Abstract
The interest and thus the number of publications on the supply chains of bast fiber plants has steadily increased in recent years. A number of specific technical terms related to methods and their use for individual areas of the supply chain are often interpreted and used in very different ways. Therefore, the aim of this publication is to increase the clarity of the description of the operations and to improve the understanding of the sequence and the purpose of the process steps. This is based on a selected review of the relevant literature as well as on suggestions for their classification
1. Introduction
Bast fibers, such as flax and hemp, have been used by humanity for thousands of years [1,2,3,4]. Evidence of the use of bast fibers especially hemp and flax/linen has been found in ancient society throughout human history including the cultivation and use of flax/linen in Ancient Egypt [5] or presence of linen in Swiss dwellings [6,7]. In the recent past several Asian and European communities cultivated and processed hemp for textiles [8]. Due to a combination of reasons, the production of bast fibers drastically reduced as more attention was given to other fiber sources. A significant reason was the mechanization of the cotton spinning system and later the invention of the cotton gin in 1793, which made cotton an economically very competitive fiber compared to hemp and linen. A far more extensive influence, however, is the development and introduction of synthetic, petroleum-based fiber materials beginning from the first decades of the 20th century. The (thereafter following) social ostracizing of hemp which was a major bast crop grown in Europe and the United States dealt a major blow to the development of the processing technology for hemp and bast fibers in general. As a result, the processing technology for hemp and other bast fibers has since lagged behind, hence higher production costs. For example according to Schmitz et al. (as quoted by [9]), the production cost of hemp fibers in Germany was five to ten times compared to cotton or synthetic fibers. However, recently there has been renewed interest in finding environmentally friendly alternatives to cotton and synthetic fibers for both clothing and technical applications. Bast fibers have a great potential to provide this alternative due to their high yield per unit area as compared to cotton, limited or no need for chemicals during growth and usually no need for irrigation [10]. It is therefore important to develop an efficient and commercially viable system of extracting the bast fibers from the plant stems to fully benefit from the opportunities provided by bast fibers.
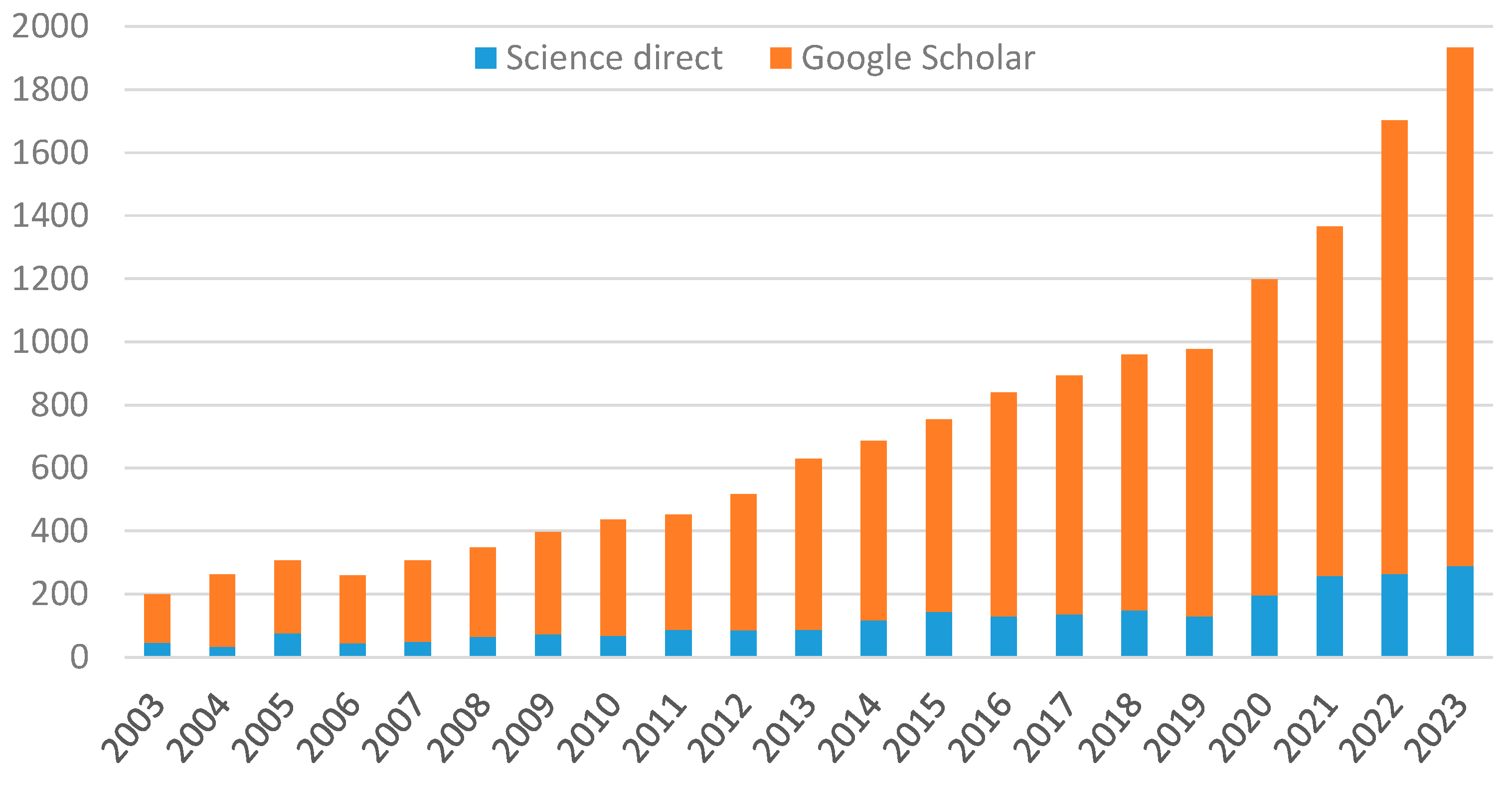
Based on increasing research in this field, a large number of papers have been published in recent years (Figure 1) dealing with various aspects of post-harvest treatment of bast fiber straw (stalks), the subsequent fiber extraction as well as possibilities of further fiber modifications by means of biological, chemical, or other measures. A few selected ones are Akin et al., 2004 [11]; Antonov et al., 2007 [12]; Crônier et al., 2005 [13]; Di Candillo et al., 2010 [14]; Djemiel et al., 2017 [15]; Fernando et al., 2019 [16]; Foulk et al., 2008 [17]; George et al., 2015 [18]; Jankauskiene et al., 2006 [19]; Mazian et al., 2018 [20]; Lee et al., 2020 [21]; Liu et al., 2016 [22]; Lyu et al., 2021 [23]; Pakarinen et al., 2012 [24]; Réquilé et al., 2021 [25]; Ribeiro et al., 2015 [26]; Parikh et al., 2011 [27]; Tamburini et al., 2003 [28]; Thygesen et al., 2013 [29]; Valladares Juarez 2009 [30].
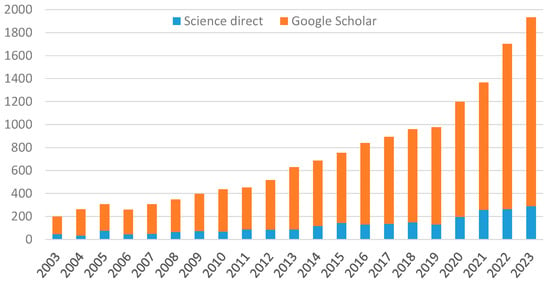
Figure 1.
Number of published articles related to hemp and flax retting 2003–2023.
Nevertheless, this still shows a very diverse understanding of the metabolic processes in the post-harvest period, the classification of the individual steps in the entire process chain and their definition. In order to be able to correctly elucidate and evaluate the influence of different process factors, and in particular on the resulting properties of raw materials, intermediate and final products, a clear understanding of the entire process chain is essential.
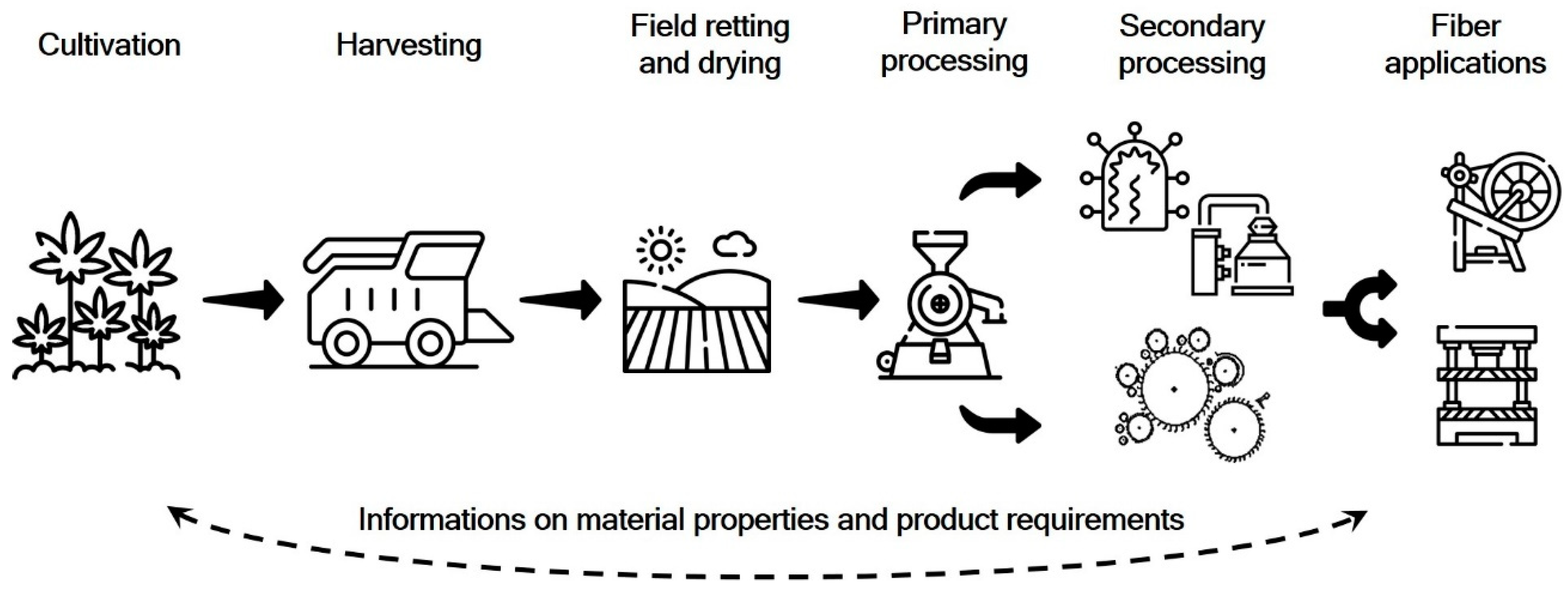
These considerations are initially based on the choice of location with corresponding weather conditions, crop type and variety, as well as the corresponding arable and plant agronomic measures during the cultivation phase. This also results in essential framework conditions for the harvest and the subsequent post-harvest period on field. At this specific point, the retting process is defined, during which the fiber plant straw is subject to the natural weather conditions, together with the necessary drying (Figure 2).
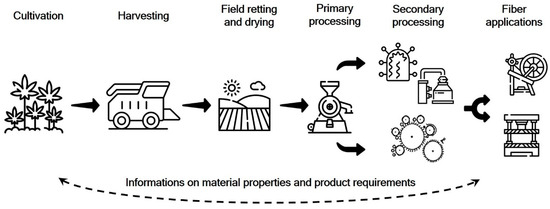
Figure 2.
Procedural steps and information flow along the production chain (modified from [31]).
In the case of processes other than dew or field retting, they can also follow field drying. In any case, the fiber plant straw is retted first in order to be able to carry out the subsequent mechanical fiber recovery by decortication, cleaning and, if necessary, opening of the coarse fiber bundles. This can be defined as primary processing of bast fiber straw. Afterwards, the resulting fibers can be further processed using biological, chemical, or even physical methods. Here, processes such as cottonization or degumming are to be considered. Otherwise valuable publications, both as reviews or as research findings do not make this fundamentally important distinction [23,32].
The retting process involves the controlled decomposition of those substances that bind the fiber containing tissues to the other components of the stalk as well as the fibers to each other (to form so called bundles). It is described as one of the most important steps in the whole supply chain of fibers from bast fiber plants such as hemp and flax since it affects both the ease of performing the subsequent mechanical processing steps as well as the quality of the resulting fibers. However, despite its long history, retting process of bast fiber straw is not yet fully developed to produce satisfactory fiber quality at a reasonable cost. Some reasons are, for example, the unpredictability of the course of field/dew retting due to random weather conditions. Furthermore, there is a lack of suitable and easy to apply methods for determining the optimal or final point of retting, which would contribute significantly to achieving uniformity and quality of the bast fibers. The other important question is the rettability of the bast stem. This may be understood by examining the significance of the different matrix substances to the process of retting. To what extent does the degradation of a given matrix substance (e.g., pectin, lignin and hemicellulose) contribute to the ease of separation of the fibers from other stem tissues (i.e., rettability). At the moment, a larger proportion of bast fibers are used in areas where certain variations in physical and mechanical quality parameters are tolerable. For example, for heat insulation and reinforcement in composites for less-demanding structures. For applications where high uniformity of quality parameters are paramount, for example in high performance load bearing composites materials, fibers for spinning and blending with cotton, bast fiber use is limited by the wide variance of its properties. These variations depend on a number of factors including; plant varieties or its inherent variability, weather during the growing and retting period and the method of retting among others. A better insight of the retting process will lead to the production of better quality fibers with more uniform distribution of mechanical and physical properties. More understanding of the retting process should also lead to an optimized setting of the operational parameters of the subsequent straw processing and thus, better predictability of the fiber properties based on given raw material properties.
Further processing (or secondary processing) of the bast fibers after straw retting and their separation from the woody parts of the stalks provides opportunity for further modification and improvement in fiber quality [33]. This can be a chemical or biological treatment or the so-called cottonization process which aims to produce cotton-like fibers from bast fibers. The methods used at the moment are however still very expensive and thus, in many scenarios economically less competitive to cotton and synthetic fibers.
Using the example of hemp and flax, this article attempts to categorize the different procedure steps in the process chain from harvest of the plant to the secondary processing of the fibers. For this purpose, selected literature sources on the state of the art of the individual methods are assigned accordingly. Attempts at further development of the existing retting processes and alternative methods are also discussed.
Overall, the aim of this review paper is to provide an alternative framework/structure for the classification of the processes, procedures, steps, treatments or methods used in the above mentioned process chain. In addition, the authors identify and try to clarify the contradicting and misleading use of terminologies in this field. Although a large spectrum of publications have been cited in this work, the major focus is to appropriately classify the process within the general framework suggested by the authors rather than repeating relations to influencing or resulting parameters of retting and degumming. The differentiation of the feed raw material (straw or decorticated bast), the lack of which leads to uncertainty in much of the literature on bast fiber production, plays an important role in the classification system suggested in this paper.
