Development of Belt-Type Microstructure Array Flexible Mold and Asymmetric Hot Roller Embossing Process Technology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
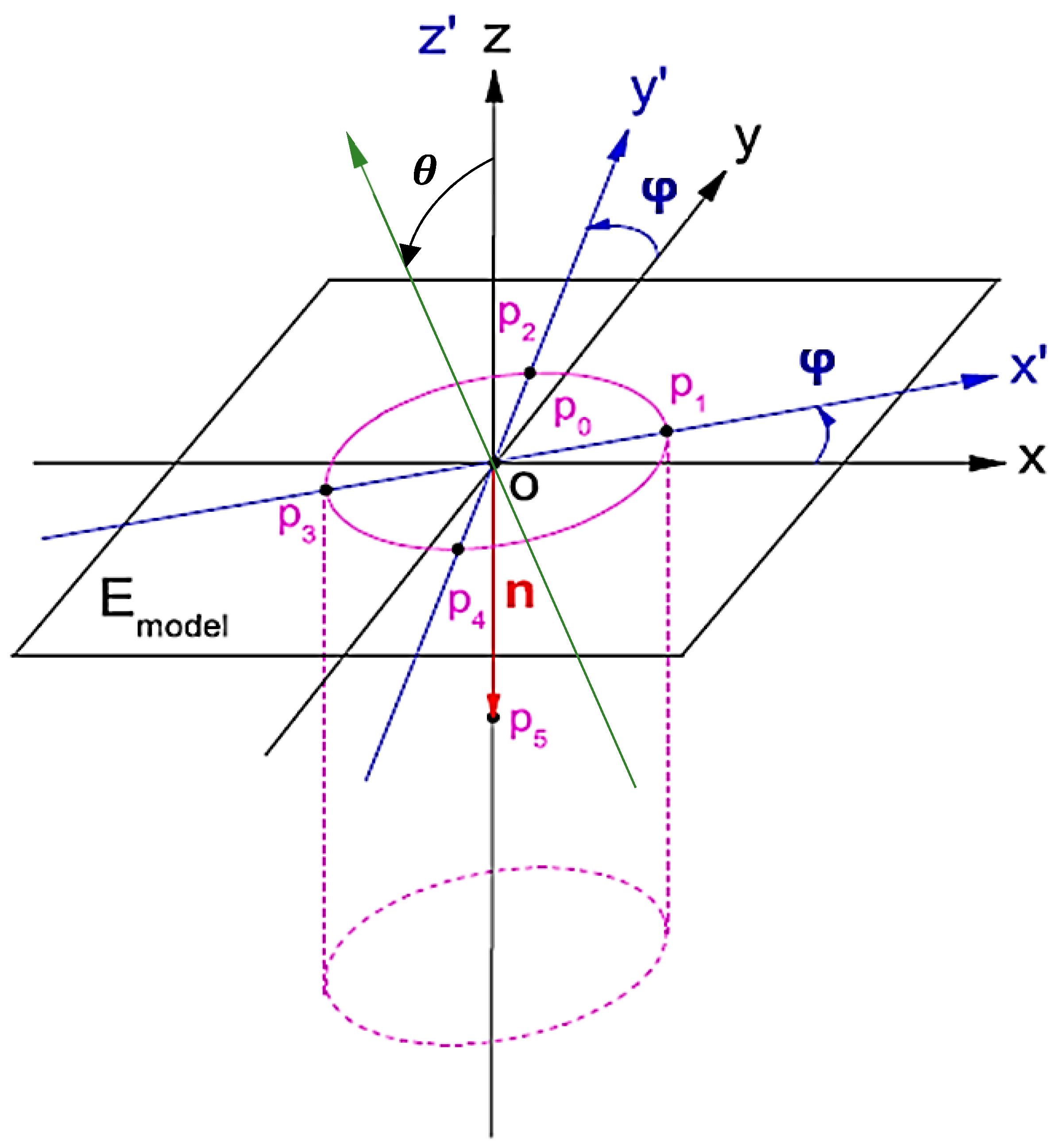
2. Asymmetric Principle for Roller Embossing System
2.1. Expressions Related to the Tip (Microstructure) Imprinting on the Substrate
2.1.1. General Expressions
2.1.2. Case One: Cylinder-Shape Tip
2.1.3. Case Two: Sphere-Shape Tip
2.2. Intersections of Model and Pattern
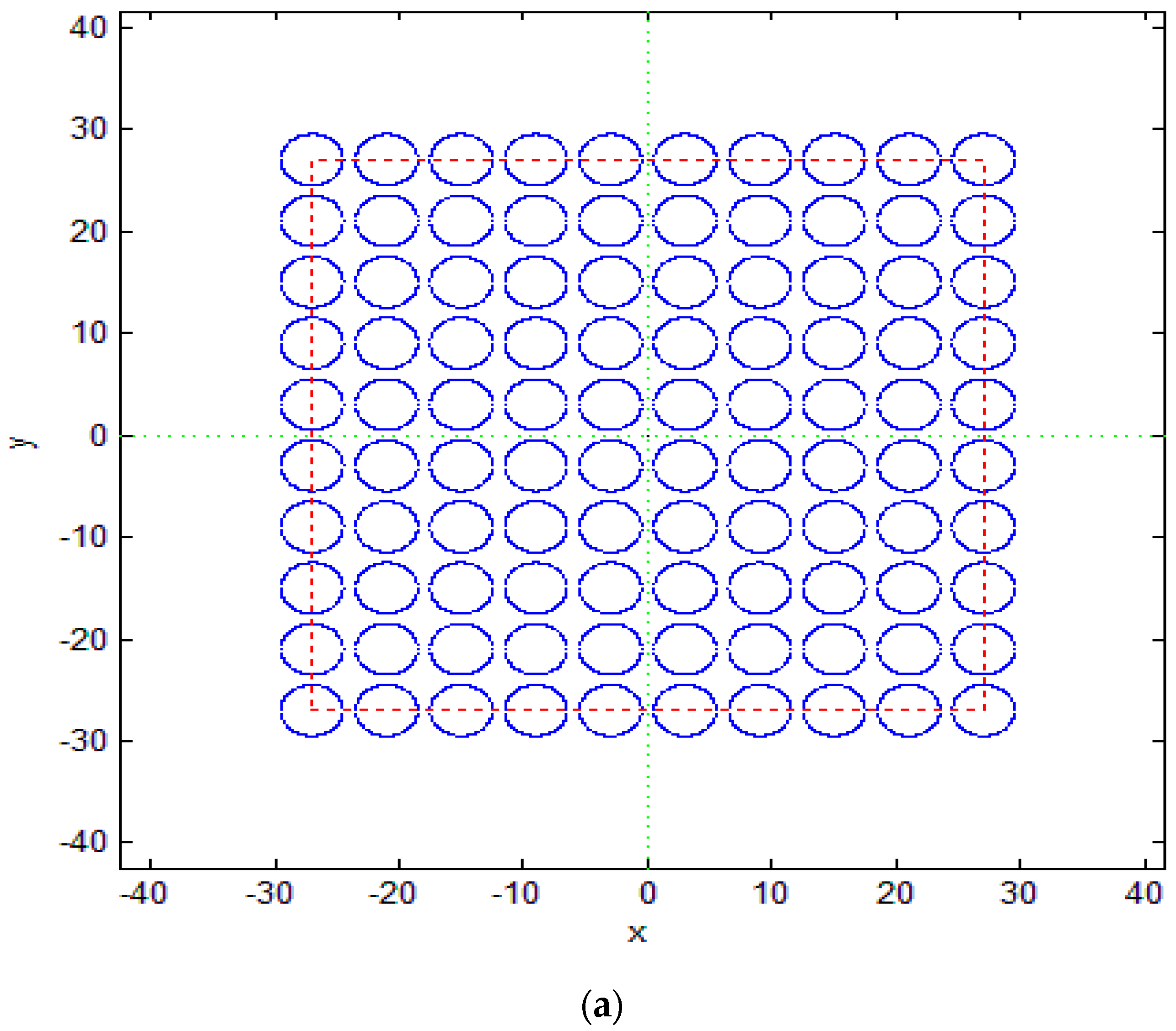
2.3. Circular Column Arrays
3. Experimental
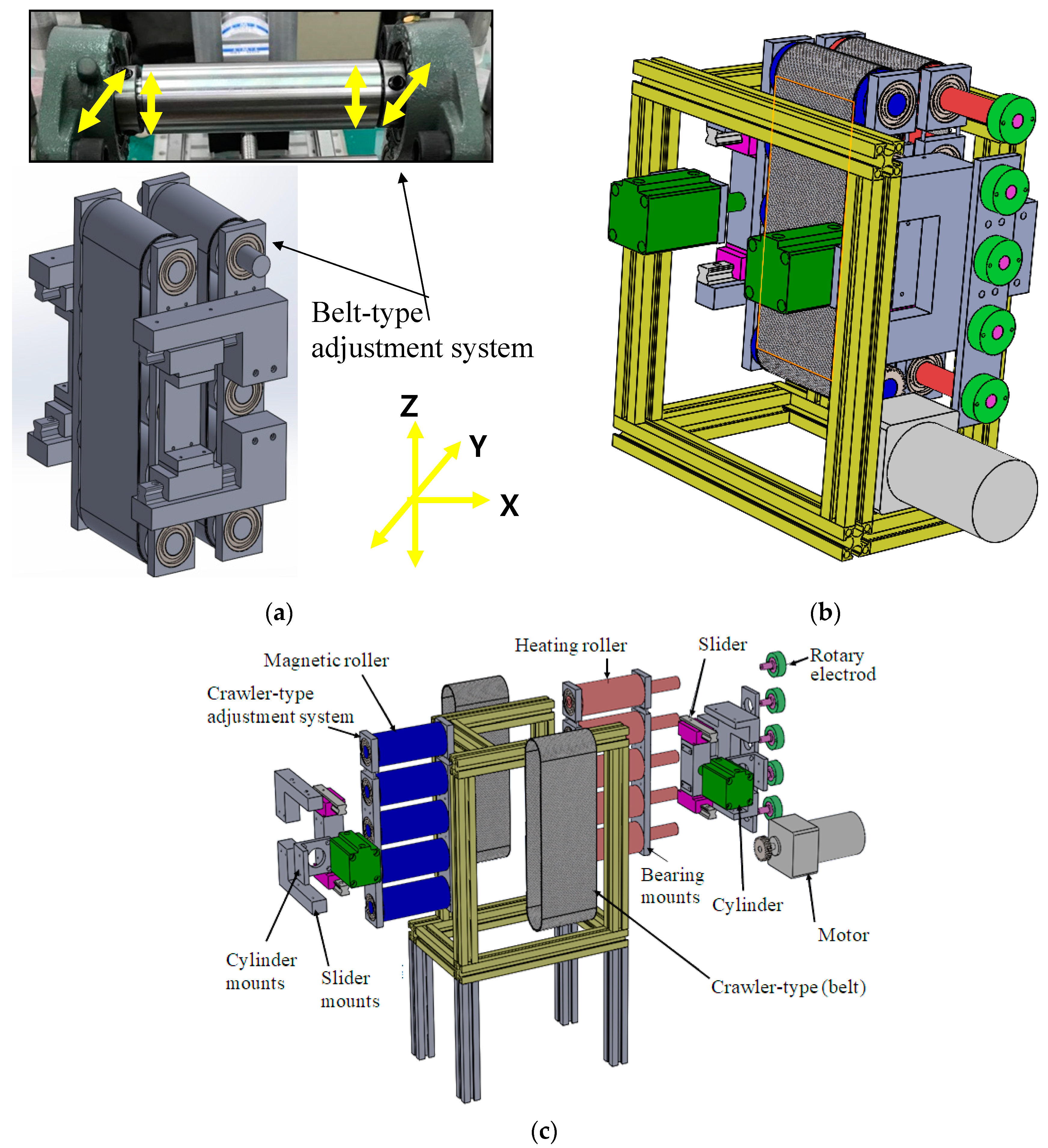
3.1. Belt-Type Microstructure Array Hot roller Embossing System
3.1.1. Design and Manufacturing of Belt-type Hot Roller Embossing Process System
3.1.2. Establishment of Belt-type Microstructure Array Hot roller Embossing Process Technology
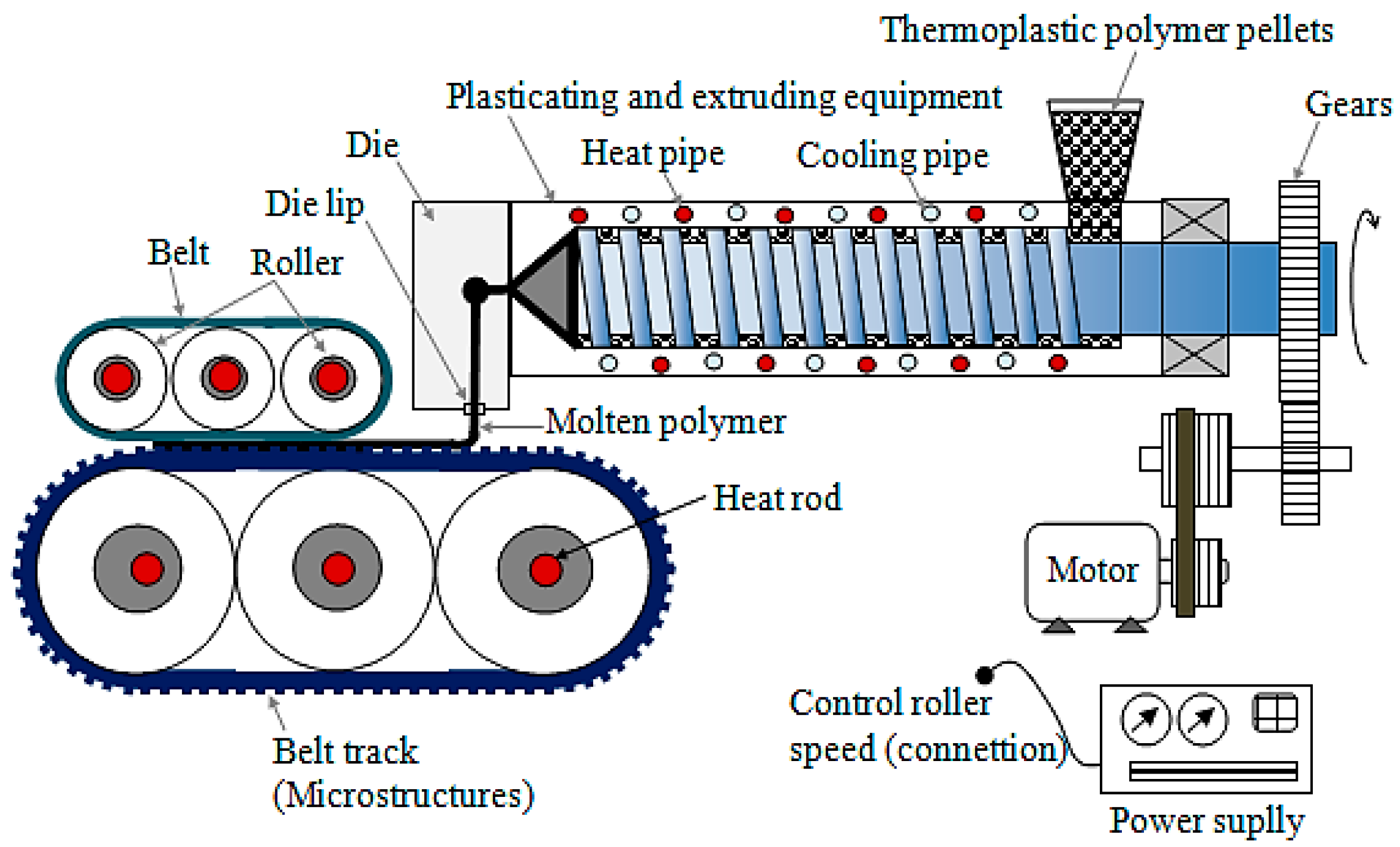
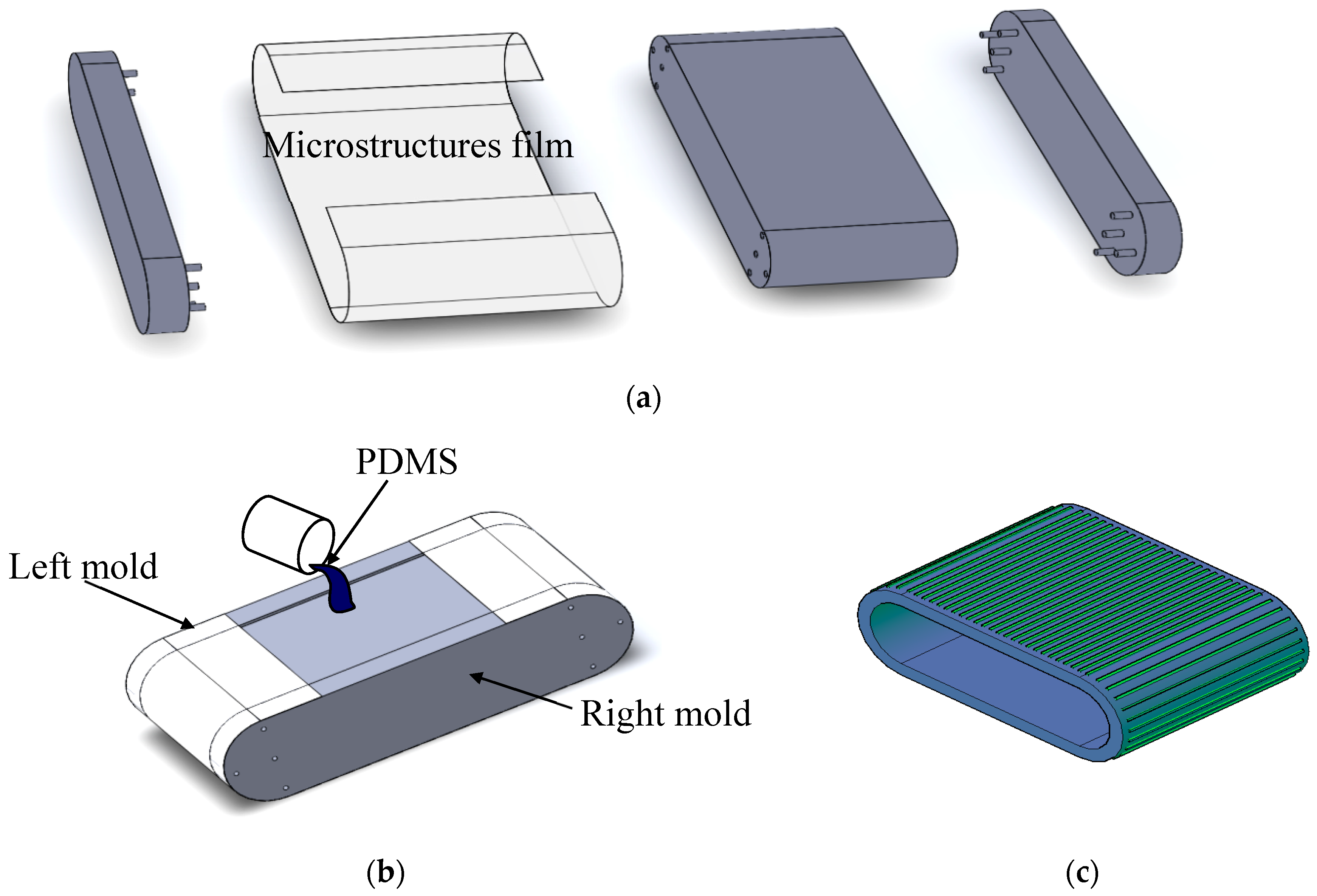
3.2. Innovative Production Method of a Microstructure Belt of Coated Casting Technology
3.2.1. Discussion on the Forming Method of the Traditional Roller Microstructure
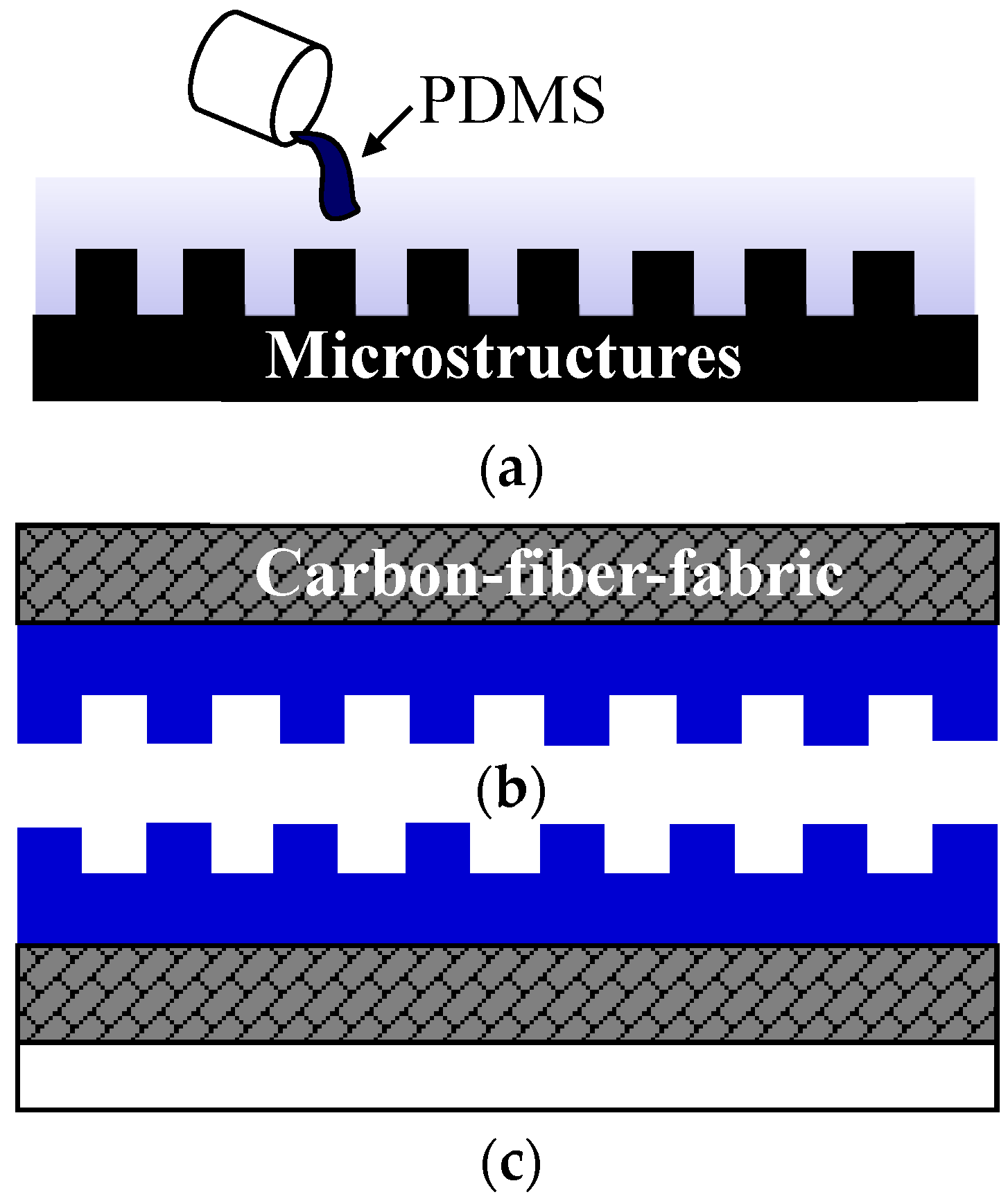
3.2.2. Manufacturing of Multi-layer Coated Casting Technology Microstructure Belt
