Abstract
Flax fibers used for various applications are obtained from flax stems. Retting followed by drying and mechanical separation leads to the production of fibers. This review article discusses the application of electro-technologies in the production of bast fibers from the flax stem. In these technologies, flax stems harvested from the field are subjected to microwave assisted retting, followed by electro–osmotic dewatering which reduces the water content of the stems. Dewatered stems are transferred to a microwave chamber for further drying, thus retted stems are obtained for further processing.
1. Introduction
Natural agriculture fiber has been used all over the world since ancient times. In the past, plant fiber was used for making clothes, but now it has a wide range of applications from automotive to aerospace industries [1]. Plant fibers are used as a better replacement for synthetic fibers in a wide range of applications. The natural fibers are of different types, which are from plant and animal origin. Our topic of interest is plant fibers, especially fibers from plant stems like flax, hemp, etc. Studies show that replacement of synthetic fiber with natural agricultural fiber has increased in the field of biocomposites. Natural fibers are low in density, biodegradable and its value is dependent on the quality of the final product. However, the big disadvantage of natural fibers is that they do not have same consistency in quality as compared to synthetic fibers. This inconsistency is due to a variety of reasons such as climate, crop variety, retting process, and processing equipment used for fibers [2]. In natural fibers, climatic conditions play an important role in fiber production. Low temperature and high relative humidity during growing season contribute to fineness and length of fiber. Flax (Linum usitatissimum L.) is a plant, which is widely growing globally and is used in various food and industrial products. The seeds of hemp and flax are used in the food industry for making oil, cattle feed etc. The stem is used for the production of fiber, bio composites, high quality paper and many other industrial applications. Flax plant belongs to the family Linaceae. Flax seeds are primarily used in the food industry, while the plant stems are used in fiber production. The stem height of flax plants range from 0.20 m to 1.50 m [3]. Different crop varieties have different cellulose and non-cellulosic contents which are key factors for retting and fiber quality [4]. Flax and hemp fibers are biodegradable, sustainable, renewable, economical, and easily available in Western Canada. Bio fiber for the textile industry, production of bio-composite materials and the paper industry are produced from flax and hemp straw [5]. Retting is a very important factor for processing of fiber and ultimately fiber quality. The flax stems after retting process always contain high amount of water. The drying of retted stem is conducted by hot air drying [6]. The hot air drying method is very inefficient, since the major part of the energy will be wasted in forcing the air through the bale. Other disadvantage of hot air drying is lengthy drying time during the falling rate period. Retting and drying are the two important energy intensive processes, which determine the quality of the fiber. Therefore, those processes should be conducted with better precision for getting high quality fibers. This review paper discusses the application of electro-technologies in various steps in the processing of bast fiber from flax stem.
2. Structure of Natural Agricultural Fibers
The knowledge of physical and chemical structure of the plant is really important in the designing of processing of fibers using electro-technologies, because those are the factors affecting the quality of the final product. The structure of fiber is really complicated. A widely used natural fiber, flax has a non-uniform structure. It is semi cylindrical in shape where the fiber diameter becomes narrower towards the end. Flax fiber is a composite structure. Flax fibers, when placed in the bast (i.e., cortex) region of the stem, lie between the protective cuticle/epidermis barrier and the lignified core tissues. Pectin serves as a glue to hold fibers together in bundles and the bundles to non-fiber tissues [7]. Hemicelluloses, pectin, and lignin act like a matrix where as, cellulose acts like reinforcement to the matrix. This is the reason why it is difficult to separate a single fiber from a bundle. It always comes with 4–10 fibers sticking together in a bundle [8,9] and can be separated individually for different characterizations. Flax fiber consists of cellulose, hemicelluloses, and lignin in various proportions [10]. There are other compounds in flax fiber such as pectin, wax, minerals, and water-soluble compounds in addition to the main components. Cellulose, hemicellulose, lignin, pectin and ash components in various fibrous plants are shown in Table 1 [11]. Cellulose is the main component contributing strength to the fiber [12]. For composite production, fiber with high cellulose content gives more strength to the final product. The study also found that the tensile strength of retted hemp fiber was not less than that of un-retted fiber because its cellulose content is high after retting. For the same diameter of fiber, more force to apply for the separation of non-retted fiber bundles which made them weaker compared to retted fibers [10,13].

Table 1.
Chemical composition of selected natural fibers.
| Type of fiber | Cellulose (%) | Lignin (%) | Hemicellulose (%) | Pectin (%) | Ash (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fiber flax | 71 | 2.2 | 18.6– 20.6 | 2.3 | – |
| Seed flax | 43–47 | 21–23 | 24–26 | – | 5 |
| Kenaf | 31–57 | 15–19 | 21.5–23 | – | 2–5 |
| Jute | 45–71.5 | 12–26 | 13.6–21 | 0.2 | 0.5–2 |
| Hemp | 57–77 | 3.7–13 | 14–22.4 | 0.9 | 0.8 |
| Ramie | 68.6–91 | 0.6–0.7 | 5–16.7 | 1.9 | – |
3. Retting
The most important and energy intensive step in the processing of flax stem is retting, which is the separation or loosening of bast fibers from shive (lignocellulosic core tissues inside the flax stem) core and other non-fiber fractions, leading to a major problem in flax fiber processing [7,14]. Retting should be done very carefully; otherwise, the process will be ended up either under-retting or over-retting. Under-retted flax produces coarser low quality fibers with shive and cuticular fragments, and over-retting results in maximum destruction of cellulose that leads to excessive thinning of fiber [15]. Two conventional retting methods, namely water retting and dew retting have been used to extract fibers for textile and other commercial applications. The duration of these processes range from 1–2 weeks depending upon the variety of flax. Even though the quality of fiber by water retting is much higher than that of newer methods, this practice has been largely discontinued everywhere because of its high expense and the pollution and contamination arising from fermentation of the plant material. Enzyme assisted retting is a relatively new process which is considered to be a replacement for the conventional retting methods. Enzyme assisted retting is performed by introducing enzymes like pectinases to the plant stem surface which disintegrate pectin and hemicellulose which then separate fiber from the non-fiber tissues [16]. The duration of this process ranges from 8 hours to 24 h. Non-reusability of enzymes is a main concern, which affects the cost effectiveness of the process. Type of retting and duration and bacterial species used in retting are responsible for quality of bast fiber in terms of strength and fineness. The conventional field- or dew retting has several shortcomings and various uncontrollable factors, which can affect the final quality of the fiber, although the bulk of available linen has been treated in this way. There are several studies conducted for the retting of flax stems by using methods other than water retting like dew retting, steam explotion retting (violent boiling of water with stems into steam which initiates separation of fibers), enzyme retting, etc. [14,17,18]. ECCO Gleittechnik GmbH (Seeshaupt, Germany) has developed an ultrasound-retting process to separate the bast fibers from the rough plant straw, which are neither subjected to dew nor to water retting. The process separates the fibers from the woody components to a degree sufficient for technical and non-textile applications.
