Effect of Density and Fiber Size on Porosity and Thermal Conductivity of Fiberboard Mats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
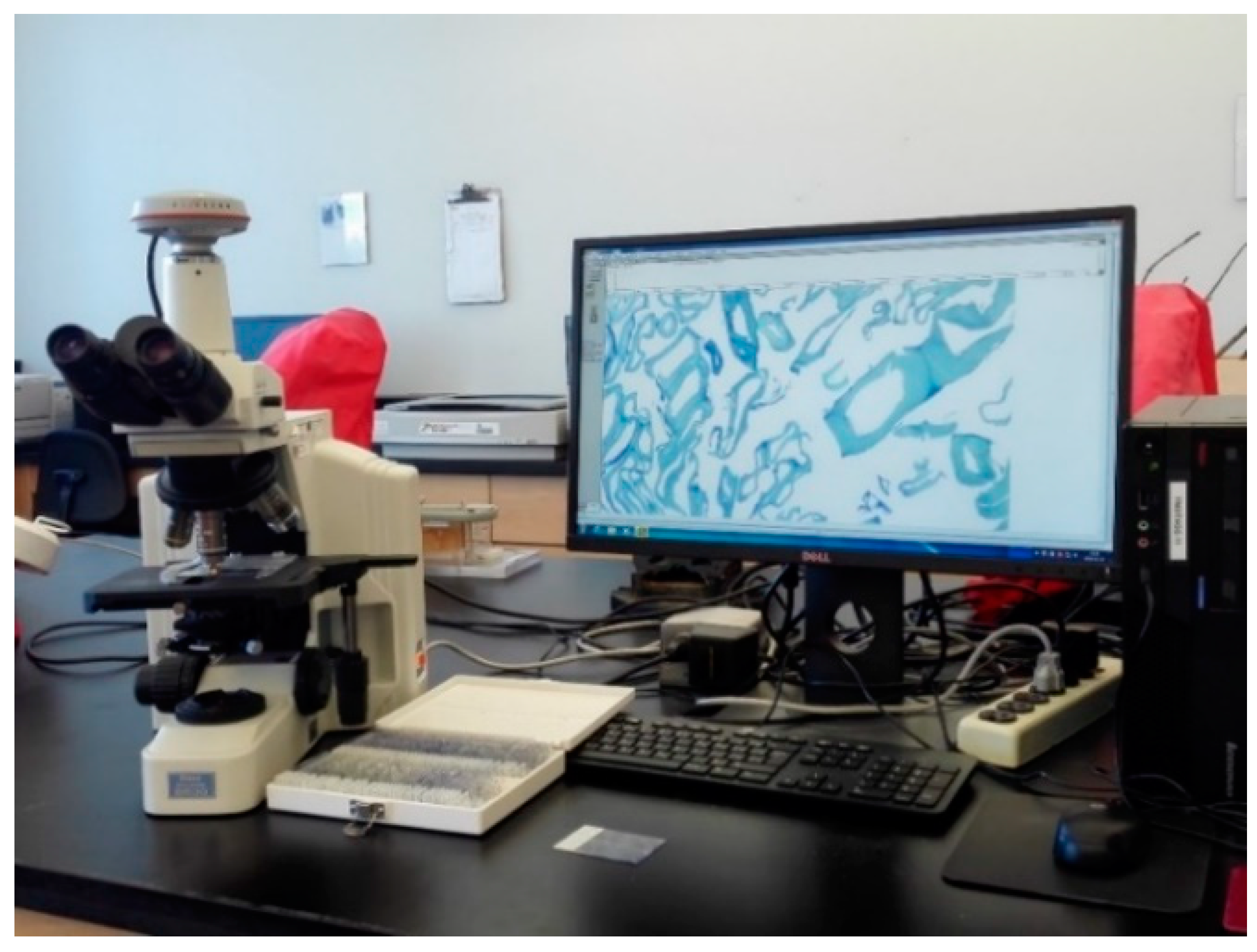
2.1. Refining and Characterization of Fiber Size
2.2. Homogeneous Density Profile Approach and Density Profile Measurements
2.3. Mat Anhydrous Density Determination
2.4. Specimen Preparation for Porosity and Thermal Conductivity Determination
