Interfacial Diffusion and Copper Alloy Layer Wear Mechanism in Cu-20Pb-5Sn/45 Steel Bimetallic Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
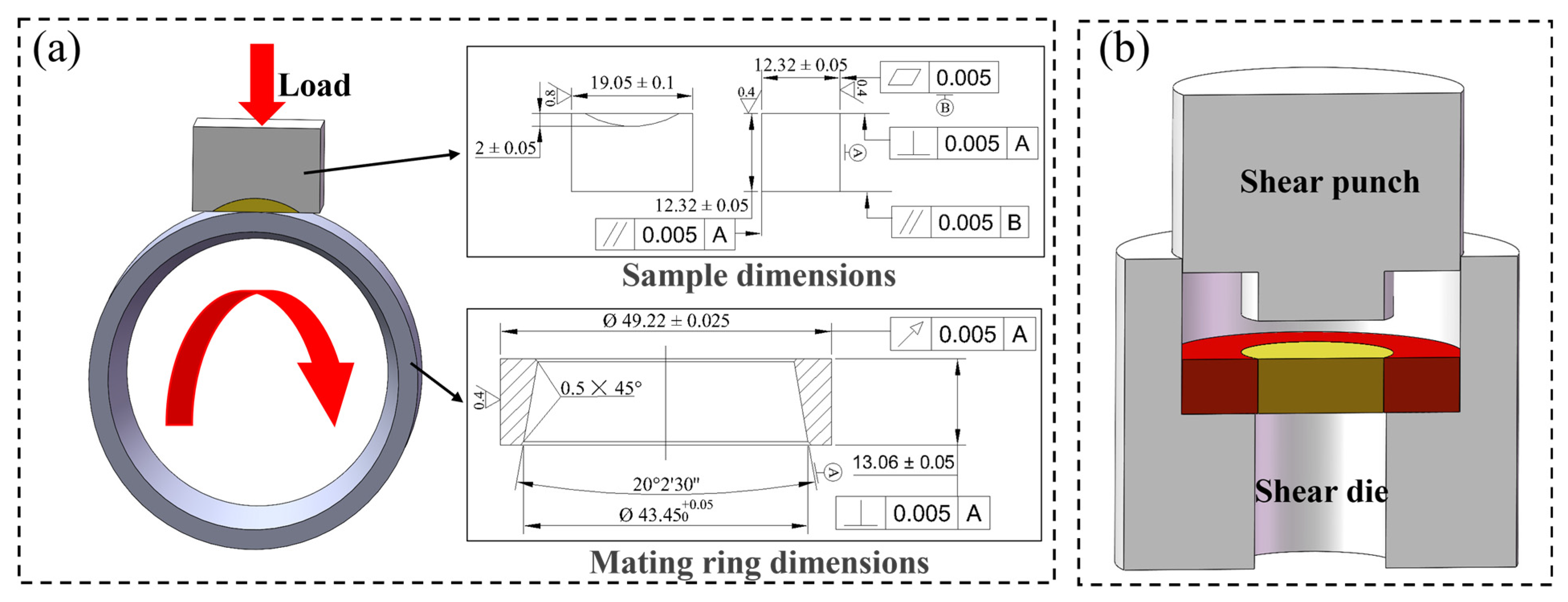