It is true that more detailed descriptions may be found in other publications but in many instances misleading terminologies are used, as later discussed in this paper. The new value of this paper is to provide a fundamental framework (post-harvest, primary processing and secondary processing) to correct these misnomers or at the very least to initiate a debate on the importance of the use of the right terminologies in the field of bast fiber processing. The proper attribution of a given procedural step or method in their right place on the bast fiber processing chain will give a better context for evaluating existing findings and (citing) literature thereon. Furthermore, it might increase the chance of successful transferability from the lab to practice in the field, for example, many papers focus on degumming but fail to consider the prior process of decortication, which is very important if such processes are to be adopted in practice.
2. Definition and Clarification of Terms
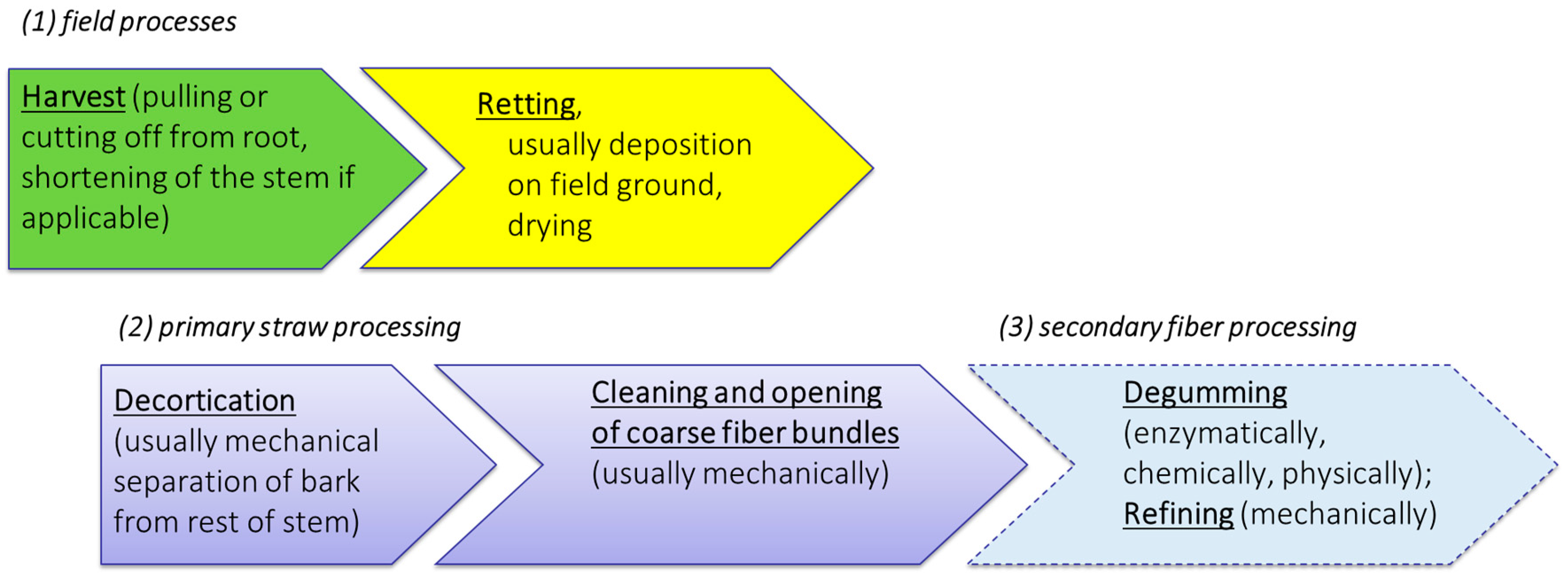
Initially, it seems sensible and expedient to consider and describe the process chain for the provision and processing of bast fiber plant material according to the individual steps. According to our proposal, distinction should be made among field processes, primary processing and secondary (or further) processing (Figure 3).
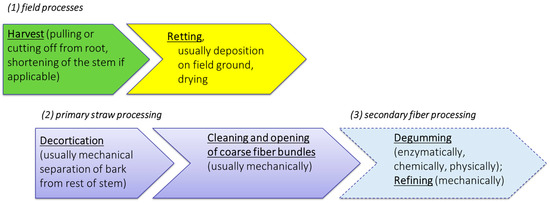
Figure 3.
Procedural steps for the provision of fiber plant straw and its processing.
Harvesting and post-harvest processes take place exclusively as agricultural procedures under the influence of natural weather conditions. This also includes the essential step of field retting, which coincides with the drying of the plant material until a storable dry matter content is reached.
Subsequent to retting, treatments applied to bast fiber plant material for the purpose of fiber extraction can be divided into primary processing and, secondary or further processing. Primary processing includes all treatments (usually mechanical) that help in the separation of the bast material from the woody core. Here, the major steps include the destruction of the natural stem structure by decortication and commonly the cleaning of the resulting fiber-shive-mixture as well as initial refining of coarser bast in to fiber bundle structures. The main aim of secondary processing is the individualization and purification of the fibers. This is mainly achieved by the removal of the residual matrix substances in a process called degumming. Another major secondary process is cottonization, where the long fibers are usually mechanically processed to obtain properties similar to cotton fibers.
The term retting is rightly used in most literature that deal with the treatment of straw as a whole or stems in particular from bast fiber plants [34,35,36] while degumming is mainly used for treatment of bast material after primary processing [37,38,39].
However, it is not uncommon to find use of the term degumming and retting in an interchangeable manner in many literatures about extraction of bast fibers, which leads to much confusion. For example, Parikh et al. [40], Ramaswany et al. [41], Morrison et al. [42] all use the term retting to refer to the treatments applied to the fibers after decortication. This, in our view is not appropriate. A review by Tahir et al. [27], although extensive, also refers to processes involving both whole stalks as well as decorticated bark generally as retting. This lack of distinction between the primary and secondary processes may lead to much confusion especially in cases where attempts are made to compare the properties of the resulting intermediates. Although a somewhat more recent overview by Lee et al. [21] provides a comprehensive assessment of natural fiber-reinforced plastics in this respect, it does not adequately reflect the differences and the classification of the process steps of fiber production (primary processing) and fiber refinement (secondary processing) based on the cited literature.
Thus, it is also suggested here for general understanding that the term retting be used for treatment applied to the whole stem material (straw) whereas degumming is used on the bast material after decortication/separation from woody core. During the degumming process the aim is to purify and further individualize the fibers by removal, of as much as possible, of the remaining matrix/gummy substances [37,43].
3. Morphology of Stem and Retting Mechanism
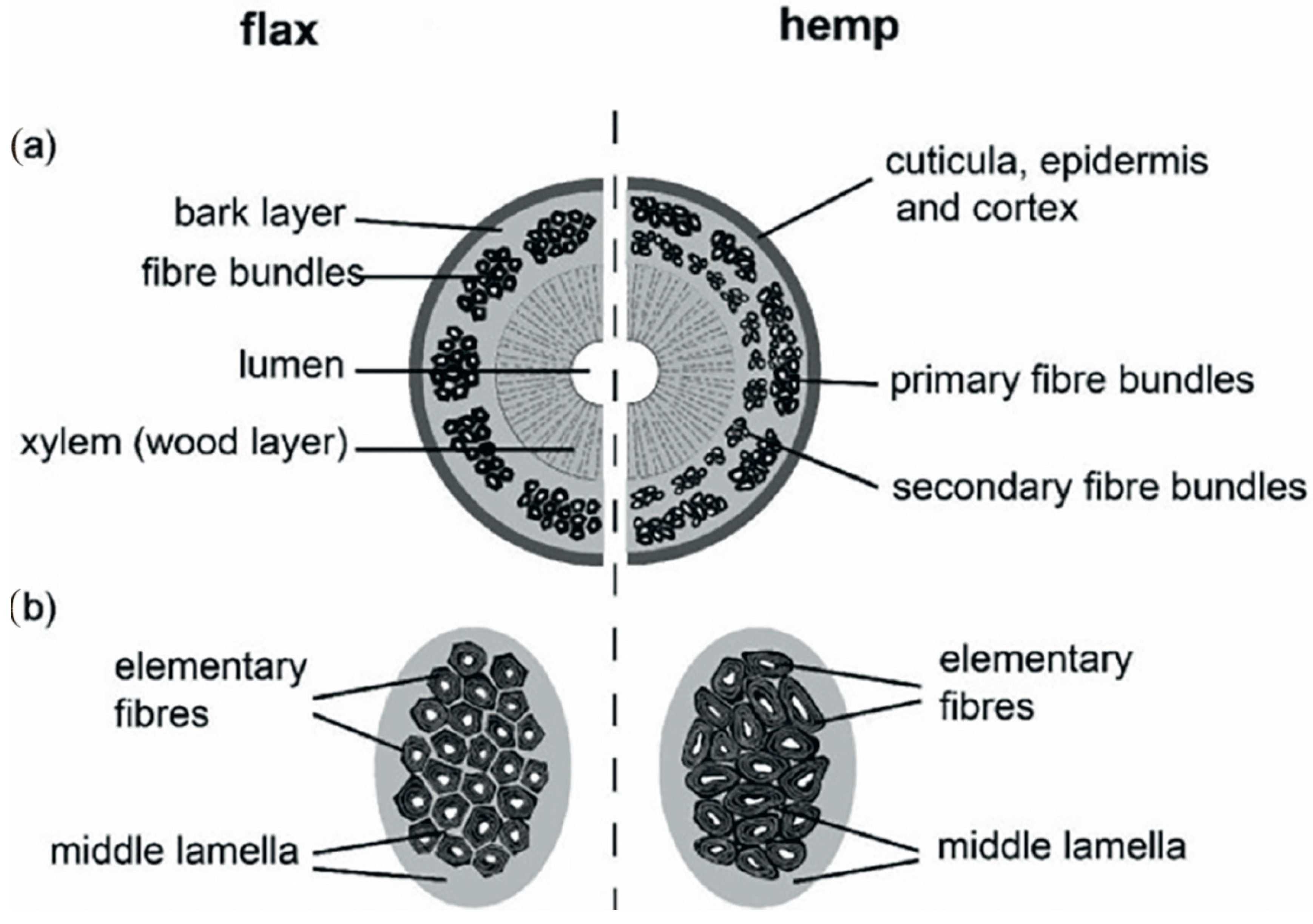
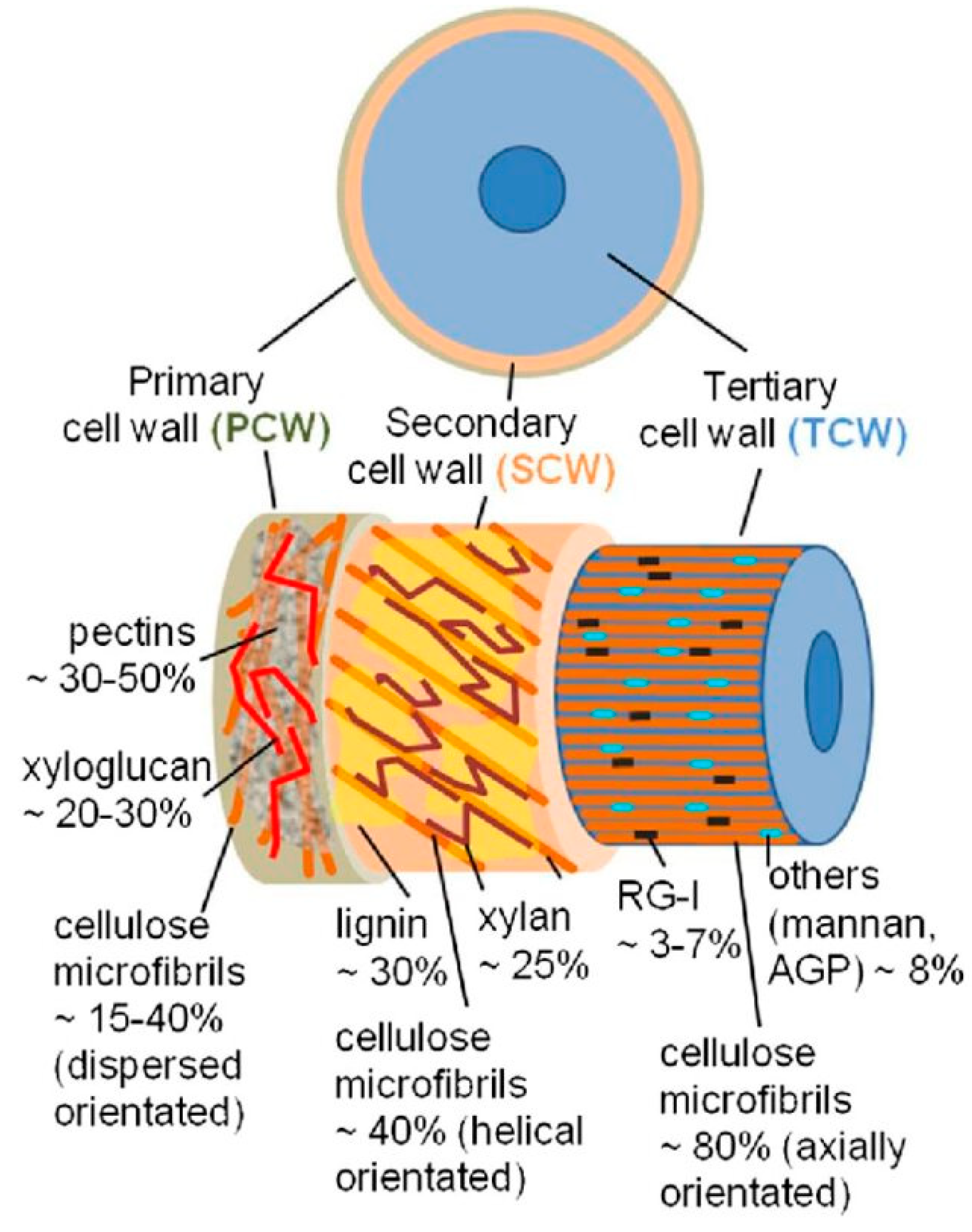
Bast fibers are obtained from the outer layers of plant stems in the phloem region and can contain both primary and secondary fibers [44]. Common bast fiber crops include flax and hemp, which grow well in most regions of the world, and ramie, jute and kenaf that thrive in warmer tropical climates. Unlike other natural fibers such as cotton or wool, which come in individual and separate forms with little impurity, bast fibers are by nature intimately bonded to the matrix material in specific structures and tissues of the plant stem (Figure 4).
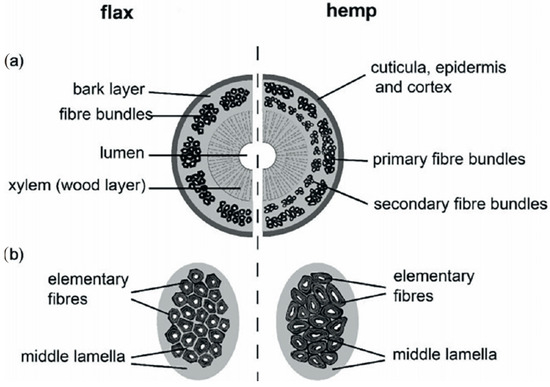
Figure 4.
