Effect of Cerium Nitrate Content on the Performance of Ce(III)/CF/BN/EPN Heat Exchanger Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Preparation of Ce Coating
2.3. Preparation of Ce Coating Characterisation Sample
2.4. Material Characterisation and Performance Testing
3. Results and Discussion
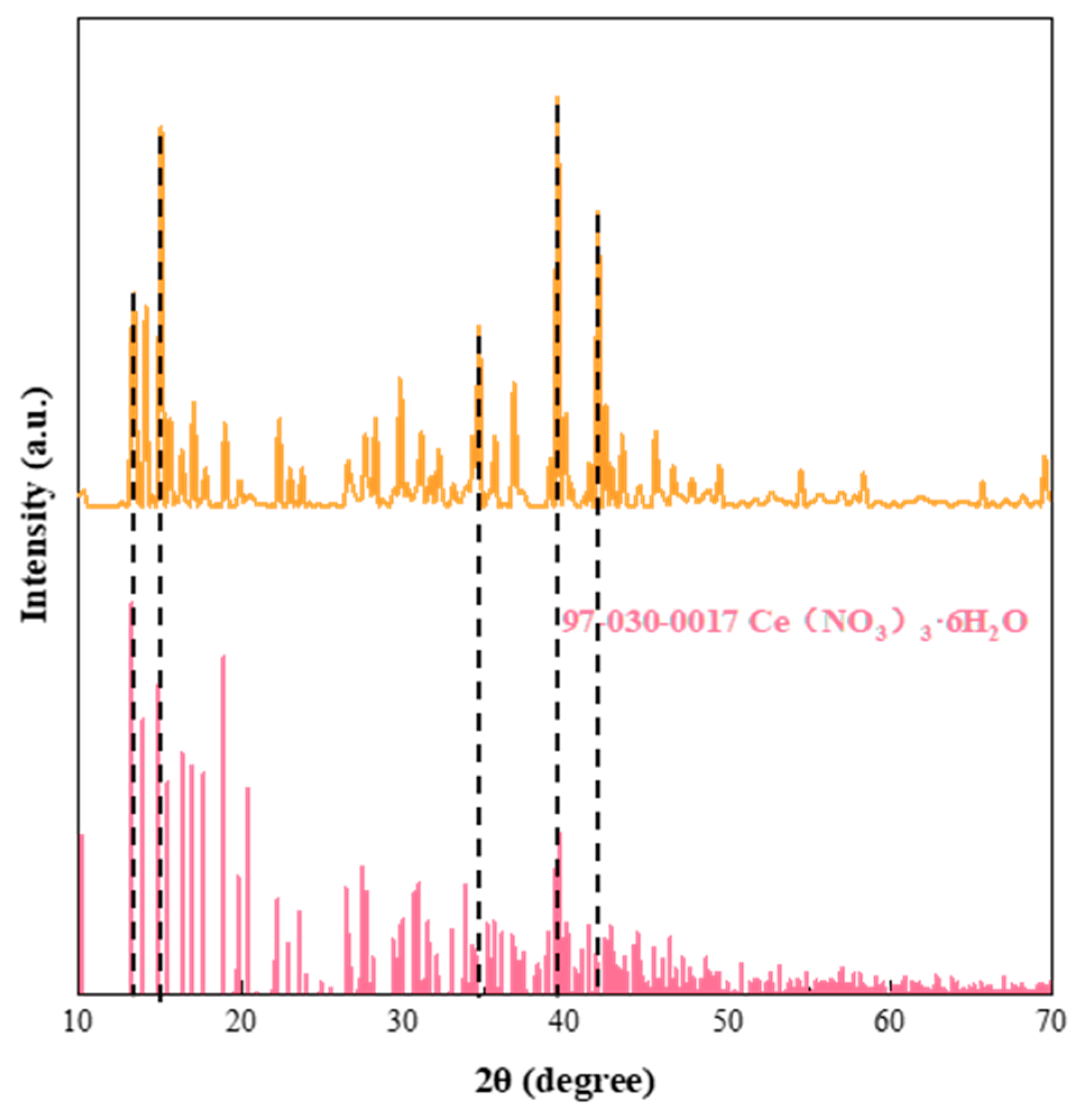
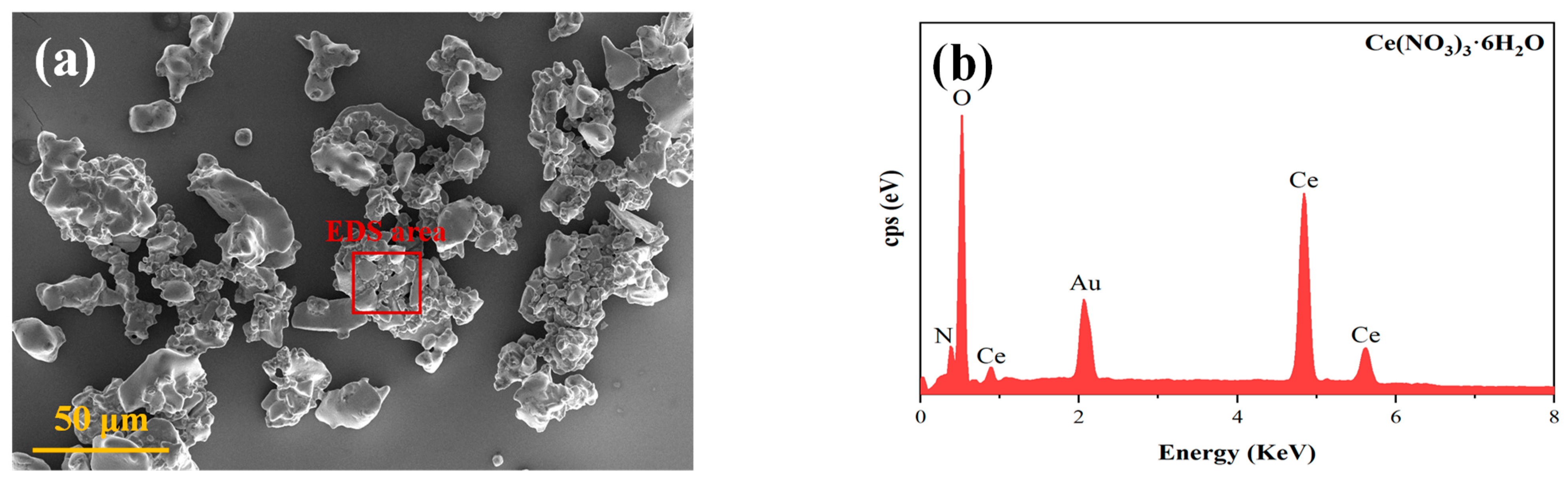
3.1. Characterisation of the Physical and Chemical Properties of Ce(NO3)3-6H2O
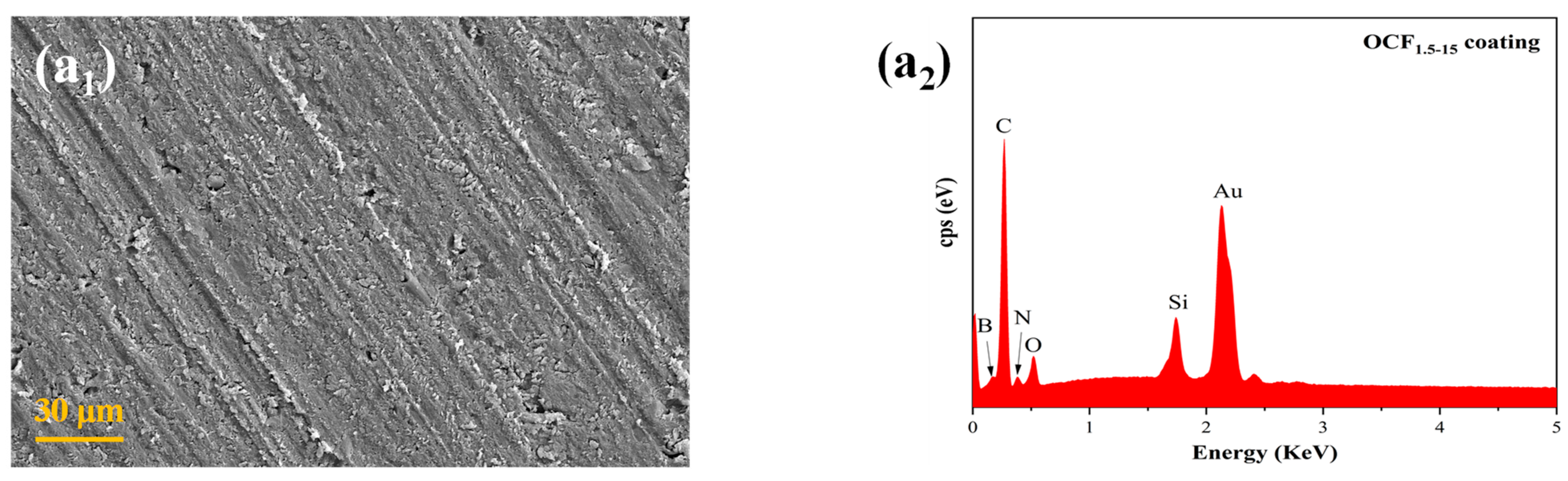
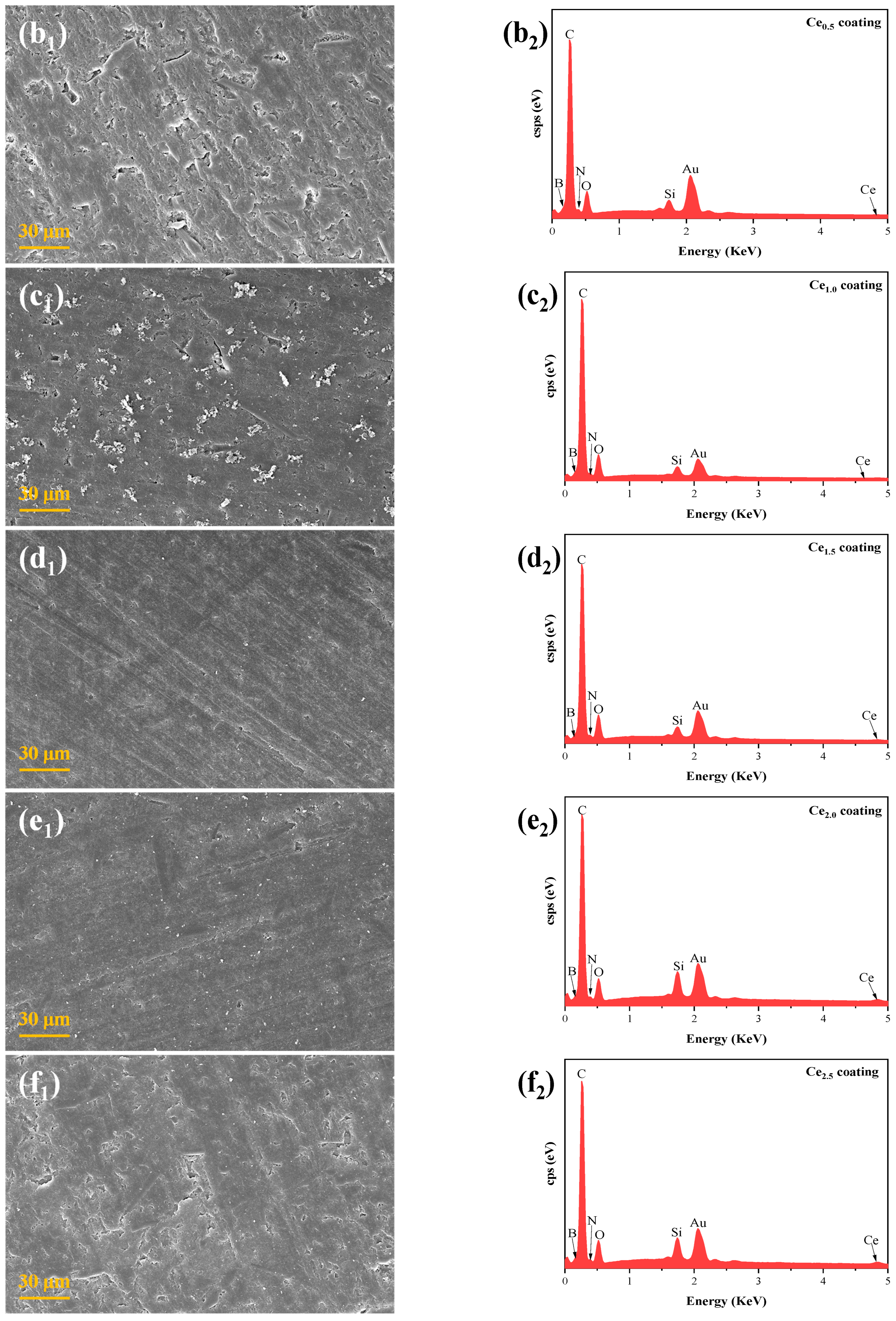
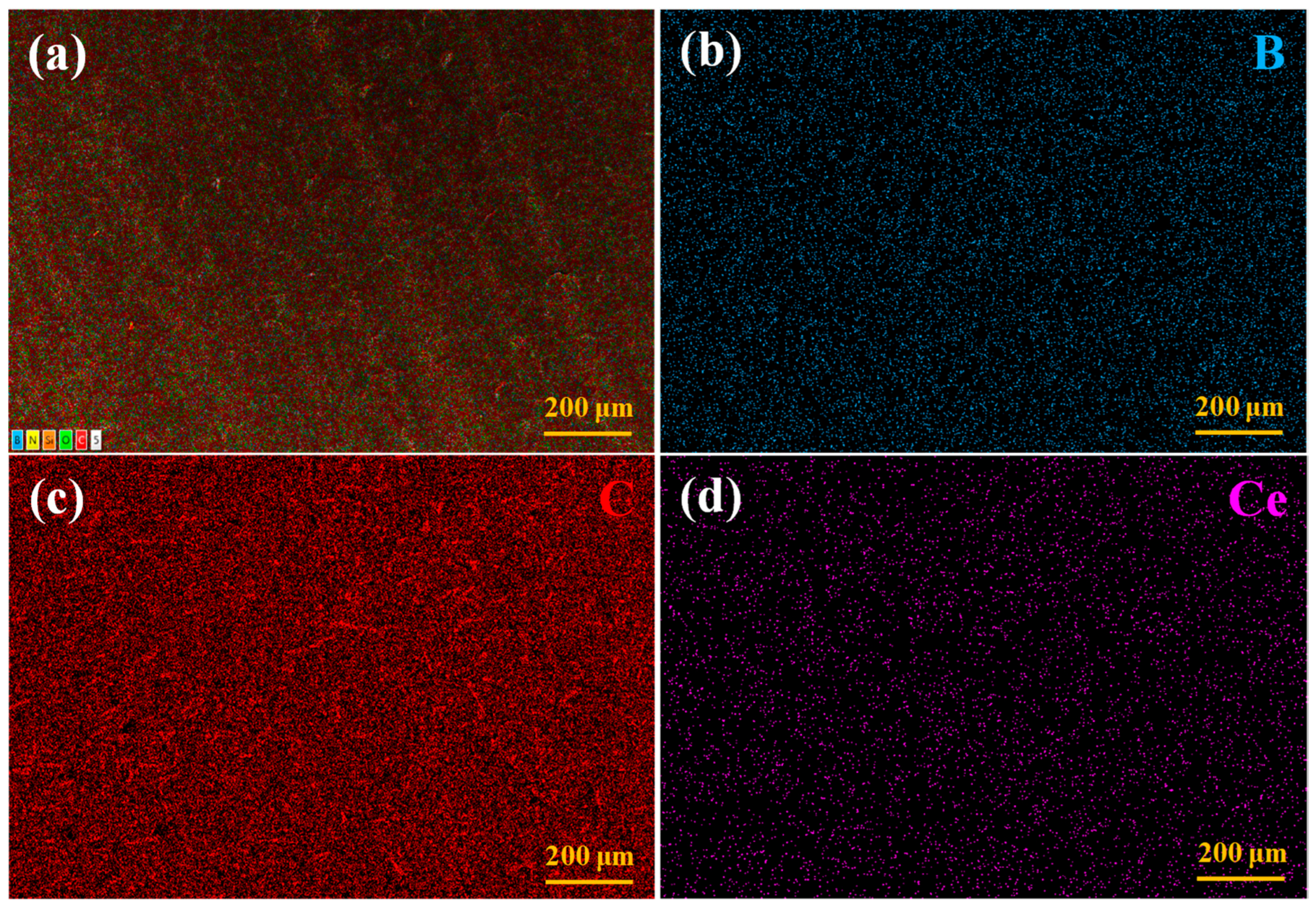
3.2. Microscopic Morphology of the Coatings
3.3. TC of Ce Coatings
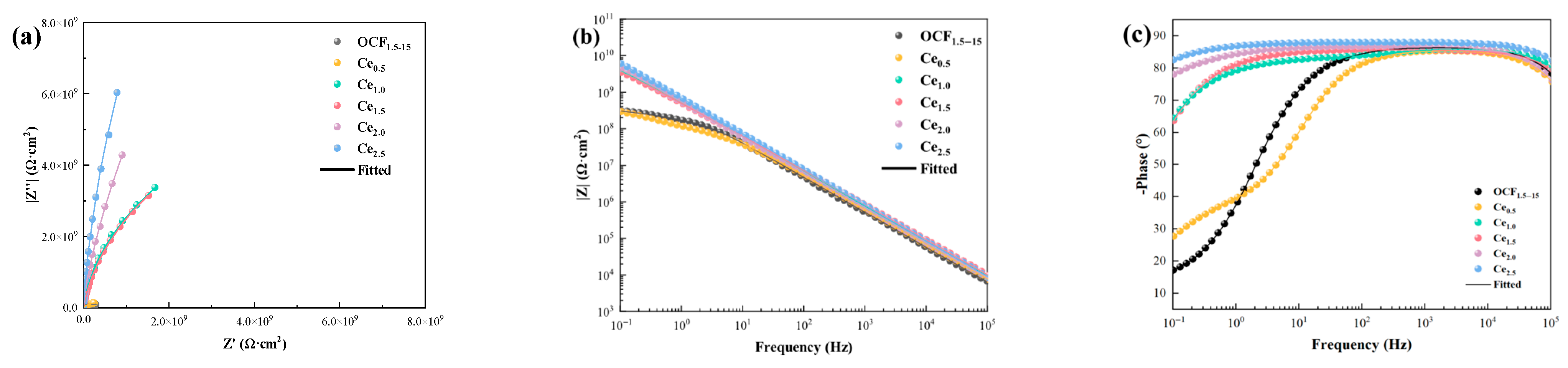
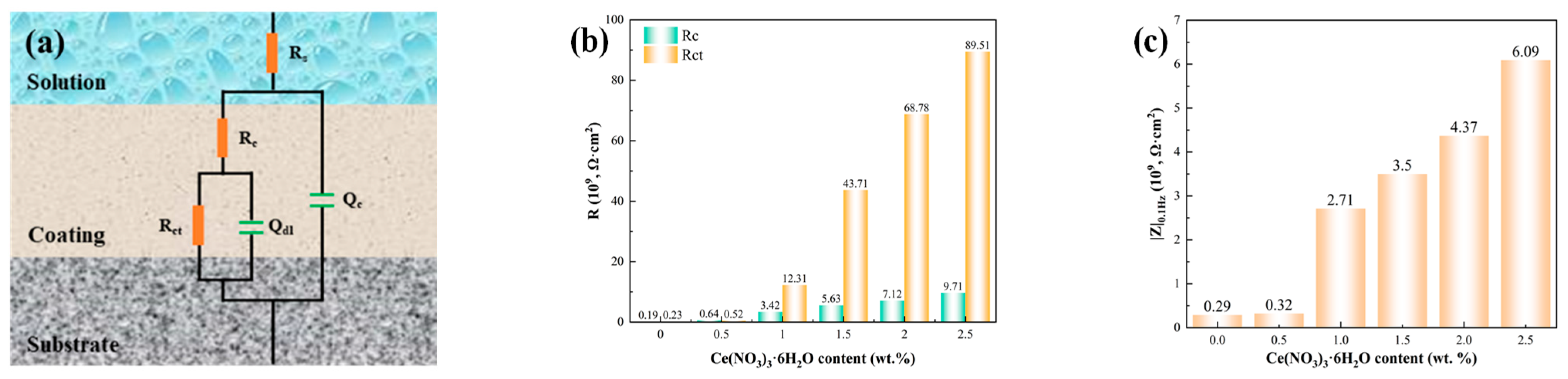
3.4. Corrosion-Resistant Properties of Coatings
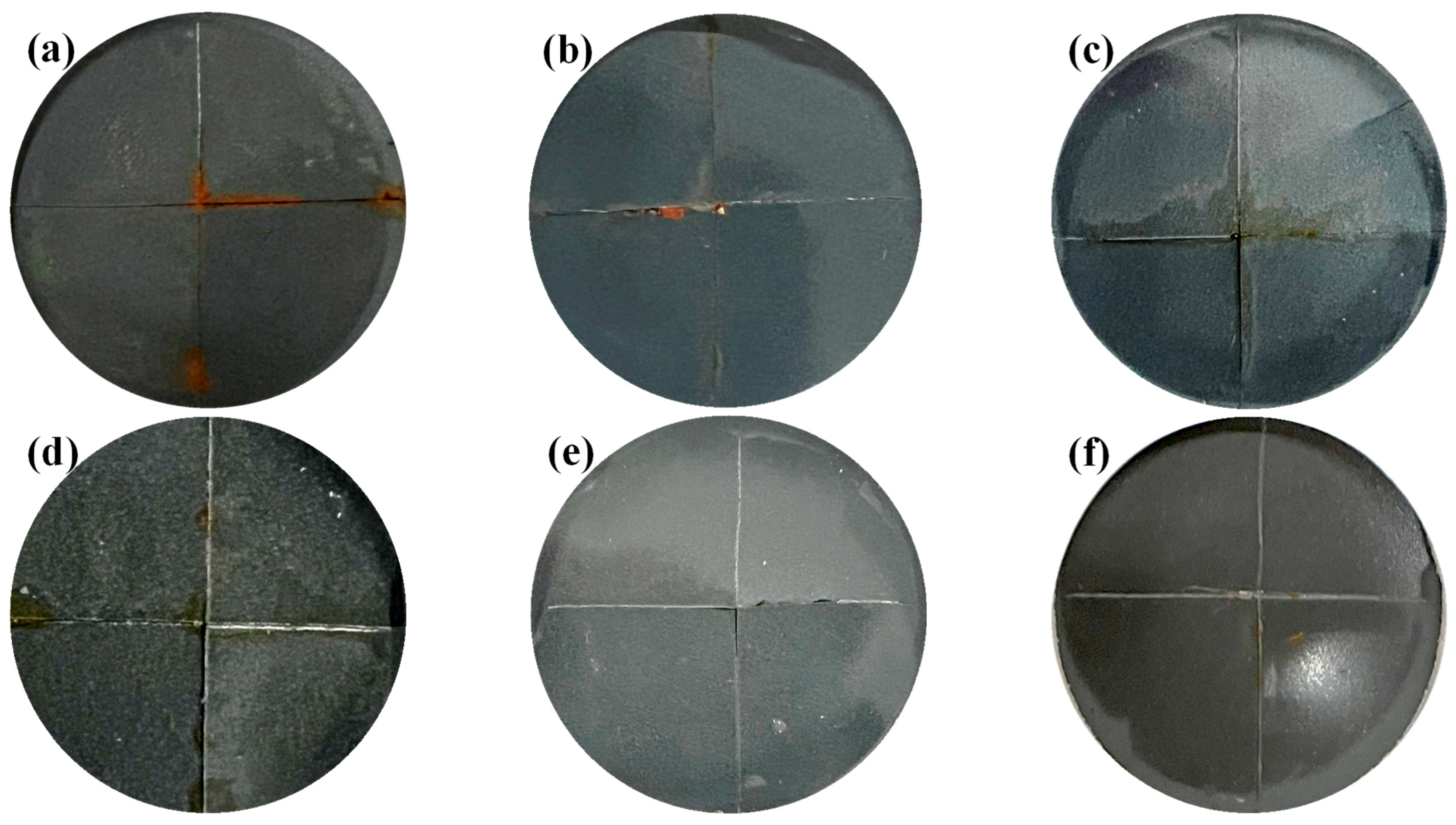
3.5. Self-Healing Properties of Coatings
3.5.1. Macroscopic Morphology of Coating Damage
3.5.2. Microscopic Morphology of the Base Metal at the Damage Site
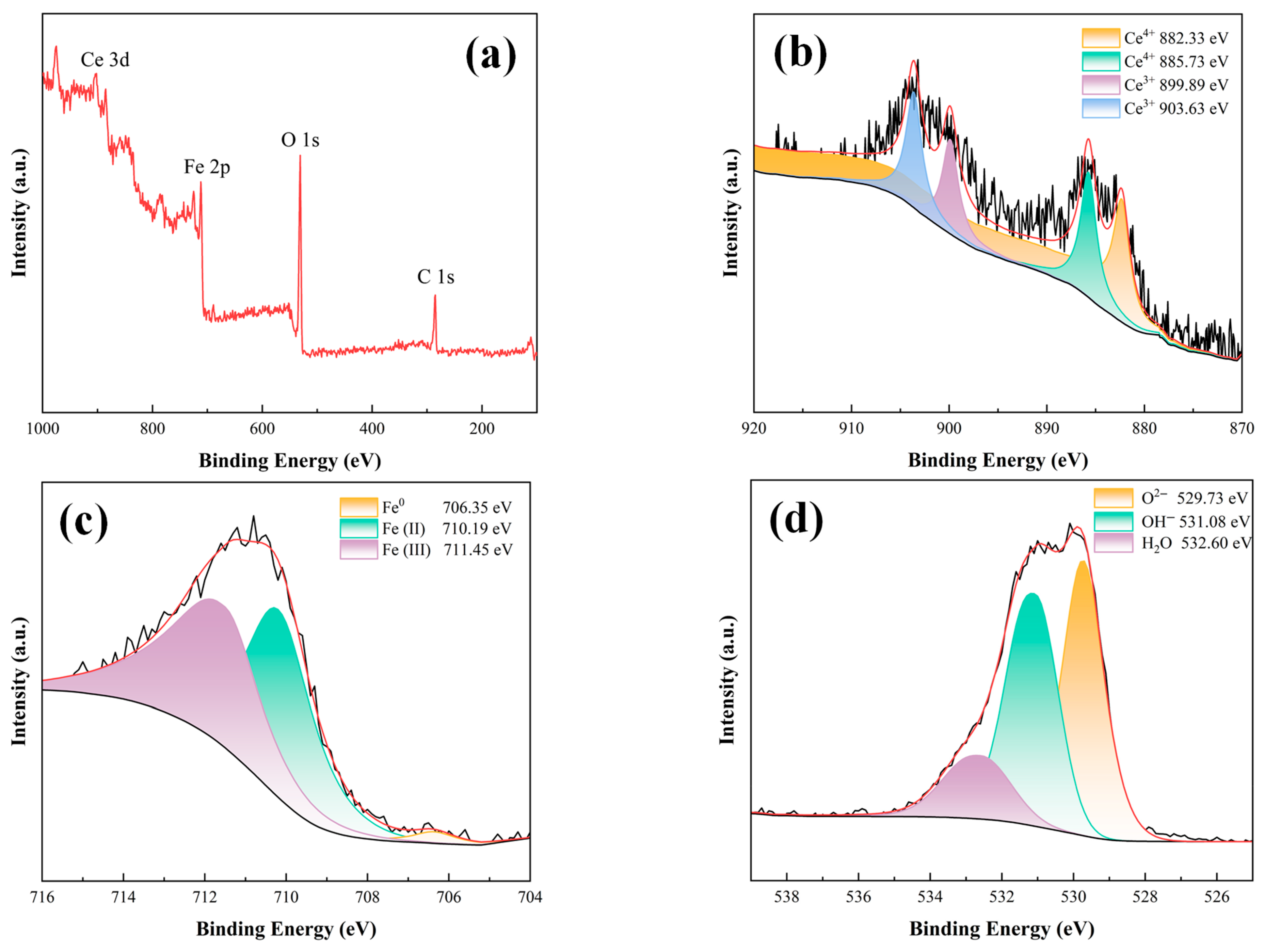
3.5.3. Compositional Analyses of Substrate Metal Surface Products at Breaks
4. The Influence of Ce(NO3)3·6H2O Content on Coating Properties
5. Conclusions
- The incorporation of cerium nitrate into the OCF1.5–15 coating has no significant impact on its TC. When the coating is doped with cerium nitrate, both the corrosion resistance and self-repairing performance of the coating are enhanced with the increase in cerium nitrate content;
- The Ce2.5 coating offers outstanding performance in terms of its TC, corrosion resistance, corrosion inhibitor-assisted healing capability, and long-term reliability. The TC is about 1.4 W/(m·K). Additionally, it shows outstanding corrosion resistance, with the impedance modulus at |Z|0.1 Hz reaching 6.08 × 109 Ω·cm2 after 4 weeks of immersion in 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution at 80 °C—representing a 32% improvement compared to the OCF1.5–15 coating;
