The Influence of Ni Incorporation on the Surface Porosity and Corrosion Resistance of CrBN Coatings on 45 Steel in Seawater
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Coatings Deposition
2.2. Structural Characterization and Morphology Observation
2.3. Electrochemical Properties Measurement
- (1)
- Open circuit potential (OCP): The sample was soaked in 3.5 wt% NaCl solution, and the variation in potential was recorded for 3600 s.
- (2)
- Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS): After OCP test, the stable open circuit potential was set as the starting potential, the scanning frequency was set from 1 mHz to 100 kHz, and the amplitude of the AC excitation signal was set to 10 mV.
- (3)
- Potential dynamic polarization test (PDP): After EIS test, the relationship of potential and current for sample was measured by PP test. The scanning range was set from −1.0 V to 1.0 V with the scanning rate of 20 mV/min. During the test, the current sensitivity was set to be automatic.
3. Results and Discussion
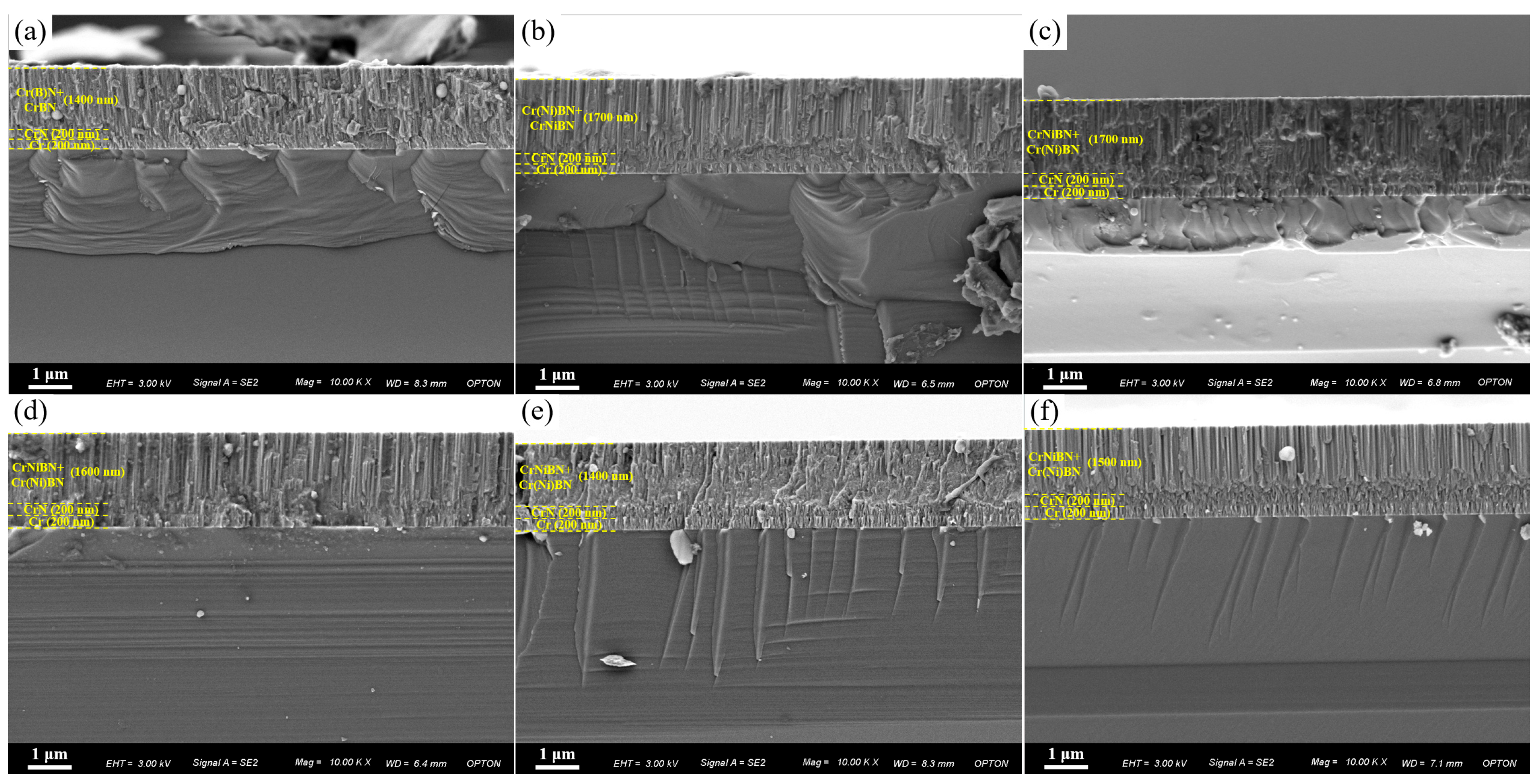
3.1. Microstructure of CrNiBN Coatings
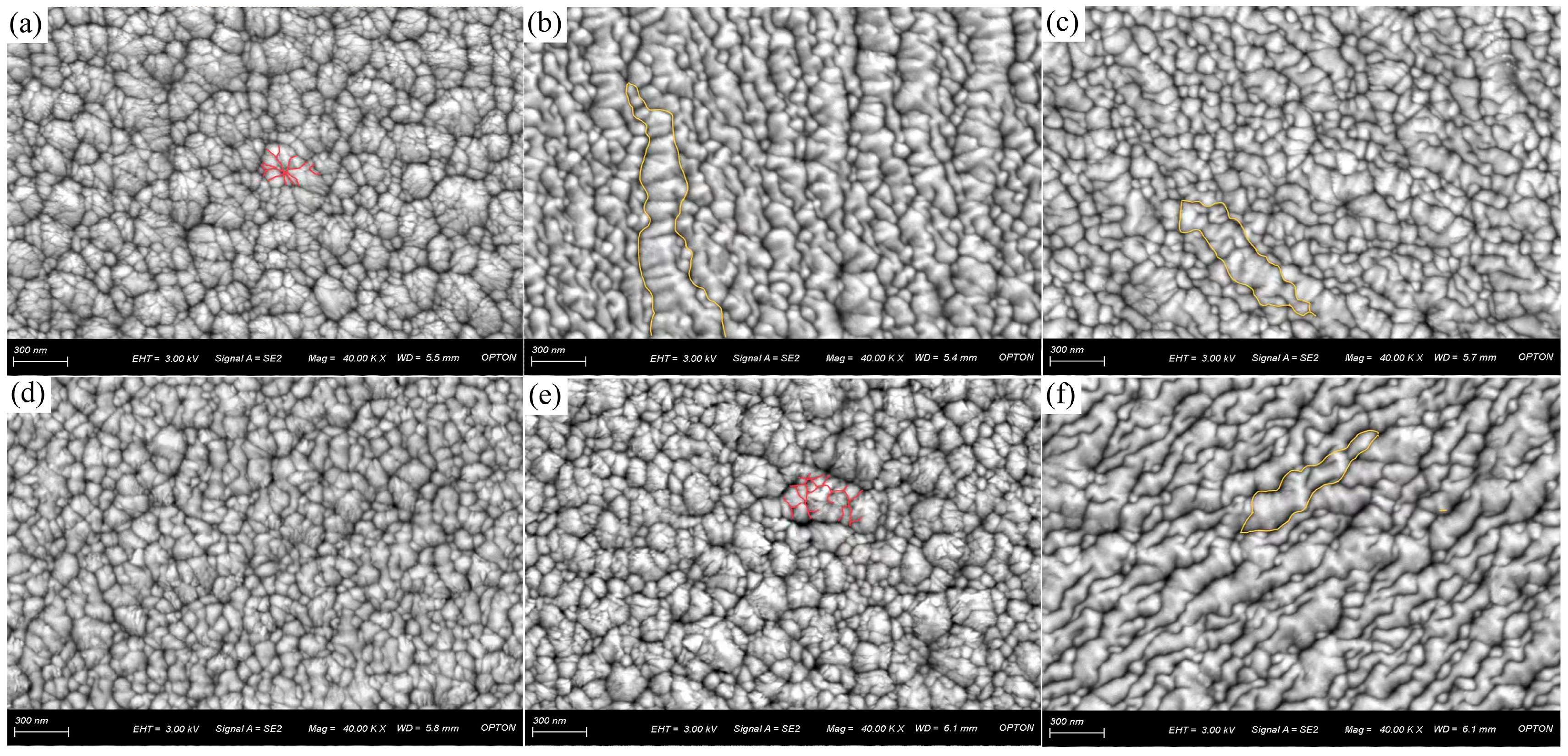
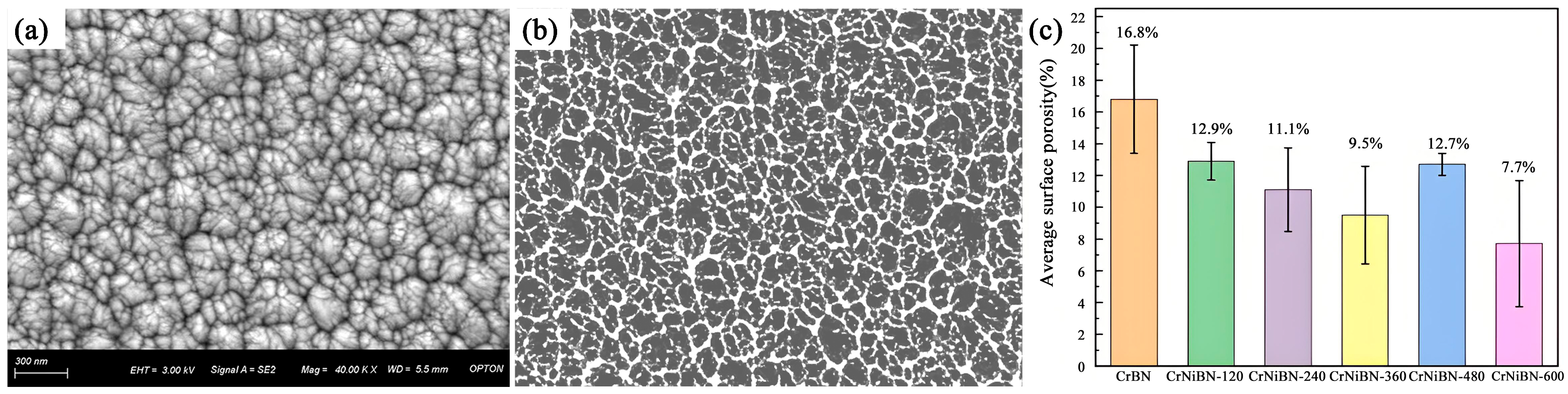
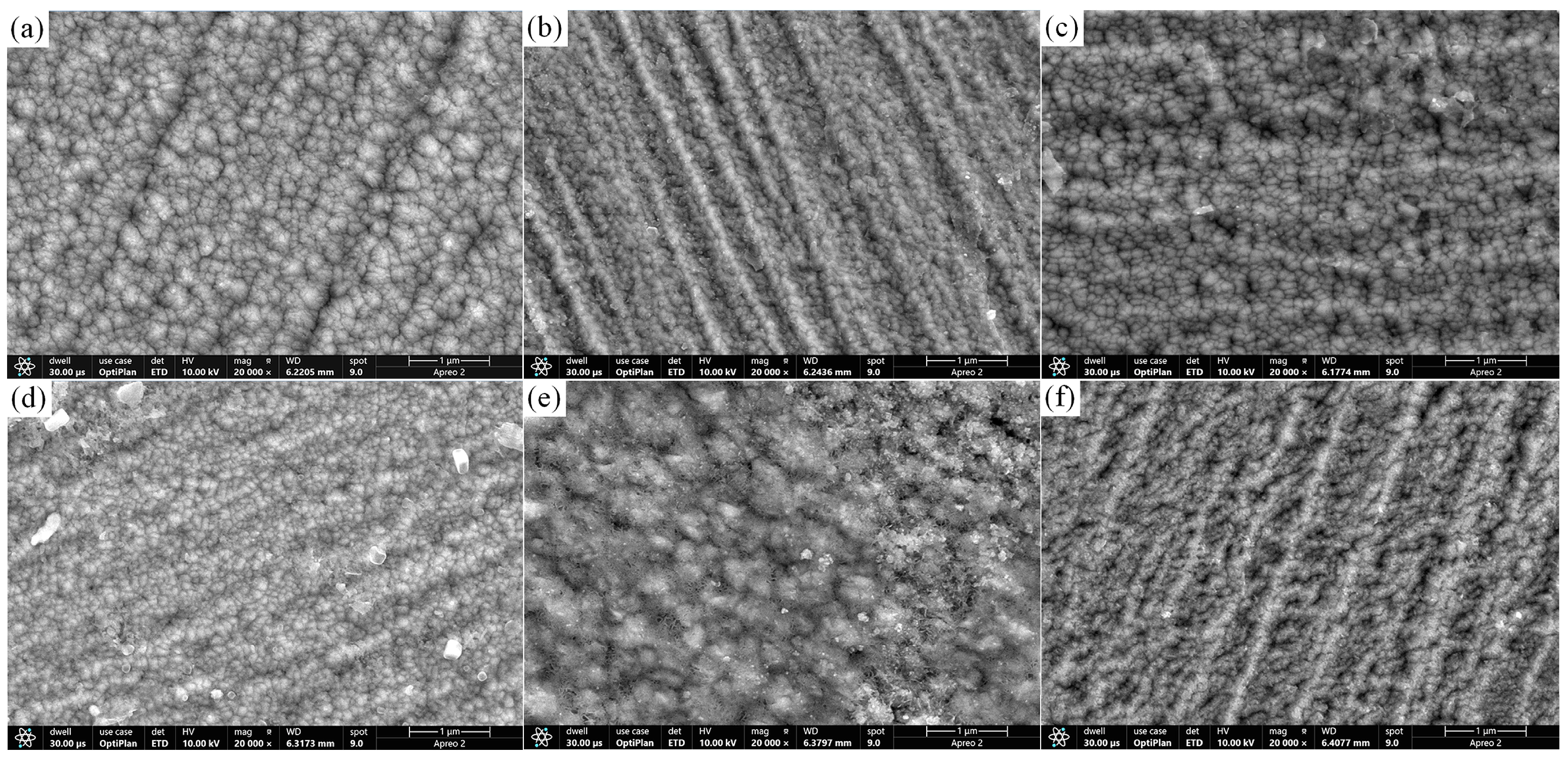
3.2. Surface Morphology and Surface Porosity of CrNiBN Coatings
