Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies ANKRD36 Gene as a Novel and Common Biomarker of Disease Progression in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
Abstract
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Definitions of Clinical Phases of Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML) for Staging
2.3. Criteria for Assessment of Treatment Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia
2.3.1. Complete Hematological Response (CHR)
2.3.2. Cytogenetic Response (CyR)
2.3.3. Criteria for Calculation of Molecular Response (MR)
2.4. Criteria for Calculation of European LeukemiaNet (ELN) Responses and Survival
2.5. Criteria for Documenting Adverse Events
2.6. Ethical Approval
2.7. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
2.8. Whole-Exome Sequencing
2.9. Exome Sequencing Data Analysis
2.10. Primary Analysis
2.11. Validation of Mutation by Sanger Sequencing
2.12. Statistical Analysis of Patient Clinical Data
2.13. Protein Modeling Studies
3. Results
| Characteristics | Japan | Iraq [43] | US [44] | EU [45] | India [46] | Our Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| # of Patients | 506 | 100 | 1106 | 210 | 90 | 141 |
| Mean Age, years | 51.7 | 41.1 | 55 | 38.6 | 36.4 | |
| Male | 349 | 58% | 59% | 54% | 57% | 60.2% |
| Female | 157 | 42% | 41% | 46% | 42.2% | 39.8% |
| Male:Female Ratio | 2.2:1 | 1.4:1 | 1.4:1 | 1:1 | 1.4:1 | 1.6:1 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) Mean | 4 | 12.28 | 12.6 | 9.41 | 10.1 | |
| WBC count (×109/L) Mean | 45.26 | 19 | 80.2 | 182 | 317.9 | |
| Platelets (×109/L) Mean | 47.2 | 341.5 | 77 | 373 | 328 | 400.2 |
| Characteristics | Patient Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CP-CML, n (%) | AP-CML, n (%) | BC-CML, n (%) | p-Value | |
| # of Patients | 123 (87.2) | 6 (4.3) | 12 (8.5) | |
| Age, Years | ||||
| Mean (Range) | 35.5 (9–7) | 35.6 (27–43) | 38.1 (29–50) | |
| Gender | ||||
| Male | 74 (60.2) | 4 (66.67) | 8 (66.7) | p = 0.6004 |
| Female | 49 (39.8) | 2 (33.33) | 4 (33.3) | p = 0.5987 |
| p-Value | p = 0.0272 | p = 0.3980 | p = 0.2933 | |
| Male:Female Ratio | 1.5:1 | 2:1 | 2:1 | |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) Mean | 10.1 | |||
| <12g/dl | 69 (56.1) | 5 (83.3) | 9 (75) | p = 0.0642 |
| >12g/dl | 14 (11.4) | 1 (16.7) | 3 (25) | p = 0.2609 |
| p-Value | p = 0.0024 | p = 0.2154 | p = 0.1380 | |
| WBC count (×109/L) Mean | 313.7 | 315 | 325 | |
| <50 | 20 (16.3) | 1 (20) | 2 (16.7) | p = 0.8276 |
| >/=50 | 64 (52) | 5 (80) | 10 (83.3) | p = 0.0184 |
| p-Value | p = 0.0052 | p = 0.2752 | p = 0.0661 | |
| Platelets (×109/L) Mean | 400.2 | |||
| <450 | 75 (61) | 4 (66.7) | 10 (83.3) | p = 0.2528 |
| >/=450 | 33 (26.8) | 2 (33.3) | 2 (16.7) | p = 0.8722 |
| p-Value | p = 0.0011 | p = 0.4786 | p = 0.0661 | |
| Imatinib | ||||
| Yes | 82 (66.7) | 4 (66.7) | 7 (58.3) | p = 0.7260 |
| Nilotinib as 2nd Line | ||||
| Yes | 41 (33.3) | 4 (66.7) | 8 (66.7) | p = 0.0065 |
| Hydroxyurea | ||||
| Yes | 82 (66.7) | 3 (50) | 10 (83.3) | p = 0.9967 |
| Interferon | ||||
| Yes | 41 (33.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | p = 0.0038 |
| Chemotherapy | ||||
| Yes | 10 (8.1) | 4 (66.7) | 9 (75) | p < 0.0001 |