4. Role of Electromagnetic Energy in Retting of Flax Stem
The fibers are attached together as well as to the outer skin and bark by chemical bonds. Usual retting methods allow the degradation of pectin bonds and wax due to the action of micro organisms and enzymes. However, this process is lengthy and not economical as well. Retting could be done by establishing electromagnetic radiations on the stems for shorter duration. However, in the literature, it is seen that the energy of electromagnetic waves are way much less than that of the strong covalent bonds with which the fibers are attached. Microwave generator at 2450 MHz frequency produces 1 J/mol whereas the energy required to break a C-H bond is 413 KJ/mol [19]. Therefore, it is clearly stated that microwave energy is very much insufficient to break strong bonds, which binds the fibers close together to the stem. Nevertheless, at the same time, there are plenty of researchers proved the effect of microwave in chemical reactions like biomass processing; irradiation etc. and non-thermal effect of microwave played an important role in the reactions [20,21,22]. Studies are conducted on the effect of microwave in unfolding proteins. George et al., in 2008, compared the effects of microwave exposure, ambient heating and a combination of both on citrate synthase unfolding by measuring its binding to the chaperone a-crystalline. The results show with a high level of confidence that unfolding occurs at significantly lower temperatures whenever microwave heating is used. This supports the hypothesis that microwaves have a non-thermal effect on protein conformation that could take the form of a direct interaction of the electromagnetic field with the protein or its water of hydration [23]. When electromagnetic energy applied to any material, it generates heat energy volumetrically due to its nature of converting electromagnetic energy into mechanical energy. This generation of heat energy is due to dipole rotation. Sato in 2001, [24] conducted studies on microwave irradiation at constant temperature to define the existence of non-thermal effect of microwave, because there was a claim that the irradiation happened only due to temperature produced by microwave. During his experiments, no cell death was observed at 35 °C, whereas at 45, 47 and 50 °C, the death rates of Escherichia coli exposed to microwave irradiation were higher than those obtained in conventional heat sterilization at the same temperature. The microwaves either caused ions to accelerate and collide with other molecules or caused dipoles to rotate and line up rapidly with alternating (2450 million times/s) electric field resulting in a change in secondary and tertiary structure of proteins of microorganisms. The most commonly used electromagnetic energy for post harvest processing drying, pasteurization and extraction is microwave, so this review article is going to focus more on microwave as an energy source for retting of natural fiber plants. Banik et al., (2003), conducted studies on the bio effect of microwave irradiation and concluded that microwave effects were established at all the areas from microbial cells to animals and human system and they revealed that microwave could athermally induce different physiological effects [25]. The thermal effect of microwave is explained by Maxwell’s equation [26]. The dielectric properties of the materials are the main property parameters of the Maxwell’s equations, and therefore significantly influence the efficiency of electromagnetic (EM) energy coupled into the materials, EM field distribution, and conversion of EM energy into thermal energy within those materials. From engineering point of view, dielectric property is the most important property associated with microwave heating. The dielectric properties of a material are described by the complex relative permittivity (ε* relative to that of free space) in the following relationship:
ε* = ε′ − j ε′′
wherej= √ − 1
wherej= √ − 1
The real part ε’ is the dielectric constant that reflects the ability of the material to store electric energy when in an electromagnetic field; the imaginary part ε′′ is the dielectric loss factor that influences the conversion of electromagnetic energy into thermal energy. The ratio of the real and imaginary parts of permittivity represents another important parameter tangent of loss angle (tan δ = ε′/ε′′), which along with dielectric constant determines the attenuation of microwave power in heating. When the water soaked stem is subjected to electromagnetic heating, the thermal and non-thermal effects enhances the retting [19]. Fundamental knowledge of the structural and chemical characteristics of fibrous plants is important for designing a strategy using microwave to produce fibers with specific properties required for industrial applications. Calcium levels are especially high in the protective barrier of the flax stem and likely help stabilize pectins and thereby plant tissues in that location. The aim of applying microwave or any electromagnetic energy is to release the fibers from the plants by breaking these bonds, especially pectin bonds. First, we consider the non-thermal effect of microwave in retting of biofibers. Some researchers worked on the effect of microwave on the degradation of biomass, which explained the non-thermal effect of microwave in biomass treatment to denature the strong chemical bonds. Tsubaki and Azuma in 2011, conducted studies on microwave-assisted irradiation of biomass, especially on rice straw, bamboo and other fiber rich plants. According to their study, delignification was accelerated above 180 °C corresponding to release of hemicelluloses, supporting splitting of bonds between lignin and carbohydrates. However, glass transition temperature of lignin (130–200 °C) is usually lower than that of cellulose (230–250 °C) and close to hemicellulose (160–200 °C) under dry state. Glass transition temperatures of lignin and hemicelluloses unlike cellulose lowered with increase in moisture content. Therefore heating biomass in water close to the glass transition temperature of cellulose and extraction with solvents having various range of polarity is a strategy for refinery of biomass. This explained the role of soaking as a pre treatment before retting using electromagnetic energy. Water is used in microwave assisted retting, because water is a readily available and environment friendly solvent for microwave assisted treatment [27]. Non-thermal effects of microwave in breaking of composites are already proven and the same non-thermal effect can be used for the release of fiber from the plants by breaking the binding forces. Temperature of retting process should be kept to a minimum to avoid the damage of fiber due to high temperature [28]. However, for the pectin and hemicelluloses to breakdown to release the fiber, temperature and microwave both plays a role. So microwave energy along with a high temperature of 90–95 °C to 20 min is suitable for the retting method. High temperature of more than 120 °C and longer duration leads to bioconversion of biomass into energy [29]. Chemical compositions of fibers from plant stem origin (flax, hemp, ramie, etc.) show similarities that results in the structural similarities [30]. In this review, flax plant is taken as an example and the application of electro- technologies on the various steps of processing of flax plant is explained.
5. Microwave Assisted Retting Process of Flax
The microwave system for the retting process is shown in the Figure 1.
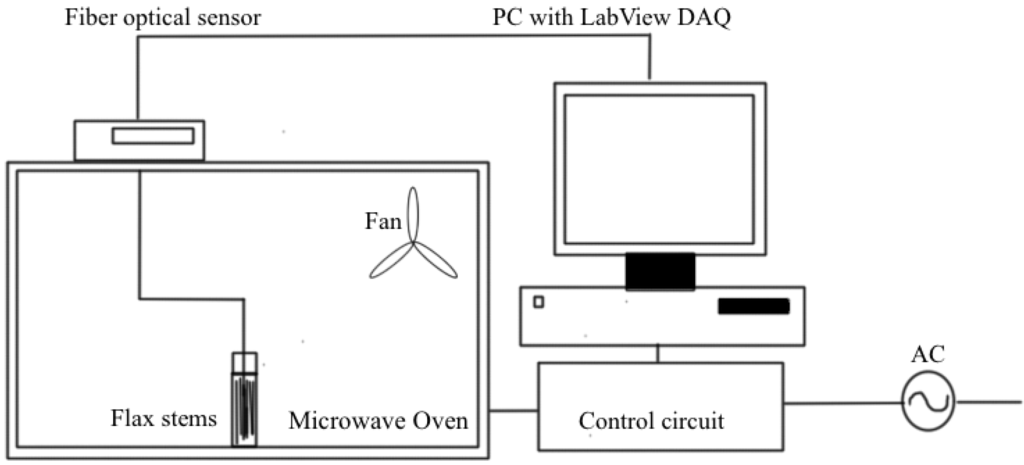
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of a microwave treatment system [28].