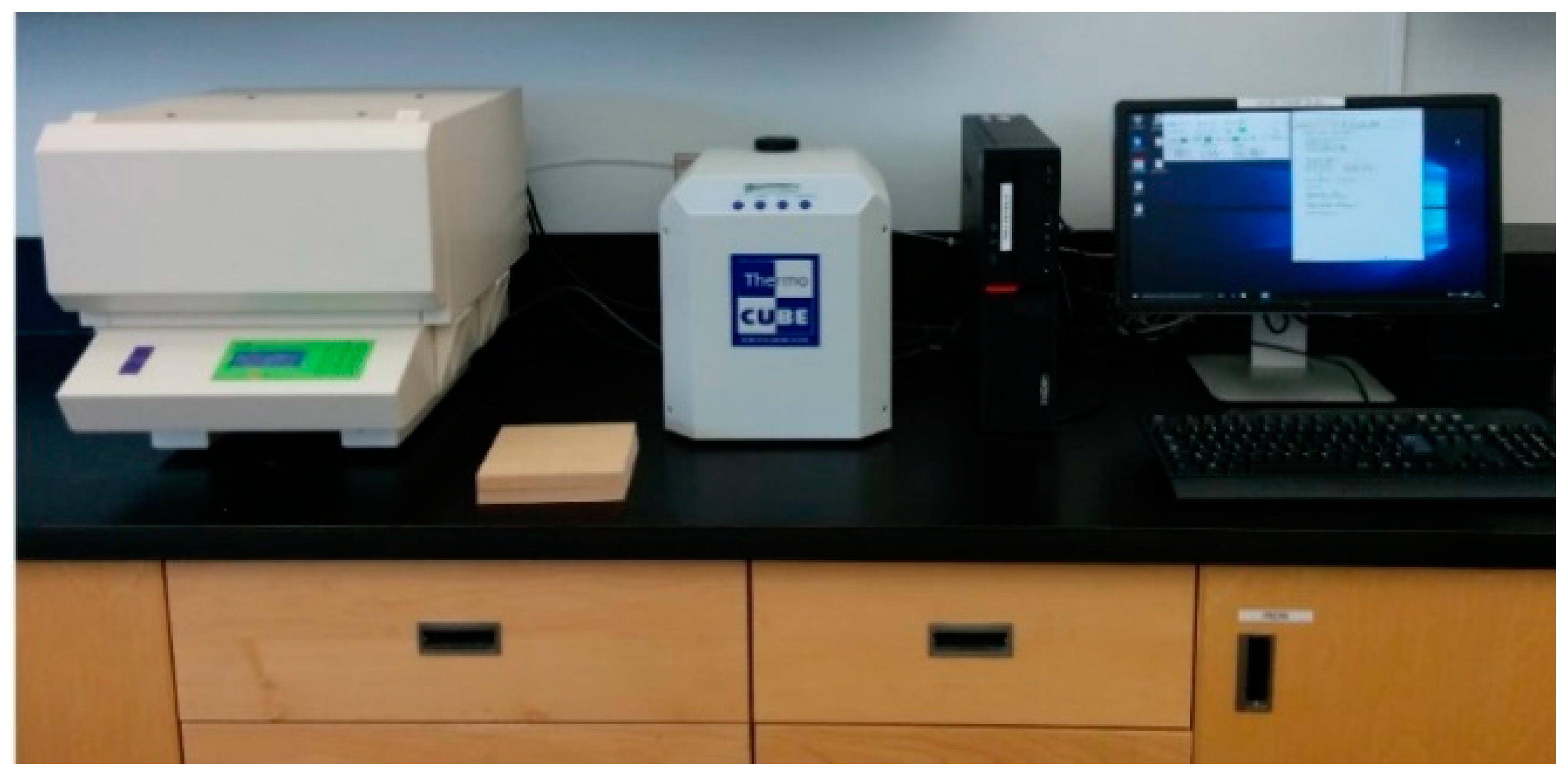
2.5. Porosity Determination
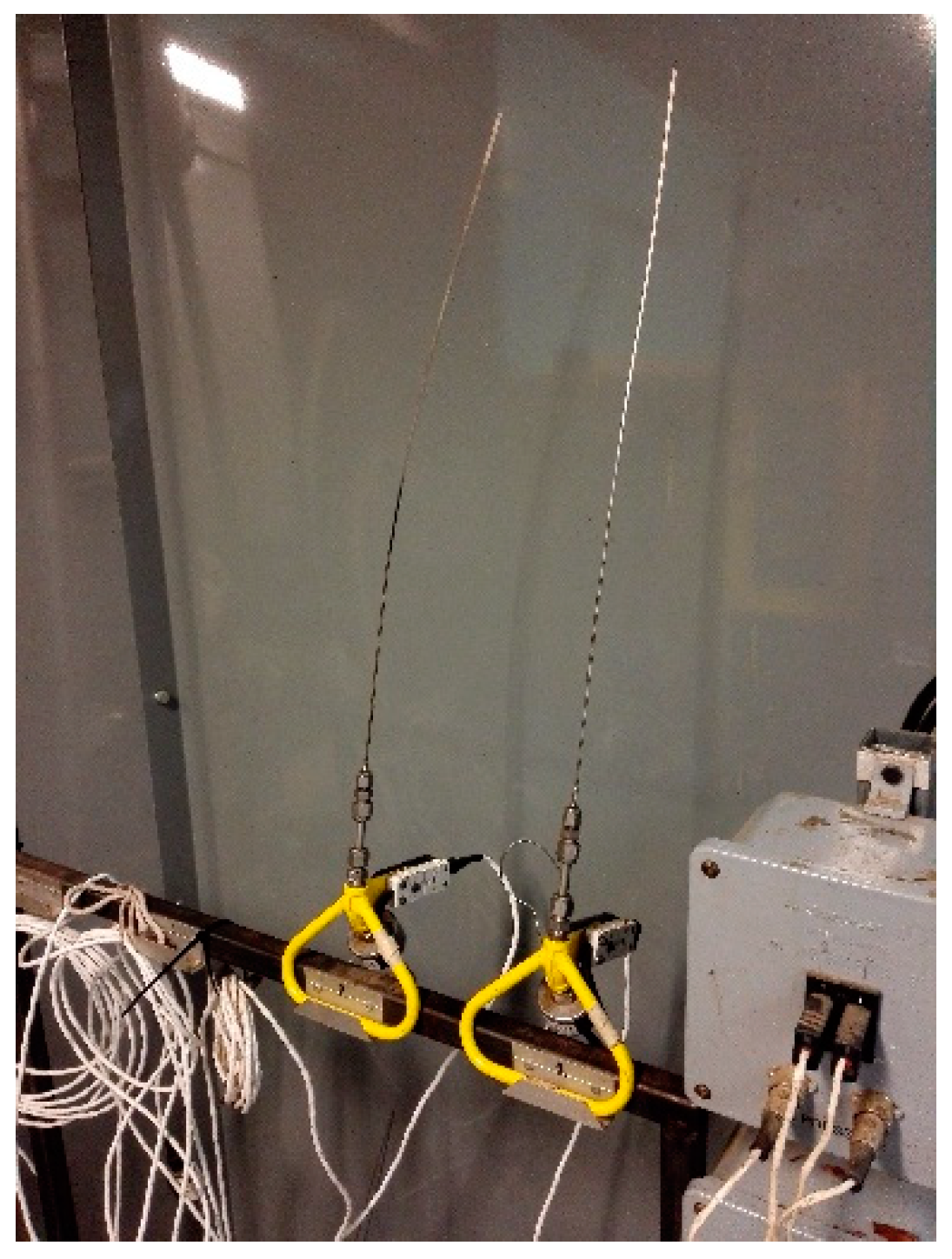
2.6. Thermal Conductivity Determination
2.7. Experimental Design
3. Results
3.1. Mat Porosity and Fiber Bundles
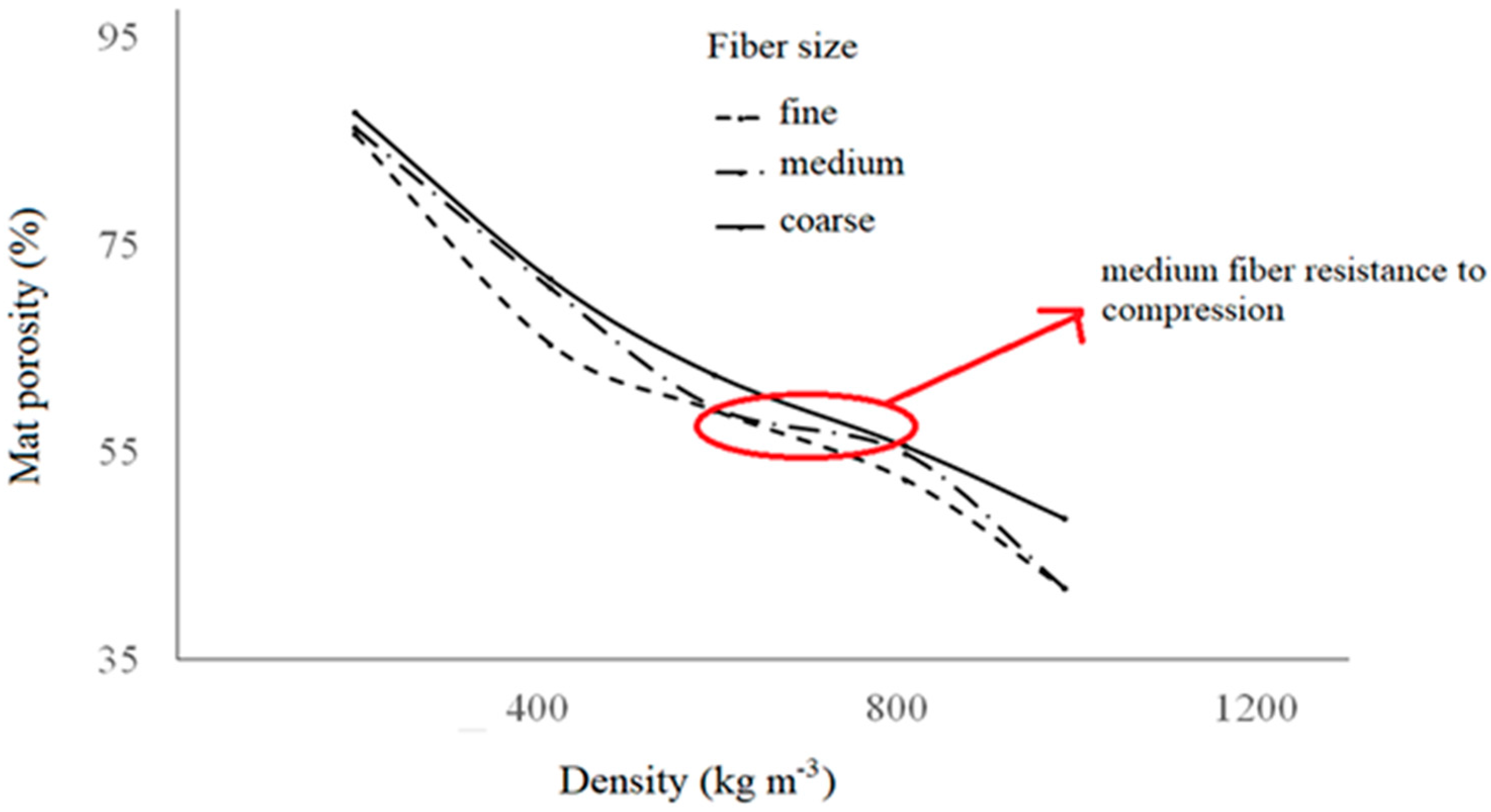
3.2. Effect of Fiber Size and Density on Mat Porosity
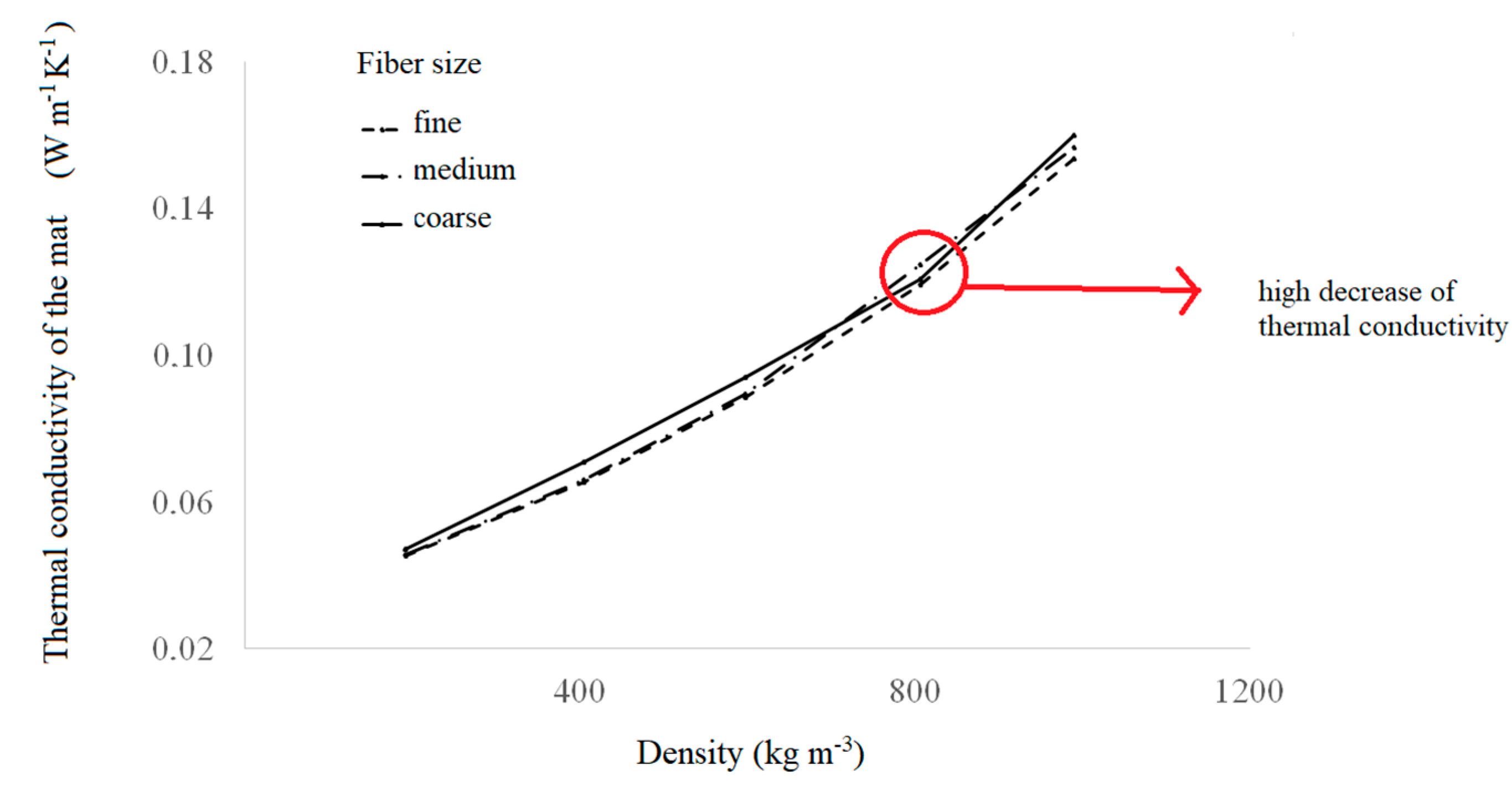
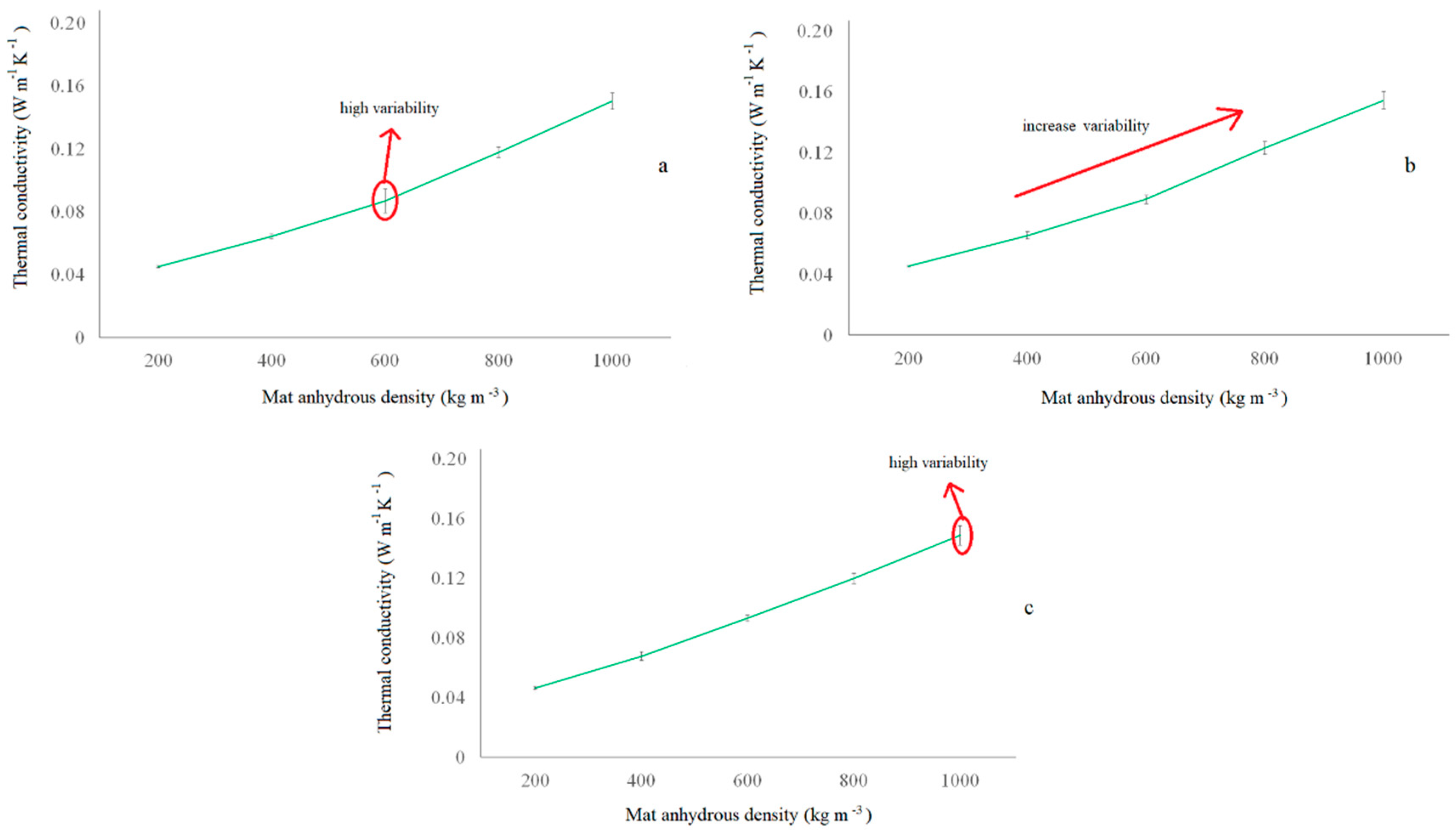
3.3. Effect of Fiber Size and Density on Thermal Conductivity of the Mat
