Recent Developments in R.F. Magnetron Sputtered Thin Films for pH Sensing Applications—An Overview
Abstract
:1. Introduction
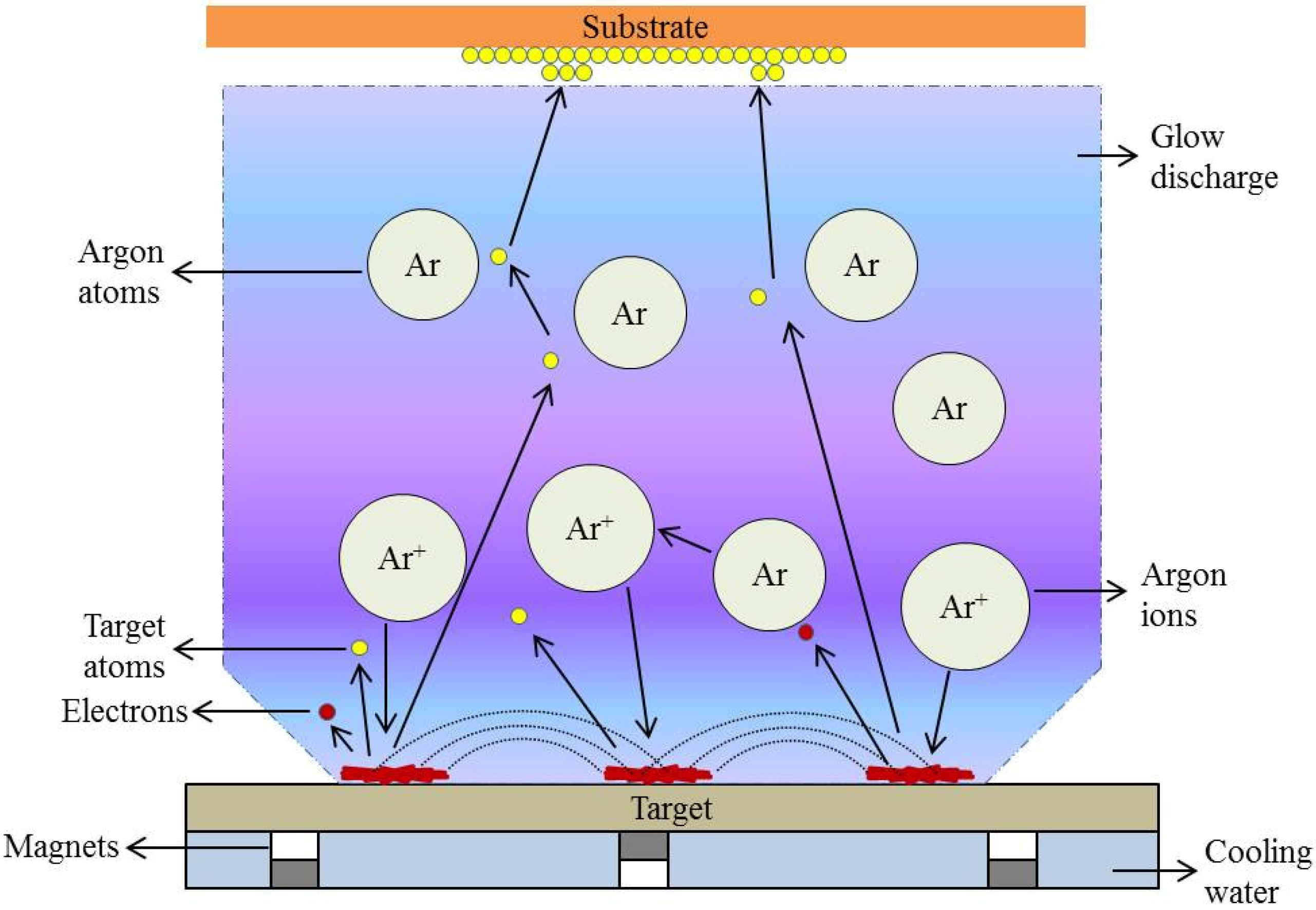
2. R.F. Magnetron Sputtering
3. pH Sensing Mechanism
4. pH Sensor Performance
4.1. Sensitivity
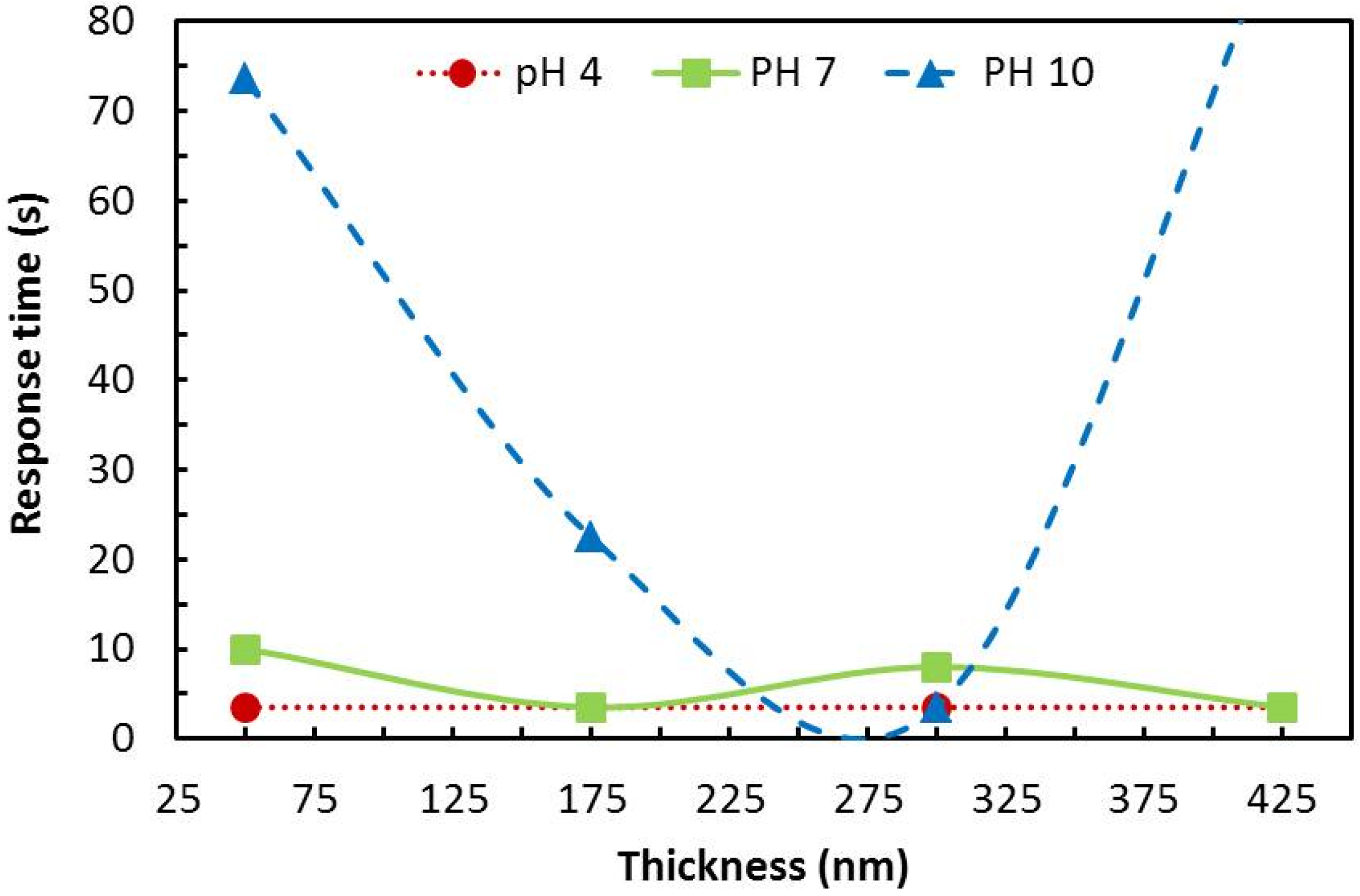
4.2. Response Time
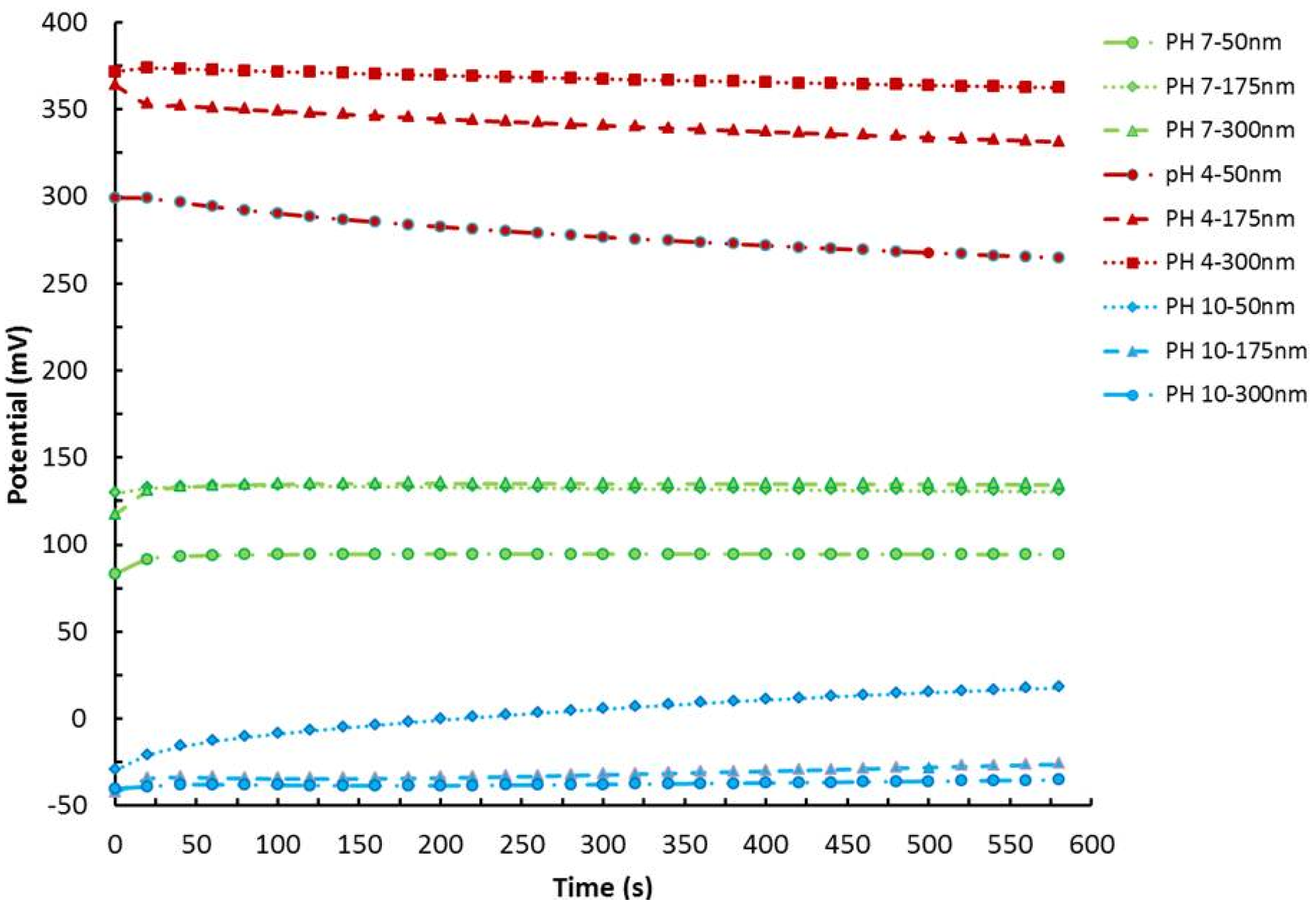
4.3. Drift Rate
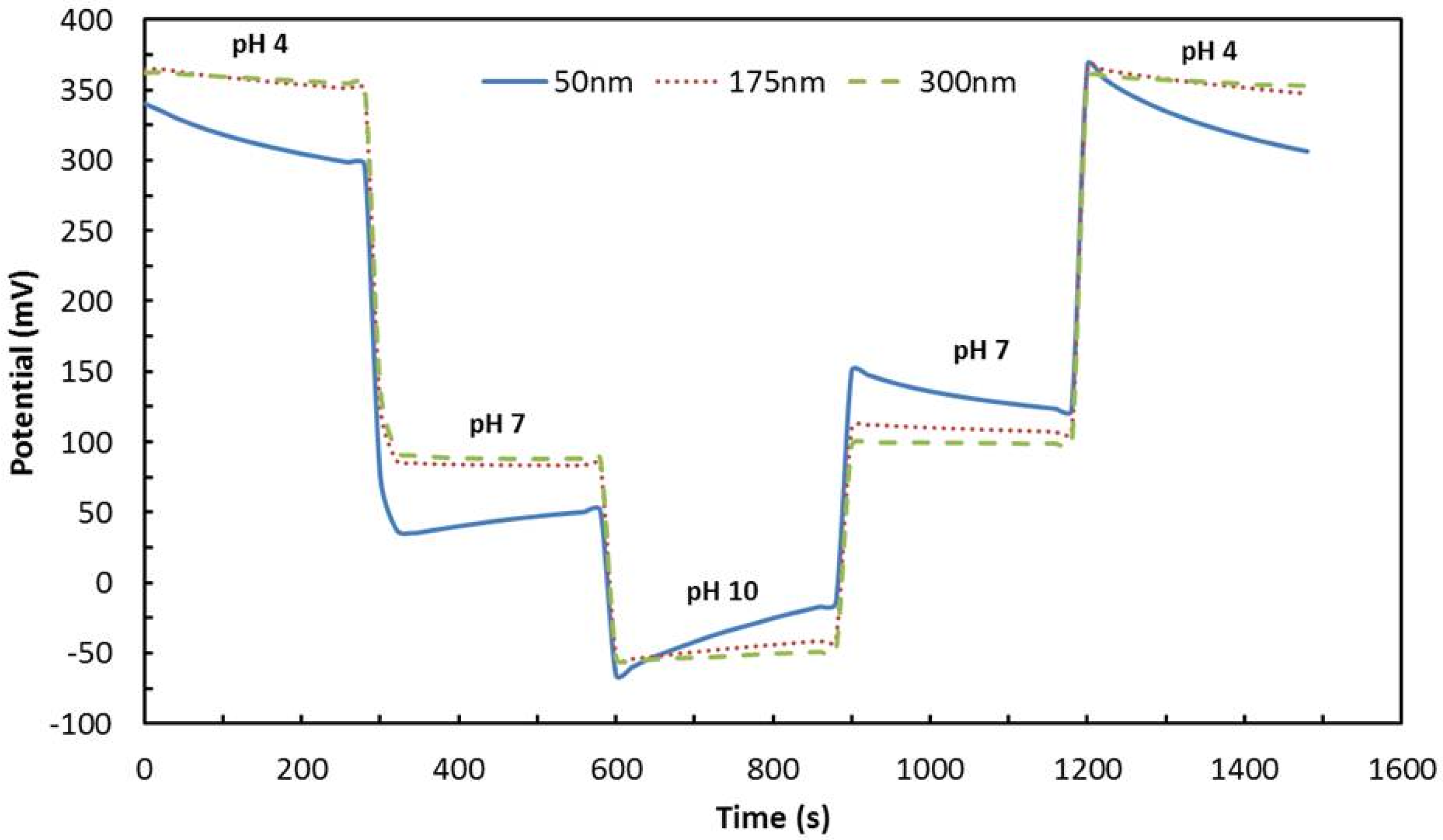
4.4. Hysteresis
4.5. Temperature Coefficient of Sensitivity
4.6. Reversibility
4.7. Resolution
5. pH Sensing Materials and Applications
| pH sensing material | Sputtering target material | pH test solution | pH Sensitivity (mV/pH) | Response time (s) | Drift rate (mV/h) | Hysteresis (mV) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RuO2 | RuO2 | 4–10 | 58.5 | < 3 | – | – | [20] |
| RuO2 | Ru | 4–10 | 49.8–59.1 | < 1 | 0.38 | 4.36 | [22] |
| RuN-RuOx | Ru | 1-13 | 55.52–57.05 | 30 | – | – | [23] |
| Ta2O5 | Ta | 1–10 | 56.19 | – | – | ~5 | [28] |
| SnO2 | SnO2 | 2–12 | 59 | – | – | 7–11 | [68] |
| TiO2:Ru | TiO2, Ru | 1–13 | 55.20 | < 1 | 1.03–1.16 | – | [69] |
| IrO2 & Ta2O5 | Ir, Ta2O5 | 2–13 | 59.44–59.50 | < 15 | < 0.1 | – | [70] |
| AlN | Al | 4–10 | 54.5 | – | – | – | [71] |
| TiO2 | TiO2 | 1–13 | 56.21 | – | – | – | [72] |
| WO3-IrO2 | WO3-Ir | 2–12 | 0.168 µA/pH | < 7 | – | – | [73] |
| RuOx | Ru | 5.5–11 | 52–58 | < 2 | 1–2 | – | [74] |
| GdTixOy | Gd, Ti | 2–12 | 64.13 | – | 0.4 | < 1 | [75] |


6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fierro, S.; Seishima, R.; Osamu, N.; Hideyuki, S.; Yasuaki, E. In vivo pH monitoring using boron doped diamond microelectrode and silver needles: Application to stomach disorder diagnosis. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohlmann, F.J. What is pH, and How is it Measured? A Technical Handbook for Industry; Hach Company: Loveland, CO, SUA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Korostynska, O.; Arshak, K.; Gill, E.; Arshak, A. Review on state-of-the-art in polymer based pH sensors. Sensors 2007, 7, 3027–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Privett, B.J.; Shin, J.H.; Schoenfisch, M.H. Electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 4723–4741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.D.; Cao, H.; Deb, S.; Chiao, M.; Chiao, J.C. A flexible pH sensor based on the iridium oxide sensing film. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2011, 169, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eftekhari, A. pH sensor based on deposited film of lead oxide on aluminum substrate electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 3, 234–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Schoot, B.H.; Bergveld, P. ISFET based enzyme sensors. Biosensors 1987, 3, 161–186. [Google Scholar]
- Yuqing, M.; Jianguo, G.; Jianrong, C. Ion sensitive field effect transducer-based biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2003, 21, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, M. Ion-sensitive field-effect transistor for biological sensing. Sensors 2009, 9, 7111–7131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olthuis, W.; Robben, M.A.M.; Bergveld, P.; Bos, M.; Van der Linden, W.E. pH sensor properties of electrochemically grown iridium oxide. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1990, 2, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinlen, P.J.; Heider, J.E.; Hubbard, D.E. A solid-state pH sensor based on a nafion-coated iridium oxide indicator electrode and a polymer-based silver chloride reference electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 1, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richter, A.; Paschew, G.; Klatt, S.; Lienig, J.; Arndt, K.; Adler, H.P. Review on hydrogel-based pH sensors and microsensors. Sensors 2008, 1, 561–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerlach, G.; Guenther, M.; Sorber, J.; Suchaneck, G.; Arndt, K.F.; Richter, A. Chemical and pH sensors based on the swelling behavior of hydrogels. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 111–112, 555–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezbaruah, A.N.; Zhang, T.C. Fabrication of anodically electrodeposited iridium oxide film pH microelectrodes for microenvironmental studies. Anal. Chem. 2002, 74, 5726–5733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ges, I.A.; Ivanov, B.L.; Schaffer, D.K.; Lima, E.A.; Werdich, A.A.; Baudenbacher, F.J. Thin-film IrOx pH microelectrode for microfluidic-based microsystems. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2005, 2, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.Y.; Yang, S. Fabrication method and characterization of electrodeposited and heat-treated iridium oxide films for pH sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 196, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.M.; Huang, W.; Rao, S.; Cao, H.; Tata, U.; Chiao, Mu.; Chiao, J. Sol-Gel iridium oxide-based pH sensor array on flexible polyimide substrate. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 10, 3857–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.M.; Rao, S.; Seo, Y.; Schadt, K.; Hao, Y.; Chiao, J.C. Micro pH sensors based on iridium oxide nanotubes. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prats-Alfonso, E.; Abad, L.; Casañ-Pastor, N.; Gonzalo-Ruiz, J.; Baldrich, E. Iridium oxide pH sensor for biomedical applications. Case urea–urease in real urine samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 1, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, D.K.; Sardarinejad, A.; Alameh, K. High-sensitivity pH sensor employing a sub-micron ruthenium oxide thin-film in conjunction with a thick reference electrode. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 203, 300–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sardarinejad, A.; Maurya, D.K.; Alameh, K. The effects of sensing electrode thickness on ruthenium oxide thin-film pH sensor. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2014, 214, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.-H.; Chou, J.-C. Preparation and characteristics of ruthenium dioxide for pH array sensors with real-time measurement system. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 128, 603–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.; Liu, S.; Chen, S. Sensing characteristics of ruthenium films fabricated by radio frequency sputtering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 3, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuiykov, S.; O’Brien, D.; Best, M. Water quality assessment by an integrated multi-sensor based on semiconductor RuO2 nanostructures. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2009, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fog, A.; Buck, R.P. Electronic semiconducting oxides as pH sensors. Sens. Actuators 1984, 5, 137–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.C.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, C.C. Electrochromic property of sol-gel derived TiO2 thin film for pH sensor. IFMBE Proc. 2011, 35, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bahari, N.; Zain, A.M.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Sheng, D.B.C.; Othman, M. Study on pH sensing properties of RF magnetron sputtered tantalum pentoxide (Ta2O5) thin film. In Proceedings of 2010 IEEE International Conference on Semiconductor Electronics, Melaka, Malaysia, 28–30 June 2010; pp. 76–78.