- The form in which the inorganic corrosion inhibitor exists within the coating plays a critical role in determining the coating’s performance. As cerium nitrate is dissolved in acetone during the preparation process, Ce3+ ions are uniformly dispersed throughout the coating. Consequently, the doping of cerium nitrate does not trigger changes in the distribution of fillers within the coating and does not produce holes with an extension of the service time. From this, it can be concluded that while the doping of cerium nitrate does not significantly affect the TC of the coating, it effectively enhances the coating’s corrosion resistance. When the coating is completely saturated by the electrolyte, Ce3+ will be dissolved in water, forming a protective passivation film on the surface of the carbon steel substrate to inhibit the corrosion of carbon steel.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zou, C.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, G.; Xiong, B. Energy revolution: From a fossil energy era to a new energy era. Nat. Gas Ind. B 2016, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, C.; Zhou, X.; Wei, L. Thermal characteristics study on the gathering and transportation process of crude oil by mixing with hot water. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2025, 69, 106065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez, D.A.; Perez, T.; Simison, S.N. The influence of microstructure and chemical composition of carbon and low alloy steels in CO2 corrosion. A state-of-the-art appraisal. Mater. Des. 2003, 24, 561–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovyeva, V.A.; Almuhammadi, K.H.; Badeghaish, W.O. Current downhole corrosion control solutions and trends in the oil and gas industry: A review. Materials 2023, 16, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Xu, F.; Cui, Y.; Bao, D.; Yuan, S.; Sun, Y.; Pei, L.