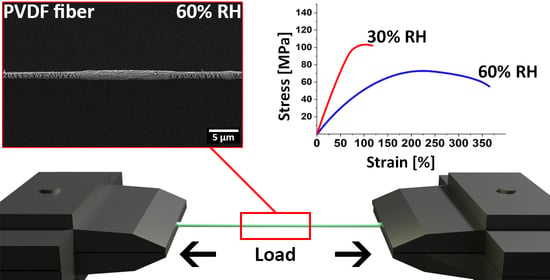
Humidity Controlled Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Electrospinning
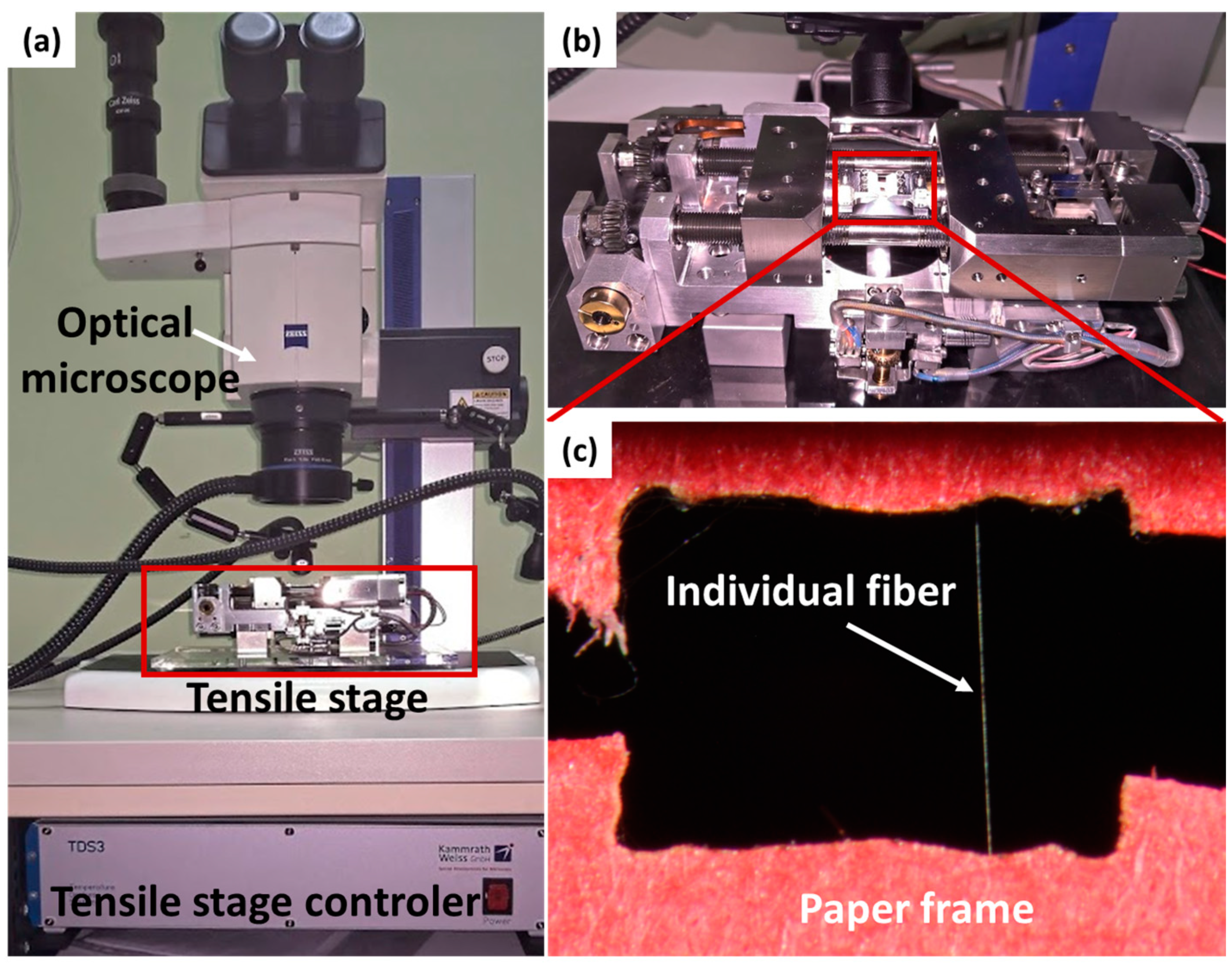
2.2. Mechanical Testing and Microscopy
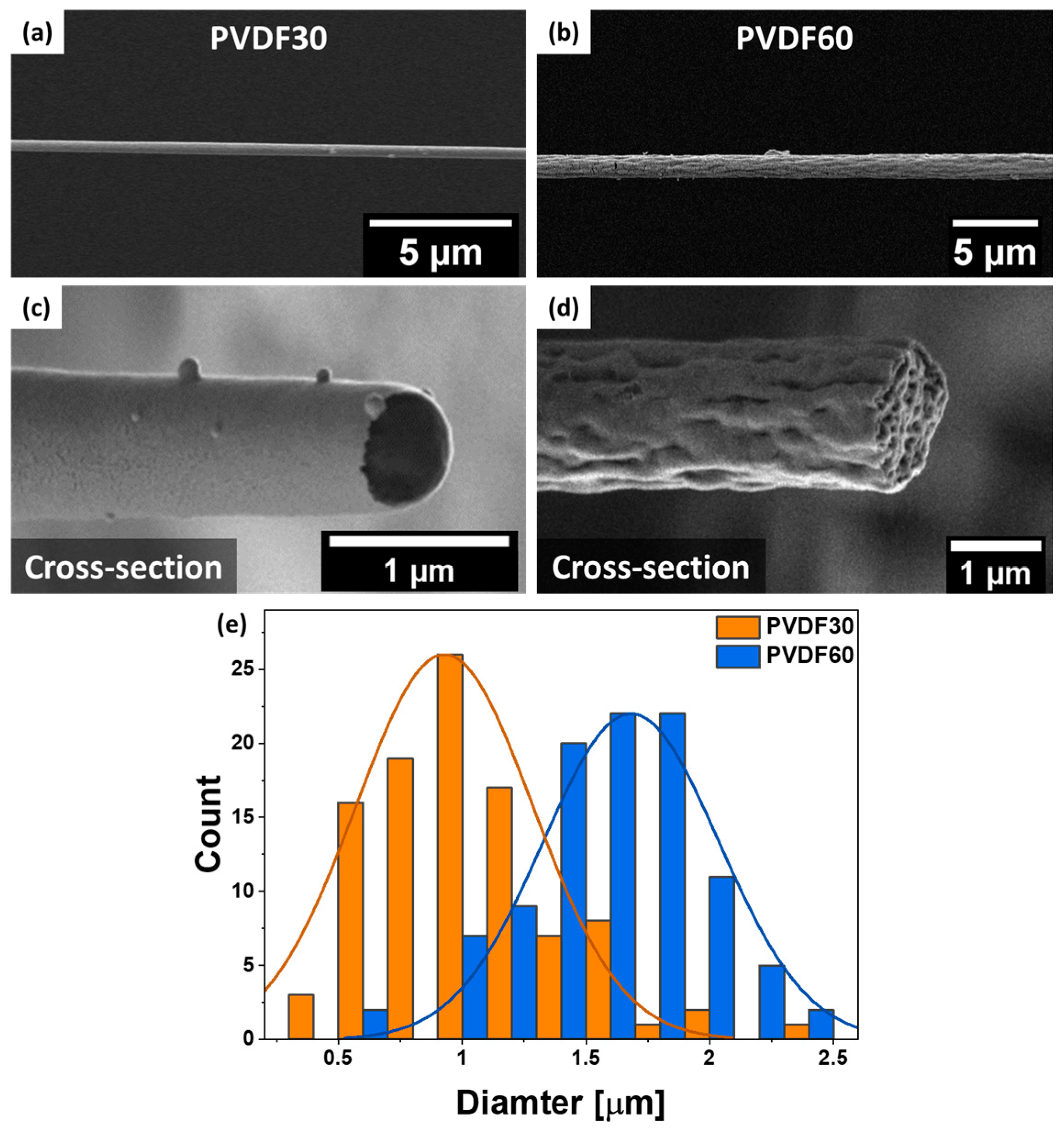
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Jiang, J.; Hou, J.; Li, Q. Internal Structure of Amorphous Electrospun Nanofiber: Oriented Molecular Chains. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awal, A.; Sain, M.; Chowdhury, M. Preparation of cellulose-based nano-composite fibers by electrospinning and understanding the effect of processing parameters. Compos. Part B Eng. 2011, 42, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inai, R.; Kotaki, M.; Ramakrishna, S. Structure and properties of electrospun PLLA single nanofibres. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metwally, S.; Karbowniczek, J.E.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Marzec, M.M.; Gruszczyński, A.; Bernasik, A.; Staczewicz, U.; Stachewicz, U.; Gruszczyński, A.; Bernasik, A.; et al. Single-Step Approach to Tailor Surface Chemistry and Potential on Electrospun PCL Fibers for Tissue Engineering Application. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 6, 1801211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ura, D.P.; Karbowniczek, J.E.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Metwally, S.; Kopyściański, M.; Stachewicz, U. Cell Integration with Electrospun PMMA Nanofibers, Microfibers, Ribbons, and Films: A Microscopy Study. Bioengineering 2019, 6, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Ura, D.P.; Metwally, S.; Gruszczyński, A.; Stachewicz, U. Biomimicking wetting properties of spider web from Linothele megatheloides with electrospun fibers. Mater. Lett. 2018, 233, 211–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Ura, D.P.; Gajek, M.; Marzec, M.M.; Berent, K.; Bernasik, A.; Chiverton, J.P.; Stachewicz, U. Fiber-Based Composite Meshes with Controlled Mechanical and Wetting Properties for Water Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 1665–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapczyk-Korczak, J.; Szewczyk, P.K.; Ura, D.P.; Bailey, R.J.; Bilotti, E.; Stachewicz, U. Improving water harvesting efficiency of fog collectors with electrospun random and aligned Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) fibers. Sustain. Mater. Technol. 2020, 25, e00191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busolo, T.; Ura, D.P.; Kim, S.K.; Marzec, M.M.; Bernasik, A.; Stachewicz, U.; Kar-Narayan, S. Surface potential tailoring of PMMA fibers by electrospinning for enhanced triboelectric performance. Nano Energy 2019, 57, 500–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.