Drought Tolerance and Application of Marker-Assisted Selection in Sorghum
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
Impact of Drought in Sorghum
2. Mechanisms of Drought Tolerance in Sorghum
2.1. Physiological Mechanisms
2.1.1. Stay-Green Sorghum
2.1.2. Leaf Rolling and Stomata Conductance
2.1.3. Chlorophyll Content
2.2. Morphological Mechanism
2.2.1. Roots and Root System
2.2.2. Biomass Production
2.2.3. Root to Shoot Ratio
2.3. Biochemical Mechanism
3. Marker-Assisted Selection for Enhancing Drought Tolerance in Sorghum
3.1. Molecular Markers in Sorghum Genotyping
3.2. Maker-Assisted Backcrossing
3.3. Foreground and Background Selection
3.4. QTL Mapping for Yield in Sorghum
3.5. QTL Pyramiding for Drought Tolerance in Sorghum
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panagoulia, D.; Dimou, G. Definition and Effects of Droughts; National Technical University of Athens: Athens, Greece, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bibi, A.; Sadaqat, H.A.; Tahir, M.H.N.; Akram, H.M. Screening of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor Var Moench) for drought tolerance at seedling stage in polyethylene glycol. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2012, 22, 671–678. [Google Scholar]
- Muui, C.W.; Muasya, R.M.; Kirubi, D.T. Participatory identification and evaluation of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench) landraces from lower eastern Kenya. Int. Res. J. Agric. Sci. Soil Sci. 2013, 3, 283–290. [Google Scholar]
- MacCarthy, D.S.; Adam, M.; Freduah, B.S.; Fosu-Mensah, B.Y.; Ampim, P.A.Y.; Ly, M.; Traore, P.S.; Adiku, S.G.K. Climate Change Impact and Variability on Cereal Productivity among Smallholder Farmers under Future Production Systems in West Africa. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrell, A.K.; Douglas, A.C.L. Maintaining green leaf area in grain sorghum increases yield in a water limited environment. In Proceedings of the Third Australian Sorghum Conference, Tamworth, Australia, 20–22 February 1996; Australian Institute of Agricultural Science, Occasional Publication: Melbourne, Australia, 1996. No. 93. [Google Scholar]
- Borrell, A.K.; Hammer, G.L. Nitrogen dynamics in stay-green and senescent sorghum hybrids grown under varying levels of water supply. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 1295–1307. [Google Scholar]
- Borrell, A.K.; van Oosterom, E.J.; Mullet, J.E.; George-Jaeggli, B.; Jordan, D.R.; Klein, P.E.; Hammer, G.L. Stay-green alleles individually enhance grain yield in sorghum under drought by modifying canopy development and water uptake patterns. New Phytol. 2014, 203, 817–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habyarimana, E.; Laureti, D.; Di Fonzo, N.; Lorenzoni, C. Biomass production and drought resistance at the seedling stage and in field conditions in sorghum. Maydica 2002, 47, 303–309. [Google Scholar]
- Kebede, H.; Subudhi, P.K.; Rosenow, D.T.; Nguyen, H.T. Quantitative trait loci influencing drought tolerance in grain sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2001, 103, 266–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, N.R.; Ragimasalawada, M.; Sabbavarapu, M.M.; Nadoor, S.; Patil, J.V. Detection and validation of stay-green QTL in post-rainy sorghum involving widely adapted cultivar, M35-1 and a popular stay-green genotype B35. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 909. [Google Scholar]
- Rosenow, D.T.; Clark, L.E. Drought tolerance in sorghum. In Proceedings of the 36th Annual Corn and Sorghum Industry Research Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 9–11 December 1981; pp. 18–31. [Google Scholar]
- Sarshad, A.; Talei, D.; Torabi, M.; Rafiei, F.; Nejatkhah, P. Morphological and biochemical responses of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench under drought stress. SN Appl. Sci. 2021, 3, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO). Climate Change and Food Security: Risks and Responses. 2015. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/i5188e/i5188e.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2021).