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Wang, H. Novel thermal conductivity and anti-corrosion coating with hydrophobic properties for heat exchanger applications. Prog. Org. Coat. 2024, 186, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Zhang, M.; Cui, Y.; Bao, D.; Peng, J.; Gao, Y.; Lin, D.; Geng, H.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, H. A novel polymer composite coating with high thermal conductivity and unique anti-corrosion performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 439, 135660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Gao, B.; Wang, M.; Yuan, Z.; Shen, J.; Zhao, J.; Feng, Y. Strategies for enhancing thermal conductivity of polymer-based thermal interface materials: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 56, 1064–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, X.; Liao, K.; Leng, J.; Qin, M.; Lyu, X.; He, G.; Zhao, S.; He, T.; Zheng, D. Effects of OCF content and oxidation treatment on thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance of CF/BN/EPN coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 481, 130664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Shang, Y.; Su, F.; Hu, Q.; Patil, R.R.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Guo, Z. Thermally conductive anticorrosive epoxy nanocomposites with tannic acid-modified boron nitride nanosheets. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 20371–20381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenker, M.; Balzer, M.; Kappl, H. Corrosion protection with hard coatings on steel: Past approaches and current research efforts. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 257, 182–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayan, P.P.; Al-Maadeed, M. Self-repairing composites for corrosion protection: A review on recent strategies and evaluation methods. Materials 2019, 12, 2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Amiery, A.A.; Isahak, W.N.R.W.; Al-Azzawi, W.K. Corrosion inhibitors: Natural and synthetic organic inhibitors. Lubricants 2023, 11, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.A.; Amin, S.; Mohamed, A.A. Current and emerging trends of inorganic, organic and eco-friendly corrosion inhibitors. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 31877–31920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, D.S.; Verma, C.; Quraishi, M.A. Molecular structural aspects of organic corrosion inhibitors: Experimental and computational insights. J. Mol. Struct. 2021, 1227, 129374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, C.; Ebenso, E.E.; Quraishi, M.A.; Hussain, M.C. Recent developments in sustainable corrosion inhibitors: Design, performance and industrial scale applications. Mater. Adv. 2021, 2, 3806–3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, P.N.; Amini, R.; Kardar, P.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Epoxy-ester coating reinforced with cerium (III)-tannic acid-based hybrid pigment for effective mild-steel substrate corrosion protection. Prog. Org. Coat. 2021, 161, 106485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danaee, I.; Darmiani, E.; Rashed, G.R.; Zaarei, D. Self-healing and anticorrosive properties of Ce (III)/Ce (IV) in nanoclay–epoxy coatings. Iran. Polym. J. 2014, 23, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, S.; Nawaz, M.; Kahraman, R.; Ahmed, E.M.; Shakoor, R. Effect of the modified hybrid particle on the corrosion inhibition performance of polyolefin based coatings for carbon steel. J. Sci. Adv. Mater. Devices 2022, 7, 100466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, C.; Huang, Y.; Hao, W.; Zhang, D.; Luo, X.; Ma, L.; Wang, J.; Chowwanonthapunya, T.; Dong, C.; Li, X. Multi-action self-healing coatings with simultaneous recovery of corrosion resistance and adhesion strength. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 101, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liao, K.; Hu, J.; Qin, M.; He, T.; Ou, T.; Fan, Y.; Leng, J.; He, G. Effects of h-BN content and silane functionalization on thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance of h-BN/EPN coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 476, 130185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Qin, M.; Yan, Y.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; He, G.; Jiang, P.; Wu, H.; Liao, K. Effects of Na2MoO4 Content on the Properties of CF/BN/EPN Heat Exchangers Coatings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2025, 345, 131127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Y.; Fei, G.; Wang, C.; Shen, Y.; Zhu, K.; Sun, L.; Rang, N.; Guo, D.; Wallace, G.G. Functionalizing graphene with titanate coupling agents as reinforcement for one-component waterborne poly (urethane-acrylate) anticorrosion coatings. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 359, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Kang, Y.; Li, D.; Liu, Y.C. Catalytic oxidation of sulfur dioxide over α-Fe2O3/SiO2 catalyst promoted with Co and Ce oxides. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2020, 37, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandamalla, A.; Manchala, S.; Verma, A.; Fu, Y.-P.; Shanker, V. Development of highly efficient Ce(MoO4)2/g-C3N4 composite for the photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and ciprofloxacin under visible light. J. Mol. Struct. 2024, 1297, 136896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arul, N.S.; Mangalaraj, D.; Ramachandran, R.; Grace, A.N.; Han, J.I. Fabrication of CeO2/Fe2O3 composite nanospindles for enhanced visible light driven photocatalysts and supercapacitor electrodes. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 15248–15258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latha, P.; Prakash, K.; Karuthapandian, S. Facile fabrication of visible light-driven CeO2/PMMA thin film photocatalyst for degradation of CR and MO dyes. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2018, 44, 5223–5240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purbia, R.; Choi, S.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Ye, B.; Jeong, B.; Lee, D.H.; Park, H.; Kim, H.-D.; Baik, J.M. Cu-and Ce-promoted nano-heterostructures on vanadate catalysts for low-temperature NH3–SCR activity with improved SO2 and water resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 437, 135427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, J.; Chong, Y.; Liu, J. Inhibition effect of green Betaine type surfactants on Q235 steel in 1 mol·L−1 hydrochloric acid: The experimental and theoretical research. J. Mol. Struct. 2022, 1262, 133023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Huang, Y.; Wang, H.; Huang, L.; Hu, L.; Zhong, H.; He, Z. A novel composite of almandine supported humboldtine nanospheres, in situ synthesized from natural almandine, possesses high removal efficiency of Cr (VI) over a wide pH range. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 383, 121199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, W.; Dong, B.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, T.; Fan, Y.; Yang, W. Insight into electrochemical passivation behavior and surface chemistry of 2205 duplex stainless steel: Effect of tensile elastic stress. Corros. Sci. 2021, 193, 109903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarantuya, L.; Sevjidsuren, G.; Altantsog, P.; Tsogbadrakh, N. Synthesis, structure and electronic properties of Li4Ti5O12 anode material for lithium ion batteries. Solid State Phenom. 