Calcium Chloride Treated Highly Elastane Cotton Fabrics as Antibacterial, Comfortable and Environmentally Friendly Materials
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Treatments with Calcium Chloride Solutions
2.2. Add-On Calculation
2.3. Antibacterial Activity
2.4. Thermal Resistance
2.5. Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Diffusion
2.6. Water Vapor Permeability (WVP) and Water Vapor Resistance (WVR)
2.7. Bending Length and Bending Rigidity Measurement
2.8. Color Measurement
2.9. Characterization Analyses
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
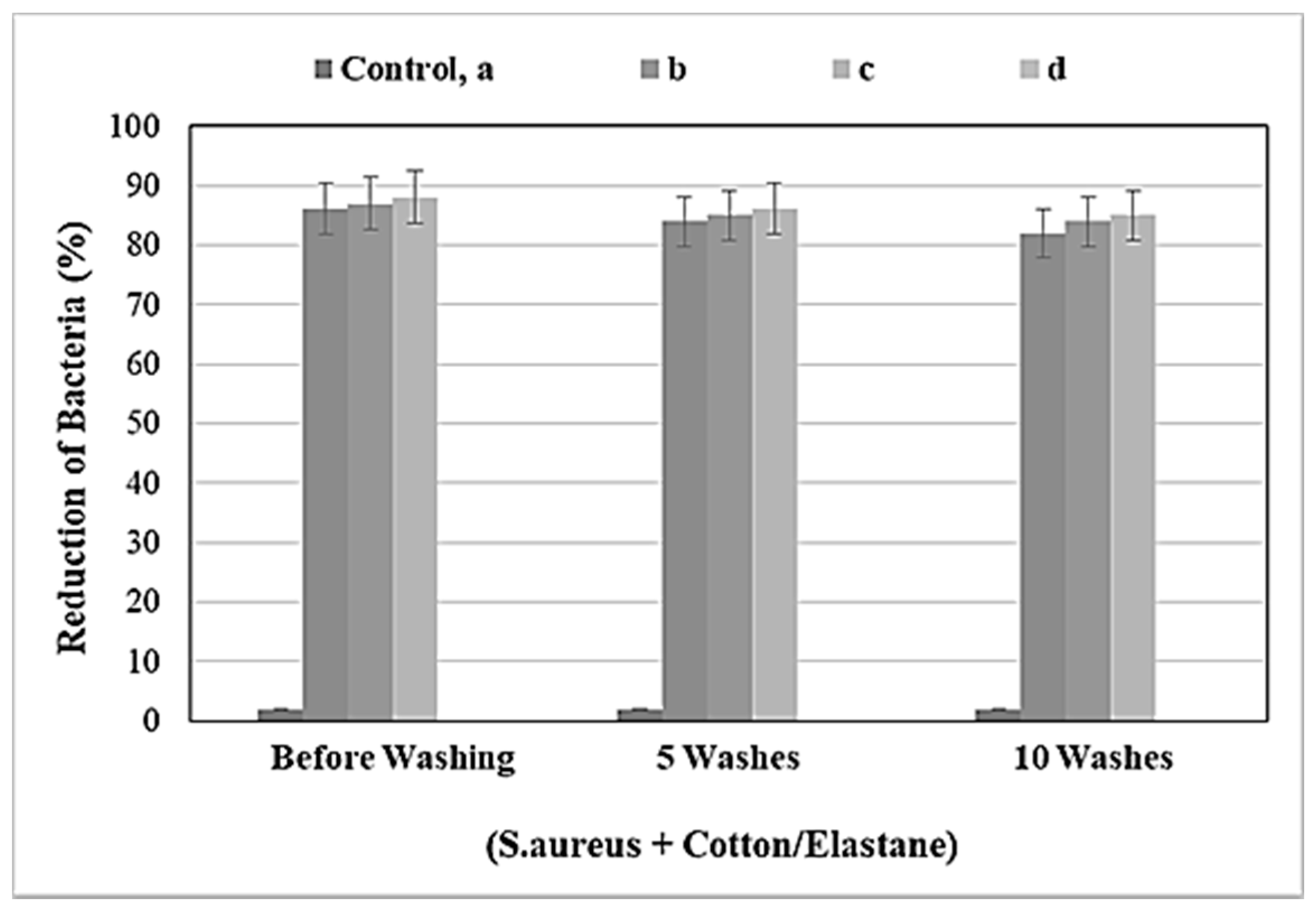
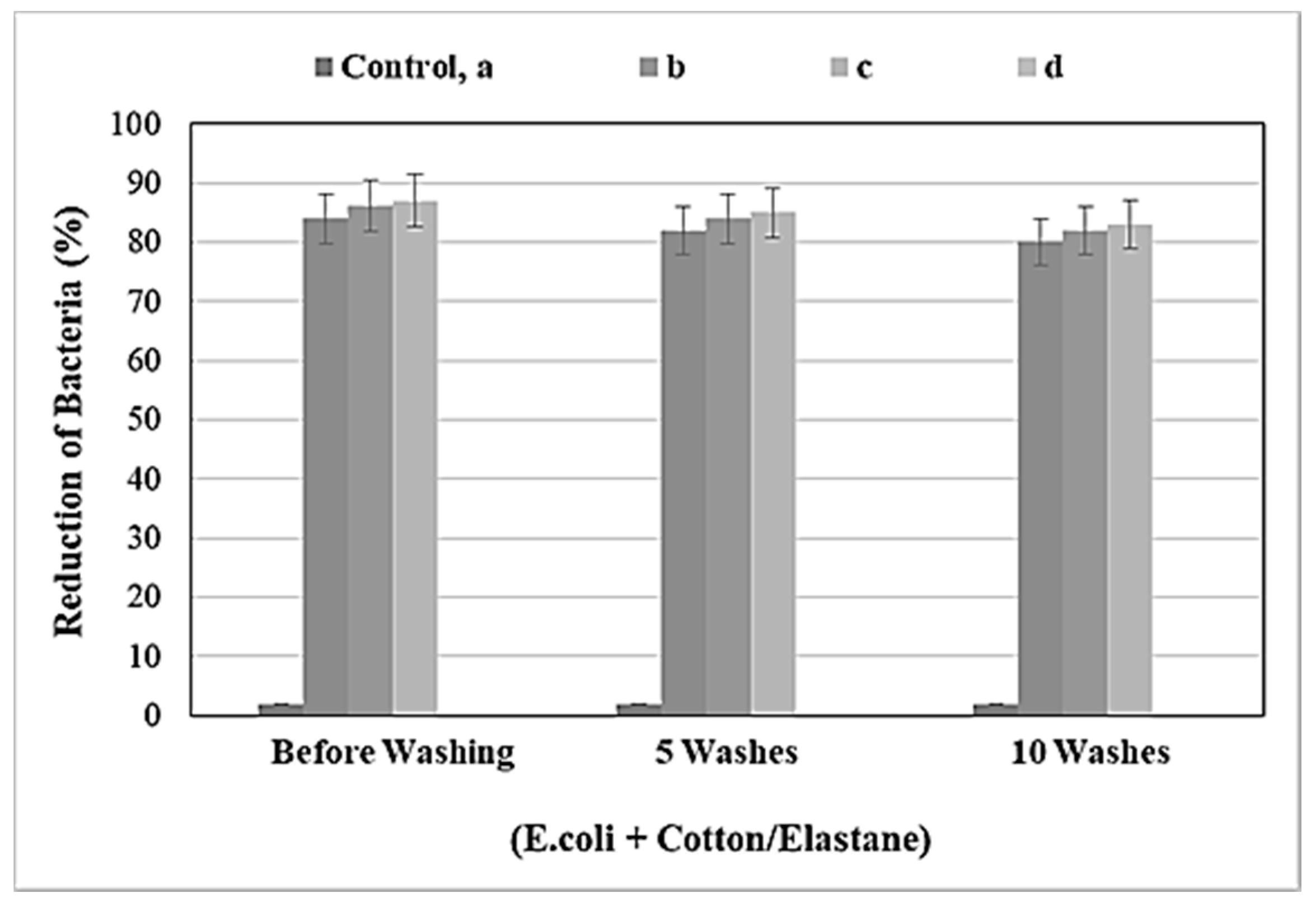
3.1. Antibacterial Activity
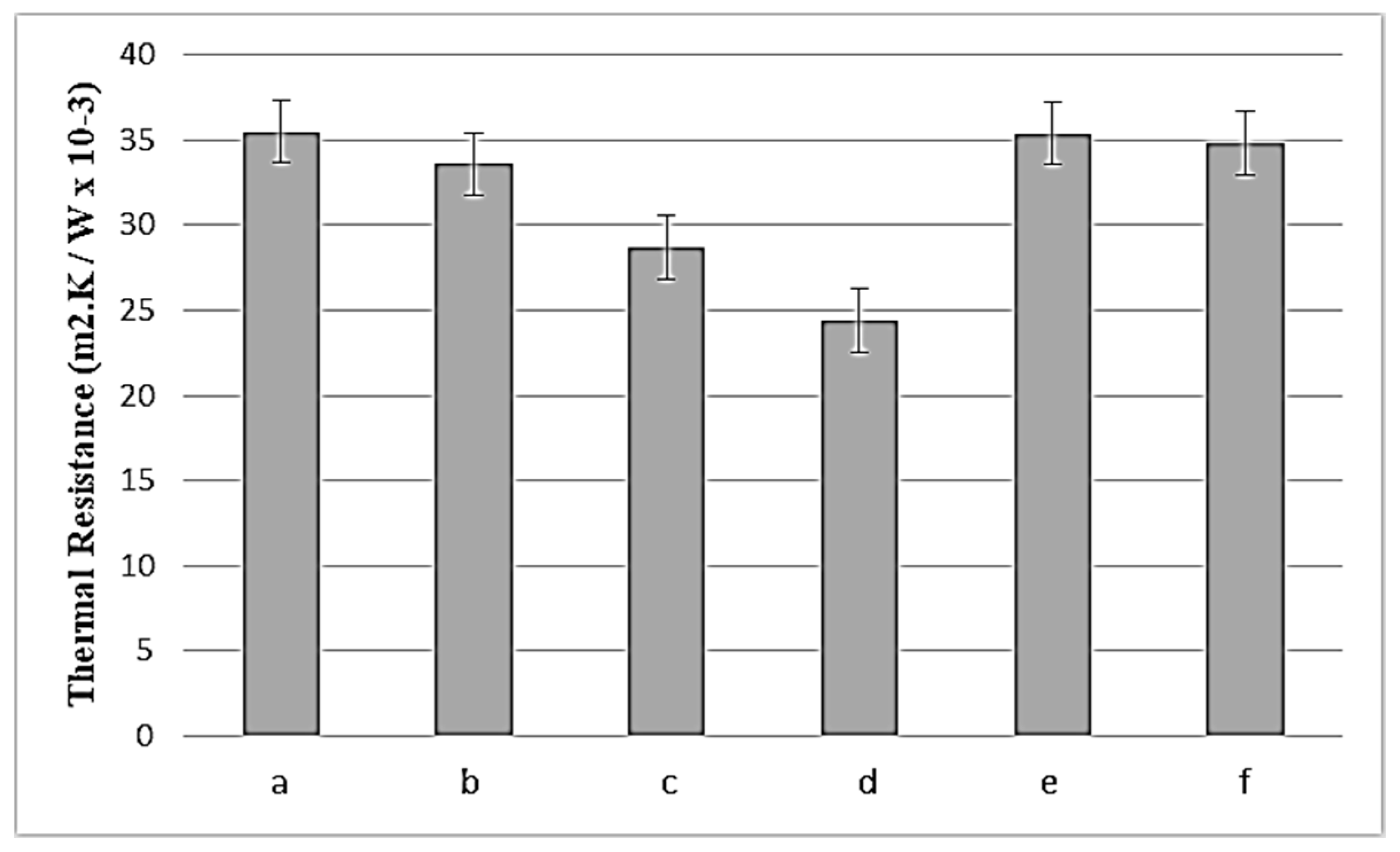
3.2. Thermal Resistance
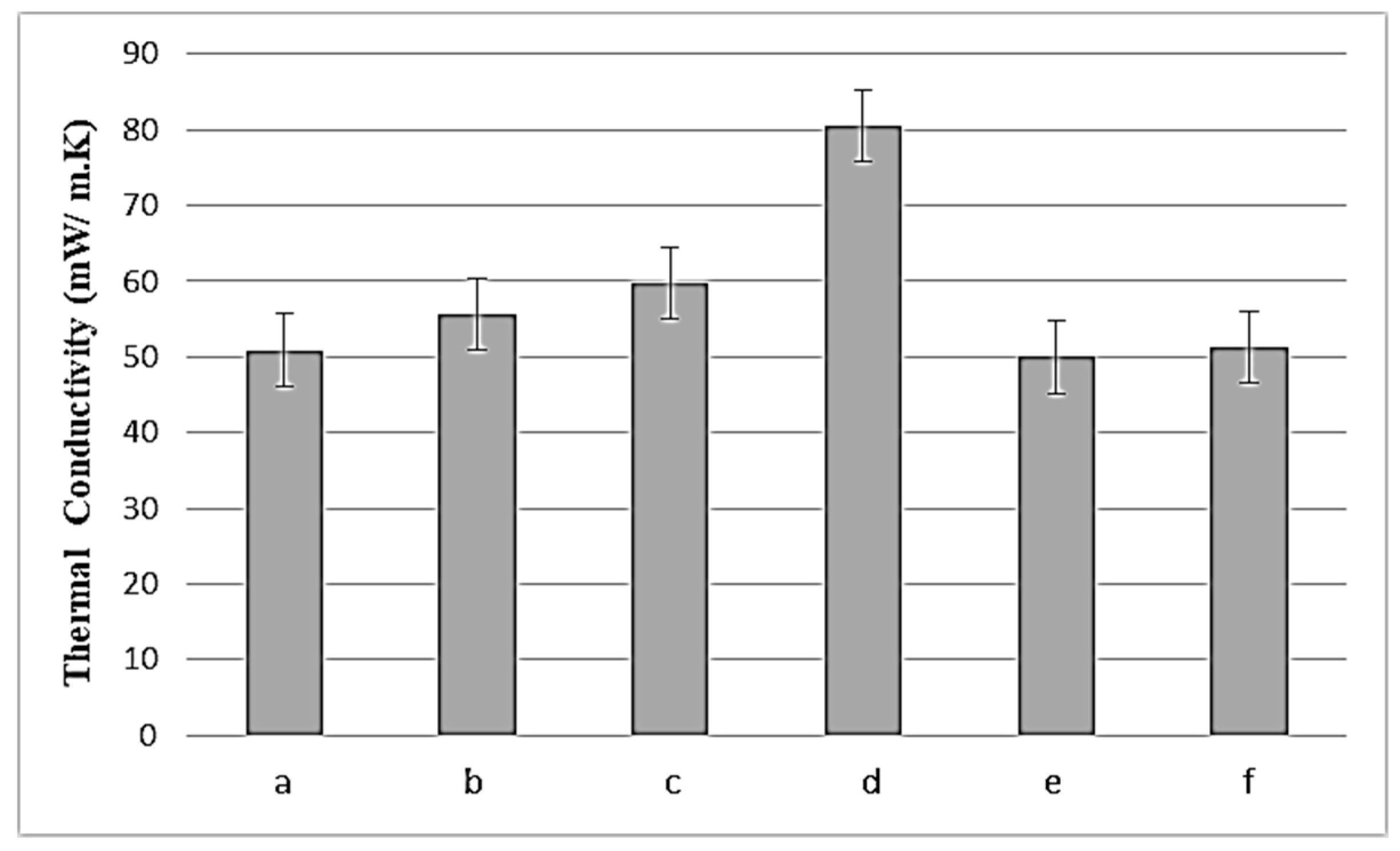
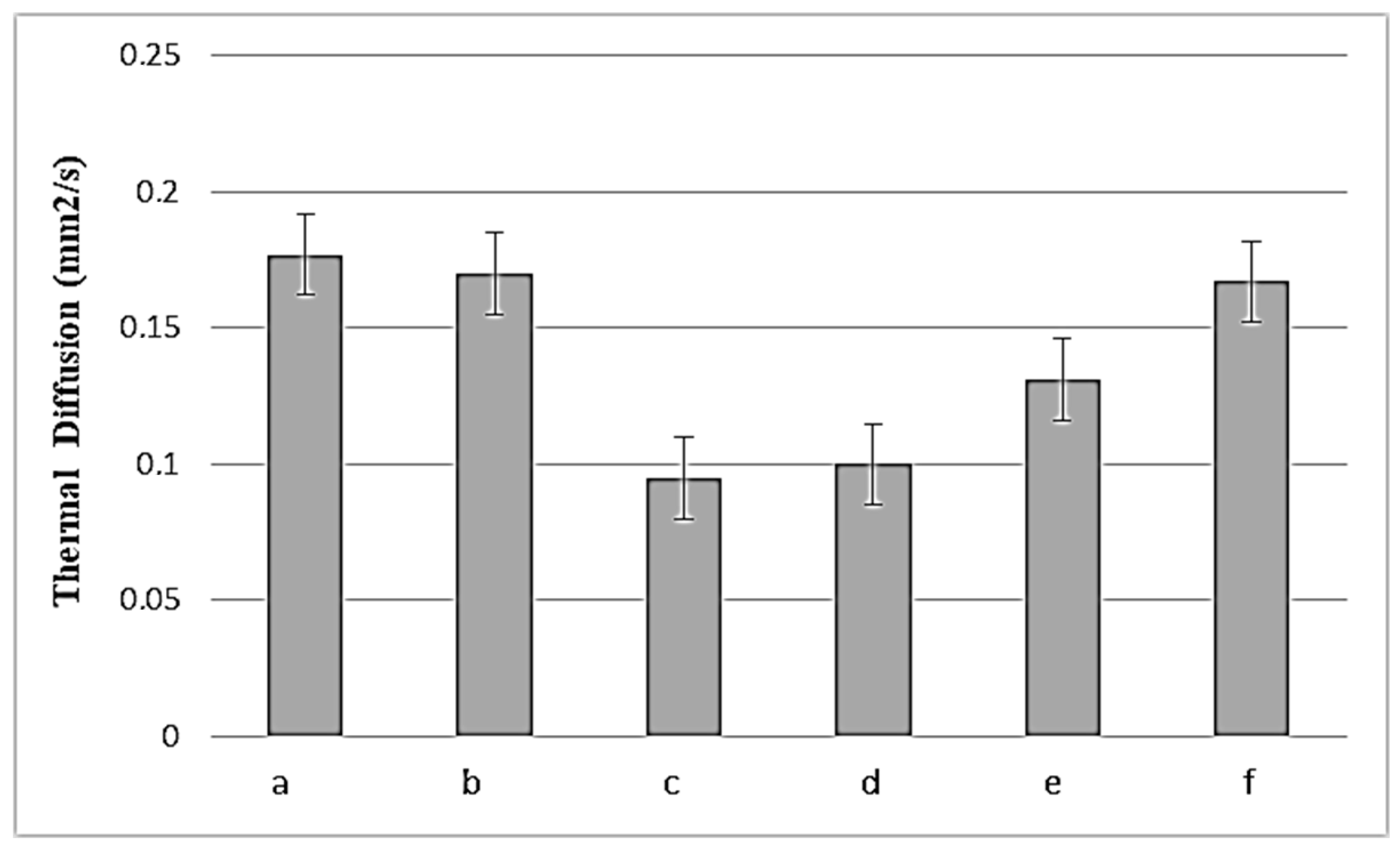
3.3. Thermal Conductivity and Thermal Diffusion
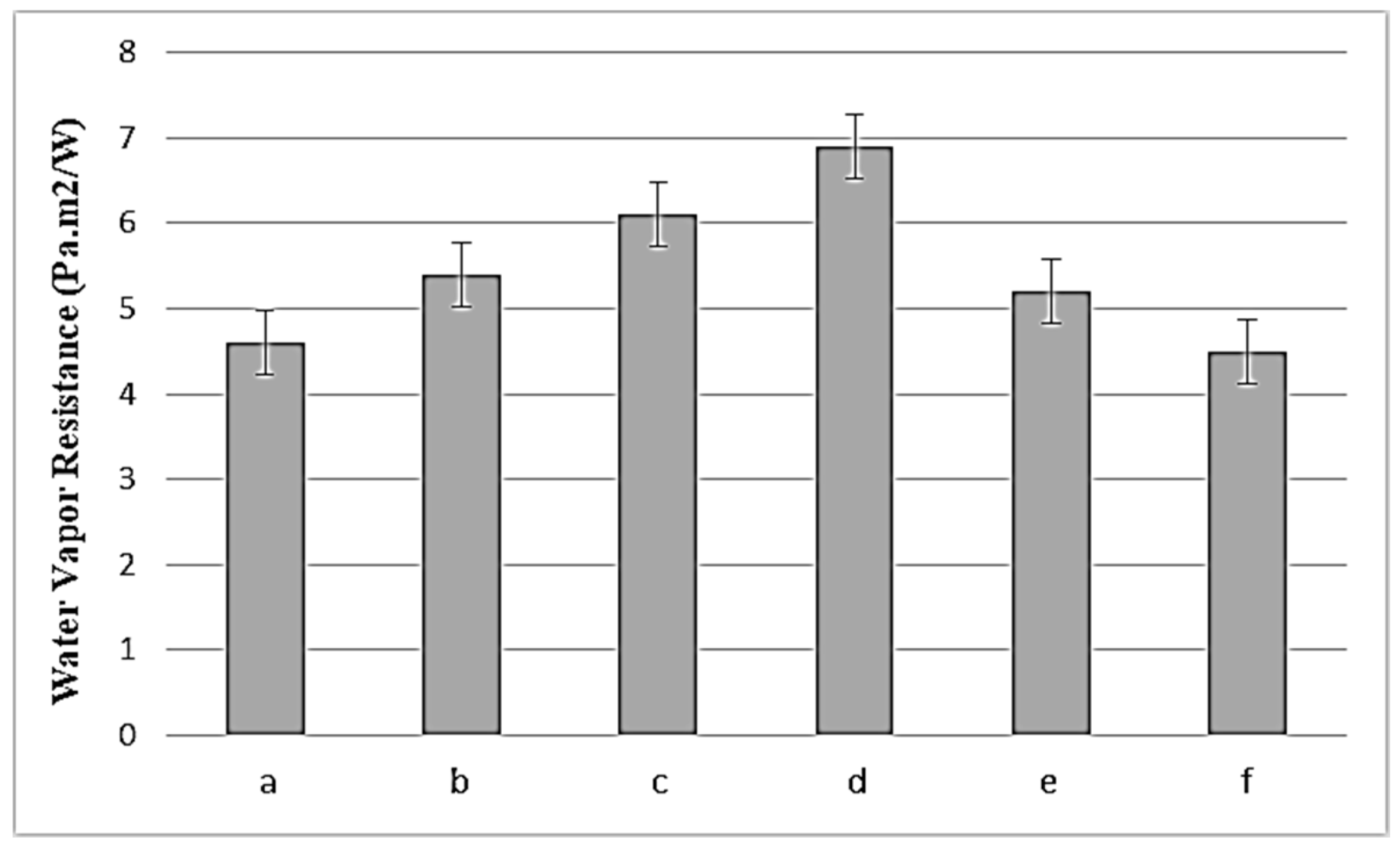
3.4. WVR
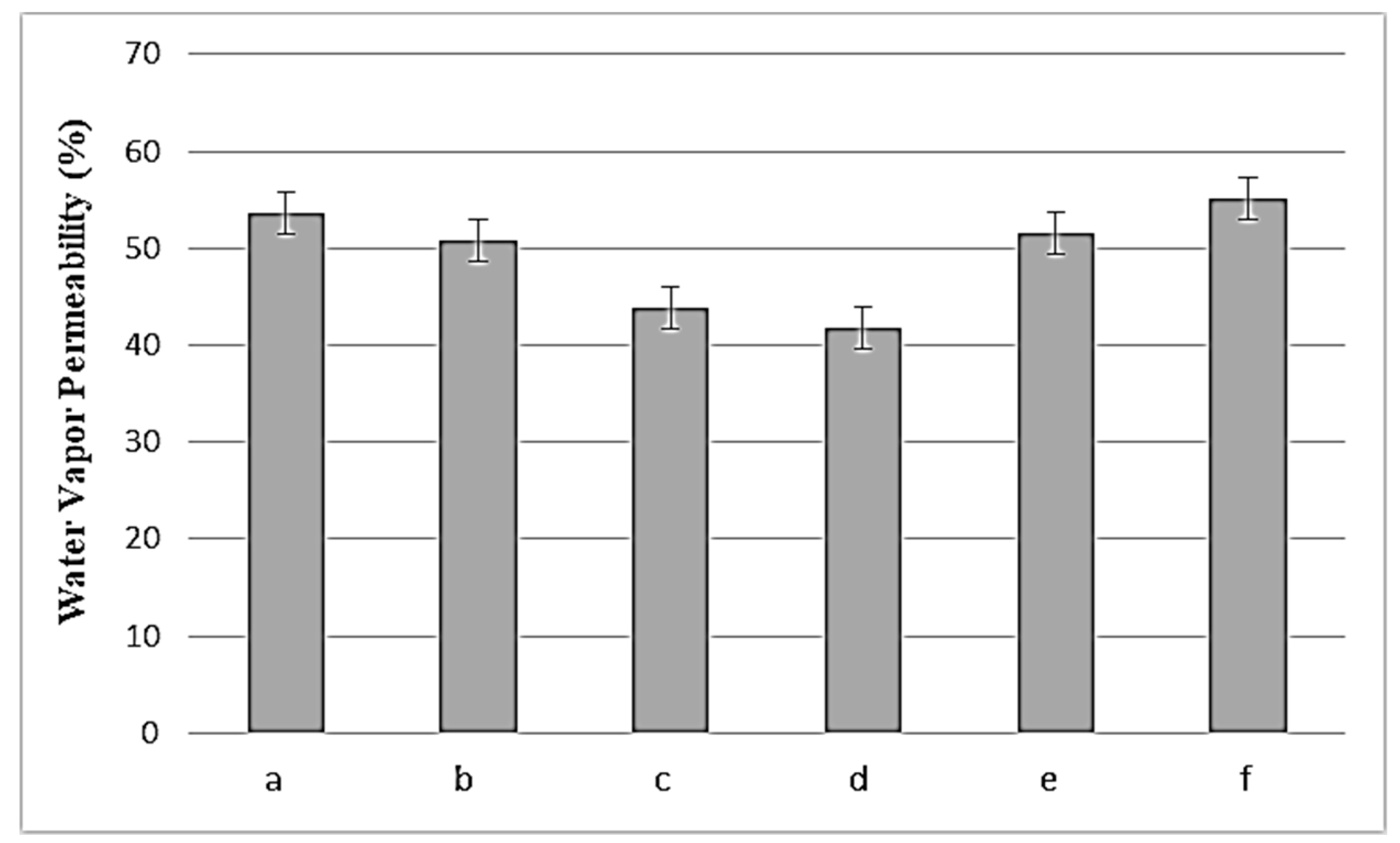
3.5. WVP
3.6. Bending Length and Bending Rigidity Results
3.7. WI and YI Results
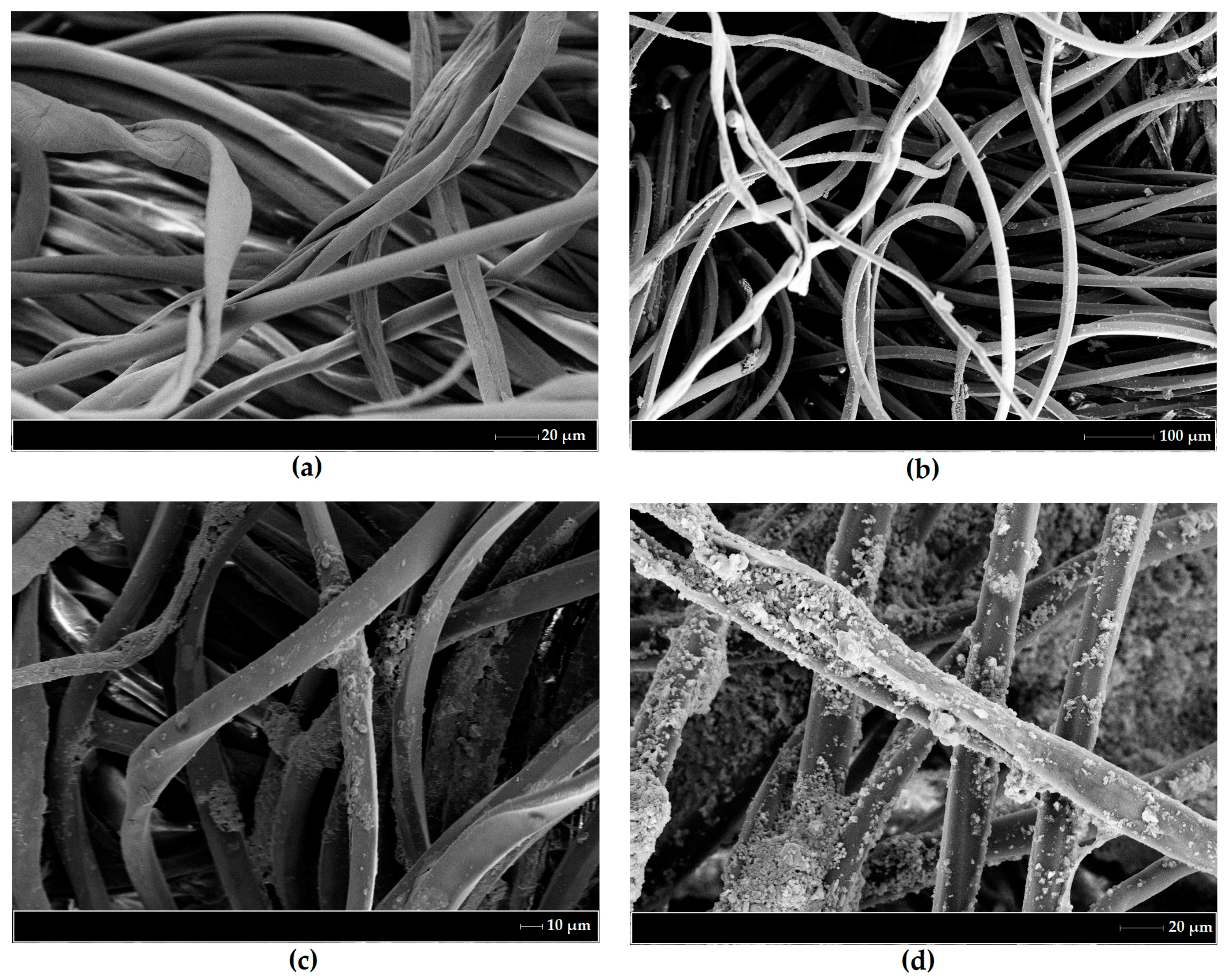
3.8. SEM Results
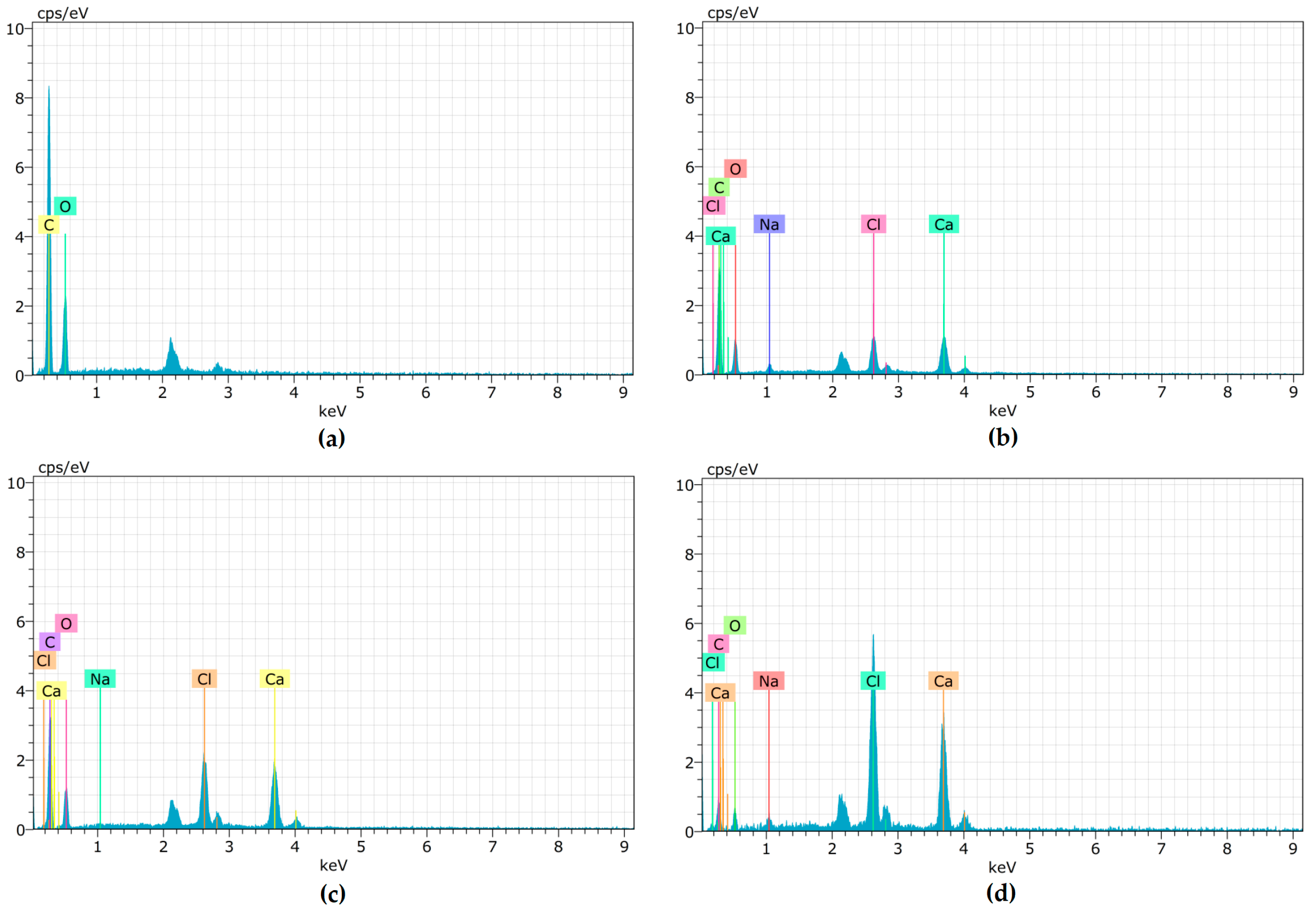
3.9. EDX Results
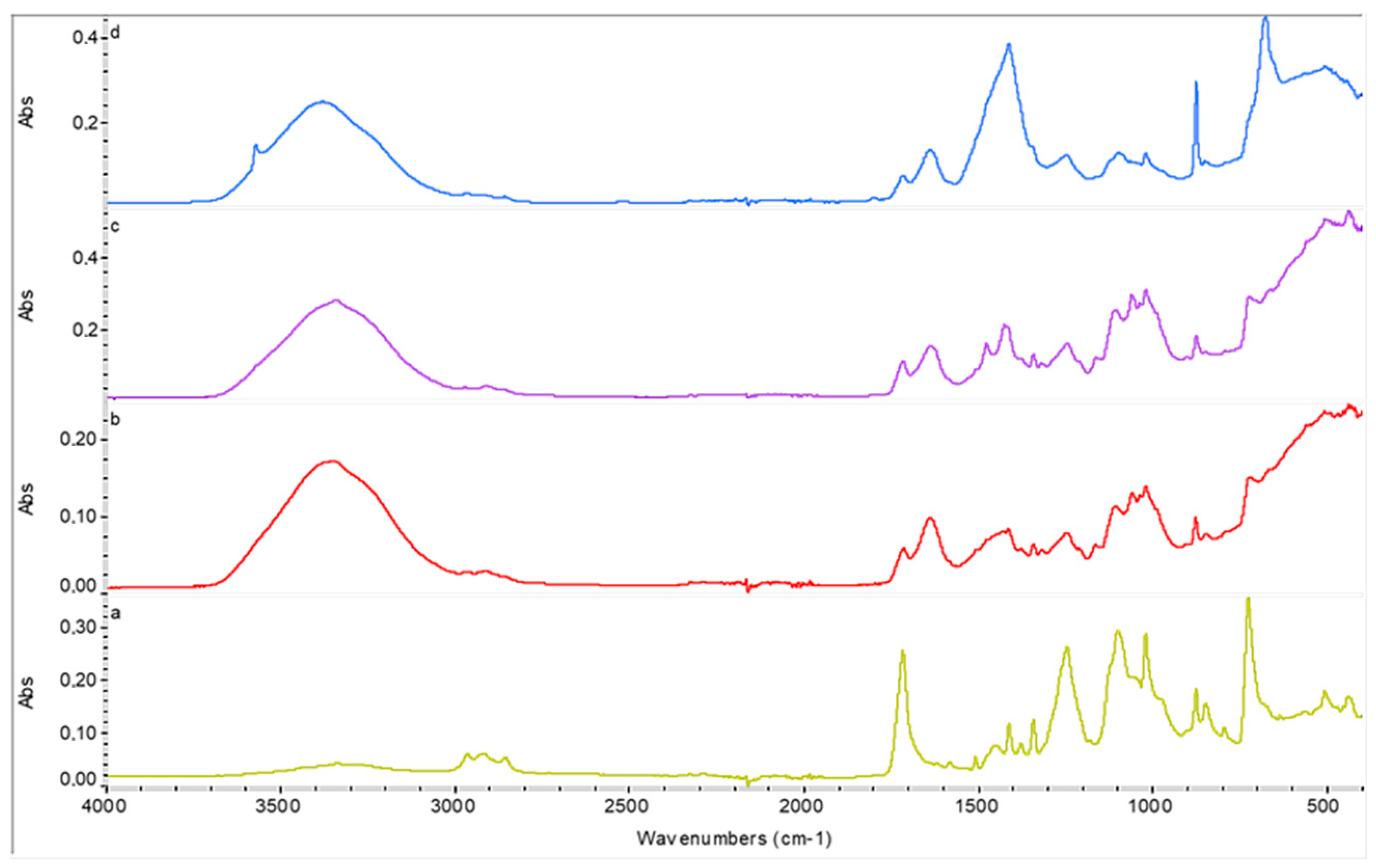