- Ogbaga, C.C.; Stepien, P.; Dyson, B.C.; Rattray, N.J.W.; Ellis, D.I.; Goodacre, R.; Johnson, G.N. Biochemical Analyses of Sorghum Varieties Reveal Differential Responses to Drought. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Saddam, S.; Bibi, A.; Sadaqat, H.A.; Usman, B.F. Comparison of 10 sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) genotypes under various water stress regimes. J. Anim. Plant Sci. 2014, 24, 1811–1820. [Google Scholar]
- Azzouz-Olden, F.; Hunt, A.G.; Dinkins, R. Transcriptome analysis of drought-tolerant sorghum genotypeSC56 in response to water stress reveals an oxidative stress defense strategy. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 3291–3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walulu, R.S.; Rosenow, D.T.; Wester, D.B.; Nguyen, H.T. Inheritance of the Stay-Green Trait in Sorghum. Crop Sci. 1994, 34, 970–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringo, J.; Beatrice, W.; Mary, M.; Deshpande, S.; Rathore, A.; Mneney, E.; Gudu, S. Combining 637 ability of some sorghum lines for dry lands and sub-humid environments of East Africa. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 10, 2048–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sory, S. Marker Assisted Selection for Post-Flowering Drought Tolerance in [Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench]. PhD Thesis, University of Ghana, Accra, Ghana, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Edema, R.; Amoding, G.L. Validating simple sequence repeats (SSR) markers for 514 introgression of stay- green quantitative trait loci (QTLs) into elite sorghum lines. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 14, 3101–3111. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.A.; Abbas, A.; Awan, S.I.; Jabran, K.; Gardezi, S.D.A. Correlated response of various morph physiological characters with grain yield in sorghum landraces at different growth phases. JAPS 2011, 21, 671–679. [Google Scholar]
- Ejeta, G.; Knoll, J.E. Marker-assisted selection in sorghum. In Genomic Assisted Crop Improvement; Varshney, R.K., Tuberosa, R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 187–205. [Google Scholar]
- Kapanigowda, M.H.; Perumal, R.; Djanaguiraman, M.; Aiken, R.M.; Tesso, T.; Prasad, P.V.; Little, C.R. Genotypic variation in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] exotic germplasm collections for drought and disease tolerance. Springer Plus 2013, 2, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eggen, M.; Ozdogan, M.; Zaitchik, B.; Ademe, D.; Foltz, J.; Simane, B. Vulnerability of sorghum production to extreme, sub-seasonal weather under climate change. Environ. Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Turner, N.C.; Khan, T.; Du, Y.L.; Xiong, J.L.; Colmer, T.D.; Devilla, R.; Stefanova, K.; Siddique, K.H.M. Response of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) to terminal drought: Leaf stomatal conductance, pod abscisic acid concentration, and seed set. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 1973–1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gano, B.; Dembele, J.S.B.; Tovignan, T.K.; Sine, B.; Vadez, V.; Diouf, D.; Audebert, A. Adaptation Responses to Early Drought Stress of West Africa Sorghum Varieties. Agronomy 2021, 11, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammer, G.L.; McLean, G.; Chapman, S.; Zheng, B.; Doherty, A.; Harrison, M.T.; van Oosterom, E.; Jordan, D. Crop design for specific adaptation in variable dry-land production environments. Crop. Pasture Sci. 2014, 65, 614–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craufurd, P.Q.; Peacock, J.M. Effect of Heat and Drought Stress on Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor). II. Grain Yield. Exp. Agric. 1993, 29, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadebe, S.T.; Modi, A.T.; Mabhaudhi, T. Drought tolerance and water use of cereal crops: A focus on sorghum as a food security crop in sub-Saharan Africa. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2017, 203, 177–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuinstra, M.R.; Grote, E.M.; Goldsbrough, P.B.; Ejeta, G. Genetic analysis of post-flowering drought tolerance and components of grain development in [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Mol. Breed. 1997, 3, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Wang, R.G.; Mao, G.; Koczan, J.M. Identification of Drought Tolerance Determinants by Genetic Analysis of Root Response to Drought Stress and Abscisic Acid. Plant Physiol. 2006, 142, 1065–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, A.; Ramzan, F.; Ramzan, Y.; Zulfiqar, F.; Ahsan, M.; Lim, K.B. Molecular Markers Improve Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crops: A Review. Plants 2020, 9, 1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badigannavar, A.; Teme, N.; de Oliveira, A.C.; Li, G.; Vaksmann, M.; Viana, V.E.; Ganapathi, T.R.; Sarsu, F. Physiological, genetic and molecular basis of drought resilience in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Plant Physiol. Rep. 2018, 23, 670–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, S.P.; Albrizio, R.; Vajja, N.R. Sorghum. In Crop Yield Response Water Stress; Steduto, P., Hsaio, T.C., Fereres, E., Raes, D., Eds.; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2012; Volume 66, pp. 144–151. [Google Scholar]
- Verma, R.; Kumar, R.; Nath, A. Drought Resistance Mechanism and Adaptation to Water Stress in Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Int. J. Bio-Resour. Stress Manag. 2018, 9, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, H.; Howarth, C.J. Five ways to stay-green. J. Exp. Bot. 2000, 51, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwamahonje, A.; Eleblu, J.S.Y.; Ofori, K.; Feyissa, T.; Deshpande, S.; Tongoona, T. Evaluation of Traits’ Performance Contributing to Drought Tolerance in Sorghum. Agronomy 2021, 11, 1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, S.; Chhabra, A.K.; Behl, R.K.; Bisht, S.S. Genotypic divergence analysis for stay-green characters in Wheat (Triticum aestivum L. em. Thell). South Pac. J. Nat. Sci. 2008, 26, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kassahun, B.; Bidinger, F.R.; Hash, C.T.; Kuruvinashetti, M.S. Stay-green expression in early generation sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] QTL introgression lines. Euphytica 2010, 172, 351–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrell, A.K.; Hammer, G.L.; Henzell, R.G. Does maintaining green leaf area in sorghum improve yield under drought? II. Dry matter production and yield. Crop Sci. 2000, 40, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenow, D.T. Breeding for resistance to root and stalk rot in Texas. In Sorghum Root and Stalk Diseases: A Critical Review: Proceedings of the Consultative Discussion of Research Needs and Strategies for Control of Sorghum Root and Stalk Diseases, Research Conference, Bellagio, Italy, 27 November–2 December 1983; ICRISAT: Andhra Pradesh, India, 1984; pp. 209–217. [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez, A.C.; Subudhi, P.K.; Rosenow, D.T.; Nguyen, H.T. Mapping QTLs associated with drought resistance in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amelework, B.; Shimelis, H.; Tongoona, P.; Laing, M. Physiological mechanisms of drought tolerance in sorghum, genetic basis and breeding methods: A review. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 2015, 10, 3029–3040. [Google Scholar]
