Absorption and Transport Characteristics and Mechanisms of Carnosic Acid
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
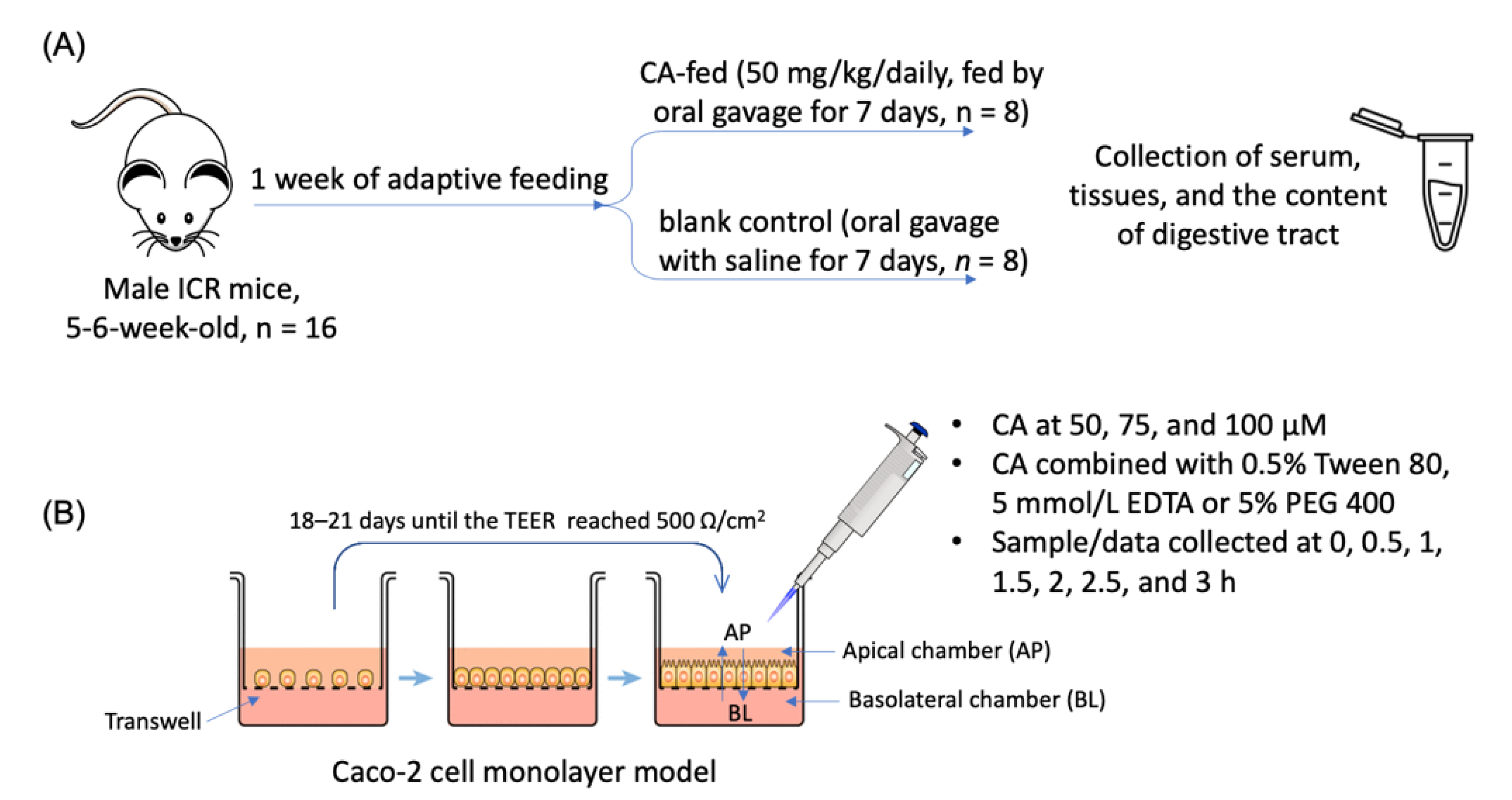
2.1. Animals, Cells, Reagents, and Instruments
2.2. Animal Experiment
2.3. Determination of Tissue Distribution of CA in Mice by HPLC
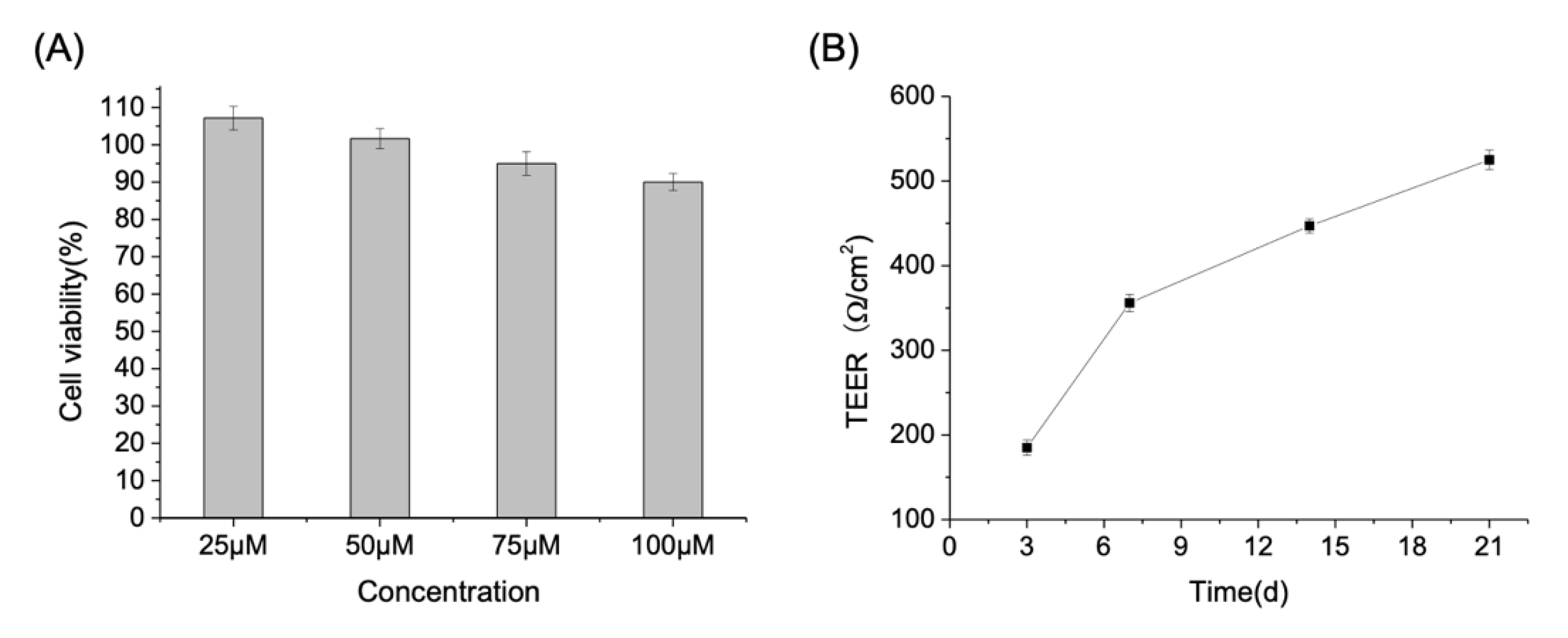
2.4. Establishment of Caco-2 Cell Monolayer Model
2.5. Trans-Enterocyte Transport of CA in Caco-2 Cell Monolayer
2.5.1. Effect of Incubation Time and Dose on the Trans-Enterocyte Transport of CA
2.5.2. Effect of Verapamil, PEG 400, and EDTA on the Trans-Enterocyte Transport of CA
2.5.3. Determination of CA Concentration
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Tissue Distribution of CA in Mice after Long-Term Oral Administration
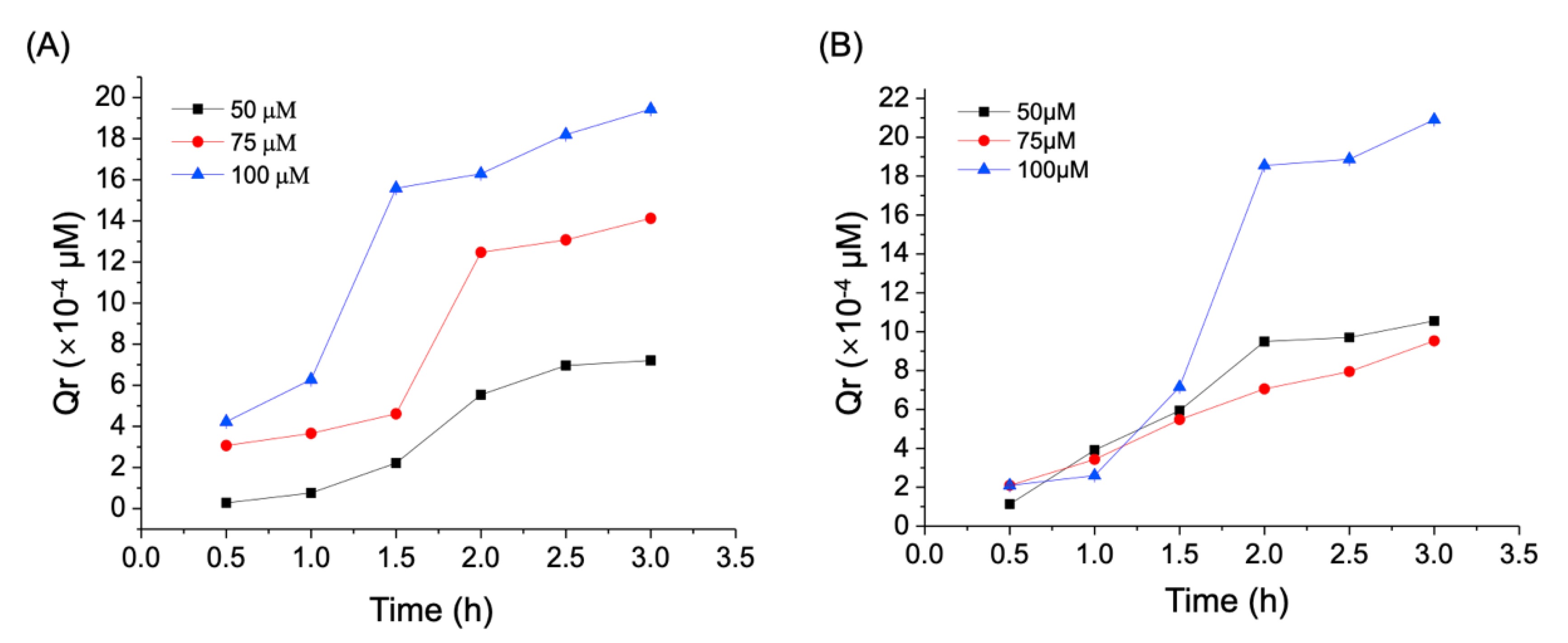
3.2. Trans-Enterocyte Transport of CA in Caco-2 Monolayer Model
3.3. Effect of Verapamil and PEG 400 on the Trans-Enterocyte of CA
3.4. Effect of EDTA on the Trans-Enterocyte of CA
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CA | carnosic acid |
| AP | apical side |
| BL | basolateral side |
| PEG | polyethylene glycol |
| Papp | apparent permeability coefficient |
| Qr | cumulative migration |
| P-gp | P-glycoprotein |
References
- Petiwala, S.M.; Johnson, J.J. Diterpenes from rosemary (Rosmarinus officinalis): Defining their potential for anti-cancer activity. Cancer Lett. 2015, 367, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panpan, Z.; Hao, W. Research progress on chemical constituents and biological activities of diterpenoids from rosemary. Strait Pharm. J. 2020, 32, 37–41. [Google Scholar]
- Bernardes, W.A.; Lucarini, R.; Tozatti, M.G.; Souza, M.G.M.; Andrade Silva, M.L.; Da Silva Filho, A.A.; Gomes Martins, C.H.; Miller Crotti, A.E.; Pauletti, P.M.; Groppo, M.; et al. Antimicrobial activity of Rosmarinus officinalis against oral pathogens: Relevance of carnosic acid and carnosol. Chem. Biodivers. 2010, 7, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Activity, A.; Acid, C.; Ganjun, R.Y.; Peibo, L.I.; Hui, Y. Anti-MRSA Activity of Carnosic Acid in Rosemary. Chin. J. Mod. Appl. Pharm. 2012, 29, 571–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duggal, J.; Harrison, J.S.; Studzinski, G.P.; Wang, X. Involvement of MicroRNA181a in Differentiation and Cell Cycle Arrest Induced by a Plant-derived Antioxidant Carnosic Acid and Vitamin D Analog Doxercalciferol in Human Leukemia Cells. MicroRNA 2012, 1, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Wang, D. Protective role of carnosic acid against liver injury. Hepatol. Res. 2016, 46, 607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Takikawa, Y.; Satoh, T.; Yoshioka, Y.; Kosaka, K.; Tatemichi, Y.; Suzuki, K. Carnosic acid prevents obesity and hepatic steatosis in ob/ob mice. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Z.; Zhong, L.; Wu, Y.; Wan, X.; Yang, H.; Xu, X.; Li, P. Carnosic acid improves diabetic nephropathy by activating Nrf2/ARE and inhibition of NF-κB pathway. Phytomedicine 2018, 47, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, N.N.; Zhou, Q.; Huang, Q.; Liu, K.J. Carnosic acid cooperates with tamoxifen to induce apoptosis associated with Caspase-3 activation in breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 89, 827–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Einbond, L.S.; Wu, H.A.; Kashiwazaki, R.; He, K.; Roller, M.; Su, T.; Wang, X.; Goldsberry, S. Carnosic acid inhibits the growth of ER-negative human breast cancer cells and synergizes with curcumin. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 1160–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zia-Ul-Haq, M. Past, Present and Future of Carotenoids Research. Carotenoids: Structure and Function in the Human Body; Zia-Ul-Haq, M., Dewanjee, S., Riaz, M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Basingstoke, UK, 2021; pp. 827–854. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.X. Studies on the Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism of Carnosic Acid in Rats. Ph.D. Thesis, Shenyang Pharmaceutical University, Shenyang, China, December 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Doolaege, E.H.; Raes, K.; De Vos, F.; Verhé, R.; De Smet, S. Absorption, Distribution and Elimination of Carnosic Acid, A Natural Antioxidant from Rosmarinus officinalis, in Rats. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2011, 66, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Xu, C.; Chen, P.; Hu, J.; Hu, R.; Huang, M.; Bi, H. Development, validation, and application of a novel 7-day Caco-2 cell culture system. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2014, 70, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, C.L.; Praça, C.; Martins, P.A.T.; Batista de Carvalho, A.L.M.; Ferreira, L.; Marques, M.P.M.; Moreno, M.J. Re-use of caco-2 monolayers in permeability assays—Validation regarding cell monolayer integrity. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanqing, L.; Li, H. Study on caco-2 cell culture and cell monolayer model establishment. J. Appropr. Clin. Medicat. 2018, 11, 161–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Gao, Z.; Song, M.; Ouyang, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, L.; William, D.; Cai, X.; Cao, Y.; et al. Identification of terpenoids from Rubus corchorifolius L. f. leaves and their anti-proliferative effects on human cancer cells. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freireich, E.J.; Gehan, E.A.; Rall, D.P.; Schmidt, L.H.; Skipper, H.E. Quantitative comparison of toxicity of anticancer agents in mouse, rat, hamster, dog, monkey, and man. Cancer Chemother Rep. 1966, 50, 219–244. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Romo Vaquero, M.; García Villalba, R.; Larrosa, M.; Yáñez-Gascón, M.J.; Fromentin, E.; Flanagan, J.; Roller, M.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; Espín, J.C.; García-Conesa, M.T. Bioavailability of the major bioactive diterpenoids in a rosemary extract: Metabolic profile in the intestine, liver, plasma, and brain of Zucker rats. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013, 57, 1834–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yen, C.C.; Liu, Y.T.; Lin, Y.J.; Yang, Y.C.; Chen, C.C.; Yao, H.T.; Chen, H.W.; Lii, C.K. Bioavailability of the diterpenoid 14-deoxy-11,12-didehydroandrographolide in rats and up-regulation of hepatic drug-metabolizing enzyme and drug transporter expression. Phytomedicine 2019, 61, 152841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soler-Rivas, C.; Marín, F.R.; Santoyo, S.; García-Risco, M.R.; Señoráns, F.J.; Reglero, G. Testing and Enhancing the in Vitro Bioaccessibility and Bioavailability of Rosmarinus officinalis Extracts with a High Level of Antioxidant Abietanes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 58, 1144–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williamson, G.; Kay, C.D.; Crozier, A. The Bioavailability, Transport, and Bioactivity of Dietary Flavonoids: A Review from a Historical Perspective. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2018, 17, 1054–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozdal, T.; Sela, D.A.; Xiao, J.; Boyacioglu, D.; Chen, F.; Capanoglu, E. The Reciprocal Interactions between Polyphenols and Gut Microbiota and Effects on Bioaccessibility. Nutrients 2016, 8, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romo-Vaquero, M.; Selma, M.V.; Larrosa, M.; Obiol, M.; García-Villalba, R.; González-Barrio, R.; Issaly, N.; Flanagan, J.; Roller, M.; Tomás-Barberán, F.A.; et al. A rosemary extract rich in carnosic acid selectively modulates caecum microbiota and inhibits β-glucosidase activity, altering fiber and short chain fatty acids fecal excretion in lean and obese female rats. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, J.; Huang, J.; Zhao, D.; Du, B.; Wang, M. Protective effect of rosmarinic acid and carnosic acid against streptozotocin-induced oxidation, glycation, inflammation and microbiota imbalance in diabetic rats. Food Funct. 2018, 9, 851–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Yan, H.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Tu, P. Characterization of in vitro and in vivo metabolites of carnosic acid, a natural antioxidant, by high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 89, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sambuy, Y.; De Angelis, I.; Ranaldi, G.; Scarino, M.L.; Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. The Caco-2 cell line as a model of the intestinal barrier: Influence of cell and culture-related factors on Caco-2 cell functional characteristics. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2005, 21, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kigen, G.; Edwards, G. Drug-transporter mediated interactions between anthelminthic and antiretroviral drugs across the Caco-2 cell monolayers. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2017, 18, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thongon, N.; Chamniansawat, S. The inhibitory role of purinergic P2Y receptor on Mg2+ transport across intestinal epithelium-like Caco-2 monolayer. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 69, 129–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Shen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, J.; Fan, K.; Zhan, X. Characterization of a novel polysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum and its absorption mechanism in Caco-2 cells and mice model. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Chow, E.C.; Liu, S.; Du, Y.; Pang, K.S. The Caco-2 cell monolayer: Usefulness and limitations. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2008, 4, 395–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giacomini, K.M.; Huang, S.-M.; Tweedie, D.J.K.M.G. Membrane transporters in drug development NIH Public Access. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 215–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas, P.A.; Kratz, J.M.; Hernández, A.; Costa, G.M.; Ospina, L.F.; Baena, Y.; Simões, C.M.O.; Jimenez-Kairuz, Á.; Aragon, M. In vitro intestinal permeability studies, pharmacokinetics and tissue distribution of 6-methylcoumarin after oral and intraperitoneal administration in Wistar rats. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2017, 53, 16081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Florea, B.I.; Van Der Sandt, I.C.J.; Schrier, S.M.; Kooiman, K.; Deryckere, K.; De Boer, A.G.; Junginger, H.E.; Borchard, G. Evidence of P-glycoprotein mediated apical to basolateral transport of flunisolide in human broncho-tracheal epithelial cells (Calu-3). Br. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 134, 1555–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodaei, D.; Baradaran, B.; Valizadeh, H.; Zakeri-Milani, P. Effects of polyethylene glycols on intestinal efflux pump expression and activity in Caco-2 cells. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 51, 745–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashiru-Oredope, D.A.I.; Patel, N.; Forbes, B.; Patel, R.; Basit, A.W. The effect of polyoxyethylene polymers on the transport of ranitidine in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 409, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rege, B.D.; Kao, J.P.Y.; Polli, J.E. Effects of nonionic surfactants on membrane transporters in Caco-2 cell monolayers. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 16, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yao, M.; Morrison, R.A.; Chong, S. Commonly used surfactant, Tween 80, improves absorption of P-glycoprotein substrate, digoxin, in rats. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2003, 26, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artursson, P.; Borchardt, R.T. Intestinal drug absorption and metabolism in cell cultures: Caco-2 and beyond. Pharm. Res. 1997, 14, 1655–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibangou, I.B.; Bureau, F.; Allouche, S.; Arhan, P.; Bouglé, D. Interactions between ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) and iron absorption pathways, in the Caco-2 model. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2008, 46, 3414–3416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Li, J.; Ning, F.; Wijaya, W.; Chen, Y.; Xiao, J.; Cao, Y.; Huang, Q. Improving: In vitro bioaccessibility and bioactivity of carnosic acid using a lecithin-based nanoemulsion system. Food Funct. 2021, 12, 1558–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Body Weight (week, g) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | |
| Control | 33.96 ± 1.2 | 35.1 ± 2.1 | 36.9 ± 2.3 | 38.5 ± 1.1 | 40.5 ± 2.2 |
| CA | 33.2 ± 0.9 | 34.8 ± 2.5 | 37.1 ± 1.8 | 38.9 ± 2.4 | 41.2 ± 3.1 |
| Sample | Concentration (nmol/g or mL) |
|---|---|
| Serum | 15.22 ± 0.02 |
| Liver | 10.56 ± 0.01 |
| Kidney | 0.66 ± 0.02 |
| Stomach | 35.98 ± 0.09 |
| Small intestine | 1.87 ± 0.00 |
| Cecum | 2965.10 ± 3.31 |
| Colon | 179.43 ± 0.26 |
| Heart | 0.75 ± 0.00 |
| Lung | 1.68 ± 0.00 |
| Spleen | 13.42 ± 0.01 |
| Gastric content | 1.08 ± 0.00 |
| Small intestine content | 13.93 ± 0.01 |
| Cecal content | 0.15 ± 0.00 |
| Colonic content | 74.54 ± 0.21 |
| Concentration of CA (μM) | Time (h) | Papp (10−6 cm/s) | Efflux Ratio | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP-BL | BL-AP | |||
| 50 | 0.5 | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 0.12 ± 0.10 | 0.42 |
| 1.0 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 0.21 ± 0.09 | 0.58 | |
| 1.5 | 0.69 ± 0.09 | 0.36 ± 0.06 | 0.52 | |
| 2.0 | 1.11 ± 0.04 | 0.49 ± 0.07 | 0.44 | |
| 2.5 | 0.57 ± 0.03 | 0.56 ± 0.05 | 0.98 | |
| 3.0 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 0.29 ± 0.03 | 1.32 | |
| Average | 0.53 ± 0.02 | 0.33 ± 0.03 | 0.62 | |
| 75 | 0.5 | 1.03 ± 0.01 | 0.91 ± 0.02 | 0.88 |
| 1.0 | 1.08 ± 0.04 | 0.86 ± 0.05 | 0.79 | |
| 1.5 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 0.79 ± 0.07 | 0.95 | |
| 2.0 | 1.84 ± 0.10 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.33 | |
| 2.5 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 0.41 ± 0.03 | 0.49 | |
| 3.0 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.38 ± 0.03 | 0.61 | |
| Average | 1.04 ± 0.05 | 0.66 ± 0.06 | 0.63 | |
| 100 | 0.5 | 1.10 ± 0.10 | 0.39 ± 0.03 | 0.35 |
| 1.0 | 1.32 ± 0.09 | 0.56 ± 0.04 | 0.42 | |
| 1.5 | 2.36 ± 0.08 | 2.53 ± 0.03 | 1.07 | |
| 2.0 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 1.33 ± 0.05 | 1.52 | |
| 2.5 | 0.85 ± 0.05 | 1.45 ± 0.01 | 1.70 | |
| 3.0 | 0.80 ± 0.09 | 1.23 ± 0.03 | 1.53 | |
| Average | 1.20 ± 0.07 | 1.24 ± 0.04 | 1.03 | |
| Concentration of CA (μM) | Time (h) | Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CA | CA + Verapamil | CA + PEG400 | CA + EDTA | ||
| 50 | 0.5 | 0.28 ± 0.07 | 1.98 ± 0.06 * | 3.76 ± 0.17 * | 0.50 ± 0.01 * |
| 1.0 | 0.36 ± 0.01 | 1.89 ± 0.09 * | 3.96 ± 0.10 * | 0.24 ± 0.08 | |
| 1.5 | 0.69 ± 0.09 | 1.84 ± 0.06 * | 2.35 ± 0.01 * | 0.62 ± 0.02 | |
| 2.0 | 1.11 ± 0.04 | 2.08 ± 0.10 * | 1.86 ± 0.35 * | 0.92 ± 0.00 * | |