-H.; Lee, S.-S.; Choi, G.-J.; Park, I.-K. Churros-like Polyvinylidene Fluoride Nanofibers for Enhancing Output Performance of Triboelectric Nanogenerators. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 17824–17832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koç, M.; Paralı, L.; Şan, O. Fabrication and vibrational energy harvesting characterization of flexible piezoelectric nanogenerator (PEN) based on PVDF/PZT. Polym. Test. 2020, 90, 106695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Thomopoulos, S.; Xia, Y. Nanofibers in Regenerative Medicine: Electrospun Nanofibers for Regenerative Medicine (Adv. Healthcare Mater. 1/2012). Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2012, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asran, A.S.; Henning, S.; Michler, G.H. Polyvinyl alcohol-collagen-hydroxyapatite biocomposite nanofibrous scaffold: Mimicking the key features of natural bone at the nanoscale level. Polymer 2010, 51, 868–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anu Bhushani, J.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Electrospinning and electrospraying techniques: Potential food based applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 38, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sri Abirami Saraswathi, M.S.; Rana, D.; Divya, K.; Gowrishankar, S.; Nagendran, A. Versatility of hydrophilic and antifouling PVDF ultrafiltration membranes tailored with polyhexanide coated copper oxide nanoparticles. Polym. Test. 2020, 84, 106367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, H. Electrospun nylon 6 nanofiber reinforced BIS-GMA/TEGDMA dental restorative composite resins. Polymer 2004, 45, 2427–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.S.; Reneker, D.H. Mechanical properties of composites using ultrafine electrospun fibers. Polym. Compos. 1999, 20, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Chen, Y.; Duan, G.; Mei, C.; Greiner, A.; Agarwal, S. Electrospun nanofiber reinforced composites: A review. Polym. Chem. 2018, 9, 2685–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luoh, R.; Hahn, H.T. Electrospun nanocomposite fiber mats as gas sensors. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2006, 66, 2436–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chew, S.; Wen, Y.; Dzenis, Y.; Leong, K. The Role of Electrospinning in the Emerging Field of Nanomedicine. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 4751–4770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawłowska, S.; Rinoldi, C.; Nakielski, P.; Ziai, Y.; Urbanek, O.; Li, X.; Kowalewski, T.A.; Ding, B.; Pierini, F. Ultraviolet Light-Assisted Electrospinning of Core–Shell Fully Cross-Linked P(NIPAAm- co -NIPMAAm) Hydrogel-Based Nanofibers for Thermally Induced Drug Delivery Self-Regulation. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burman, M.; Arinstein, A.; Zussman, E. Free flight of an oscillated string pendulum as a tool for the mechanical characterization of an individual polymer nanofiber. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 93, 193118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, S.-F.; Woodrow, K.A. Relationships between mechanical properties and drug release from electrospun fibers of PCL and PLGA blends. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2017, 65, 724–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keun Kwon, I.; Kidoaki, S.; Matsuda, T. Electrospun nano- to microfiber fabrics made of biodegradable copolyesters: Structural characteristics, mechanical properties and cell adhesion potential. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3929–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersson, R.L.; Ström, V.; Gedde, U.W.; Mallon, P.E.; Hedenqvist, M.S.; Olsson, R.T. Micromechanics of ultra-toughened electrospun PMMA/PEO fibres as revealed by in-situ tensile testing in an electron microscope. Sci. Rep. 2014, 3, 6335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukiman, M.S.; Andriyana, A.; Ang, B.C.; Metselaar, H.S.C. Elastic properties of electrospun PVDF nanofibrous membranes: Experimental investigation and numerical modelling using pixel-based finite element method. Polym. Test. 2020, 81, 106218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadian, M.; Haghi, A.K. Systematic parameter study for nano-fiber fabrication via electrospinning process. Bulg. Chem. Commun. 2014, 46, 545–555. [Google Scholar]
- Haider, A.; Haider, S.; Kang, I.K. A comprehensive review summarizing the effect of electrospinning parameters and potential applications of nanofibers in biomedical and biotechnology. Arab. J. Chem. 2018, 11, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Bui, N.-N.; Manickam, S.S.; McCutcheon, J.R. Controlling electrospun nanofiber morphology and mechanical properties using humidity. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1734–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Janković, B.; Baumgartner, S.; Kocbek, P. The impact of relative humidity during electrospinning on the morphology and mechanical properties of nanofibers. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 456, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Gradys, A.; Kim, S.K.; Persano, L.; Marzec, M.; Kryshtal, A.; Busolo, T.; Toncelli, A.; Pisignano, D.; Bernasik, A.; et al. Enhanced Piezoelectricity of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride Fibers for Energy Harvesting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 13575–13583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fashandi, H.; Karimi, M. Characterization of porosity of polystyrene fibers electrospun at humid atmosphere. Thermochim. Acta 2012, 547, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Qin, X.H. Effect of Relative Humidity on the Morphology of Electrospun Gelatin Aqueous Solutions. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 941–944, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barua, B.; Saha, M.C. Influence of humidity, temperature, and annealing on microstructure and tensile properties of electrospun polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2018, 58, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peresin, M.S.; Habibi, Y.; Vesterinen, A.-H.; Rojas, O.J.; Pawlak, J.J.; Seppälä, J.V. Effect of Moisture on Electrospun Nanofiber Composites of Poly(vinyl alcohol) and Cellulose Nanocrystals. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venault, A.; Chang, Y.; Wang, D.-M.; Bouyer, D. A Review on Polymeric Membranes and Hydrogels Prepared by Vapor-Induced Phase Separation Process. Polym. Rev. 2013, 53, 568–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Thomas, N.L. Fabricating porous poly(lactic acid) fibres via electrospinning. Eur. Polym. J. 2018, 99, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadi, B.; Yousefi, A.A.; Bellah, S.M. Effect of tensile strain rate and elongation on crystalline structure and piezoelectric properties of PVDF thin films. Polym. Test. 2007, 26, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bormashenko, Y.; Pogreb, R.; Stanevsky, O.; Bormashenko, E. Vibrational spectrum of PVDF and its interpretation. Polym. Test. 2004, 23, 791–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, Y. Rheology, morphology and mechanical properties of compatibilized poly(vinylidene fluoride) (PVDF)/thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) blends. Polym. Test. 2008, 27, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szewczyk, P.K.; Metwally, S.; Karbowniczek, J.E.; Marzec, M.M.; Stodolak-Zych, E.; Gruszczyński, A.; Bernasik, A.; Stachewicz, U.; Stodolak-Zych, E.; Gruszczyn, A. Surface-Potential-Controlled