Critical Velocity of High-Performance Yarn Transversely Impacted by Razor Blade
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
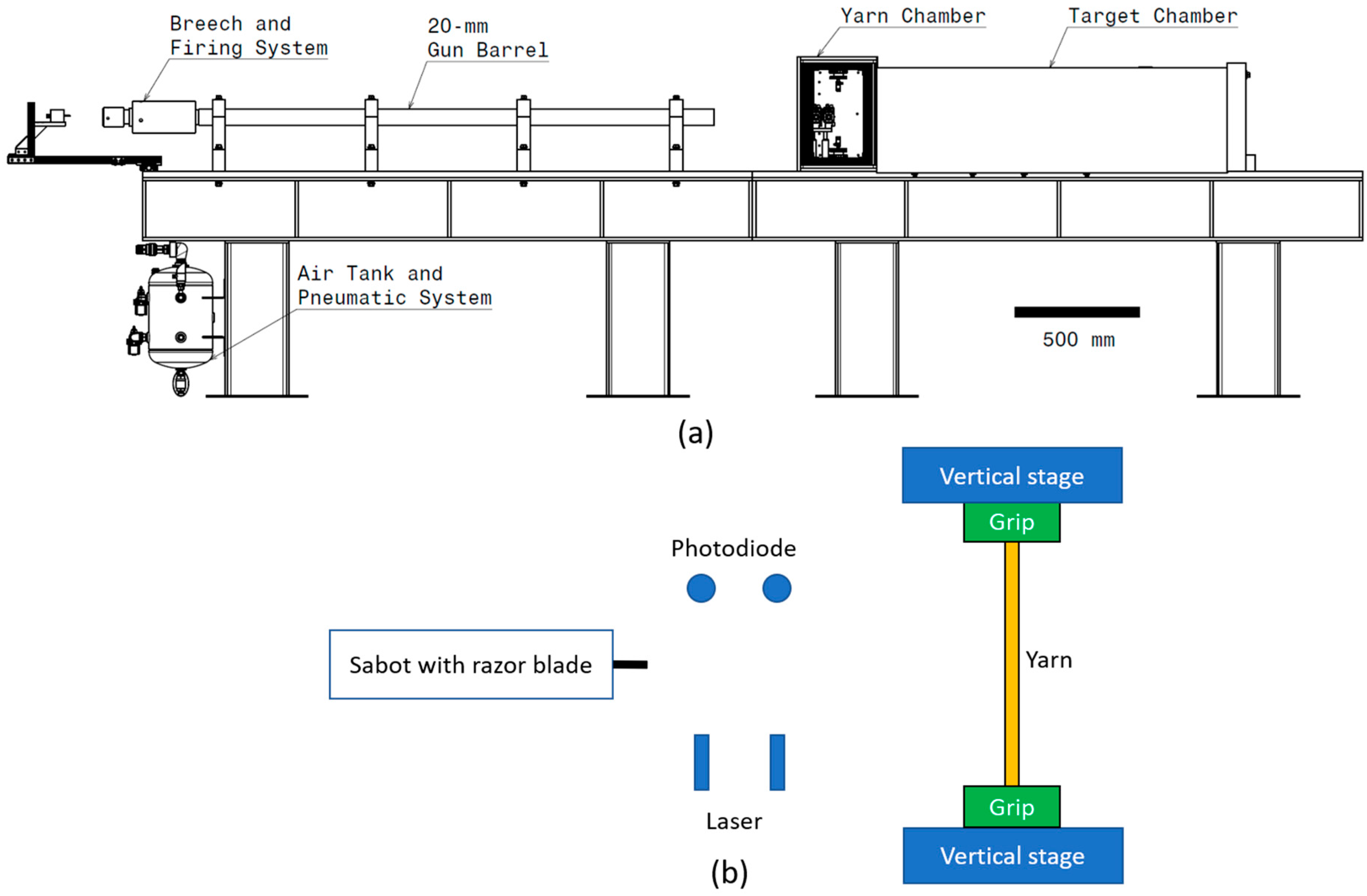
2.1. Ballistic Experiments
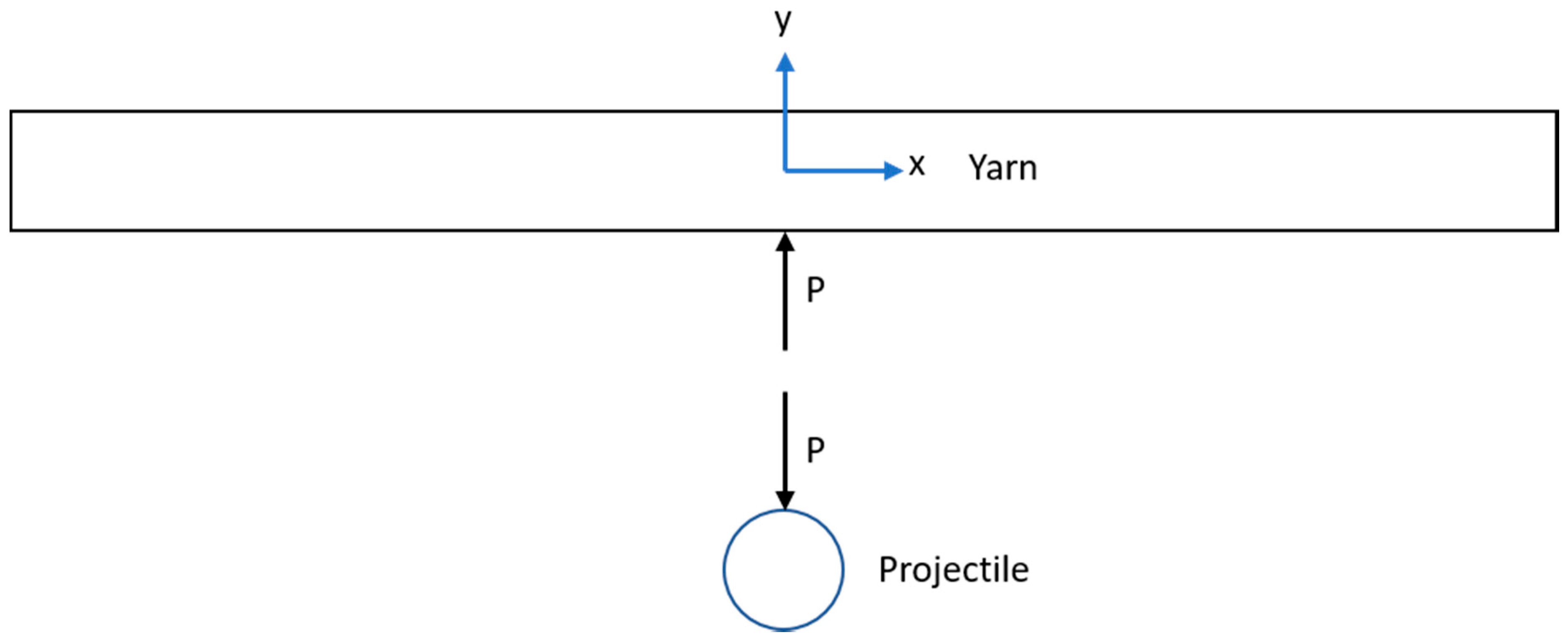
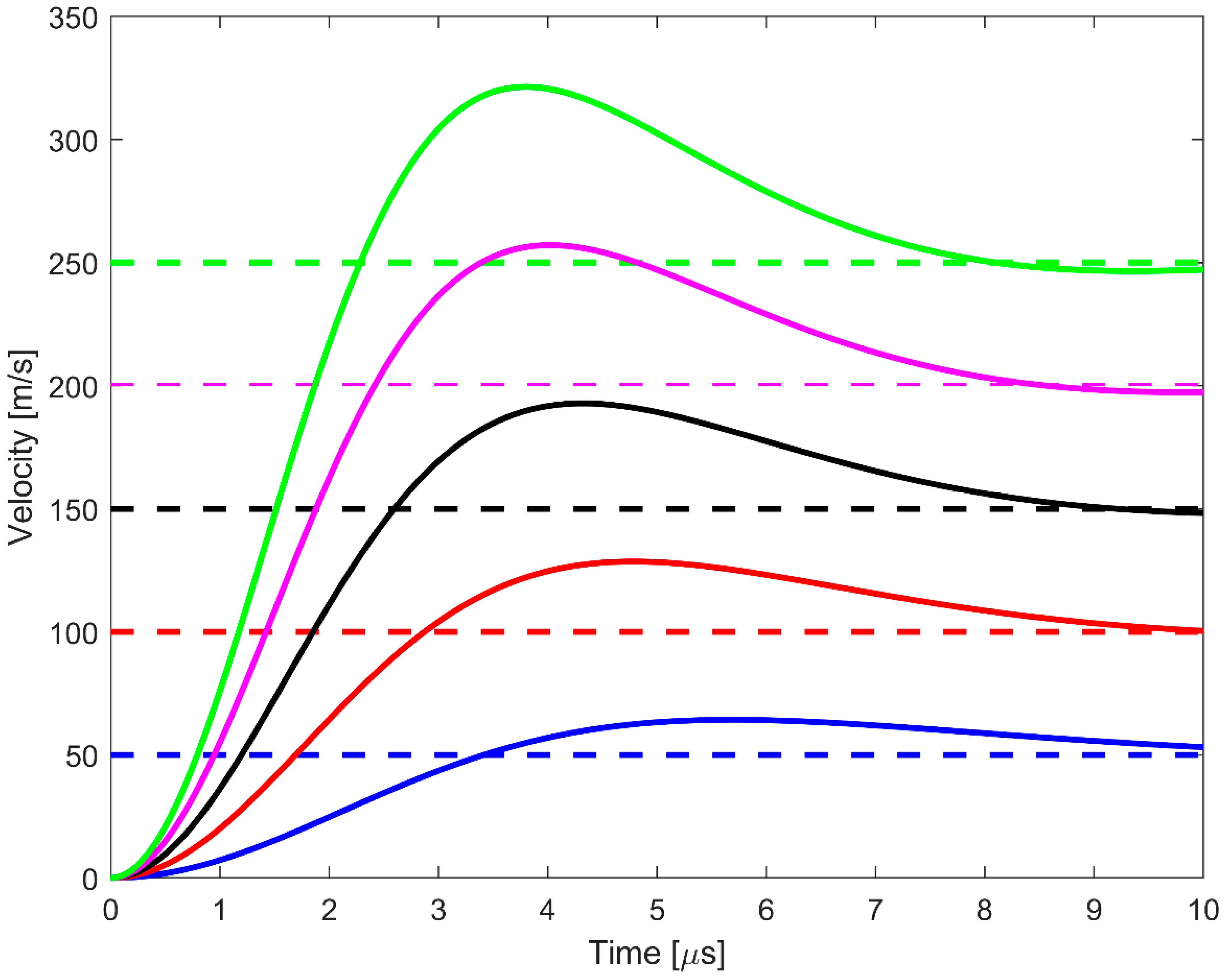
2.2. Euler–Bernoulli Beam Model
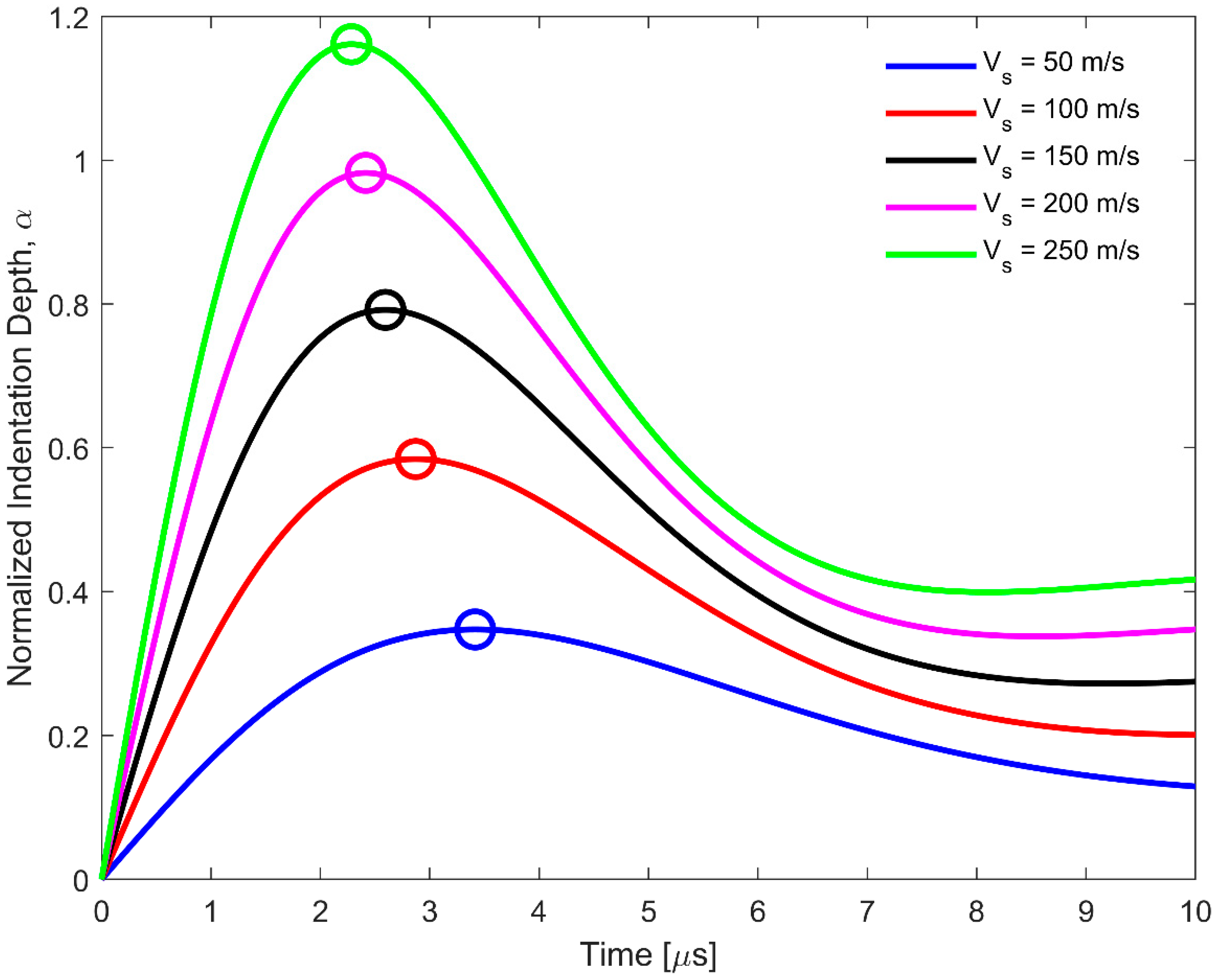
2.3. Hertzian Contact Model
3. Results
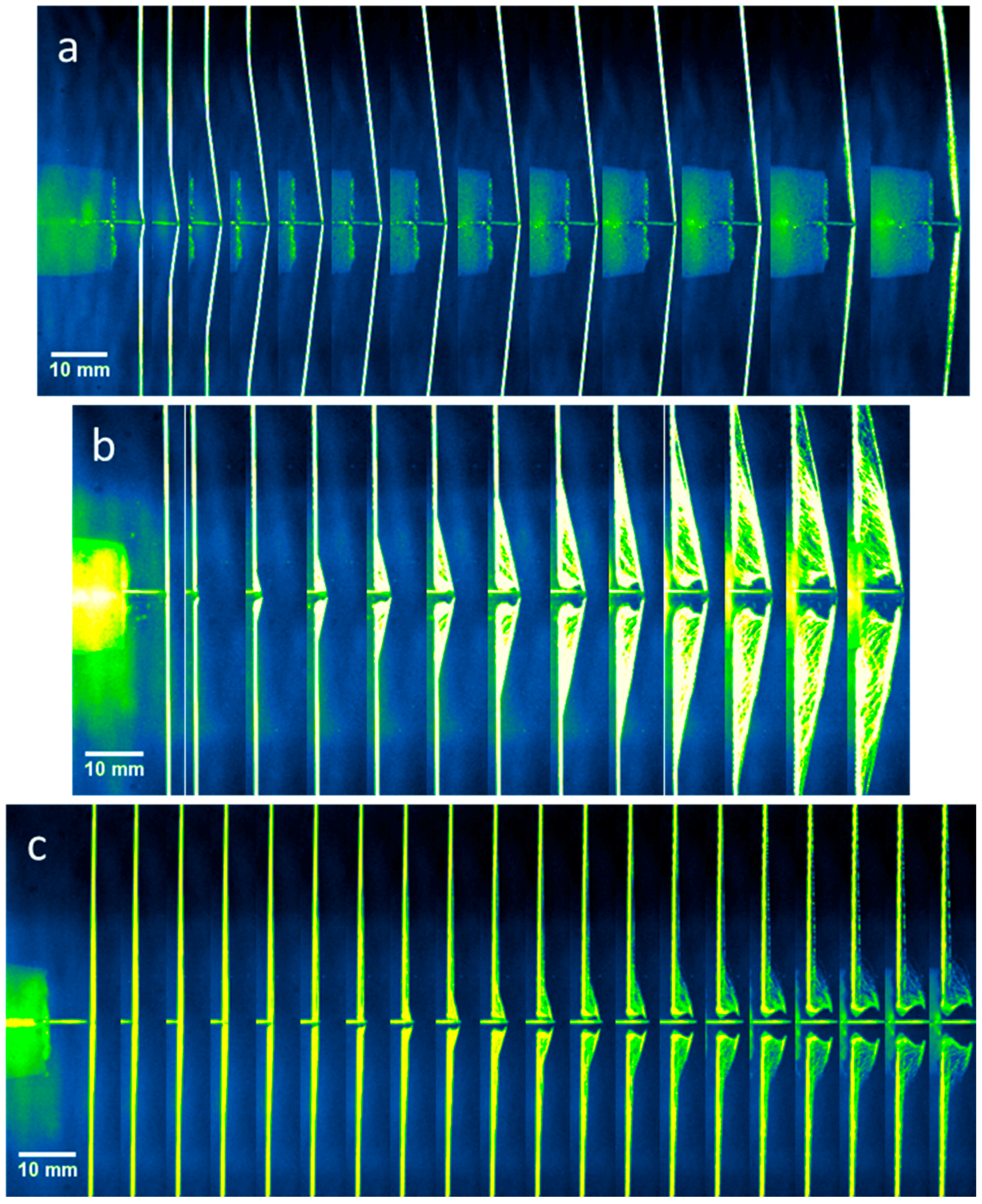
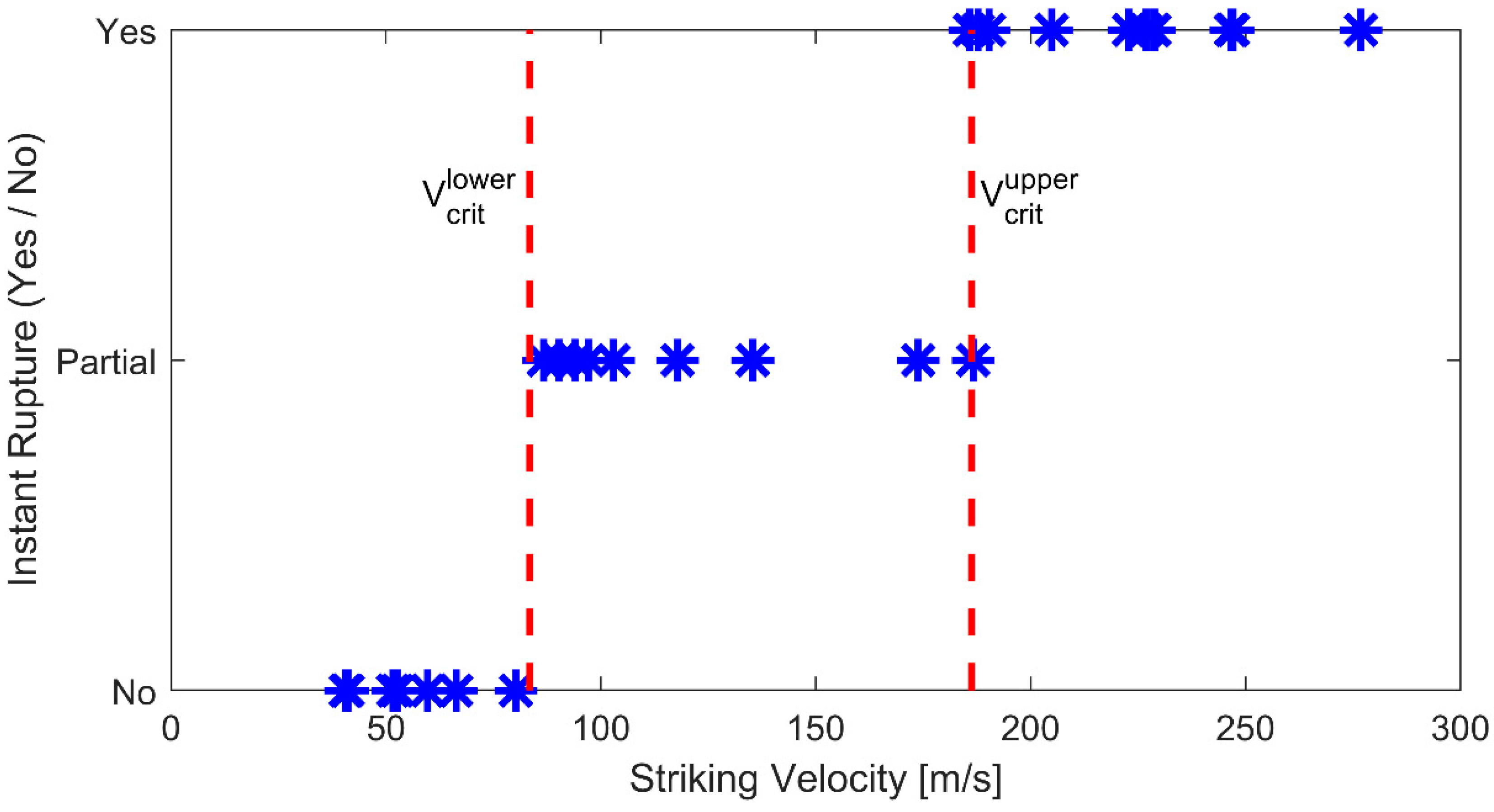
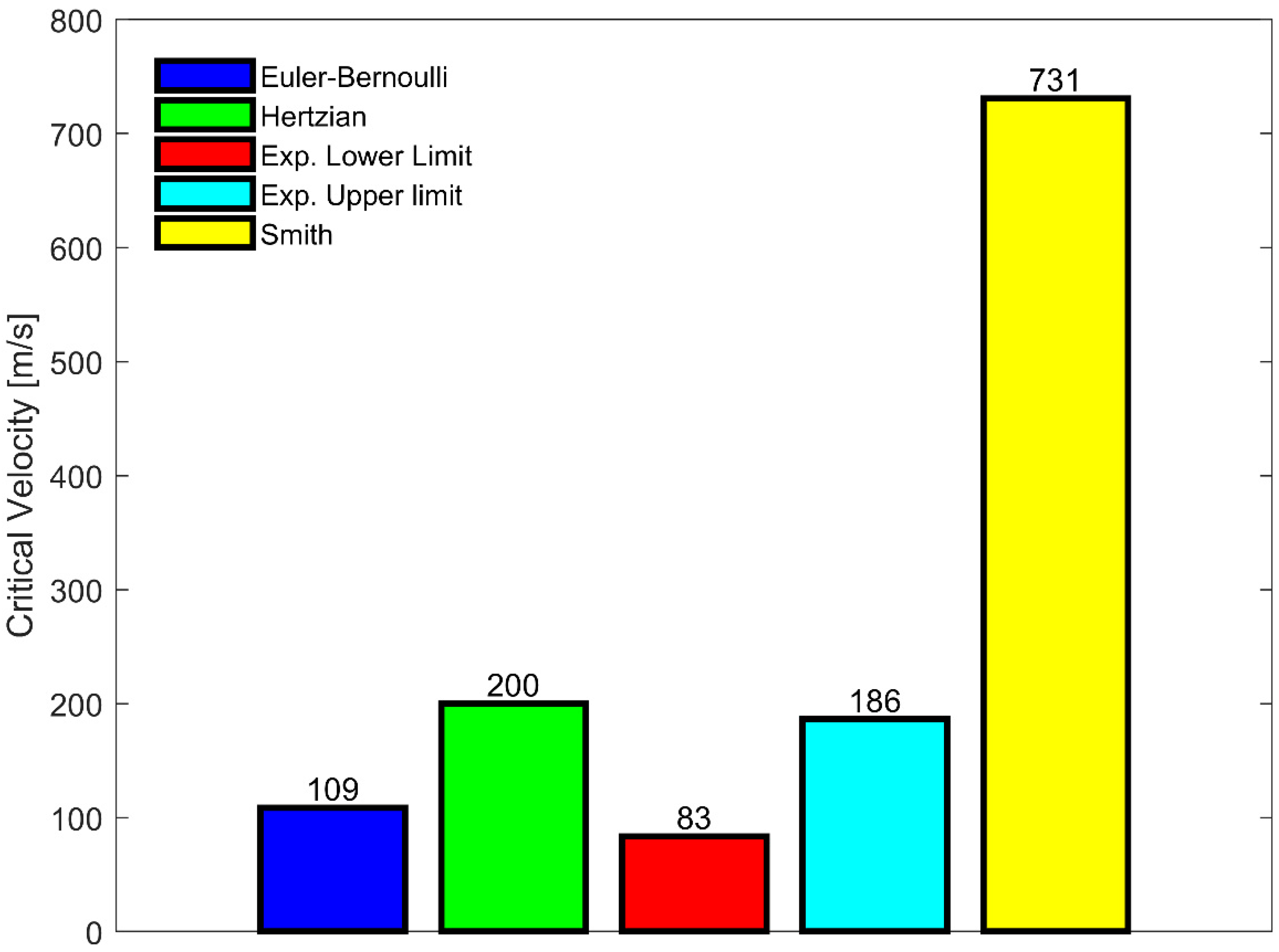
3.1. Ballistic Experiments
3.2. Hertzian Contact Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, J.C.; McCrackin, F.L.; Schiefer, H.F. Stress-Strain Relationships in Yarns Subjected to Rapid Impact Loading: Part V: Wave