Structure of bast fiber plants: (a) cross section of stem and (b) fiber bundle of flax and hemp [45] (Originally published in: Bast Fiber Textiles Addressed Improvement of Human Life. Under license CCBY 3.0. Available from: 10.5772/intechopen.105161).
This requires great effort during separation process of the fibers. As a result, after extraction from the stem (as a total from straw), the bast fibers appear in form of groups (so-called bundles) of single elements or even collectives thereof, are relatively coarse, often contain higher impurities consisting of residual non cellulosic polysaccharides and lignin that affect the fiber properties [46,47].
A retting process is necessary to loosen the matrix material that binds the fibers to each other and to the other structures of the stem. However, for the purpose of material processing, retting mainly refers to the process whose aim is to ease the separation of the whole bast (ie phloem fibers and other phloem material) from the xylem (woody core).
The retting of bast fiber stalks essentially takes place through the action of biological organisms and their associated enzymatic activity as mentioned before. The degradation of pectin is considered as a major factor responsible for achieving retting and subsequent fiber separation since most bast fibers are surrounded by pectin rich middle lamella and parenchyma cells [48,49] (Figure 5). Although pectin may appear in smaller quantities compared to the total matrix binding substances, its strategic location between the cell walls makes its degradation of utmost importance to the retting process [6]. The use of pectin level as a measure for retting and rettability has even been demonstrated to be feasible except for large scale applications due to the time consuming nature of the measuring technique [50]. In the case of flax fibers, Evans et al. [48] suggests that retting can result strictly from the degradation of the unmethylated or low-esterified homogalacturonan (as most abundant pectin subtype) regions which occur throughout the flax stem wall.
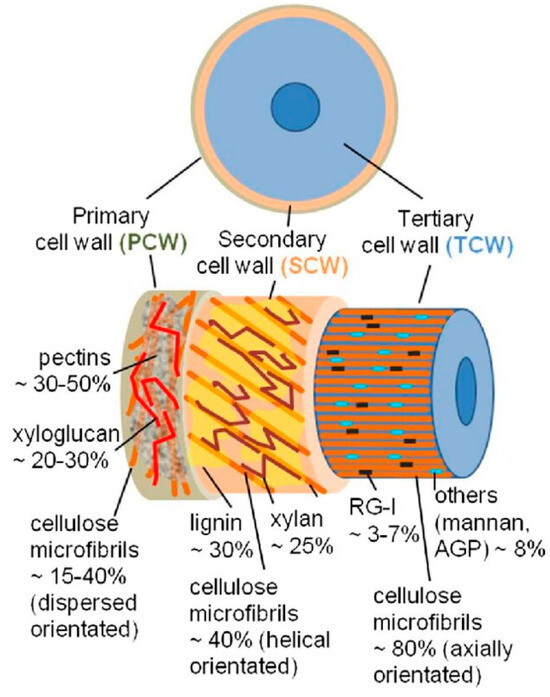
Figure 5.
Schematic illustration of the layers in elementary fibers [51]. (Originally published in: Key Stages of Fiber Development as Determinants of Bast Fiber Yield and Quality. Under CC BY 3.0 license. Available from 10.3390/fib6020020); RG-I—Rhamnoglalcturonan I; AGP—Arabinogalactan.
The cell wall is generally built up in layers and consists of primary and secondary, and sometimes tertiary, walls (Figure 5). An intercellular matrix, the middle lamella, lies between neighboring cells. Here, the middle lamella and the primary wall of cells next to it are also referred to as a compound middle lamella, whose chemical structure is complex.
Therefore, a targeted approach in terms of the area and the substances is important in developing an effective retting method. Although pectin degradation plays a major role in bast fiber retting, it is clear that fiber quality (and retting) of bast fibers is also significantly affected by other matrix substances that should not be ignored. An important example is lignin whose degradation may not be very significant in the initial separation of the fibers from the woody part of the stem (which are called shives in its broken form) but it greatly affects fiber quality and appears to always remain in residual quantities in on the fibers [52]. Therefore, while the degradation of pectin is the major factor in the separation of fibers from the rest of the stem materials, lignin degradation is an important factor for the further separation of fiber bundles into individual fibers [53,54]. Lignin is known to be more resistant to biological and enzymatic degradation, which partly explains its relatively high residual component in bast fibers as compared to pectin [16]. Small bundles of bast fibers bound by this recalcitrant lignin still exist after retting. The lignin content in the resulting fibers has been shown to affect the physical and mechanical properties of cellulosic fibers [55,56]. Of course, this can only be finally assessed from the perspective of the corresponding field of application for the fibers.
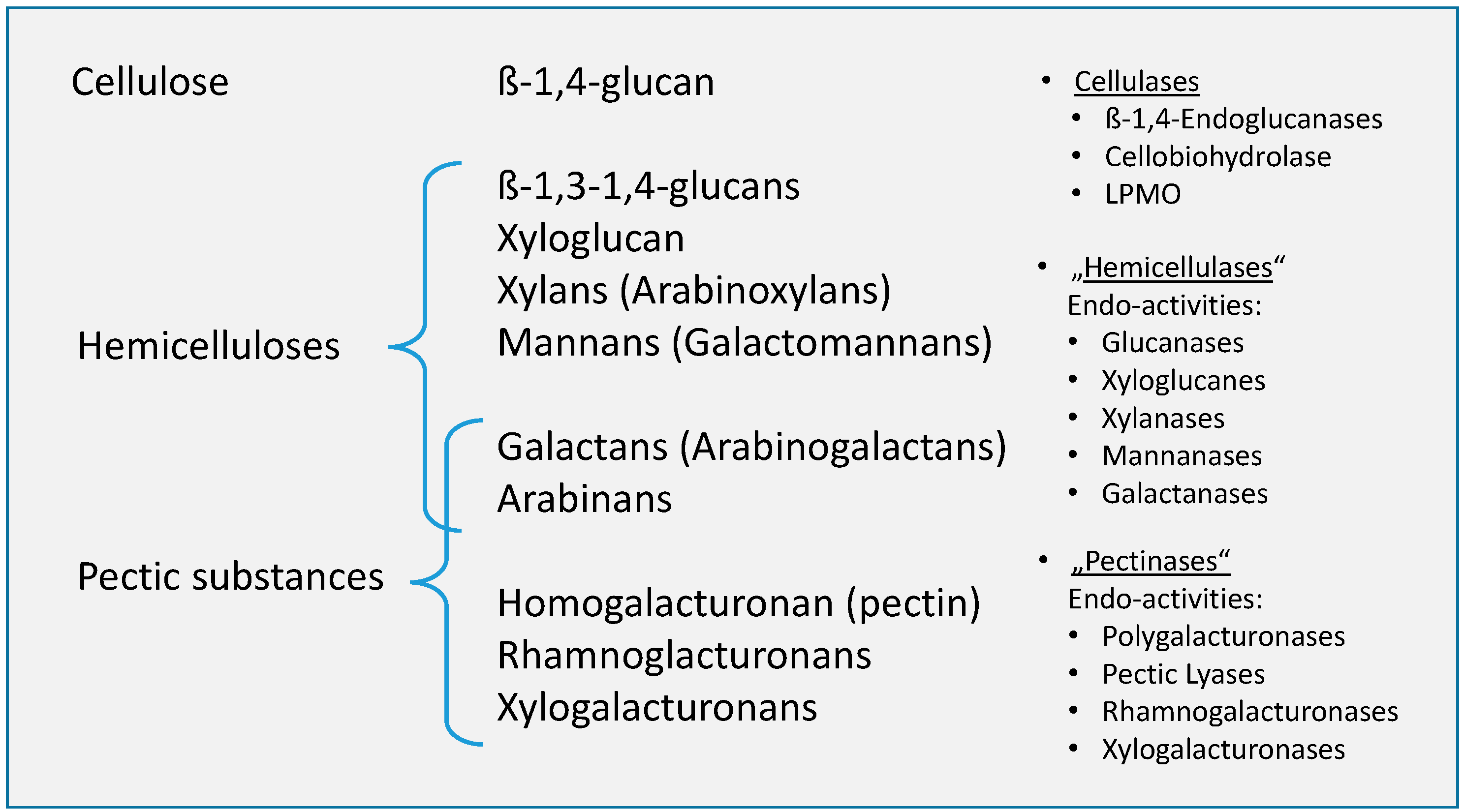
The main drivers in “natural” retting processes are the enzymes produced by microorganisms, which usually have a specific degradation effects (Figure 6).
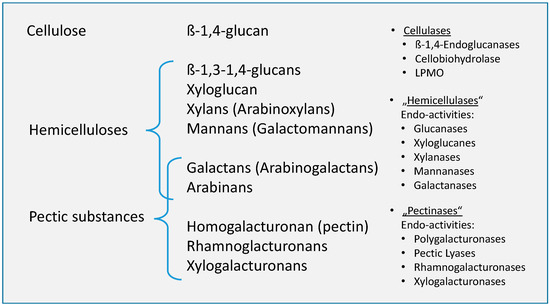
Figure 6.
Structural (left) and molecular cell wall components (middle) and enzymes (right) responsible for their decomposition (adapted from Kühnel [57]).
It is therefore important that these other substances that form part of the matrix material in the stems are taken into consideration in any given study of retting since they may affect fiber quality and the manufacturing process [58].
Basically, it seems to be difficult to distinguish between pectins and hemicelluloses, especially in the current literature on its decomposition in tissues of bast fiber plants. Both are seen as the subject of the necessary or desired microbial decomposition during retting [59]. The matrix in which the microfibrillar cellulose scaffold is embedded consists of pectins or pectic substances as well as non-cellulosic polysaccharides, which are collectively referred to as hemicelluloses. A comparable classification, which sees pectins and hemicellulose equally as the object or target of retting, can also be found, for example, in Konczewicz et al. [60].
Whereas the degradation of matrix substances are encouraged during retting, cellulose degrading processes are not desired since they would deteriorate the quality-determining fiber properties for most structural applications [16,21].
4. Retting Methods and Attempts at Improvement
Very extensive research on the topic of retting—both field/dew or water-based—was carried out in the decades when cotton and synthetic fibers had not yet been introduced and bast fibers (along with wool) dominated the production and use of this class of materials. With the renaissance of traditional bast fibers in particular in Europe from the mid-80s in the last century, research also experienced a further upswing and corresponding publications appeared. Despite more recent research, the essential principles of such works are certainly still valid today, but due to the diverse origins of such works in the important cultivation countries of that era (e.g., France, Italy, Ireland, Russia or Germany), a detailed analysis is not possible here. However, due to frequent citations, e.g., Tanner 1922 [61]; Ruschmann 1923 [62]; Dujardin 1948 [63]; Turner 1954 [64]; or Sharma and van Summere 1992 [65] shall be named.
Traditionally the retting process is carried out either through water or dew retting [27].
4.1. Traditional Retting Methods
4.1.1. Dew Retting
Dew retting, which is considered the oldest method of retting of bast fiber crops [65], is currently the most popular method used for processing bast fibers in Europe and North America. It involves the spreading of the harvested biomass in the field where fungi and bacteria colonize the straw and degrade the matrix polymers [65]. The cut (or in case of fiber flax pulled) stems are laid in swaths on the field thereby providing suitable conditions for growth of both fungi and bacteria under the influence of natural weather conditions such as dew or precipitation. Laying the straw on the ground in swaths could also makes it easy for the bacteria and fungi found in the soil access and colonize the straw. However, Law et al. [35] have argued that although there was some overlap of the most abundant bacteria from the soil and those present during retting, the bacteria on the retting stem were not greatly influenced by the soil treatment since they existed on the stem before cutting. In spite of low costs, ease of application and the attempts at improving the process, dew retting still remains only practical in limited regions of the world, that naturally have the optimum temperature and moisture required for the process [66]. However, the agricultural land remains occupied and cannot be used during the process, often for indeterminate duration [67]. Another major disadvantage is that dew retting produces fibers with highly non-uniform properties [68] partly due to its dependence on the weather at the retting time. The material has to be regularly turned in order to achieve uniform retting. Considerable experience is needed to determine the end point of dew retting [65]. The development of definitive and accurate tests for the end of retting point in dew retting would greatly contribute to the improvement of the uniformity of quality in dew retted fibers. In spite of the above limitations, dew retting is still the method of choice in preparing bast fiber straw for its subsequent processing especially in Europe mainly since it is a much more environmentally friendly process that produces no polluted waste water [50].
The importance and the mechanisms of fungal activities in the dew retting of bast fiber plants have been studied for some time. For example, Speri [69] refers to earlier work on fungal species that colonize the plant during the dew retting of flax: Aspergillus sp. [70,71,72], Macrophomina phaseolina [71], Rhizopus oryzae [73], Mucor sp. [70], Chaetomium sp., Phoma sp., Fusarium sp. and various Penicillium sp. [74,75]. Important active principles are a high pectinase activity and the ability to metabolize non-cellulosic structures without attacking cellulosic fibers. Also highlighted is the ability to penetrate the cuticular surface of the stem [70]. According to the work of Sisti et al. [76] further species have to be recognized such as Cladosporium sp., Rhodotorula sp., Epicoccum nigrum, Alternaria alternate, Aureobasidium pullulans, and Rhizomucor pusillus [26,77,78]. In addition, lignin is also frequently mentioned as an object of degradation by (dew) retting. However, special enzymes or a combination are required for the degradation of lignin, whereby only the white rot fungus (which belongs to the basidiomycetes) is capable of degrading such compounds. Bacteria with a corresponding enzyme spectrum are still in research, especially with regard to wood.
Although the role of bacteria (or at least their presence) in dew retting of flax was known for a long time [65], it was generally suggested that fungal colonies were the main microbiota responsible for dew retting [54,70]. However, recent studies that use other techniques/methods such as scanning electron microscopy (SEM), high throughput sequencing (HTS) or enzyme activity assay have shed more light on the presence and role of bacteria in dew retting. Thereby, it could be shown that bacterial activity and fungal-bacterial interaction also contribute considerably to the dew retting process [15,16,32,79].
According to Liu et al. [79] and Fernando et al. [16] fungi were the first invading species during dew retting of hemp (after harvest) with varying concentration of different species as the retting period progressed. Although, there was no bacterial species identified on the fresh stem samples, bacteria such as Pseudomonas spp., Rhizobium soli, Massilia aurea, and Pantoea quickly became dominant throughout the retting period.
The use of DNA sequencing has allowed for a better and broader characterization of the of the bacterial and fungal population present during dew retting [15,26,79] which were not easily identifiable by previous methods. However, the nature of the contribution of the bacterial population and interaction with the fungal population during the dew retting process may be better understood by a combination of methods. For example, Fernando et al. [16] used gene sequencing, SEM as well as monitoring changes in the dry matter composition to get a fuller picture while Liu et al. [79] combined gene sequencing, protein extraction and enzyme activity assay in their study.