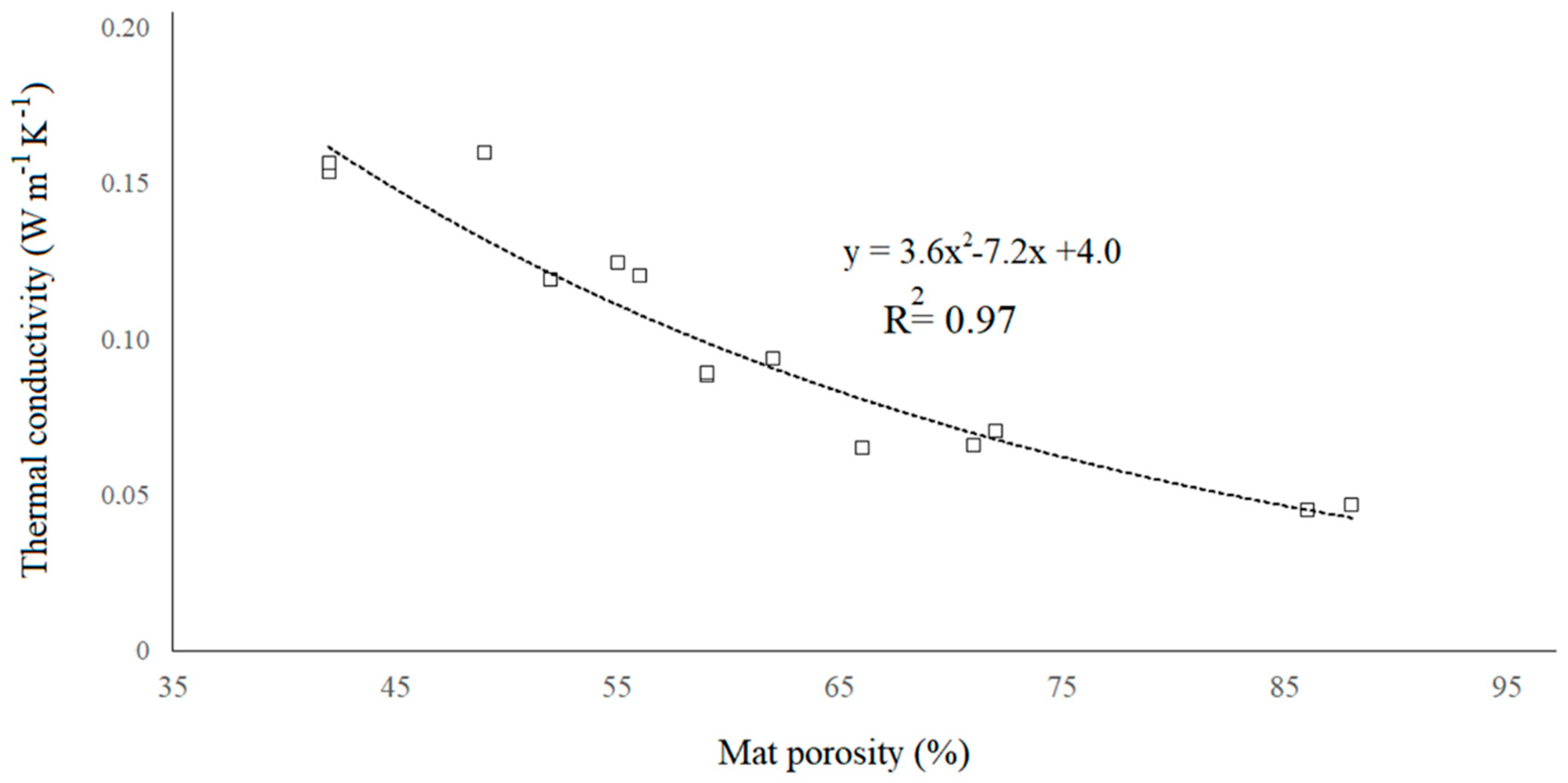
3.4. Thermal Conductivity in Relation to Mat Porosity
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Fiber size affected the porosity and thermal conductivity of the mat. This indicates that fiber size should be considered in predictive models.
- The fiber mats made with medium fiber size (between 0.60 and 0.71 mm) showed a higher resistance to compression. The mats made with coarse fibers (3.00 mm) presented a higher level of fracture and collapse which affected their capacity for heat conduction.
- The results of this investigation suggested that heat conduction is more efficient during the compression of mats with fine fibers (0.044–0.14 mm). This indicated that fine fibers had a lower tendency to produce void spaces in the fiber mat.
- The void space affected heat conduction efficiency through the mat thickness.