Cell Proliferation and Collagen Mineralization on Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Fiber Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 5, 582–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, G.; Chang, J.; Maltby, T.; Steckler, F.; Jomaa, M.; Sun, J.; Edusei, J.; Zhang, D.; Vilches, A.; Gao, S.; et al. Bioinspired Multiresonant Acoustic Devices Based on Electrospun Piezoelectric Polymeric Nanofibers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 34643–34657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezen, M.; Plank, H.; Fisslthaler, E.; Chernev, B.; Zankel, A.; Tchernychova, E.; Blümel, A.; List, E.J.W.; Grogger, W.; Pölt, P. An investigation on focused electron/ion beam induced degradation mechanisms of conjugated polymers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 20235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaarour, B.; Zhu, L.; Huang, C.; Jin, X. Fabrication of a polyvinylidene fluoride cactus-like nanofiber through one-step electrospinning. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 42353–42360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Schultz, J.M.; Yeh, F.; Hsiao, B.S.; Chu, B. In-Situ Simultaneous Synchrotron Small- and Wide-Angle X-ray Scattering Measurement of Poly(vinylidene fluoride) Fibers under Deformation. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 1765–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterlin, A. Molecular model of drawing polyethylene and polypropylene. J. Mater. Sci. 1971, 6, 490–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, N.S.; Grubb, D.T. Deformation of lamellar structures: Simultaneous small- and wide-angle X-ray scattering studies of polyamide-6. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2002, 40, 691–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schultz, J.M. Microstructural aspects of failure in semicrystalline polymers. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1984, 24, 770–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Rutledge, G.C. Ultrafine high performance polyethylene fibers. J. Mater. Sci. 2018, 53, 3049–3063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arinstein, A.; Burman, M.; Gendelman, O.; Zussman, E. Effect of supramolecular structure on polymer nanofibre elasticity. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 59–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Barber, A.H. Extreme Toughness Exhibited in Electrospun Polystyrene Fibers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2017, 302, 1700084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachewicz, U.; Bailey, R.J.; Wang, W.; Barber, A.H. Size dependent mechanical properties of electrospun polymer fibers from a composite structure. Polymer 2012, 53, 5132–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Lacroix, M.; Pellerin, C. Molecular Orientation in Electrospun Fibers: From Mats to Single Fibers. Macromolecules 2013, 46, 9473–9493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, C.T.; Tan, E.P.S.S.; Ng, S.Y. Effects of crystalline morphology on the tensile properties of electrospun polymer nanofibers. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 141908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papkov, D.; Zou, Y.; Andalib, M.N.; Goponenko, A.; Cheng, S.Z.D.; Dzenis, Y.A. Simultaneously Strong and Tough Ultrafine Continuous Nanofibers. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 3324–3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-M.; Chou, M.-H.; Zeng, W.-Y. Piezoelectric Response of Aligned Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride/Carbon Nanotube Nanofibrous Membranes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
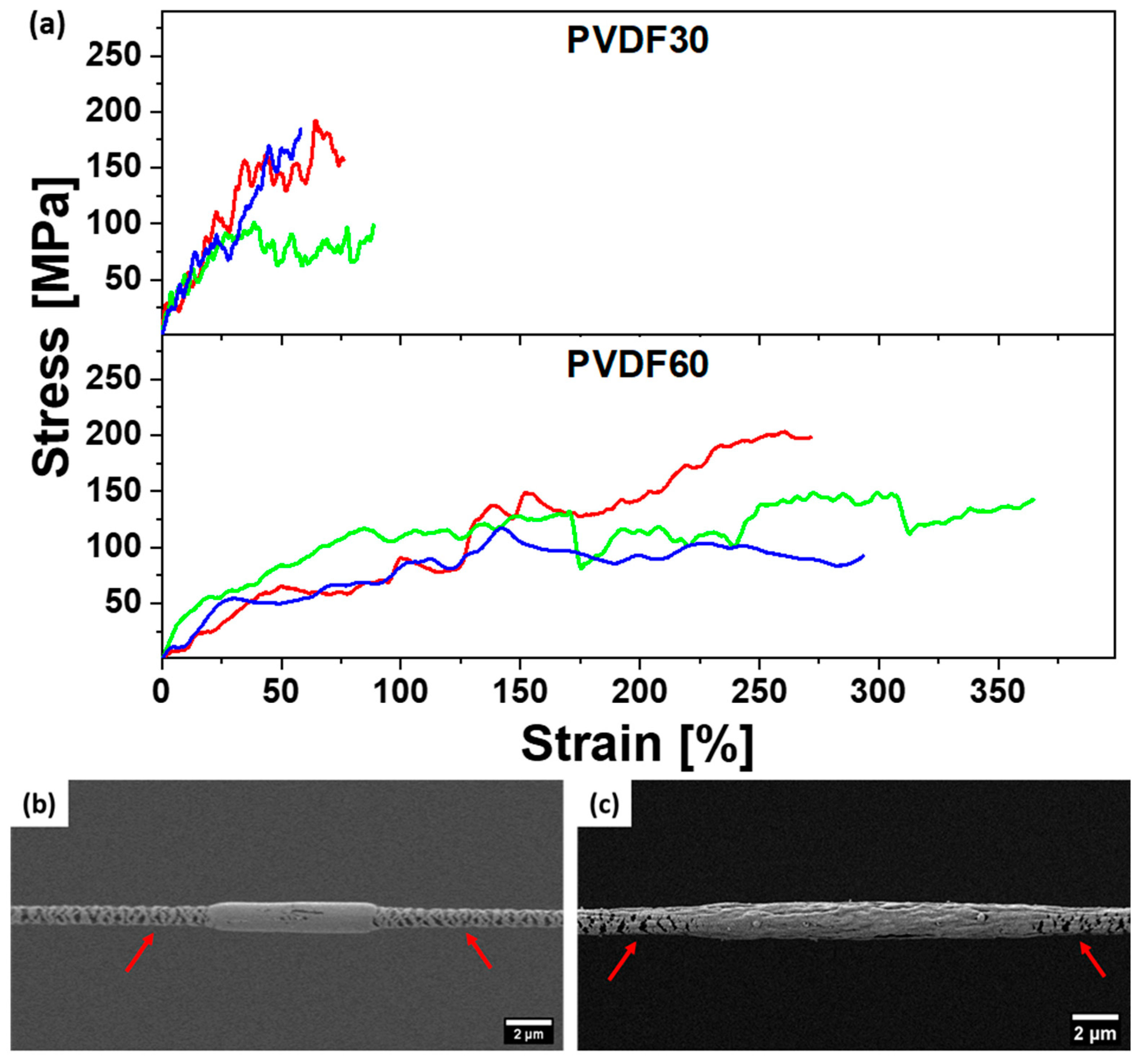
| Sample | Strain at Failure εf [%] | Toughness W [MPa] | Tensile Strength Rm [MPa] | Strain at Maximum Stress εmax [%] | Young’s Modulus [MPa] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PVDF30 | 74.19 ± 12.46 | 69.83 ± 13.94 | 159.1 ± 41.1 | 53.64 ± 10.96 | 13.3 ± 4.3 |
| PVDF60 | 309.89 ± 39.74 | 312.11 ± 70.74 | 156.3 ± 35.6 | 225.08 ± 58.93 | 3.5 ± 1.2 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szewczyk, P.K.; Ura, D.P.; Stachewicz, U. Humidity Controlled Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Fibers. Fibers 2020, 8, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib8100065
Szewczyk PK, Ura DP, Stachewicz U. Humidity Controlled Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Fibers. Fibers. 2020; 8(10):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib8100065
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzewczyk, Piotr K., Daniel P. Ura, and Urszula Stachewicz. 2020. "Humidity Controlled Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Fibers" Fibers 8, no. 10: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib8100065
APA StyleSzewczyk, P. K., Ura, D. P., & Stachewicz, U. (2020). Humidity Controlled Mechanical Properties of Electrospun Polyvinylidene Fluoride (PVDF) Fibers. Fibers, 8(10), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib8100065