Two important points are noteworthy from Djemiel et al. [15]: The first being that in fact a more diverse community of bacteria exists in dew retting as compared to fungal community. Ribeiro et al. [26] and Liu et al. [79] also report a higher bacterial diversity as compared to fungi during dew retting. This should further caution against ignoring the role of bacteria in dew retting. The second point is that the practice of swath turning showed a significant effect on the bacterial community. Therefore, further inquiry into the practice of swath turning with consideration of its effect on both fungal and bacterial population could help to improve uniformity in quality of bast fibers.
More recent research as of [35,80] have highlighted, in particular, the role of bacteria in field retting of hemp, as well. The studies showed that such organisms associated with the harvested biomass were already present in/on the hemp stalks at the time of mowing (Massilia, Pseudomonas and Sphingomonas). A significant influence of the soil bacteria by the contact of the stalks with the soil during the retting process could not be proven [35]. An increase in the phylum Bacteroidetes, especially of the genus Chryseobacterium, was determined especially towards the end of the retting process. However, this did not apply to the experimental variant with low moisture content. Thus, the increased cellulose degradation during over-retting of the fibers after the degradation of pectin is particularly associated with Bacteroidetes, as their cellulolytic activity is also known from studies on other fiber plants or agricultural soils. Another very recent study addresses different methods of extraction and analysis of the microbial genome from stem biomass [81].
In conclusion, it is clear from the literature that both fungal and bacterial activities contribute to dew retting. Fungal species play a significant role from the beginning by breaking down the matrix substances especially pectin. Bacterial population and activity increase later in the retting period and seem to take advantage of the structural weakening of the stem tissue by the fungi to penetrate into the inner stem tissue.
Irrespective of the microbiological background, the selected mechanization as well as environmental factors during growth, harvest and post-harvest period have a significant influence on the course of the dew retting. This is particularly important as scientists (and practitioners) are looking for ways to improve retting results in these areas. The choice of location for cultivation determines the weather and the soil conditions (and thus partly the microbial community, see above). An important factor is, of course, the choice of variety, especially in the case of hemp with its wide variety of breeding directions (especially biomass/straw, seeds, and secondary metabolites such as cannabinoids). Furthermore, due to the developmental stages of the plant, the harvesting time has an important influence on the course of the dew retting [20,82]. Associated with this are the weather conditions as a prerequisite for the microbiological activity. In connection with the developmental stage of the plants, further reference is made to studies that show the influence of, for example, other molecules such as tannins and essential oils or also changes in the stem surface (cuticle, remnants of trichomes, stomata) [83].
4.1.2. Water Retting
A closer look at the microbiota of water and dew retting shows marked difference in the population of microorganisms responsible in each case. Even for the similar lignocellulosic material, different bacterial phyla/species are present during water retting and dew retting, which may be attributed to the anaerobic and aerobic environments in water and dew retting, respectively [15].
In water retting, the stems are immersed in water and are colonized by bacteria that produce enzymes to eventually degrade the complex polymer matrix [28,34,84,85]. Unlike in dew retting where both fungi and bacteria are shown to play significant roles in the retting process, water retting appears to be principally as a result of bacterial activity [14,28]. Although certain fungi are known to live in aquatic environment [86], no literature was found on the presence and activity of fungi to show that they significantly contribute to the degradation of the matrix material during water retting. In the case of bacteria, both aerobic and anaerobic bacteria are present during water retting [28,87,88]. Tamburini et al. [87] showed that aerobic bacteria are present at the initial stages of retting but are overtaken by anaerobic bacteria as the dissolved oxygen in the water is depleted. In this same study, both aerobic and anaerobic pectinolytic bacteria, which were present during water retting, were isolated. The Bacillus spp. (aerobic) were dominant in the beginning but were succeeded by Clostridium spp. (anaerobic) when the oxygen was used up. The study seems to suggest that the aerobic pectinolytic bacteria play a minor role in the retting process due to their lack of acid polygalacturonase activity as compared to their anaerobic counterparts. However, according to Sharma and van Sumere [65], continuous aeration of the retting liquor by blowing air into the it accelerated retting apparently due to increased activity of the aerobic bacteria. Therefore, the more probable reason for the limited participation of aerobic bacteria in water retting is simply due to the quick exhaustion of dissolved oxygen from the water.
Although water retting produces better quality fibers (i.e., finer and stronger) than dew retting, it has been largely abandoned in many parts of the world in favor of dew retting due to extensive pollution of water streams and the putrid smell produced by water retting [21,54]. Nevertheless, studies are known to address the wastewater problem and to look for alternative uses for the waste water from retting [89,90,91]. Another focus, in terms of the assumed nutrient content, is its use as fertilizer [92] or, with reference to retting of other fiber resources, its use for electricity production [93].
An interesting approach to avoiding the use of fresh water has been investigated by using seawater [88]. These results showed that this treatment gave good results in reducing pectin structures. In addition, pectinolytic strains isolated from seawater retting tanks showed high pectinase activity and are seen as the basis for further improvement of the retting process.
4.2. Stand Retting
In areas with especially wet autumns, conditions around and after harvest time are potentially suitable for dew retting, but not for field drying. In other regions, there are essentially no appropriate conditions for field retting e.g., in the continental climate, due to a combination of cold and especially dry environmental conditions. Different strategies for alternative methods to field drying and retting have been developed in the past in search of alternatives or to minimize the risks of harvest loss in such regions.
One of these examples refers to work on the chemical desiccation of flax in Ireland [94,95]. Different kinds of application of herbicides on the crop, either on the living plant or on the already harvested crop laying in swaths, have been investigated. Later studies also used the application of desiccants to flax followed by stand retting to provide fine fibers for processing with cotton depending on the timing of the application [96]. Alternatives to the spraying of herbicides include the use of open flames to terminate plant growth or allow the plants to die naturally [97]. Of course, it is not appropriate to use herbicides or even thermal energy, which is essentially based on fossil sources, to provide sustainable raw materials. Moreover, in contrast to the harvesting of flax, such an approach is not technically possible in an average hemp stand at harvest time.
In Nordic countries such as Finland where the normal harvesting period in autumn is cold and rainy, the risk of molds destroying the hemp harvests are high. A so called dry-line-method, where hemp crops are left standing in the field all through winter and are harvested in spring, is suggested as a possible solution to this problem [98,99].
The harvest in late winter or very early spring falls in a period with less work on the farms, in contrast to the harvest of summer crops. Here, there are labor peaks due to harvest overlaps of several crops, as well as seedbed preparation for the following crop. Furthermore, harvesting of stand/frost retted hemp stalks in winter period allows additional or larger periods for gathering dry straw [100].
During the winter, temperatures below zero degrees (frost) promote the detachment of the fiber containing bast from the wood. One frost event is already sufficient to completely separate the bast tissue from the stem due to the mechanical stress caused by ice expansion in the stem [99]. This simplifies the subsequent mechanical fiber extraction from the hemp straw. However, further disintegration and exposure to environmental conditions can also lead to over-retting and a corresponding influence on the resulting fiber properties. In addition to the detachment and separation of shives, harvest losses of up to 40% can occur [98]. On the other hand, the hemp stalks have an optimal water content of less than 15% in the following spring and can be pressed directly into bales without further drying [98]. Potentially high biomass losses during the spring harvest of hemp have been confirmed in further studies from Latvia, whereby these can even be up to 80% depending on the selected harvesting method [101]. However, the negative influence on the mechanical properties of the resulting fibers, which was also determined in these studies, is also offset by the procedural advantages of a low-effort (i.e., cost-reduced harvesting mechanization). The detailed investigations on mechanical properties of frost-retted hemp fiber bundles and fibers from cultivation in Estonia also show a clearly negative influence on strength [102]. Nevertheless, a use in non-structural composites is considered feasible. Interesting are the results on the chemical composition of the fibers, which differ significantly from the characteristic values from conventional cultivation, especially due to the late sowing and comparatively short vegetation period. On the one hand, a lower lignin content was determined, but due to the lack of suitable environmental conditions for retting microorganisms, a significantly higher content of fiber-cementing substances such as pectin was also determined on the other hand.
However, according to Kymäläinen [103], frost retted fibers yield bent, folded and curly fibers with high proportion of small diameter fibers. These are not necessarily desirable fiber properties for mechanically demanding applications, so further research of the frost retting mechanism is required to improve them. However, better hygienic quality [104] and climate dictated suitability of frost retting for particular regions make it suitable for producing fibers at a reasonable price for applications such as insulation, filters or packaging material where low material cost is an important factor [99,103]. In spite of the limitations, this process may provide an alternative to dew retting which may also be applied in other regions [100].
However, not much about the mechanism of winter retting is known as well as the extent of the contribution of biological degradation to or in this retting process. According to Sharma [94], bacteria have a role to play in the retting of desiccated flax especially under cool and damp conditions which enhance bacterial growth and activity. However, during frost retting the role of bacteria in retting during the cold winter is not sufficiently understood. According to Kymäläinen [104], early frost reduced the amount of total bacteria in hemp tissues of outer layers and the amount of bacteria decreased in the inner fraction of the hemp stem. The same study [104] further states that slow freezing or recrystallization causes cellular damage and release of cellular material during thawing which provides substrates for enzyme activity and microbial growth. However, since the low temperatures (as is the case during winter retting period) is known to inhibit microbial activity, an inquiry into the interaction between the role of microbes in frost retting and the weather conditions is necessary. Therefore, unlike in water and dew retting where bacterial and fungal activity plays the central role in retting, physical processes may play a more significant role in stand retting. Hemp stalks are relatively resistant to mold at that time as the nutrient content decreases during retting [98,105]. However, further research has shown that during the winter and spring period there was a clear increase in the amount of molds, bacteria and yeasts, especially in the standing stems in the field but also in the fiber and shive fractions [106]. Several genera have been identified (Alternaria, Cladosporium, Fusarium, Mucor and Penicillium) but their content could be reduced, for example, by subsequent mechanical or other processing of the straw or fiber. Later investigations confirmed the increasing amount of both bacteria and fungi from autumn (before frost) to early frost and further until spring as well as possibilities of reduction by technical processes other than enzymatic fiber treatment [107]. Interestingly, winter conditions did not have a direct effect on the chemical composition of the bast tissue where only the content of minerals (ash) and water-soluble extracts changed. However, the physical effect of winter conditions obviously enables better accessibility for subsequent fiber treatment by, for example, enzymes. Further stand retting experiments were conducted from 2002 to 2004 in the Baltic state of Lithuania [108]. Comparison of fungal contamination on flax stems that had been pulled and laid in swath with those that had been left standing showed different colonization over a period of up to 90 days. Depending on the annual weather conditions, mainly Alternaria, Cladosporium and Fusarium were found, whereby their frequency was significantly lower in the standing crop. Thus, in some circumstances, the stand retting is an alternative if the conditions for a swath retting in autumn are unfavorable.
Further attempts to make use of potential advantages from stand/winter retting are reported from Italy and Germany more recently. The intention to develop an alternative supply chain with reduced technical and organizational effort led to the use of a more or less unmodified self-propelled forage harvester to harvest a stand-retted hemp crop [109]. It was assumed that the weather conditions in the trial region in the north of Italy would not be sufficient for a reasonable field retting in autumn and furthermore, work peaks could be shifted to December, for example. An easier separation of the fibrous components from the woody core of the hemp straw could also be confirmed from these trials. Further investigations into the influence of different parameters such as water content, temperatures or microorganisms were obviously not the subject of the trials, which is why the results are not presented.
In the search for alternative crops for cultivation as a second in rotation that can also utilize nutrient surpluses, fiber hemp has also been the focus of extensive research in Germany [110]. Sown after the earliest clearing cereal in July, it remains standing in the field until the following winter or spring. Earlier results on easier fiber extraction from respective straw have been confirmed, although there can easily be an overweighting of the fiber yield due to shive losses during straw recovery. The fiber properties after mechanical processing showed comparatively low fiber widths, higher strain as well as strength. Comparable to the results of Pasila [99], however, this does not affect processing into, for example, composites. However, unintended negative effects on the resulting fiber properties in the case of unfavorable weather conditions (i.e., too warm and humid) must also be taken into account here.
Experimental evidence of the effect of temperatures below freezing on unretted hemp stalks showed that the bast can be easily separated from the woody stalk core and fiber-cementing substances can be separated in the subsequent processes [111]. There were certainly considerable effects on the resulting fiber properties.
To develop stand/frost retting as a viable alternative even under temperate climates, further research to understand this process should be carried out including, among others, the examination of the effect of winter conditions on the morphological, structural, the chemical and biochemical composition of hemp.
4.3. Alternative Methods to Retting of Straw
Due to the shortcomings of the traditional retting methods such as high dependence on the weather conditions in dew retting, difficulty to determine the end point of retting and other factors which make the traditional methods less controllable, more efforts to produce better fibers with more uniform properties are needed. Several alternative methods and attempts at improving the traditional methods with the aim of developing processes with more controllable parameters to achieve uniformity in the physical properties of the fibers have been explored. These alternatives include inoculation with bacterial or fungal cultures, enzymatic treatment, chemical treatment, direct ensiling and mechanical decortication. Sometimes the different methods are used in combination to achieve better retting and better fiber qualities. For example chemical chelators and enzymes [112], physical and chemical processes in steam explosion technique [113], mechanical agitation and heating with caustic formulation [40]. Occasionally, it is also indicated that the efficacy of such or similar methods can be improved by mechanically stressing the stems to break its outer tissue layers (i.e., cuticle and epidermis) [16,67]. This can be achieved, for example, by turning the swath for uniform field drying and retting, which must be carried out in the postharvest period anyway.
However, a clear distinction should be made between those approaches that aim to improve the subsequent processability of the stalks (i.e., retting) and those that aim to minimize the non-cellulosic components of fiber bundles after their extraction from stem biomass (most frequently referred to as degumming). A very recent review [114] provides a very comprehensive insight into, among other things, the systematic activity of microorganisms and relevant enzymes during retting and degumming. However, without detailed knowledge of the primary sources, as well here it is difficult to distinguish between the reference level “stalk” on the one hand and “fiber bundle/fiber” on the other and thus it is hard to make a targeted classification in the process chain.