- During the porosity measurements, fiber bundles and fiber cell wall fractures were observed. This had an impact on mat compression and heat conduction of the fiber mats.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Von Haas, G. Investigation of the Hot Pressing of Wood Composite-Mats under Special Consideration of the Compression Behavior, the Permeability, the Temperature Conductivity and Sorption-Speed. Ph.D. Thesis, Hamburg University, Hamburg, Germany, 1998. (In Germany). [Google Scholar]
- Thoemen, H.; Humphrey, P.E. Modeling the physical process relevant during hot pressing of wood-based composites. Part I. Heat and mass transfer. Holz Roh Werkst. 2006, 64, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoemen, H.; Haselein, C.; Humphrey, P.E. Modeling the physical process relevant during hot pressing of wood-based composites. Part II. Rheology. Holz Roh Werkst. 2006, 64, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavazović, Z.; Deteix, J.; Cloutier, A.; Fortin, A. Numerical modeling of the medium-density fiberboard hot pressing process, Part I: Coupled heat and mass transfer model. Wood Fiber Sci. 2012, 42, 168–188. [Google Scholar]
- Kavazović, Z.; Deteix, J.; Fortin, A.; Cloutier, A. Numerical modeling of the medium-density fiberboard hot pressing process, Part II: Mechanical and heat and mass transfer models. Wood Fiber Sci. 2012, 44, 243–262. [Google Scholar]
- Humphrey, P.E. Physical Aspects of Wood Particleboard Manufacture. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Wales, Cardiff, UK, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Kayihan, F.; Johnson, J.A. Heat and moisture movement in wood composite materials during the pressing operation—A simplified model. In Book Numerical Methods in Heat Transfer, 2nd ed.; Lewis, K., Morgan, B.A., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1983; Volume 2, pp. 511–531. [Google Scholar]
- Zambori, B.G.; Kamke, F.A.; Watson, L.T. Sensibility analysis of internal mat environment during hot pressing. Wood Fiber Sci. 2004, 36, 195–209. [Google Scholar]
- Kavazović, Z.; Deteix, J.; Cloutier, A.; Fortin, A. Sensitivity study of a numerical model of heat and mass transfer involved during the medium-density fiberboard hot pressing process. Wood Fiber Sci. 2010, 42, 130–149. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, G.; Ibach, R.; Faillace, M.; Gnatowski, M.; Glaeser, J.; Haight, J. Laboratory and exterior decay of wood-plastic composite boards: Voids analysis and computed tomography. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 12, 263–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siau, J. Wood: Influence of Moisture on Physical Properties; Department of Wood Science and Forest Products, Virginia polytechnic Institute and State University: Blacksburg, VA, USA, 1995; p. 227. [Google Scholar]
