Effects of Ti6Al4V Substrate Roughness on the Surface Morphology, Mechanical Properties, and Cell Proliferation of Diamond-like Carbon Films
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
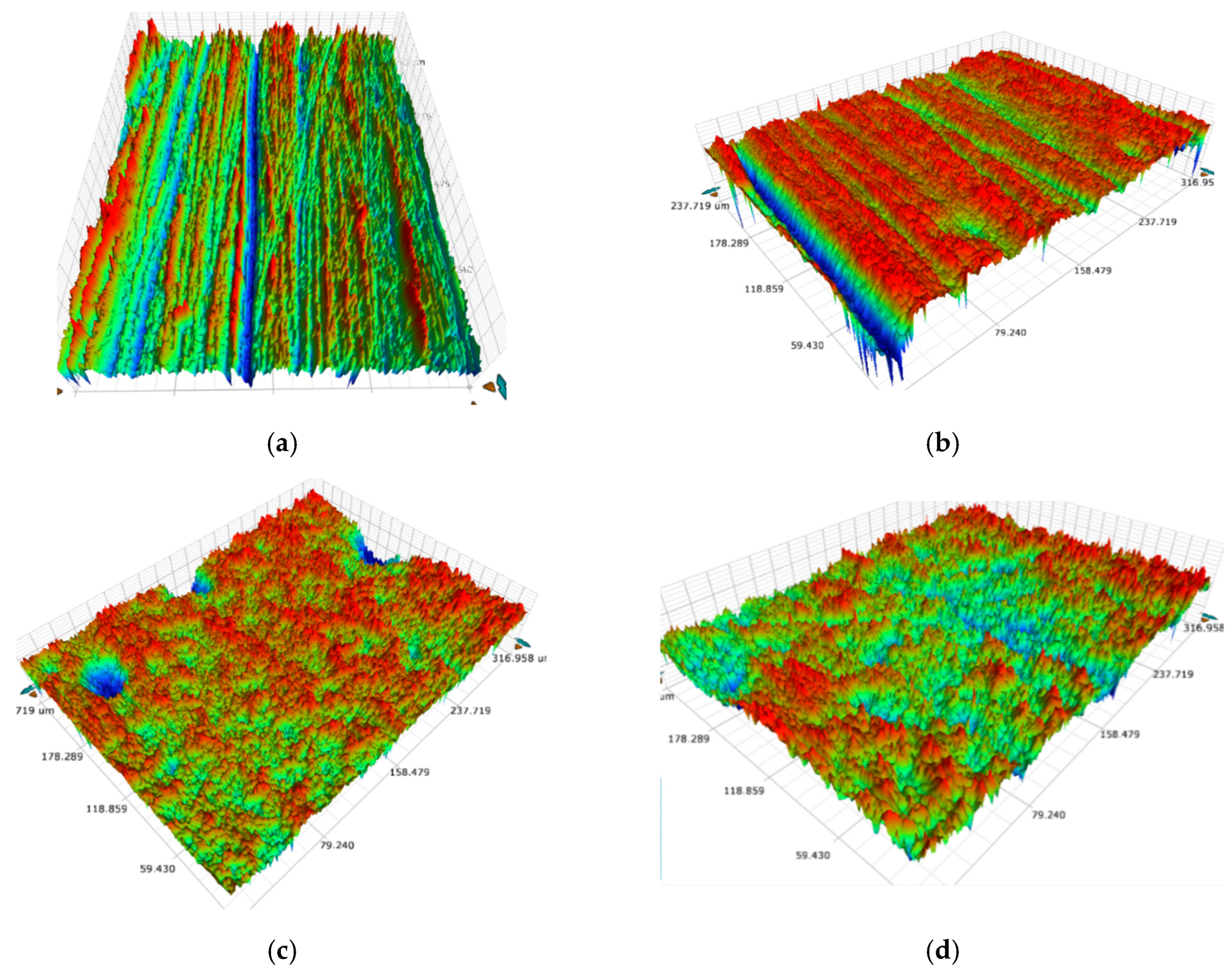
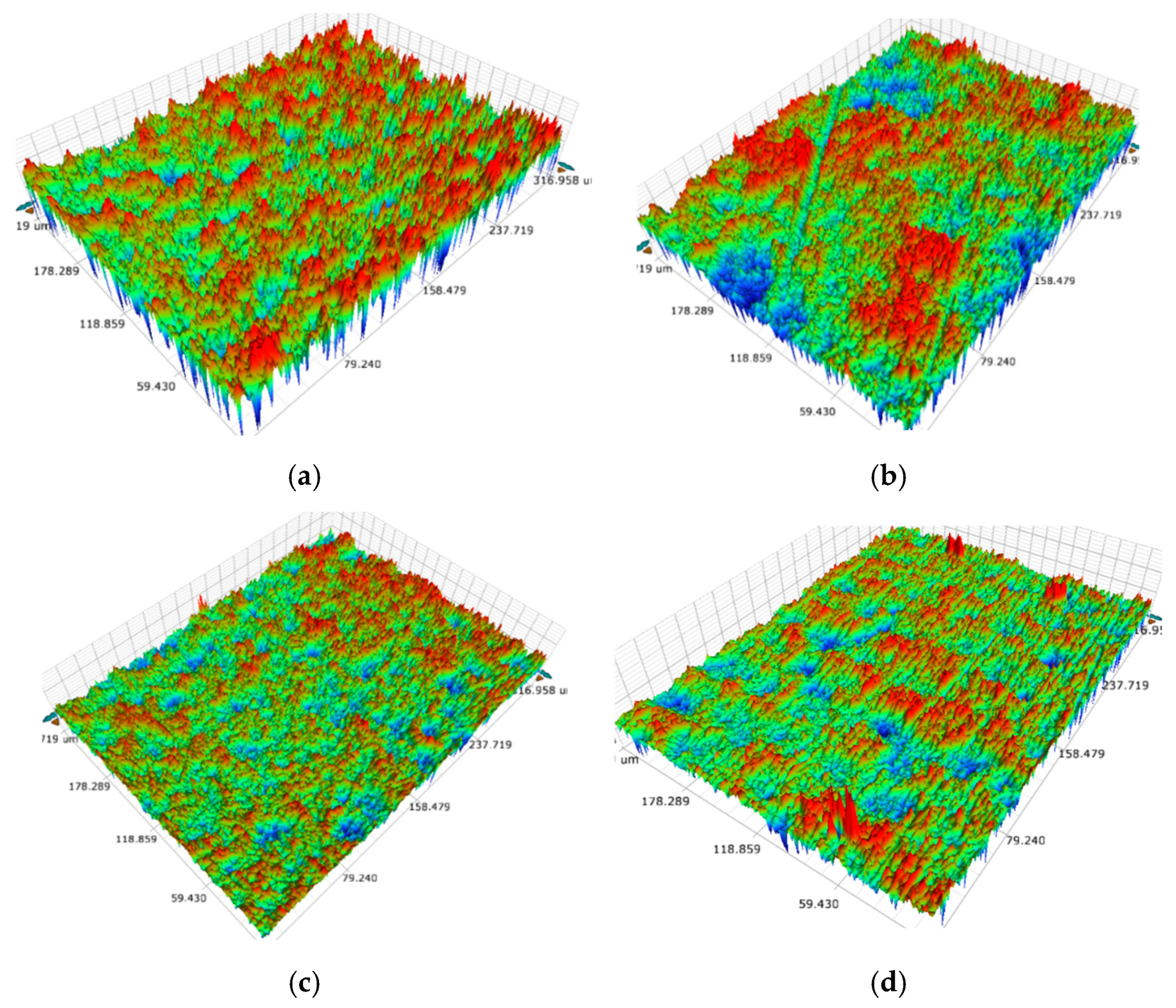
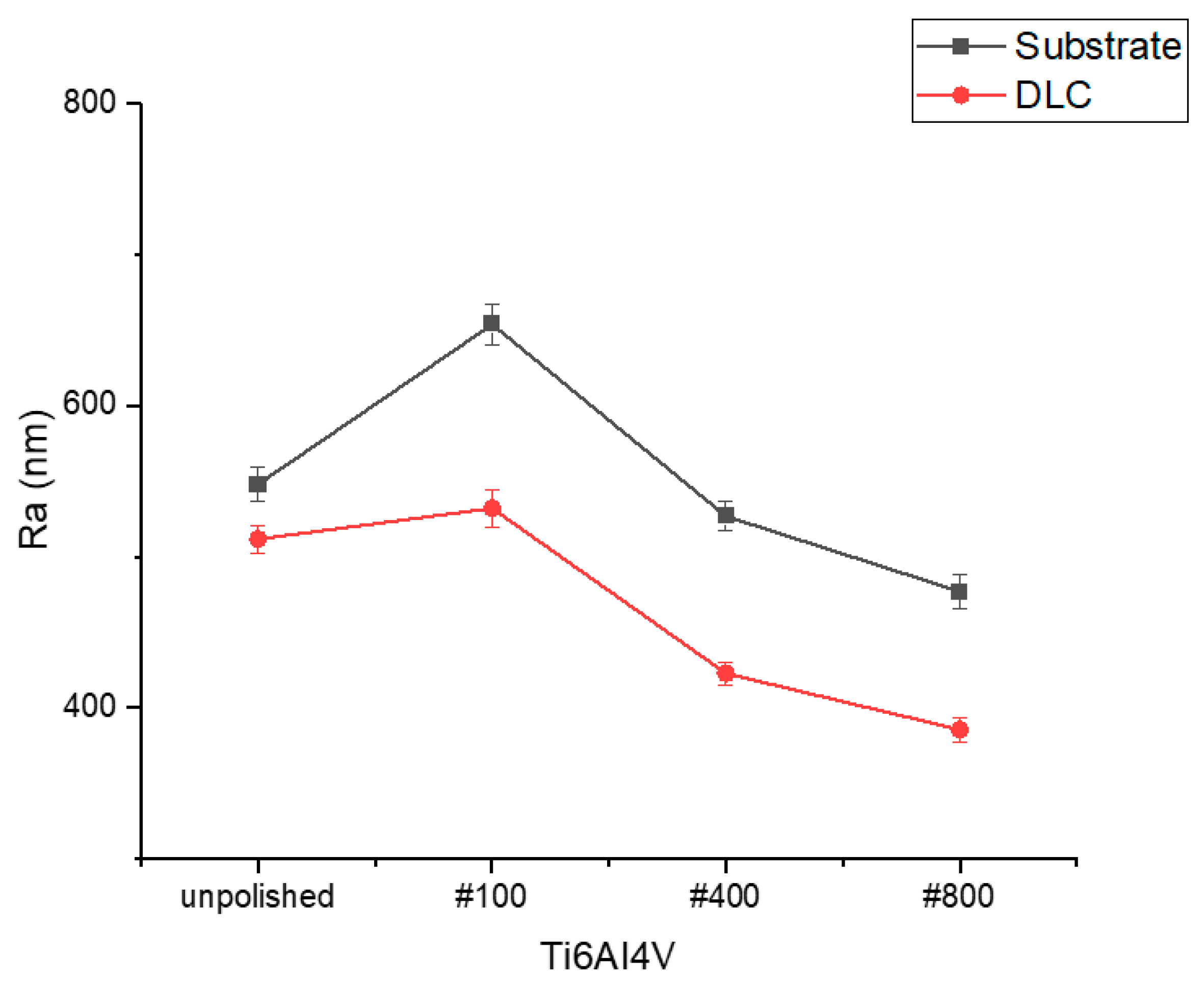
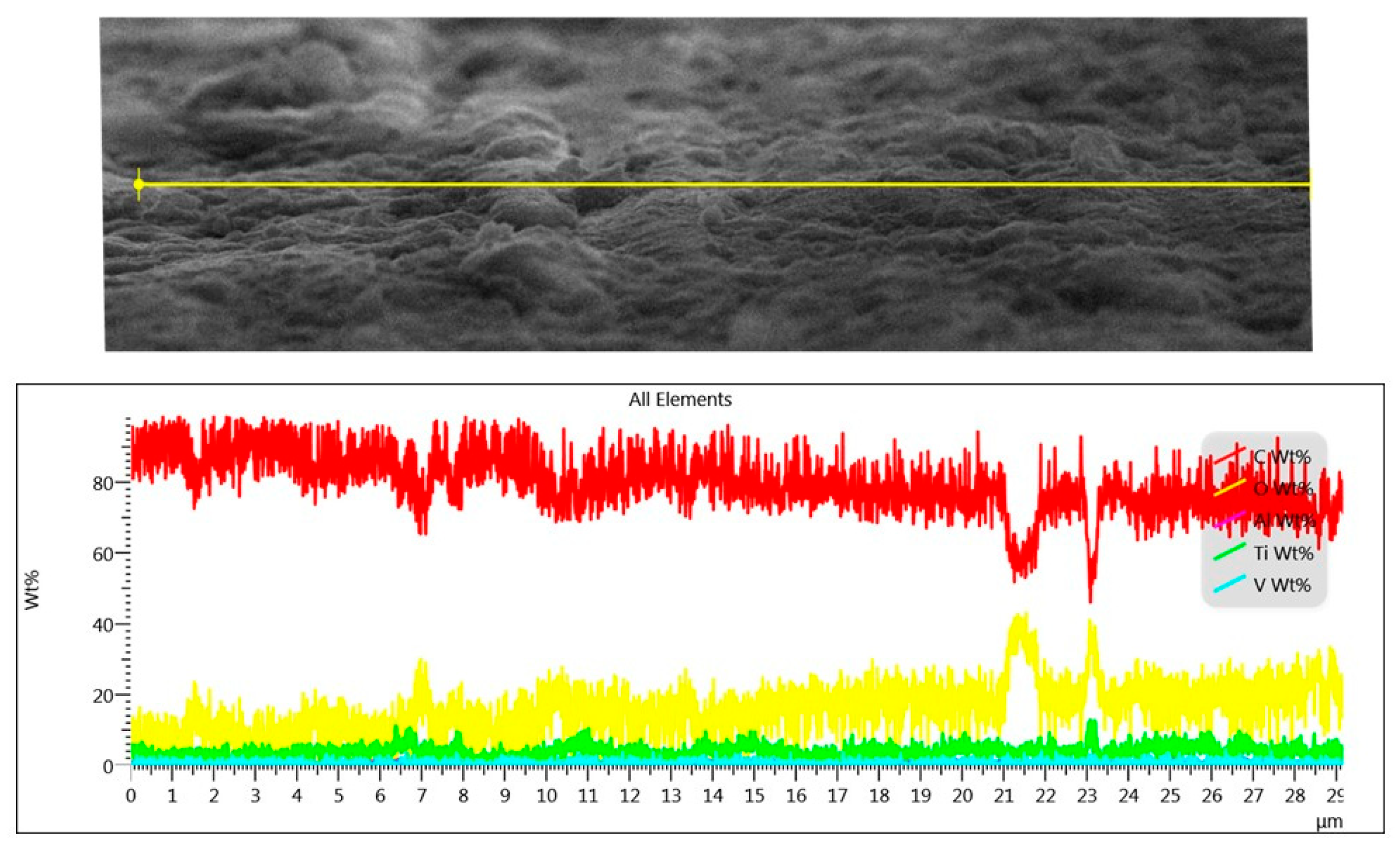
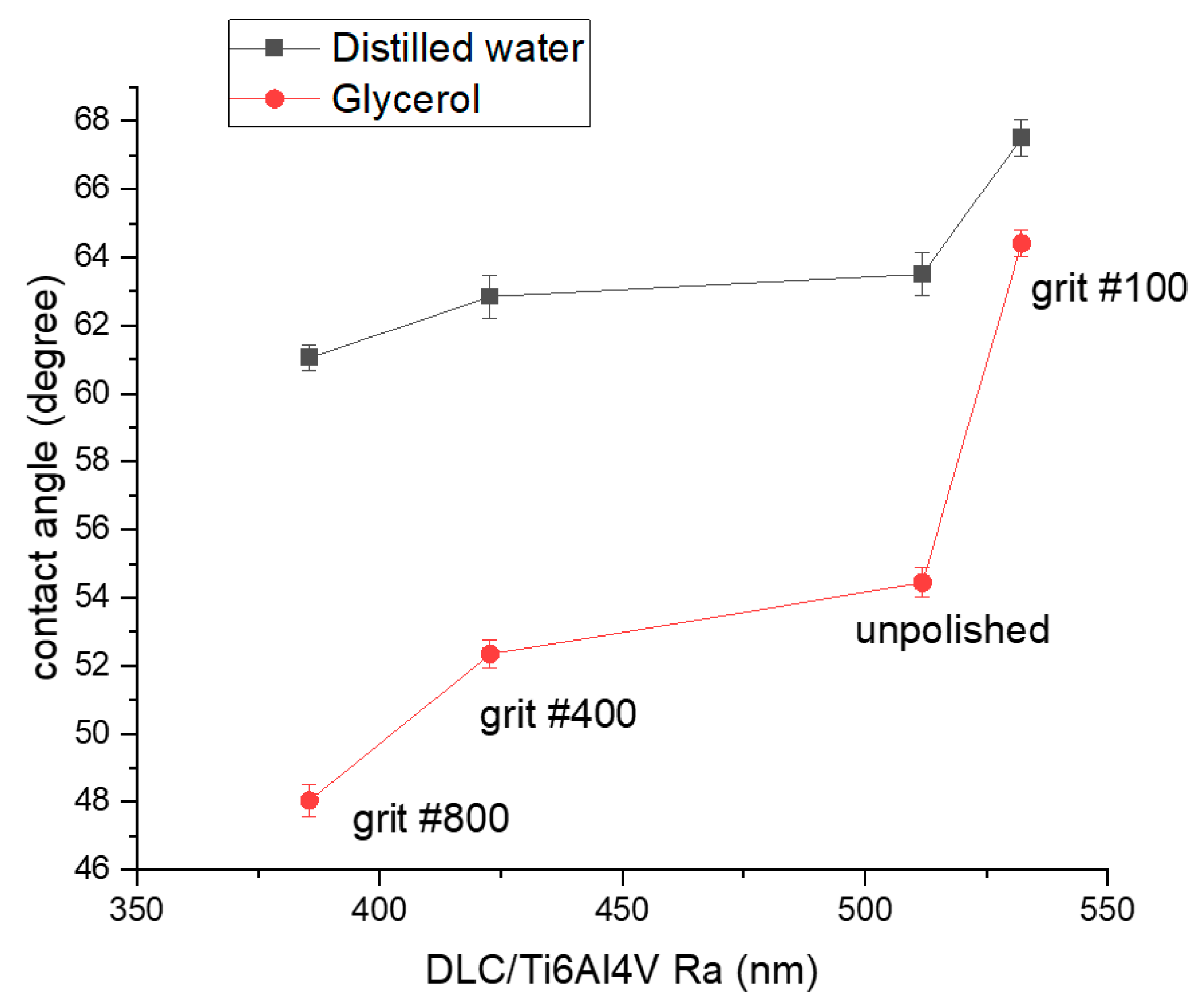
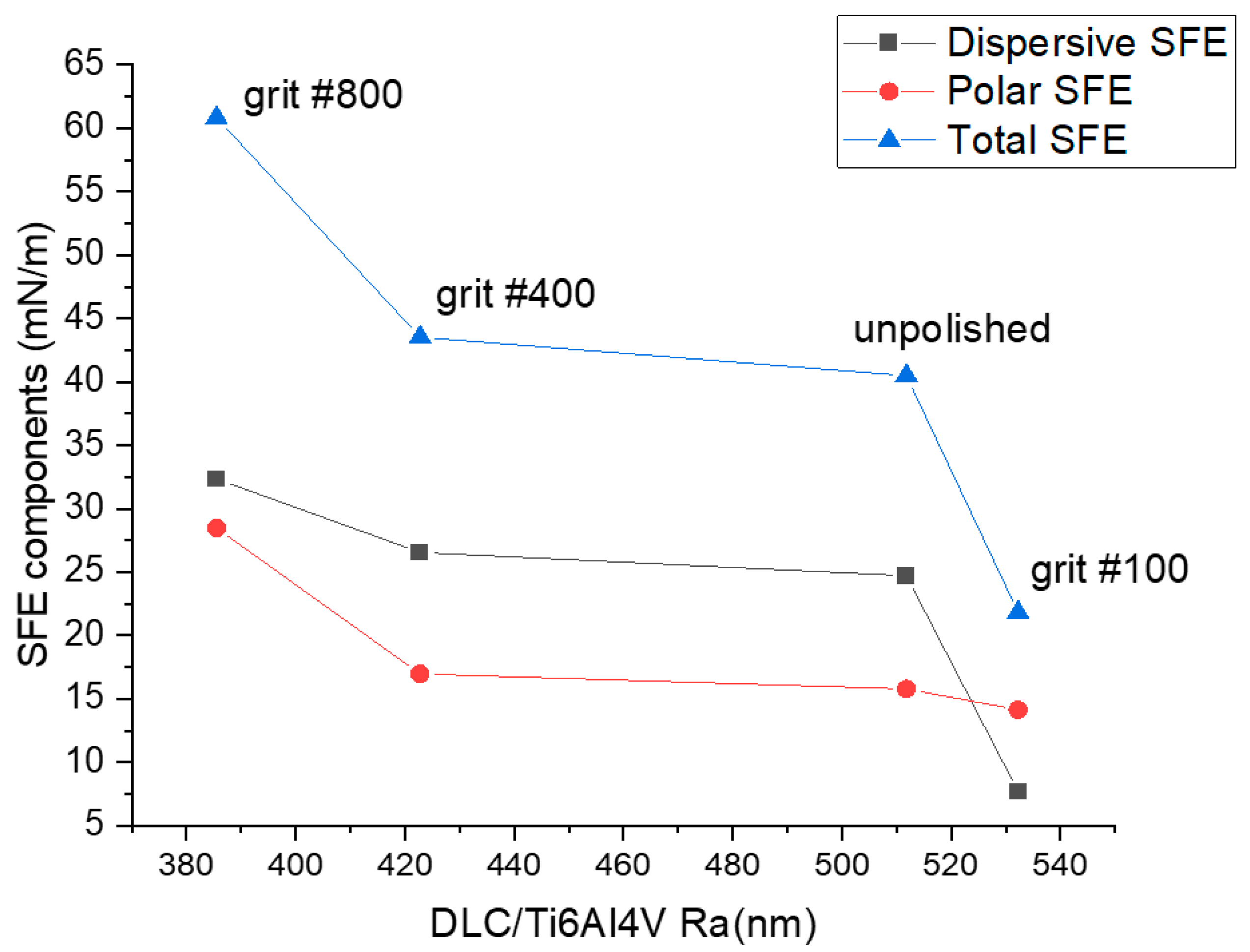
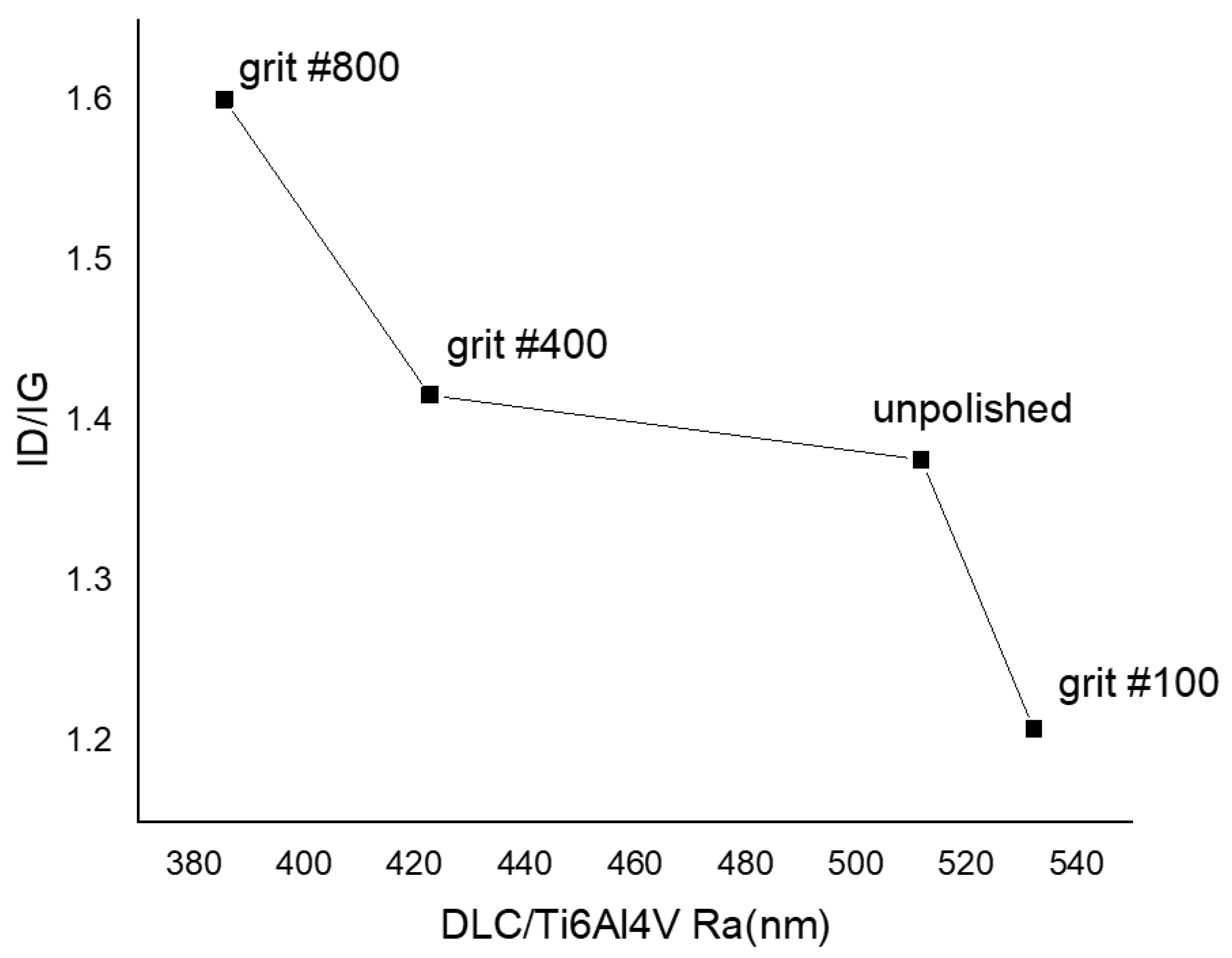
3.1. Surface Morphology, Wettability, and Surface Free Energy
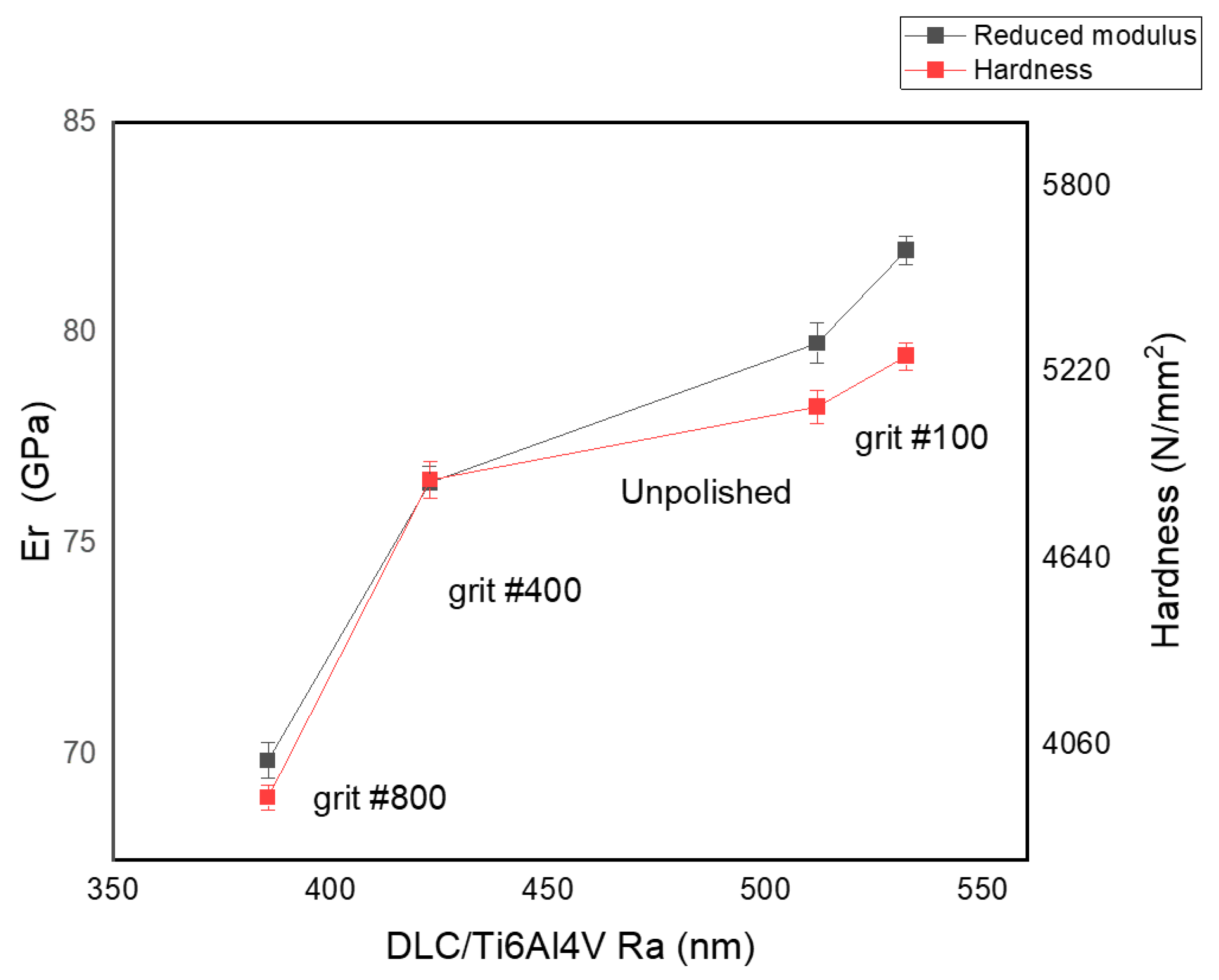
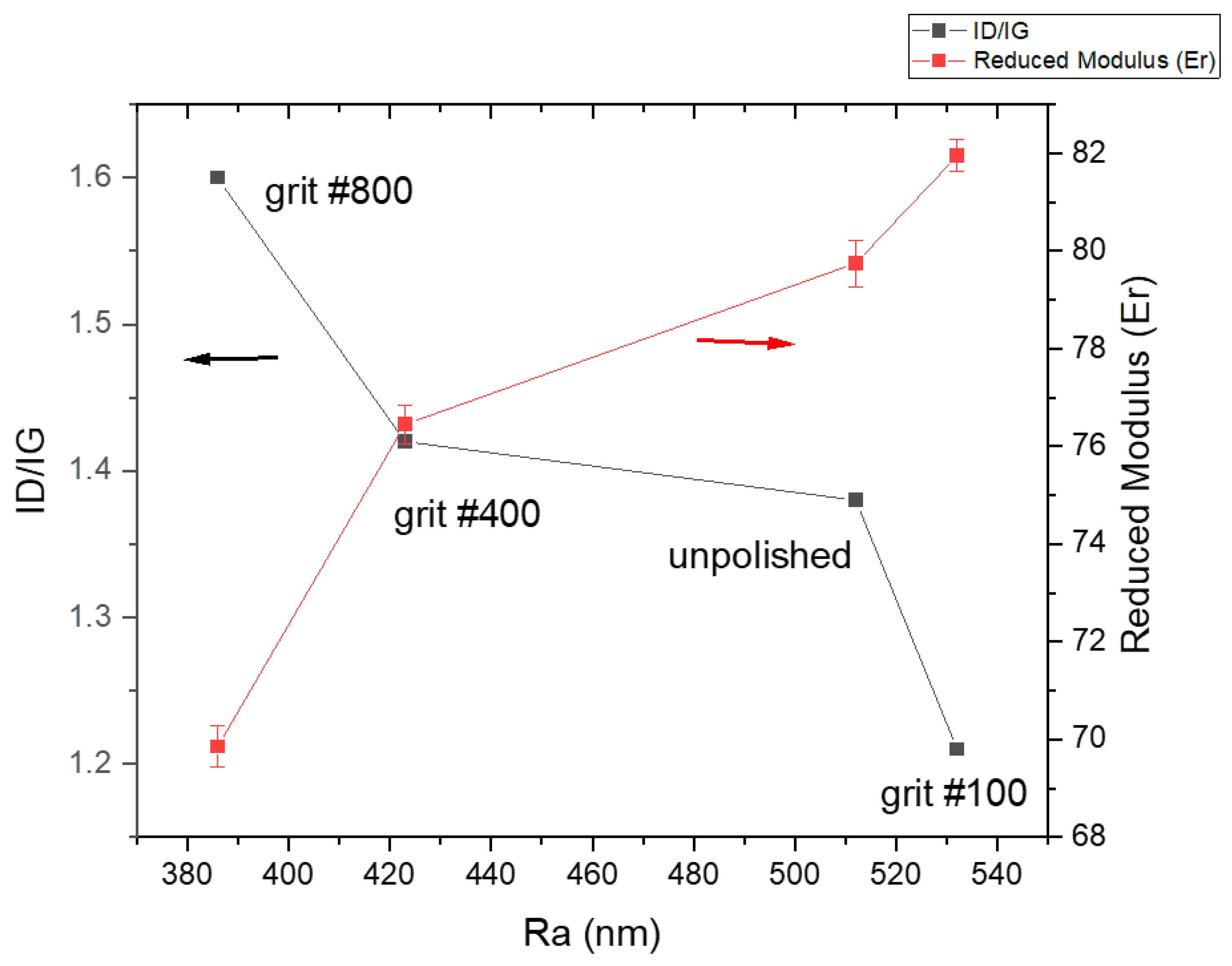
3.2. Mechanical Properties
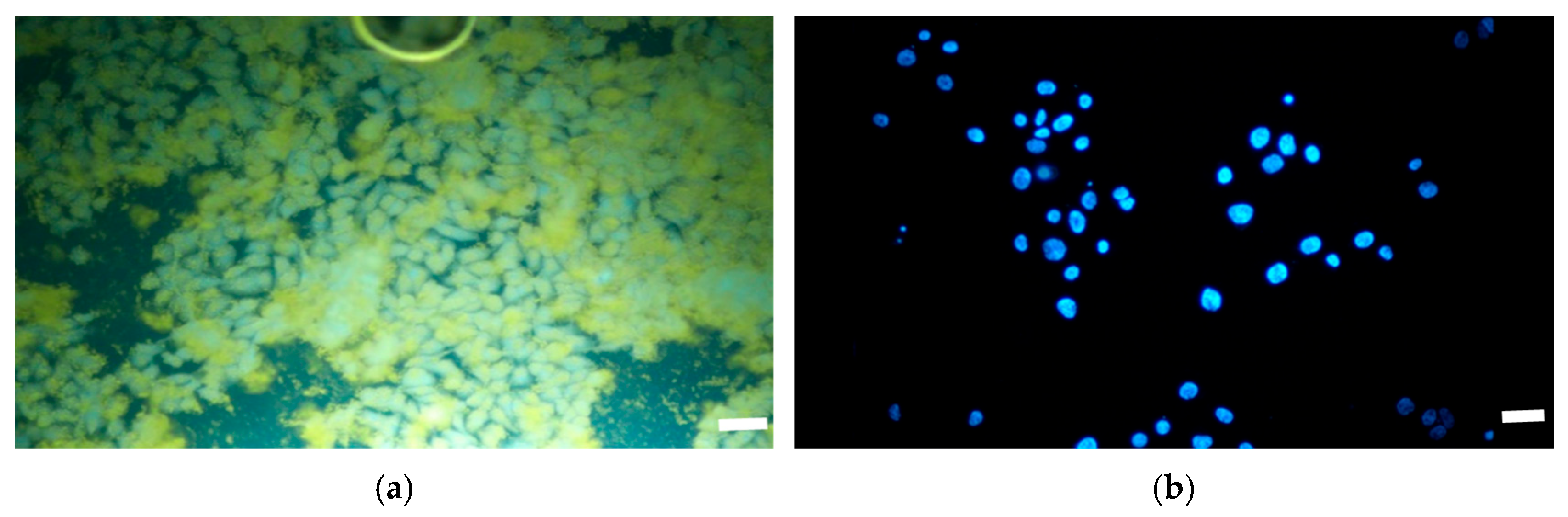
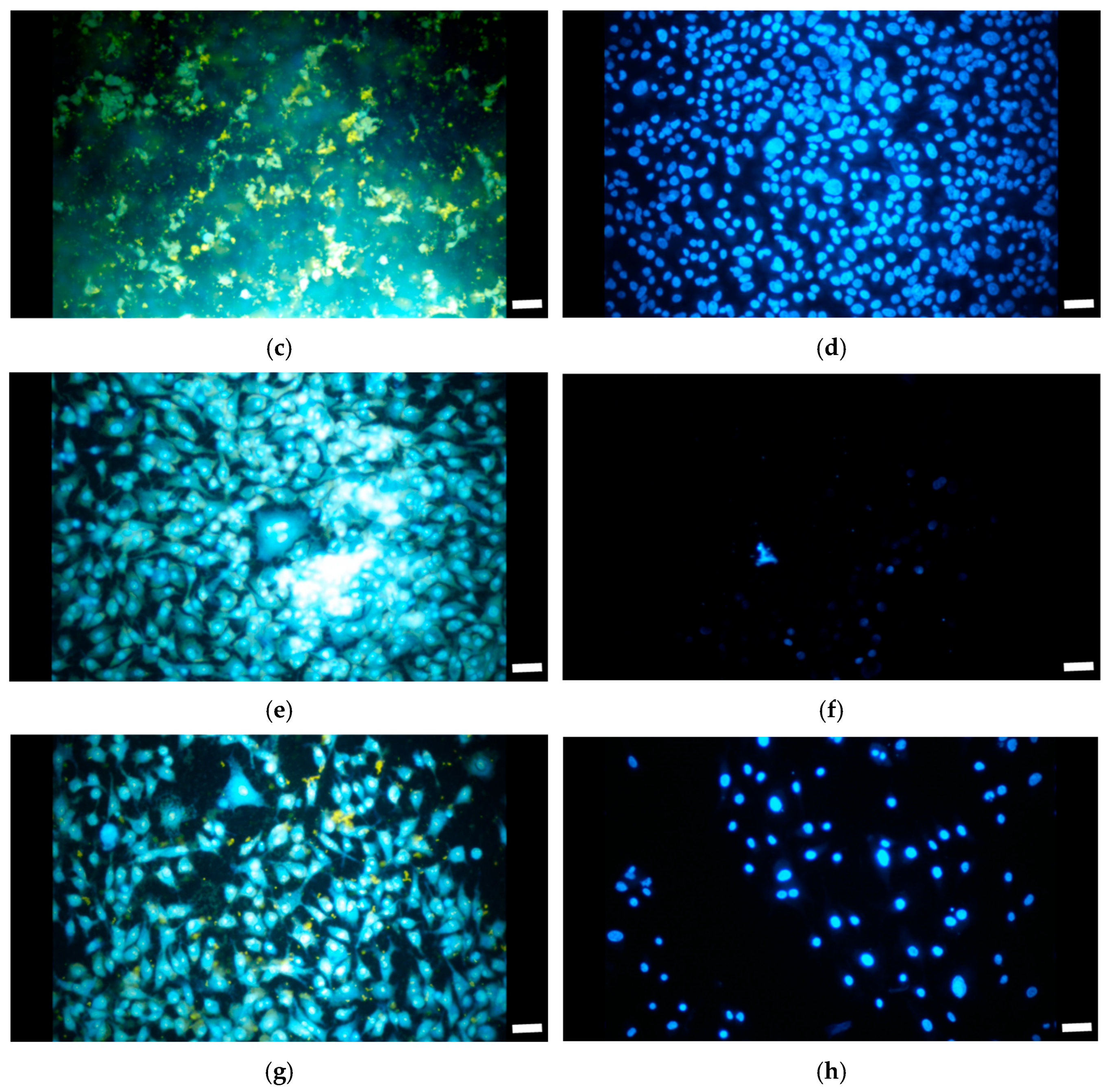
3.3. Cell Growth and Proliferation with A549 Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DLC | Diamond-like carbon |
| SFE | Surface free energy |
| IBD | Ion-beam deposition |
| AFM | Atomic force microscopy |
| SEM | Scanning electron microscopy |
| EDS | Energy-dispersive spectroscopy |
| Ra | Surface roughness (arithmetical mean) |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| H | Hardness |
| Er | Reduced modulus |
References
- Ramakrishna, S.; Mayer, J.; Wintermantel, E.; Leong, K.W. Biomedical applications of polymer–composite materials: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1189–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, D.L.; Gresser, J.D.; Trantolo, D.J.; Cattaneo, M.V.; Lewandrowski, K.-U.; Yaszemski, M.J. Biomaterials Engineering and Devices: Human Applications; Volume 2: Orthopedic, Dental, and Bone Graft Applications; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.B.; Bronzino, J.D. (Eds.) Biomaterials: Principles and Applications, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeppner, D.W.; Chandrasekaran, V. Fretting in orthopaedic implants: A review. Wear 1994, 173, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Gotoh, E. Comparison of metal release from various metallic biomaterials in vitro. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wapner, K.L. Implications of metallic corrosion in total knee arthroplasty. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1991, 271, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, J.C.M.; Sordi, M.B.; Kanazawa, M.; Ravindran, S.; Henriques, B.; Silva, F.S.; Aparicio, C.; Cooper, L.F. Nano-scale modification of titanium implant surfaces to enhance osseointegration. Acta Biomater. 2019, 94, 112–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Mao, L.; Shi, Y.; Fu, W.; Hu, Y. Biocompatibility of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy implants with laser microgrooved surfaces. Mater. Technol. 2020, 37, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, M.; Zhang, S.; Qiu, J.; Liu, G.; Guo, F.; Xu, J.; Chen, M. Enhanced tribological properties and cyto-biocompatibility of dental Ti6Al4V alloy via laser surface texturing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 33, 4105–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melo-Fonseca, F.; Gasik, M.; Freitas, P.P.; Carvalho, D.N.; Pinto, I.M.; Silva, F.S.; Miranda, G. Hydrothermal treatment of laser micro-textured Ti6Al4V systems for osseointegration of orthopaedic implants. Opt. Laser Eng. 2024, 183, 108511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Mu, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, Y.; Ma, Z.; Xu, J.; Di, K. Enhanced wear resistance, corrosion resistance and biocompatibility on micro-texture Ti6Al4V surfaces by pulse laser remelted. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 513, 132528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Gaddam, A.; Naveena, H.A.; Prajapati, D.; Dimov, S.; Bhatia, D.; Mishra, A.; Sofronov, Y.; Vadali, M. Improving the cell adhesion and antibacterial behaviour on Ti6Al4V through micro and nano hierarchical laser surface texturing. Surf. Interfaces 2025, 58, 105857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelínek, M.; Smetana, K.; Kocourek, T.; Dvořánková, B.; Zemek, J.; Remsa, J.; Luxbacher, T. Biocompatibility and sp3/sp2 Ratio of Laser Created DLC Films. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2010, 169, 89–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Pan, W.-J.; Hung, M.-S. The Effects of Substrate Roughness and Associated Surface Properties on the Biocompatibility of Diamond-Like Carbon Films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 224, 8–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Peng, K.-S.; Hung, M.-S. The Effect of Hydrogen and Acetylene Mixing Ratios on the Surface, Mechanical and Biocompatible Properties of Diamond-Like Carbon Films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2016, 63, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotzmann, G.; Beckmann, J.; Scholz, B.; Herrmann, U.; Wetzel, C. Low-Energy Electron-Beam Modification of DLC Coatings Reduces Cell Count While Maintaining Biocompatibility. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 336, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongpanya, P.; Pintitraratibodee, N.; Thumanu, K.; Euaruksakul, C. Improvement of Corrosion Resistance and Biocompatibility of 316L Stainless Steel for Joint Replacement Application by Ti-Doped and Ti-Interlayered DLC Films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 425, 