4.3.1. Inoculation
The idea of isolating microbes with known enzymatic activity towards the degradation of major materials that form part of the matrix substance in the stems of bast plants (such as pectin) is not new. Thus, it has been found in literature as early as 1984 (Hunter and Brown, as cited by Sharma et al. [115]) and has also been suggested by more recent scholars [26]. Early attempts involved the use of bacterial isolates Bacillius subtilis, which produces mainly pectin-lyase and xylanase, and Erwinia carotovora, which produces only pectin-lyase, on dessicated flax, where the retting of desiccated flax straw was found to be enhanced by the spraying cell suspension of B. subtilis [94]. More potential benefits of the use of bacterial and fungal cultures are apparent where up to nine bacterial species (including Rhizomucor pusillus and Fusarium lateritium, Trichoderma virens, Alternaria alternata, Fusarium oxysporum, and Fusarium equiseti) were successfully isolated and used for retting of flax straw, but resulting in fibers with varying qualities [70]. A potential advantage is that bacteria or fungi that are efficient in retting may be introduced to the straws even if they do not form the native colony of the soil. For example, the fungi R. pusillus isolated from South Carolina flax which had not been isolated anywhere before showed a high retting efficiency in the tests, and could be used to enhance retting in environments where it does not naturally occur. Thygesen et al. [29] used a laboratory-based setup to demonstrate the effects of inoculation of hemp stalk sections with the mutated white rot fungus Phlebia radiata Cel 26 on a selective degradation of the epidermis as well as the lignified middle lamella. When this white rot fungus was applied direct to bast fibers, it showed higher selectivity in depectinisation compared to Ceriporiopsis subvermispora and compared to a classical water retting. A later study by [36] showed that stronger fibers with more homogeneous properties can be produced for composite applications by using the dependence of the depectinisation selectivity on the stem section. Inoculation of manual peeled fibers (which indeed is probably better to refer to as bast or bark) with selected fungi resulted in less reduction in the strength of fibers from the lower section than those from the upper stem section. When considering the whole hemp stalk independent of the origin of the fibrous tissue, fungal retting with P. radiata Cel 26 showed better mechanical properties in contrast to C. subvermispora.
Inoculation with bacterial/fungal suspensions may also allow the influencing of the time of the start of colonization of the stem tissue. For example, through inoculation A. alternate may also be used as a primary colonizer although it has been reported to be active in latter retting process [70]. This method may also be useful for targeting fiber properties by using certain types of fungi (white rot fungi), here on green hemp fiber material sealed in bags [116]. This has produced desirable properties of cross-linked fibers known for a particular application or industry (for example, improving strength and interfacial bonding in composites).
The use of inoculum from microbial isolates has not only been used in dew retting but also in water retting. The addition of anaerobic Clostridium sp. and aerobic Bacillus sp. in retting liquor accelerated the retting process of hemp and significantly increased the fiber quality [14]. This further opens possibilities of developing a more controllable retting process for stem material by varying the dose and time of adding the inoculum. While the aerobic bacteria does not show significant activity in degrading pectin, the use of aerobic inoculum in addition to the anaerobic inoculum increases the speed of retting. This speeds up the retting process since the addition of aerobic bacteria inoculum most likely rapidly generates the anoxic environment needed by anaerobic bacteria to grow [87].
4.3.2. Enzymatic Treatment
Another attempt at developing an alternative retting process is the direct application of enzymes to ret fiber crop straw. In distinction to this, however, enzymatic processes are also used to degum subsequently mechanically extracted bast fiber structures. Enzyme retting appears to have a better commercial prospect as compared to chemical treatment in terms of costs [117,118]. In addition, effluents from enzyme treatments tend to be more environmentally friendly [119] by, for example, reuse [120] which increases economic success in the increasingly environmentally conscious society since the products may be marketed as ecofriendly. The enzymes may be obtained from pectinase producing fungi or bacteria by methods such as solid state fermentation and submerged fermentation [36,121,122] or from commercial producers. The degradation of pectin is a major factor that correlates to the degree of retting [50], therefore pectinase can be considered the most important enzyme for retting. Due to the specific action of enzymes, a consortium/mixture of enzymes may be necessary to target the different substances that make up the stem matrix for a more efficient retting [48]. For example, the commercial retting enzyme flaxzyme, which contains pectinases, hemicellulases and cellulases, was used for the retting of flax leading to a considerable reduction of the retting time from several days to within 24 h [123,124,125]. Further commercial Enzymes such as Bioprep 300L, Flaxzyme, Lyvelin, Texazyme BFE or Viscozyme have been used in different formulations to achieve the required fiber characteristics at different levels [12,112,114,126]. However, enzymes that contain cellulases tend to lead to reduced fiber strength [17].
Protective structures of fiber crop stems such as the epidermis may prevent the pectinase enzyme from reaching the pectin compounds and would therefore need to be degraded by other means (usually mechanical) to give access to the inner stem structures. The use of surfactants that reduce surface tension of the water, therefore facilitating better access to the inner stem tissues, have proved useful in improving retting [67,127]. The enzyme formulations are commonly used together with a chelator (mostly ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid EDTA) [128]. According to Akin et al. [11] the regions between the fibers, the cambium and the middle lamellae are susceptible to degradation by enzymes but the epidermis was only effectively degraded with addition of chelator to the enzyme formulation. In addition, the mature plant tissue, the middle lamella is often converted to calcium pectate thereby cementing the cells firmly [129] and hence the need for chelators. Chelators remove Ca++ and destabilize pectin molecules and therefore contribute to the removal of matrix compounds holding fibers within the stem and have been shown to improve retting as well as subsequent mechanical fiber extraction when used with enzyme formulations [112]. The addition of chelators help to reduce the amount of enzymes used in retting by up to 50-fold [11].
The ability to make different formulations with different enzymes and concentrations [128] makes enzyme retting process a good and versatile alternative method for achieving particular fiber characteristics as far as process control is concerned. To prevent the deterioration of the of fiber strength due to continued enzymatic activity, thorough rinsing is required or denaturing treatment should be carried out at the end of the process [11]
Enzymatic treatments are mentioned to be also very suitable for the modification of fiber properties after fiber separation in a process and are often referred to as cottonization [130], as well. However, this term should rather be used when (pre-)prepared fiber elements such as bundles are refined or shortened by mechanical processes.
4.3.3. Retting Enhancement by Additional Chemical Treatment
The exclusive use of chemical substances for retting bast fiber stalks has been scientifically investigated, but is essentially not practiced. Such processes are mainly used for the degumming of fibers following mechanical fiber extraction from the straw. Detailed information on this can be found in a subsequent chapter of the manuscript. Evidence for the use of chemicals in the retting of plant stems can only be found in the literature almost exclusively in connection with other processes, such as stand retting with the aid of herbicides (see Section 4.2). Sharma [129] refers to older literature [63] with research results on the effects of, for example, acids or bases. However, these led to poor yields and low fiber qualities. The additional statement about high costs nevertheless remains valid and must be supplemented by the fact that the use of chemicals in the production of sustainable materials is not appropriate and (at least) potentially harmful to the environment [45].
Where chemical retting of straw is mentioned in literature, it refers mainly to the use of chelators commonly in combination with other procedures as well. This technique appears to be more popular for flax and hemp and it uses compounds such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), cyclohexanediamintetetraacetic (CDTA), sodium tripolyphosphate (Na5P3O10), oxalic acid (C2H2O4) [127,131]. The most common chelators used show high binding capabilities with calcium ions at high pH (above 4). Chemical retting with EDTA and oxalic acid involves the formation of complex compounds referred to as chelates. The acids act as chelators to bind with the calcium in the calcium pectate to form complex compounds making it easier to separate them separate them from the fibers [129]. Since chelators have optimal metal binding capacities at high pH, NaOH is added to the formulation to neutralize the acids produced during incubation therefore keeping the pH of the liquor high [131]. By chelating metal ions from pectin complex, non-cellulosic plant materials (pectin and hemicellulose) can be extracted using alkaline solutions of chelating agents [129]. The use of chelators at high pH appear to be the most successful/optimal way of chemical retting that is less aggressive (compared to mineral acids or boiling in alkali) judging from the fine fibers that are produced [131] and since the process does not require additional energy in terms of heating and mechanical agitation. Other chelating agents include trisodium phosphate, sodium gluconate [131], diethylenetetraacetic acid, tetrasodium salt (Trilon TB), diethylenediaminepentaacetic acid, and Penta sodium salt (DTPA) [129].
Detergents have also been tested for retting and usually in combination with acids or chelating agents. The use of such surfactants is shown to improve the retting of flax probably due to their ability to solubilize proteins and the reduction of the surface tension of water to allow easier access to the matrix material by the chelator, therefore enhancing its action [127]. Other methods using chemicals have been developed and used in the context of plant breeding in order to enable effective and complete fiber extraction [132,133].
4.3.4. Physical Treatment
Methods that involve the physical disruption of the integrity of the plant structure through various means have also been applied to loosen the fibers from the woody core.
Steam explosion treatment is a method for breaking down biomass that is used in the processing of fibrous source materials as well. However, if one follows the relevant literature on this topic, a sometimes-incorrect interpretation of the underlying research results of the referenced primary sources becomes apparent. For example, experiments mentioned in all three sources in (Manian et al.) [32] do not deal with the processing of stems, but of fiber bast or fiber bundles [134,135,136].
Considering relevant literature in the area of other lignocellulose biomasses, it would have to be assumed that the entire stem biomass is dissolved and that it may not be possible to distinguish between the desired yield of fiber elements from the bast and those from other tissue parts of the stem (essentially the xylem or woody inner core).
Literature references on the use of steam explosion treatment of bast fiber stalks could not be found. However, in one research project, unpressurized steam treatment in a flow reactor was used for retting in order to investigate the release of certain elements or compounds from different hemp samples [137]. The treatment of hemp stalks resulted in an easier detachment of the bast layer from the xylem, but was not investigated in more detail.
Another physical effect, caused by radio frequency, has been investigated over a time period by a group of researchers to improve the retting of bast fiber stalks. The intention was to enhance the efficiency of water retting [138] or to assist enzymatic retting [139] of flax stem samples. Pre-soaking, adapted power levels and application duration in combination with the control of the water temperature can lead to an optimization of the process control and the resulting material properties.
Microwaves, as well part of the electromagnetic spectrum, have also been investigated to support retting processes. A good overview of the relationship between biological principles and the possibilities and effects of electromagnetic energy on the processing of flax can be found in Nair et al. [140]. In-depth investigations have shown the positive influence of already known process parameters such as pre-soaking, microwave power, temperature and process time on the structural decomposition of non-cellulosic, fiber cementing polysaccharides [141]. The positive results of the assisted treatment of flax stalks could also be transferred to hemp stalks on an experimental basis [142].
A comparison between the use of radio frequency and microwave assistance of enzyme retting has shown that the latter has a more significant effect under comparable process conditions with slightly lower mechanical properties of the resulting fibers [143].
Ultrasound as another physical effect has also been investigated and applied to assist the separation of fiber and non-fiber components. In contrast to the aforementioned methods, this is a mechanical wave and not electromagnetic radiation. Konczewicz et al. [60] have investigated osmotic effects in aqueous environment, where water is continuously passed through the biomass of the straw. The fibers, the woody core and the pectin absorb the water and swell thereby exerting considerable physical pressure on the cuticle, which causes it to break. The exposed pectin as well as other soluble substances are diluted and carried away in the circulating water. Thus, the separation of the fibers from each other is enhanced and resulting in reasonable fiber quality. The whole process was combined with ultrasound treatment to make it more effective.
4.3.5. Ensiling
In the search for alternative raw materials for the pulp industry, supply procedures based on wet preservation (“silage”) of flax [144] and hemp [145] biomass were investigated for the first time in the mid-90s of the last century. From there, further scientific work dealt with the anaerobic storage of freshly harvested hemp and its use in fiber-reinforced plastics [146,147]. In the same period, a series of in-depth studies began, in particular on harvesting and storage variants, the use of additional preservatives and the resulting fiber properties after thermo-mechanical processing of the whole plant material [148,149,150].
In contrast to dew retting, ensiling offers the significant advantage of being completely independent of unpredictable weather conditions. This also means that the fields are cleared immediately after harvesting, so that the value of hemp as preceding crop can be utilized in the subsequent crop. The ensiling process is a well-established agricultural practice and the effects of the anaerobic storage processes on the properties of the bast part of the plant material are comparable to the results of common retting procedures. Based on a patent specification of Clarke et al. [151], a publication reports on a so-called bag retting process. It is shown as well that the enzymatic activity of mainly anaerobic bacteria removes non-cellulosic components of the hemp fibers in silage stock [116].
5. Further Processing and Refining
Further processing or refining refers to the subsequent processes, performed after separation of the fibrous bast (or coarse fiber bundles) from the woody core, generally referred to as “primary processing” of straw. Refining of bast fibers provides opportunity for further modification and improvement in fiber quality to make it suitable for a particular end use. This can be a chemical, physical or biological treatment or the so called cottonization process which aims to produce cotton-like fibers from bast fibers [45,152]. Here, too, it is difficult to differentiate or clearly separate the definitions in the literature, as the methods mentioned above are sometimes also summarized under Schenek [153] or mixed with the term cottonization [154]. All of these methods work by further separating the fiber bundles into individual fibers and removing the remaining binding substances and impurities. This is inevitably accompanied by a refinement (i.e., an improvement in fiber fineness). This is also associated with a reduction in fiber length (i.e., the proportion of shorter fibers increases) [153]. With appropriate process control, it is possible to achieve the required staple lengths for combined spinning with other fibers [45].
A qualified review of the known, experimental and practiced procedures and methods would far exceed the aim and scope of this paper. However, an overview should be given in order enable the intended procedural differentiation from the retting of straw.
5.1. Degumming
Chemical treatment is usually applied to bast or fibers and provides an alternative process, which allows for more control of the degumming parameters and the quality of the resulting fibers. Furthermore, chemical treatments have proved most effective in removing lignin which usually resistant to most biological and enzymatic treatments [52,155].
The direct use of chemicals, including alkali bases, neutral salts, or detergents, is known to dissolve or emulsify the hemicellulose, pectin and lignin that form the matrix substance in the bast fiber-containing tissues of the stem. This process is normally preceded by the decomposition of the matrix and encrusting substances through de-polymerization by the use of oxidizing agents or acid treatments [156]. This process may involve scouring using acids or boiling in alkalis to degrade the matrix material and is usually applied after removal of the shives through mechanical processes such as decortication [157]. For example chemical degumming with sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and other alkalis are commonly used for processing of kenaf bast [41,42] and ramie fibers [37]. Just as for flax and hemp, chemical degumming of kenaf is usually carried out after decortication [40,42]. This process considerably shortens the degumming time but it reduces the mechanical properties of the resulting fibers [41] and requires heating which increases energy costs [40]. More recent approaches propose a combination of chemical and biological degumming in order to improve interfacial bonding of hemp fibers with a polypropylene matrix [158] or to obtain high quality spinnable fibers from ramie [43].
A special process for separating coarse fiber structures using an initial mechanical process for the production of so called fiber tapes, but then supplemented with a chemical or cooking process under pressure, was patented [159]. It seems to be in practice as such fibers are available under the trademark “Flasin” [160,161].
However, the use of chemical treatment in industrial practice is severely limited due to material costs, the sometimes negative impact on individual fiber quality parameters and, above all, concerns about environmental compatibility.