- Hata, T.; Kawai, S.; Ebihara, T.; Sasaki, H. Production of particleboards with a steam injection press V. Effects of particle geometry on temperature behaviors in particle mats and on-air permeabilities of boards. Mokuzai Gakkaishi 1993, 39, 161–168. [Google Scholar]
- Kamke, F.A.; Zylkowski, S.C. Effect of wood-based panel characteristics on thermal conductivity. For. Prod. J. 1989, 39, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Delisée, C.; Badel, E.; Lux, J.; Malvestio, J. Caractérisation microstructurale 3D et densification locale d`isolants fibreux cellulosiques sollicites en compression. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2009, 13, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoemen, H.; Klueppel, A. An investigation on the permeability of different wood furnish materials. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sackey, E.K.; Smith, G.D. Characterizing macro-voids of uncompressed mats and finished particleboard panels using response surface methodology and X-ray CT. Holzforschung 2010, 64, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, B.M.; Larfeldt, J.; Leckner, B.; Gustavsson, M. Thermal conductivity and diffusivity of wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 1999, 33, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belley, D. Détermination des Propriétés de Transfert de Chaleur et de Masse des Panneaux de Fibres de bois MDF. Master’s Thesis, Univeristé Laval, Québec, QC, Canada, 2009. (In French). [Google Scholar]
- Rebolledo, P.; Cloutier, A.; Yemele, M.-C. Gas permeability of fiberboard mats as a function of density and fiber size. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffey, N. Wood microscopical techniques. In Wood Formation in Trees; Chaffey, N., Ed.; Taylors and Francis: New York, NY, USA, 2002; Chapter 3; pp. 17–40. [Google Scholar]
- ISO 8302:1991. Thermal Insulation—Determination of Steady-State Thermal Resistance and Related Properties—Guarded Hot Plate Apparatus; Technical Committee ISO/TC 163; International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Dogu, D.; Tirak, K.; Candan, Z.; Unsal, O. Anatomical investigation of thermally compressed wood panels. Bioresources 2010, 5, 2640–2663. [Google Scholar]