127734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; He, Z.; Huang, H.; He, F.; Chen, Y.; Wu, P.; Li, M.; Penkov, O.V.; Wu, H. Improved biocompatibility of durable Si-DLC periodical nanocomposite coatings modified by plasma treatment for medical implants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2025, 695, 162907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Ren, L.; Guo, C.; Liang, L.; Dai, Y.; Tang, K.; Lu, L.; Qi, F.; She, J.; Wang, L.; et al. Enhanced Corrosion Resistance, Mechanical Properties, and Biocompatibility of N-DLC Coatings Prepared on WE43 Alloy via FCVA Technology. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 178106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Bu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.; Wu, L. Photochemical grafting of fluorinate alkenes on DLC coated Ti6Al4V to improve in vitro cytocompatibility, friction and corrosion resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 208, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joska, L.; Fojt, J.; Mestek, O.; Cvrcek, L.; Brezina, V. The effect of a DLC coating adhesion layer on the corrosion behavior of titanium and the Ti6Al4V alloy for dental implants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2012, 206, 4899–4906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabarczyk, J.; Gaj, J.; Pazik, B.; Kaczorowski, W.; Januszewicz, B. Tribocorrosion behavior of Ti6Al4V alloy after thermo-chemical treatment and DLC deposition for biomedical applications. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rojas, F.; Kovylina, M.; Pinilla-Cienfuegos, E.; Borrero-López, Ó.; Bendavid, A.; Martin, P.J.; Hoffman, M. Effect of a DLC film on the sliding-wear behaviour of Ti6Al4V: Implications for dental implants. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2023, 460, 129409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Peng, J.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Qiu, X. Diamond-like carbon coatings in the biomedical field: Properties, applications and future development. Coatings 2022, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, R.; Pai, N.; Khandekar, R.; Aslam, R.; Wang, Q.; Yan, Z.; Rosenkranz, A. DLC coatings in biomedical applications—Review on current advantages, existing challenges, and future directions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 487, 131006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Arnell, R.D. The Effect of Substrate Surface Roughness on the Wear of DLC Coatings. Wear 2000, 239, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvadori, M.C.; Martins, D.R.; Cattani, M. DLC Coating Roughness as a Function of Film Thickness. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2006, 200, 5119–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoque, M.J.; Li, L.; Ma, J.; Cha, H.; Sett, S.; Yan, X.; Rabbi, K.F.; Ho, J.Y.; Khodakarami, S.; Suwala, J.; et al. Ultra-Resilient Multi-Layer Fluorinated Diamond-Like Carbon Hydrophobic Surfaces. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of Solid Surfaces to Wetting by Water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, M.S.; Borhan, A. A Volume-Corrected Wenzel Model. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 8875–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, T. An Essay on the Cohesion of Fluids. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. 1805, 95, 65–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owens, D.K.; Wendt, R.C. Estimation of the surface free energy of polymers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1969, 13, 1741–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Good, R.J. Contact Angle, Wetting, and Adhesion: A Critical Review. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1992, 6, 1269–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, M. Modification Methods of Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings and the Performance in Machining Applications. Coatings 2022, 12, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Nakatani, T.; Ousaka, D.; Oozawa, S.; Sasai, Y.; Kasahara, S. Development of Antimicrobial Surfaces Using Diamond-Like Carbon or Diamond-Like Carbon-Based Coatings. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, K.; Wang, F.; Zheng, W. Improving Frictional Properties of DLC Films by Surface Energy Manipulation. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11388–11394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifahmadian, O.; Pakseresht, A.; Mirzaei, S.; Eliáš, M.; Galusek, D. Mechanically Robust Hydrophobic Fluorine-Doped Diamond-Like Carbon Film on Glass Substrate. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2023, 138, 110252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczorowski, W.; Batory, D.; Szymański, W.; Lauk, K.; Stolarczyk, J. Barrier Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings on Polydimethylsiloxane Substrates. Materials 2022, 15, 3883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malisz, K.; Świeczko-Żurek, B.; Sionkowska, A. Preparation and Characterization of Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings for Biomedical Applications—A Review. Materials 2023, 16, 3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, N.; Rakowski, R.T.; Franks, J.; Woolliams, P.; Weaver, P.; Jones, B.J. The Effect of Substrate Geometry and Surface Orientation on the Film Structure of DLC Deposited Using PECVD. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 254, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pougoum, F.; Jedrzejczak, A.; Azzi, M.; Martinu, L.; Klemberg-Sapieha, J.-E. Effect of Interface Roughness on the Tribo-Corrosion Behavior of Diamond-Like Carbon Coatings on Titanium Alloy. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2022, 40, 033405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laumer, J.; O’Leary, S.K. An Adhesion Analysis of Thin Carbon Films Deposited onto Curved and Flat Ti-6Al-4V Substrates Using RF Magnetron Sputtering and Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition Techniques. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2019, 30, 5185–5193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Yang, J.-F. A Finite Element Analysis of the Effects of Residual Stress, Substrate Roughness and Non-Uniform Stress Distribution on the Mechanical Properties of Diamond-Like Carbon Films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2011, 20, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, F.C.; Lee, S.C.; Wei, C.H.; Tyan, S.L. Correlation between ID/IG Ratio from Visible Raman Spectra and sp2/sp3 Ratio from XPS Spectra of Annealed Hydrogenated DLC Film. Mater. Trans. 2006, 47, 1847–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentile, F.; Tirinato, L.; Battista, E.; Causa, F.; Liberale, C.; di Fabrizio, E.; Decuzzi, P. Cells Preferentially Grow on Rough Substrates. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 7205–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arima, Y.; Iwata, H. Effect of Wettability and Surface Functional Groups on Protein Adsorption and Cell Adhesion Using Well-Defined Mixed Self-Assembled Monolayers. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3074–3082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majhy, B.; Priyadarshini, P.; Sen, A.K. Effect of Surface Energy and Roughness on Cell Adhesion for Biosensor Applications. RSC Adv. 2021, 11, 15467–15476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.I.; Abrams, G.A.; Bertics, P.J.; Murphy, C.J.; Nealey, P.F. Epithelial Contact Guidance on Well-Defined Micro- and Nanostructured Substrates. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 1881–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Element | Ti | Al | V | Fe | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt%) | Balanced | 6.0% | 4.0% | ≤0.25% | ≤0.2% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wei, C.; Wu, B.-C.; Hung, M.-S. Effects of Ti6Al4V Substrate Roughness on the Surface Morphology, Mechanical Properties, and Cell Proliferation of Diamond-like Carbon Films. Coatings 2025, 15, 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091086
Wei C, Wu B-C, Hung M-S. Effects of Ti6Al4V Substrate Roughness on the Surface Morphology, Mechanical Properties, and Cell Proliferation of Diamond-like Carbon Films. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091086
Chicago/Turabian StyleWei, Chehung, Bo-Cheng Wu, and Min-Sheng Hung. 2025. "Effects of Ti6Al4V Substrate Roughness on the Surface Morphology, Mechanical Properties, and Cell Proliferation of Diamond-like Carbon Films" Coatings 15, no. 9: 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091086
APA StyleWei, C., Wu, B.-C., & Hung, M.-S. (2025). Effects of Ti6Al4V Substrate Roughness on the Surface Morphology, Mechanical Properties, and Cell Proliferation of Diamond-like Carbon Films. Coatings, 15(9), 1086. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091086