Biological degumming is similar to water retting but is performed on decorticated bast fibers, not on the whole stem or straw. Bacteria with known pectinolytic activity are added to water to enhance the process [14,39,162]. More recent research work has focused on the technological optimization of such systems for the degumming of flax fibers [163] as well as hemp bast and a detailed examination of the active microbiome [164].
In enzymatic treatments, mixtures/variations of enzymes can also be used to optimize the degumming and thus the properties of bast fibers. Sharma applied a mixture of enzymes to target residual non-cellulosic polysaccharides on roves of dew-retted flax fibers leading to improvement in the quality number of the resulting yarn [165]. Antonov et al. used different variations of Texazym enzyme to improve the fineness and cleanliness properties of hemp fibers in what they called enzymatic “cottonization”. The enzymes were also applied to improve the quality of flax rovings to enhance the spinning, tensile strength and coefficient of variation [12]. A large number of further experimental studies particularly on the degumming of ramie has been carried out and published in recent years [166,167,168].
A solid-sate fermentation approach could be interesting in terms of reducing the amount of water required for biological degumming [169].
Physical treatments have been investigated due to their specific effects on the morphological structure of the fiber containing tissues. Steam explosion, as a basically physical effect, of alkali-impregnated semi-retted hemp fiber bundles was investigated as an effective way of degrading pectin to produce elementary fibers [134,135,136]. Song et al. [170] have attempted to perform alkali free steam explosion to extract bast fibers (ramie) by treating the fibers with deep eutectic solvents afterwards but the quality was slightly poorer than fibers from the traditional alkali boiling method in terms of gum content. In their studies, Sutka et al. [171] compared the effects of steam-explosion treatment on dew retted and chemically pre-treated fibers. Keller [172] was able to show in his studies comparing two processing methods for hemp fibers that steam explosion treatment enables better degumming and better mechanical properties compared to a biological process. As another physical principle, ultrasonic treatment was developed and used to obtain high-quality fibers without the use of chemicals after decortication and opening of unretted flax or hemp stalks [173]. Renouard et al. [174] stated a remarkable degradation of hemicelluloses after treating flax or hemp fibers with ultrasonic processing. A more recent research has shown the assisting effect of ultrasound treatment for alkali based degumming [175].
5.2. Cottonization
Cottonization refers to refining the long, coarse bast fiber bundles into dimensions (length and fineness) that allow for pure processing in short staple spinning and/or blending with natural short staple fibers, for example, cotton [176]. This can be achieved through mechanical forces, but with great risks of damage to the fiber and greater proportions of fiber waste [135]. Some effort has been made to develop less aggressive means of cottonization. For example, the process of steam explosion with the addition of mild alkaline solutions (NaOH) was used in the secondary processing of bast fibers after separation from the woody core [113,136]. The treatment requires pressure-resistant reactors as well as adapted temperature and time control. Taking into account the literature on the method cited therein, Moussa et al. [177] showed that this steam explosion treatment is suitable for producing isolated hemp fibers of an application-oriented quality even without chemical additives.
6. Conclusions
The overview of the literature on supply chains presented here, especially for flax and hemp, can certainly not be complete for reasons of scope, readability and comprehensibility of the manuscript. Nevertheless, it is clear that the terms used in the context of processing bast fiber plants are often ambiguous and sometimes used very differently.
It seems appropriate to start with a clear understanding of the respective purpose and the sequence of the individual process steps from harvesting the crop to the final fiber quality. It is therefore proposed to distinguish between two basic phases. This primarily takes into account the processes that concern the handling of the agriculturally produced biomass in the field and take place before the actual initial processing of the resulting fiber plant straw. Thus, the term, and the different processes of retting bast fiber crops should refer exclusively to the treatment of whole stalk biomass. Incidentally, this is also in line with the use of the term in one of the world’s most traditional and professional hemp industries in France [178]. Occasionally, a series of process steps that include retting is also summarized under the term fiber extraction [45]. This seems problematic since the microbial metabolic processes (or, if practiced, the chemically or physically induced decomposition) of fiber-cementing substances degradation in the stem material do not initially result in any real separation of the corresponding plant tissue parts (bast) from the rest of the plant (woody inner core).
The initial (physical) separation takes place during the—usually stationary—primary processing of the straw. Using different technologies, this is divided into the four main processes of bale opening, decortication, cleaning, and opening of coarse fiber bundles [179].
The resulting fiber mass are generally already suitable for applications in a range of technical (non-woven) products. However, the use of fibers in high value-added applications such as apparel textiles or highly resilient composite materials often requires further processing (or secondary processing). The aim here, among others, is to remove any remaining or additional fiber-accompanying substances after retting. This mainly concerns compounds that still bind fiber elements together. Therefore, from the term “gum”, which is commonly used in English, the name of this process step—degumming—can be derived.
In terms of nomenclature and material, this paper proposes (and encourages) clear differentiation between the terminology used for the treatments applied to whole stem biomass after harvest (i.e., straw or stalk) and the terminology for the treatments applied to the extracted fiber mass after mechanical separation (primary processing). Similar treatment agents such as enzymes, chemicals, microorganisms and physical force may be applied to whole stems as well as to bast material but the procedures (retting vs degumming) differ depending on the substrate (Table 1).

Table 1.
Differentiation between terms for procedures/methods before and after primary processing.
It is hoped to facilitate the understanding of this part of the supply chain for interested readers of journal articles and practitioners or newcomers in the field. Scientific work based on published findings is particularly dependent on clear definitions and terminology. The increasing number of publications in recent years illustrates the great interest and diverse potential in the field of (bast) fiber plants. The selected review and statements given here are intended to support the transferability and usefulness in all areas of their application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.A. and H.-J.G.; validation, M.A. and H.-J.G.; data curation, M.A. and H.-J.G.; writing original draft, M.A. and H.-J.G.; review and editing, M.A. and H.-J.G.; drawings, M.A. and H.-J.G. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The author of this work used collections of magazines (paper form) and legal electronic databases.
Acknowledgments
M.A. received funding by German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF); project reference 01LZ1708C; icons for Figure 2 kindly provided by www.flaticon.com (accessed 21 December 2023).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Clarke, R.C. Botany of the Genus Cannabis. In Advances in Hemp Research; Ranalli, P., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999; pp. 1–19. [Google Scholar]
- Tourangeau, W. Re-Defining Environmental Harms: Green Criminology and the State of Canada’s Hemp Industry. Can. J. Criminol. Crim. Justice 2015, 57, 528–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.-B. Genetic Evidence for Early Flax Domestication with Capsular Dehiscence. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 2011, 58, 1119–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kvavadze, E.; Bar-Yosef, O.; Belfer-Cohen, A.; Boaretto, E.; Jakeli, N.; Matskevich, Z.; Meshveliani, T. 30,000-Year-Old Wild Flax Fibers. Science 2009, 325, 1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melelli, A.; Shah, D.U.; Hapsari, G.; Cortopassi, R.; Durand, S.; Arnould, O.; Placet, V.; Benazeth, D.; Beaugrand, J.; Jamme, F.; et al. Lessons on Textile History and Fibre Durability from a 4000-Year-Old Egyptian Flax Yarn. Nat. Plants 2021, 7, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akin, D.E. Linen Most Useful: Perspectives on Structure, Chemistry, and Enzymes for Retting Flax. ISRN Biotechnol. 2013, 186534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegret, S. The History of Hemp. In Hemp: Industrial Production and Uses; CAB International: Bar sur Aube, France, 2013; pp. 4–25. ISBN 978-1-84593-792-8. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, R.C. Traditional Fiber Hemp (Cannabis) Production, Processing, Yarn Making, and Weaving Strategies—Functional Constraints and Regional Responses. Part 2. J. Nat. Fibers 2010, 7, 229–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carus, M.; Gahle, C.; Pendarovski, C.; Vogt, D.; Ortmann, S.; Grotenhermen, F.; Breuer, T.; Schmidt, C. Studie Zur Markt- Und Konkurrenz—Situation Bei Naturfasern Und Naturfaser- Werkstoffen (Deutschland Und EU). Available online: http://nova-institut.de/pdf/08-01-Flachs-Hanf_Buch_Carus_et_al.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2019).
- Smith-Heisters, S. Environmental Costs of Hemp Prohibition in the United States. J. Ind. Hemp 2008, 13, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.; Henriksson, G.; Evans, J.D.; Adamsen, A.P.S.; Foulk, J.A.; Dodd, R.B. Progress in Enzyme-Retting of Flax. J. Nat. Fibers 2004, 1, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonov, V.; Marek, J.; Bjelkova, M.; Smirous, P.; Fischer, H. Easily Available Enzymes as Natural Retting Agents. Biotechnol. J. 2007, 2, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crônier, D.; Monties, B.; Chabbert, B. Structure and Chemical Composition of Bast Fibers Isolated from Developing Hemp Stem. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8279–8289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Candilo, M.; Bonatti, P.M.; Guidetti, C.; Focher, B.; Grippo, C.; Tamburini, E.; Mastromei, G. Effects of Selected Pectinolytic Bacterial Strains on Water-Retting of Hemp and Fibre Properties. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2010, 108, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djemiel, C.; Grec, S.; Hawkins, S. Characterization of Bacterial and Fungal Community Dynamics by High-Throughput Sequencing (HTS) Metabarcoding during Flax Dew-Retting. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, D.; Thygesen, A.; Meyer, A.S.; Daniel, G. Elucidating Field Retting Mechanisms of Hemp Fibres for Biocomposites: Effects of Microbial Actions and Interactions on the Cellular Micro-Morphology and Ultrastructure of Hemp Stems and Bast Fibres. BioResources 2019, 14, 4047–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulk, J.A.; Akin, D.E.; Dodd, R.B. Influence of Pectinolytic Enzymes on Retting Effectiveness and Resultant Fiber Properties. BioResources 2008, 3, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, M.; Mussone, P.G.; Bressler, D.C. Improving the Accessibility of Hemp Fibres Using Caustic to Swell the Macrostructure for Enzymatic Enhancement. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 67, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankauskienė, Z.; Bačelis, K.; Vitkauskas, A. Evaluation of Water-Retted Flax Fibre for Quality Parameters. Mater. Sci. 2006, 12, 171–174. [Google Scholar]
- Mazian, B.; Bergeret, A.; Benezet, J.-C.; Malhautier, L. Influence of Field Retting Duration on the Biochemical, Microstructural, Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Hemp Fibres Harvested at the Beginning of Flowering. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 116, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.H.; Khalina, A.; Lee, S.H.; Liu, M. A Comprehensive Review on Bast Fibre Retting Process for Optimal Performance in Fibre-Reinforced Polymer Composites. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 2020, e6074063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Silva, D.A.S.; Fernando, D.; Meyer, A.S.; Madsen, B.; Daniel, G.; Thygesen, A. Controlled Retting of Hemp Fibres: Effect of Hydrothermal Pre-Treatment and Enzymatic Retting on the Mechanical Properties of Unidirectional Hemp/Epoxy Composites. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 88, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Hurren, C. Degumming Methods for Bast Fibers—A Mini Review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 174, 114158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakarinen, A.; Zhang, J.; Brock, T.; Maijala, P.; Viikari, L. Enzymatic Accessibility of Fiber Hemp Is Enhanced by Enzymatic or Chemical Removal of Pectin. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 107, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Réquilé, S.; Mazian, B.; Grégoire, M.; Musio, S.; Gautreau, M.; Nuez, L.; Day, A.; Thiébeau, P.; Philippe, F.; Chabbert, B.; et al. Exploring the Dew Retting Feasibility of Hemp in Very Contrasting European Environments: Influence on the Tensile Mechanical Properties of Fibres and Composites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 164, 113337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, A.; Pochart, P.; Day, A.; Mennuni, S.; Bono, P.; Baret, J.-L.; Spadoni, J.-L.; Mangin, I. Microbial Diversity Observed during Hemp Retting. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 99, 4471–4484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, P.M.; Ahmed, A.B.; SaifulAzry, S.; Ahmed, Z. Retting Process of Some Bast Plant Fibres and Its Effect on Fibre Quality: A Review. BioResources 2011, 6, 5260–5281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, E.; León, A.G.; Perito, B.; Mastromei, G. Characterization of Bacterial Pectinolytic Strains Involved in the Water Retting Process. Environ. Microbiol. 2003, 5, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thygesen, A.; Liu, M.; Meyer, A.S.; Daniel, G. Hemp Fibres: Enzymatic Effect of Microbial Processing on Fibre Bundle Structure. In Proceedings of the Risoe International Symposium on Materials, Risoe, Denmark, 2–5 September 2013; Volume 34, pp. 373–380. [Google Scholar]
- Valladares Juárez, A.G.; Dreyer, J.; Göpel, P.K.; Koschke, N.; Frank, D.; Märkl, H.; Müller, R. Characterisation of a New Thermoalkaliphilic Bacterium for the Production of High-Quality Hemp Fibres, Geobacillus Thermoglucosidasius Strain PB94A. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2009, 83, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müssig, J.; Harig, H. Filze Und Vliese aus Hanffasern. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium “Biorohstoff Hanf”, Nova-Institut, Hürth, Germany, 27 February–2 March 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Manian, A.P.; Cordin, M.; Pham, T. Extraction of Cellulose Fibers from Flax and Hemp: A Review. Cellulose 2021, 28, 8275–8294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapliyal, D.; Verma, S.; Sen, P.; Kumar, R.; Thakur, A.; Tiwari, A.K.; Singh, D.; Verros, G.D.; Arya, R.K. Natural Fibers Composites: Origin, Importance, Consumption Pattern, and Challenges. J. Compos. Sci. 2023, 7, 506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankauskienė, Z.; Butkutė, B.; Gruzdevienė, E.; Cesevičienė, J.; Fernando, A.L. Chemical Composition and Physical Properties of Dew- and Water-Retted Hemp Fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 75, 206–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, A.D.; McNees, C.R.; Moe, L.A. The Microbiology of Hemp Retting in a Controlled Environment: Steering the Hemp Microbiome towards More Consistent Fiber Production. Agronomy 2020, 10, 492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Fernando, D.; Daniel, G.; Madsen, B.; Meyer, A.S.; Ale, M.T.; Thygesen, A. Effect of Harvest Time and Field Retting Duration on the Chemical Composition, Morphology and Mechanical Properties of Hemp Fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 69, 29–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.D.; Shah, S.R. Degumming of Decorticated Ramie: Effects of Alkalis on Gummy Compositions Vis-à-Vis Their Properties. J. Text. Inst. 2007, 98, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kundu, P.K.; Sarmah, R.; Sarkar, C.R. Chemical Degumming and Fibre Characteristics of Ramie at Different Stages of Crop Growth. Indian J. Fibre Text. Res. 1996, 21, 205–209. [Google Scholar]
- Angelini, L.G.; Scalabrelli, M.; Tavarini, S.; Cinelli, P.; Anguillesi, I.; Lazzeri, A. Ramie Fibers in a Comparison between Chemical and Microbiological Retting Proposed for Application in Biocomposites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 75, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, D.V.; Calamari, T.A.; Sawhney, A.P.S.; Blanchard, E.J.; Screen, F.J.; Warnock, M.; Muller, D.H.; Stryjewski, D.D. Improved Chemical Retting of Kenaf Fibers. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramaswamy, G.N.; Ruff, C.G.; Boyd, C.R. Effect of Bacterial and Chemical Retting on Kenaf Fiber Quality. Text. Res. J. 1994, 64, 305–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, W.H.; Akin, D.E.; Ramaswamy, G.; Baldwin, B. Evaluating Chemically Retted Kenaf Using Chemical, Histochemical, and Microspectrophotometric Analyses. Text. Res. J. 1996, 66, 651–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wulandari, A.P.; Kusmoro, J.; Ernawati, E.E. Standardization of Chemical Degumming and Biodegumming of Ramie Fiber Processing for Natural Fiber Supply Chain Strategy as A Source of Textile Raw Materials in Indonesia. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2023, 1211, 012008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiyoto, S.; Yoshinaga, A.; Fernandez-Tendero, E.; Day, A.; Chabbert, B.; Takabe, K. Distribution of Lignin, Hemicellulose, and Arabinogalactan Protein in Hemp Phloem Fibers. Microsc. Microanal. 2018, 24, 442–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimniewska, M. Hemp Fibre Properties and Processing Target Textile: A Review. Materials 2022, 15, 1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.E. Flax—Structure, Chemistry, Retting and Processing. In Industrial Applications of Natural Fibres; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010; pp. 87–108. ISBN 978-0-470-66032-4. [Google Scholar]