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of a microwave treatment system [28].
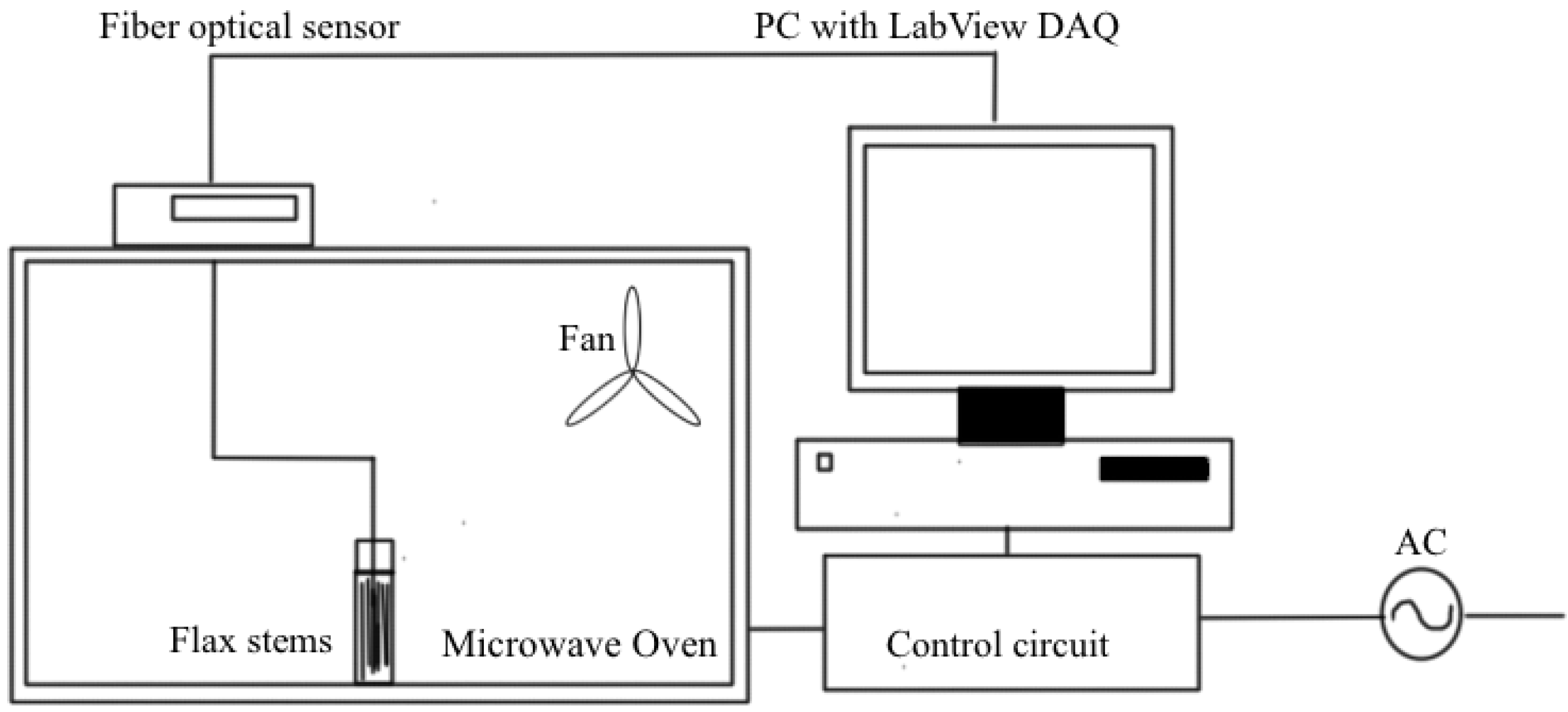
The flax stems were harvested using combine harvester and they were collected as bales and stored without doing any treatment and those are subjected to microwave-assisted retting process. The first step is to pre-treat the samples by soaking them in the water. The soaking time has to be varied from 12 to 24 h. This has to be optimized by conducting the lab tests. Glass transition temperatures of compounds are reduced due to soaking with water and hence at lower temperature, compounds decomposed, which helps the breaking of bonds that held those fiber bundles to the stem at lower temperatures [27]. The power of microwave is another main factor of concern while doing microwave assisted retting. The maximum temperature attained by the flax straw will be determined by the energy applied to the flax samples. The microwave power of 100 W is applied to the flax straw-water mixture of 50 g, which has the initial power of 2 W/g. The microwave treatment time should be less because; the pre-treatment with water itself initiates the process and microwave energy adding up the speed of decomposition of stronger covalent bonds. The treated flax stem samples were subjected to fried test, which is, the test to find out the retting efficiency [9]. 4 flax stems were taken in a test tube, and 8 ml of boiled water added into it. Then the closed test tube is vortexed for 10 s. After that, the test tube is shaken hard vertically four times. Then, the test tube is opened and retting efficiency is checked. Retting efficiency is measured on a scale of 0–3. After fried test, if no fiber peeled off from the stem, the Fried test value is 0, at the same time if all the fiber peels off, the reading is 3.
6. Electro-Osmotic Dewatering of Retted Flax Stem
The microwave assisted retting is done and the resultant stem is of high moisture content. For further processing of fiber, the stems are to be dried completely. The drying of the retted straws is an important step in the extraction of fibers. This is usually a lengthy process if done by air-drying, and requires much energy for controlled heat drying since the quality of the fibers must be maintained. The energy required for pressing-induced dewatering is many times smaller than that required for heat induced water removal. For example, only 7 kJ/kg is needed to expel water at an average pressure of 7 kPa versus roughly 2320 kJ/kg for heat-induced water removal [31]. A two-step process is proposed. The first step is to dewater the retted straw using a method based on electro-osmosis [32,33]. Electro-osmotic dewatering removed the bulk of free water from the kelp in a rapid and energy efficient manner. This procedure will be used for the design of a novel electro-osmotic dewatering system for the retted straws and fibers. The study is to design a lab scale electro-osmotic dewatering system for the initial dewatering of the flax stem followed by microwave drying for shorter duration to reduce the moisture content of the flax stems to a final dried product.
6.1. Design of Electro-Osmotic Dewatering Apparatus
The mechanism of electro-osmotic dewatering is as shown in the figure (Figure 2) below:
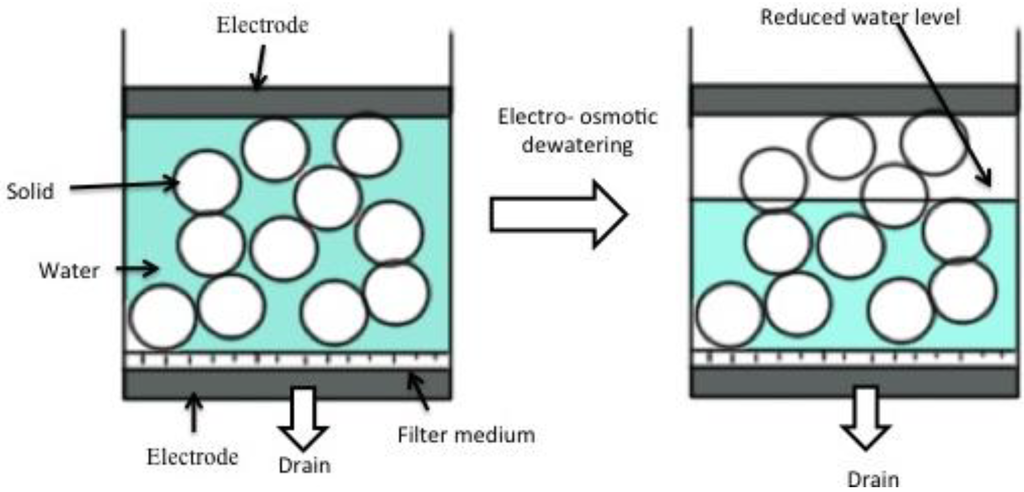
Figure 2.