3.10. FTIR-ATR Results
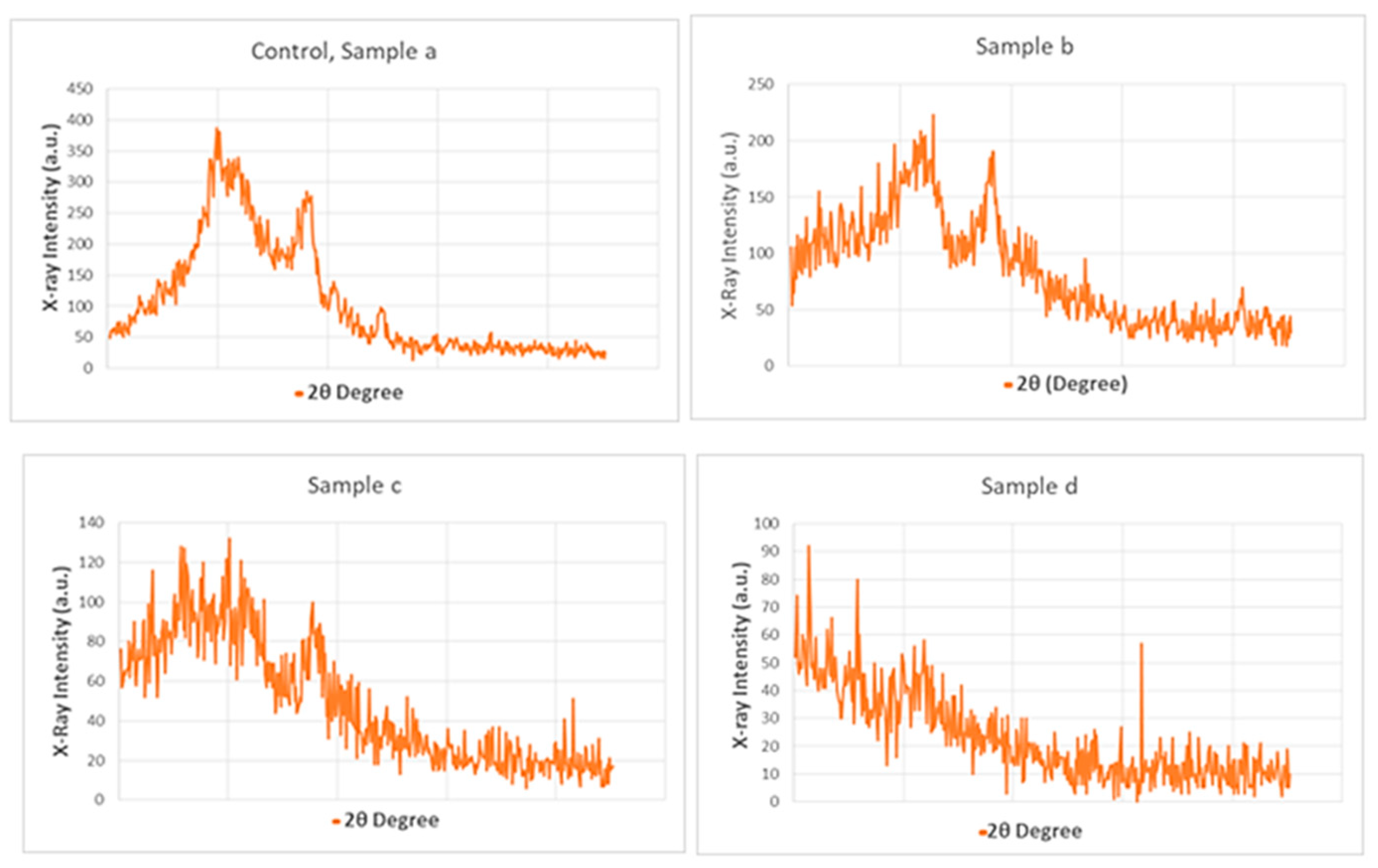
3.11. XRD Results
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tonelli, A.E.; Srinivasarao, M. Polymers From the Inside Out-An Introduction to Macromolecules; John Wiley & Sons Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 189–192. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, B.K.; Singh, J.P. Factors contributing to absorbency behaviour of pile fabrics. Res. J. Text. Appar. 2014, 18, 81–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öner, E.; Atasağun, H.G.; Okur, A.; Beden, A.R.; Durur, G. Evaluation of moisture management properties on knitted fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2013, 104, 699–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troynikov, O.; Wardiningsih, W. Moisture management properties of wool/ polyester and wool/bamboo knitted fabrics for the sportswear base layer. Text. Res. J. 2011, 81, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherzadeh, R.; Gorji, M.; Latifi, M.; Payvandy, P.; Kong, L.X. Evolution of moisture management behavior of high-wicking 3D warp knitted spacer fabrics. Fibers Polym. 2012, 13, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, C.