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Bimetallic Specimens
2.2. Microstructure and Performance Characterization
3. Results
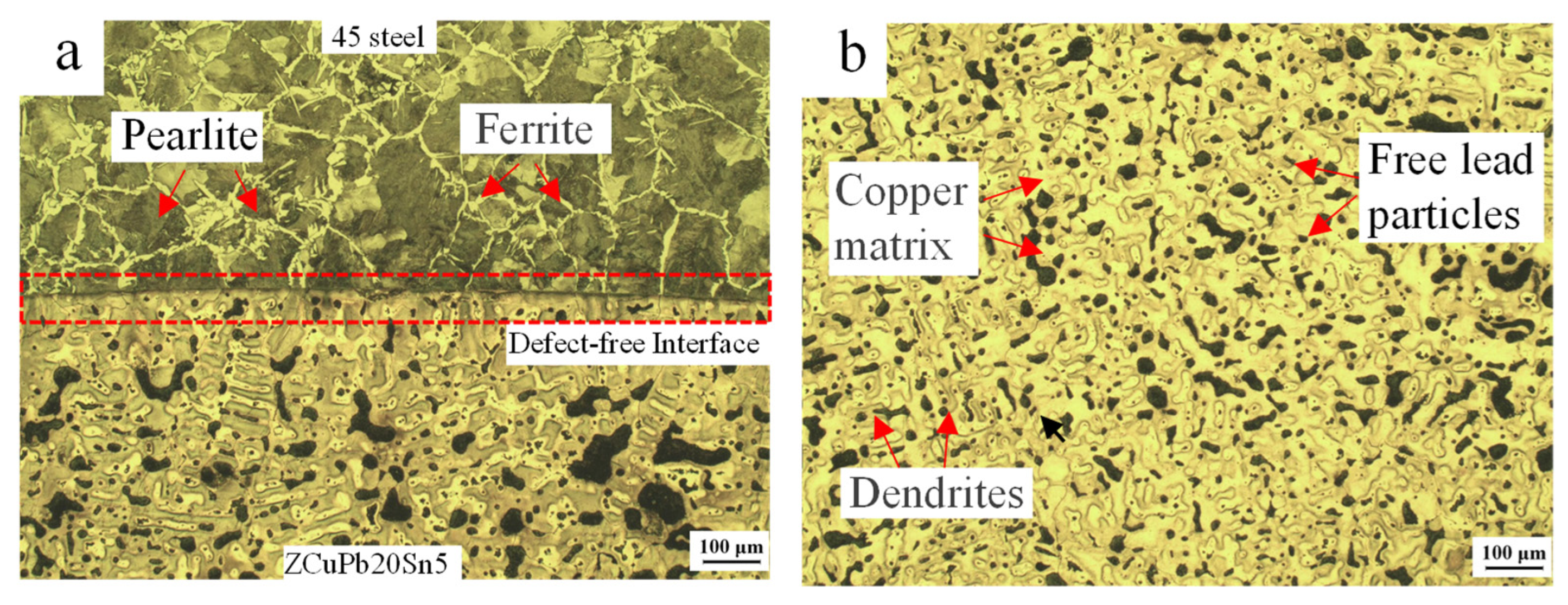
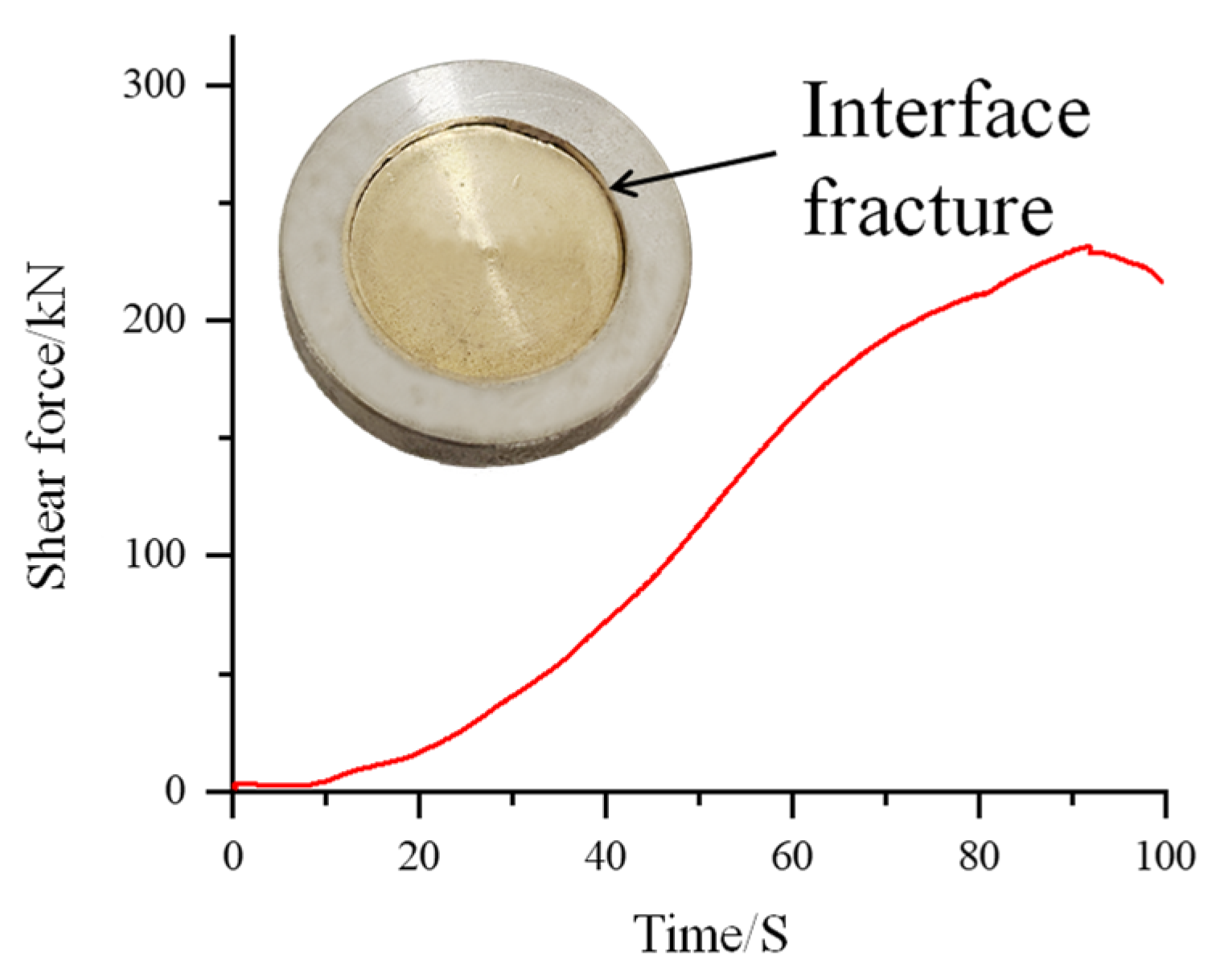