Process of dewatering by electro osmosis dehydration [34].
Figure 2.
Process of dewatering by electro osmosis dehydration [34].
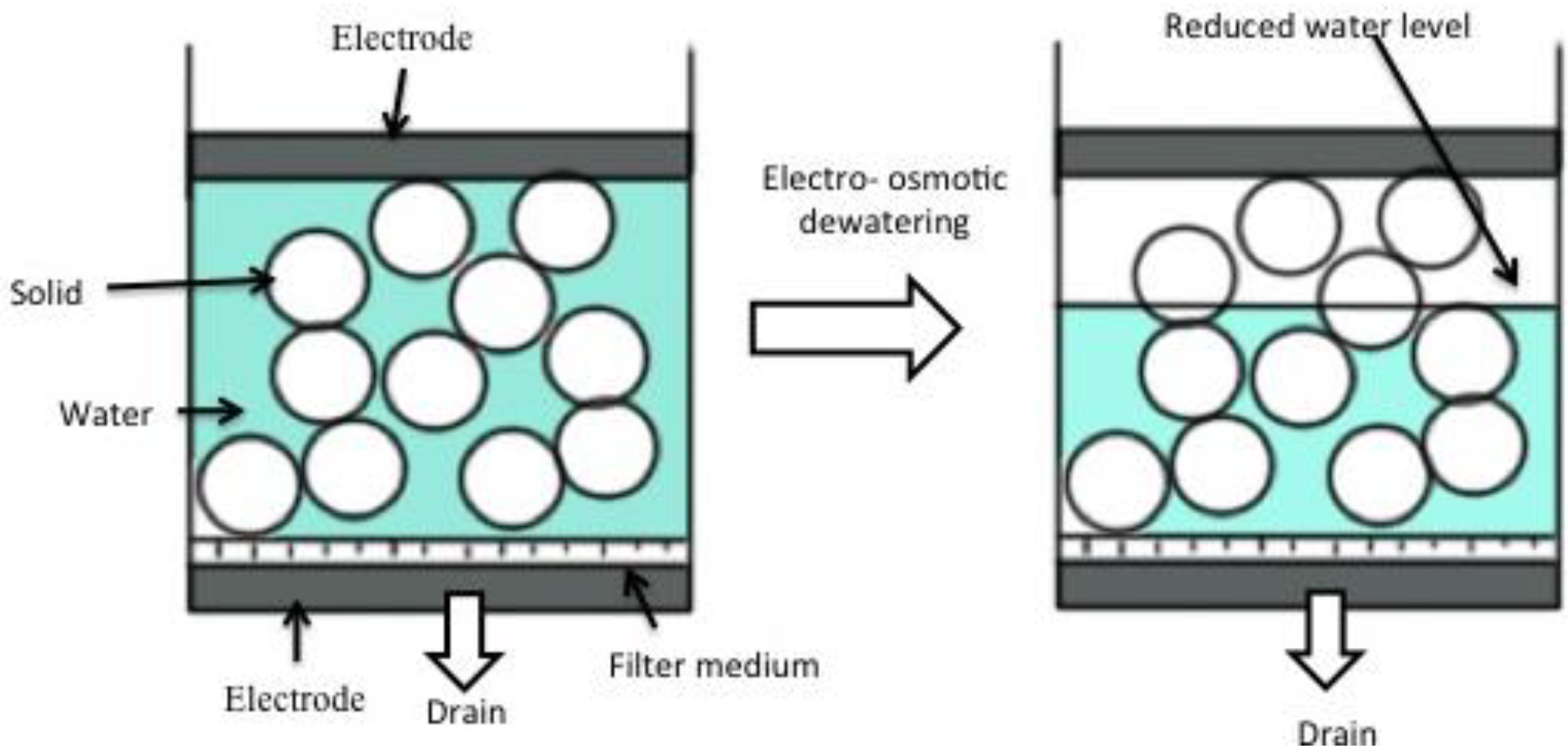
Electro-osmotic dewatering (EOD) is performed by applying an external electric field under direct current (DC) condition to a semisolid material placed between two electrodes. In the process of EOD for a bed of semisolid material of which the initial water content is uniform throughout the bed, as shown in Figure 2, EOD proceeds downwards and the water content in part of the material near the upper electrode opposite to the drainage surface is locally reduced, resulting in an increase of electrical contact resistance between the upper electrode and the material being dewatered [35,36,37,38]. Most separation technologies are based on a single driving force, such as: molecular size for membrane filtration; density of particles for gravitational separation; ionic mobility of colloidal particles for electrophoresis; and pressure diffusion for centrifugation. An improved approach to separation is to exploit two or more driving forces in a single step to increase dewatering efficiency [32,39]. For applying EOD practically to various kinds of materials, it is important essentially to increase the dewatering rate, and to decrease the final water content and the electric power consumption for water removal to a maximum level [40]. From these points of view, various applications of electric field, which are different from continuous DC condition, have been attempted to improve the performance of EOD. In order to reduce the negative effect for dewatering, which is characteristic of EOD, such as the increase of electrical contact resistance, many investigations have been carried out for better and higher performance of EOD. The mechanism of EOD is different from that of such widely used dewatering processes as mechanical methods using fluid pressure, compressive and centrifugal forces. EOD has some advantages compared with mechanical dewatering methods, and it can be more effective for solid–liquid mixtures consisting of colloidal particles and gelatinous and biological materials that are not successfully dewatered by mechanical methods. In this context, we have to discuss the main factors to be considered for the design of electro–osmotic dewatering system for flax.