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Koushik, C.V. Effect of blend proportion on moisture management characteristics of bamboo/cotton knitted fabrics. J. Text. Inst. 2013, 104, 1320–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özdil, N.; Süpüren, G.; Özçelik, G.; Pruchova, J. A study on the moisture transport properties of the cotton knitted fabrics in single jersey structure. Tekst. Konfeksiyon 2009, 19, 218–223. [Google Scholar]
- Jhanji, Y.; Gupta, D.; Kothari, V.K. Moisture management properties of plated knit structures with varying fiber types. J. Text. Inst. 2015, 106, 663–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathinamoorthy, R. Moisture management characteristics of knitted casein fabric. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 2017, 42, 488–494. [Google Scholar]
- Bedek, G.; Salaün, F.; Martinkovska, Z.; Devaux, E.; Dupont, D. Evaluation of thermal and moisture management properties on knitted fabrics and comparison with a physiological model in warm conditions. Appl. Ergon. 2011, 42, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bivainyte, A.; Mikučioniene, D. Investigation on the dynamic water absorption of double-layered weft knitted fabrics. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2011, 6, 64–70. [Google Scholar]
- Supuren, G.; Oglakcioglu, N.; Ozdil, N.; Marmarali, A. Moisture management and thermal absorptivity properties of double-face knitted fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2011, 81, 1320–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peršin, Z.; Stana-Kleinschek, K.; Kreže, T. Hydrophilic/hydrophobic characteristics of different cellulose fibres monitored by tensiometry. Croat. Chem. Acta 2002, 75, 271–280. [Google Scholar]
- Mittal, M.; Chaudhary, R. Experimental Study on the Water Absorption and Surface Characteristics of Alkali Treated Pineapple Leaf Fibre and Coconut Husk Fibre. Int. J. Appl. Eng. Res. 2018, 13, 12237–12243. [Google Scholar]
- Murphy, B.G.; Macormac, A.R. The absorbency of terry towels: Part I: Effect of home laundering. Text. Res. J. 1958, 28, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samanta, K.K.; Jassal, M.; Agrawal, A.K. Improvement in water and oil absorbency of textile substrate by atmospheric pressure cold plasma treatment. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 203, 1336–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Barker, R.L. Moisture management properties of heat-resistant workwear fabrics—Effects of hydrophilic finishes and hygroscopic fiber blends. Text. Res. J. 2004, 74, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Barker, R.L. Comfort properties of heat-resistant protective workwear in varying conditions of physical activity and environment. Part I: Thermophysical and sensorial properties of fabrics. Text. Res. J. 2005, 75, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampath, M.; Senthilkumar, M. Effect of moisture management finish on comfort characteristics of microdenier polyester knitted fabrics. J. Ind. Text. 2009, 39, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chance, L.H.; Leonard, E.K.; Reeves, W.A. The treatment of cotton with formaldehyde in calcium chloride solutions. Text. Res. J. 1962, 32, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glampedaki, P.; Jocic, D.; Warmoeskerken, M.M. Moisture absorption capacity of polyamide 6, 6 fabrics surface functionalised by chitosan-based hydrogel finishes. Prog. Org. Coat. 2011, 72, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AATCC Technical Manual; AATCC: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2012; Volume 87, pp. 90–94.
- AATCC Technical Manual; AATCC: Raleigh, NC, USA, 2009; Volume 84, pp. 143–145.
- ISO Technical Manual; ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 1993; Volume 2, pp. 1–15.
- Fan, J.; Qian, X. New functions and applications of Walter, the sweating fabric manikin. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 92, 641–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 1995; Volume 7, pp. 1–4.
- Roy, S.; Ghosh, S.; Bhowmick, N. Mechanism of bacterial attachment on textile fibrous media. J. Text. Inst. 2019, 110, 916–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilinc, M.; Yildiz, K.; Tekin, A.; Kilinc, N.; Uzun, M. The Investigation of Antimicrobial Properties of Ag–Alginate Impregnated Polyester/Viscose Nonwoven Fabric. Int. J. Adv. Eng. Pure Sci. 2019, 31, 97–103. [Google Scholar]
- Dobay, O.; Laub, K.; Stercz, B.; Kéri, A.; Balázs, B.; Tóthpál, A.; Kardos, S.; Jaikumpun, P.; Ruksakiet, K.; Quinton, P.M.; et al. Bicarbonate Inhibits Bacterial Growth and Biofilm Formation of Prevalent Cystic Fibrosis Pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bajaj, P. Finishing of textile materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2002, 