| Splenomegaly | ||||
| <5 cm | 4 (3.3) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | p = 0.4358 |
| 5–8 cm | 9 (7.3) | 1 (16.7) | 3 (25) | p = 0.0619 |
| >8 cm | 70 (56.9) | 5 (83.3) | 9 (75) | p = 0.0732 |
| No splenomegaly | 40 (32.5) | 0 (0) | 0 | p = 0.0044 |
| Hepatomegaly | ||||
| Yes | 35 (28.5) | 4 (66.7) | 8 (66.7) | p = 0.0014 |
| Anemia | ||||
| Yes | 97 (78.9) | 5 (83.3) | 9 (75) | p = 0.9807 |
| Pregnant | ||||
| Yes | 4 (8.2) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | p = 0.2090 |
| Survival Status | ||||
| Confirmed Deaths | 10 (8.1) | 0 (0) | 9 (75) | p = 0.0003 |
| Alive at Last Follow-Up (Overall Survival) | 113 (91.9) | 6 (100) | 3 (25) | p = 0.0003 |
| Variant Type | ID 1 | ID 2 | ID 3 | ID 4 | TD 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of SNPs | 88,892 | 90,562 | 88,725 | 90,441 | 86,484 |
| Synonymous Variants | 11,945 | 12,268 | 11,810 | 12,053 | 11,444 |
| Missense Variants | 11,139 | 11,467 | 11,116 | 11,408 | 10,776 |
| Stop Gained | 88 | 111 | 107 | 109 | 107 |
| Stop Lost | 41 | 40 | 48 | 44 | 41 |
| Number of INDELs | 9911 | 10,000 | 10,126 | 10,003 | 9637 |
| Frameshift Variants | 312 | 310 | 322 | 322 | 296 |
| Inframe Insertions | 178 | 169 | 165 | 175 | 166 |
| Inframe Deletions | 200 | 195 | 208 | 186 | 184 |
| % found in dbSNP142 | 97.1 | 97.0 | 96.9 | 96.9 | 96.9 |
| Het/Hom Ratio | 1.4 | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.6 | 1.1 |
| Ts/Tv Ratio | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 2.3 |
3.1. Exome Sequencing: Initial Screening for Novel Genes
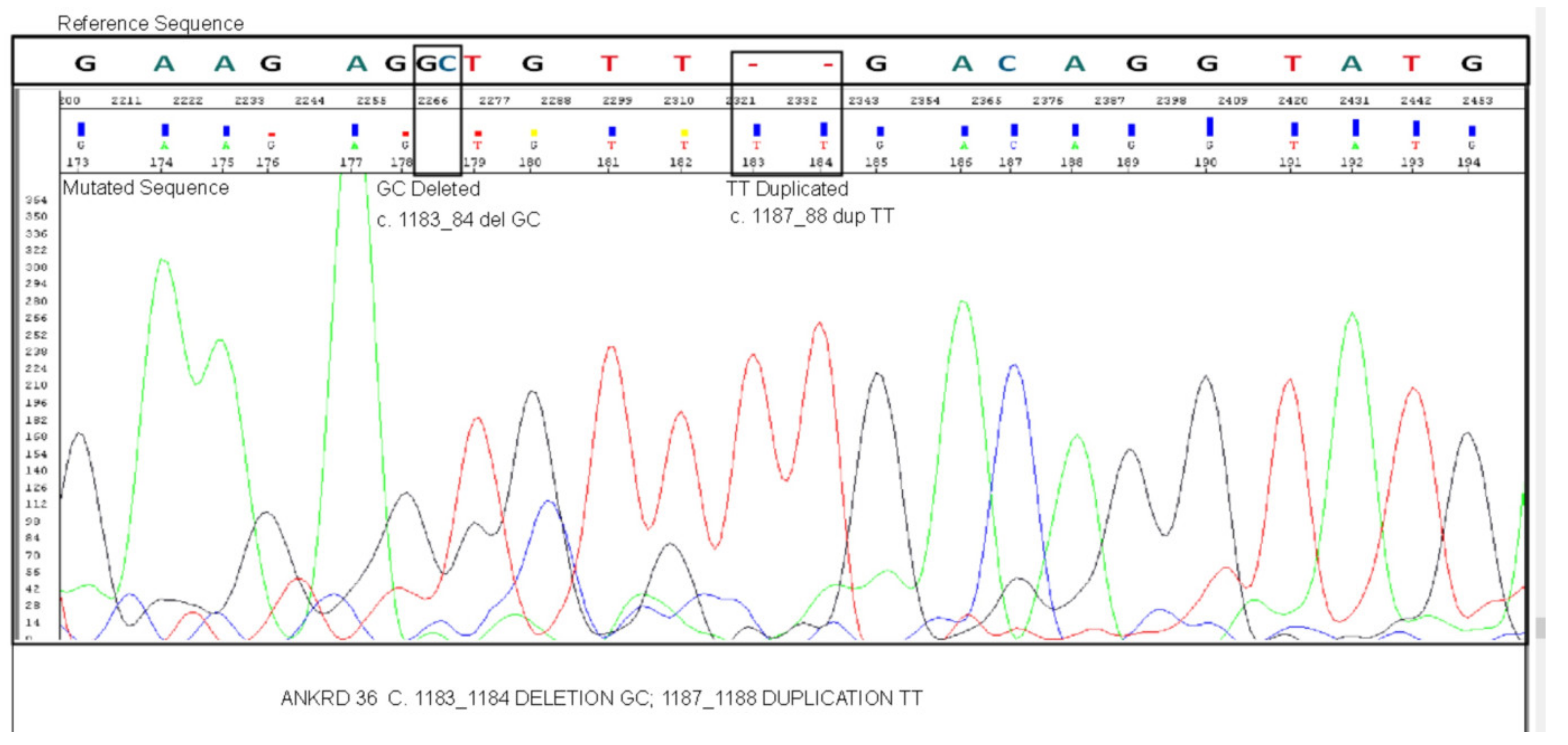
3.2. Mutation Validation by Sanger Sequencing
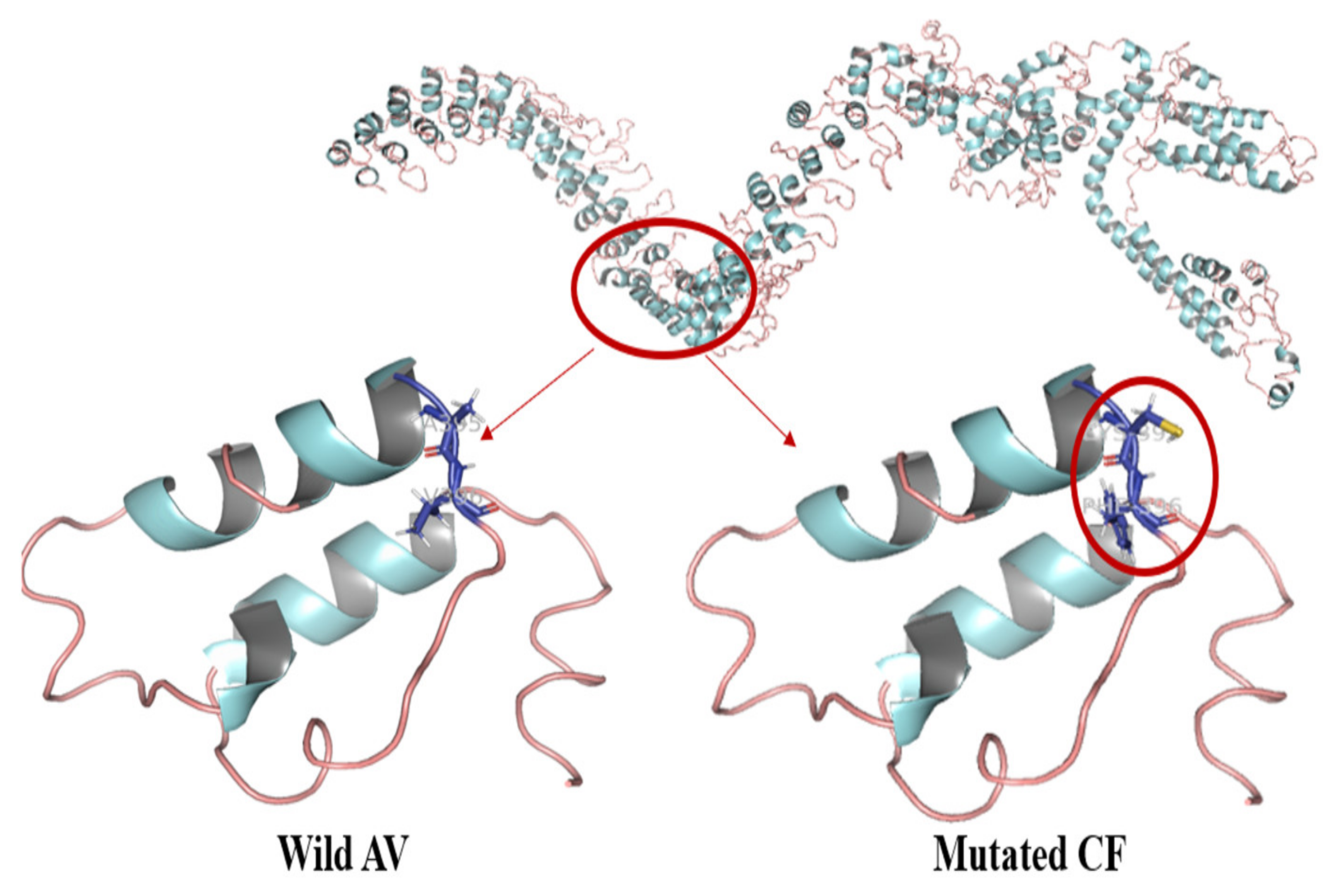
3.3. Protein Modeling Studies
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ning, L.; Hu, C.; Lu, P.; Que, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, D. Trends in disease burden of chronic myeloid leukemia at the global, regional, and national levels: A population-based epidemiologic study. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flis, S.; Chojnacki, T. Chronic myelogenous leukemia, a still unsolved problem: Pitfalls and new therapeutic possibilities. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 825–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, M.M.; Santos, M.L.C.; Marques, H.S.; Gonçalves, V.L.d.S.; Araújo, G.R.L.; Lopes, L.W.; Apolonio, J.S.; Silva, C.S.; Santos, L.K.D.S.; Cuzzuol, B.R.; et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia-from the Philadelphia chromosome to specific target drugs: A literature review. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 12, 69–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgeon, M.L. Clinical Hematology: Theory and Procedures, 5th ed.; Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 363–367. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, J.; Lang, F. Third-line therapy for chronic myeloid leukemia: Current status and future directions. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasser, A.; Hussein, A.; Chamba, C.; Yonazi, M.; Mushi, R.; Schuh, A.; Luzzatto, L. Molecular response to imatinib in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in Tanzania. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 1403–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.-J.; Liu, Y.-F.; Xu, L.-Z.; Long, Z.-J.; Huang, D.; Yang, Y.; Liu, B.; Feng, J.-X.; Pan, Y.-J.; Yan, J.-S.; et al. The Philadelphia chromosome in leukemogenesis. Chin. J. Cancer 2016, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbour, E.; Kantarjian, H. Chronic myeloid leukemia: 2018 update on diagnosis, therapy and monitoring. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 442–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintás-Cardama, A.; Cortes, J. Molecular biology of bcr-abl1–positive chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009, 113, 1619–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.A.M. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia in the Era of Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors: An Evolving Paradigm of Molecularly Targeted Therapy. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2016, 20, 315–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soverini, S.; Abruzzese, E.; Bocchia, M.; Bonifacio, M.; Galimberti, S.; Gozzini, A.; Iurlo, A.; Luciano, L.; Pregno, P.; Rosti, G.; et al. Next-generation sequencing for BCR-ABL1 kinase domain mutation testing in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: A position paper. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sessions, J. Chronic myeloid leukemia in 2007. Am. J. Heal. Pharm. 2007, 64, S4–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valent, P.; Herndlhofer, S.; Schneeweiß, M.; Boidol, B.; Ringler, A.; Kubicek, S.; Gleixner, K.V.; Hoermann, G.; Hadzijusufovic, E.; Müllauer, L.; et al. TKI rotation-induced persistent deep molecular response in multi-resistant blast crisis of Ph+ CML. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 23061–23072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotagama, K.; Chang, Y.; Mangone, M. miRNAs as Biomarkers in Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Drug Dev. Res. 2015, 76, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shet, A.; Jahagirdar, B.N.; Verfaillie, C. Chronic myelogenous leukemia: Mechanisms underlying disease progression. Leukemia 2002, 16, 1402–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branford, S.; Wang, P.; Yeung, D.T.; Thomson, D.; Purins, A.; Wadham, C.; Shahrin, N.H.; Marum, J.E.; Nataren, N.; Parker, W.T.; et al. Integrative genomic analysis reveals cancer-associated mutations at diagnosis of CML in patients with high-risk disease. Blood 2018, 132, 948–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Wu, M.; Sun, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J. Identifying Dysregulated lncRNA-Associated ceRNA Network Biomarkers in CML Based on Dynamical Network Biomarkers. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 5189549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baccarani, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Rosti, G.; Hochhaus, A.; Soverini, S.; Apperley, J.F.; Cervantes, F.; Clark, R.E.; Cortes, J.E.; Guilhot, F.; et al. European LeukemiaNet recommendations for the management of chronic myeloid leukemia: 2013. Blood 2013, 122, 872–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, J.E.; Talpaz, M.; O’Brien, S.; Faderl, S.; Garcia-Manero, G.; Ferrajoli, A.; Verstovsek, S.; Rios, M.B.; Shan, J.; Kantarjian, H.M. Staging of chronic myeloid leukemia in the imatinib era. Cancer 2006, 106, 1306–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttorp, M.; Millot, F.; Sembill, S.; Deutsch, H.; Metzler, M. Definition, Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Essential Criteria for Diagnosis of Pediatric Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Cancers 2021, 13, 798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cagnetta, A.; Garuti, A.; Marani, C.; Cea, M.; Miglino, M.; Rocco, I.; Palermo, C.; Fugazza, G.; Cirmena, G.; Colombo, N.; et al. Evaluating treatment response of chronic myeloid leukemia: Emerging science and technology. Curr. Cancer Drug Targets 2013, 13, 779–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, N.; White, E.H.; Müller, M.C.; Saglio, G.; Hochhaus, A. Standardized definitions of molecular response in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2012, 26, 2172–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahon, F.-X.; Etienne, G. Deep Molecular Response in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: The New Goal of Therapy? Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, J.; Rixe, O. Overall Survival: Still the Gold Standard. Cancer J. 2009, 15, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, J.; Goel, M.; Khanna, P. Understanding survival analysis: Kaplan-Meier estimate. Int. J. Ayurveda Res. 2010, 1, 274–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Medical Association. Ethics Unit. Declaration of Helsinki 2007. Available online: www.wma.net/e/ethicsunit/helsinki.htm (accessed on 11 February 2021).
- Goodyear, E.; Krleza-Jeric, M.D.; Lemmens, K. The Declaration of Helsinki. BMJ 2007, 335, 624–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, S.C.; Lin, S.-W.; Lai, K.-M. An evaluation of the performance of five extraction methods: Chelex® 100, QIAamp® DNA Blood Mini Kit, QIAamp® DNA Investigator Kit, QIAsymphony® DNA Investigator® Kit and DNA IQ™. Sci. Justice 2015, 55, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Absar, M.; Mahmood, A.; Akhtar, T.; Basit, S.; Ramzan, K.; Jameel, A.; Afzal, S.; Ullah, A.; Qureshi, K.; Alanazi, N.; et al. Whole exome sequencing identifies a novel FANCD2 gene splice site mutation associated with disease progression in chronic myeloid leukemia: Implication in targeted therapy of advanced phase CML. Pak. J Pharm. Sci. 2020, 33, 1419–1426. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Retterer, K.; Juusola, J.; Cho, M.T.; Vitazka, P.; Millan, F.; Gibellini, F.; Vertino-Bell, A.; Smaoui, N.; Neidich, J.; Monaghan, K.G.; et al. Clinical application of whole-exome sequencing across clinical indications. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AlAsiri, S.; Basit, S.; Wood-Trageser, M.; Yatsenko, S.A.; Jeffries, E.P.; Surti, U.; Ketterer, D.M.; Afzal, S.; Ramzan, K.; Haque, M.F.-U.; et al. Exome sequencing reveals MCM8 mutation underlies ovarian failure and chromosomal instability. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 125, 258–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carson, A.R.; Smith, E.N.; Matsui, H.; Brækkan, S.K.; Jepsen, K.; Hansen, J.-B.; Frazer, A.K. Effective filtering strategies to improve data quality from population-based whole exome sequencing studies. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsiatis, A.C.; Norris-Kirby, A.; Rich, R.G.; Hafez, M.J.; Gocke, C.D.; Eshleman, J.R.; Murphy, K.M. Comparison of Sanger Sequencing, Pyrosequencing, and Melting Curve Analysis for the Detection of KRAS Mutations: Diagnostic and Clinical Implications. J. Mol. Diagn. 2010, 12, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, T.F.; Mullikin, J.C.; Biesecker, L.G.; Program, T.N.C.S. Systematic Evaluation of Sanger Validation of Next-Generation Sequencing Variants. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 647–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Horta, O.; Duman, D.; Foster, J.; Sırmacı, A.; Gonzalez, M.; Mahdieh, N.; Fotouhi, N.; Bonyadi, M.; Cengiz, F.B.; Menendez, I.; et al. Whole-Exome Sequencing Efficiently Detects Rare Mutations in Autosomal Recessive Nonsyndromic Hearing Loss. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Foundation for Statistical Computing; R Development Core Team R. A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Development Core Team R: Vienna, Austria, 2008; ISBN 3-900051-07-0. [Google Scholar]
- Sokal, J.E.; Cox, E.B.; Baccarani, M.; Tura, S.; Gomez, G.A.; Robertson, J.E.; Tso, C.Y.; Brau, T.J.; Clarkson, B.D.; Cervantes, F.; et al. Prognostic discrimination in good-risk chronic granulocytic leukemia. Blood 1984, 63, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasford, J.; Pfirrmann, M.; Hehlmann, R.; Allan, N.C.; Baccarani, M.; Kluin-Nelemans, J.C.; Alimena, G.; Steegmann, J.L.; Ansari, H. A New Prognostic Score for Survival of Patients with Chronic Myeloid Leukemia Treated With Interferon Alfa Writing Committee for the Collaborative CML Prognostic Factors Project Group. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1998, 90, 850–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasford, J.; Baccarani, M.; Hoffmann, V.; Guilhot, J.; Saussele, S.; Rosti, G.; Guilhot, F.; Porkka, K.; Ossenkoppele, G.; Lindoerfer, D.; et al. Predicting complete cytogenetic response and subsequent progression-free survival in 2060 patients with CML on imatinib treatment: The EUTOS score. Blood 2011, 118, 686–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuntegowdanahalli, L.C.; Kanakasetty, G.B.; Thanky, A.H.; Dasappa, L.; Jacob, L.A.; Mallekavu, S.B.; Lakkavalli, R.K.; Kadabur, L.N.; Haleshappa, R.A. Prognostic and predictive implications of Sokal, Euro and EUTOS scores in chronic myeloid leukaemia in the imatinib era—experience from a tertiary oncology centre in Southern India. Ecancermedicalscience 2016, 10, 679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, R.; Roy, A.; Xu, D.; Poisson, J.; Zhang, Y. The I-TASSER Suite: Protein structure and function prediction. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 7–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeLano, W.L. Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsl. Protein Crystallogr. 2002, 40, 82–92. [Google Scholar]