The main factors are:
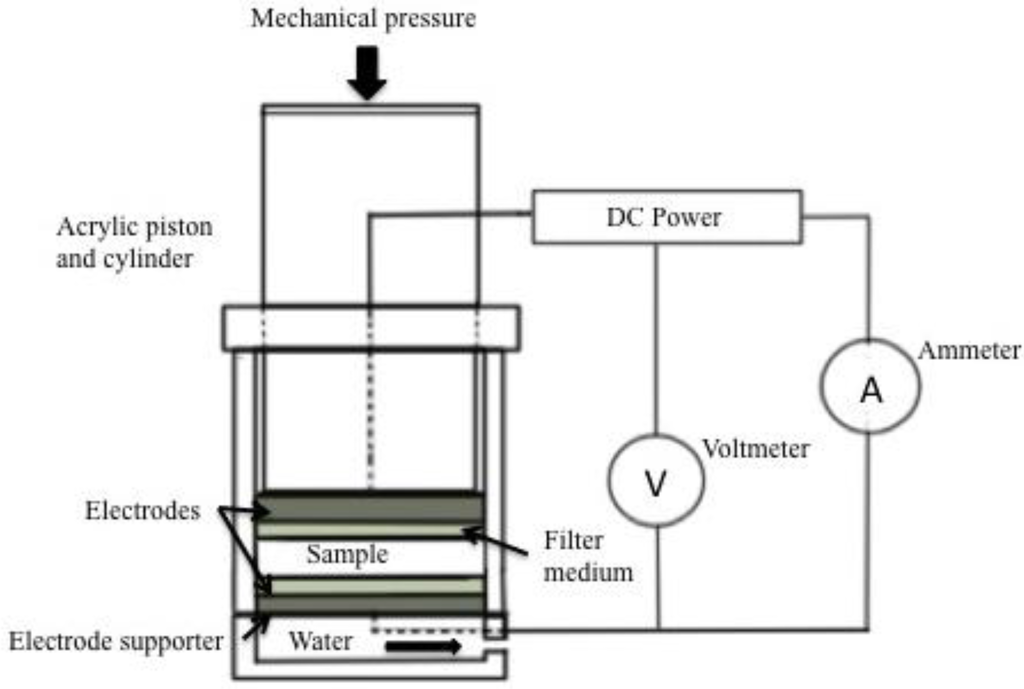
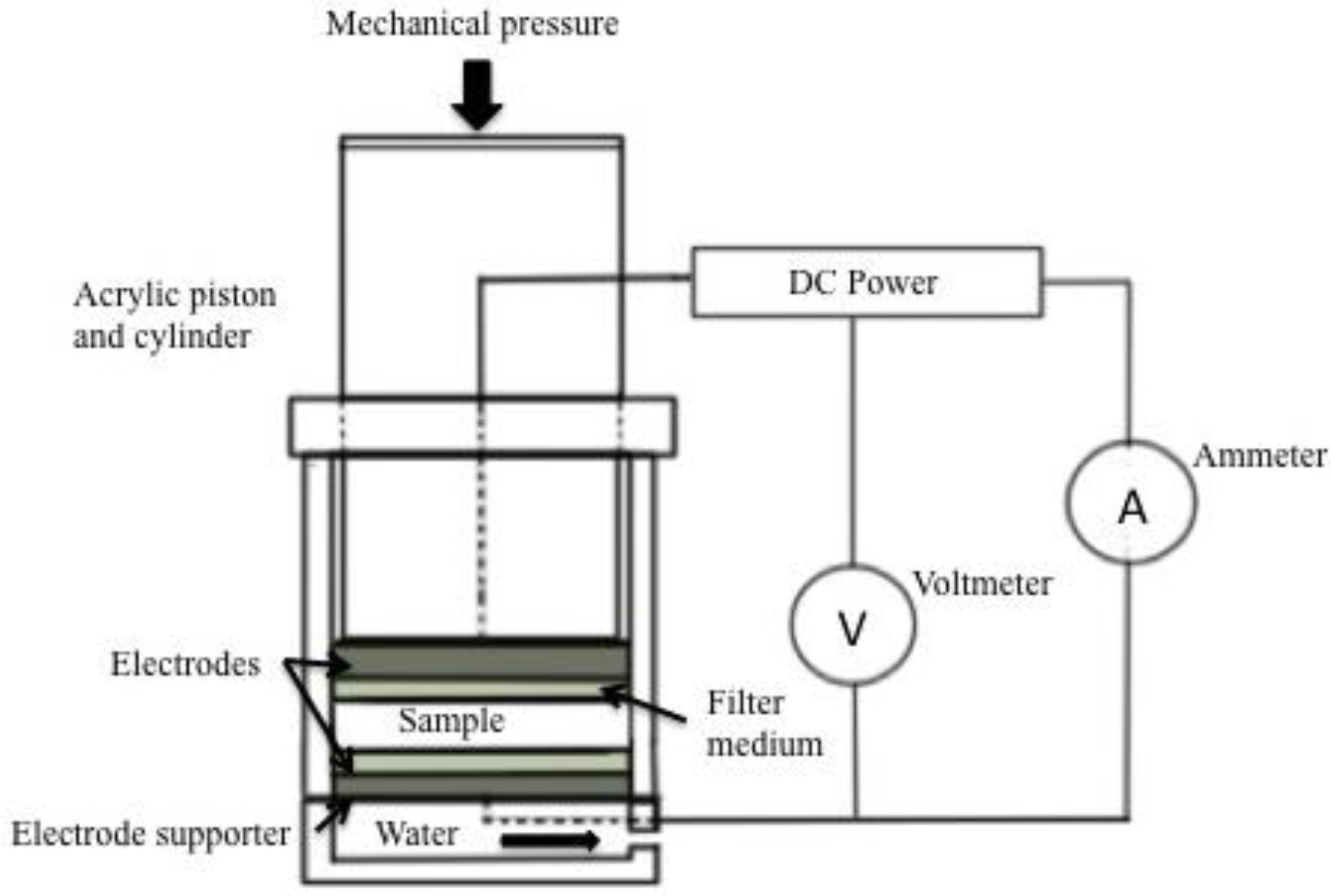
- The quantity of flax to be dewatered.
- Zeta potential of the flax-water mixture (The electric potential between the solid and liquid components, which is a function of the geometry, the pH, and the ion concentration of the substance)
- The pressure applied (combination of pressure and electro-osmosis is proved to be more economical than electro-osmosis alone [34].
- Type of membrane used.

Figure 3.
Pressurized electro-osmotic dewatering.
Figure 3.
Pressurized electro-osmotic dewatering.

For the design of electro osmotic dewatering of flax, treatment time is one of the most important factors to be considered and it is to be derived in terms of initial and final solid concentrations [41]. In an electro-osmotic cell, the volume of the sample in the cell V, is expressed as the product of cross sectional area of the cell and the thickness of the sample:
where A is the cross sectional are of the sample and L is the thickness of the sample.
The density of the sample is expressed as,
where ρs is the density of the sample, M is the total mass of the sludge in the cell and V is the volume of the sludge in the cell.
V = A L
ρs = M/V
Substituting Equation 2 into Equation 3, the total mass of the sample is,
Before the treatment, solid concentration of the samples is
Where SD1 is the initial solid concentration of the sample and ms is the mass of the dry sample. After the electro osmotic dewatering, the solid concentration is,
where SD2 is the final solid concentration of the sample and Vol is the volume of water collected to reduce the solid concentration from SD1 to SD2.
M = ρs AL
SD1 = ms/M
SD2 = ms/(M − Vol)
Substituting Equation 5 into 6, therefore,
To obtain the treatment time, consider the current is constant, then the voltage from the power supply has to increase. In this case, the variation in the voltage is a function of time whereas the potential difference across RD (VD) is kept constant as (Figure 4).