2018, 271, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Sun, Y.; Wan, D.; Wan, H.; Wang, Y. FeOOH coupling and nitrogen vacancies functionalized g-C3N4 heterojunction for efficient degradation of antibiotics: Performance evaluation, active species evolution and mechanism insight. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 903, 163898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalil, P.A.; Faiz, M.; Tabet, N.; Hamdan, N.; Hussain, Z. A study of the stability of tungstophosphoric acid, H3PW12O40, using synchrotron XPS, XANES, hexane cracking, XRD, and IR spectroscopy. J. Catal. 2003, 217, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgheib, A.; Zarebidaki, A.; Attar, M.M. Enhanced barrier properties of epoxy coating containing CaCO3 microparticles modified with cerium nitrate. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 144, 105660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgheib, A.; Mohammadzadeh Attar, M.; Zarebidaki, A. Evaluation of corrosion inhibition of mild steel in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution by cerium nitrate. Met. Mater. Int. 2020, 26, 1634–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| [No.] | Title | Specification | Model | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Ce(NO3)3·6H2O | AR | 99.99% | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Shanghai, China |
| 2 | CF | commodity-grade | φ5 × 20 μm | Shanghai Mitsuda Nano New Material Co., Shanghai, China |
| 3 | h-BNNs | commodity-grade | 100 nm | Shanghai Mitsuda Nano New Material Co., Shanghai, China |
| 4 | EPN | commodity-grade | NPPN-630 L | South Asia Plastic Industry Co., Taiwan, China |
| 5 | curing agent | commodity-grade | Ancamine 2280 | Shanghai Evonik Speciality Chemicals Co., Shanghai, China |
