Modified Asphalt Prepared by Coating Rubber Powder with Waste Cooking Oil: Performance Evaluation and Mechanism Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
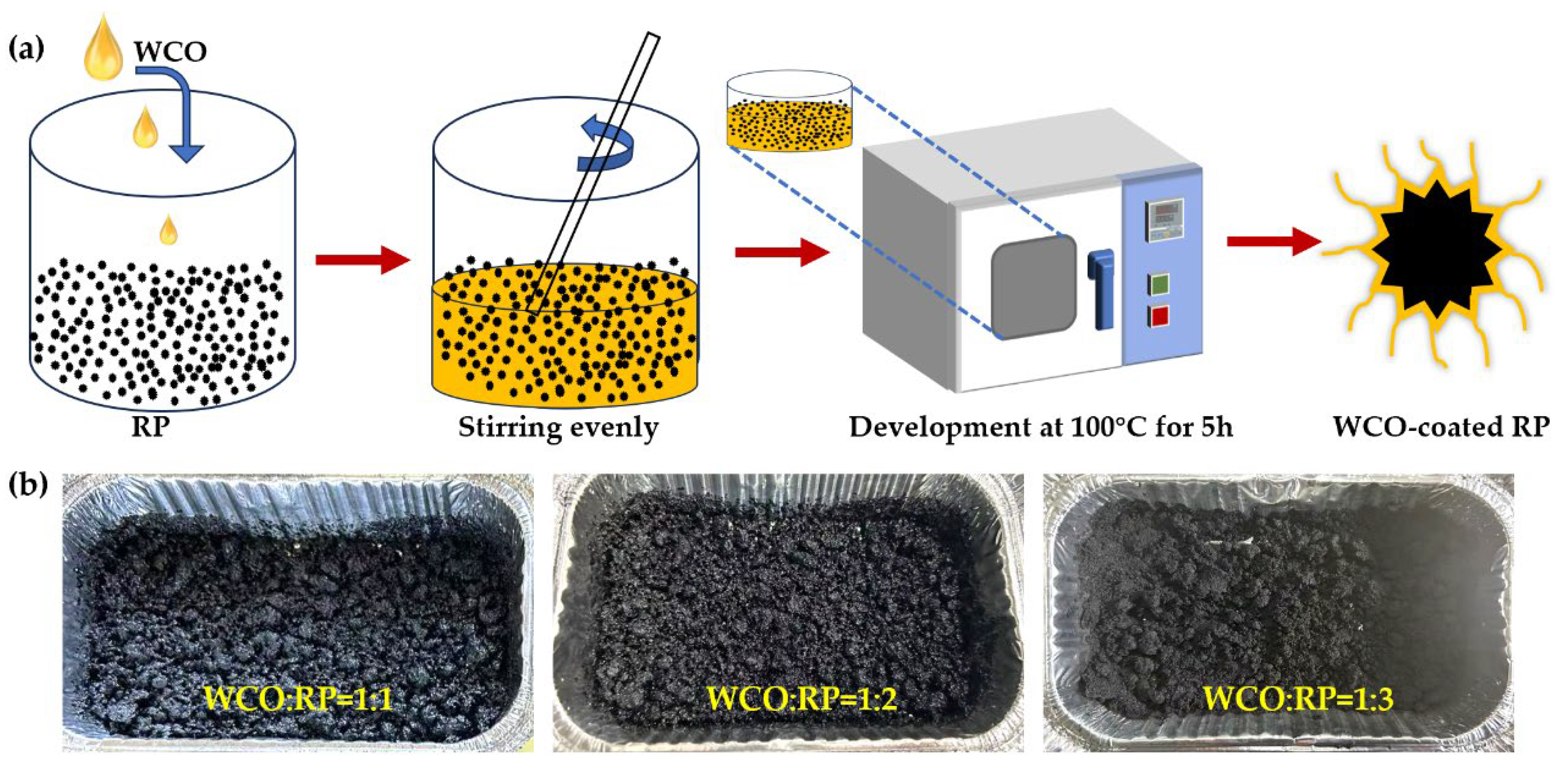
2.2. The Process of WCO Pre-Treatment RP
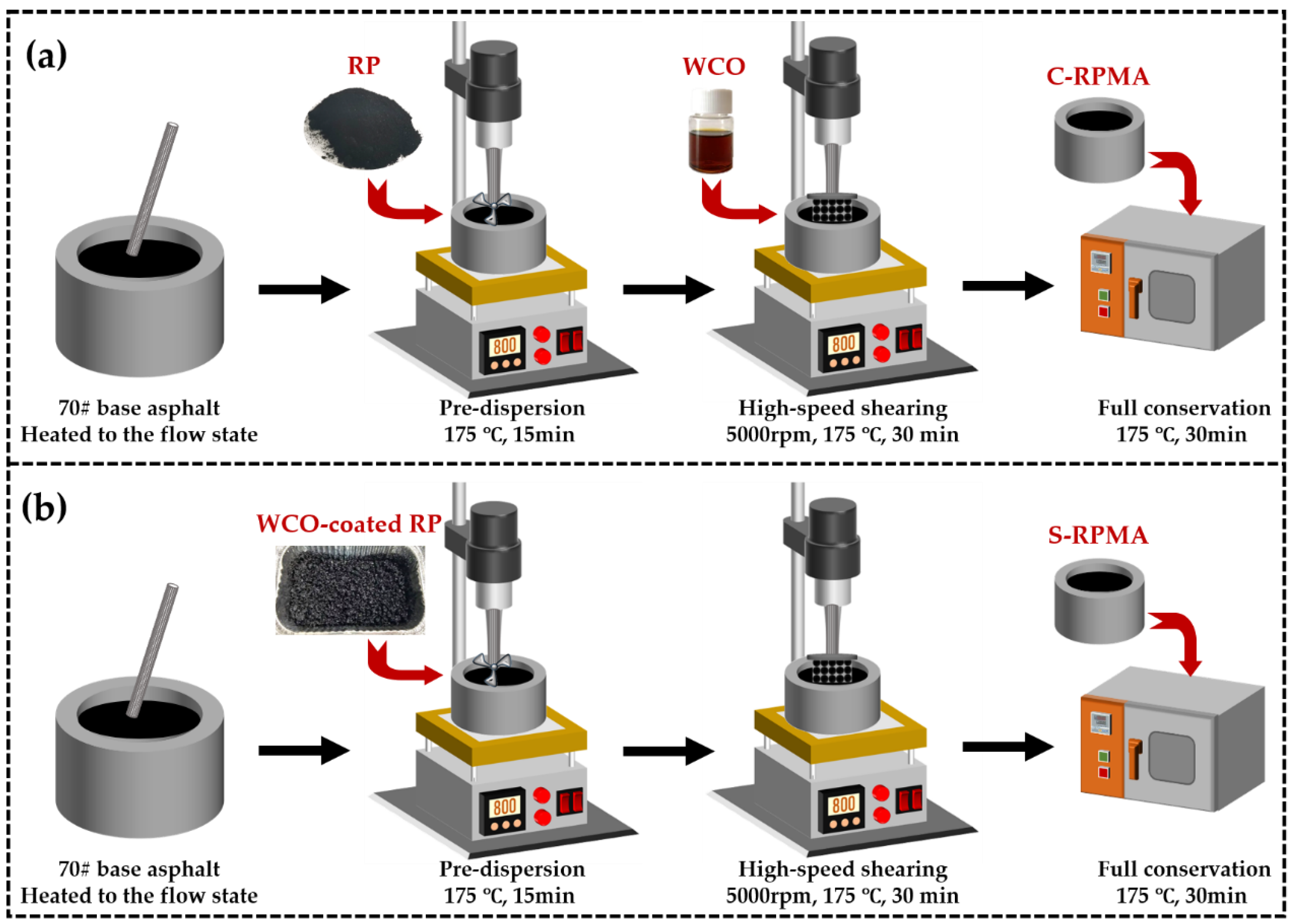
2.3. The Preparation of Different RPMAs
2.4. Characterization Method of RP
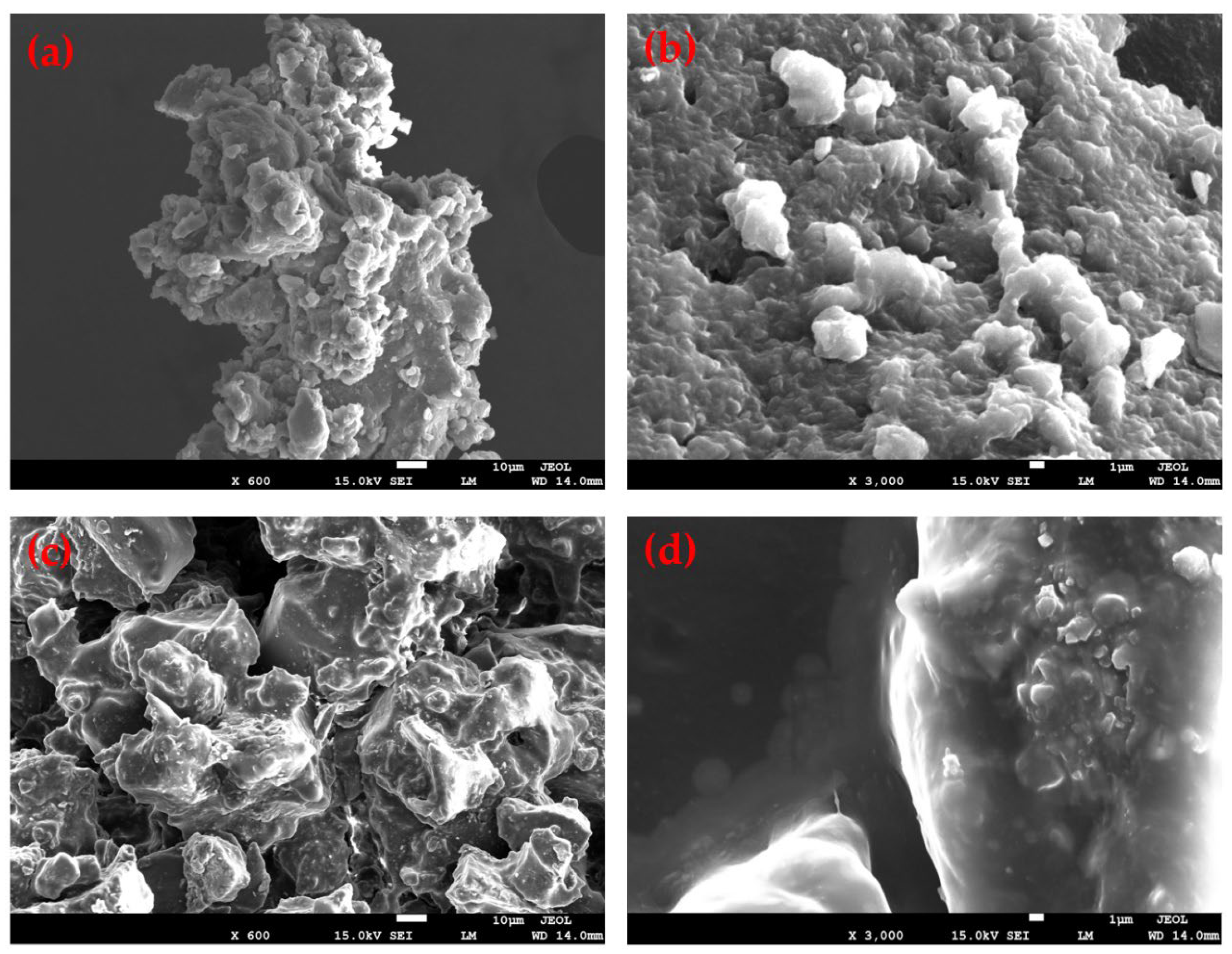
2.4.1. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Test
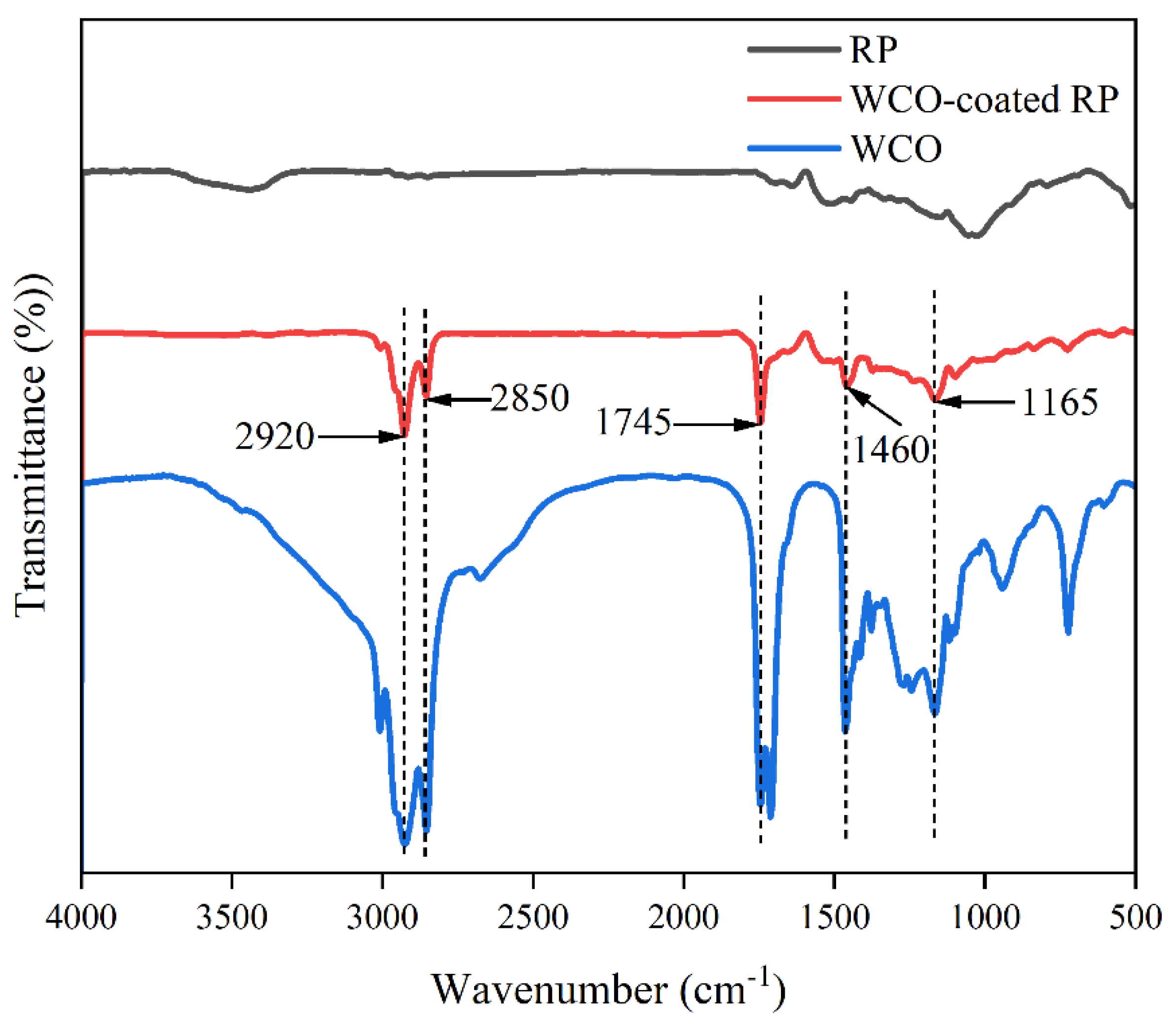
2.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR) Test
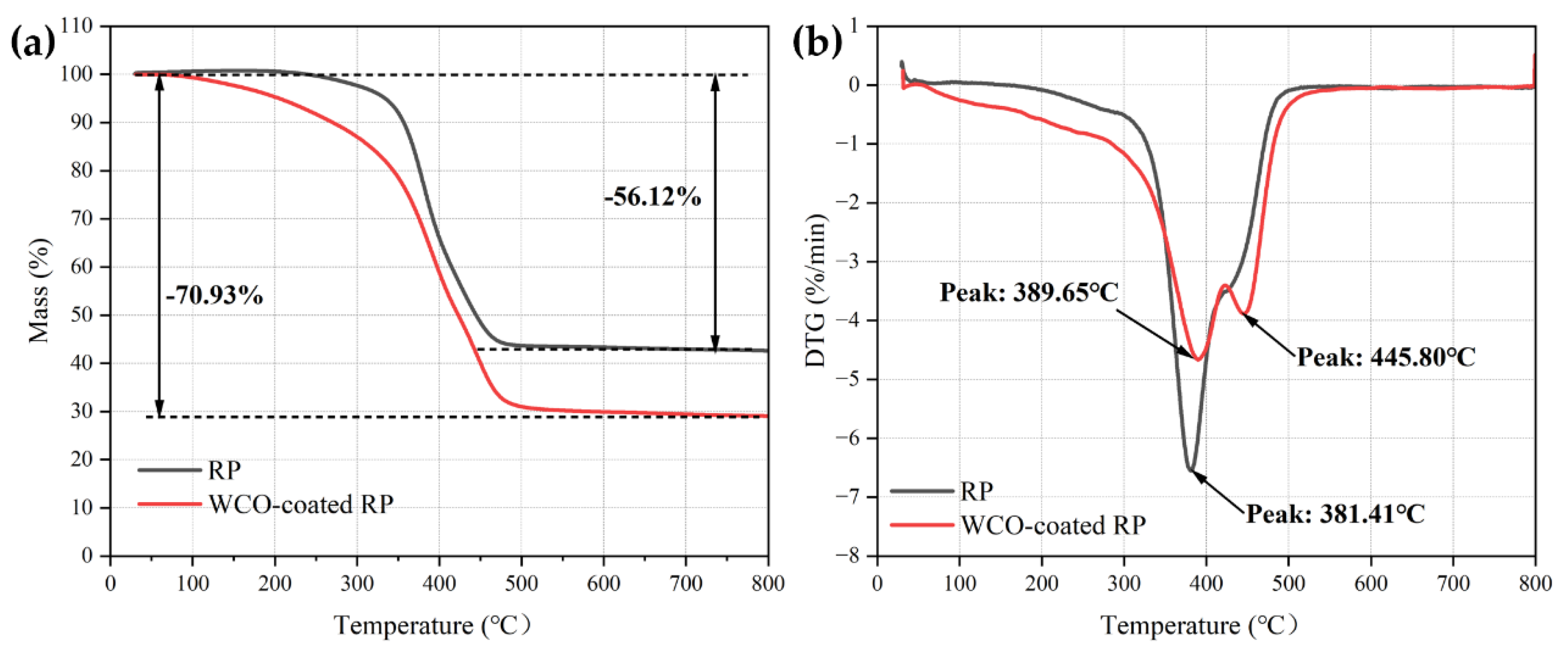
2.4.3. Thermogravimetric (TG) Test
2.5. Characterization Method of RPMA
2.5.1. Storage Stability Test
2.5.2. Rheological Performance Test
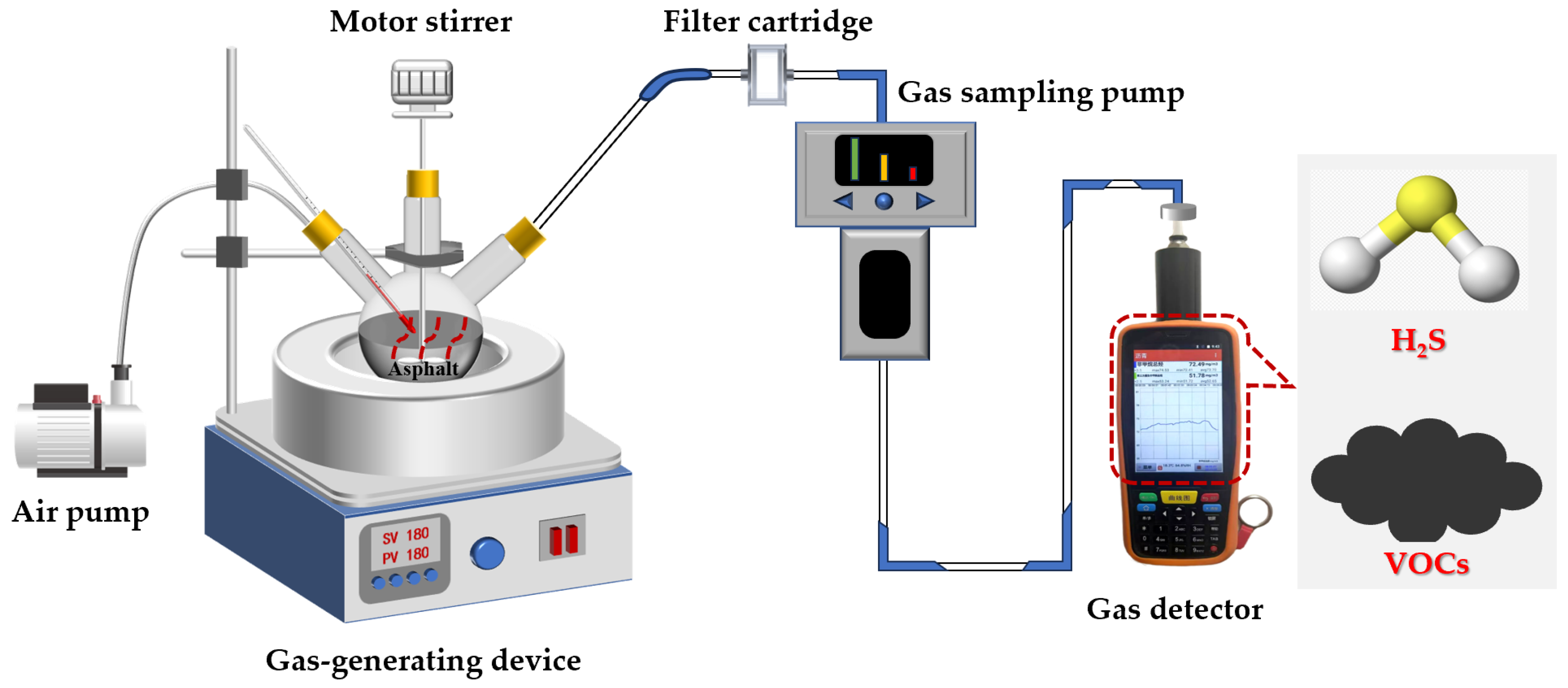
2.5.3. Flue Gas Collection and Testing Methods
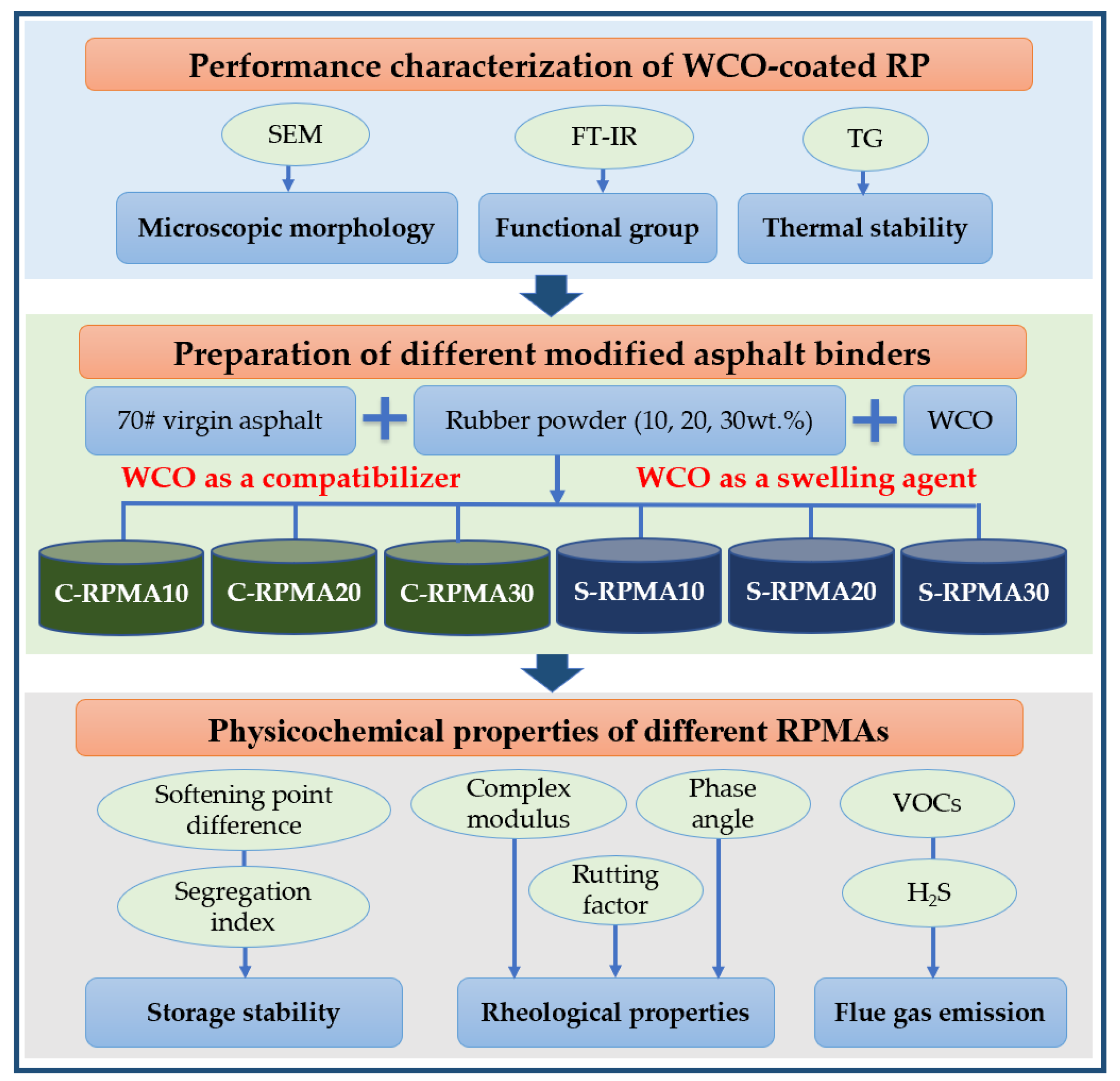
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance Characterization of WCO-Coated RP
3.1.1. Morphology
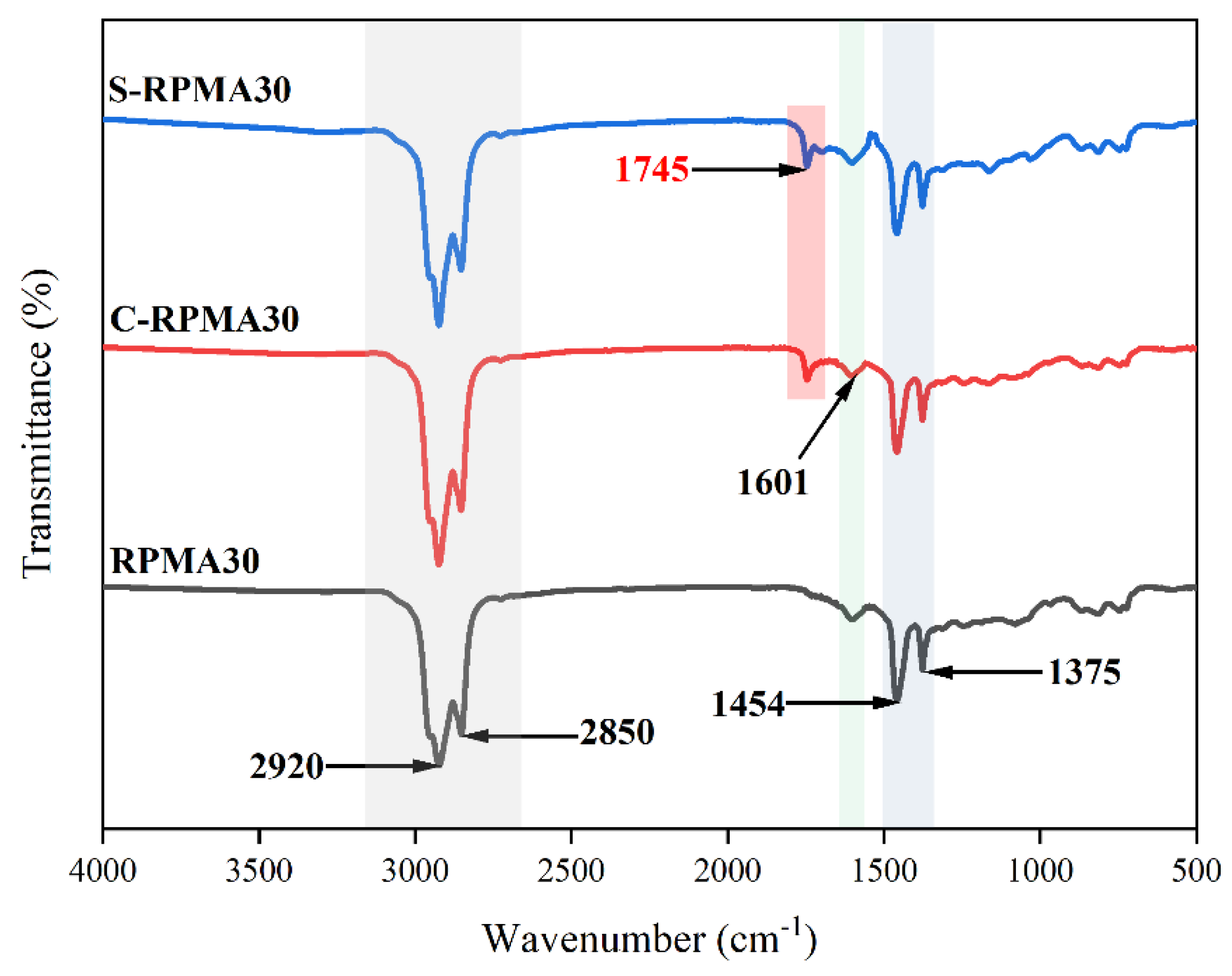
3.1.2. Functional Groups
3.1.3. Thermal Stability
3.2. Storage Stability Analysis of RPMA
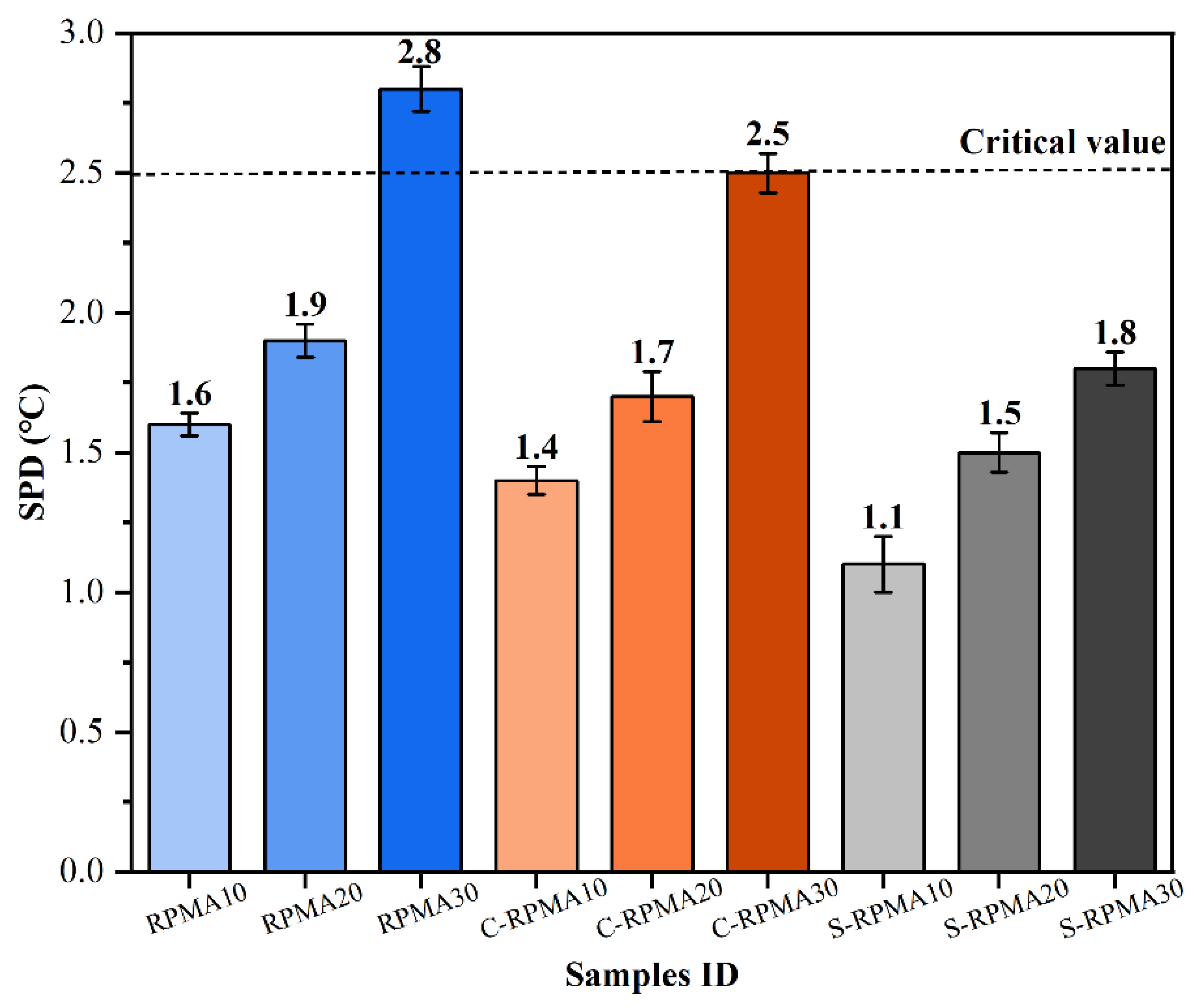
3.2.1. Softening Point Difference (SPD)
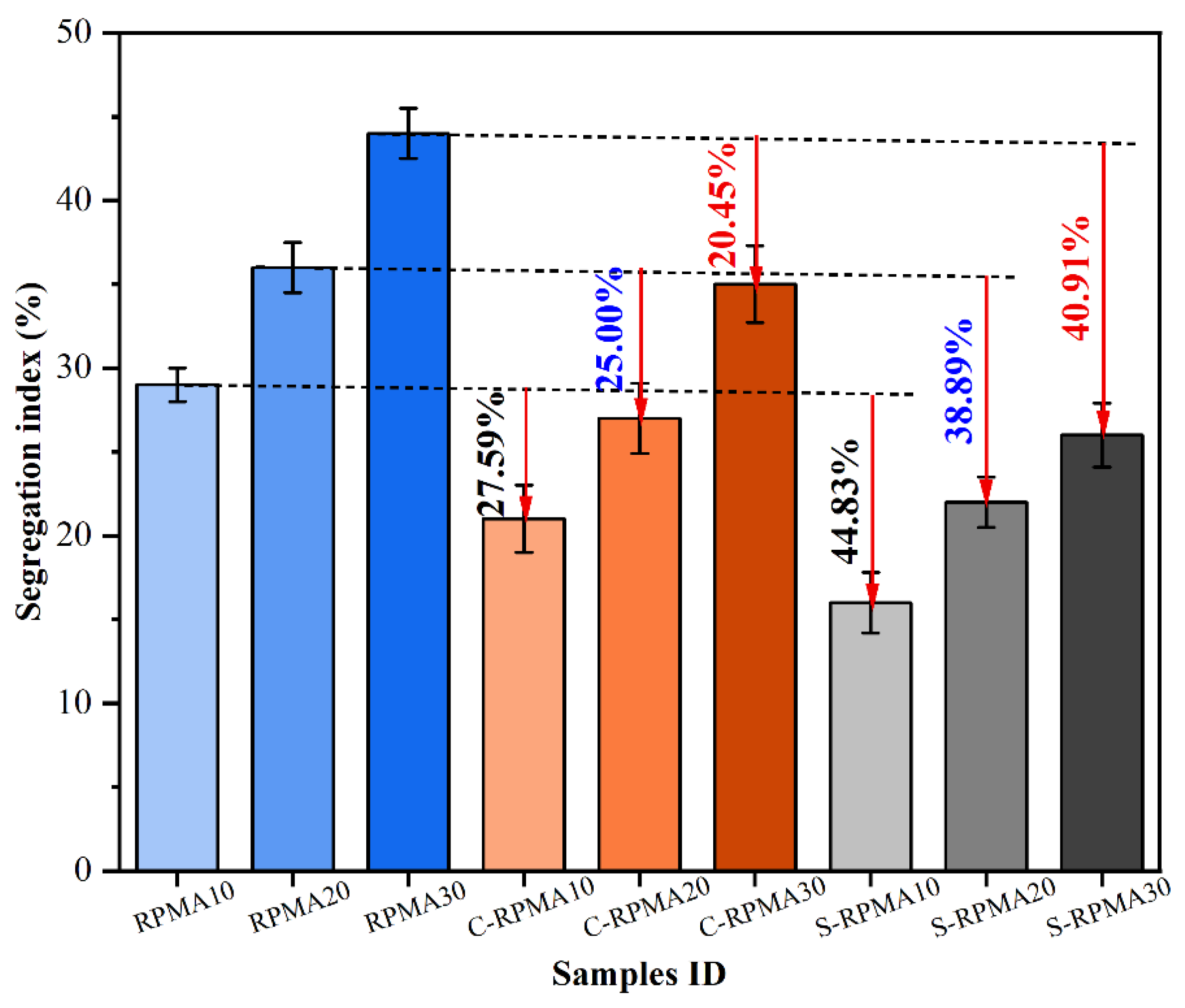
3.2.2. Segregation Index (SI)
3.3. Rheological Properties Analysis of RPMA
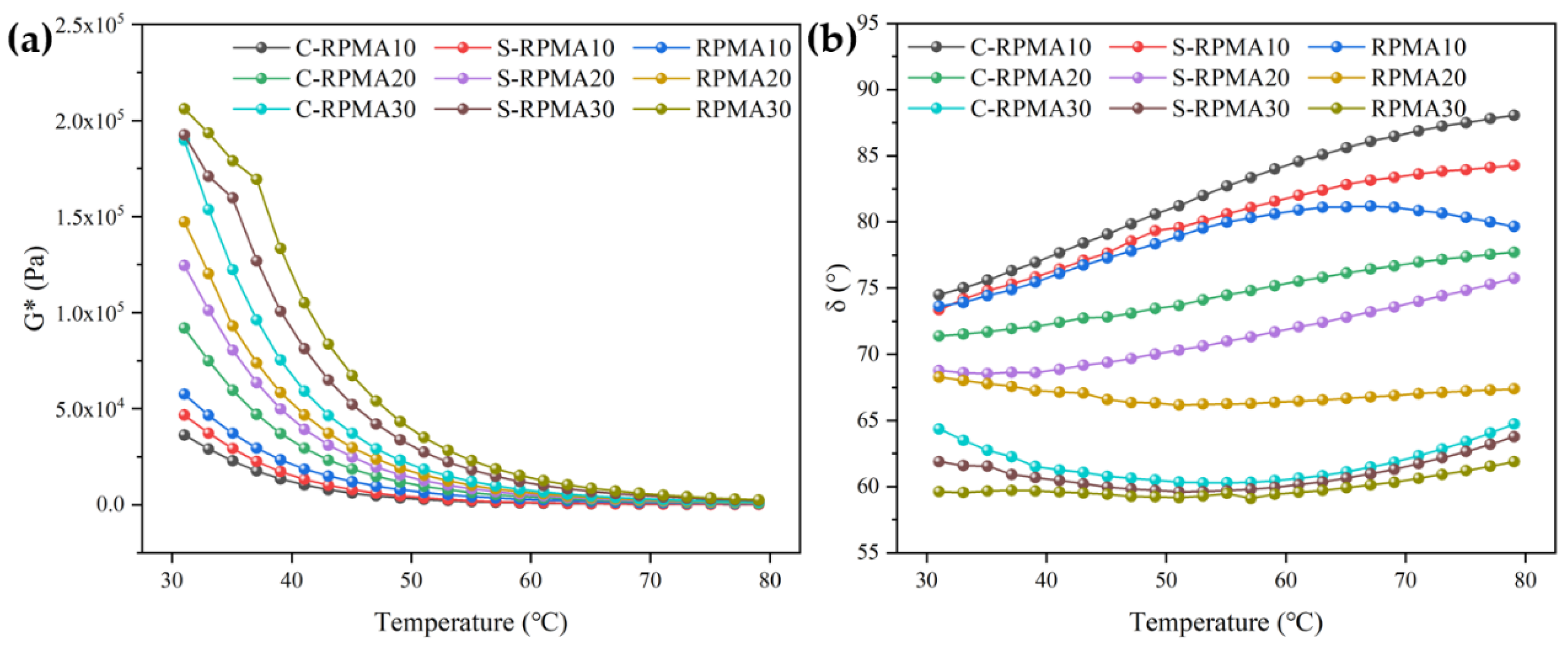
3.3.1. Complex Modulus (G*) and Phase Angle (δ)
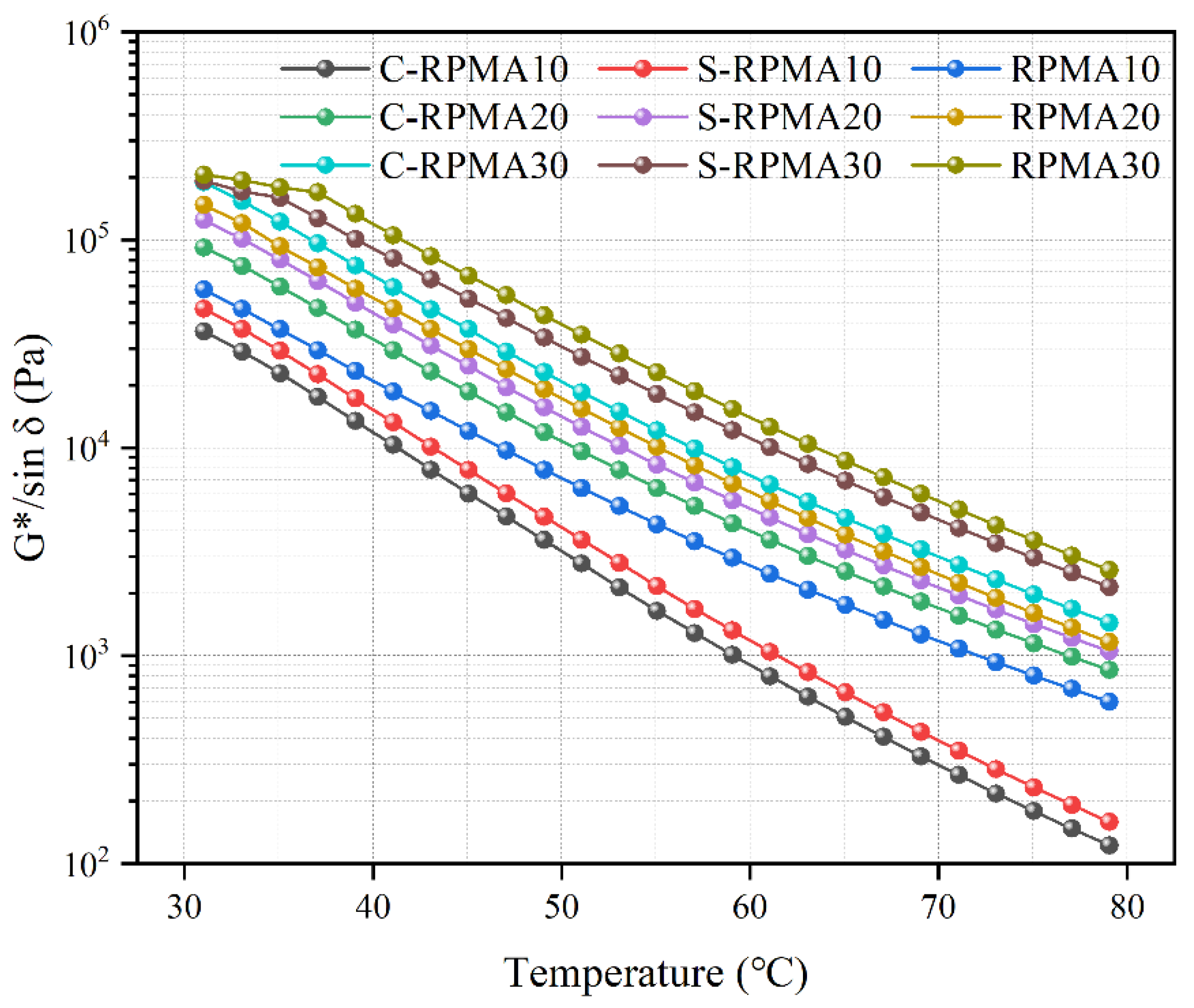
3.3.2. Rutting Factor (G*/sin δ)
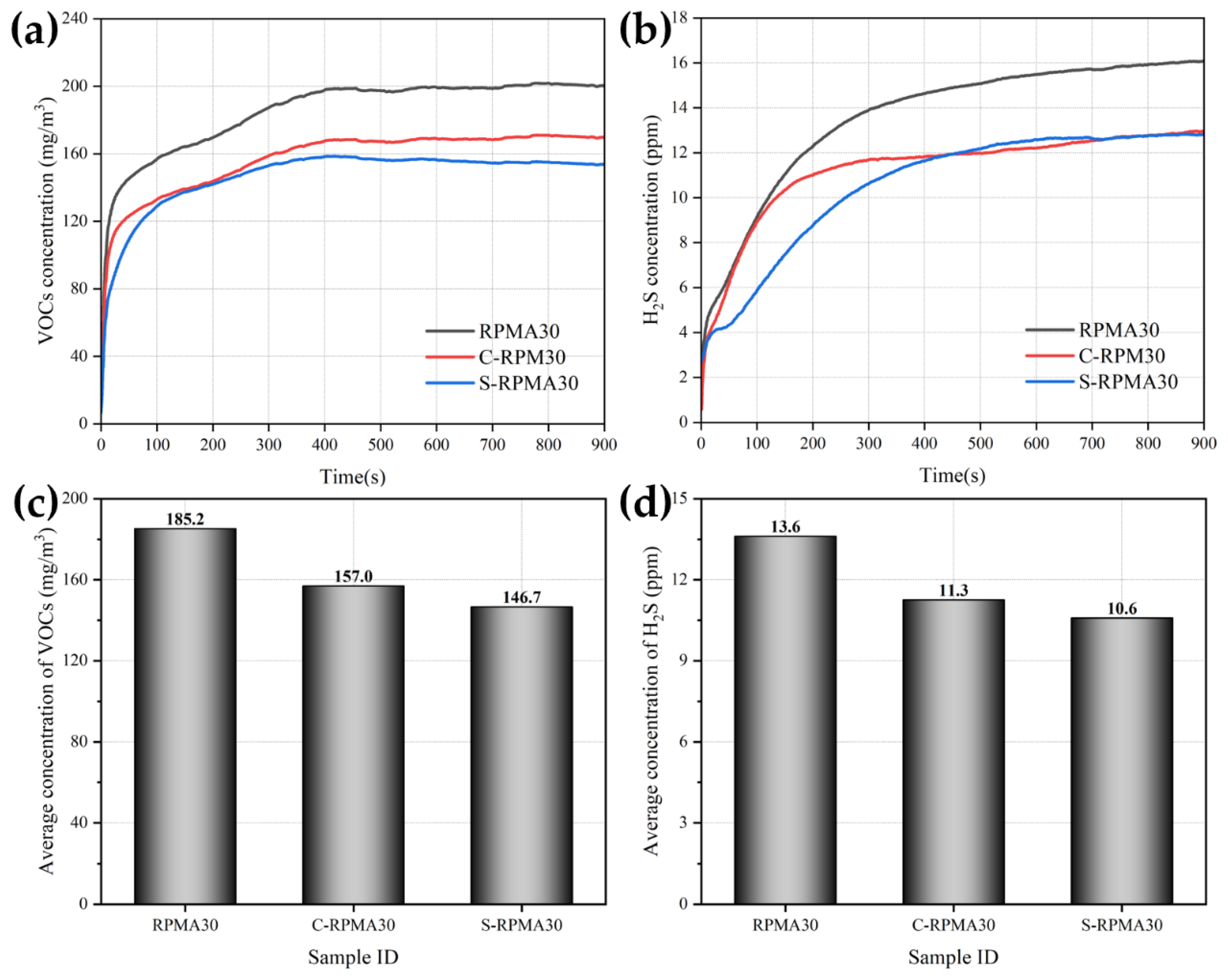
3.4. Flue Gas Emission Analysis of RPMA
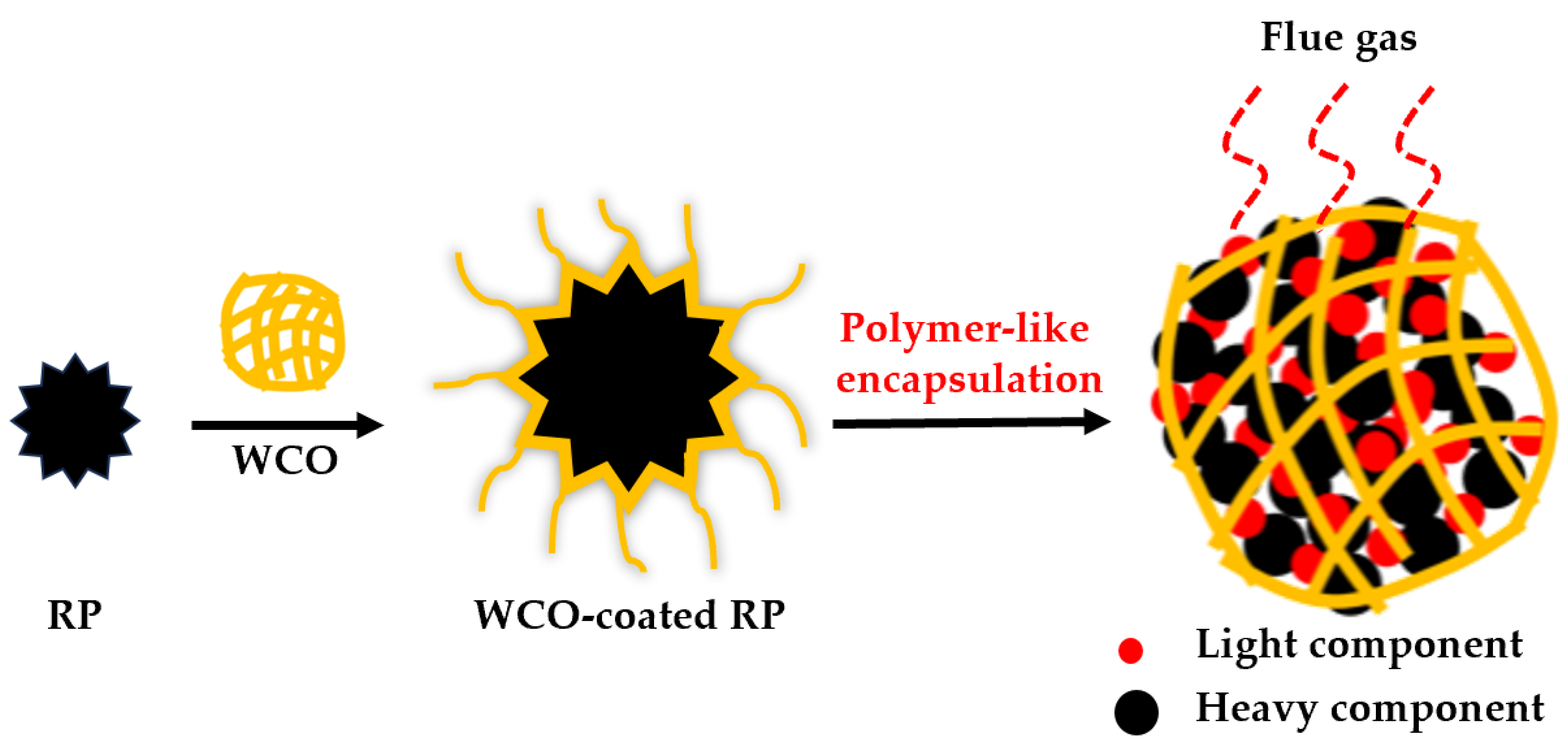
3.5. Modification Mechanism of WCO to RPMA
3.6. Flue Gas Suppression Mechanism of WCO to RPMA
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- After being coated with WCO, the surface of the RP becomes smoother, and noticeable aggregation and adhesion between particles are observed, indicating the formation of a uniform and continuous coating layer on the RP surface. The presence of the WCO coating film on the surface of the RP is confirmed by FT-IR and TG analyses. Moreover, the peak temperature of thermal weight loss for the coating film is observed at 389.65 °C, indicating that no significant thermal degradation occurs during the application of RPMA.
- (2)