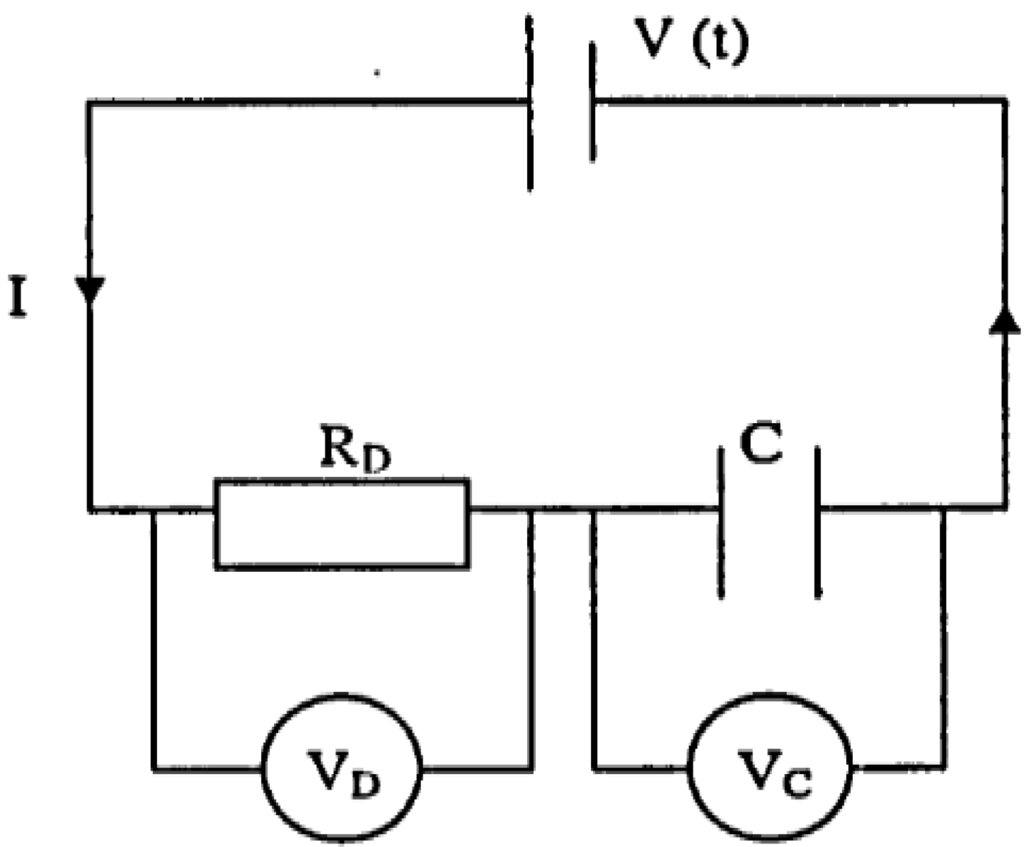
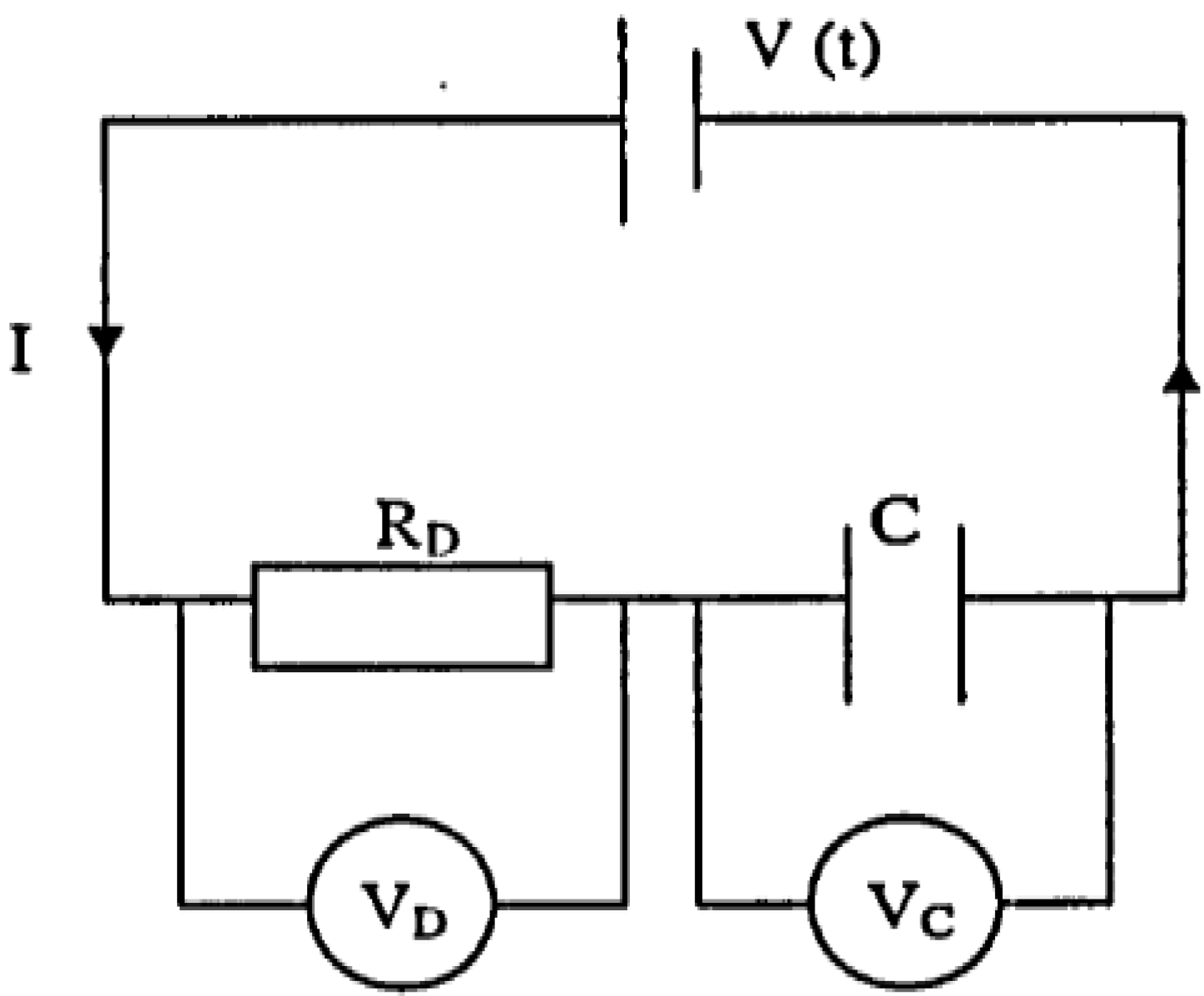 When the power supply switched on, the initial voltage V0 is independent of the capacitor C. Thus,
At any instant, the voltage from the power supply, Vt is the sum of the voltage across RD (VD)
and the voltage across across C (Vc). Thus,
When the power supply switched on, the initial voltage V0 is independent of the capacitor C. Thus,
At any instant, the voltage from the power supply, Vt is the sum of the voltage across RD (VD)
and the voltage across across C (Vc). Thus,
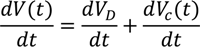 During the electro osmotic dewatering process, the voltage across C (VC) varies with time and VD is a constant. Thus,
During the electro osmotic dewatering process, the voltage across C (VC) varies with time and VD is a constant. Thus,
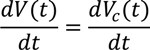 Therefore the change of voltage from the power supply per unit time is equal to the change of voltage across C (VC) per unit time. Cumulative volume of water collected by electro osmosis is
Therefore the change of voltage from the power supply per unit time is equal to the change of voltage across C (VC) per unit time. Cumulative volume of water collected by electro osmosis is
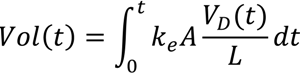 Substituting equation 8 in 13, the cumulative volume of collected water is,
Substituting equation 8 in 13, the cumulative volume of collected water is,
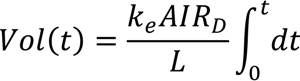
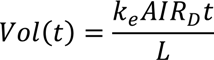 From the Equation.15, the time of the dewatering can be expressed in terms of solid concentration. By substituting Equation 15 into 7, the required treatment time to obtain desired solid concentration from SD1 to SD2 is
From the Equation.15, the time of the dewatering can be expressed in terms of solid concentration. By substituting Equation 15 into 7, the required treatment time to obtain desired solid concentration from SD1 to SD2 is
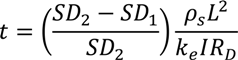 By rewriting the equation 16, the final solid concentration after a particular treatment time is
By rewriting the equation 16, the final solid concentration after a particular treatment time is
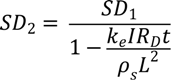 From the above equation, it can be seen that increasing the treatment time increases the final solid concentration, which is expected [42].
