The Impact of Sampling Season and Catching Site (Wild and Aquaculture) on Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods and Materials
2.1. Specimen Collection and Sampling Sites
2.2. Fish Sampling and Processing
2.3. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification of 16S rRNA and Amplicon Sequencing
2.4. Sequence Data Processing
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
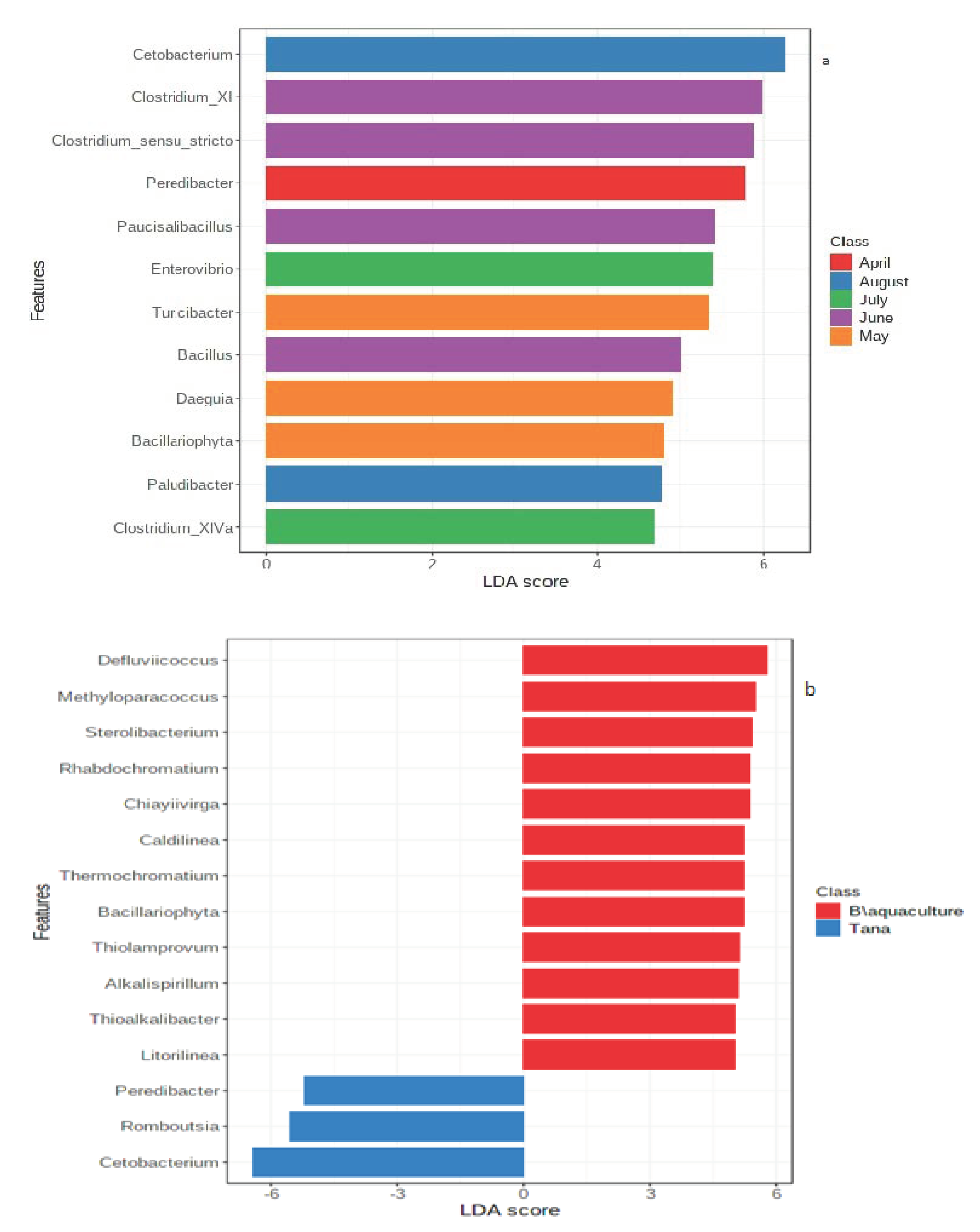
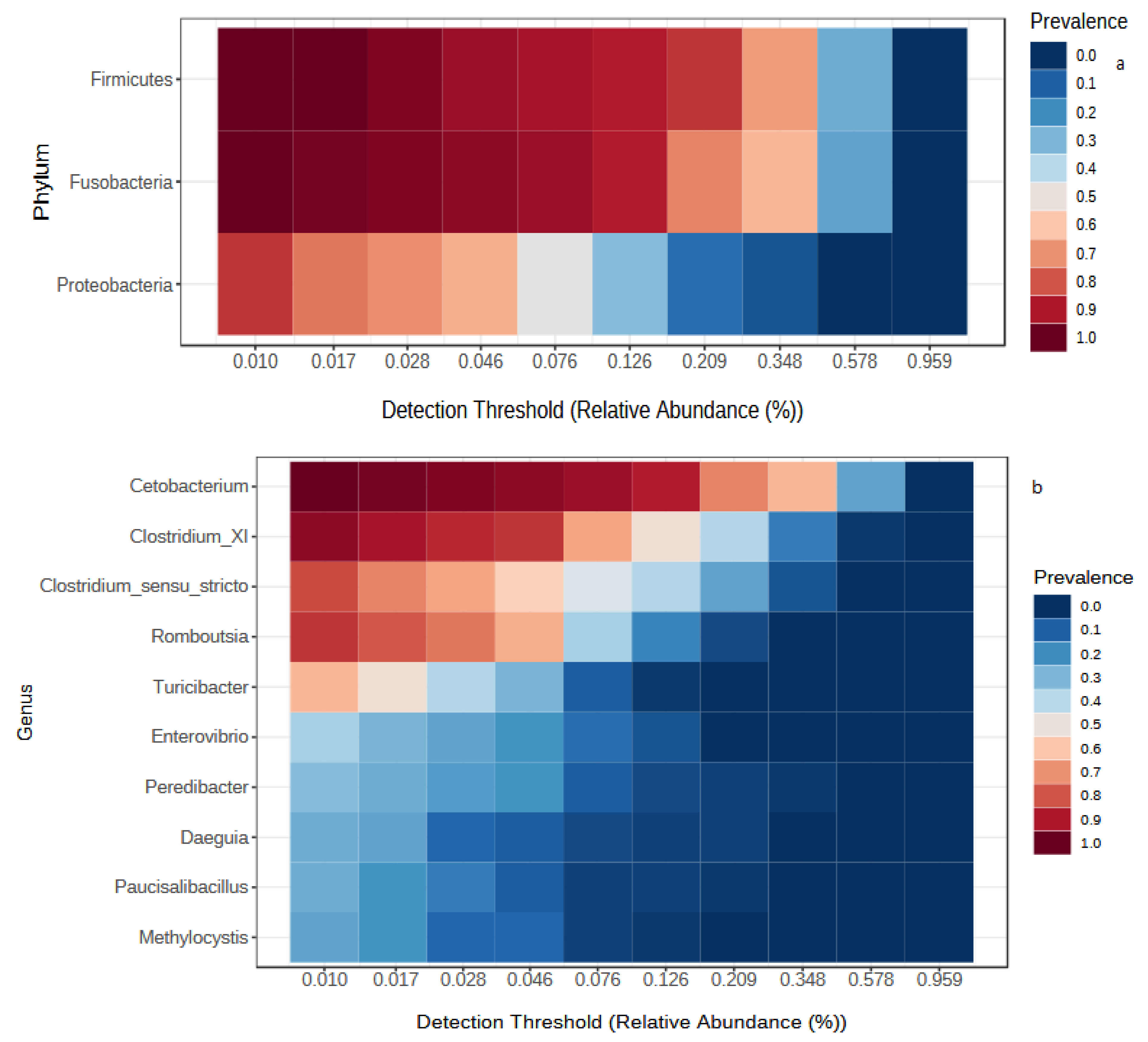
3.1. Temporal Comparison of Gut Microbiota of Wild Fish from the Lake
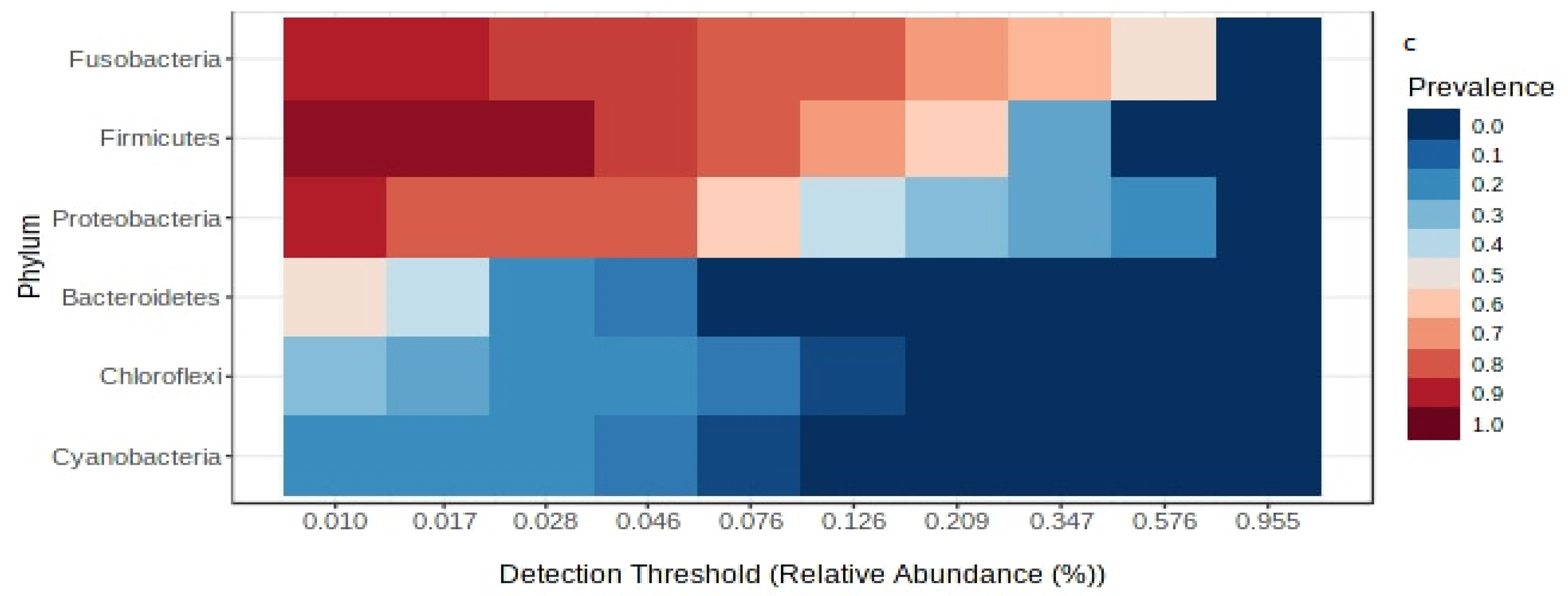
3.2. Comparison of Gut Microbiota between Wild and Captive Fish
4. Discussion
4.1. Overall Core Microbiota Composition
4.2. Seasonal Variation of Gut Microbial Communities
4.3. Comparison of Wild and Captive Fish Gut Microbiota
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Prabu, E.; Rajagopalsamy, C.B.T.; Ahilan, B.; Jeevagan, I.J.M.A.; Renuhadevi, M. Tilapia—An Excellent Candidate Species for World Aquaculture: A Review. Annu. Res. Rev. Biol. 2019, 31, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesfahun, A. Food and feeding habits of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (L.) in Ethiopian water bodies: A review. Int. J. Fish. Aquat. Stud. 2018, 6, 43–47. [Google Scholar]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Magouz, F.I.; Mansour, M.; Saleh, A.A.; Asely, A.M.E.; Fadl, S.E.; Ahmed, H.A.; Al-Ghanim, K.A.; Mahboob, S.; Al-Misned, F. Evaluation of Yeast Fermented Poultry By-Product Meal in Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) Feed: Effects on Growth Performance, Digestive Enzymes Activity, Innate Immunity, and Antioxidant Capacity. Front. Vet. Sci. 2020, 6, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khedr, N. Effect of Fish meal and Plant protein alternatives on the histological picture of different organs on Nile tilapia in Egypt. Benha Vet. Med. J. 2015, 28, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerai, D.B.; Fitzsimmons, K.M.; Collier, R.J.; Duff, G.C. Evaluation of Brewer’s Waste as Partial Replacement of Fish Meal Protein in Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, Diets. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2008, 39, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azaza, M.S.; Dhraïef, M.N.; Kraïem, M.M. Effects of water temperature on growth and sex ratio of juvenile Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus (Linnaeus) reared in geothermal waters in southern Tunisia. J. Therm. Biol. 2008, 33, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebouças, V.T.; Lima, F.R.; Cavalcante, D.D. Tolerance of Nile tilapia juveniles to highly acidic rearing water. Acta Sci. Anim. Sci. 2015, 37, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pandit, N.P.; Nakamura, M. Effect of High Temperature on Survival, Growth and Feed Conversion Ratio of Nile Tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus. Our Nat. 2010, 8, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henson, M.N.; Aday, D.D.; Rice, J.A. Thermal Tolerance and Survival of Nile Tilapia and Blue Tilapia under Rapid and Natural Temperature Declination Rates. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 2018, 147, 278–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flint, H.J.; Scott, K.P.; Louis, P.; Duncan, S.H. The role of the gut microbiota in nutrition and health. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 9, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.K. Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish: Role of gastrointestinal microbiota in fish. Aquac. Res. 2010, 41, 1553–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, R.L.; Volkoff, H. Gut Microbiota and Energy Homeostasis in Fish. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Harbi, A.H.; Naim Uddin, M. Seasonal variation in the intestinal bacterial flora of hybrid tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus × Oreochromis aureus) cultured in earthen ponds in Saudi Arabia. Aquaculture 2004, 229, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovda, M.B.; Fontanillas, R.; McGurk, C.; Obach, A.; Rosnes, J.T. Seasonal variations in the intestinal microbiota of farmed Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.): Seasonal variations in the intestinal microbiota of Salmo salar L. Aquac. Res. 2012, 43, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkasi, K.Z.; Abell, G.C.J.; Taylor, R.S.; Neuman, C.; Hatje, E.; Tamplin, M.L.; Katouli, M.; Bowman, J.P. Pyrosequencing-based characterization of gastrointestinal bacteria of Atlantic salmon ( Salmo salar L.) within a commercial mariculture system. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2014, 117, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagi, T.; Tanaka, D.; Iwamura, Y.; Hoshino, T. Diversity and seasonal changes in lactic acid bacteria in the intestinal tract of cultured freshwater fish. Aquaculture 2004, 234, 335–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullam, K.E.; Essinger, S.D.; Lozupone, C.A.; O’Connor, M.P.; Rosen, G.L.; Knight, R.; Kilham, S.S.; Russell, J.A. Environmental and ecological factors that shape the gut bacterial communities of fish: A meta-analysis: FISH GUT BACTERIAL COMMUNITIES. Mol. Ecol. 2012, 21, 3363–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Sun, Y.; Liu, Y.; Qiao, F.; Chen, L.; Liu, W.-T.; Du, Z.; Li, E. Response of Gut Microbiota to Salinity Change in Two Euryhaline Aquatic Animals with Reverse Salinity Preference. Aquaculture 2016, 454, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkasi, K.Z.; Taylor, R.S.; Abell, G.C.J.; Tamplin, M.L.; Glencross, B.D.; Bowman, J.P. Atlantic Salmon (Salmo salar L.) Gastrointestinal Microbial Community Dynamics in Relation to Digesta Properties and Diet. Microb. Ecol. 2016, 71, 589–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehler, C.E.; Secombes, C.J.; Martin, S.A.M. Environmental and physiological factors shape the gut microbiota of Atlantic salmon parr (Salmo salar L.). Aquaculture 2017, 467, 149–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Givens, C.; Ransom, B.; Bano, N.; Hollibaugh, J. Comparison of the gut microbiomes of 12 bony fish and 3 shark species. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2015, 518, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas Leiva, J.; Opazo, R.; Remond, C.; Uribe, E.; Velez, A.; Romero, J. Characterization of the intestinal microbiota of wild caught and farmed fine flounder (Paralichthys adspersus). Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2017, 45, 370–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijverberg, J.; Sibbing, F.A.; Dejen, E. Lake Tana: Source of the Blue Nile. In The Nile; Dumont, H.J., Ed.; Monographiae Biologicae; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2009; Volume 89, pp. 163–192. ISBN 978-1-4020-9725-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengistu, A.A.; Aragaw, C.; Mengist, M.; Goshu, G. The Fish and the Fisheries of Lake Tana. In Social and Ecological System Dynamics; Stave, K., Goshu, G., Aynalem, S., Eds.; AESS Interdisciplinary Environmental Studies and Sciences Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 157–177. ISBN 978-3-319-45753-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshu, G.; Aynalem, S. Problem Overview of the Lake Tana Basin. In Social and Ecological System Dynamics; Stave, K., Goshu, G., Aynalem, S., Eds.; AESS Interdisciplinary Environmental Studies and Sciences Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 9–23. ISBN 978-3-319-45753-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goshu, G.; Koelmans, A.A.; de Klein, J.J.M. Water Quality of Lake Tana Basin, Upper Blue Nile, Ethiopia. A Review of Available Data. In Social and Ecological System Dynamics; Stave, K., Goshu, G., Aynalem, S., Eds.; AESS Interdisciplinary Environmental Studies and Sciences Series; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 127–141. ISBN 978-3-319-45753-6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondie, A.; Mengistu, S.; Vijverberg, J.; Dejen, E. Seasonal variation in primary production of a large high altitude tropical lake (Lake Tana, Ethiopia): Effects of nutrient availability and water transparency. Aquat. Ecol. 2007, 41, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emama Ligdi, E.; Kahloun, M.E.; Meire, P. Ecohydrological status of Lake Tana—A shallow highland lake in the Blue Nile (Abbay) basin in Ethiopia: Review. Ecohydrol. Hydrobiol. 2010, 10, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereded, N.K.; Curto, M.; Domig, K.J.; Abebe, G.B.; Fanta, S.W.; Waidbacher, H.; Meimberg, H. Metabarcoding Analyses of Gut Microbiota of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) from Lake Awassa and Lake Chamo, Ethiopia. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deriggi Pisani, G.; Inoue, L.; Moraes, G. Stress responses to handling in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus Linnaeus): Assessment of eugenol as an alternative anesthetic. Acta Sci. Biol. Sci. 2006, 28, 269–274. [Google Scholar]