- Compared with a compatibilizer, when WCO is used as a swelling agent for RP, the storage stability of the prepared RPMA is better, and the SPD value of RPMA with 30% RP dosing is only 1.8 °C, and the reduction of SI value reaches 40.91%. Meanwhile, comparing different RPMAs, it is found that the high-temperature performance of modified asphalt with the addition of WCO is all reduced, but S-RPMA shows better high-temperature rutting resistance compared with C-RPMA.
- (3)
- The addition of WCO can effectively suppress the fume emissions of RPMA to a certain extent. Notably, when WCO coated the RP, the average concentrations of VOCs and H2S in the prepared S-RPMA30 are 146.7 mg/m3 and 10.6 ppm, respectively, which are reduced by 20.8% and 22.1% compared to the original RPMA30. The WCO-coated RP forms a polymer-like encapsulation structure, which serves as an effective physical barrier at elevated temperatures, significantly mitigating the release of harmful emissions from RPMA.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, H.; Wang, H.; Lin, J.; Yang, J.; Yao, Y. Study on the Effect of SBS/HVA/CRM Composite-Modified Asphalt on the Performance of Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Polymers 2024, 16, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Hao, Q.L.; Xu, S.; Han, X.; Yi, J.; Sun, G. Preparation and performance evaluation of bio-based polyurethane modified asphalt binders: Towards greener and more sustainable asphalt modifier. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 476, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Z.; Pei, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, Z.; Wang, W.; Gao, J. A comprehensive review of rheological behaviors of asphalt binders, mastics, and mixtures from a generalized rheology perspective. Fuel 2025, 393, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, H. Comparative study on asphalt pavement rut based on analytical models and test data. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2020, 21, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Falchetto, A.C.; Zhou, B.; Wang, W. Sustainable Materials and Structures Used in Pavement Engineering. Materials 2025, 18, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleyedath, A.; Becerril, E.I.G., Jr.; Ali, A.; Mehta, Y. Development of a framework for the structural design of long-lasting porous asphalt pavement for high-traffic volume roadways. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 470, 140638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Dong, R.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Y.; Guo, F.; Wei, X.; Li, B.; Huang, Y. Rheological Properties and Influence Mechanisms of Twin-Screw Activated Rubber Powder Composite SBS-Modified Asphalt. Materials 2025, 18, 2359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, X.; Sha, T.; Wang, D.; Niu, B.; Wang, R.; Hou, X. A Rheological Study of the High-Temperature Properties of Fast-Melting SBS/Epoxy-Modified Asphalt Binders. Polymers 2025, 17, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Cao, D.; Xia, L.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, M.; Huang, Y. Preparation and Pavement Performance of Highly Viscoelastic Antifatigue Asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2025, 37, 04025058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Yu, C.; Xing, C.; Tan, Y.; Wang, G.; Qin, L.; Tian, Z. Comprehensive study on the applicability of evaluation index for rubber modified asphalt rheological property. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 470, 140520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Tian, H.; Fan, W.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H. Application of Unprocessed Waste Tyres in Pavement Base Structures: A Study on Deformation and Stress Analysis Using Finite Element Simulation. Materials 2025, 18, 914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, D.; Pei, Y.; Han, B.; Khoo, S.Y.; Norton, M.; Adams, S.D.; Kouzani, A.Z. Comparative analysis of waste tyre treatment technologies: Environmental and economic perspectives. Renew. Sust. Energ. Rev. 2025, 216, 115691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Huang, Y.; Jin, K.; Zhou, Z. Properties and mechanism of SBS/crumb rubber composite high viscosity modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 378, 134534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Bao, Z.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Hu, H.; Jin, L. Interaction during co-pyrolysis of different rubbers using rapid infrared-heating fixed bed: Products distribution, tar quality and tar composition. Fuel 2024, 364, 131065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyshye, S.; Lypko, Y.; Demchuk, Y.; Kukhar, O.; Korchak, B.; Pochapska, I.; Zhytnetskyi, I. Characteristics and Applications of Waste Tire Pyrolysis Products: A Review. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2024, 18, 244–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagurskyy, A.; Grynyshyn, O.; Khlibyshyn, Y.; Korchak, B. Use of Rubber Crumb Obtained from Waste Car Tires for the Production of Road Bitumen and Roofing Materials from Residues of Ukrainian Oil Processing. Chem. Chem. Technol. 2023, 17, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Zhang, H.; Ge, D.; Lv, S.; Ju, Z. The interaction mechanism of activated crumb rubber modified asphalt during the preparation process. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2025, 26, 2481919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Su, Q.; Li, G.; Cao, D.; Yao, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, S. Enhancing Reutilization of Waste Tires and Sustainability of Environment: Analysis of the Performance and Emission Reduction Mechanism of High Content Rubber Modified Asphalt. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Zhou, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhao, Y.; Cheng, M. Evaluation of VOCs inhibited effects and rheological properties of asphalt with high-content waste rubber powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 300, 124320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, S.; Xie, J.; Yang, C.; Yang, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, Q. Utilization of high contents desulfurized crumb rubber in developing an asphalt rubber pellets modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 402, 133043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhu, H.; Li, R.; Yang, X.; Tan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Lei, L. Application of functionalized graphene oxide in the preparation of crumb rubber modified asphalt with excellent storage stability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 450, 138488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, N.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, R.; Zhu, H.; Huang, W. Emission behavior of crumb rubber modified asphalt in the production process. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 340, 130850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Yang, C.; Li, A.; Wang, P.