3.3. Process Procedures of Continuous Film Microstructure Hot Roller Embossing
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Discussion of the Mechanical Properties of a Belt Made of Composite Metal Powders and Fiber
4.1.1. Discussion of the Mechanical Properties of a Belt Made of Composite Metal Powders
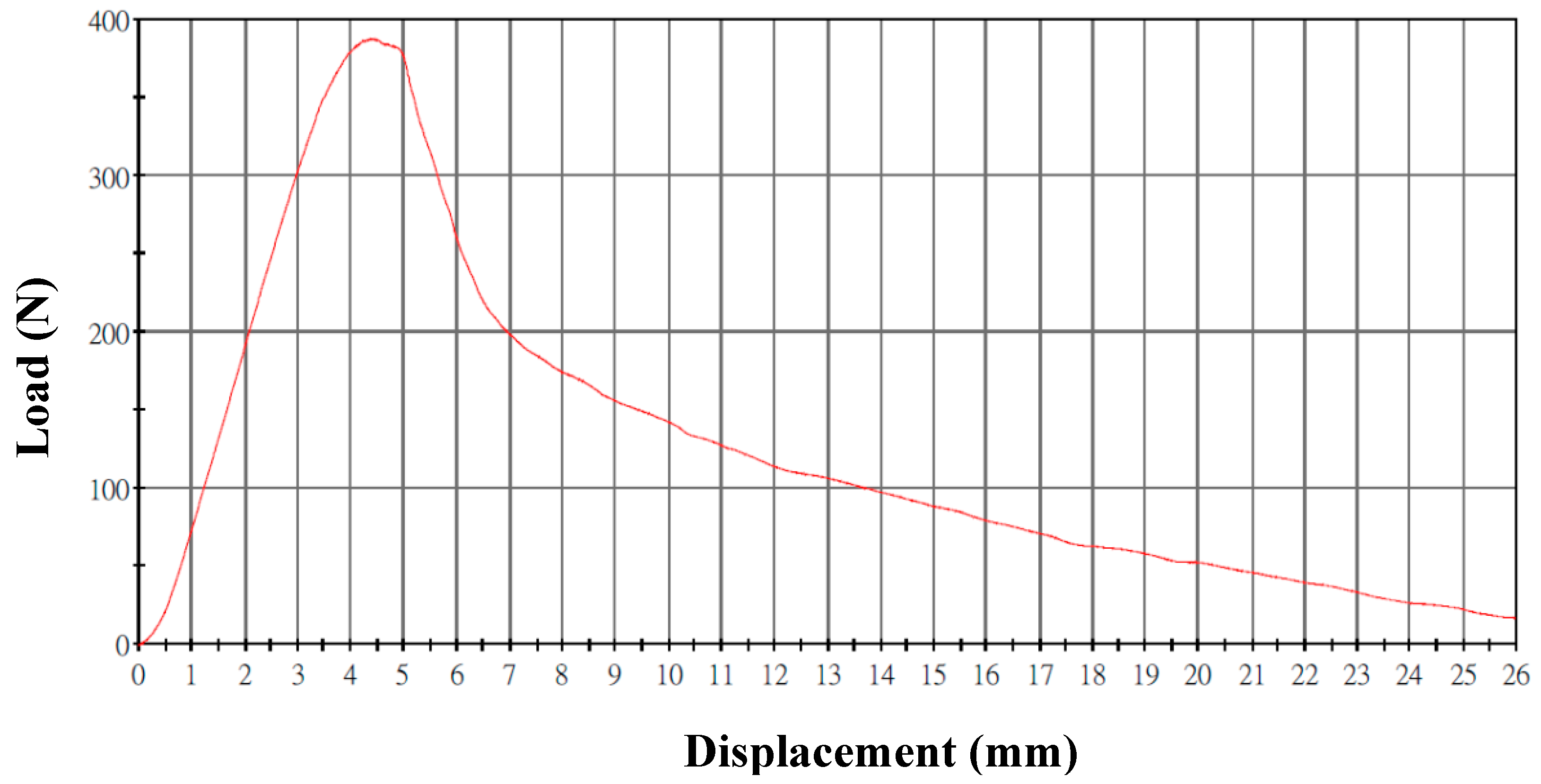
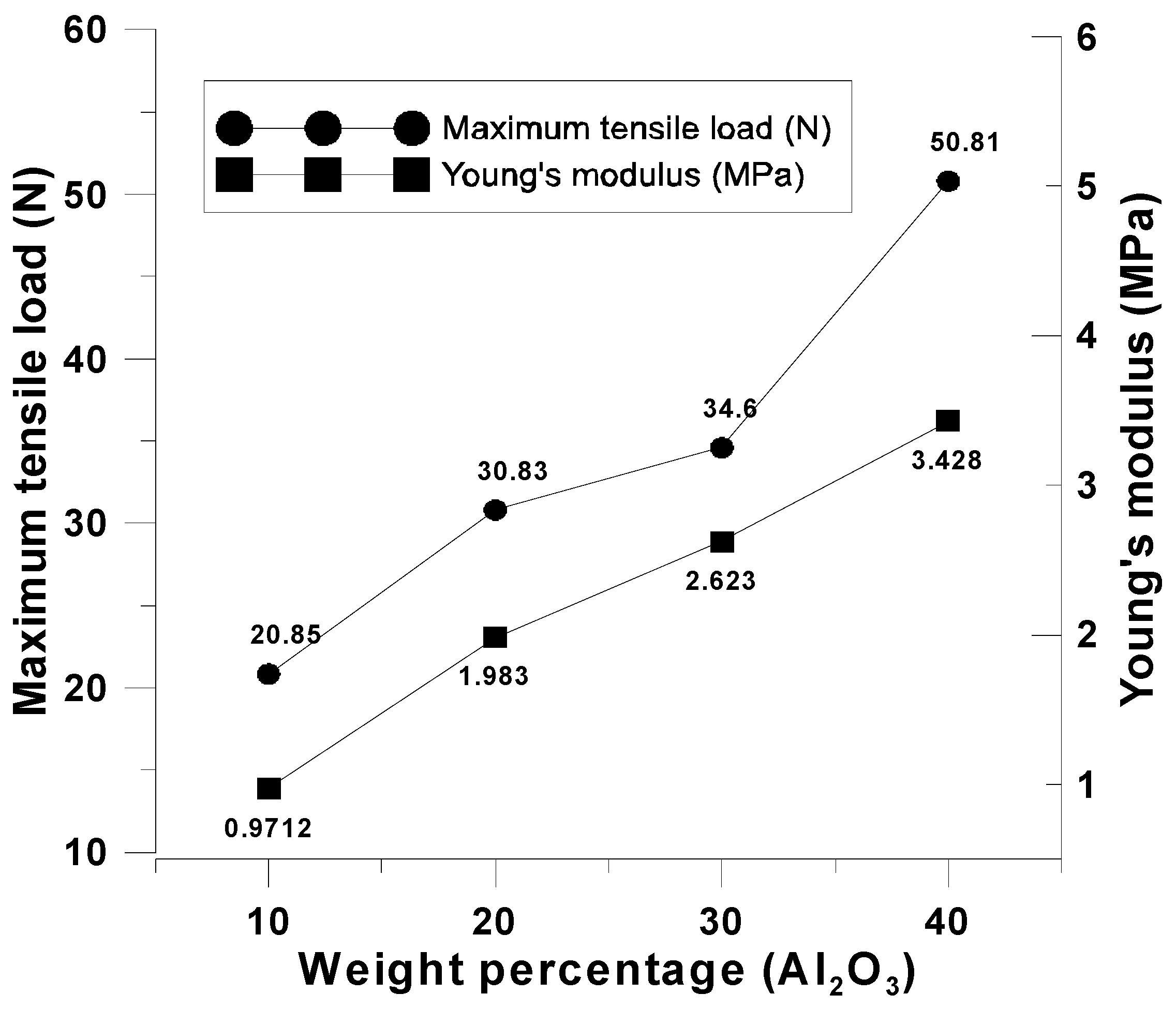
4.1.2. Discussion of the Mechanical Properties of a Belt Made of Carbon Fiber Woven with Composite Oxide Powder
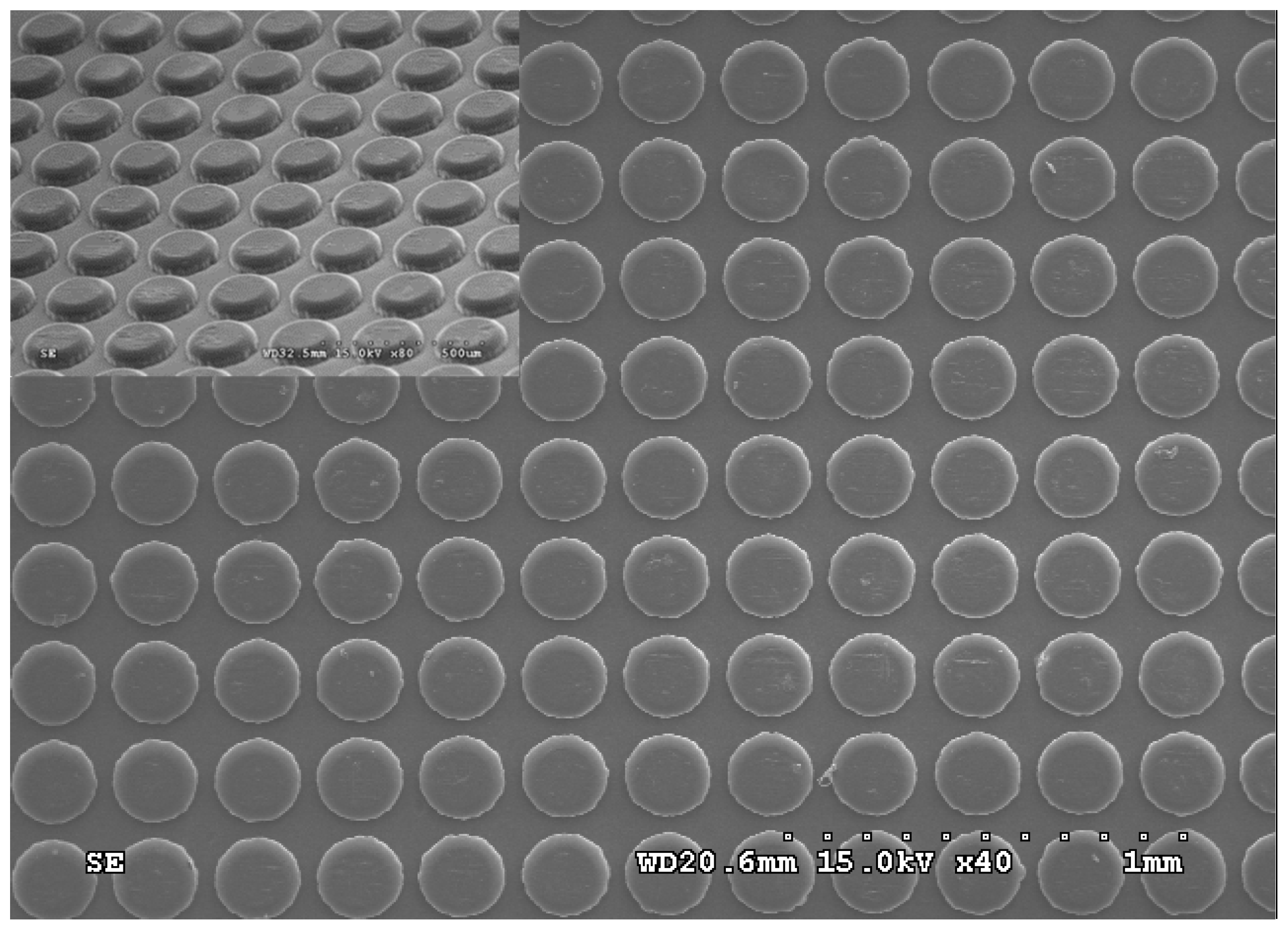
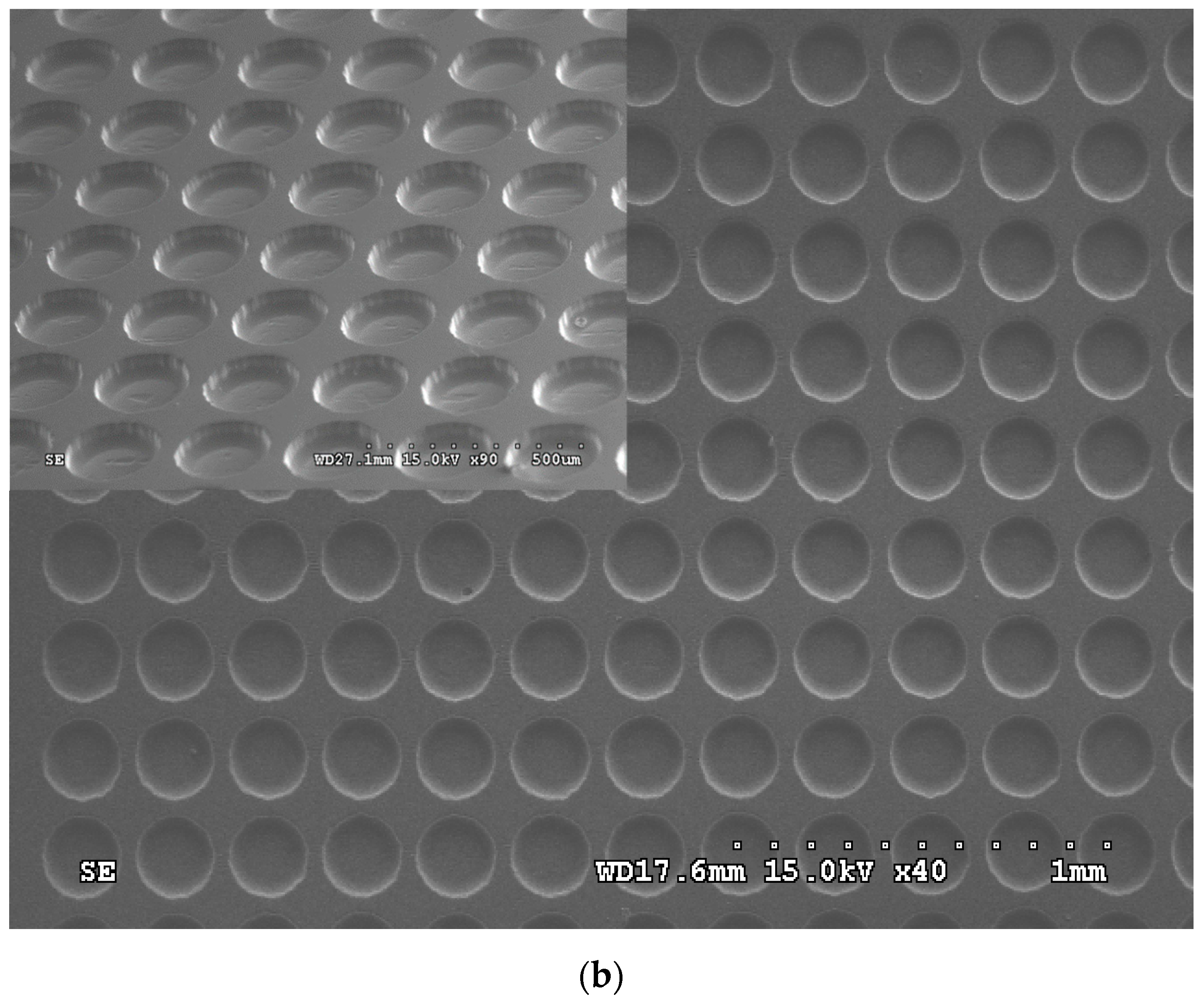
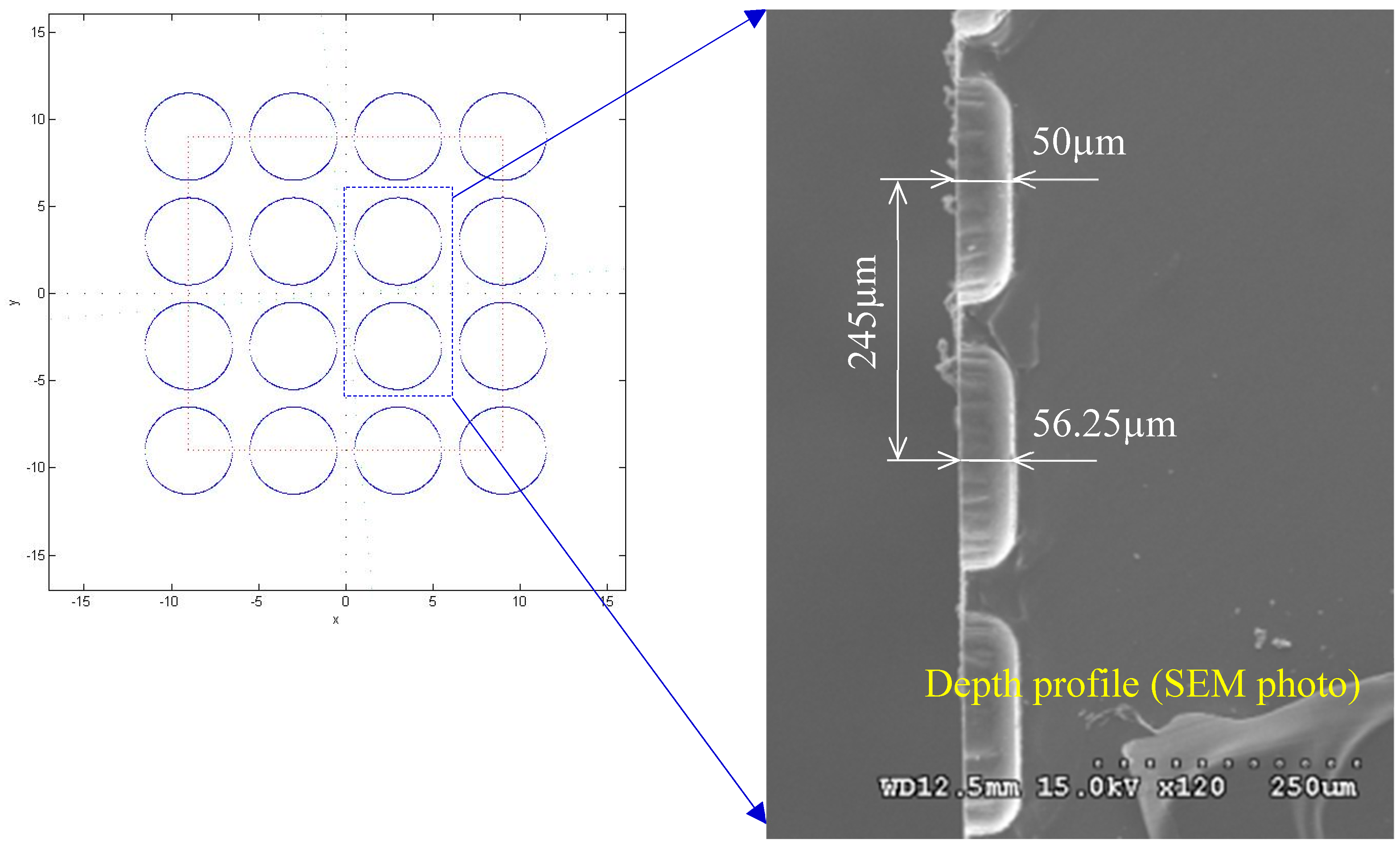
4.2. Discussion on the Replication and Forming of Belt-Type Microstructure Hot Roller Embossing
4.2.1. Discussion on the Forming of Belt-Type PDMS Soft Mold Hot Roller Embossing
4.2.2. Discussion on Composite Belt PDMS Soft Mold Hot Roller Embossing Forming
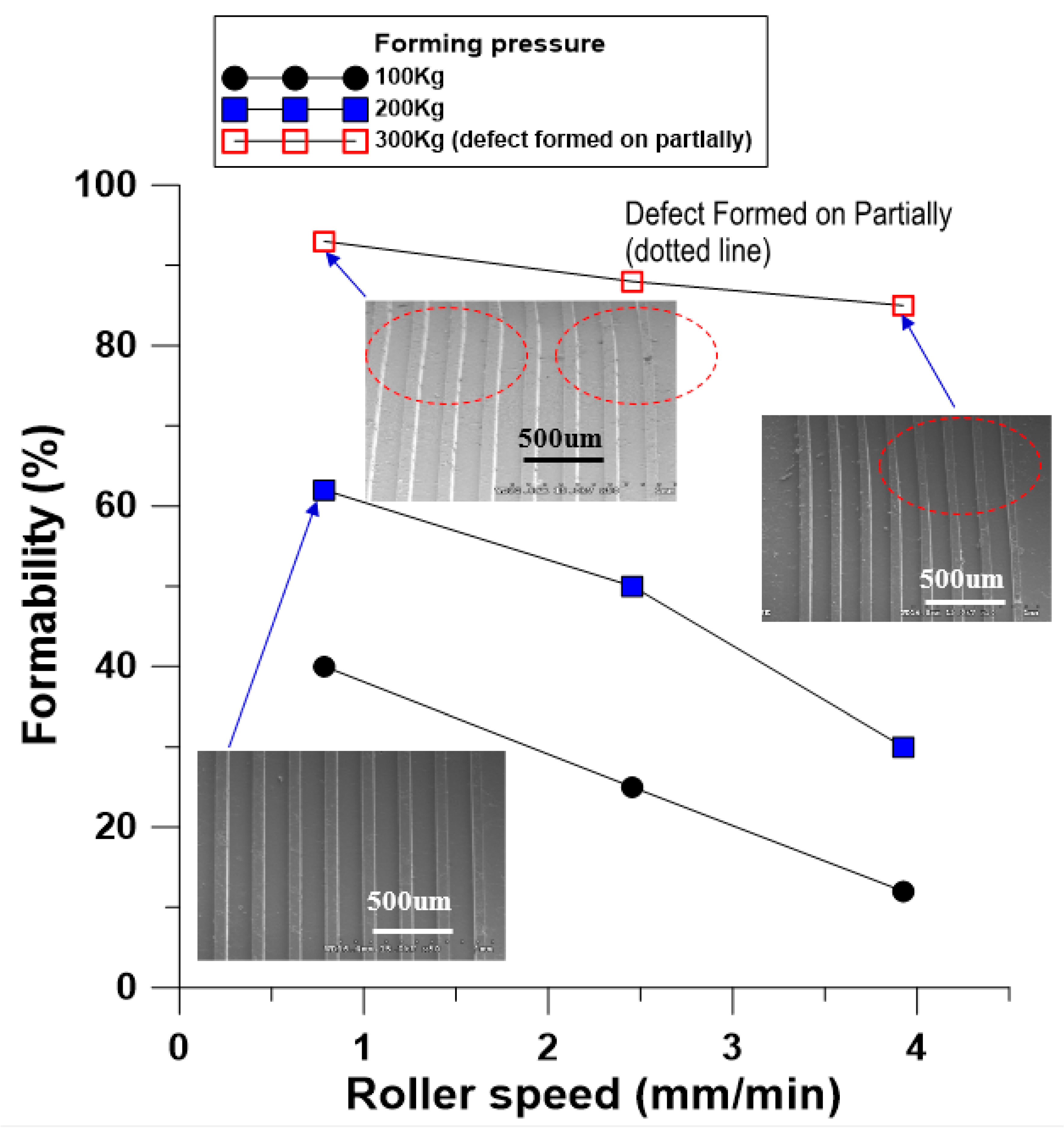
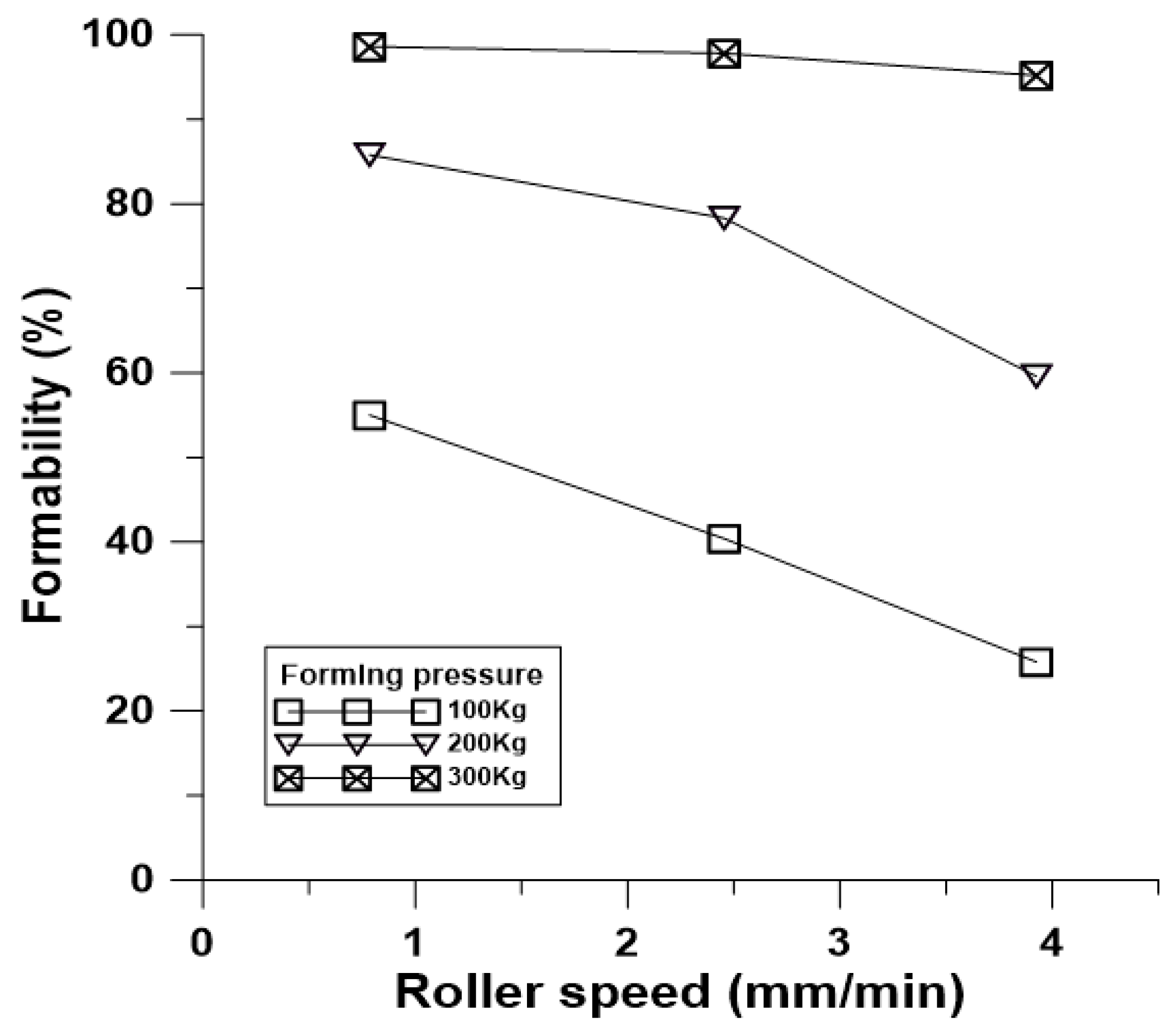
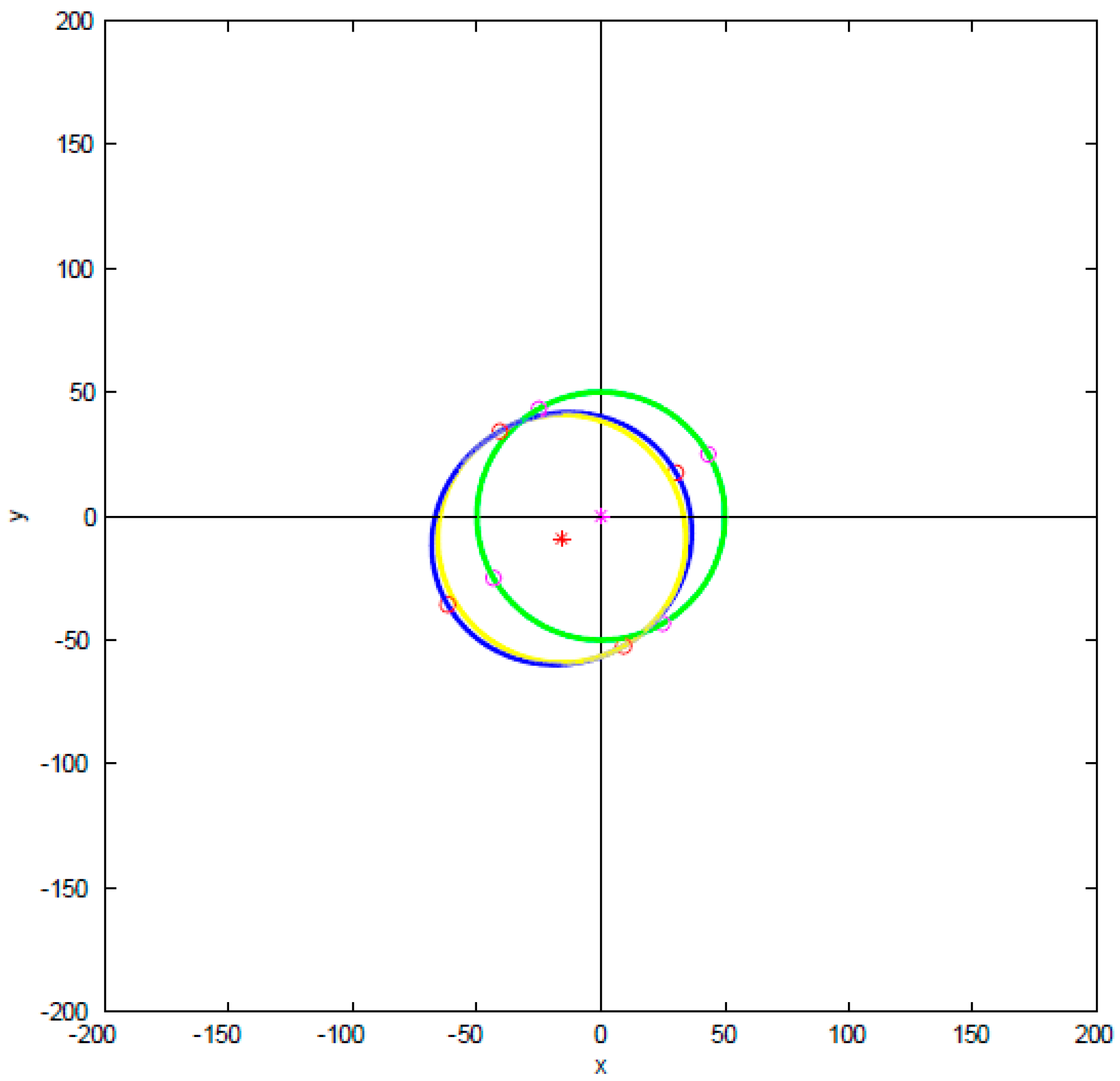
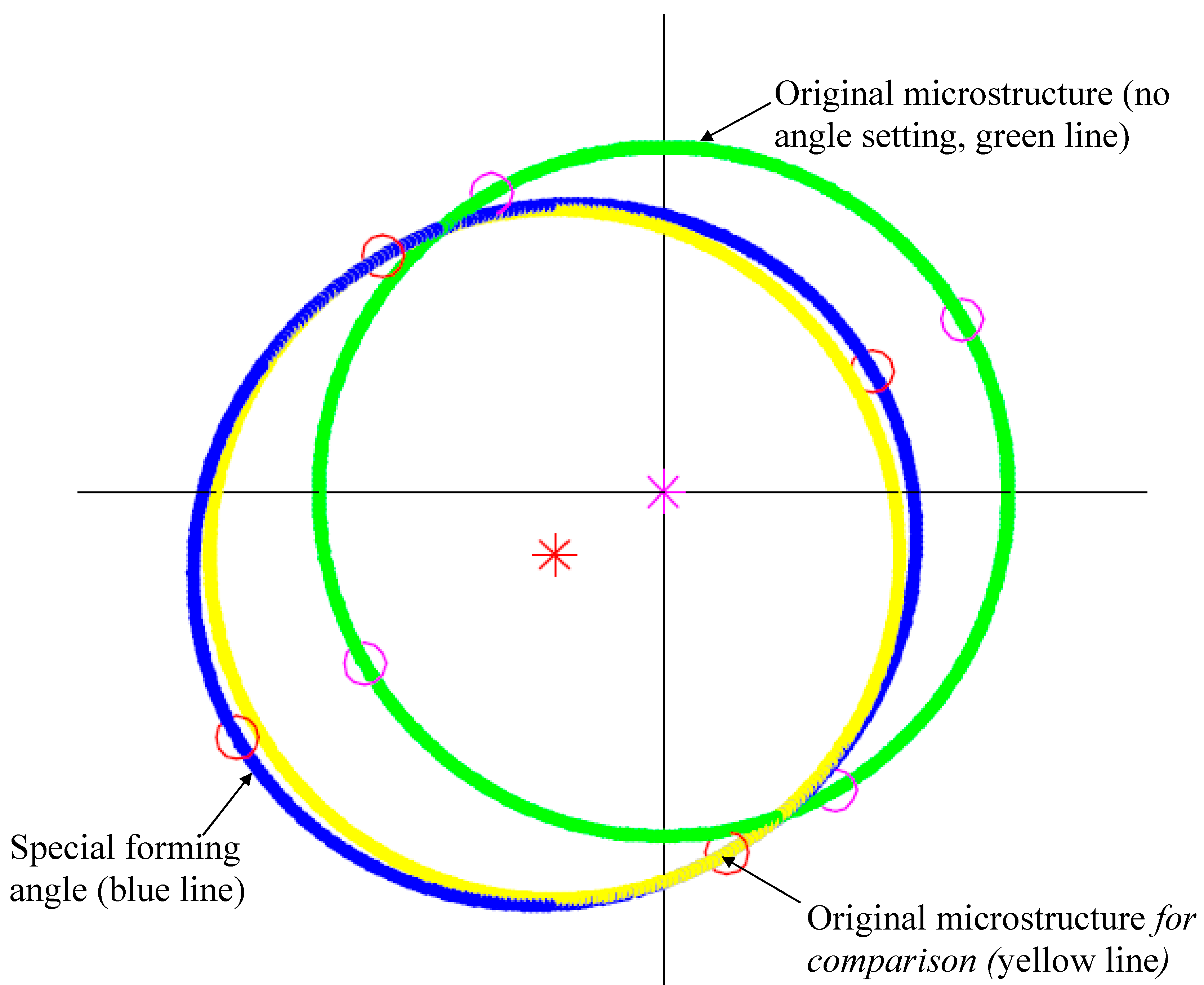
4.3. Analysis and Discussion of Rolling Formability and Simulation and Prediction of Belt Microstructure Rolling with Special Forming Angle
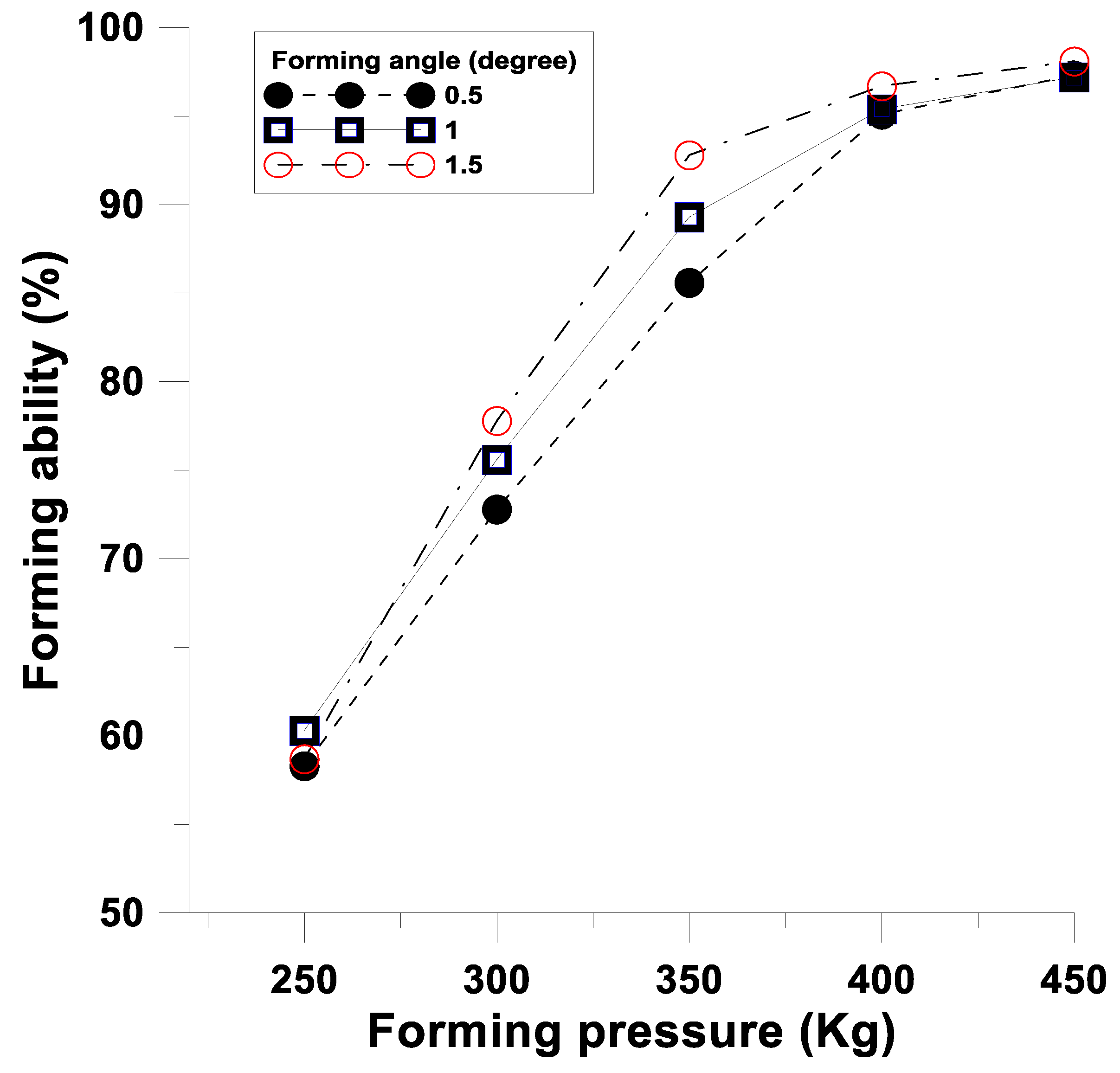