- Khazaal, M.S.; Hamdan, F.B.; Al-Mayah, Q.S. Association ofBCR/ABLtranscript variants with different blood parameters and demographic features in Iraqi chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2019, 7, e809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, S.M.; Levy, A.R.; Davis, C.; Holyoake, T.; Cortes, J. A Multinational Study of Health State Preference Values Associated with Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia. Value Health 2010, 13, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hoffmann, V.S.; Baccarani, M.; Hasford, J.; Lindoerfer, D.; Burgstaller, S.; Sertic, D.; Costeas, P.; Mayer, J.; Indrak, K.; Everaus, H.; et al. The EUTOS population-based registry: Incidence and clinical characteristics of 2904 CML patients in 20 European Countries. Leukemia 2015, 29, 1336–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meena, L.P.; Kumar, S.; Gupta, V.K.; Bharti, A.; Gupta, V.; Shukla, J. A study to determine the clinical, hematological, cytogenetic, and molecular profile in CML patient in and around Eastern UP, India. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 2450–2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The UniProt Consortium. UniProt: The universal protein knowledgebase in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, D1. [Google Scholar]
- Koene, H.R.; Kleijer, M.; Algra, J.; Roos, D.; Borne, A.E.V.D.; De Haas, M. Fc gammaRIIIa-158V/F polymorphism influences the binding of IgG by natural killer cell Fc gammaRIIIa, independently of the Fc gammaRIIIa-48L/R/H phenotype. Blood 1997, 90, 1109–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizaki, M.; the New TARGET Investigators; Takahashi, N.; Iriyama, N.; Okamoto, S.; Ono, T.; Usui, N.; Inokuchi, K.; Nakaseko, C.; Kurokawa, M.; et al. Efficacy and safety of tyrosine kinase inhibitors for newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia over a 5-year period: Results from the Japanese registry obtained by the New TARGET system. Int. J. Hematol. 2019, 109, 426–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervantes, F.; López-Garrido, P.; Montero, M.-I.; Jonte, F.; Martínez, J.; Hernandez-Boluda, J.C.; Calbacho, M.; Sureda, A.; Pérez-Rus, G.; Nieto, J.B.; et al. Early intervention during imatinib therapy in patients with newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: A study of the Spanish PETHEMA group. Haematologica 2010, 95, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O‘Brien, S.G.; Guilhot, F.; Larson, R.; Gathmann, I.; Baccarani, M.; Cervantes, F.; Cornelissen, J.J.; Fischer, T.; Hochhaus, A.; Hughes, T.; et al. Imatinib Compared with Interferon and Low-Dose Cytarabine for Newly Diagnosed Chronic-Phase Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 994–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Tripathi, A.; Tripathi, P.; Singh, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, R.K. Malondialdehyde and protein carbonyl as biomarkers for oxidative stress and disease progression in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. In Vivo 2008, 22, 525–528. [Google Scholar]
- Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Oksvold, P.; Kampf, C.; Djureinovic, D.; Odeberg, J.; Habuka, M.; Tahmasebpoor, S.; Danielsson, A.; Edlund, K.; et al. Analysis of the Human Tissue-specific Expression by Genome-wide Integration of Transcriptomics and Antibody-based Proteomics. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Han, J.; Jin, J.; Su, F.; Zhang, J.; Huang, W.; Xiao, F.; Pan, Q.; et al. Screening of circular RNAs and validation of circANKRD36 associated with inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1865–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Zhang, L.; Meng, J. Circular RNA ANKRD36 attends to lipopolysaccharide-aroused MRC-5 cell injury via regulating microRNA-31-3p. BioFactors 2020, 46, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, H.; Jin, Q.; Wu, D. Silencing circANKRD36 protects H9c2 cells against lipopolysaccharide-induced injury via up-regulating miR-138. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2019, 111, 104300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, M.J.; Johnstone, E.C.; Walton, R. Identification and characterization of ANKK1: A novel kinase gene closely linked to DRD2 on chromosome band 11q23.1. Hum. Mutat. 2004, 23, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosavi, L.K.; Cammett, T.J.; Desrosiers, D.C.; Peng, Z.-Y. The ankyrin repeat as molecular architecture for protein recognition. Protein Sci. 2004, 13, 1435–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Chavez, F. The rules of variation: Amino acid exchange according to the rotating circular genetic code. J. Theor. Biol. 2010, 264, 711–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yamada, Y.; Arai, T.; Kojima, S.; Sugawara, S.; Kato, M.; Okato, A.; Yamazaki, K.; Naya, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Regulation of antitumor miR-144-5p targets oncogenes: Direct regulation of syndecan-3 and its clinical significance. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 2919–2936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perilli, L.; Tessarollo, S.; Albertoni, L.; Curtarello, M.; Pastò, A.; Brunetti, E.; Fassan, M.; Rugge, M.; Indraccolo, S.; Amadori, A.; et al. Silencing of miR-182 is associated with modulation of tumorigenesis through apoptosis induction in an experimental model of colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, T.; Liu, G.X.; Cui, J.X.; Zhang, K.C.; Chen, Z.D.; Chen, L.; Wei, B.; Huang, X.H. Exome sequencing of gastric cancers screened the differences of clinicopathological phenotypes between the mutant and the wide-type of frequently mutated genes. Zhonghua yi xue za zhi 2018, 98, 2242–2245. [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet, L.; Wood, V.; Kadeva, N.; Cornwell, G.; Codognotto, S.; Stephenson, E.; Ilic, D. Generation of KCL040 clinical grade human embryonic stem cell line. Stem Cell Res. 2016, 16, 173–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Garcia, P.G. The Role of the PIM1 Kinase in T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma. 2017. Available online: https://lib.ugent.be/fulltxt/RUG01/002/349/919/RUG01-002349919_2017_0001_AC.pdf (accessed on 11 May 2021).