3.3. Electrochemical Properties
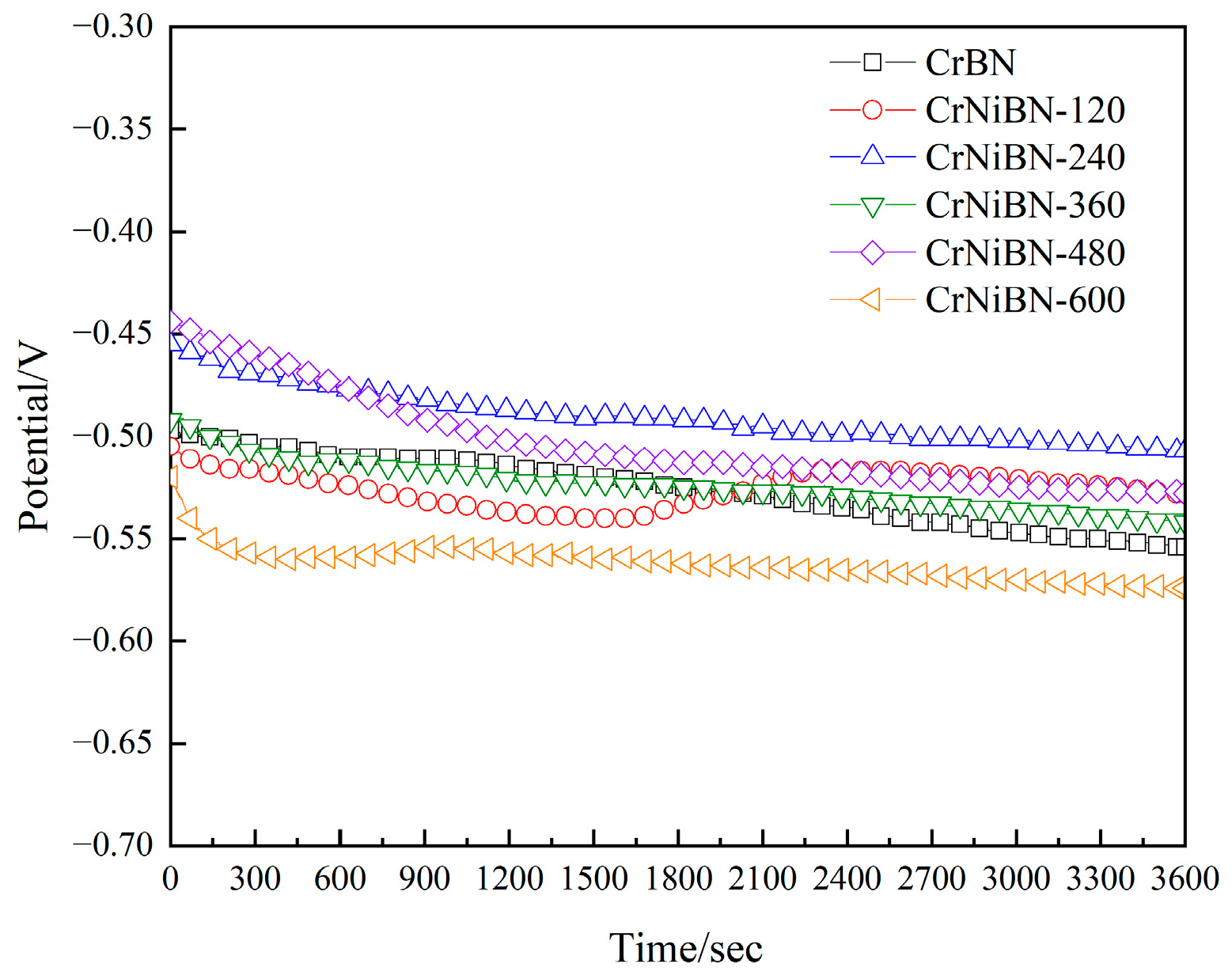
3.3.1. Analysis of Open Circuit Potential Results
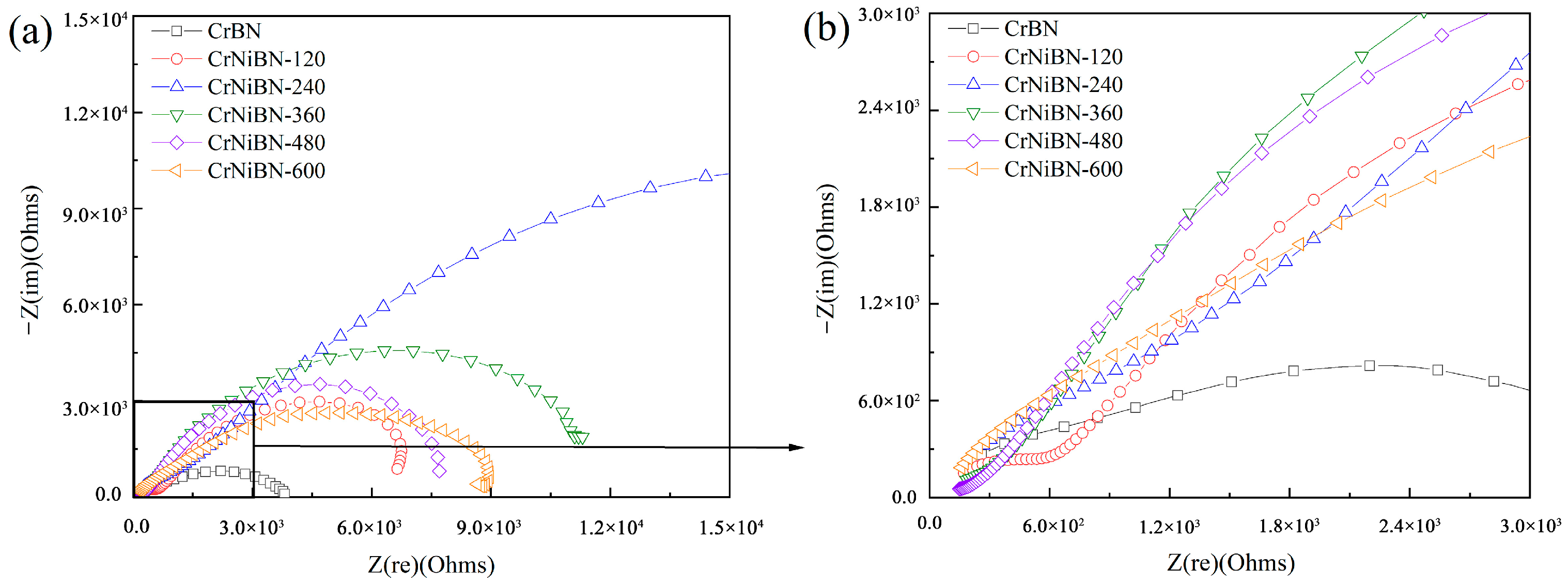
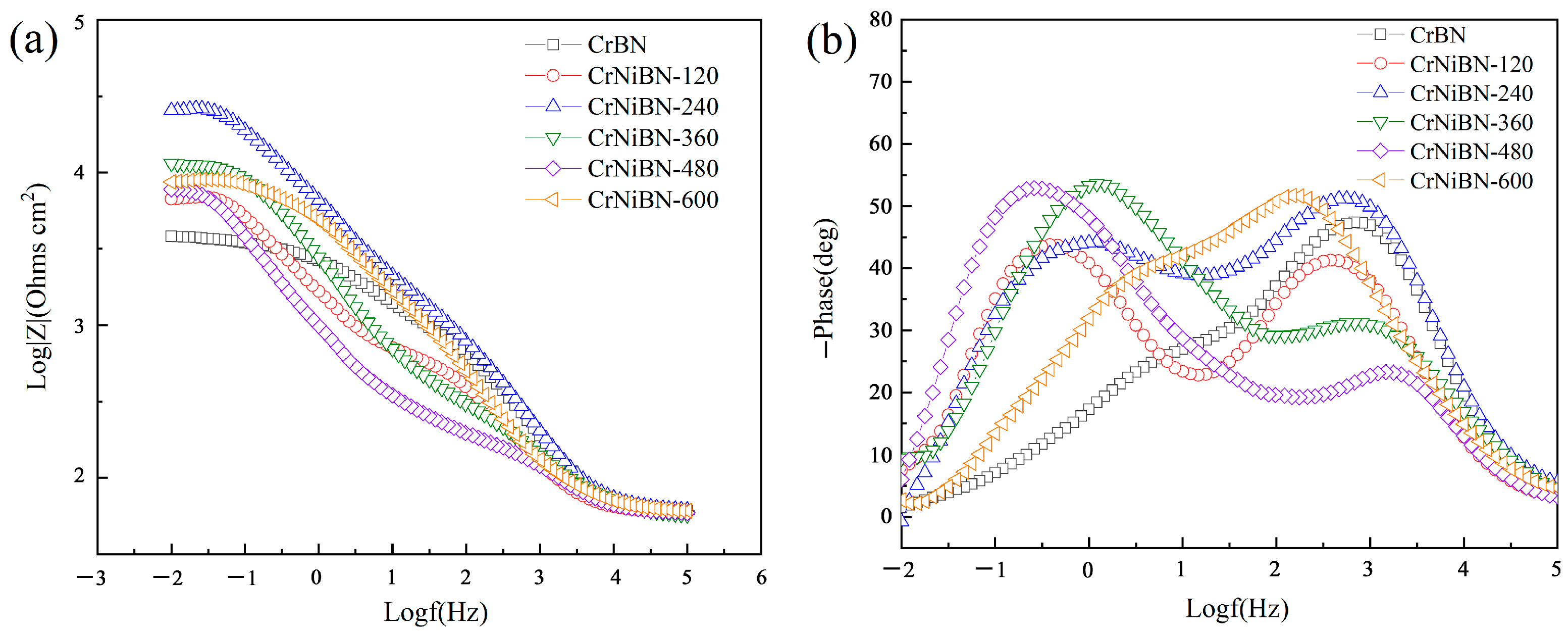
3.3.2. Analysis of Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy Results
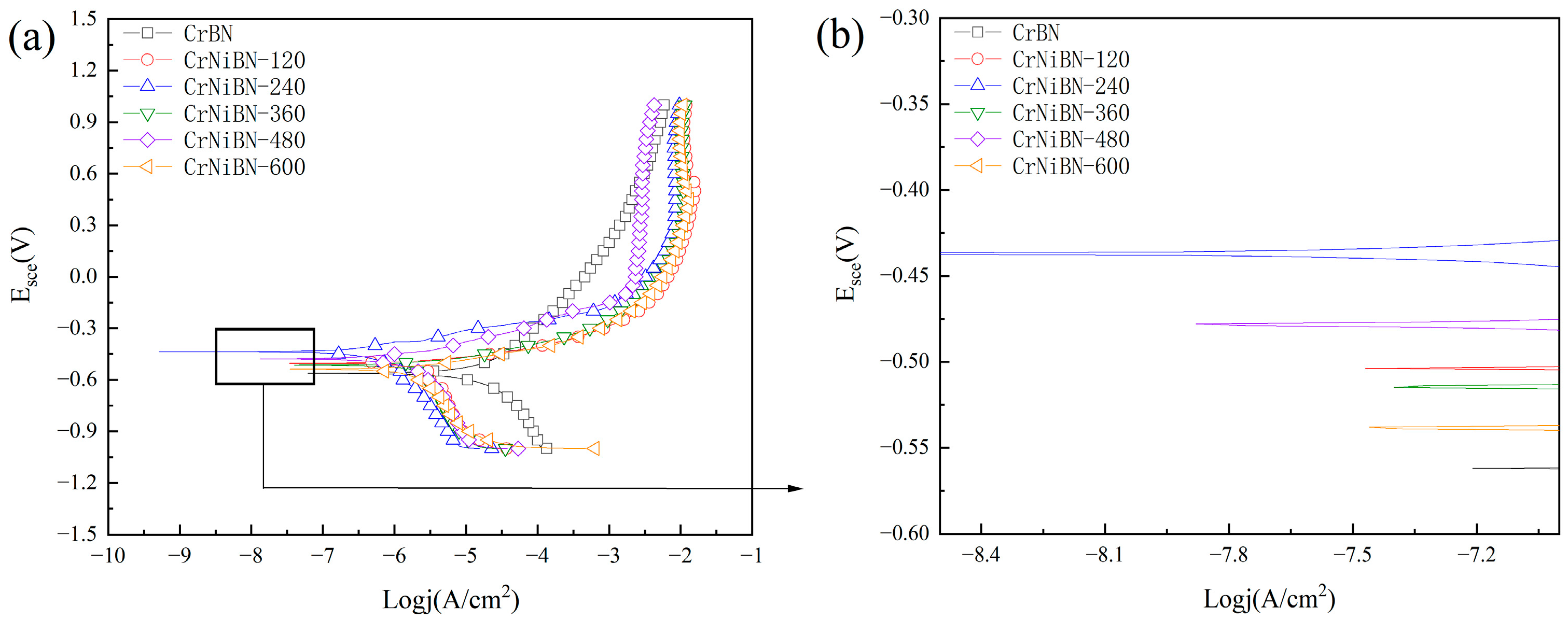
3.3.3. Analysis of Potential Dynamic Polarization Results
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- As compared to the CrBN coating, the surface morphology of CrNiBN coatings became compact with lower surface porosity. It could hinder the penetration channel.
- (2)
- After Ni incorporation, the open-circuit potential increased from −0.554 V to −0.507 V due to the low surface porosity and relative positive potential of Ni. It indicates that the occurrence of corrosion for CrNiBN coating became hard.