Propagation in Long Textile Yarns Impacted Transversely. Text. Res. J. 1958, 28, 288–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudspeth, M.; Chu, J.-M.; Jewell, E.; Lim, B.; Ytuarte, E.; Tsutsui, W.; Horner, S.; Zheng, J.; Chen, W. Effect of projectile nose geometry on the critical velocity and failure of yarn subjected to transverse impact. Text. Res. J. 2016, 87, 953–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocron, S.; Kirchdoerfer, T.; King, N.; Freitas, C.J. Modeling of fabric impact with high speed imaging and nickel-chromium wires validation. J. Appl. Mech. 2011, 78, 051007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Field, J.; Sun, Q. A high speed photographic study of impact on fibres and woven fabrics (from 19th International Congress on High-Speed Photography and Photonics 1990). SPIE Milest. Ser. MS 1995, 109, 57–66. [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth, M.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J. Why the Smith theory over-predicts instant rupture velocities during fiber transverse impact. Text. Res. J. 2015, 86, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.D.; Chocron, S. Why Impacted Yarns Break at Lower Speed Than Classical Theory Predicts. J. Appl. Mech. 2011, 78, 051021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazhenov, S.; Dukhovskii, I.; Kovalev, P.; Rozhkov, A. The fracture of SVM aramide fibers upon a high-velocity transverse impact. Polym. Sci. Ser. AC/C Vysokomolekuliarnye Soedineniia 2001, 43, 61–71. [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth, M.; Li, D.; Spatola, J.