- Budakci, M.; Pelit, H.; Sonmez, A.; Korkmaz, M. The effects of densification and heat post-treatment on hardness and morphological properties of wood materials. Bioresources 2016, 11, 7822–7838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, H.; Doumalin, P.; Delisée, C.; Dupre, J.C.; Malvestio, J.; Germaneau, A. 3D mechanical analysis of low-density wood-based fiberboards by X-ray microcomputed tomography and Digital Volume Correlation. J. Mater. Sci. 2012, 48, 3198–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, P.; Staffan Lundström, T.; Wikström, T. A method to measure the permeability of dry fiber mats. Wood Fiber Sci. 2006, 38, 417–426. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, C.; Dai, C.; Smith, G. A generalized mat consolidation model for wood composites. Holzforschung 2008, 62, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoemen, H.; Walther, T.; Wiegmann, A. 3D simulation of macroscopic heat and mass transfer properties from the microstructure of wood fibre networks. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2008, 68, 608–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliseris, J.; Handra, H.; Kabel, M.; Dix, B.; Plinke, B. Virtual characterization of MDF fiber network. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2017, 75, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolton, A.J.; Humphrey, P.E. The permeability of wood-based composite materials. Holzforschung 1994, 48, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Yu, C.; Xu, C.; He, G. Heat and mass transfer in wood composite panels during hot pressing. Part 4. Experimental investigation and model validation. Holzforschung 2007, 61, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Yu, C.; Zhou, X. Heat and mass transfer in wood composite panels during hotpressing: Part II Modeling void formation and mat permeability. Wood Fiber Sci. 2005, 37, 242–257. [Google Scholar]
- Li, P.; Dai, C.; Wang, S. A simulation of void variation in wood-strand composites during consolidation. Holzforschung 2009, 63, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, W.; Duval, H.; Pierre, F.; Perré, P. A novel device to measure gaseous permeability over a wide range of pressures: Characterization of slip flow for Norway spruce, European beech, and wood-based materials. Holzforschung 2017, 71, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonderegger, W.; Nienz, P. Thermal conductivity and water vapour transmission properties of wood-based materials. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2009, 67, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselein, C.R. Numerical Simulation of Pressing Wood-Fiber Composites. Ph.D. Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis, OR, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Kamke, F.A.; Casey, L. Fundamentals of flakeboard manufacture: Internal-mat conditions. For. Prod J. 1989, 38, 38–44. [Google Scholar]