- (3)
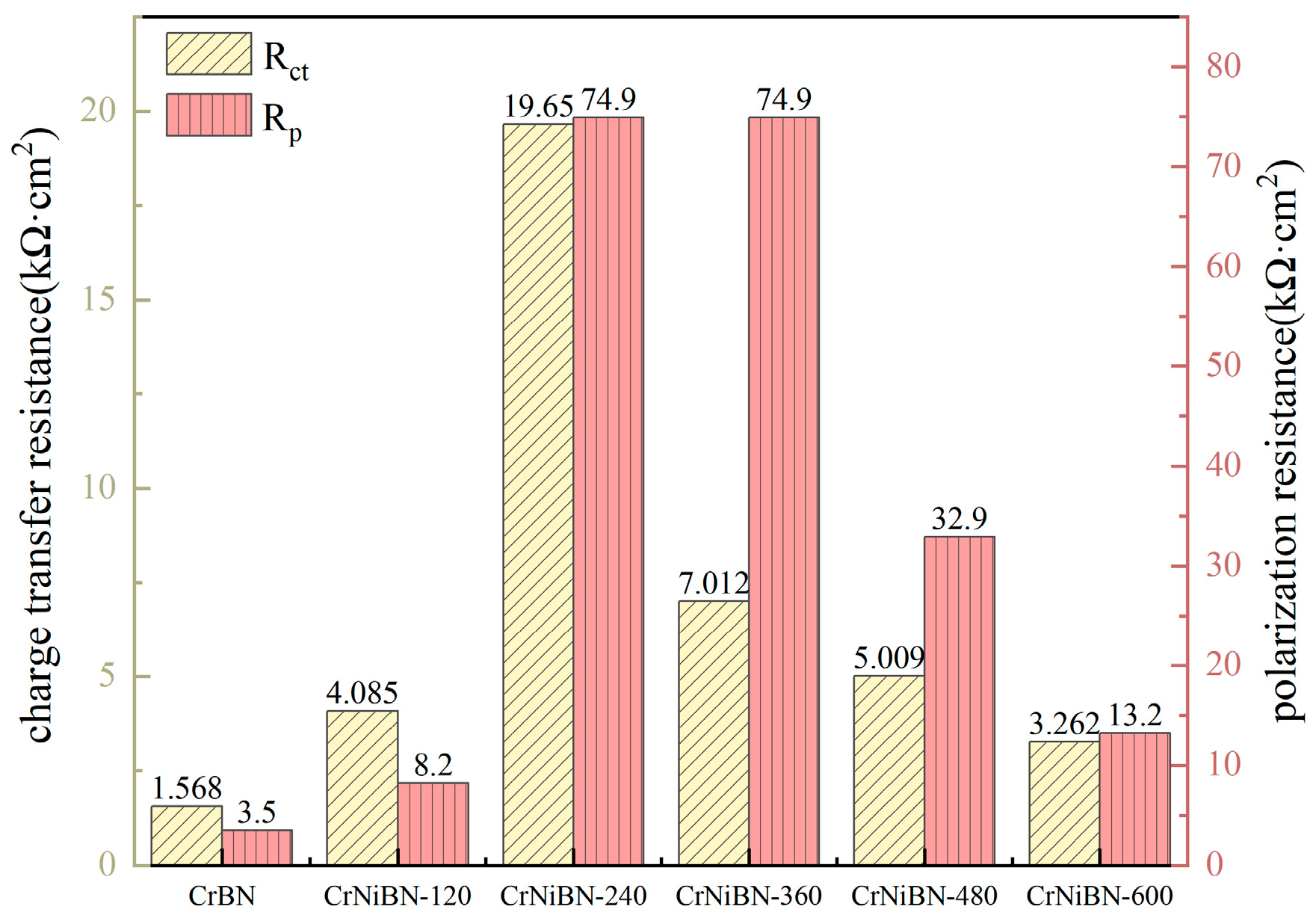
- Owing to the combination effect of moderate surface porosity, the highest self-corrosion potential and less oxidation, the CrNiBN-240 coating presented the best corrosion resistance with the highest charge transfer resistance of 1.965 × 104 Ω·cm2 and the highest polarization resistance of 74.9 kΩ·cm2.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SEM | Scanning Electron Microscope |
| EIS | Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy |
| PDP | Potentio-dynamic Polarization |
| OCP | Open Circuit Potential |
References
- Li, T.; Long, H.; Qiu, C.; Wang, M.; Li, D.; Dong, Z.; Gui, Y. Multi-objective optimization of process parameters of 45 steel laser cladding Ni60PTA alloy powder. Coatings 2022, 12, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, A.T.; Sharma, N.; Soliman, M.S.; Rayes, M.M.; Sharma, R.C.; Elkaseer, A. Effect of wiper edge geometry on machining performance while turning AISI 1045 steel in dry conditions using the VIKOR-ML approach. Machines 2013, 11, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, H.; Tian, F.; Wei, Q.; Qin, J.; Luo, G.; Shen, Q. Hardness gradient multilayer coating for enhancing tribological property of AISI 1045 steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2025, 512, 132405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, C.; Tang, S. Improving the corrosion resistance and mechanical property of 45 steel surface by laser cladding with Ni60CuMoW alloy powder. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2013, 228, S296–S300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, W.; Xu, Y.; Luo, X.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Song, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C. Effect of WC-17Co content on microstructure, mechanical properties and wear resistance of WC-17Co/Ni composites produced with cold spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 493, 131252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velasco, S.C.; Cavaleiro, A.; Carvalho, S. Functional properties of ceramic-Ag nanocomposite coatings produced by magnetron sputtering. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2016, 84, 158–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Shi, Q.; Ge, X.; Wang, W. Multilayer coatings for tribology: A mini review. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maskavizan, A.J.; Quintana, J.P.; Dalibón, E.L.; Márquez, A.B.; Brühl, S.P.; Farina, S.B. Evaluation of wear and corrosion resistance in acidic and chloride solutions of cathodic arc PVD chromium nitride coatings on untreated and plasma nitrided AISI 4140 steel. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2024, 494, 131476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Yin, X.; Meng, F.; Liu, C. The microstructure and wear resistance of laser cladding Ni60/60%WC composite coatings. Metals 2025, 15, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, F.; Zhu, P.; Meng, F.; Xue, Q.; Huang, F. Achieving very low wear rates in binary transition-metal nitrides: The case of magnetron sputtered dense and highly oriented VN coatings. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2014, 248, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Yang, X.; Li, X.; Chai, C.; Liu, W. Study on microstructure and properties of nickel-based self-lubricating coating by laser cladding. Coatings 2022, 12, 753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, S. Tribocorrosion of CrN coatings on different steel substrates. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2024, 484, 130829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Pan, Y.; Tang, G.; Liang, D.; Hu, H.; Liu, X.; Liang, Z. Facile fabrication of TiN coatings to enhance the corrosion resistance of stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2024, 494, 131450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruden, A.; Restrepo-Parra, E.; Paladines, A.U.; Sequeda, F. Corrosion resistance of CrN thin films produced by dc magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 270, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Shu, X.; Liu, E.; Han, Z.; Li, X.; Tang, B. Assessments on corrosion, tribological and impact fatigue performance of Ti- and TiN-coated stainless steels by plasma surface alloying technique. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2014, 239, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Luan, J.; Xie, F.; Zhang, Z.; Evaristo, M.; Cavaleiro, A. The green lubricant coatings deposited by physical vapor deposition for demanding tribological applications: A review. Coatings 2024, 14, 828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudak, O.E.; Bahr, A.; Kutrowatz, P.; Wojcik, T.; Bohrn, F.; Solyom, L.; Schuster, R.; Shang, L.; Hunold, O.; Polcik, P.; et al. Pitting corrosion—Preferred chloride diffusion pathways in physical vapordeposited AlCrN coatings. Corros. Sci. 2023, 211, 110901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, S. Toward hard yet tough ceramic coatings. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2014, 258, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Liu, D.; Shao, T. Microstructure and mechanical properties of TiAlSiN nano-composite coatings deposited by ion beam assisted deposition. Sci. China Technol. Sci. 2015, 58, 1682–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, G.; Wood, R.J.K.; Wang, S.C.; Xue, Q. Fabrication of CrAlN nanocomposite films with high hardness and excellent anti-wear performance for gear application. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2010, 204, 3517–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, E.; Sanjinés, R.; Karimi, A.; Esteve, J.; Levy, F. Mechanical properties of nanocomposite and multilayered Cr-Si-N sputtered thin films. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2004, 180–181, 570–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Chung, W.; Cho, Y.; Kim, K. Synthesis and mechanical properties of Cr-Si-N coatings deposited by a hybrid system of arc ion plating and sputtering techniques. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2004, 188–189, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Kim, K. Microstructural control of Cr-Si-N films by a hybrid arc ion plating and magnetron sputtering process. Acta Mater. 2009, 57, 4974–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, Y.; Hong, J.; Kim, G.; Lee, H.; Han, J. Effect of Si addition to CrN coatings on the corrosion resistance of CrN/stainless steel coating/substrate system in a deaerated 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. Surf. Coat. Tech. 2007, 201, 9518–9523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, C.; Man, J.; Zhang, D.; Wan, Y.; Sun, H. Electrochemical corrosion and tribocorrosion behavior of CrN and CrAlN coatings in artificial seawater. Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 2024, 21, 3569–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wan, W.; Zhang, X. Effect of Ni doping on the microstructure and toughness of CrAlN coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 026414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, F.; Kong, J. The influence of Ni concentration on the structure, mechanical and tribological properties of Ni-CrSiN coatings in seawater. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 819, 152998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, F.; Kong, J. Electrochemical properties promotion of CrSiN coatings in seawater via Ni incorporation. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 856, 157450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jin, X.; Zhou, F. Comparison of mechanical and tribological properties of CrBN coatings modified by Ni or Cu incorporation. Friction 2022, 10, 516–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Image Processing and Analysis in Java. Available online: https://imagej.net/ij/.
- AlMarzooqi, F.; Bilad, M.; Mansoor, B.; Arafat, H. A comparative study of image analysis and porometry techniques for characterization of porous membranes. J. Mater. Sci. 2016, 51, 2017–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, J.; Zhao, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Enhancing the flux of brackish water TFCRO membrane by improving support surface porosity via a secondary pore-forming method. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 498, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Yao, Y.; Ding, Z.; Yang, W.; Liu, J. Effect of Si3N4/TaC particles on the structure and properties of microarc oxidation coatings on TC4 alloy. Coatings 2022, 12, 1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, H.; Zhylinski, V.; Vereschaka, A.; Chayeuski, V.; Huo, Y.; Milovich, F.; Sotova, C.; Seleznev, A.; Salychits, O. Comparison of the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of the Cr-CrN, Ti-TiN, Zr-ZrN, and Mo-MoN coatings. Coatings 2023, 13, 750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Yao, J.; Dong, H.; Chen, Z.; Liu, X. Enhancing the corrosion resistance of passivation films via the synergistic effects of graphene oxide and epoxy resin. Coatings 2025, 15, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anandan, C.; Grips, V.; Selvi, V.; Rajam, K. Electrochemical studies of stainless steel implanted with nitrogen and oxygen by plasma immersion ion implantation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhou, F.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, L.; Lee, S. Effect of titanium or chromium content on the electrochemical properties of amorphous carbon coatings in simulated body fluid. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 112, 603–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sui, J.; Cai, W. Effect of bias voltage on the structure and electrochemical corrosion behaviour of hydrogenated amorphous carbon(a-C:H)films on NiTi alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2007, 201, 6906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, R.; Ma, S.; Chu, P. Corrosion behaviour of titanium alloy in the presence of serum proteins. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2010, 19, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, A.; Liu, E.; Zhang, S.; Tan, S.; Hing, P.; Annergren, I.; Gao, J. Impedance study on electrochemical characteristic of sputtered DLC films. Thin Solid Film. 2003, 426, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawiec, H.; Vignal, V.; Schwarzenboeck, E.; Banas, J. Role of plastic deformation and microstructure in the micro-electrochemical behaviour of Ti-6Al-4V in sodium chloride solution. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 104, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Alfantazi, A. Effect of microstructure and temperature on electrochemical behavior of niobium in phosphate-buffered saline solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2013, 160, C1–C11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, C.; Liu, C.; Huang, M. Improvement in corrosion resistance of CrN coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 365, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speight, J.G. Lange’s Handbook of Chemistry, 17th ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 6.81–6.142. [Google Scholar]


| Process | Cr Target Power | CrB2 Target Power | NiCr Target Power | Ar Flow | N2 Flow | Bias Voltage | Time | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-layer transition architecture | Cr tier | 1150 W | -- | -- | 50 sccm | -- | −80 V | 10 min |
| CrN tier | 1150 W | -- | -- | 50 sccm | OEM 50% | −80 V | 15 min | |
| Cr(Ni)BN tier | 1150 W | 0 W → 720 W | 0 W → Set point | 50 sccm | OEM 50% | −80 V | 15 min | |
| Top layer | CrBN | 1150 W | 720 W | Set point: 0 W | 50 sccm | OEM 50% | −80 V | 80 min |
| CrNiBN-120 | 1150 W | 720 W | Set point: 120 W | 50 sccm | OEM 50% | −80 V | 75 min | |
| CrNiBN-240 | 1150 W | 720 W | Set point: 240 W | 50 sccm | OEM 50% | −80 V | 70 min | |
| CrNiBN-360 | 1150 W | 720 W | Set point: 360 W | 50 sccm | OEM 50% | −80 V | 65 min | |
| CrNiBN-480 | 1150 W | 720 W | Set point: 480 W | 50 sccm | OEM 50% | −80 V | 60 min | |
| CrNiBN-600 | 1150 W | 720 W | Set point: 600 W | 50 sccm | OEM 50% | −80 V | 55 min | |
| Coatings | Rs (Ω·cm2) | (CPE-Y0)po (F/cm2) | (CPE-n)po | Rpo (Ω·cm2) | (CPE-Y0)dl (F/cm2) | (CPE-n)dl | Rct (Ω·cm2) | Inhibition Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CrBN | 29.75 | 8.691 × 10−6 | 0.8252 | 3.620 × 102 | 1.786 × 10−4 | 0.5544 | 1.568 × 103 | -- |
| CrNiBN-120 | 27.97 | 4.119 × 10−5 | 0.7213 | 2.844 × 102 | 4.647 × 10−4 | 0.7253 | 4.085 × 103 | 260 |
| CrNiBN-240 | 29.79 | 1.074 × 10−5 | 0.7944 | 6.779 × 102 | 9.100 × 10−5 | 0.6128 | 1.965 × 104 | 1253 |
| CrNiBN-360 | 26.90 | 5.624 × 10−5 | 0.6564 | 2.064 × 102 | 1.292 × 10−4 | 0.7641 | 7.012 × 103 | 447 |
| CrNiBN-480 | 27.62 | 8.501 × 10−5 | 0.6390 | 1.078 × 102 | 5.046 × 10−4 | 0.7396 | 5.009 × 103 | 319 |
| CrNiBN-600 | 29.90 | 4.026 × 10−5 | 0.7127 | 1.390 × 103 | 7.644 × 10−5 | 0.7149 | 3.262 × 103 | 220 |
| Coatings | Ecorr (E vs. SCE) | Icorr (nA/cm2) | βa (V) | βc (V) | Rp (kΩ·cm2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CrBN | −0.5627 | 12490 | 0.197 | 0.208 | 3.5 |
| CrNiBN-120 | −0.5047 | 2898 | 0.059 | 0.755 | 8.2 |
| CrNiBN-240 | −0.4379 | 410.5 | 0.101 | 0.237 | 74.9 |
| CrNiBN-360 | −0.4369 | 456.2 | 0.101 | 0.356 | 74.9 |
| CrNiBN-480 | −0.4760 | 1020 | 0.102 | 0.317 | 32.9 |
| CrNiBN-600 | −0.5411 | 1839 | 0.069 | 0.29 | 13.2 |
| CrNiBN-480 | Cr (at%) | Ni (at%) | B (at%) | N (at%) | O (at%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Region 1 | 29.90 | 6.90 | 10.65 | 47.94 | 4.61 |
| Region 2 | 30.33 | 6.91 | 13.19 | 46.86 | 2.72 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhou, Z.; Wu, X.; Wang, Q.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, Z. The Influence of Ni Incorporation on the Surface Porosity and Corrosion Resistance of CrBN Coatings on 45 Steel in Seawater. Coatings 2025, 15, 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070804
Zhou Z, Wu X, Wang Q, Zhao G, Zhou Z. The Influence of Ni Incorporation on the Surface Porosity and Corrosion Resistance of CrBN Coatings on 45 Steel in Seawater. Coatings. 2025; 15(7):804. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070804
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhou, Zhidong, Xue Wu, Qianzhi Wang, Gai Zhao, and Zhifeng Zhou. 2025. "The Influence of Ni Incorporation on the Surface Porosity and Corrosion Resistance of CrBN Coatings on 45 Steel in Seawater" Coatings 15, no. 7: 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070804
APA StyleZhou, Z., Wu, X., Wang, Q., Zhao, G., & Zhou, Z. (2025). The Influence of Ni Incorporation on the Surface Porosity and Corrosion Resistance of CrBN Coatings on 45 Steel in Seawater. Coatings, 15(7), 804. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070804