- De Lacerda, C.F.; Cambraia, J.; Oliva, M.A.; Ruiz, H.A. Osmotic adjustment in roots and leaves of two sorghum genotypes under NaCl stress. Braz. J. Plant Physiol. 2003, 15, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadioglu, A.; Terzi, R. A dehydration avoidance mechanism: Leaf rolling. Bot. Rev. 2007, 73, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Wang, S.; Cao, B.; Cao, D.; Leng, G.; Li, H.; Yin, L.; Shan, L.; Deng, X. Genotypic Variation in Growth and Physiological Response to Drought Stress and Re-Watering Reveals the Critical Role of Recovery in Drought Adaptation in Maize Seedlings. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.; Huang, B. Involvement of antioxidants and lipid peroxidation in the adaptation of two cool-season grasses to localized drought stress. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2001, 45, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, M.; Karim, F. Screening of some cultivars/lines of black gram (Vigna mungo L. Hepper) for resistance to water stresses. Trop. Agric. 1991, 68, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Estill, K.; Delaney, R.H.; Smith, W.K.; Ditterlin, R.L. Water relations and productivity of alfalfa leaf chlorophyll variants. Crop Sci. 1991, 31, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbanti, L.; Sher, A.; Girolamo, G.D.; Cirillo, E.; Ansar, M. Growth and physiological response of two biomass sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] genotypes bred for different environments, to contrasting levels of soil moisture. Ital. J. Agron. 2015, 10, 673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getnet, Z.; Husen, A.; Fetene, M.; Yemata, G. Growth, Water Status, Physiological, Biochemical and Yield Response of Stay-Green Sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Varieties-A Field Trial Under Drought-Prone Area in Amhara Regional State, Ethiopia. J. Agron. 2015, 14, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bibi, A.; Sadaqat, H.A.; Akram, H.M.; Mohammed, M.I. Physiological markers for screening sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) germplasm under water stress condition. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 2010, 12, 451–455. [Google Scholar]
- Grieder, C.; Trachsel, S.; Hund, A. Early vertical distribution of roots and its association with drought tolerance in tropical maize. Plant Soil 2014, 377, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routley, R.; Broad, I.; McLean, G.; Whish, J.; Hammer, G. The effect of row configuration on yield reliability in grain sorghum: I. Yield, water use efficiency and soil water extraction. In Proceedings of the Eleventh Australian Agronomy Conference, Geelong, Australia, 2–6 February 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Robertson, M.J.; Fukai, S.; Ludlow, M.M.; Hammer, G.L. Water extraction by grain sorghum in a sub-humid environment. II. Extraction in relation to root growth. Field Crop. Res. 1993, 33, 99–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blum, A. Sorghum physiology. In Physiology and Biotechnology Integration for Plant Breeding; Nguyen, H.T., Blum, A., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2004; pp. 141–223. [Google Scholar]
- Yambao, E.B.; Ingram, K.T.; Real, J.G. Root xylem influence on the water relations and drought resistance of rice. J. Exp. Bot. 1992, 43, 925–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, J.P. Steep, cheap and deep: An ideotype to optimize water and N acquisition by maize root systems. Ann. Bot. 2013, 112, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Chen, X.; Hong, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Xu, P.; Ke, S.D.; Liu, H.; Zhu, J.; Oliver, D.J.; Xiang, C. Activated expression of an Arabidopsis HD-START protein confers drought tolerance with improved root system and reduced stomatal density. Plant Cell 2008, 20, 1134–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simova-Stoilova, L.; Vassileva, V.; Feller, U. Selection and Breeding of Suitable Crop Genotypes for Drought and Heat Periods in a Changing Climate: Which Morphological and Physiological Properties Should Be Considered? Agriculture 2016, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogbaga, C.C.; Bajhaiya, A.K.; Gupta, S.K. Improvements in biomass production: Learning lessons from the bioenergy plants maize and sorghum. J. Environ. Biol. 2019, 40, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottman, M.; Kimball, B.; Pinter, P.; Wall, G.; Vanderlip, R.; Leavitt, S.; Lamorte, R.; Matthias, A.; Brooks, T. Elevated Co increases 2 sorghum biomass under drought conditions. New Phytol. 2001, 150, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sher, A.; Barbanti, L.; Ansar, M. Growth response and plant water status in forage sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] cultivars subjected to decreasing levels of soil moisture. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2013, 7, 801–808. [Google Scholar]