- Blake, A.W.; Marcus, S.E.; Copeland, J.E.; Blackburn, R.S.; Knox, J.P. In Situ Analysis of Cell Wall Polymers Associated with Phloem Fibre Cells in Stems of Hemp, Cannabis sativa L. Planta 2008, 228, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, J.D.; Akin, D.E.; Foulk, J.A. Flax-Retting by Polygalacturonase-Containing Enzyme Mixtures and Effects on Fiber Properties. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 97, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Henriksson, G.; Johansson, G. Polygalacturonase Is the Key Component in Enzymatic Retting of Flax. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 81, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meijer, W.J.M.; Vertregt, N.; Rutgers, B.; van de Waart, M. The Pectin Content as a Measure of the Retting and Rettability of Flax. Ind. Crops Prod. 1995, 4, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokshina, N.; Chernova, T.; Galinousky, D.; Gorshkov, O.; Gorshkova, T. Key Stages of Fiber Development as Determinants of Bast Fiber Yield and Quality. Fibers 2018, 6, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.M.; Postle, R.; Kessler, R.W.; Kessler, W. Removing Pectin and Lignin During Chemical Processing of Hemp for Textile Applications. Text. Res. J. 2003, 73, 664–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, R.; Hurren, C.J.; Kaynak, A.; Wang, X. Correlating the Fineness and Residual Gum Content of Degummed Hemp Fibres. Fibers Polym. 2002, 3, 129–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Morrison III, W.H.; Archibald, D.D.; Sharma, H.S.S.; Akin, D.E. Chemical and Physical Characterization of Water- and Dew-Retted Flax Fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2000, 12, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, M.; Chowdhury, F.T.; Ahmed, S.; Das, A.; Islam, M.R.; Khan, H. Value Addition to Jute: Assessing the Effect of Artificial Reduction of Lignin on Jute Diversification. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-Y.; Fei, B.-H.; Yu, Y.; Cheng, H.-T.; Wang, C.-G. Effect of the Amount of Lignin on Tensile Properties of Single Wood Fibers. For. Sci. Pract. 2013, 15, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühnel, S. Modulation von Fasereigenschaften Durch Den Einsatz von Enzymen. In Proceedings of the Innovationsakademie Bioökonomie, Berlin/Brandenburg, Germany, 10 November 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.S.S.; Faughey, G.; Lyons, G. Comparison of Physical, Chemical, and Thermal Characteristics of Water-, Dew-, and Enzyme-Retted Flax Fibers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1999, 74, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourmaud, A.; Siniscalco, D.; Foucat, L.; Goudenhooft, C.; Falourd, X.; Pontoire, B.; Arnould, O.; Beaugrand, J.; Baley, C. Evolution of Flax Cell Wall Ultrastructure and Mechanical Properties during the Retting Step. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 206, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konczewicz, W.; Kryszak, N.; Nowaczkiewicz, E.; Kozlowski, R.; Wojtysiak, J.; Podsiedlik, W. Osmosis Phenomena Based Degumming of Bast Fibrous Plants as a Promising Method in Primary Processing. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2013, 571, 116–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanner, F.W. Microbiology of Flax Retting. Bot. Gaz. 1922, 74, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruschmann, G. Grundlagen der Röste: Eine Wissenschaftlich-Technische Einführung für Bakteriologen, Landwirte, Röster, Spinner und Fachschüler; S. Hirzel: Zurich, Switzerland, 1923. [Google Scholar]
- Dujardin, A. The Retting of Flax; Carswell & Son Ltd.: Belfast, UK, 1948. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, A.J. Quality in Flax; Linen Industry Research Association: Lambeg, UK, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.S.S. The Biology and Processing of Flax; M Publications: Belfast, UK, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Mazian, B.; Cariou, S.; Chaignaud, M.; Fanlo, J.-L.; Fauconnier, M.-L.; Bergeret, A.; Malhautier, L. Evolution of Temporal Dynamic of Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) and Odors of Hemp Stem during Field Retting. Planta 2019, 250, 1983–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.E.; Dodd, R.B.; Perkins, W.; Henriksson, G.; Eriksson, K.-E.L. Spray Enzymatic Retting: A New Method for Processing Flax Fibers. Text. Res. J. 2000, 70, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placet, V.; Day, A.; Beaugrand, J. The Influence of Unintended Field Retting on the Physicochemical and Mechanical Properties of Industrial Hemp Bast Fibres. J. Mater. Sci. 2017, 52, 5759–5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speri, M. Insights on Microbial and Biochemical Aspects of Retting for Bast Fiber Plant Processing in a Bioreactor. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Verona, Department of Biotechnology, Verona, Italy, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Henriksson, G.; Akin, D.E.; Hanlin, R.T.; Rodriguez, C.; Archibald, D.D.; Rigsby, L.L.; Eriksson, K.L. Identification and Retting Efficiencies of Fungi Isolated from Dew-Retted Flax in the United States and Europe. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1997, 63, 3950–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, Z.; Akhter, F. Jute Retting: An Overview. Available online: https://scialert.net/abstract/?doi=jbs.2001.685.688 (accessed on 22 December 2023).
- Yadav, S. Purification and Characterization of Pectin Lyase Produced by Aspergillus Terricola and Its Application in Retting of Natural Fibers. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2009, 159, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Z.; Wang, S.; Bergeron, H.; Zhang, J.; Lau, P.C.K. A Flax-Retting Endopolygalacturonase-Encoding Gene from Rhizopus Oryzae. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 2008, 94, 563–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booth, I.; Goodman, A.M.; Grishanov, S.A.; Harwood, R.J. A Mechanical Investigation of the Retting Process in Dew-Retted Hemp (Cannabis sativa). Ann. Appl. Biol. 2004, 145, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, S.M.G.; Pelissari, F.A.; Vitorello, C.B.M. Screening and Genetic Improvement of Pectinolytic Fungi for Degumming of Textile Fibers. Braz. J. Microbiol. 2001, 32, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sisti, L.; Totaro, G.; Vannini, M.; Fabbri, P.; Kalia, S.; Zatta, A.; Celli, A. Evaluation of the Retting Process as a Pre-Treatment of Vegetable Fibers for the Preparation of High-Performance Polymer Biocomposites. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 81, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.E.; Rigsby, L.L.; Henriksson, G.; Eriksson, K.-E.L. Structural Effects on Flax Stems of Three Potential Retting Fungi. Text. Res. J. 1998, 68, 515–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H. An Alternative Method of Flax Retting during Dry Weather. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1986, 109, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ale, M.T.; Kołaczkowski, B.; Fernando, D.; Daniel, G.; Meyer, A.S.; Thygesen, A. Comparison of Traditional Field Retting and Phlebia Radiata Cel 26 Retting of Hemp Fibres for Fibre-Reinforced Composites. AMB Express 2017, 7, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hossain, M.M.; Siddiquee, S.; Kumar, V. Critical Factors for Optimum Biodegradation of Bast Fiber’s Gums in Bacterial Retting. Fibers 2021, 9, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bou Orm, E.; Sauvagère, S.; Rocher, J.; Benezet, J.-C.; Bayle, S.; Siatka, C.; Bergeret, A.; Malhautier, L. Estimating the Bias Related to DNA Recovery from Hemp Stems for Retting Microbial Community Investigation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 4665–4681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bleuze, L.; Chabbert, B.; Lashermes, G.; Recous, S. Hemp Harvest Time Impacts on the Dynamics of Microbial Colonization and Hemp Stems Degradation during Dew Retting. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 145, 112122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konczewicz, W.; Zimniewska, M.; Valera, M.A. The Selection of a Retting Method for the Extraction of Bast Fibers as Response to Challenges in Composite Reinforcement. Text. Res. J. 2018, 88, 2104–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, P.; Mahapatra, B.S.; Pramanick, B.; Kumar, A.; Negi, M.S.; Paul, J.; Shukla, D.K.; Singh, S.P. Quality Optimization of Flax Fibre through Durational Management of Water Retting Technology under Sub-Tropical Climate. Ind. Crops Prod. 2021, 162, 113277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, P.; Raghavan, V.; Gariepy, Y.; Du, J. Characterization of Flax Water Retting of Different Durations in Laboratory Condition and Evaluation of Its Fiber Properties. BioResources 2015, 10, 3553–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossart, H.-P.; Van den Wyngaert, S.; Kagami, M.; Wurzbacher, C.; Cunliffe, M.; Rojas-Jimenez, K. Fungi in Aquatic Ecosystems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 339–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamburini, E.; León, A.G.; Perito, B.; Di Candilo, M.; Mastromei, G. Exploitation of Bacterial Pectinolytic Strains for Improvement of Hemp Water Retting. Euphytica 2004, 140, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.L.; Zhu, R.Y.; Chen, J.Y.; Chen, J.M.; Feng, X.X. Seawater-Retting Treatment of Hemp and Characterization of Bacterial Strains Involved in the Retting Process. Process Biochem. 2008, 43, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou-Elela, S.I.; Ali, M.E.M.; Ibrahim, H.S. Combined Treatment of Retting Flax Wastewater Using Fenton Oxidation and Granular Activated Carbon. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 511–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.P.; Liu, P.F.; Ling, H.Z.; Cai, B.Y.; Song, G.; Ping, W.X. Using Bacteria Addition and Reusing Retting Water Technologies to Accelerate Flax Degumming. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2014, 522–524, 374–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawzy, M.; Badr, N.; Abou-Elela, S. Remediation and Reuse of Retting Flax Wastewater. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 11, 1961–1968. [Google Scholar]
- Castaldini, M.; Miclaus, N.; Miclaus, N. Effects of Hemp Retting Water on the Composition of Soil Bacterial Community and on Wheat Yield. Ital. J. Agron. 2001, 5, 21–27. [Google Scholar]
- Jayashree, C.; Sweta, S.; Arulazhagan, P.; Yeom, I.T.; Iqbal, M.I.I.; Rajesh Banu, J. Electricity Generation from Retting Wastewater Consisting of Recalcitrant Compounds Using Continuous Upflow Microbial Fuel Cell. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2015, 20, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.S.S. The Role of Bacteria in Retting of Desiccated Flax during Damp Weather. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1986, 24, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.S.S. Effects of the Application of Chemical Additives to Desiccated Flax on Retting. Biotechnol. Lett. 1986, 8, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampaio, S.; Bishop, D.; Shen, J. Physical and Chemical Properties of Flax Fibres from Stand-Retted Crops Desiccated at Different Stages of Maturity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2005, 21, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, O. Standröste von Flachs—Innovation in der Flachserntetechnik. In Proceedings of the VDI/MEG Kolloquium Agrartechnik: Erzeugung, Aufbereitung und Verarbeitung von Naturfasern für Nichttextile Zwecke, Bonn, Germany, 6–7 August 1997; Volume 22, pp. 101–107. [Google Scholar]
- Pasila, A. The Effect of Frost on Fibre Plants and Their Processing. Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. Sci. Technol. Sect. A Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 2000, 353, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasila, A. The Dry-Line Method in Bast Fibre Production. Ph.D. Dissertation, Department of Agricultural Engineering and Household Technology, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann, T.; Pecenka, R.; Schemel, H.; Gusovius, H.-J. Process-Technological Evaluation of Harvesting Hemp in Winter. J. Nat. Fibers 2013, 10, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanovs, S.; Adamovics, A.; Rucins, A. Investigation of the Technological Spring Harvesting Variants of the Industrial Hemp Stalk Mass. Agron. Res. 2015, 13, 73–82. [Google Scholar]
- Marrot, L.; Alao, P.F.; Mikli, V.; Kers, J. Properties of Frost-Retted Hemp Fibers for the Reinforcement of Composites. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 16017–16028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kymäläinen, H.-R. Quality of Linum usitatissimum L. (Flax and Linseed) and Cannabis sativa L. (Fibre Hemp) during the Production Chain of Fibre Raw Material for Thermal Insulations; University of Helsinki: Helsinki, Finland, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Kymäläinen, H.-R. Hygienic Quality of Stem Fractions of Mechanically Processed Fiber Hemp and Linseed. Agric. Food Sci. 2005, 14, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kymäläinen, H.-R.; Hautala, M.; Kuisma, R.; Pasila, A. Capillarity of Flax/Linseed (Linum usitatissimum L.) and Fibre Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) Straw Fractions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 14, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nykter, M. Microbial Quality of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) from Plants to Thermal Insulation. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nykter, M.; Kymäläinen, H.-R.; Thomsen, A.B.; Lilholt, H.; Koponen, H.; Sjöberg, A.-M.; Thygesen, A. Effects of Thermal and Enzymatic Treatments and Harvesting Time on the Microbial Quality and Chemical Composition of Fibre Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.). Biomass Bioenergy 2008, 32, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Repeèkienë, J.; Lugauskas, A.; Jankauskiene, Z. Diversity of Fungal Species on Laid and Stand-Retted Flax. Bot. Lith. 2007, 13, 51–59. [Google Scholar]
- Assirelli, A.; Dal Re, L.; Esposito, S.; Cocchi, A.; Santangelo, E. The Mechanical Harvesting of Hemp Using In-Field Stand-Retting: A Simpler Approach Converted to the Production of Fibers for Industrial Use. Sustainability 2020, 12, 8795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, S. Der Anbau von Faserhanf (Cannabis sativa L.) als Winterzwischenfrucht. Ph.D. Dissertation, Bergische Universität, Wuppertal, Germany, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Guan, Z.; Li, Z. Application of Cryogenic and Mechanical Treatment in Degumming of Hemp Stems. Biosyst. Eng. 2018, 174, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.E.; Himmelsbach, D.S.; Morrison, W.H. Biobased Fiber Production: Enzyme Retting for Flax/Linen Fibers. J. Polym. Environ. 2000, 8, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvageon, T.; Lavoie, J.-M.; Segovia, C.; Brosse, N. Toward the Cottonization of Hemp Fibers by Steam Explosion—Part 1: Defibration and Morphological Characterization. Text. Res. J. 2018, 88, 1047–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Summerscales, J. A Review of Bast Fibres and Their Composites: Part 4~Organisms and Enzyme Processes. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2021, 140, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.S.S.; Mercer, P.C.; Brown, A.E. A Review of Recent Research on the Retting of Flax in Northern Ireland. Int. Biodeterior. 1989, 25, 327–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pickering, K.L.; Farrell, R.L. Analysis of Green Hemp Fibre Reinforced Composites Using Bag Retting and White Rot Fungal Treatments. Ind. Crops Prod. 2009, 29, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, P.; He, F.; Yang, Y.; Ao, M.; Ouyang, J.; Liu, Y.; Yu, L. In-Situ Microbial Degumming Technology with Bacillus Sp. HG-28 for Industrial Production of Ramie Fibers. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 97, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne, M.R.L. 5B—Bast Fibres: Hemp Cultivation and Production. In Handbook of Natural Fibres, 2nd ed.; Kozłowski, R.M., Mackiewicz-Talarczyk, M., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Series in Textiles; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, MA, USA, 2020; pp. 163–196. ISBN 978-0-12-818398-4. [Google Scholar]
- Subash, M.C.; Muthiah, P. Eco-Friendly Degumming of Natural Fibers for Textile Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Clean. Eng. Technol. 2021, 5, 100304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moawad, H.; Abd El-Rahim, W.M.; Hashem, M.M.; Gebreil, G.M.; Sabbor, A.; Sedik, M.Z. Retting and Degumming of Flax Using Biotechnology Eco-Friendly Approach. Egypt. J. Chem. 2019, 62, 2033–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiliveri, S.R.; Koti, S.; Linga, V.R. Retting and Degumming of Natural Fibers by Pectinolytic Enzymes Produced from Bacillus Tequilensis SV11-UV37 Using Solid State Fermentation. SpringerPlus 2016, 5, 559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henriksson, G.; Akin, D.E.; Slomczynski, D.; Eriksson, K.-E.L. Production of Highly Efficient Enzymes for Flax Retting by Rhizomucor Pusillus. J. Biotechnol. 1999, 68, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.E.; Morrison, W.H.; Gamble, G.R.; Rigsby, L.L.; Henriksson, G.; Eriksson, K.-E.L. Effect of Retting Enzymes on the Structure and Composition of Flax Cell Walls. Text. Res. J. 1997, 67, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Prez, J.; Van Vuure, A.W.; Ivens, J.; Aerts, G.; Van de Voorde, I. Enzymatic Treatment of Flax for Use in Composites. Biotechnol. Rep. 2018, 20, e00294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Sumere, C.F.; Sharma, H.S.S. (PDF) Analyses of Fine Flax Fibre Produced by Enzymatic Retting. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/281414439_Analyses_of_fine_flax_fibre_produced_by_enzymatic_retting (accessed on 9 September 2019).