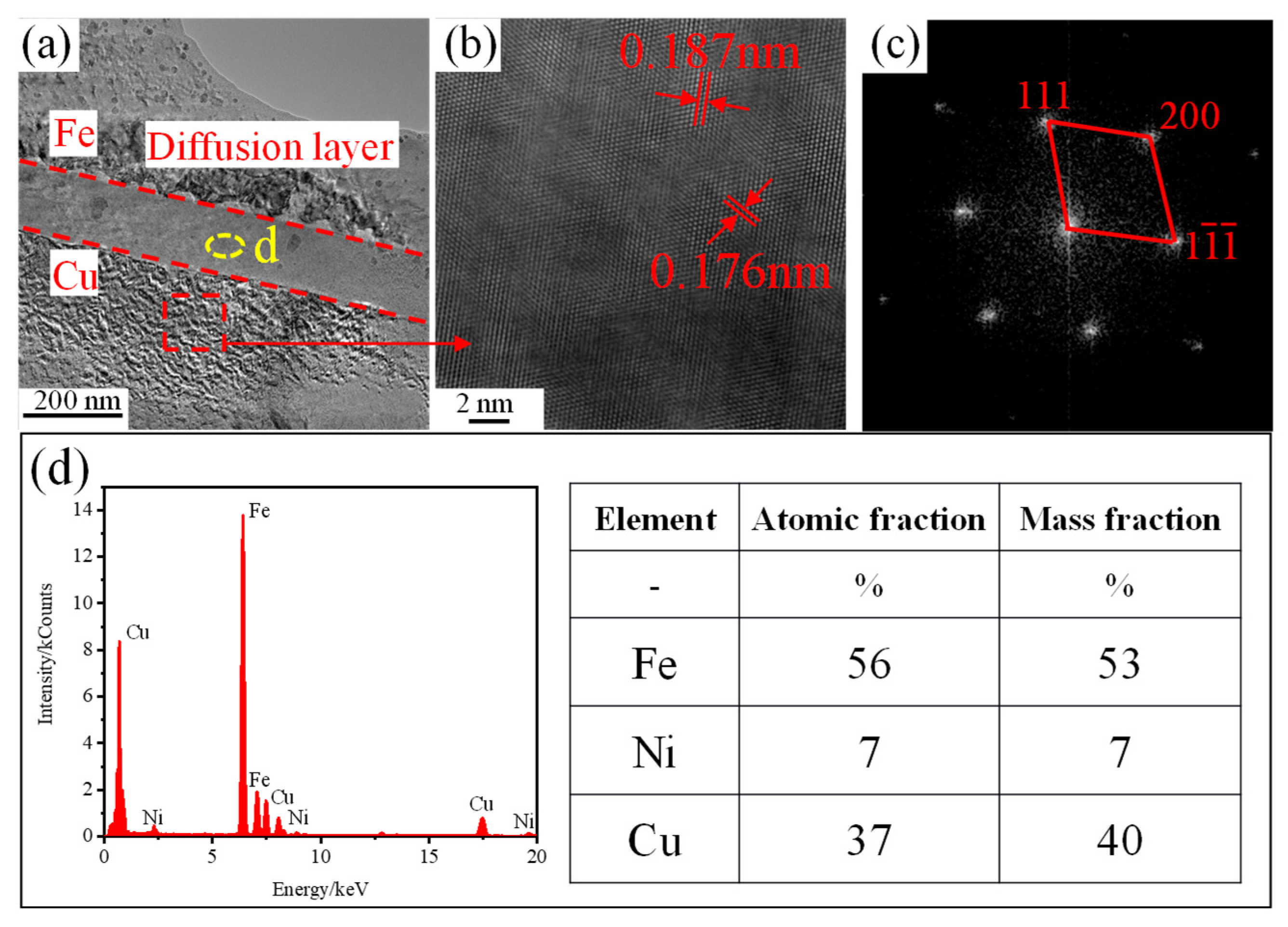
3.1. Microstructure and Properties of Cu-20Pb-5Sn/45 Steel Bimetallic Interface
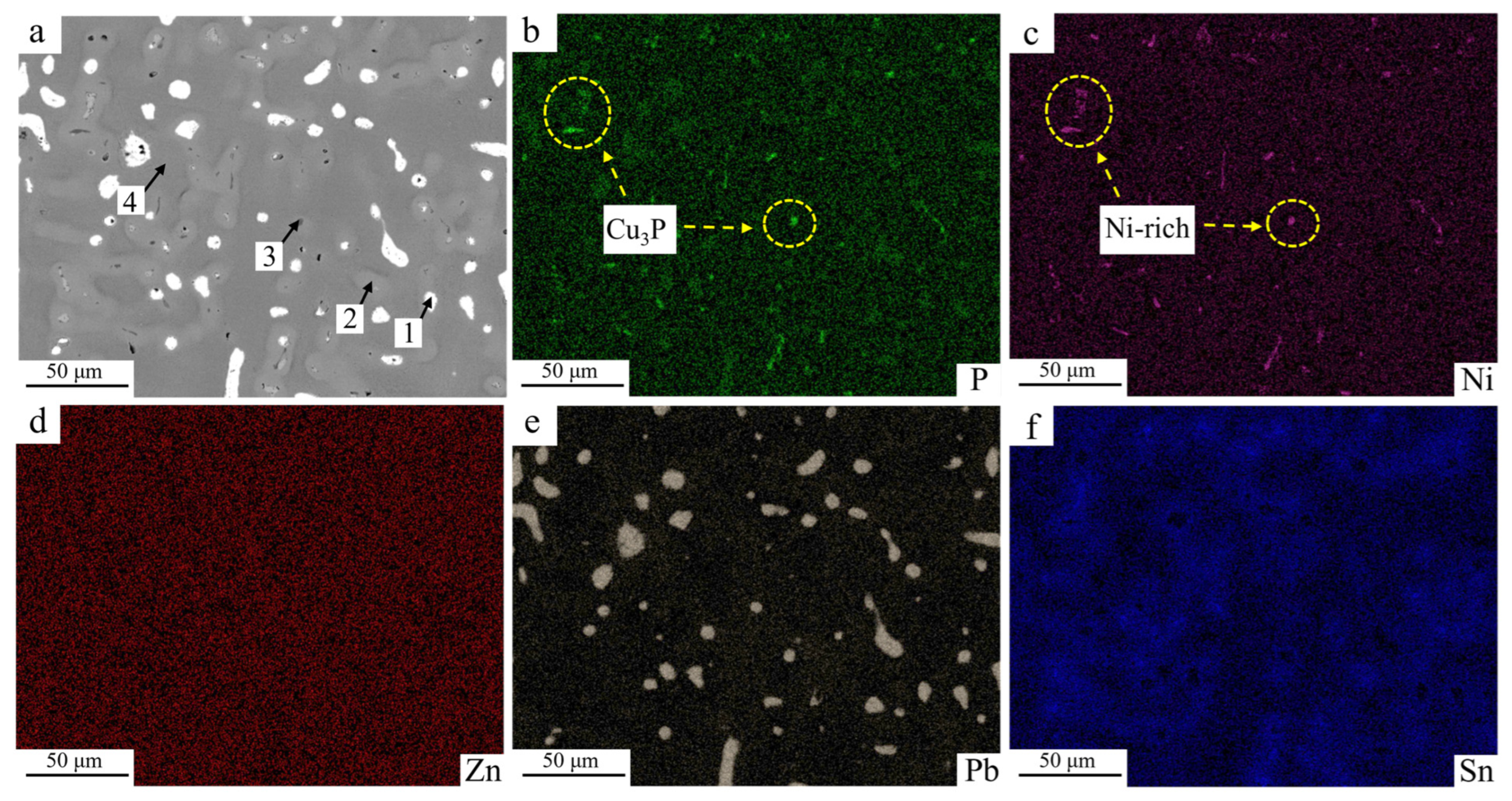
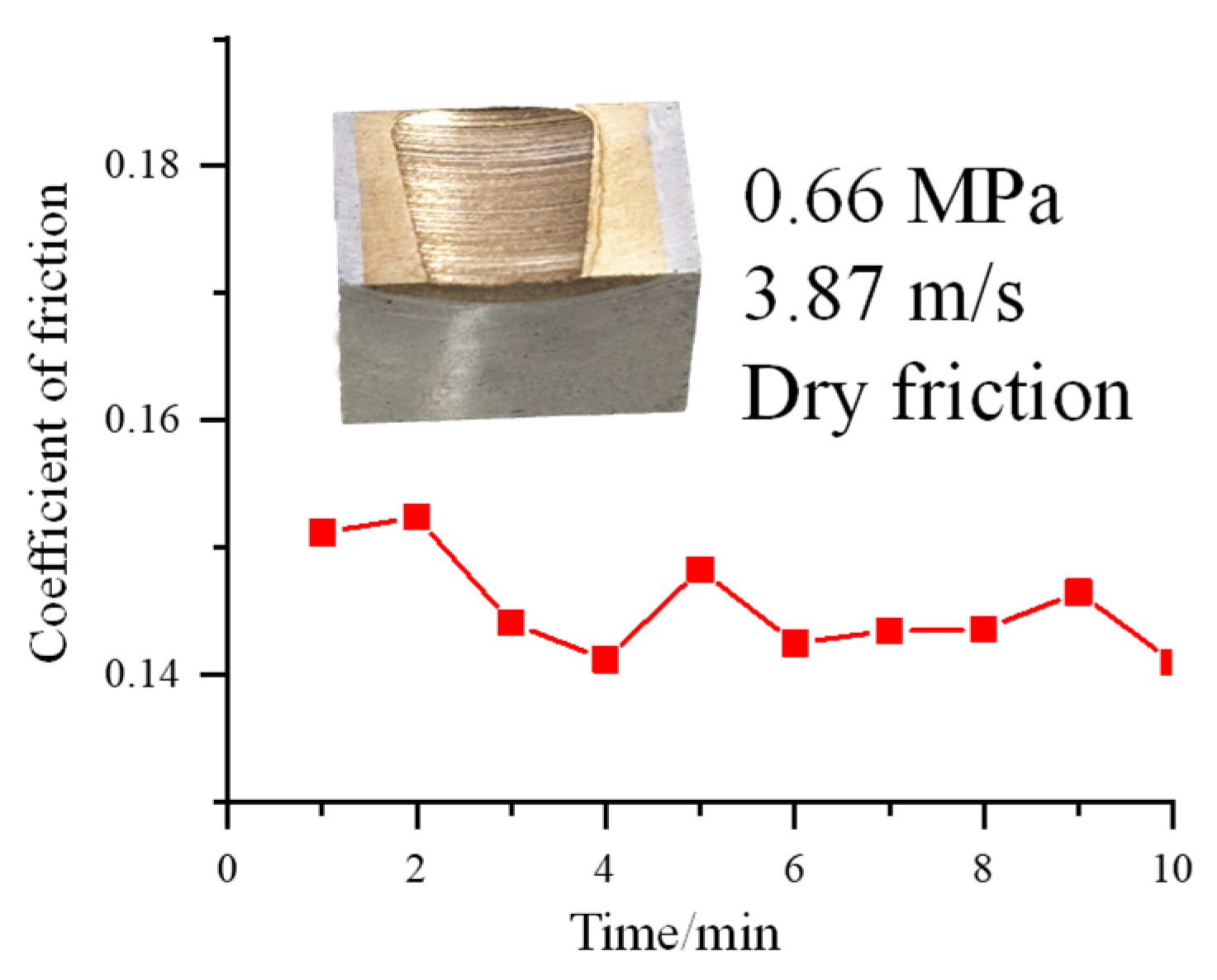