4.4. Effect of Large Angle Numerical Simulation and Unequal Rolling Pressure on the Accuracy of the Special Forming Angle
4.4.1. Numerical Simulation Analysis of Large Angle of the Special Forming Angle
4.4.2. Effect of Unequal Rolling Pressure on the Accuracy of the Special Forming Angle
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nouet, P.; Michel, B. Special issue on Design, Test, Integration and Packaging of MEMS and MOEMS. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 3825. [Google Scholar]
- Nordstrom, M.; Zauner, D.A.; Boisen, A.; Hubner, J. Single-mode waveguides with SU-8 polymer core and cladding for MOEMS applications. J. Lightwave Technol. 2017, 25, 1284–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandner, T.; Grasshoff, T.; Gaumont, E.; Schenk, H.; Kenda, A. Translatory MOEMS actuator and system integration for miniaturized Fourier transform spectrometers. J. Micro/Nanolithography 2014, 13, 011115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Zhou, Y.; Dou, R.; Wang, W.; Yin, B.; Yang, M.B. Effect of the core-forming polymer on phase morphology and mechanical properties of PA6/EPDM-g-MA/HDPE ternary blends. Polymer 2015, 56, 395–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.B.; Gong, F. Deep drawing of cylindrical cups using polymer powder medium based flexible forming. Int. J. Precis. Eng. and Manuf. Green Technol. 