- Chen, M.; Jin, Y.; Qu, X.; Jin, Q.; Zhao, J. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy study of Ta2O5 based EIOS pH sensors in acid environment. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 71, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, D.; Yoo, W.J.; Seo, J.K.; Shin, S.H.; Han, K.; Kim, S.G.; Park, J.; Lee, B. Fiber-optic pH sensor based on Sol-Gel film immobilized with neutral red. Opt. Rev. 2013, 2, 209–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanc-Gostkiewicz, M.; Sophocleous, M.; Atkinson, J.K.; Garcia-Breijo, E. Performance of miniaturized thick-film solid state pH sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2013, 202, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veeramani, M.S.; Shyam, P.; Ratchagar, N.P.; Chadha, A.; Bhattacharya, E.; Pavan, S. A miniaturized pH sensor with an embedded counter electrode and a readout circuit. IEEE Sens. J. 2013, 5, 1941–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Park, I.; Hao, Z.; Holman, H.N.; Pisano, A.P. Quantitative studies of long-term stable, top-down fabricated silicon nanowire pH sensors. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 107, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Ren, Q.; Yuan, X.; Wen, W.; Chen, W.; Zhan, D. Iridium oxide based coaxial pH ultramicroelectrode. Electrochem. Commun. 2014, 40, 35–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grieger, C.; Köster, F. Creation of functional layers for pH sensors by galvanic deposition of antimony and bismuth. Sci. J. Chem. 2014, 2, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Park, J. Fabrication and characterization of multilayered nanoporous platinum films deposited by electroplating and nonionic surfactant molds. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 277, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Arnell, R.D. Magnetron sputtering: A review of recent developments and applications. Vacuum 2000, 56, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musil, J.; Baroch, P.; Viček, J.; Nam, K.H.; Han, J.G. Reactive magnetron sputtering of thin films: Present status and trends. Thin Solid