From the above equation, it can be seen that increasing the treatment time increases the final solid concentration, which is expected [42].
SD2 = M × SD1/(M − Vol)
Vol = (SD2−SD1)M/SD2
Vol = (SD2−SD1)M/SD2

Figure 4.
Electro osmotic dewatering at constant current.
Figure 4.
Electro osmotic dewatering at constant current.

VD = IRD
V0 = IRD
Vt = VD + Vc
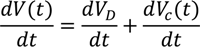
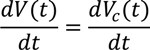
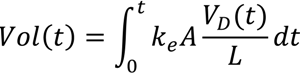
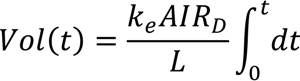
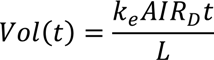
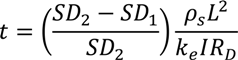
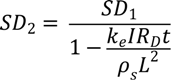
6.2. Design Parameters for Dewatering of Flax
6.2.1. Sample Thickness
From Equation 16, it is clearly seen that treatment time is directly proportional to square of the sample thickness.
t α L2
6.2.2. Applied Current
From Equation 16, the treatment time is inversely proportional to the current [43].
t α 1/I
6.2.3. Power Supply
The resistance of dewatering system is minimum when the dewatering starts (R0 = V0/I). During the dewatering process, the voltage from the power supply needs to be increased with the time of treatment in order to maintain the constant current as resistance increases with time due to electro chemical reaction and desiccation at the anode.
6.2.4. Pressure
When pressure is applied to the highly watered flax sample, the stress is carried by water in the void spaces as well as in the samples. The increase in pressure causes the void space water to drain off. However, from equation 14, the electro osmotic flow is independent of pressure [44]. In practice, the electro osmotic dewatering process can be enhanced by the application of pressure produces a significant overall improvement of volume of water obtained.
6.2.5. Type of Electrodes
The main criterion in the selection of electrodes is that they must be sufficiently electrically conductive. Besides that, the rate of electrochemical reaction taking place at the electrodes has also to be considered in the selection of electrode material. This is because the surface electrical resistivity of the electrode increases when electrochemical reaction occurs and high surface electrical resistivity results in a shorter time over which constant current could be maintained. Therefore, an electrode material with a low rate of electrochemical reaction should be selected in the electro osmotic dewatering process as this not only provides a longer time over which constant current could be maintained, but also saves electrical energy due to high surface resistance [45]. Dewatering could be conducted to reduce the moisture content to a minimum level. The flax stems are not fully dried after electro-osmotic dewatering. Therefore, the dewatered flax stem has to be subjected to microwave drying at controlled temperature for drying it completely.
6.2.6. Microwave-Drying of Flax Straw
Nair et al., in 2012, conducted studies on microwave drying of high moisture flax stems to final moisture content of 9% wet basis and compared the results with hot air drying. Flax straw was cut into 0.15 m lengths. The middle part of the plant stem was chosen for the experiment to ensure uniformity in carrying out drying tests. Flax straw samples (25 g) were placed in a jar full of water for 48 hours at room temperature to ensure fully wet conditions. The wetted samples (68–70% w.b.) had their surface water removed using a manually operated centrifugal rotator (salad spinner). The samples were then weighed, and transferred to the microwave apparatus. The microwave drying was done at a temperature of 40 °C, 60 °C or 80 °C. The drying was conducted in an intermittent microwave supply system. The temperature of the drying was almost constant throughout the experiment. The apparatus was adjusted in such a way that, it switched off the microwave generator automatically when the temperature increased beyond the set point and microwave power switched on when the temperature of the product decreased below the set point. The maximum variation was ±3 °C [28]. The drying was conducted till it reached the final moisture content of 9% (wet basis). Three replicates of each test were done. Flax straw with same initial moisture content were dried by using hot air of 40 °C, 60 °C or 80 °C and the results were compared. At the drying temperatures of 40 °C, 60 °C and 80°C microwave convective drying took 30.8%, 54.8% and 48.5% less time, respectively, than hot air drying. Among the microwave-convective drying conditions tested, drying at 80 °C method proved to be the most suitable in terms of drying time. Color change and tensile strength were compared and there was no significant difference in the color change and tensile strength between microwave and hot air dried flax stem samples. Dried flax stem is suitable for the final step of fiber separation, mostly by passed through a mechanical separator to separate fiber and shives. The application of electro-technologies assures the quality and uniformity of the final product, which has to be used from superior products.
7. Conclusions
The role of electro-technologies in the processing of fibrous plants from retting till the final step of fiber production is discussed. Microwave and radio frequency are the possible electro-magnetic energies to be used for the fibrous plant retting. The non-thermal effect of microwave makes the process of retting less energy intensive and less time consuming when compared to other retting methods like water retting, enzyme retting, etc. Electro-magnetic energy accelerates the process of release of cellulose by removing binder materials like pectin, lignin wax, etc. [45]. Electro-osmosis is a quick method for dewatering of high moisture fibrous plant after retting. Electro-osmosis followed by microwave drying is also a post retting process, which saves a large amount of energy when compared to time taking hot air drying. The uniformity of drying and quickness of the process are assured in the above process.