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J. The effects of off-axis transverse deflection loading on the failure strain of various high-performance fibers. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 897–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; Gillespie, J.W., Jr.; Keefe, M. Dynamic modeling of Kevlar KM2 single fiber subjected to transverse impact. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2015, 67–68, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sockalingam, S.; John, W.; Gillespie, J.; Keefe, M. Modeling the fiber length-scale response of Kevlar KM2 yarn during transverse impact. Text. Res. J. 2017, 87, 2242–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudspeth, M.C. Multi-Axial Failure of High-Performance Fiber during Transverse Impact. Ph.D. Thesis, Purdue University, West Lafayette, IN, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, B.H.; Chu, J.-M.; Chen, W. Mechanical Behavior of High-Performance Yarns Transversely Loaded by Different Indenters. Fibers 2018, 6, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, W.; Zheng, J. Improved quasi-static twin-fiber transverse compression of several high-performance fibers. Text. Res. J. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Casem, D.; Hudspeth, M.; Nie, X.; Sun, J.; Chen, W. Transverse compression of two high-performance ballistic fibers. Text. Res. J. 2016, 86, 502–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.F. Wave Propagation in Structure: Spectral Analysis Using Fast Discrete Fourier Transforms; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Doyle, J.F. Guided Explorations of the Mechanics of Solids and Structures; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Popov, V.L. Contact Mechanics and Friction; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, M.; Chen, W.; Weerasooriya, T. Mechanical Properties of Kevlar® KM2 Single Fiber. J. Eng. Mater. Technol. 2005, 127, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Versteeg, H.K.; Malalasekera, W. An Introduction to Computational Fluid Dynamics: The Finite Volume Method; Pearson Education: London, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]