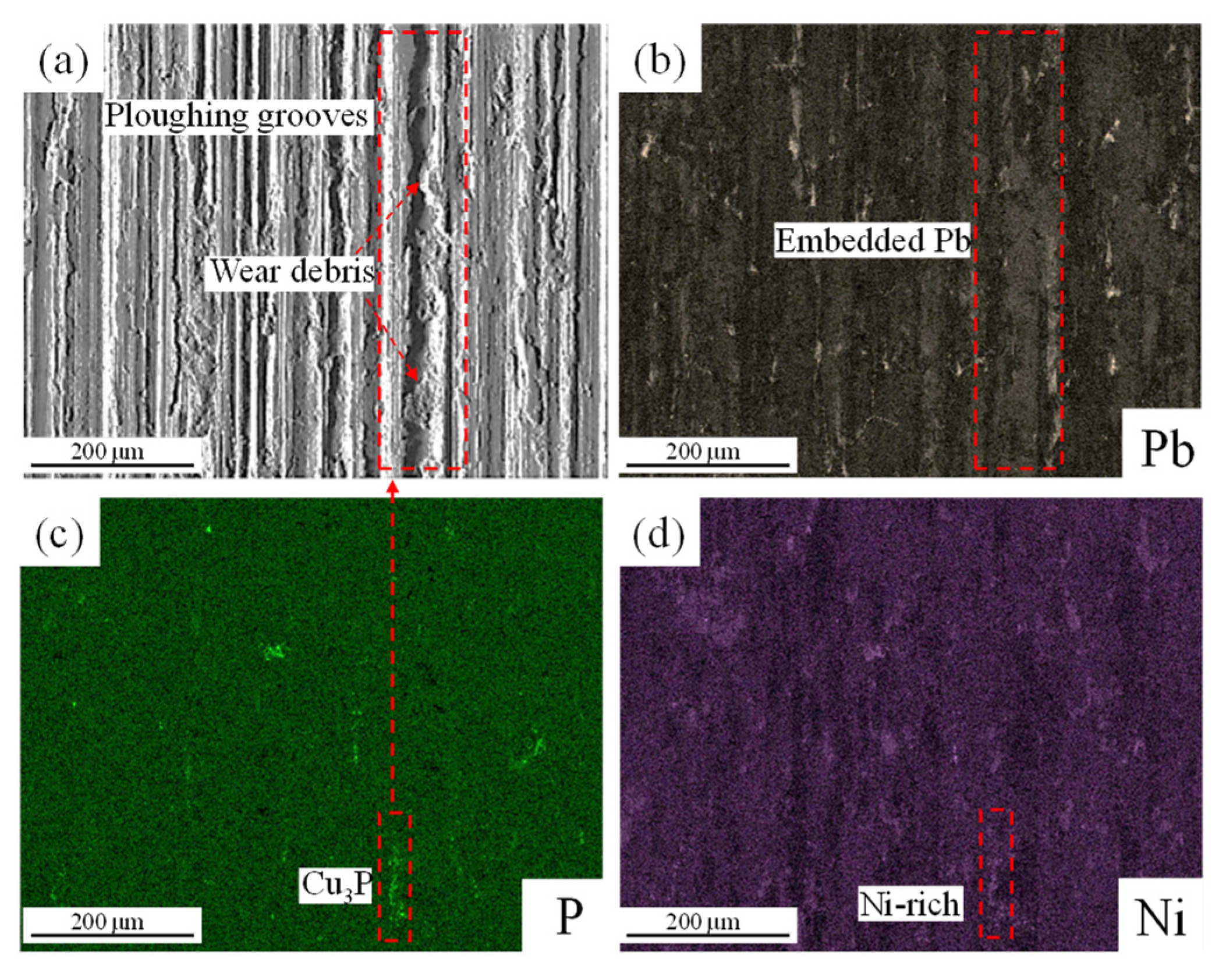
3.2. Microstructure and Properties of Cu-20Pb-5Sn/45 Steel Bimetallic Copper Alloy Layer
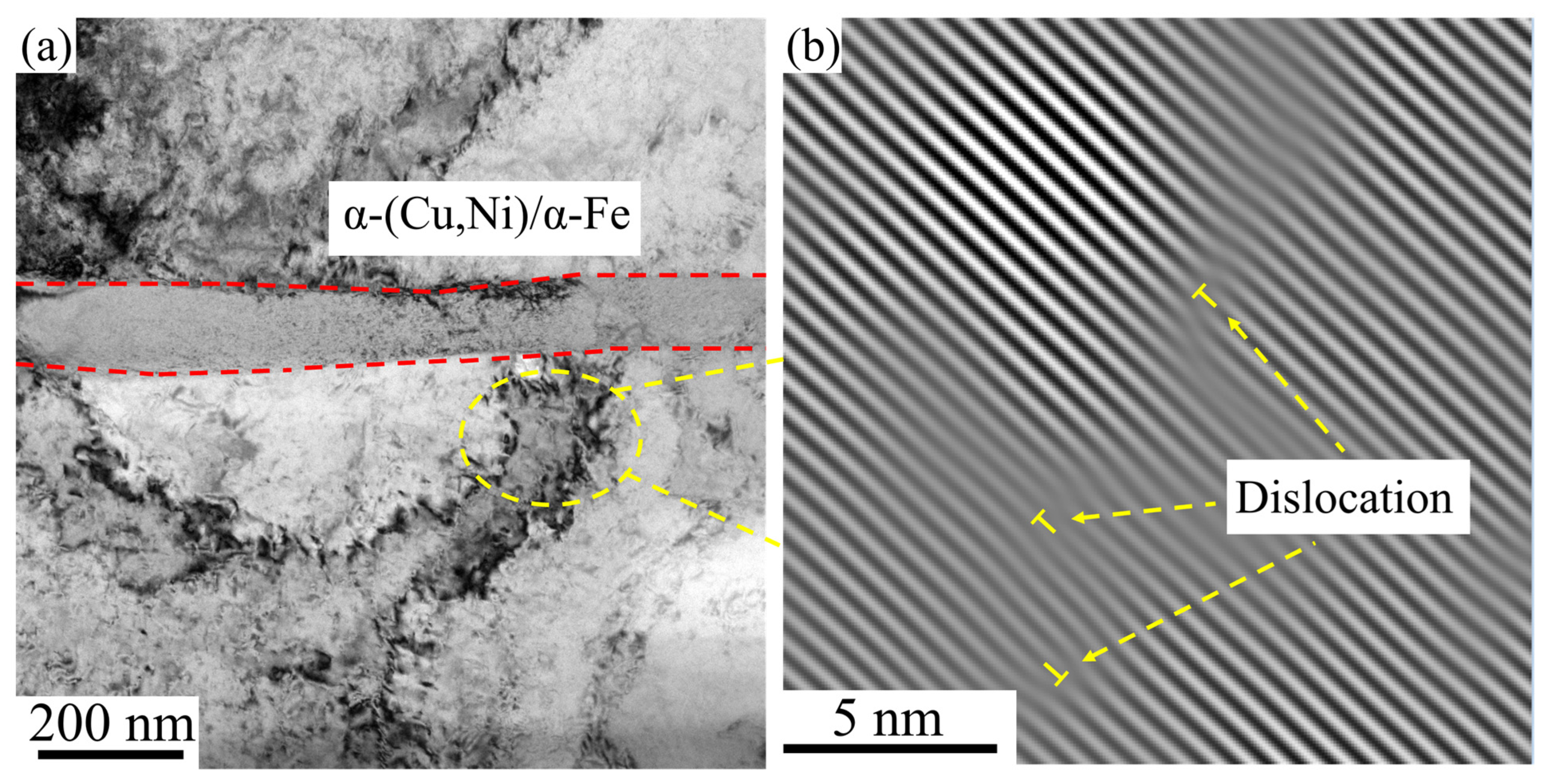
3.3. Interface Diffusion and Copper Alloy Layer Wear of the Mechanism Behavior
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The Cu-20Pb-5Sn/45 steel interface forms a metallurgically bonded α-(Cu,Ni)/α-Fe diffusion layer with an interfacial shear strength of 227.58 MPa. This high bonding strength results from the synergistic contribution of fine columnar grains in the diffusion layer and the interplay of high- and low-angle grain boundaries.