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, Z. Flue gas composition of waste rubber modified asphalt (WRMA) and effect of deodorants on hazardous constituents and WRMA. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 403, 123814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, J.; Pei, J.; Ma, W.; Hu, Z.; Guan, Y. Evaluation of the compatibility between rubber and asphalt based on molecular dynamics simulation. Front. Struct. Civ. Eng. 2020, 14, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Characterizing Compatibility of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt by Customized Drainage Method. J. Test. Eval. 2021, 49, 3204–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hu, M.; Sun, D.; Lu, T.; Sun, G.; Ling, S.; Xu, L. Understanding the role of waste cooking oil residue during the preparation of rubber asphalt. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 167, 105235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borinelli, J.B.; Portillo-Estrada, M.; Costa, J.O.; Pajares, A.; Blom, J.; Hernando, D.; Vuye, C. Emission reduction agents: A solution to inhibit the emission of harmful volatile organic compounds from crumb rubber modified bitumen. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, T.; Cao, P.; Zhou, J.; Liu, Z.; Dong, Z. Characterization of emissions from rubber modified asphalt and their impact on environmental burden: Insights into composition variability and hazard assessment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2024, 477, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y.; Ji, J.; You, Z.; Zhang, Y. A review on compatibility between crumb rubber and asphalt binder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 297, 123820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Xiao, F.; Amirkhanian, S.N. Surface activation of scrap tire crumb rubber to improve compatibility of rubberized asphalt. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2021, 169, 105518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.; Amutio, M.; Lopez, G.; Santamaria, L.; Bilbao, J.; Olazar, M. Improving bio-oil properties through the fast co-pyrolysis of lignocellulosic biomass and waste tyres. Waste Manag. 