- Tari, I.; Laskay, G.; Takacs, Z.; Poor, P. Responses of Sorghum to Abiotic Stresses: A Review. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2012, 199, 264–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assefa, Y.; Staggenborg, S.A. Phenotypic changes in grain sorghum over the last five decades. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 2011, 197, 249–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.M.; Nadira, U.A.; Cao, F.; He, X.; Zhang, G.; Wu, F.J.P. Physiological and molecular analysis on root growth associated with the tolerance to aluminium and drought individual and combined in Tibetan wild and cultivated barley. Planta 2016, 243, 973–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Wei, F.; Huo, Y.; Xia, Z.J.; Fi, P.S. Comparative physiological and molecular analyses of two contrasting flue-cured tobacco genotypes under progressive drought stress. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoah, J.N.; Antwi-Berko, D. Comparative Physiological, Biochemical and Transcript Response to Drought in Sorghum Genotypes. Biotechnol. J. Int. 2020, 24, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishor, P.B.K.; Sangam, S.; Amrutha, R.; Laxmi, P.; Naidu, K.; Rao, K.R.S.S.; Reddy, K.J.; Theriapan, P.; Sreenivasulu, N. Regulation of proline biosynthesis, degradation, uptake and transport in higher plants: Its implications in plant growth and abiotic stress tolerance. Curr. Sci. 2005, 88, 424–438. [Google Scholar]
- Ogbaga, C.C.; Stepien, P.; Johnson, G.N. Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) varieties adopt strongly contrasting strategies in response to drought. Physiol. Plant. 2014, 152, 389–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadeem, M.A.; Nawaz, M.A.; Shahid, M.Q.; Doğan, Y.; Comertpay, G.; Yıldız, M.; Hatipoğlu, R.; Ahmad, F.; Alsaleh, A.; Labhane, N.; et al. DNA molecular markers in plant breeding: Current status and recent advancements in genomic selection and genome editing. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2018, 32, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhare, A.A.; Sakhare, S.B.; Kulwal, P.L.; Dhumale, D.B.; Kharkar, A. RAPD Profile studies in Sorghum foridentification of hybrids and their parents. Int. J. Integr. Biol. 2008, 3, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Motlhaodi, T.; Geleta, M.; Chite, S.; Fatih, M.; Ortiz, R.; Bryngelsson, T. Genetic diversity in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] germplasm from Southern Africa as revealed by microsatellite markers and agro-morphological traits. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2016, 63, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, M.B. Genetic diversity: From protein electrophoresis to RAPDs. In Proceedings of the Fiftieth Annual Corn and Sorghum Industry Research Conference, Chicago, IL, USA, 6–7 December 1995; pp. 256–271. [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich, P.R.; Doebley, J. Restriction fragment variation in the nuclear and chloroplast genomes of cultivated and wild Sorghum bicolor. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1992, 85, 293–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vos, P.; Hogers, R.; Bleeker, M.; Reijans, M.; van de Lee, T.; Hornes, M.; Frijters, A.; Pot, J.; Peleman, J.; Kuiper, M. AFLP: A new technique for DNA finger printing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1995, 23, 4407–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.; McCelland, M. Fingerprinting genomes using PCR with arbitrary primers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990, 18, 7213–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasoma, C.; Lungu, D.; Mweetwa, A.; Munyinda, K.; Kaimoyo, E. Microsatellite Marker Application in the Assessement of Sorghum Genetic Diversity. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Advances in Agricultural, Biological and Environmental Sciences, London, UK, 22–23 July 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Disasa, T.; Feyissa, T.; Admassu, B.; Paliwal, R.; Villiers, S.D.; Odeny, D.A. Molecular evaluation of Ethiopian sweet sorghum germplasm and their contribution to regional breeding programs. Aust. J. Crop Sci. 2016, 10, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakiyama, N.S.; Ramos, H.C.C.; Caixeta, E.T.; Pereira, M.G. Plant breeding with marker-assisted selection in Brazil. Crop Breed. Appl. Biotechnol. 2014, 14, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calviño, M.; Miclaus, M.; Bruggmann, R.; Messing, J. Molecular Markers for Sweet Sorghum Based on Microarray Expression Data. Rice 2009, 2, 129–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Rafii, M.Y.; Ismail, M.R.; Mahmood, M.; Rahim, H.A.; Alam, M.A.; Ashkani, S.; Malek, M.A.; Latif, M.A. Marker-assisted backcrossing: A useful method for rice improvement. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2015, 29, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prohens, J. Plant breeding: A success story to be continued thanks to the advances in genomics. Front. Plant Sci. 2011, 2, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, N.P.; Toole, O.; John, C. Field Screening for Drought Tolerance in Crop Plants with Emphasis on Rice. In Proceedings of the International Workshop on Field Screening for Drought Tolerance in Rice 2002, Patancheru, India, 11–14 December 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Crasta, O.R.; Xu, W.W.; Rosenow, D.T.; Mullet, J.; Nguyen, H.T. Mapping of post-flowering drought resistance traits in grain sorghum: Association between QTLs influencing premature senescence and maturity. Mol. Genet. Genom. 1999, 262, 579–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, K.R. Genetic Analysis of the Sorghum bicolor Stay-Green Drought Tolerance Trait. Ph.D. Thesis, Texas A&M University, College Station, TX, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Subudhi, P.K.; Rosenow, D.T.; Nguyen, H.T. Quantitative trait loci for the stay green trait in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench): Consistency across genetic backgrounds and environments. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2000, 101, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hash, C.T.; Raj, A.G.B.; Lindup, S.; Sharma, A.; Beniwal, C.R.; Folkertsma, R.T.; Mahalakshmi, V.; Zerbini, E.; Blummel, M. Opportunities for marker- assisted selection (MAS) to improve the feed quality of crop residues in pearl millet and sorghum. Field Crop. Res. 2003, 84, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baloch, F.S.; Alsaleh, A.; Shahid, M.Q.; Çiftçi, V.; de Miera, L.E.S.; Aasim, M.; Nadeem, M.A.; Aktaş, H.; Özkan, H.; Hatipoğlu, R. A Whole Genome DArTseq and SNP Analysis for Genetic Diversity Assessmentin Durum Wheat from Central Fertile Crescent. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0167821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwamahonje, A.; Eleblu, J.S.Y.; Ofori, K.; Feyissa, T.; Deshpande, S.; Garcia-Oliveira, A.L.; Bohar, R.; Kigoni, M.; Tongoona, P. Introgression of QTLs for Drought Tolerance into Farmers’ Preferred Sorghum Varieties. Agriculture 2021, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menz, M.A.; Klein, R.R.; Mullet, J.E.; Obert, J.A.; Unruh, N.C.; Klein, P.E. A high-density genetic map of Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench based on 2926 AFLP, RFLP and, SSR markers. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 483–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, R.N.; Madhusudhana, R.; Mohan, S.M.; Chakravarthi, D.V.; Mehtre, S.P.; Seetharama, N.; Patil, J.V. [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] Mapping QTL for grain yield and other agronomic traits in post-rainy sorghum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 1921–1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholova, J.; Deshpande, S.; Madhusudhana, R.; Blummel, M.; Borrell, A.; Hammer, G. Improving Post-Rainy Sorghum Varieties to Meet the Growing Grain and Fodder Demand in India—Phase 2; Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research: Canberra, Australia, 2019; p. 29. [Google Scholar]
- Paterson, A.H.; Bowers, J.E.; Bruggmann, R.; Dubchak, I.; Grimwood, J.; Gundlach, H.; Haberer, G.; Hellsten, U.; Mitros, T.; Poliakov, A.; et al. The Sorghum bicolor genome and the diversification of grasses. Nature 2009, 457, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mace, E.S.; Singh, V.; Van Oosterom, E.J.; Hammer, G.L.; Hunt, C.H.; Jordan, D.R. QTL for nodal root angle in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] co-locate with QTL for traits associated with drought adaptation. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2012, 124, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris-Shultz, K.R.; Hayes, C.M.; Knoll, J.E. Mapping QTLs and Identification of Genes Associated with Drought Resistance in Sorghum. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1931, 11–40. [Google Scholar]
- Gorthy, S.; Narasu, L.; Gaddameedi, A.; Sharma, H.C.; Kotla, A.; Deshpande, S.P.; Are, A.K. Introgression Introgression of Shoot Fly [Atherigona soccata (L.) Moench] Resistance QTLs into Elite Post-rainy Season Sorghum Varieties Using Marker Assisted Backcrossing (MABC). Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouedraogo, N.; Sanou, J.; Gracen, V.; Tongoona, P. Incorporation of stay-green Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) in elite sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] variety through marker-assisted selection at early generation. J. Appl. Biosci. 2017, 111, 10867–10876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussmann, B.I.G.; Hess, D.E.; Omanya, G.O.; Folkertsma, R.T.; Reddy, B.V.S.; Kayentao, M.; Welz, H.G.; Geiger, H.H. Genomics regions influencing resistance to the parasitic weed Striga hermonthica in two recombinant inbred population of sorghum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2004, 109, 1005–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Child, K.L.; Faridi, M.I.; Menz, M.A.; Klein, R.R.; Klein, P.E.; Price, H.J.; Mullet, J.E.; Stelly, D. Integrated karyotyping of sorghum by in situ hybridization of landed BACS. Genome 2002, 45, 402–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukumaran, S.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Zhu, C.; Bai, G.; Perumal, R.; Tuinstra, M.R.; Prasad, P.V.V.; Sharon, E.; Mitchell, S.E.; et al. QTL Mapping for Grain Yield, Flowering Time, and Stay-Green Traits in Sorghum with Genotyping-by-Sequencing Marker. Crop Sci. 2016, 56, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hospital, F. Size of donor chromosome segments around introgressed loci and reduction of linkage drag in marker-assisted backcross programs. Genetics 2001, 158, 1363–1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidou, M.; Souley, A.K.M.; Kapran, I.; Souleymane, O.; Danquah, E.Y.; Ofori, K.; Gracen, V.; Ba, M.N. Genetic Variability and Its Implications on Early Generation Sorghum Lines Selection for Yield, Yield Contributing Traits and Resistance to Sorghum Midge. Int. J. Agron. 