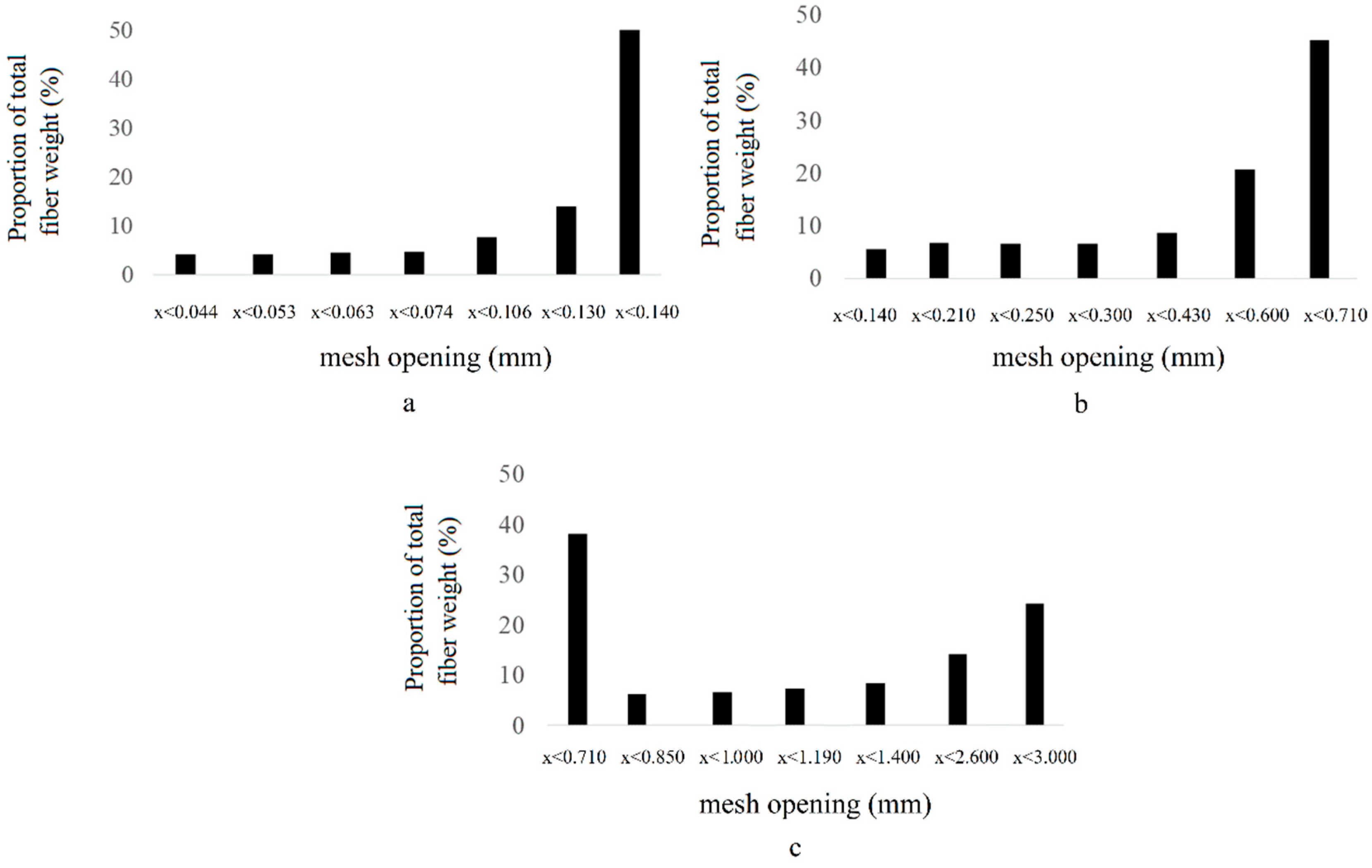

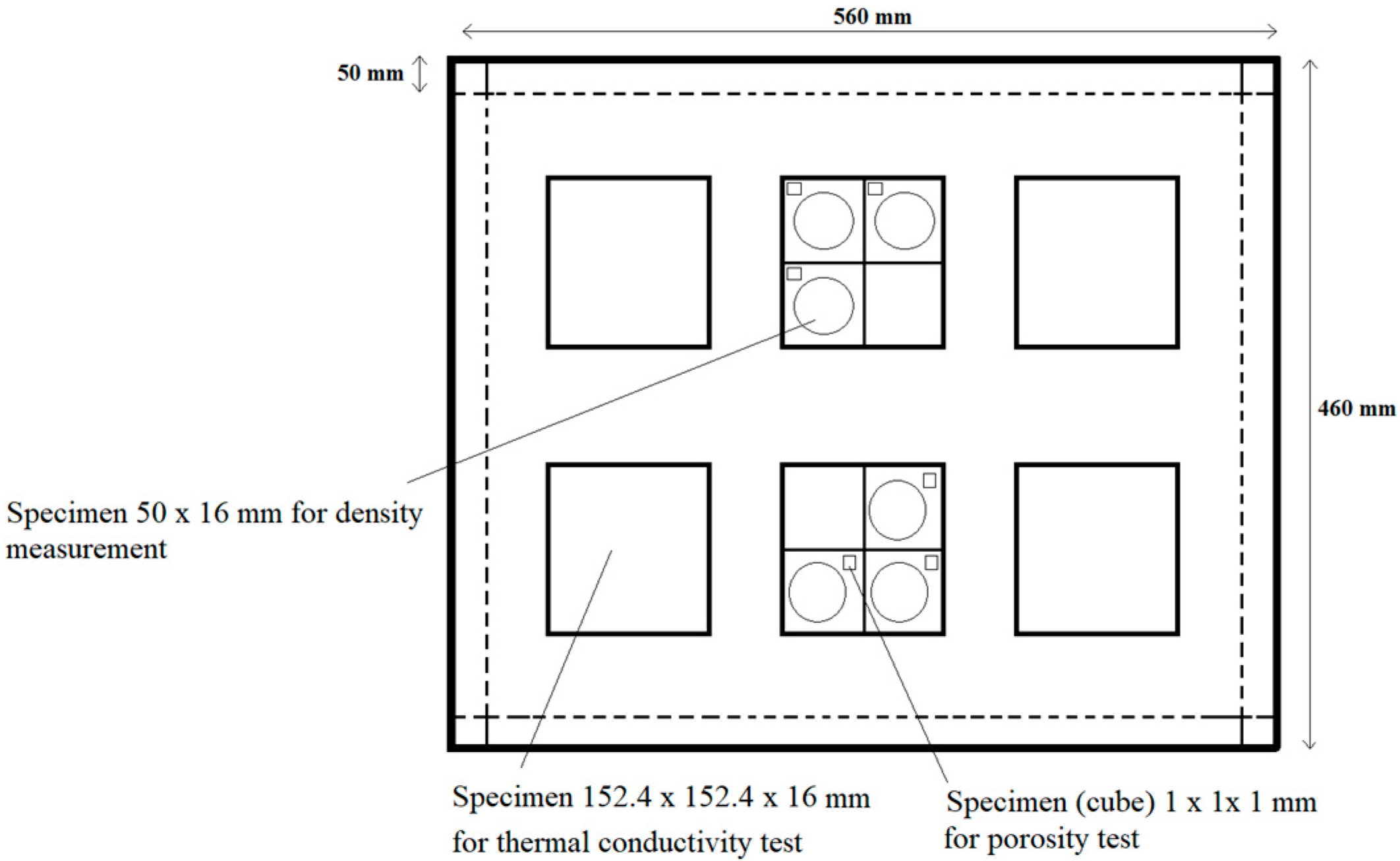
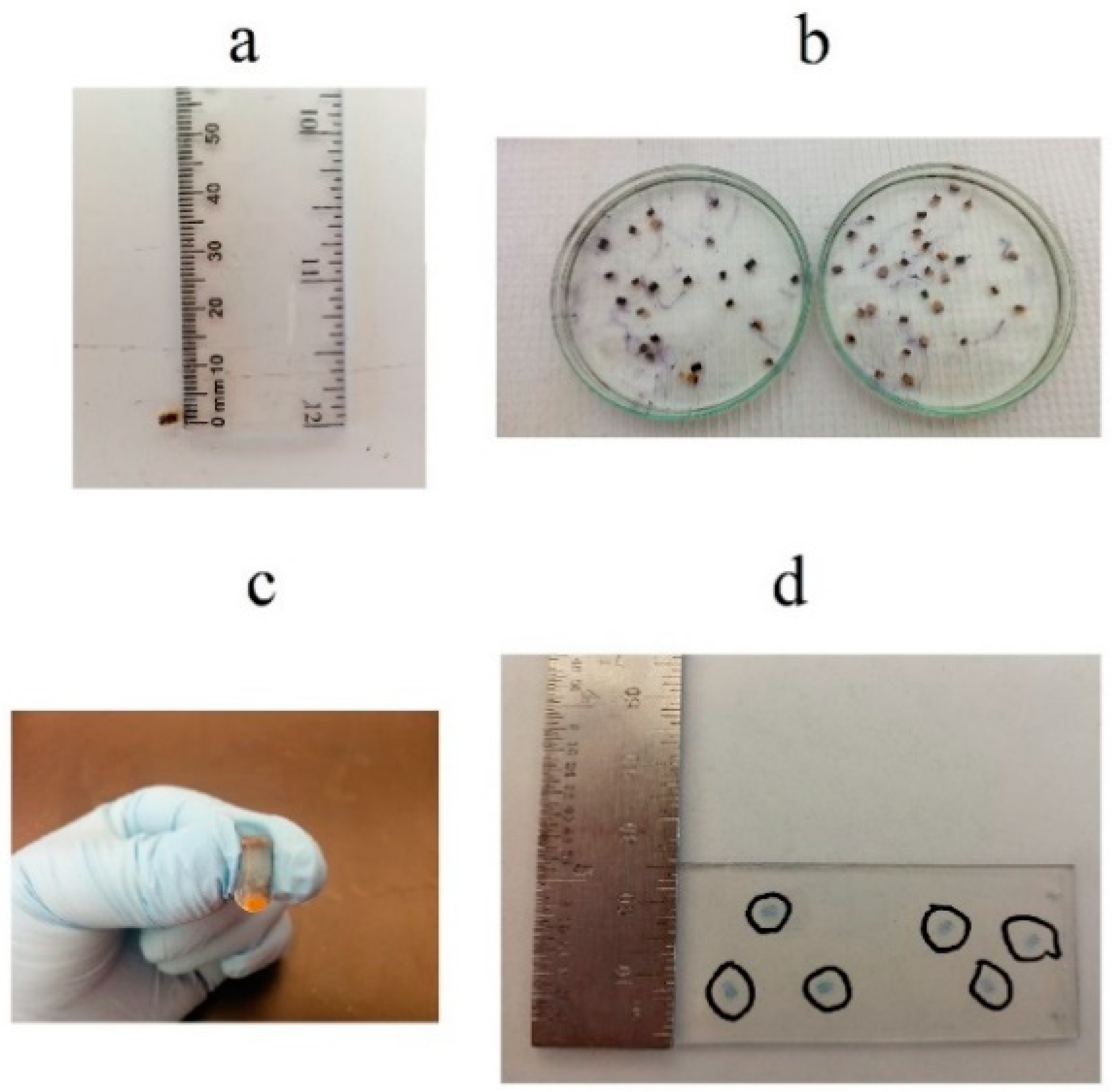

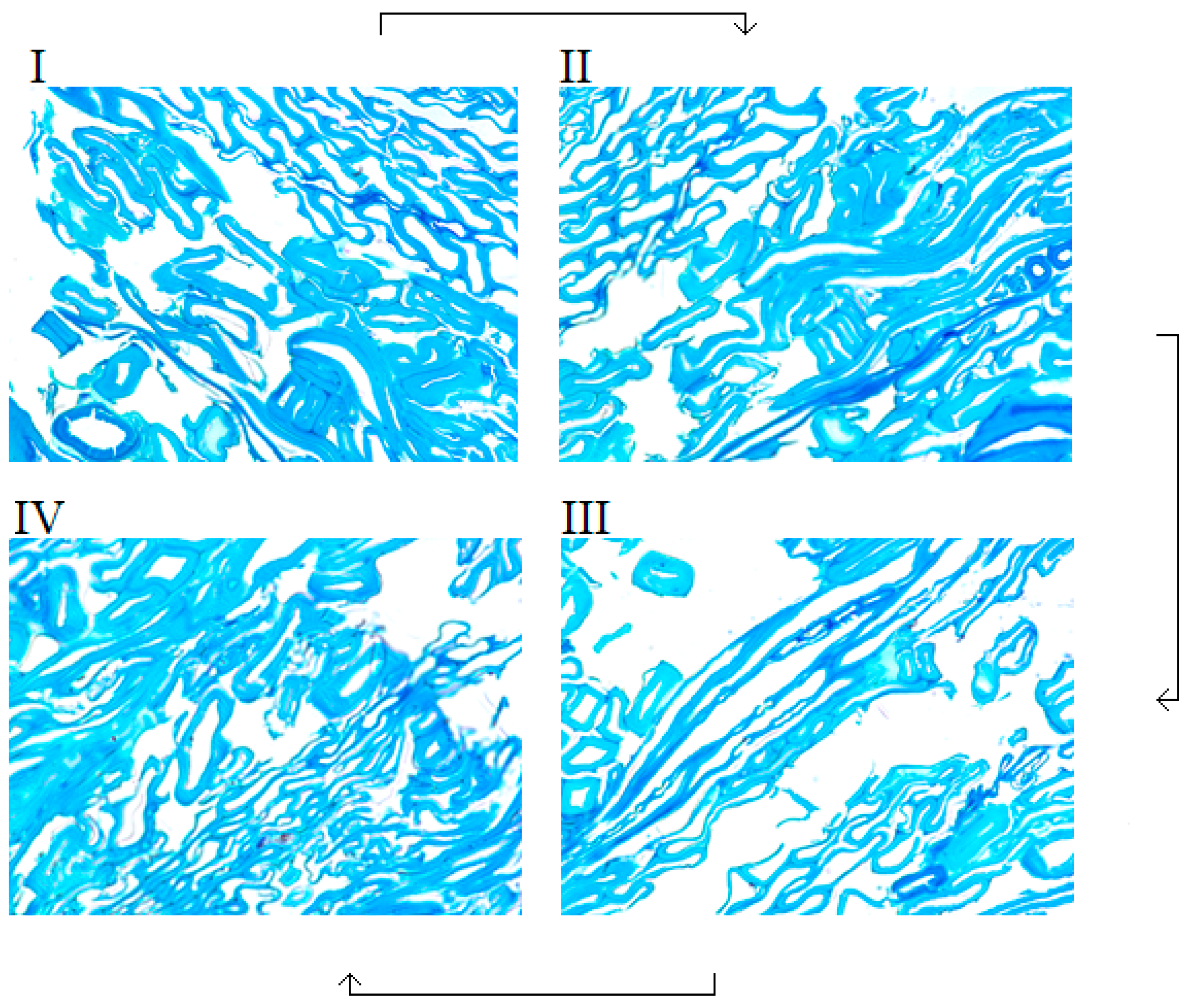

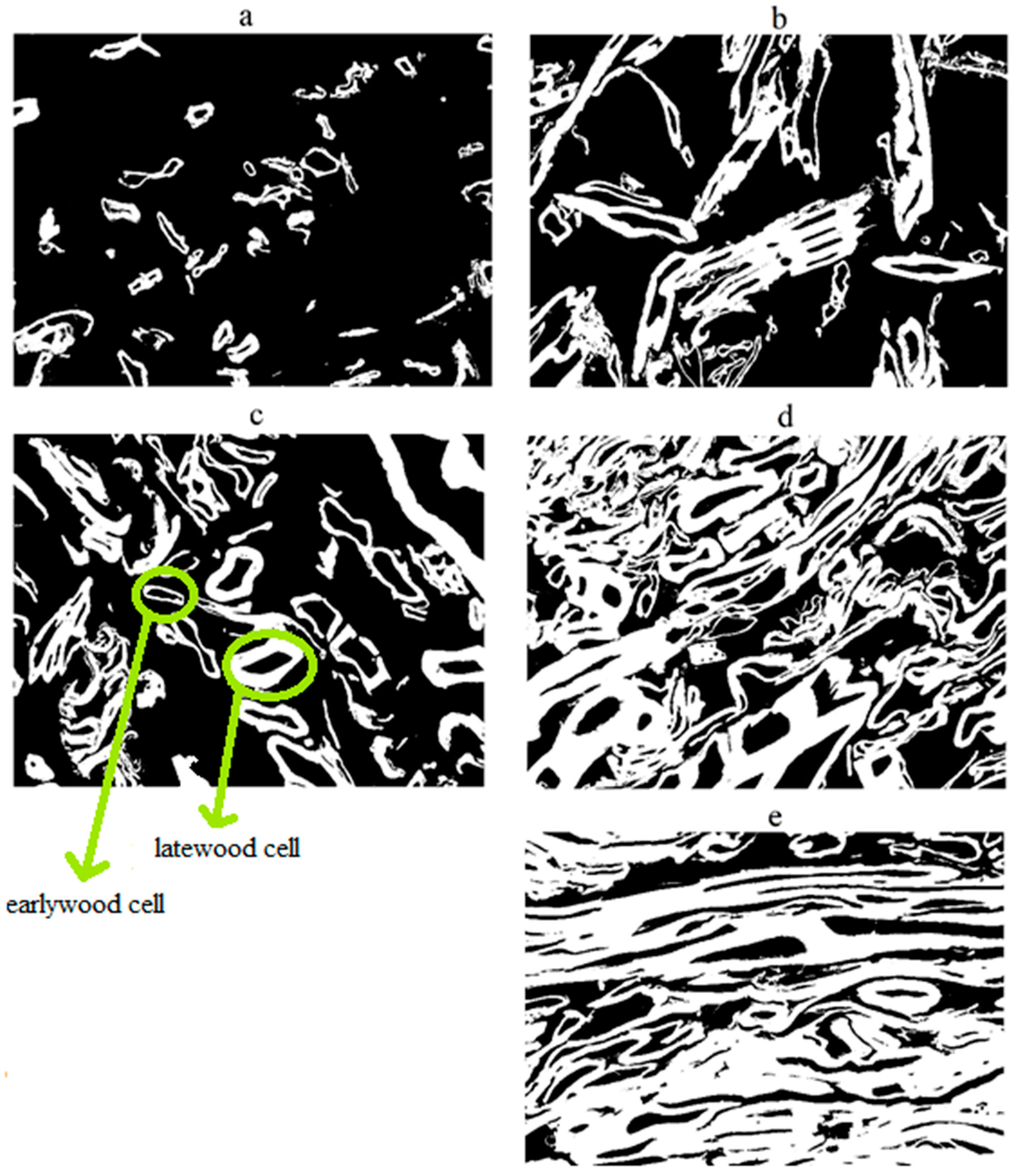
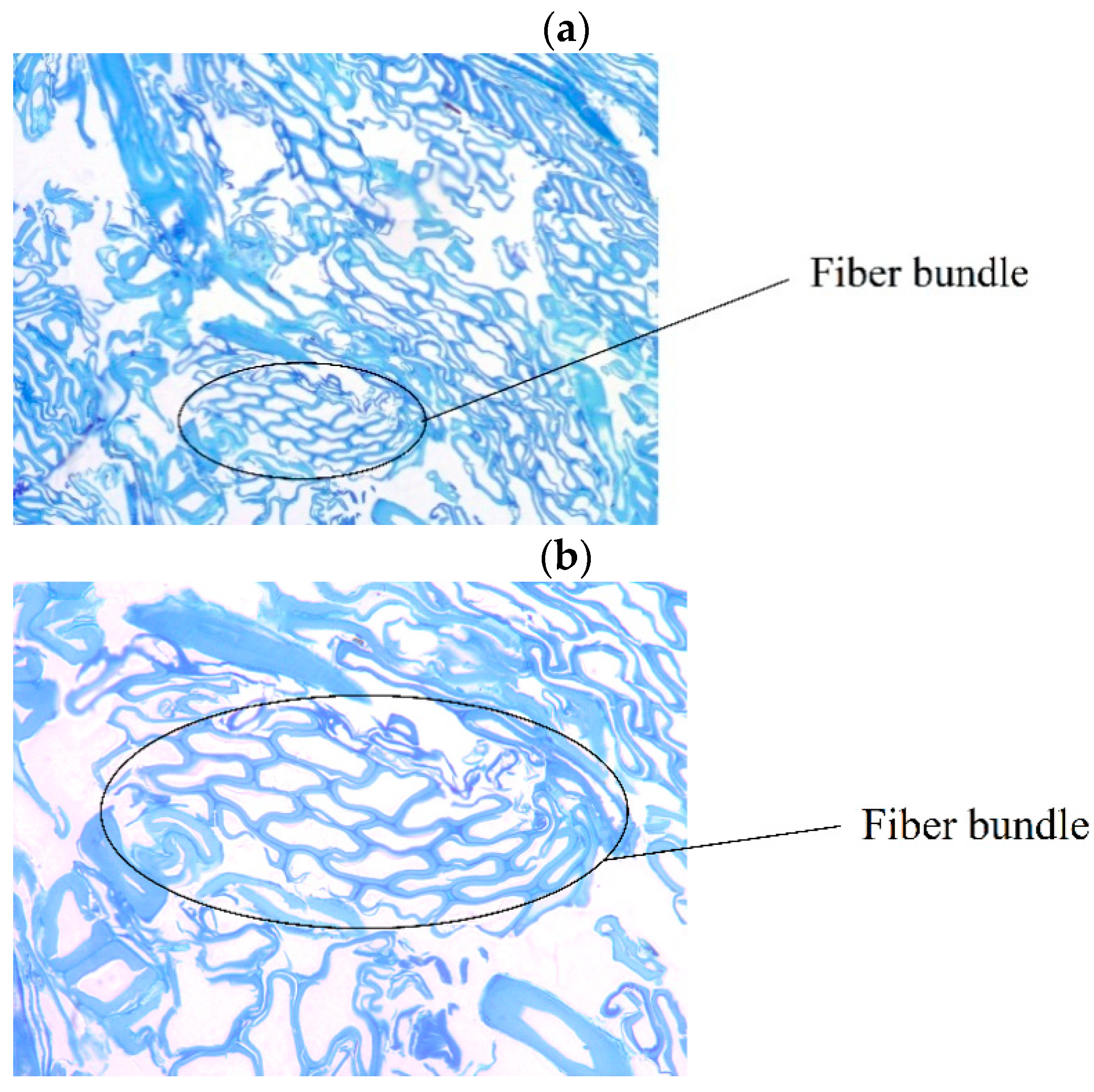
| Fiber Size | Plates Rotation Speed (rpm) | Pressure (bars) | Holding Time (s) | Plate Spacing (mm) | Temperature (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine | 2750 | 8 | 120 | 0.10 | 170 |
| Medium | 2000 | 8 | 120 | 0.25 | 170 |
| Coarse | 2000 | 8 | 120 | 0.60 | 170 |
| Source | Degrees of Freedom | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F-Value | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mat density | 4 | 670,202 | 167,550 | 3907.4 | <0.0001 |
| Fiber size | 2 | 10,660 | 5330 | 124.3 | <0.0001 |
| Mat density × fiber size | 8 | 4515 | 564 | 13.2 | <0.0001 |
| Source | DF | Sum of Squares | Mean Square | F Value | Pr > F |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mat density | 4 | 0.25554 | 0.06388 | 5292.1 | <0.0001 |
| Fiber size | 2 | 0.00016 | 0.00008 | 6.7 | 0.0020 |
| Mat density × fiber size | 8 | 0.00041 | 0.00005 | 4.28 | 0.0001 |
| Fiber Size | α1 | α2 | α3 | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fine | 8.13 × 10−8 | 5.28 × 10−5 | 0.03 | 0.98 |
| Medium | 7.81 × 10−8 | 6.22 × 10−5 | 0.03 | 0.99 |
| Coarse | 6.27 × 10−8 | 7.25 × 10−5 | 0.03 | 0.99 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rebolledo, P.; Cloutier, A.; Yemele, M.-C. Effect of Density and Fiber Size on Porosity and Thermal Conductivity of Fiberboard Mats. Fibers 2018, 6, 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040081
Rebolledo P, Cloutier A, Yemele M-C. Effect of Density and Fiber Size on Porosity and Thermal Conductivity of Fiberboard Mats. Fibers. 2018; 6(4):81. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040081
Chicago/Turabian StyleRebolledo, Pamela, Alain Cloutier, and Martin-Claude Yemele. 2018. "Effect of Density and Fiber Size on Porosity and Thermal Conductivity of Fiberboard Mats" Fibers 6, no. 4: 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040081
APA StyleRebolledo, P., Cloutier, A., & Yemele, M.-C. (2018). Effect of Density and Fiber Size on Porosity and Thermal Conductivity of Fiberboard Mats. Fibers, 6(4), 81. https://doi.org/10.3390/fib6040081