- (2)
- Under dry sliding conditions, the copper alloy layer exhibits a stable friction coefficient of 0.145 and a low wear rate of 7.3665 × 10−6 mm3/(N·m). The excellent tribological performance is primarily attributed to the α-(Cu,Ni) matrix reinforced by hard Cu3P and Ni-rich phases, which resist frictional shear stresses, while dispersed Pb particles provide self-lubricating properties.
- (3)
- The α-(Cu,Ni)/α-Fe solid-solution interface effectively impedes dislocation propagation to the diffusion layer under frictional loads, reducing dislocation pile-up. This interfacial blocking effect, combined with the hard phases and self-lubricating Pb particles in the copper alloy layer, ensures stable frictional behavior during sliding.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Osipovich, K.; Vorontsov, A.; Chumaevskii, A.; Gurianov, D.; Shamarin, N.; Savchenko, N.; Kolubaev, E. Characterization of a Bimetallic Multilayered Composite “Stainless Steel/Copper” Fabricated with Wire-Feed Electron Beam Additive Manufacturing. Metals 2021, 11, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senatore, A.; Risitano, G.; Scappaticci, L.; D’andrea, D. Investigation of the Tribological Properties of Different Textured Lead Bronze Coatings under Severe Load Conditions. Lubricants 2021, 9, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, F.; Schmitz, K. Geometric design of axial piston machine slipper-bearings made of high-performance plastics. Forsch. Ingenieurwesen 2025, 89, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bandyopadhyay, A.; Zhang, Y.; Onuike, B. Additive manufacturing of bimetallic structures. Virtual Phys. Prototyping. 2022, 17, 256–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.; Sharma, S.M. High Temperature Friction and Wear Characteristics of Fe–Cu–C Based Self-Lubricating Material. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2017, 70, 2641–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perini, M.; Silvestri, A.T. Multi-material bronze-steel plain bearings produced by laser-directed energy deposition. Rapid Prototyp. J. 2024, 30, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pervikov, A.; Khrustalyov, A.; Filippov, A.; Mironov, Y.; Lozhkomoev, A.; Lerner, M.; Tarasov, S. Structural, Mechanical, and Tribological Characterization of Magnetic Pulse Compacted Fe–Cu Bimetallic Particles Produced by Electric Explosion of Dissimilar Metal Wires. Metals 2019, 9, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zykova, A.; Chumaevskii, A.; Vorontsov, A.; Kalashnikov, K.; Gurianov, D.; Gusarova, A.; Kolubaev, E. Evolution of microstructure and properties of Fe-Cu, manufactured by electron beam additive manufacturing with subsequent friction stir processing. Mater. Lett. 2022, 307, 131023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Shi, Z.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xing, M.; Ren, X.; Xu, H. Study on the bonding mechanism and performance optimization of Cu-12Sn-2Ni/42CrMo bimetallic interface controlled by Ag doping. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 38, 3277–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xu, H.; Ren, X. Effect of electromagnetic stirring current on the microstructure, mechanical and tribological properties of copper/steel bimetal. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 47, 113126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Yan, Q.; Li, G.; Zhang, X. The Influence of Cu/Fe Ratio on the Tribological Behavior of Brake Friction Materials. Tribol. Lett. 2017, 66, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Raja, P.; Katiyar, J.K.; Ramkumar, P. Effect of friction modifiers compositions on tribological properties of Cu-Sn alloy/Al2O3 brake composite material. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2020, 235, 1541–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D′ANdrea, D.; Epasto, G.; Bonanno, A.; Guglielmino, E.; Benazzi, G. Failure analysis of anti-friction coating for cylinder blocks in axial piston pumps. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 104, 126–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Equey, S.; Houriet, A.; Mischler, S. Wear and frictional mechanisms of copper-based bearing alloys. Wear 2011, 273, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Tang, B.; Wang, L.; Wang, D.; Dong, W.; Li, X. Microstructure, Microhardness and Tribological Properties of Bronze–Steel Bimetallic Composite Produced by Vacuum Diffusion Welding. Materials 2022, 15, 1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, C. Improved interfacial strength in bimetallic additive manufacturing of aluminum bronze/steel by controlling interface melting. J. Manuf. Process. 