2019, 85, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Huang, S.; Guo, X.; Duan, W. Crumb waste tire rubber surface modification by plasma polymerization of ethanol and its application on oil-well cement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 409, 325–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badughaish, A.; Li, J.; Amirkhanian, S.; Xiao, F. Adhesion and segregation characteristics of crumb rubberized binders based on solution-soaked methods. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 354, 131762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y.; Cao, J.; Wang, X.; Wang, S. Conventional properties, rheological properties, and storage stability of crumb rubber modified asphalt with WCO and ABS. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 392, 131987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; Guo, W.; Su, C.; Nie, L. Influence of compatibilizer component on the properties of modified asphalt for disposable medical masks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Ding, Z.; Luo, H.; Lu, Z.; Li, S.; Zhao, X.; Huang, B.; Lin, J. Effectiveness of composite fume suppression and deodorizing agents in improving performance and reducing emissions of rubber modified asphalt. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 485, 1144397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liu, Q.; Wang, H.; Wang, J.; He, L.; Wu, P. Effect of kaolin and sepiolite on fume emissions of rubber modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 416, 135276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, G.; Ning, W.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, K.; Cao, L.; Ding, Y. A comprehensive review on asphalt fume suppression and energy saving technologies in asphalt pavement industry. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Jing, F.; Zhao, R.; Li, C.; Cai, J.; Wang, Q.; Xie, H. Waste Cooking Oil-Modified Epoxy Asphalt Rubber Binders with Improved Compatibility and Extended Allowable Construction Time. Molecules 2022, 27, 7061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, X.; Dong, R.; Shi, C.; Yang, J.; Leng, Z. The influence of the mass ratio of crumb rubber and waste cooking oil on the properties of rubberised bio-rejuvenator and rejuvenated asphalt. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2023, 24, 578–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Cao, Z.; Zhou, X. Full-component cascade utilization of waste cooking oil in asphalt materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 404, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elahi, Z.; Jakarni, F.M.; Muniandy, R.; Hassim, S.; Ab Razak, M.S.; Ansari, A.H.; Ben Zair, M.M. Waste Cooking Oil as a Sustainable Bio Modifier for Asphalt Modification: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 11506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG-E20; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. Highway Science Research Institute of the Ministry of Transport: Beijing, China, 2011.
- Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Leng, B.; Wu, S.; Chen, D.; Zhao, Z. Investigation on storage stability, H2S emission and rheological properties of modified asphalt with different pretreated waste rubber powder. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 456, 142469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Hao, P.; Dou, Z.; Wang, J.; Ma, L. Rheological, healing and microstructural properties of unmodified and crumb rubber modified asphalt incorporated with graphene/carbon black composite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 305, 124512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Xiao, M.; Liu, S.; Chen, H.; Wen, Z.; Liu, P.; Rao, R.; Qian, G. Investigation of rheological properties and modification mechanism of bio-oil/crumb rubber modified asphalt reinforced by fiber. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 455, 139202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liu, Y.; Rong, H.; Liang, M.; Liu, Y.; Huang, R. Research on high and low temperature rheological properties of TPU/SBR composite modified asphalt. Mater. Res. Express 2024, 11, 025301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Physical properties | Performance indicators | Relative density (%) | Water content (%) | Metal content (%) | Fiber content (%) |
| Requirements | 1.10–1.30 | ≤1 | ≤0.05 | ≤0.1 | |
| Values | 1.14 | 0.43 | 0.007 | 0.07 | |
| Chemical properties | Performance indicators | Ash content (%) | Acetone extract (%) | Carbon Black (%) | |
| Requirements | ≤8 | ≤22 | 28–38 | ||
| Values | 5 | 13 | 34 | ||
| Performance Indicators | Values |
|---|---|
| Density (25 °C, g/cm3) | 0.91 |
| Viscosity (60 °C, mm2/s) | 72 |