| 6 | APTES | AR | 99% | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Shanghai, China |
| 7 | ethanol | AR | 99.9% | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Shanghai, China |
| 8 | ammonia | AR | 99.9% | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Shanghai, China |
| 9 | acetone | AR | 99.9% | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Shanghai, China |
| 10 | oxalate | AR | 99.9% | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Shanghai, China |
| 11 | ammonium nitrate | AR | 99.9% | Shanghai McLean Biochemical Technology Co., Shanghai, China |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, Y.; Wu, J.; Liu, M.; Meng, Q.; Zhou, J.; Feng, D.; Li, Y.; Xie, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, X.; et al. Effect of Cerium Nitrate Content on the Performance of Ce(III)/CF/BN/EPN Heat Exchanger Coatings. Coatings 2025, 15, 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070818
Yan Y, Wu J, Liu M, Meng Q, Zhou J, Feng D, Li Y, Xie Z, Li J, Jiang X, et al. Effect of Cerium Nitrate Content on the Performance of Ce(III)/CF/BN/EPN Heat Exchanger Coatings. Coatings. 2025; 15(7):818. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070818
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Yongbo, Jirong Wu, Mingxing Liu, Qinghua Meng, Jing Zhou, Danyang Feng, Yi Li, Zhijie Xie, Jinyang Li, Xinhui Jiang, and et al. 2025. "Effect of Cerium Nitrate Content on the Performance of Ce(III)/CF/BN/EPN Heat Exchanger Coatings" Coatings 15, no. 7: 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070818
APA StyleYan, Y., Wu, J., Liu, M., Meng, Q., Zhou, J., Feng, D., Li, Y., Xie, Z., Li, J., Jiang, X., Tang, J., Shi, X., & Zhang, J. (2025). Effect of Cerium Nitrate Content on the Performance of Ce(III)/CF/BN/EPN Heat Exchanger Coatings. Coatings, 15(7), 818. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070818