- Fischer, H.; Müssig, J.; Bluhm, C. Enzymatic Modification of Hemp Fibres for Sustainable Production of High Quality Materials. J. Nat. Fibers 2006, 3, 39–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henriksson, G.; Eriksson, K.-E.L.; Kimmel, L.; Akin, D.E. Chemical/Physical Retting of Flax Using Detergent and Oxalic Acid at High pH. Text. Res. J. 1998, 68, 942–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.E.; Foulk, J.A.; Dodd, R.B.; McAlister, D.D. Enzyme-Retting of Flax and Characterization of Processed Fibers. J. Biotechnol. 2001, 89, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.S.S. Chemical Retting of Flax Using Chelating Compounds. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1988, 113, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marek, J.; Antonov, V.; Bjelkova, M.; Smirous, P.; Fischer, H.; Janosik, S. Enzymatic Bioprocessing—New Tool of Extensive Natural Fibre Source Utilization. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Flax and Other Bast Plants, Saskatoon, SK, Canada, 20–23 July 2008; pp. 21–23. [Google Scholar]
- Adamsen, A.P.S.; Akin, D.E.; Rigsby, L.L. Chemical Retting of Flax Straw Under Alkaline Conditions. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Oever, M.J.A.; Bas, N.; van Soest, L.J.M.; Melis, C.; van Dam, J.E.G. Improved Method for Fibre Content and Quality Analysis and Their Application to Flax Genetic Diversity Investigations. Ind. Crops Prod. 2003, 18, 231–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bredemann, G. Die Bestimmung des Fasergehaltes Bei Massenuntersuchungen von Hanf, Flachs. Fasernesseln Und Anderen Bastfaserpflanzen. Faserforschung 1942, 16, 14–39. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Jaldon, C.; Dupeyre, D.; Vignon, M.R. Fibres from Semi-Retted Hemp Bundles by Steam Explosion Treatment. Biomass Bioenergy 1998, 14, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.W.; Becker, U.; Kohler, R.; Goth, B. Steam Explosion of Flax—A Superior Technique for Upgrading Fibre Value. Biomass Bioenergy 1998, 14, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignon, M.R.; Dupeyre, D.; Garcia-Jaldon, C. Morphological Characterization of Steam-Exploded Hemp Fibers and Their Utilization in Polypropylene-Based Composites. Bioresour. Technol. 1996, 58, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Väisänen, T.; Kilpeläinen, P.; Kitunen, V.; Lappalainen, R.; Tomppo, L. Effect of Steam Treatment on the Chemical Composition of Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) and Identification of the Extracted Carbohydrates and Other Compounds. Ind. Crops Prod. 2019, 131, 224–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, P.; Du, J.; Gariepy, Y.; Raghavan, V. Characterization of Radio Frequency Assisted Water Retting and Flax Fibers Obtained. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 69, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, P.; Raghavan, V.; Du, J.; Gariepy, Y.; Lyew, D.; Yang, H. Effect of Radio Frequency Pretreatment on Enzymatic Retting of Flax Stems and Resulting Fibers Properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 146, 112204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.R.; Rho, D.; Raghavan, G.S.V. Application of Electro-Technologies in Processing of Flax Fiber. Fibers 2013, 1, 21–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.R.; Kurian, J.; Yaylayan, V.; Rho, D.; Lyew, D.; Raghavan, G.S.V. Microwave-Assisted Retting and Optimization of the Process through Chemical Composition Analysis of the Matrix. Ind. Crops Prod. 2014, 52, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, G.R.; Lyew, D.; Yaylayan, V.; Raghavan, V. Application of Microwave Energy in Degumming of Hemp Stems for the Processing of Fibres. Biosyst. Eng. 2015, 131, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, P.; Du, J.; Raghavan, V.; Lyew, D.; Gariepy, Y.; Yang, H. Microwave Pretreated Enzymatic Retting of Flax Stems and Comparison with the Effect of Radio Frequency Pretreatment. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Easson, D.L.; Anderson, R.; Sharma, H.S.S. The Sealed Storage of Moist Flax with and without the Use of Chemical Preservatives. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1994, 125, 567–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeyer, E.A.A.D.; Huisman, W. New Technology for Harvesting and Storage of Fibre Hemp for Paper Pulp. J. Int. Hemp Assoc. 1994, 1, 2–41. [Google Scholar]
- von Buttlar, H.-B.; Müssig, J.; Theis, M. Products from Hemp Silage. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium ‘Biorohstoff Hanf’, Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 27 February–2 March 1997; Nova-Institut: Köln/Hürth, Germany, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Einsiedel, R.; Bayer, R.; Buttlar, H.B.V.; Scheffer, K. Fibres and Composites from Hemp Silage. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference ‘Biomass for Energy and Industry’, Würzburg, Germany, 8–11 June 1998; Kopetz, H., Weber, T., Palz, W., Chartier, P., Ferrero, G.L., Eds.; Carmen Publ.: Würzburg, Germany, 1998; pp. 509–510. [Google Scholar]
- Gusovius, H.-J.; Lühr, C.; Hoffmann, T.; Pecenka, R.; Idler, C. An Alternative to Field Retting: Fibrous Materials Based on Wet Preserved Hemp for the Manufacture of Composites. Agriculture 2019, 9, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idler, C.; Pecenka, R.; Fürll, C.; Gusovius, H.-J. Wet Processing of Hemp: An Overview. J. Nat. Fibers 2011, 8, 59–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecenka, R.; Idler, C.; Grundmann, P.; Fuerll, C.; Gusovius, H.-J. Tube Ensiling of Hemp—Initial Practical Experience. Wiss. Z. Agrartech. Forschungseinrichtungen 2007, 13, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, A.; Dennis, H.; Wang, X.; Hurren, C. Degumming of Bast Fibres 2004. U.S. Patent US20040191888A1, 30 September 2004. [Google Scholar]
- McAlister III, D.D.; Foulk, J.A.; Akin, D.E.; Annis, P.A. Cotton Fibers: Properties and Interaction with Flax Fibers in Blends: Focus on Rotor Spun Yarn. In Proceedings of the 26th International Cotton Conference Bremen, Faserinstitut, Bremen, Germany, 24–27 March 2002; pp. 207–211. [Google Scholar]
- Schenek, A. Naturfaser-Lexikon; Edition Textil; Dt. Fachverl.: Frankfurt am Main, Germany, 2001; ISBN 978-3-87150-638-3. [Google Scholar]
- Różańska, W.; Romanowska, B.; Rojewski, S. The Quantity and Quality of Flax and Hemp Fibers Obtained Using the Osmotic, Water-, and Dew-Retting Processes. Materials 2023, 16, 7436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.H.; Obendorf, S.K. Chemical and Biological Retting of Kenaf Fibers. Text. Res. J. 2006, 76, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jean, L.J.L. Process for the Chemical Retting of Lengths of Vegetable Textiles 1955. U.S. Patent US2725289A, 29 November 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, R.; Yu, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhao, J.; Shi, G.; Liu, J. Novel Scouring Method of Hemp Fibers Based on Electrochemical Techniques. Text. Res. J. 2021, 91, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Pickering, K.L. The Effect of Chelator and White Rot Fungi Treatments on Long Hemp Fibre-Reinforced Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2009, 69, 1265–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costard, H. Process for Treating Sclerenchyma Fibers, in Particular Flax 1995. World Patent WO1995001468A1, 21 June 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Koschek, K. Design of Natural Fiber Composites Utilizing Interfacial Crystallinity and Affinity. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2015, 69, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller-Hülstede, J.; Schäfer, H.; Schiffels, P.; Bottke, P.; Wark, M.; Koschek, K. Surface-Initiated Ring-Opening Polymerization of ɛ-Caprolactone as a Feasible Approach to Modify Flax Yarn. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2022, 152, 106714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.; Xu, B.; Cheng, L.; Feng, X.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, K.; Gao, M.; Liu, Z.; Liu, C.; Peng, Y. Bacterial Strain for Bast Fiber Crops Degumming and Its Bio-Degumming Technique. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 2503–2512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojtasik, W.; Majewska, K.; Dymińska, L.; Hanuza, J.; Zimniewska, M.; Preisner, M.; Szopa, J.; Wróbel-Kwiatkowska, M. Optimization of Hydrodynamic Degumming of Flax Fiber for Improved Biochemical Profile. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 206, 117621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, X.; Ma, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Ren, L. Microbial Community Structure of Anaerobic Biological Hemp Fiber Continuous Stream Degumming System. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 108057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.S.S. Enzymatic Degradation of Residual Non-Cellulosic Polysaccharides Present on Dew-Retted Flax Fibres. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1987, 26, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Feng, X.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, K.; Yi, L.; Duan, S.; Cheng, L. Improvement on Thermostability of Pectate Lyase and Its Potential Application to Ramie Degumming. Polymers 2022, 14, 2878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Duan, S.; Cheng, L.; Feng, X.; Zheng, K.; Liu, Z.; Gao, M.; Peng, Y. An Effective Degumming Technology for Ramie Fibers Based on Microbial Coculture Strategy. J. Nat. Fibers 2022, 19, 1555–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Zhou, C.; Dong, Z. Trend of Ramie Industry Development: A Review of Green Degumming and the Utilization of Processing Residues. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 384, 135487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Lin, H.; Gong, J.; Li, Z.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J. A New Method for Bio-Degumming in Less-Water Environment: Solid-State-Fermentation Progressive Bio-Degumming. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 183, 114986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Jiang, W.; Nie, K.; Zhang, Y.; Ben, H.; Han, G.; Ragauskas, A.J. An Alkali-Free Method to Manufacture Ramie Fiber. Text. Res. J. 2019, 89, 3653–3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutka, A.; Kukle, S.; Gravitis, J.; Berzins, A. Chemical and Physical Modification of Hemp Fibres by Steam Explosion Technology. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2013, 49, 012053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, A. Compounding and Mechanical Properties of Biodegradable Hemp Fibre Composites. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2003, 63, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, H.; Kloss, K.D. Ultrasonic Break down of Hemp. In Proceedings of the Symposium Bioresource Hemp, Frankfurt, Germany, 2–5 March 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Renouard, S.; Hano, C.; Doussot, J.; Blondeau, J.-P.; Lainé, E. Characterization of Ultrasonic Impact on Coir, Flax and Hemp Fibers. Mater. Lett. 2014, 129, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsa, J.; László, K.; Boguslavsky, L.; Takács, E.; Rácz, I.; Tóth, T.; Szabó, D. Effect of Mild Alkali/Ultrasound Treatment on Flax and Hemp Fibres: The Different Responses of the Two Substrates. Cellulose 2016, 23, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimniewska, M.; Zbrowski, A.; Konczewicz, W.; Majcher, A.; Przybylski, J.; Matecki, K.; Wiśniewski, M.; Kicińska-Jakubowska, A.; Mańkowski, J. Cottonisation of Decorticated Flax Fibres. Fibres Text. East. Eur. 2017, 25, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, M.; El Hage, R.; Sonnier, R.; Chrusciel, L.; Ziegler-Devin, I.; Brosse, N. Toward the Cottonization of Hemp Fibers by Steam Explosion. Flame-Retardant Fibers. Ind. Crops Prod. 2020, 151, 112242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouloc, P.; Allegret, S.; Arnaud, L. Hemp: Industrial Production and Uses; CABI: Wallingford, UK, 2013; ISBN 978-1-84593-792-8. [Google Scholar]
- Amaducci, S.; Gusovius, H.-J. Hemp—Cultivation, Extraction and Processing. In Industrial Applications of Natural Fibres; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2010; pp. 109–134. ISBN 978-0-470-66032-4. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).