S.M.; Baron, E.J. Bailey and Scott’s Diagnostic Microbiology, 7th ed.; Mosby Publisher: St. Louis, MO, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
- Meyer, F.; Paarmann, D.; D’Souza, M.; Olson, R.; Glass, E.M.; Kubal, M.; Paczian, T.; Rodriguez, A.; Stevens, R.; Wilke, A.; et al. The metagenomics RAST server—A public resource for the automatic phylogenetic and functional analysis of metagenomes. BMC Bioinform. 2008, 9, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, J.; Dowling, K.; Florentine, S. Controlled burn and immediate mobilization of potentially toxic elements in soil, from a legacy mine site in Central Victoria, Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 616–617, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, C.; Mataix-Solera, J.; Gómez, I.; García-Orenes, F.; Jordán, M.M. Microbial recolonization and chemical changes in a soil heated at different temperatures. Int. J. Wildl. Fire 2005, 14, 385–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terefe, T.; Mariscal-Sancho, I.; Peregrina, F.; Espejo, R. Influence of heating on various properties of six Mediterranean soils. A laboratory study. Geoderma 2008, 143, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, J.A.; Jansen, B.; Kalbitz, K.; Faz, A.; Martínez-Martínez, S. Salinity increases mobility of heavy metals in soils. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1318–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovannini, C.; Lucchesi, S.; Giacchetti, M. Effects of Heating on some Chemical Parameters Related to Soil Fertility and Plant Growth. Soil Sci. 1988, 149, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, E.D.; Choppala, G.; Karimian, N.; Johnston, S.G. A new pathway for hexavalent chromium formation in soil: Fire-induced alteration of iron oxides. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 247, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norme in Materia Ambientale, Italian Legislative Decree n 152; Decreto legislativo 3 aprile 2006, n. 152. 2006; (Gazzetta Ufficiale della Repubblica Italiana n. 88 Supplemento Ordinario n. 96:, 14 aprile 2006).
- Alcañiz, M.; Outeiro, L.; Francos, M.; Úbeda, X. Effects of prescribed fires on soil properties: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 613–614, 944–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomaz, E.L.; Fachin, P.A. Effects of heating on soil physical properties by using realistic peak temperature gradients. Geoderma 2014, 230–231, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamman, S.T.; Burke, I.C.; Stromberger, M.E. Relationships between microbial community structure and soil environmental conditions in a recently burned system. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2007, 39, 1703–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombao, A.; Barreiro, A.; Fontúrbel, M.T.; Martín, A.; Carballas, T.; Díaz-Raviña, M. Key factors controlling microbial community responses after a fire: Importance of severity and recurrence. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 741, 140363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitman, T.; Whitman, E.; Woolet, J.; Flannigan, M.D.; Thompson, D.K.; Parisien, M.A. Soil bacterial and fungal response to wildfires in the Canadian boreal forest across a burn severity gradient. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2019, 138, 107571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheik, C.S.; Mitchell, T.W.; Rizvi, F.Z.; Rehman, Y.; Faisal, M.; Hasnain, S.; McInerney, M.J.; Krumholz, L.R. Exposure of soil microbial communities to chromium and arsenic alters their diversity and structure. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staddon, W.J.; Duchesne, L.C.; Trevors, J.T. Microbial Diversity and Community Structure of Postdisturbance Forest Soils as Determined by Sole-Carbon-Source Utilization Patterns; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 34. [Google Scholar]
- Miranda, A.R.L.; Mendes, L.W.; Rocha, S.M.B.; Van den Brink, P.J.; Bezerra, W.M.; Melo, V.M.M.; Antunes, J.E.L.; Araujo, A.S.F. Responses of soil bacterial community after seventh yearly applications of composted tannery sludge. Geoderma 2018, 318, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierer, N.; Bradford, M.A.; Jackson, R.B. Toward an ecological classification of soil bacteria. Ecology 2007, 88, 1354–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaghoubi Khanghahi, M.; Murgese, P.; Strafella, S.; Crecchio, C. Soil biological fertility and bacterial community response to land use intensity: A case study in the Mediterranean Area. Diversity 2019, 11, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhang, C.; Wang, G.; Fang, L.; Cui, Y. Higher temporal turnover of soil fungi than bacteria during long-term secondary succession in a semiarid abandoned farmland. Soil Tillage Res. 2019, 194, 104305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaghoubi Khanghahi, M.; Cucci, G.; Lacolla, G.; Lanzellotti, L.; Crecchio, C. Soil fertility and bacterial community composition in a semiarid Mediterranean agricultural soil under long-term tillage management. Soil Use Manag. 2020, 36, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrino, E.V.; Brunetti, G.; Farrag, K. Plant Communities in Multi-Metal Contaminated Soils: A Case Study in the National Park of Alta Murgia (Apulia Region-Southern Italy). Int. J. Phytoremediation 2014, 16, 871–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunetti, G.; Farrag, K.; Soler-Rovira, P.; Ferrara, M.; Nigro, F.; Senesi, N. The effect of compost and Bacillus licheniformis on the phytoextraction of Cr, Cu, Pb and Zn by three brassicaceae species from contaminated soils in the Apulia region, Southern Italy. Geoderma 2012, 170, 322–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).