Films 2005, 1–2, 208–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N.; Vasiliev, M.; Kotovb, V.; Alameh, K. Recent developments in magneto-optic garnet-type thin-film materials synthesis. Procedia Eng. 2014, 76, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N.; Vasiliev, M.; Alameh, K. Bi3Fe5O12:Dy2O3 composite thin film materials for magneto-photonics and magneto-plasmonics. Opt. Mater. Express 2014, 4, 1866–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.N.; Vasiliev, M.; Alameh, K. Nano-structured magnetic photonic crystals for magneto-optic polarization controllers at the communication-band wavelengths. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2009, 41, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, W.W.; Aiello, Z.T.; Berliner, A.; Banerjee, P.; Zhou, S. In-situ immobilization of quantum dots in polysaccharide-based nanogels for integration of optical pH-sensing, tumor cell imaging, and drug delivery. Biomaterials 2010, 11, 3023–3031. [Google Scholar]
- Zamarreño, C.R.; Hernáez, M.; Villar, I.D.; Matías, I.R.; Arregui, F.J. Optical fiber pH sensor based on lossy-mode resonances by means of thin polymeric coatings. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 290–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Mitra, N.; Yan, E.C.Y.; Zhou, S. Multifunctional hybrid nanogel for integration of optical glucose sensing and self-regulated insulin release at physiological pH. ACS Nano 2010, 8, 4831–4839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Huang, X.; Xu, W.; Xiao, D.; Zhong, Z. A fiber-optic pH sensor based on relative Fresnel reflection technique and biocompatible coating. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2014, 28–31. [Google Scholar]
- Shao, L.; Yin, M.; Tam, H.; Albert, J. Fiber optic pH sensor with self-assembled polymer multilayer nanocoatings. Sensors 2013, 2, 1425–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Bakker, E.; Qin, Y. Electrochemical sensors. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 3965–3983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.A.; Kumar, P.; Park, D.; Shim, Y. Electrochemical sensors based on organic conjugated polymers. Sensors 2008, 1, 118–141. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, F.; Hu, S. Electrochemical sensors based on metal and semiconductor nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2009, 1–2, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimmel, D.W.; LeBlanc, G.; Meschievitz, M.E.; Cliffel, D.E. Electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 685–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, Z.; Nijhuis, C.A.; Gong, J.; Chen, X.; Kumachev, A.; Martinez, A.W.; Narovlyansky, M.; Whitesides, G.M. Electrochemical sensing in paper-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakard, B.; Segut, O.; Lakard, S.; Herlem, G.; Gharbi, T. Potentiometric miniaturized pH sensors based on polypyrrole films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 1, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bandodkar, A.J.; Hung, V.W.S.; Jia, W.; Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Windmiller, J.R.; Martinez, A.G.; Ramírez, J.; Chan, G.; Kerman, K.; Wang, J. Tattoo-based potentiometric ion-selective sensors for epidermal pH monitoring. Analyst 2013, 138, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinovart, T.; Valdés-Ramírez, G.; Windmiller, J.R.; Andrade, F.J.; Wang, J. Bandage-based wearable potentiometric sensor for monitoring wound pH. Electroanalysis 2014, 6, 1345–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuliani, C.; Matzeu, G.; Diamond, D. A potentiometric disposable sensor strip for measuring pH in saliva. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 132, 292–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Xu, Z. A novel pH potentiometric sensor based on electrochemically synthesized polybisphenol a films at an ITO electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 2, 730–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, At.; Das, An.; Chang, L.B.; Lai, C.; Lin, R.M.; Chu, F.C.; Lin, Y.H.; Chow, L.; Jeng, M.J. GaN thin film based light addressable potentiometric sensor for pH sensing application. Appl. Phys. Express 2013, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Zhang, L.F.; Lu, C.H.; Lin, J.L.; Chin, Y.L.; Sun, T.P. Development of anodic titanium oxide nanotubes applied to a pH sensor with amperometric and potentioimetric methods. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 528, 10–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, J.H.; Kang, M.; Lee, Y.; Lee, C. A nanoporous ruthenium oxide framework for amperometric sensing of glucose and potentiometric sensing of pH. Microchim. Acta 2012, 177, 211–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stred’anský, M.; Pizzariello, A.; Stred’anská, S.; Miertuš, S. Amperometric pH-sensing biosensors for urea, penicillin, and oxaloacetate. Anal. Chim. Acta 2000, 1–2, 151–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzariello, A.; Stredanský, M.; Stredanská, S.; Miertuš, S. Urea biosensor based on amperometric pH-sensing with hematein as a pH-sensitive redox mediator. Talanta 2001, 4, 763–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Song, J. Polyaniline film based amperometric pH sensor using a novel electrochemical measurement system. Electroanalysis 2009, 8, 973–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, M.A.; Hauser, P.C. Recent developments in detection methods for microfabricated analytical devices. Lab Chip 2001, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Bao, N.; Xia, X.; Peng, Y.; Chen, H. Electrochemical detection method for nonelectroactive and electroactive analytes in microchip electrophoresis. Anal. Chem. 2004, 23, 6902–6907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X. Nitric oxide (NO) electrochemical sensors. In Electrochemical Sensors, Biosensors and Their Biomedical Applications; Zhang, X., Ju, H., Wang, J., Eds.; Academic Press: Waltham, MA, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, Y.; Chou, J. Fabrication and characterization of a ruthenium nitride membrane for electrochemical pH sensors. Sensors 2009, 9, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.L.; Chou, J.C.; Lei, Z.C.; Sun, T.P.; Chung, W.Y.; Hsiung, S.K. Titanium nitride membrane application to extended gate field effect transistor pH sensor. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2001, 40, 6311–6315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harsanyi, G. Sensors in Biomedical Applications: Fundamentals, Technology and Applications; CRC Press LCC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Tsai, C.; Chou, J.; Sun, T.; Hsiung, S. Study on the sensing characteristics and hysteresis effect of the tin oxide pH electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.; Chen, C. Long-term monitor of seawater by using TiO2:Ru sensing electrode for hard calm cultivation. Eng. Technol. 2009, 53, 303–307. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, L.; Chou, Y.; Chen, K.; Lu, C.; Chao, S. A precise pH microsensor using RF-sputtering IrO2 and Ta2O5 films on Pt-electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 193, 687–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bunjongpru, W.; Porntheeraphat, S.; Trithaveesak, O.; Somwang, N.; Khomdet, P.; Jeamsaksiri, W.; Hruanun, C.; Poyai, A.; Nukeaw, J. The innovative AlN-ISFET based pH sensor. In Proceeds of ECTI-CON 2008. 5th International Conference on Electrical Engineering/Electronics, Computer, Telecommunications and Information Technology, Krabi, Thailand, 14–17 May 2008; pp. 833–836.
- Chou, J.; Laio, L. Study on pH at the point of zero charge of TiO2 pH ion-sensitive field effect transistor made by the sputtering method. Thin Solid Films 2005, 476, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, L.; Chen, K.; Chuang, Y.; Chao, S. A flexible pH-sensing structure using WO3/IrO2 junction with Al2O3 encapsulation layer. ECS Solid State Lett. 2013, 3, 28–30. [Google Scholar]
- Brischwein, M.; Grothe, H.; Weist, J.; Zottmann, M.; Ressler, J.; Wolf, B. Planar ruthenium oxide sensors for cell-on-a-chip metabolic studies. Chem. Anal. (Warsaw) 2009, 54, 1193–1201. [Google Scholar]
- Her, J.; Wu, M.; Peng, Y.; Pan, T.; Weng, W.; Pang, S.; Chi, L. High performance GdTixOy electrolyte-insulator-semiconductor pH Sensor and biosensor. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 606–620. [Google Scholar]
© 2014 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maurya, D.K.; Sardarinejad, A.; Alameh, K. Recent Developments in R.F. Magnetron Sputtered Thin Films for pH Sensing Applications—An Overview. Coatings 2014, 4, 756-771. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4040756
Maurya DK, Sardarinejad A, Alameh K. Recent Developments in R.F. Magnetron Sputtered Thin Films for pH Sensing Applications—An Overview. Coatings. 2014; 4(4):756-771. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4040756
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaurya, D. K., A. Sardarinejad, and K. Alameh. 2014. "Recent Developments in R.F. Magnetron Sputtered Thin Films for pH Sensing Applications—An Overview" Coatings 4, no. 4: 756-771. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4040756
APA StyleMaurya, D. K., Sardarinejad, A., & Alameh, K. (2014). Recent Developments in R.F. Magnetron Sputtered Thin Films for pH Sensing Applications—An Overview. Coatings, 4(4), 756-771. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings4040756