2018, 2018, 1864797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, G.; Zhai, G.; Feng, Q.; Yan, S.; Wang, A.; Zhao, Q.; Shao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zou, J.; Han, B.; et al. Identification of QTLs for eight agronomically important traits using an ultra-high-density map based on SNPs generated from high-throughput sequencing in sorghum under contrasting photoperiods. J. Exp. Bot. 2012, 63, 5451–5462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, B.F.; Kavil, S.P.; Girma, Y.; Arun, S.S.; Dadakhalandar, D.; Gurusiddesh, B.H.; Patil, A.M.; Thudi, M.; Bhairappanavar, S.; Narayana, Y.; et al. Molecular mapping of genomic regions harbouring QTLs for root and yield traits in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2013, 19, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardino, K.C.; Pastina, M.M.; Menezes, C.B.; de Sousa, S.M.; Maciel, L.S.; Carvalho, G., Jr.; Guimarães, C.T.; Barros, B.A.; Silva1, L.D.; Carneiro, P.C.S.; et al. The genetic architecture of phosphorus efficiency in sorghum involves pleiotropic QTL for root morphology and grain yield under low phosphorus availability in the soil. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shehzad, T.; Okuno, K. QTL mapping for yield and yield-contributing traits in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) with genome-based SSR markers. Euphytica 2015, 203, 17–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haussmann, B.I.G.; Mahalakshmi, V.; Reddy, B.V.S.; Seetharama, N.; Hash, C.T.; Geiger, H.H. QTL mapping of stay-green in two sorghum recombinant inbred populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2002, 106, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, S.R.; Fakrudin, B. Marker assisted pyramiding of root volume QTLs to improve drought tolerance in rabi sorghum. Res. Crop. 2017, 18, 683–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, S.; Matsuoka, M. Genetic approaches to crop improvement: Responding to environmental and population changes. Nature 2008, 9, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamal, N.M.; Gorafi, Y.S.A.; Ghanim, A.M.A. Performance of Sorghum stay-green introgression lines under post-flowering drought. Int. J. Plant Res. 2017, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar]
- Ongom, P.O. Association Mapping of Gene Regions for Drought Tolerance and Agronomic Traits in Sorghum. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]

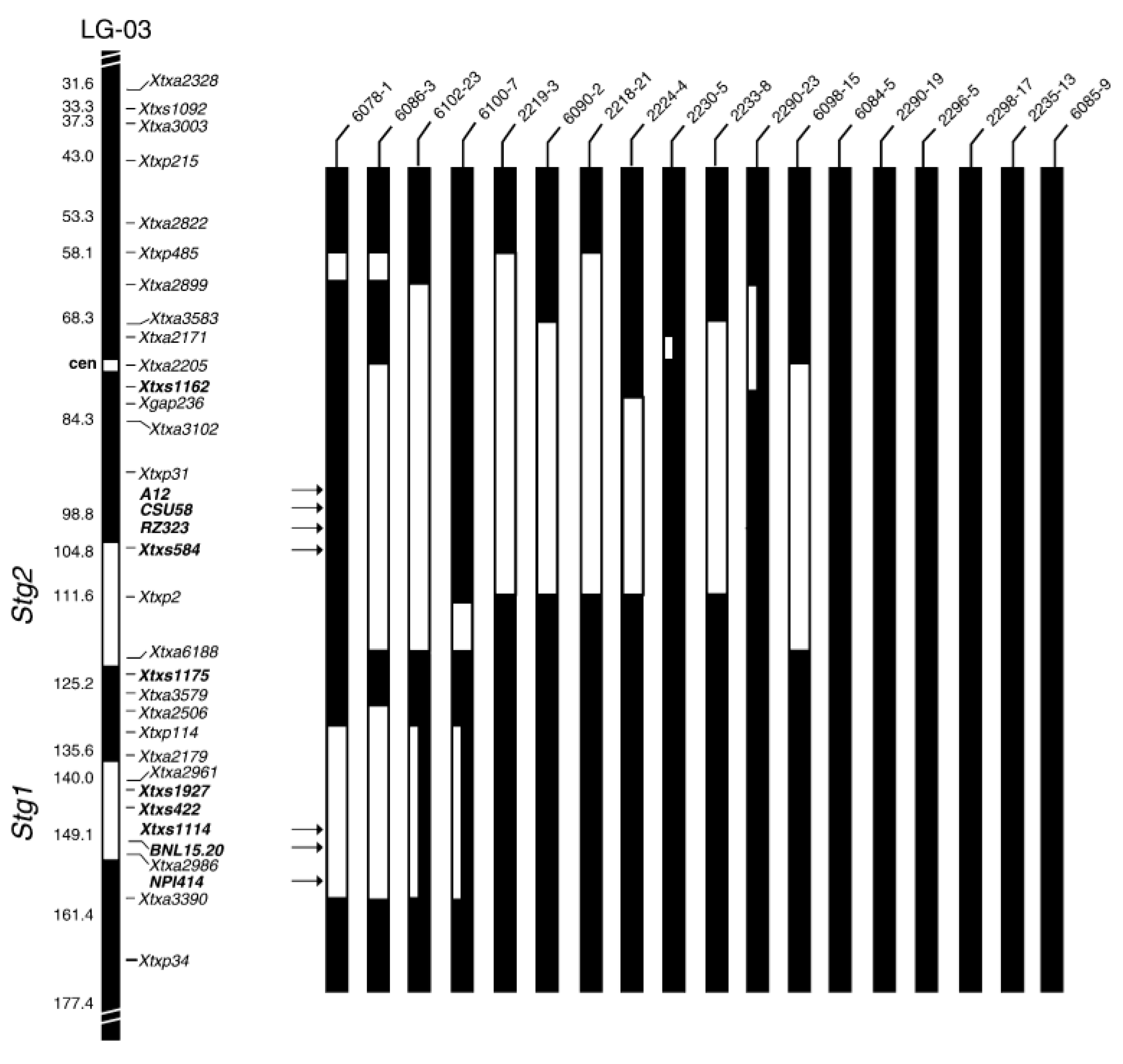


| Molecular Marker | QTL | Position in Chromosome | PV (%) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Xtxp114, Xtxp38, xiabxp 3 7 8, SSR markers | Stg1 | SB1-03 | 20 | [87,91] |
| XnhsbSFCILP67, Xtxp120, Xtxs584, and Xtxp31, SSR markers | Stg2 | SB1-03 | 30 | [87] |
| Xtxs1307, Xtxs1111, Xtxp1, Xtxp56, Xtxp286, SSRs markers | Stg3 | SB1-02 | 16 | [42,86] |
| Xtxs713, Xtxs387, Xtxp225, Xtxp15, SSR markers | Stg4 | SB1-05 | 10 | [42,86,92] |
| snpSB00049, snpSB00053, and snpSB00054, SNPs markers | Stg3A | SB1-02 | 31 | [90,93] |
| snpSB00101, snpSB00102, and snpSB00103, SNPs markers | Stg3B | SB1-02 | 31 | [90,93] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mwamahonje, A.; Eleblu, J.S.Y.; Ofori, K.; Deshpande, S.; Feyissa, T.; Tongoona, P. Drought Tolerance and Application of Marker-Assisted Selection in Sorghum. Biology 2021, 10, 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121249
Mwamahonje A, Eleblu JSY, Ofori K, Deshpande S, Feyissa T, Tongoona P. Drought Tolerance and Application of Marker-Assisted Selection in Sorghum. Biology. 2021; 10(12):1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121249
Chicago/Turabian StyleMwamahonje, Andekelile, John Saviour Yaw Eleblu, Kwadwo Ofori, Santosh Deshpande, Tileye Feyissa, and Pangirayi Tongoona. 2021. "Drought Tolerance and Application of Marker-Assisted Selection in Sorghum" Biology 10, no. 12: 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121249
APA StyleMwamahonje, A., Eleblu, J. S. Y., Ofori, K., Deshpande, S., Feyissa, T., & Tongoona, P. (2021). Drought Tolerance and Application of Marker-Assisted Selection in Sorghum. Biology, 10(12), 1249. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10121249