| 2.5 | 0.57 ± 0.03 | 0.95 ± 0.03 * | 1.89 ± 0.04 * | 0.95 ± 0.02 * | |
| 3.0 | 0.22 ± 0.02 | 1.37 ± 0.09 * | 2.34 ± 0.01 * | 1.49 ± 0.02 * | |
| Average | 0.54 ± 0.05 | 1.50 ± 0.02 * | 2.69 ± 0.04 * | 0.79 ± 0.03 * | |
| 75 | 0.5 | 1.03 ± 0.01 | 1.12 ± 0.01 * | 3.90 ± 0.10 * | 0.92 ± 0.08 |
| 1.0 | 1.08 ± 0.04 | 1.32 ± 0.01 * | 2.99 ± 0.09 * | 1.90 ± 0.08 * | |
| 1.5 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 0.85 ± 0.03 | 2.72 ± 0.46 * | 1.94 ± 0.07 * | |
| 2.0 | 1.84 ± 0.10 | 1.94 ± 0.06 * | 2.35 ± 0.10 * | 2.08 ± 0.03 * | |
| 2.5 | 0.83 ± 0.01 | 0.87 ± 0.10 | 1.52 ± 0.06 * | 1.28 ± 0.10 * | |
| 3.0 | 0.62 ± 0.01 | 0.69 ± 0.01 | 1.19 ± 0.06 * | 0.57 ± 0.01 | |
| Average | 1.04 ± 0.02 | 1.53 ± 0.04 * | 1.45 ± 0.08 * | 1.45 ± 0.05 * | |
| 100 | 0.5 | 1.10 ± 0.10 | 1.26 ± 0.02 | 3.21 ± 0.47 * | 0.38 ± 0.00 |
| 1.0 | 1.32 ± 0.09 | 1.70 ± 0.01 * | 3.59 ± 0.10 * | 2.25 ± 0.09 * | |
| 1.5 | 2.36 ± 0.08 | 2.99 ± 0.03 * | 2.89 ± 0.05 * | 1.96 ± 0.07 | |
| 2.0 | 0.87 ± 0.02 | 1.24 ± 0.02 * | 2.25 ± 0.02 * | 3.01 ± 0.03 * | |
| 2.5 | 0.85 ± 0.05 | 0.95 ± 0.05 * | 2.44 ± 0.01 * | 1.82 ± 0.08 * | |
| 3.0 | 0.80 ± 0.09 | 1.09 ± 0.02 * | 2.14 ± 0.02 * | 1.56 ± 0.07 * | |
| Average | 1.21 ± 0.03 | 1.53 ± 0.07 * | 2.76 ± 0.07 * | 1.83 ± 0.05 * | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Huang, M.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Luo, Q.; Pham, K.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, R.; Peng, Z.; et al. Absorption and Transport Characteristics and Mechanisms of Carnosic Acid. Biology 2021, 10, 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121278
Chen X, Huang M, Liu D, Li Y, Luo Q, Pham K, Wang M, Zhang J, Zhang R, Peng Z, et al. Absorption and Transport Characteristics and Mechanisms of Carnosic Acid. Biology. 2021; 10(12):1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121278
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xuexiang, Meigui Huang, Dongmei Liu, Yongze Li, Qiu Luo, Katherine Pham, Minghong Wang, Jing Zhang, Runbin Zhang, Zhixi Peng, and et al. 2021. "Absorption and Transport Characteristics and Mechanisms of Carnosic Acid" Biology 10, no. 12: 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121278
APA StyleChen, X., Huang, M., Liu, D., Li, Y., Luo, Q., Pham, K., Wang, M., Zhang, J., Zhang, R., Peng, Z., & Wu, X. (2021). Absorption and Transport Characteristics and Mechanisms of Carnosic Acid. Biology, 10(12), 1278. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121278