| Properties | Value |
|---|---|
| Number of filaments in a single yarn | 1000 |
| Fiber diameter [µm] | 9 |
| Density, [kg/m3] | 1440 |
| Yarn Young’s modulus, E [GPa] | 92.55 |
| Yarn ultimate tensile strength, [GPa] | 2.47 |
| Yarn ultimate tensile strain, [%] | 2.71 |
| Yarn dynamic transverse modulus, [GPa] | 3.45 |
| Razor blade Young’s modulus, [GPa] | 200 |
| Razor blade radius of curvature, [µm] | 2 |
| Projectile mass, Ms [g] | 28.4 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, B.H.; Chu, J.-M.; Claus, B.; Nie, Y.; Chen, W. Critical Velocity of High-Performance Yarn Transversely Impacted by Razor Blade. Fibers 2018, 6, 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040095
Lim BH, Chu J-M, Claus B, Nie Y, Chen W. Critical Velocity of High-Performance Yarn Transversely Impacted by Razor Blade. Fibers. 2018; 6(4):95. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040095
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Boon Him, Jou-Mei Chu, Benjamin Claus, Yizhou Nie, and Wayne Chen. 2018. "Critical Velocity of High-Performance Yarn Transversely Impacted by Razor Blade" Fibers 6, no. 4: 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040095
APA StyleLim, B. H., Chu, J.-M., Claus, B., Nie, Y., & Chen, W. (2018). Critical Velocity of High-Performance Yarn Transversely Impacted by Razor Blade. Fibers, 6(4), 95. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040095