| Flash point (°C) | 221 |
| Performance Indicators | Requirements | Values | Test Methods | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 0.1 mm) | 60–80 | 61 | JTG E20-2011 T0604 | |
| Softening point (°C) | 44–54 | 52 | JTG E20-2011 T0605 | |
| Ductility (15 °C, 5 cm/min) | >100 | >100 | JTG E20-2011 T0606 | |
| Dynamic viscosity (60 °C, Pa·s) | ≥180 | 201 | JTG E20-2011 T0625 | |
| Density (g/cm3) | 1.017 | / | JTG E20-2011 T0603 | |
| Wax content (%) | ≤2.2 | 1.7 | JTG E20-2011 T0615 | |
| Aging test (163 °C, 5 h) | Mass change (%) | ≤±0.8 | −0.14 | JTG E20-2011 T0609 |
| Ratio of penetration (25 °C, %) | ≥58 | 64 | ||
| Residual ductility (10 °C, cm) | ≥4 | 5.7 | ||
| Sample ID | Composition of Sample |
|---|---|
| RPMA10 | 70# base asphalt + 10%RP |
| RPMA20 | 70# base asphalt + 20%RP |
| RPMA30 | 70# base asphalt + 30%RP |
| C-RPMA10 | Compatibilizer + 70# base asphalt + 10%RP |
| C-RPMA20 | Compatibilizer + 70# base asphalt + 20%RP |
| C-RPMA30 | Compatibilizer + 70# base asphalt + 30%RP |
| S-RPMA10 | Swelling agent + 70# base asphalt + 10%RP |
| S-RPMA20 | Swelling agent + 70# base asphalt + 20%RP |
| S-RPMA30 | Swelling agent + 70# base asphalt + 30%RP |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; Yan, Y.; Han, M.; Zhao, Y. Modified Asphalt Prepared by Coating Rubber Powder with Waste Cooking Oil: Performance Evaluation and Mechanism Analysis. Coatings 2025, 15, 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070844
Zhang J, Chen M, Yan Y, Han M, Zhao Y. Modified Asphalt Prepared by Coating Rubber Powder with Waste Cooking Oil: Performance Evaluation and Mechanism Analysis. Coatings. 2025; 15(7):844. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070844
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Jianwei, Meizhu Chen, Yuan Yan, Muyan Han, and Yuechao Zhao. 2025. "Modified Asphalt Prepared by Coating Rubber Powder with Waste Cooking Oil: Performance Evaluation and Mechanism Analysis" Coatings 15, no. 7: 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070844
APA StyleZhang, J., Chen, M., Yan, Y., Han, M., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Modified Asphalt Prepared by Coating Rubber Powder with Waste Cooking Oil: Performance Evaluation and Mechanism Analysis. Coatings, 15(7), 844. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070844