2018, 5, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedini, A.; Rahimlou, P.; Asiabi, T.; Ahmadi, S.R.; Azdast, T. Effect of flow forming on mechanical properties of high density polyethylene pipes. J. Manuf. Process. 2015, 19, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Gao, J.; Yi, P.; Peng, L.; Lai, X. Investigation of reflective performance for micro-pyramid arrays by roll-to-roll UV imprinting process. Microelectron. Eng. 2017, 182, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lien, C.C.; Weng, Y.J.; Tsai, C.Y.; Wu, S.H. Gas-assisted microstructure elastic multiform UV imprint replication molding technology. Microsyst. Technol. 2017, 23, 1897–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Cha, J.; Myung, H.; Kim, S.M.; Kang, S. Continuous ultraviolet roll nanoimprinting process for replicating large-scale nano-and micropatterns. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 213101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.J.; Tsai, C.Y. Study on imprinting and replica molding of quasi-grey scale soft mold curved surface microstructure mold. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 191, 32–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Choi, S.; Lim, J.; Lee, B.S.; Kang, S. Fabrication of transparent conductive tracks and patterns on flexible substrate using a continuous UV roll imprint lithography. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 115503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.H.; Weng, Y.J.; Yang, S.Y. Magnetic fluid microstructure curved surface uniform embossing and photocuring process technology. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 27, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, S.H.; Wang, Z.F. Hot roller embossing for microfluidics: process and challenges. Microsyst. Technol. 2009, 15, 1149–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velten, T.; Bauerfeld, F.; Schuck, H.; Scherbaum, S.; Landesberger, C.; Bock, K. Roll-to-roll hot embossing of microstructures. Microsyst. Technol. 2011, 17, 619–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, N.T. Micromixers: Fundamentals, Design and Fabrication; William Andrew: Norwich, NY, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Velten, T.; Schuck, H.; Haberer, W.; Bauerfeld, F. Investigations