- Fajardo, K.V.F.; Adams, D.; Mason, C.E.; Sincan, M.; Tifft, C.; Toro, C.; Boerkoel, C.F.; Gahl, W.; Markello, T.; Program, N.C.S. Detecting false-positive signals in exome sequencing. Hum. Mutat. 2012, 33, 609–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aird, D.; Ross, M.G.; Chen, W.-S.; Danielsson, M.; Fennell, T.; Russ, C.; Jaffe, D.B.; Nusbaum, C.; Gnirke, A. Analyzing and minimizing PCR amplification bias in Illumina sequencing libraries. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bentley, D.R.; Balasubramanian, S.; Swerdlow, H.; Smith, G.P.; Milton, J.; Brown, C.G.; Hall, K.P.; Evers, D.J.; Barnes, C.L.; Bignell, H.R.; et al. Accurate whole human genome sequencing using reversible terminator chemistry. Nature 2008, 456, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koboldt, D.C.; Ding, L.; Mardis, E.R.; Wilson, R.K. Challenges of sequencing human genomes. Briefings Bioinform. 2010, 11, 484–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teer, J.K.; Bonnycastle, L.L.; Chines, P.S.; Hansen, N.F.; Aoyama, N.; Swift, A.J.; Abaan, H.O.; Albert, T.J.; Margulies, E.H.; Green, E.D.; et al. Systematic comparison of three genomic enrichment methods for massively parallel DNA sequencing. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1420–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledergerber, C.; Dessimoz, C. Base-calling for next-generation sequencing platforms. Briefings Bioinform. 2011, 12, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, D.M.; Schneider, V.A.; Graves, T.; Auger, K.; Cunningham, F.; Bouk, N.; Chen, H.-C.; Agarwala, R.; McLaren, W.; Ritchie, G.; et al. Modernizing Reference Genome Assemblies. PLoS Biol. 2011, 9, e1001091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Statistics | ID 1 | ID 2 | ID 3 | ID 4 | ID 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Number of Reads | 70,508,170 | 75,173,754 | 75,622,396 | 71,328,320 | 76,940,162 |
| Q30 (%) | 96.6 | 97.0 | 96.8 | 96.9 | 97.1 |
| Average Read Length (bp) | 101.0 | 101.0 | 101.0 | 101.0 | 101.0 |
| Total Yield (Mbp) | 7121 | 7592 | 7637 | 7204 | 7770 |
| Target Region (bp) | 60,456,963 | 60,456,963 | 60,456,963 | 60,456,963 | 60,456,963 |
| Average Depth (X) | 117.7 | 125.5 | 126.3 | 119.11 | 128.5 |
| Statistics | ID 1 | ID 2 | ID 3 | ID 4 | ID 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Mappable Reads | 70,471,133 | 75,143,023 | 75,592,332 | 71,300,726 | 76,912,816 |
| %Nonredundant Reads | 88.1 | 86.0 | 86.9 | 86.3 | 87.1 |
| %On-Target Reads | 75.2 | 77.9 | 77.7 | 78.0 | 77.7 |
| Depth of Target Region (X) | 69.1 | 74.4 | 75.5 | 70.9 | 76.9 |
| Coverage (% >10X) | 97.0 | 97.3 | 97.3 | 96.9 | 97.1 |
| Coverage (% >30X) | 82.1 | 84.0 | 84.6 | 82.9 | 84.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Iqbal, Z.; Absar, M.; Akhtar, T.; Aleem, A.; Jameel, A.; Basit, S.; Ullah, A.; Afzal, S.; Ramzan, K.; Rasool, M.; et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies ANKRD36 Gene as a Novel and Common Biomarker of Disease Progression in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Biology 2021, 10, 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111182
Iqbal Z, Absar M, Akhtar T, Aleem A, Jameel A, Basit S, Ullah A, Afzal S, Ramzan K, Rasool M, et al. Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies ANKRD36 Gene as a Novel and Common Biomarker of Disease Progression in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Biology. 2021; 10(11):1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111182
Chicago/Turabian StyleIqbal, Zafar, Muhammad Absar, Tanveer Akhtar, Aamer Aleem, Abid Jameel, Sulman Basit, Anhar Ullah, Sibtain Afzal, Khushnooda Ramzan, Mahmood Rasool, and et al. 2021. "Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies ANKRD36 Gene as a Novel and Common Biomarker of Disease Progression in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia" Biology 10, no. 11: 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111182
APA StyleIqbal, Z., Absar, M., Akhtar, T., Aleem, A., Jameel, A., Basit, S., Ullah, A., Afzal, S., Ramzan, K., Rasool, M., Karim, S., Mirza, Z., Iqbal, M., AlMajed, M., AlShehab, B., AlMukhaylid, S., AlMutairi, N., Al-anazi, N., Sabar, M. F., ... Mahmood, A. (2021). Integrated Genomic Analysis Identifies ANKRD36 Gene as a Novel and Common Biomarker of Disease Progression in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia. Biology, 10(11), 1182. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10111182