2024, 121, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mašović, R.; Miler, D.; Čular, I.; Jakovljević, S.; Šercer, M.; Žeželj, D. The Effect of Steel Electropolishing on the Tribological Behavior of a Steel–Bronze Pair in the Mixed and Boundary Lubrication Regimes. Lubricants 2023, 11, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.A.; Bairrão, N.; Farias, F.W.C.; Shamsolhodaei, A.; Shen, J.; Zhou, N.; Maawad, E.; Schell, N.; Santos, T.G.; Oliveira, J. Steel-copper functionally graded material produced by twin-wire and arc additive manufacturing (T-WAAM). Mater. Des. 2022, 213, 110270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Husseiny, M.M.; Baraka, A.A.; Oraby, O.; El-Danaf, E.A.; Salem, H.G. Fabrication of Bimetallic High-Strength Low-Alloy Steel/Si-Bronze Functionally Graded Materials Using Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2023, 7, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirsöz, R. Wear Behavior of Bronze vs. 100Cr6 Friction Pairs under Different Lubrication Conditions for Bearing Applications. Lubricants 2022, 10, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhai, W.; Sun, L.; Zhang, C. Review of preparation and application of copper–steel bimetal composites. Emerg. Mater. Res. 2019, 8, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, S.; Kusekar, S.; Belure, A.; Digole, S.; Mali, A.; Cheepu, M.; Mugale, M.; Alkunte, S.; Kim, D. Recent Progress and Scientific Challenges in Wire-Arc Additive Manufacturing of Metallic Multi-Material Structures. J. Manuf. Mater. Process. 2025, 9, 284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Meng, X.; Chen, Y.; Cao, H. A review of multi-material composite gears: Integration of lightweight and transmission performance. Thin-Walled Struct. 2025, 216, 113666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kondo, S.; Mitsuma, T.; Shibata, N.; Ikuhara, Y. Direct observation of individual dislocation interaction processes with grain boundaries. Sci. Adv. 2016, 2, e1501926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudina, D.V.; Tokarev, V.G. Copper matrix composites with metallic reinforcements. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2025, 78, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drescher, S.; Kuzmin, A.; Welter, E.; Freudenberger, J.; Smekhova, A. Component-dependent lattice distortions and atomic scale insights in multi-component Au-Cu-Ni-Pd-Pt based alloys. Nano Res. 2025, 18, 94907122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rau, J.S.; Balachandran, S.; Schneider, R.; Gumbsch, P.; Gault, B.; Greiner, C. High diffusivity pathways govern massively enhanced oxidation during tribological sliding. Acta Mater. 2021, 221, 117353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greiner, C.; Liu, Z.; Schneider, R.; Pastewka, L.; Gumbsch, P. The origin of surface microstructure evolution in sliding friction. Scr. Mater. 2018, 153, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haug, C.; Ruebeling, F.; Kashiwar, A.; Gumbsch, P.; Kübel, C.; Greiner, C. Early deformation mechanisms in the shear affected region underneath a copper sliding contact. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruebeling, F.; Xu, Y.; Richter, G.; Dini, D.; Gumbsch, P.; Greiner, C. Normal Load and Counter Body Size Influence the Initiation of Microstructural Discontinuities in Copper during Sliding. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 4750–4760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Dao, M.; Lu, L.; Suresh, S. Deformation, structural changes and damage evolution in nanotwinned copper under repeated frictional contact sliding. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 7311–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Component | C | Si | Mn | Pb | Sn | Zn | P | Ni | Cu | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu-20Pb-5Sn | 0 | 0 | 0 | 19.85 | 4.73 | 1.75 | 0.08 | 2.38 | Bal. | 0 |
| 45 Steel | 0.45 | 0.21 | 0.68 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | Bal. |
| Location | at.% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu | Zn | Sn | P | Ni | Pb | |
| 1 | 12.8 | 1.34 | 1.42 | 5.04 | 3.45 | 75.95 |
| 2 | 77.31 | 1.06 | 15.19 | 4.39 | 1.82 | 0.23 |
| 3 | 65.12 | 0.26 | 0.36 | 24.77 | 9.46 | 0.03 |
| 4 | 83.2 | 1.9 | 3.88 | 0.31 | 10.66 | 0.05 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Hu, Y.; Liu, Y. Interfacial Diffusion and Copper Alloy Layer Wear Mechanism in Cu-20Pb-5Sn/45 Steel Bimetallic Composites. Coatings 2025, 15, 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091072
Kang Y, Zhang G, Hu Y, Liu Y. Interfacial Diffusion and Copper Alloy Layer Wear Mechanism in Cu-20Pb-5Sn/45 Steel Bimetallic Composites. Coatings. 2025; 15(9):1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091072
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Yuanyuan, Guowei Zhang, Yanling Hu, and Yue Liu. 2025. "Interfacial Diffusion and Copper Alloy Layer Wear Mechanism in Cu-20Pb-5Sn/45 Steel Bimetallic Composites" Coatings 15, no. 9: 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091072
APA StyleKang, Y., Zhang, G., Hu, Y., & Liu, Y. (2025). Interfacial Diffusion and Copper Alloy Layer Wear Mechanism in Cu-20Pb-5Sn/45 Steel Bimetallic Composites. Coatings, 15(9), 1072. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15091072