- Ghanbari, M.; Shahraki, H.; Kneifel, W.; Domig, K.J. A first insight into the intestinal microbiota of snow trout (Schizothorax zarudnyi). Symbiosis 2017, 72, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shokralla, S.; Hellberg, R.S.; Handy, S.M.; King, I.; Hajibabaei, M. A DNA Mini-Barcoding System for Authentication of Processed Fish Products. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, M. Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet.journal 2011, 17, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Kobert, K.; Flouri, T.; Stamatakis, A. PEAR: A fast and accurate Illumina Paired-End reAd mergeR. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curto, M.; Winter, S.; Seiter, A.; Schmid, L.; Scheicher, K.; Barthel, L.M.F.; Plass, J.; Meimberg, H. Application of a SSR-GBS marker system on investigation of European Hedgehog species and their hybrid zone dynamics. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 2814–2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edgar, R.C.; Haas, B.J.; Clemente, J.C.; Quince, C.; Knight, R. UCHIME improves sensitivity and speed of chimera detection. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 2194–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Garrity, G.M.; Tiedje, J.M.; Cole, J.R. Naïve Bayesian Classifier for Rapid Assignment of rRNA Sequences into the New Bacterial Taxonomy. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2007, 73, 5261–5267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, J.; Liu, P.; Zhou, G.; Xia, J. Using MicrobiomeAnalyst for comprehensive statistical, functional, and meta-analysis of microbiome data. Nat. Protoc. 2020, 15, 799–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.; Waldrop, T.; Summerfelt, S.; Davidson, J.; Barrows, F.; Kenney, P.B.; Welch, T.; Wiens, G.D.; Snekvik, K.; Rawls, J.F.; et al. Aquacultured Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) Possess a Large Core Intestinal Microbiota That Is Resistant to Variation in Diet and Rearing Density. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 4974–4984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbari, M.; Kneifel, W.; Domig, K.J. A new view of the fish gut microbiome: Advances from next-generation sequencing. Aquaculture 2015, 448, 464–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giatsis, C.; Sipkema, D.; Smidt, H.; Heilig, H.; Benvenuti, G.; Verreth, J.; Verdegem, M. The impact of rearing environment on the development of gut microbiota in tilapia larvae. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldo, L.; Riera, J.L.; Tooming-Klunderud, A.; Albà, M.M.; Salzburger, W. Gut Microbiota Dynamics during Dietary Shift in Eastern African Cichlid Fishes. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0127462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roeselers, G.; Mittge, E.K.; Stephens, W.Z.; Parichy, D.M.; Cavanaugh, C.M.; Guillemin, K.; Rawls, J.F. Evidence for a core gut microbiota in the zebrafish. ISME J. 2011, 5, 1595–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, C.D.; Young, W.; Maclean, P.H.; Cookson, A.L.; Bermingham, E.N. Metagenomic insights into the roles of Proteobacteria in the gastrointestinal microbiomes of healthy dogs and cats. MicrobiologyOpen 2018, 7, e00677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharechahi, J.; Salekdeh, G.H. A metagenomic analysis of the camel rumen’s microbiome identifies the major microbes responsible for lignocellulose degradation and fermentation. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2018, 11, 216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semova, I.; Carten, J.D.; Stombaugh, J.; Mackey, L.C.; Knight, R.; Farber, S.A.; Rawls, J.F. Microbiota Regulate Intestinal Absorption and Metabolism of Fatty Acids in the Zebrafish. Cell Host Microbe 2012, 12, 277–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staley, J.T.; William, B.W. Phylum XIX. Fusobacteria Garrity and Holt 2001, 140. In Bergey’s Manual® of Systematic Bacteriology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2010; pp. 747–774. ISBN 978-0-387-68572-4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terova, G.; Díaz, N.; Rimoldi, S.; Ceccotti, C.; Gliozheni, E.; Piferrer, F. Effects of Sodium Butyrate Treatment on Histone Modifications and the Expression of Genes Related to Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms and Immune Response in European Sea Bass (Dicentrarchus Labrax) Fed a Plant-Based Diet. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, C.; Sakata, T.; Sugita, H. Novel ecological niche of Cetobacterium somerae, an anaerobic bacterium in the intestinal tracts of freshwater fish. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 46, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi-Yen, S.; Chun-Qui, L. No dietary vitamin B12 required for juvenile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus × O. aureus. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Physiol. 1993, 105, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsaied, H.E.; Soliman, T.; Abu-Taleb, H.T.; Goto, H.; Jenke-Kodam, H. Phylogenetic characterization of eukaryotic and prokaryotic gut flora of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, along niches of Lake Nasser, Egypt, based on rRNA gene high-throughput sequences. Ecol. Genet. Genomics 2019, 11, 100037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, C.; Bujan, N.; Tarnecki, A.; Davis, A.D.; Browdy, C.; Arias, C.R. Analysis of the Gut Microbiome of Nile Tilapia Oreochromis Niloticus L. Fed Diets Supplemented with Previda® and Saponin. J. Fish. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Standen, B.T.; Rodiles, A.; Peggs, D.L.; Davies, S.J.; Santos, G.A.; Merrifield, D.L. Modulation of the intestinal microbiota and morphology of tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus, following the application of a multi-species probiotic. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 8403–8417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, W.; Hu, G.; Qiu, L.; Meng, S.; Song, C.; Fan, L.; Zhao, Z.; Bing, X.; Chen, J. Gut microbiota analysis of juvenile genetically improved farmed tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) by dietary supplementation of different resveratrol concentrations. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2018, 77, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukassen, M.B.; de Jonge, N.; Bjerregaard, S.M.; Podduturi, R.; Jørgensen, N.O.G.; Petersen, M.A.; David, G.S.; da Silva, R.J.; Nielsen, J.L. Microbial Production of the Off-Flavor Geosmin in Tilapia Production in Brazilian Water Reservoirs: Importance of Bacteria in the Intestine and Other Fish-Associated Environments. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parata, L.; Mazumder, D.; Sammut, J.; Egan, S. Diet type influences the gut microbiome and nutrient assimilation of Genetically Improved Farmed Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zeng, X.; Liu, S.; Wu, F.; Li, Y.; Pan, Q. Effects of dietary four different woody forages on gut microbiota of Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Aquac. Res. 2020, are.15029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Liu, J.; Tan, H.; Yang, C.; Ren, L.; Liu, Q.; Wang, S.; Hu, F.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, R.; et al. Genetic Effects on the Gut Microbiota Assemblages of Hybrid Fish From Parents With Different Feeding Habits. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmillan, J.R.; Santucci, T. Seasonal Trends in Intestinal Bacterial Flora of Farm-Raised Channel Catfish. J. Aquat. Anim. Health 1990, 2, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, S.; Rasool, F.; Bhatti, E.; Anwar, A.; Chaughtai, M. Seasonal variations in the intestinal bacterial flora of Oreochromis niloticus cultured in farms. J. Biodivers. Environ. Sci. (JBES) 2015, 6, 2220–6663. [Google Scholar]
- Goshu, G.; Strokal, M.; Kroeze, C.; Koelmans, A.A.; de Klein, J.J.M. Assessing seasonal nitrogen export to large tropical lakes. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 731, 139199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejen, E.; Vijverberg, J.; Nagelkerke, L.A.J.; Sibbing, F.A. Temporal and spatial distribution of microcrustacean zooplankton in relation to turbidity and other environmental factors in a large tropical lake (L. Tana, Ethiopia). Hydrobiologia 2004, 513, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gashaye, D.; Goshu, G.; Tsegay, B. Temporal and spatial phytoplankton biomass dynamics in southern Gulf of Lake Tana, Northwestern Ethiopia. Int. J. Aquat. Biol. 2019, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wondmagegne, T.; Wondie, A.; Mingist, M.; Vijverberg, J. Seasonality in Abundance, Biomass and Production of the Phytoplankton of Welala and Shesher Wetlands, Lake Tana Sub-Basin (Ethiopia). J. Water Resour. Prot. 2012, 04, 877–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueki, A.; Akasaka, H.; Suzuki, D.; Ueki, K. Paludibacter propionicigenes gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel strictly anaerobic, Gram-negative, propionate-producing bacterium isolated from plant residue in irrigated rice-field soil in Japan. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2006, 56, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, Z.; Ahmed, Z.; Bakr, A. Assessment of phytoplankton species in gut and feces of cultured tilapia fish in Egyptian fishponds: Implications for feeding and bloom control. Acta Limnol. Bras. 2019, 31, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar Torres, G.; Silva, L.H.S.; Rangel, L.M.; Attayde, J.L.; Huszar, V.L.M. Cyanobacteria are controlled by omnivorous filter-feeding fish (Nile tilapia) in a tropical eutrophic reservoir. Hydrobiologia 2016, 765, 115–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheath, R.G.; Wehr, J.D. INTRODUCTION TO FRESHWATER ALGAE. In Freshwater Algae of North America; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003; pp. 1–9. ISBN 978-0-12-741550-5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulski, T.; Kozłowski, K.; Ciesielski, S. Habitat and seasonality shape the structure of tench (Tinca tinca L.) gut microbiome. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 4460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Hu, G.; Wu, W.; Qiu, L.; Bing, X.; Chen, J. Time-dependent gut microbiota analysis of juvenile Oreochromis niloticus by dietary supplementation of resveratrol. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, N.-R.; Whon, T.W.; Bae, J.-W. Proteobacteria: Microbial signature of dysbiosis in gut microbiota. Trends Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Huang, K.; Yu, J.; Ding, C.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, C.; Yuan, H.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Hu, J.; et al. Metagenomic analysis of bacterial communities and antibiotic resistance genes in the Eriocheir sinensis freshwater aquaculture environment. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, X.; Xu, M.; Li, M.; Zhao, Y.; Shao, X. Response of sediment bacterial communities to the drainage of wastewater from aquaculture ponds in different seasons. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 717, 137180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, Z.; Liu, B.; Xuan, Y.; Jiang, M.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, Y.; Lu, X.; Yu, D.; et al. Dynamic changes of microbial communities in Litopenaeus vannamei cultures and the effects of environmental factors. Aquaculture 2016, 455, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delport, T.C.; Power, M.L.; Harcourt, R.G.; Webster, K.N.; Tetu, S.G. Colony Location and Captivity Influence the Gut Microbial Community Composition of the Australian Sea Lion (Neophoca cinerea). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3440–3449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringø, E.; Zhou, Z.; Vecino, J.L.G.; Wadsworth, S.; Romero, J.; Krogdahl, Å.; Olsen, R.E.; Dimitroglou, A.; Foey, A.; Davies, S.; et al. Effect of dietary components on the gut microbiota of aquatic animals. A never-ending story? Aquac. Nutr. 2016, 22, 219–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.K.; Natrah, I.; Suyub, I.B.; Edward, M.J.; Kaman, N.; Samsudin, A.A. Comparative study of gut microbiota in wild and captive Malaysian Mahseer (Tor tambroides). MicrobiologyOpen 2019, 8, e00734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenzie, V.J.; Song, S.J.; Delsuc, F.; Prest, T.L.; Oliverio, A.M.; Korpita, T.M.; Alexiev, A.; Amato, K.R.; Metcalf, J.L.; Kowalewski, M.; et al. The Effects of Captivity on the Mammalian Gut Microbiome. Integr. Comp. Biol. 2017, 57, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holben, W.E.; Williams, P.; Saarinen, M.; Särkilahti, L.K.; Apajalahti, J.H.A. Phylogenetic Analysis of Intestinal Microflora Indicates a Novel Mycoplasma Phylotype in Farmed and Wild Salmon. Microb. Ecol. 2002, 44, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Sampling Site | Sampling Months | No. of Samples | Season |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lake Tana | April | 9 | Dry season |
| Lake Tana | May | 8 | Pre-rainy season |
| Lake Tana | June | 10 | Pre-rainy season |
| Lake Tana | July | 8 | Main rainy season |
| Lake Tana | August | 12 | Main rainy season |
| Bahir Dar aquaculture centre | August | 7 | Main rainy season |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bereded, N.K.; Abebe, G.B.; Fanta, S.W.; Curto, M.; Waidbacher, H.; Meimberg, H.; Domig, K.J. The Impact of Sampling Season and Catching Site (Wild and Aquaculture) on Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Biology 2021, 10, 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030180
Bereded NK, Abebe GB, Fanta SW, Curto M, Waidbacher H, Meimberg H, Domig KJ. The Impact of Sampling Season and Catching Site (Wild and Aquaculture) on Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Biology. 2021; 10(3):180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030180
Chicago/Turabian StyleBereded, Negash Kabtimer, Getachew Beneberu Abebe, Solomon Workneh Fanta, Manuel Curto, Herwig Waidbacher, Harald Meimberg, and Konrad J. Domig. 2021. "The Impact of Sampling Season and Catching Site (Wild and Aquaculture) on Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)" Biology 10, no. 3: 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030180
APA StyleBereded, N. K., Abebe, G. B., Fanta, S. W., Curto, M., Waidbacher, H., Meimberg, H., & Domig, K. J. (2021). The Impact of Sampling Season and Catching Site (Wild and Aquaculture) on Gut Microbiota Composition and Diversity of Nile Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus). Biology, 10(3), 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10030180