on reel-to-reel hot embossing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2010, 47, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizawa, N.; Idei, K.; Kimura, T.; Noda, D.; Hattori, T. Resin micromachining by roller hot embossing. Microsyst. Technol. 2008, 14, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gale, M.T. Replication techniques for diffractive optical elements. Microelectron. Eng. 1997, 34, 321–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, C.; Vak, D.; Angmo, D.; Ding, L.; Gao, M. One-step roll-to-roll air processed high efficiency perovskite solar cells. Nano Energy 2018, 46, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Hassinen, T.; Lee, W.H.; Ko, S. Fully solution-processed organic thin-film transistors by consecutive roll-to-roll gravure printing. Org. Electron. 2017, 42, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saarinen, J.J.; Remonen, T.; Tobjörk, D.; Aarnio, H.; Bollström, R.; Österbacka, R.; Toivakka, M. Large-Scale Roll-to-Roll Patterned Oxygen Indicators for Modified Atmosphere Packages. Packag. Technol. Sci. 2017, 30, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.J. Research and development of the asymmetric grayscale roll-to-plate processing technology. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 98, 1339–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Materials | Density (Kg·m−3) | Young’s Modulus (Gpa) | Poisson’s Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum alloy | 2770 | 71 | 0.33 |
| PDMS (10:1) | 965 | 1.72 | 0.495 |
| Arc radius (mm) | Push Distance (mm) | The Mixing Ratio of Base and Curing Agent (A:B) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) | Ultimate Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 28 | 5 | 5:1 | 1.22572 | 1.18493 |
| 10 | 5:1 | 1.34554 | 0.97491 | |
| 5 | 10:1 | 1.41427 | 1.08201 | |
| 10 | 10:1 | 1.56488 | 1.07021 | |
| 33 | 5 | 5:1 | 1.17623 | 1.73221 |
| 10 | 5:1 | 1.73983 | 1.53826 | |
| 5 | 10:1 | 1.34145 | 1.13452 | |
| 10 | 10:1 | 1.39242 | 1.08797 | |
| 0 | 0 | 10:1 | 1.96324 | 8.30731 |
| Weight Percentage (Al2O3) | Maximum Tensile Load (N) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| 10% | 20.853 | 0.97122 |
| 20% | 30.834 | 1.98342 |
| 30% | 34.603 | 2.62309 |
| 40% | 50.812 | 3.42849 |
| Sample | Maximum Tensile Load (N) | Young’s Modulus (MPa) |
|---|---|---|
| A | 386.3452 | 1048.9282 |
| B | 376.3492 | 1086.3820 |
| C | 380.7840 | 1076.2809 |
| D | 387.3342 | 1102.3927 |
| E | 384.1203 | 1089.2815 |
| Average | 382.9865 | 1080.6530 |
| Temperature (Degrees of Temperature, °C) | Screw Speed (Revolution Per Minute, RPM) | Polycarbonate Extrusion Weight (g/min) |
|---|---|---|
| 275 | 150 | 10.833 |
| 250 | 20.5 | |
| 350 | 28.667 | |
| 450 | 38.667 |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Weng, Y.-J. Development of Belt-Type Microstructure Array Flexible Mold and Asymmetric Hot Roller Embossing Process Technology. Coatings 2019, 9, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040274
Weng Y-J. Development of Belt-Type Microstructure Array Flexible Mold and Asymmetric Hot Roller Embossing Process Technology. Coatings. 2019; 9(4):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040274
Chicago/Turabian StyleWeng, Yung-Jin. 2019. "Development of Belt-Type Microstructure Array Flexible Mold and Asymmetric Hot Roller Embossing Process Technology" Coatings 9, no. 4: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040274
APA StyleWeng, Y.-J. (2019). Development of Belt-Type Microstructure Array Flexible Mold and Asymmetric Hot Roller Embossing Process Technology. Coatings, 9(4), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings9040274