83, 631–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabar, J.M.; Ogunmokun, A.I.; Taleat, T.A.A. Color and fastness properties of mordanted Bridelia ferruginea B dyed cellulosic fabric. Fash. Text. 2020, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, J. Synthesis and characterization of γ-irradiated PVA/PEG/CaCl2 hydrogel for wound dressing. Am. J. Chem. 2012, 2, 6–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
| Recipe | Chemical Agent (g/100 mL) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CaCl2 | HCl | NaHCO3 | |
| 1 | 10.00 | 3.00 | 1.77 |
| 2 | 25.00 | 3.00 | 1.77 |
| 3 | 50.00 | 3.00 | 11.12 |
| Sample | Bending Length (cm·S) | Bending Rigidity (mg·cm·S) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MD | CD | MD | CD | |
| *a | 2.16 | 1.53 | 454.68 | 175.04 |
| *b | 4.14 | 1.79 | 2709.59 | 226.32 |
| *c | 3.43 | 1.66 | 1927.45 | 221.38 |
| *d | 4.35 | 1.55 | 8099.58 | 532.04 |
| Sample | WI (Stentsby) | YI (E313) |
|---|---|---|
| *a | 72.25 | 7.57 |
| *b | 67.40 | 11.87 |
| *c | 66.53 | 11.77 |
| *d | 71.26 | 9.31 |
| Treatment | Elements (Atomic %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Na | Ca | Cl | |
| *a | 71.68 | 28.32 | - | - | - |
| *b | 44.31 | 15.80 | 2.79 | 25.27 | 11.83 |
| *c | 38.32 | 14.12 | 0.54 | 33.43 | 13.58 |
| *d | 10.92 | 6.26 | 1.80 | 50.30 | 30.73 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Varan, N.Y.; Caydamli, Y. Calcium Chloride Treated Highly Elastane Cotton Fabrics as Antibacterial, Comfortable and Environmentally Friendly Materials. Fibers 2021, 9, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9110070
Varan NY, Caydamli Y. Calcium Chloride Treated Highly Elastane Cotton Fabrics as Antibacterial, Comfortable and Environmentally Friendly Materials. Fibers. 2021; 9(11):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9110070
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaran, Nilufer Yildiz, and Yavuz Caydamli. 2021. "Calcium Chloride Treated Highly Elastane Cotton Fabrics as Antibacterial, Comfortable and Environmentally Friendly Materials" Fibers 9, no. 11: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9110070
APA StyleVaran, N. Y., & Caydamli, Y. (2021). Calcium Chloride Treated Highly Elastane Cotton Fabrics as Antibacterial, Comfortable and Environmentally Friendly Materials. Fibers, 9(11), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib9110070