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to NSERC (Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada) and FQRNT (Fonds québécois de la recherche sur la nature et les technologies) for their financial support for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Akin, D.E.; Gamble, G.R.; Morrison, W.H., III; Rigsby, L.L.; Dodd, R.B. Chemical and structural analysis of fiber and core tissues from flax. J. Sci. Food Agric. 1996, 72, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, A.B.; Thygesen, A.; Bohnc, V.; Vad Nielsen, K.; Pallesen, B.; Jørgensen, M.S. Effects of chemical–physical pre-treatment processes on hemp fibers for reinforcement of composites and for textiles. Ind. Crops Prod. 2006, 24, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegi, G. Illustrierte Flora Von Mitteleuropa; Lehmanns Verlag: Munich, Germany, 1925; Volume 5, pp. 3–38. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, H.S.S. Chemical retting of flax using chelating compounds. Ann. Appl. Biol. 1988, 113, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atton, M. Flax Culture from Flower to Fabric; The Ginger Press: Owen Sound, ON, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, G.R.; Li, Z.; Gariepy, Y.; Raghavan, G.S.V. Microwave drying of corn (Zea mays L. ssp.) for the seed industry. Dry. Technol. 2011, 29, 1291–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Sumere, C.F. Retting of Flax with Special Reference to Enzyme Retting. In The Biology and Processing of Flax; Sharma, H.S.S., Van Sumere, C.F., Eds.; M Publications: Belfast, Northern Ireland, 1992; pp. 157–198. [Google Scholar]
- Baley, C. Analysis of the flax fibres tensile behaviour and analysis of the tensile stiffness increase. Composites A 2002, 33, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.E.; Henriksson, G.; Evans, J.D.; Adamsen, A.P.S.; Foulk, J.A.; Dodd, R.B. Progress in enzyme-retting of flax. J. Nat. Fibers 2004, 1, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygsen, L.G.; Bilde-Dorensen, J.B.; Hoffmeyer, P. Visualization of dislocations in hemp fibers—A comparison between scanning electron microscopy and polarized light microscopy. Ind. Crops Prod. 2006, 24, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Hinrichsen, G. Biofibers, biodegradable polymers and biocomposites: An overview. Macromol. Mater. Eng 2000, 276–277, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, D.E.; Morrison, H., III; Rigsby, L.L.; Evans, J.D.; Foulk, J.A. Influence of water pre-soak on enzyme-retting of flax. Ind. Crops Prod. 2003, 17, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag, S.; Loha, V.; Prokop, A.; Tanner, R. The effect of fermentation (retting) time and harvest time on kudzu (Pueraria lobata) fiber strength. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 1996, 57–58, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foulk, J.A.; Akin, D.E.; Dodd, R.B. Processing techniques for improving enzyme-retting of flax. Ind. Crops Prod. 2001, 13, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallesen, B.E. The quality of combine-harvested fiber flax for industrials purposes depends on the degree of retting. Ind. Crops Prod. 1996, 5, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamsen, A.P.S.; Akin, D.E.; Rigsby, L.L. Chemical retting of flax straw under alkaline conditions. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adamsen, A.P.S.; Akin, D.E.; Rigsby, L.L. Chelating agents and enzyme retting of flax. Text. Res. J. 2002, 72, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, R.W.; Becker, U.; Kohler, R.; Goth, B. Steam explosion of flax—A superior technique for upgrading fiber value. Biomass Bioenergy 1998, 14, 237–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuchter, M.; Ondruschka, B.; Bonrath, W.; Gum, A. Microwave assisted synthesis—A critical technology overview. Green Chem. 2004, 6, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galema, S.A. Microwave Chemistry. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1997, 26, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridar, V. Microwave radiation as a catalyst for chemical reactions. Curr. Sci. 1998, 74, 446–450. [Google Scholar]
- Steel, B.C.; Bilek, M.M.; McKenzie, D.R.; dos Remedios, C.G. A technique for micro second heating and cooling of a thin biological sample. Eur. Biophys. J. 2002, 31, 378–382. [Google Scholar]
- George, D.F.; Bilek, M.M.; McKenzie, D.R. Non-thermal effects in the microwave induced unfolding of proteins observed by chaperone binding. Bioelectromagnetics 2008, 29, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, J. Observation of the Coronal Hard X-ray Sources. Astrophys. J. 2001, 558, L137–L140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banik, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Ganguly, S. Bioeffects of microwave—A brief review. Bioresour. Technol. 2003, 87, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, M.E.C.; Franca, A.S. Microwave heating of foodstuff. J. Food Eng. 2002, 53, 347–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubaki, S.; Azuma, J. Application of Microwave Technology for Utilization of Recalcitrant Biomass. In Advances in Induction and Microwave Heating of Mineral and Organic Materials; InTech: Kyoto University, Japan, 2011; ISBN: 978-953-307-522-8. [Google Scholar]
- Nair, G.R.; Liplap, P.; Gariepy, Y.; Raghavan, G.S.V. Microwave drying of flax fiber at controlled temperature. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. 2011, 1, 1103–1115. [Google Scholar]
- Budarin, V.L.; Clark, J.H.; Lanigan, B.A.; Shuttleworth, P.; Macquarrie, D.J. Microwave assisted decomposition of cellulose: A new thermochemical route for biomass exploitation. Bioresour. Technol. 2010, 101, 3776–3779. [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty, A.K.; Misra, M.; Drzal, L.T. Surface modifications of natural fibers and performance of resulting biocomposite. Compos. Interface 2001, 8, 313–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartzbcrg, H.G.; Roseneau, J.R.; Richardson, G. The Removal of Water by Expression. In Water Removal Processes: Drying and Concentration of Food and Other Materials; AlCHE Symposium Series; King, C.J., Clark, J.P., Eds.; American Institute of Chemical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1977; Volume 73. [Google Scholar]
- Lightfoot, D.G.; Raghavan, G.S.V. Combined fields dewatering of seaweed (Nereocystis luetkeana). Trans. ASABE 1994, 37, 899–906. [Google Scholar]
- Orsat, V.; Raghavan, G.S.V.; Sotorinal, S.; Lightfoot, D.G.; Gopalakrishnan, S. Roller press for electro- osmotic dewatering of biomaterials. Dry. Technol. 1999, 17, 523–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujumdar, A.S.; Yoshida, H. Electro-Osmotic Dewatering (EOD) of Bio-Materials. In Electro-Technologies for Extraction from Food Plants and Biomaterials; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; pp. 121–154. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H. Practical aspects of dewatering enhanced by electro-osmosis. Dry. Technol. 1993, 11, 787–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.; Yukawa, H. A theoretical analysis of the electroosmotic dewatering of sludge. Inter. Chem. Eng. 1988, 28, 477–485. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Yukawa, H. Analysis of dewatering processes enhanced by electro-osmosis. Fluid/Part. Sep. J. 1991, 4, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida, H.; Yukawa, H. Analysis of Electro-Osmotically Enhanced Sludge Dewatering. In Advances in Drying; Mujumdar, A.S., Ed.; Hemisphere: Bristol, UK, 1992; Volume 5, pp. 301–323. [Google Scholar]
- Lockhart, N.C. Combined field dewatering: Bridging the science-industry gap. Dry. Technol. 1992, 10, 839–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampacek, C. Electro-Osmotic and Electro-Phoretic Dewatering as Applied to Solid Liquid Separation. In Solid-Liquid Separation: A Review and a Bibliography; Poole, J.B., Doyle, D., Eds.; Her Majesty’s Stationery Office: London, UK, 1966; pp. 100–108. [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell, J.K. Conducting Phenomena: From theory to geotechnical practice. Geotechnique 1991, 41, 299–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, C.K. Design and Modelling of Electroosmotic Dewatering. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Newcastle upon Tyne, England, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Grundl, T.; Michalski, P. Electro-osmotically driven water flow in sediments. Water Res. 1996, 30, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijh, A.K.; Novak, J.P. A new theoretical approach to electro-osmotic dewatering based on non-equilibrium thermodynamics. Dry. Technol. 1997, 15, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keshwani, D.; Cheng, J.J. Switchgrass for bioethanol and other value-added applications: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2013 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
