Investigating the Rheological Impact of USP Warm Mix Modifier on Asphalt Binder
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Material
2.1.1. Asphalt
2.1.2. USP-H Warm Mix Modifier
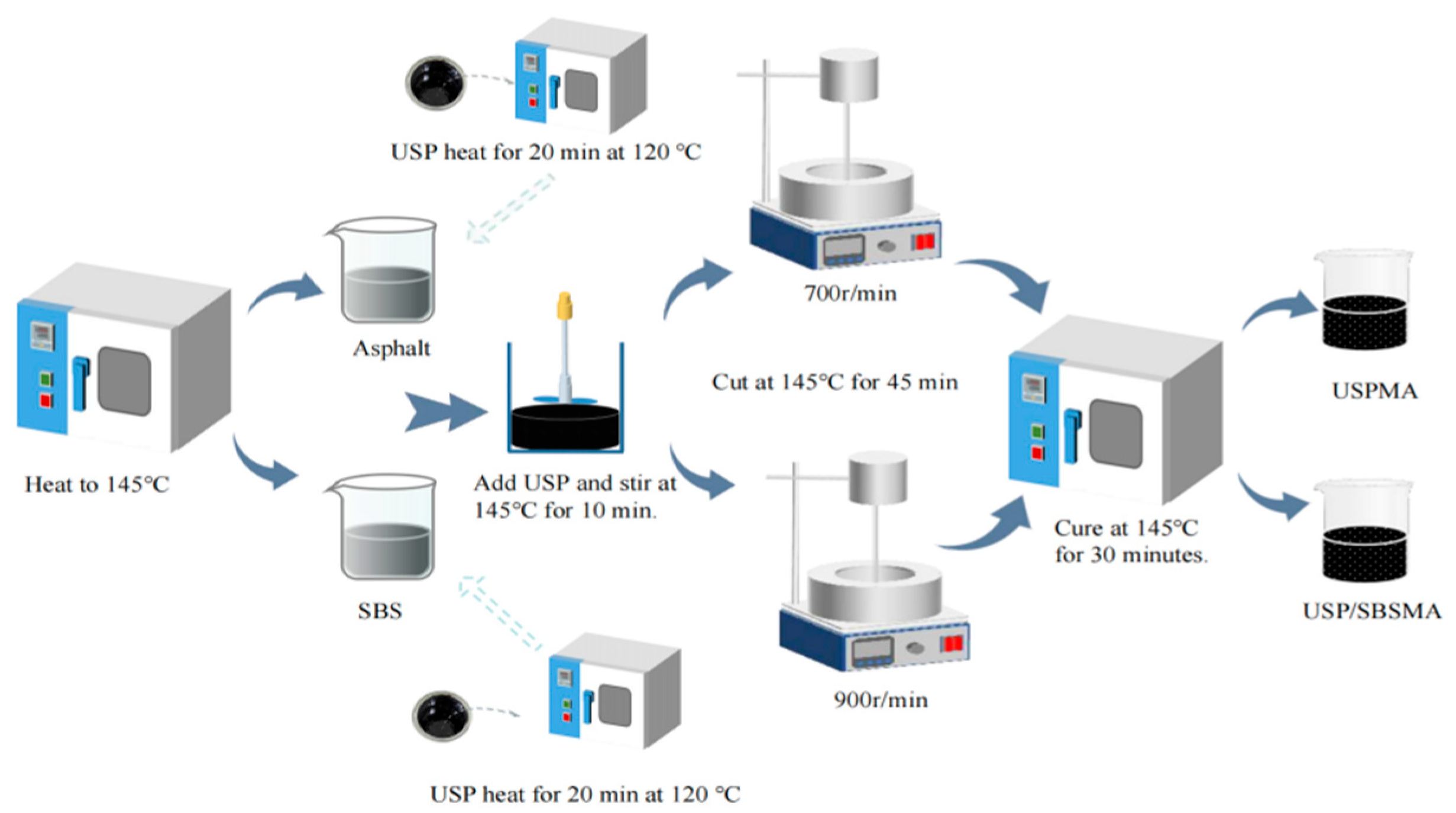
2.2. Preparation of Modified Asphalt
2.2.1. USP-Modified Asphalt (USP-A)
2.2.2. USP/SBS Composite-Modified Asphalt (USP/SBS-A)
2.3. Asphalt Aging
2.4. Test Scheme
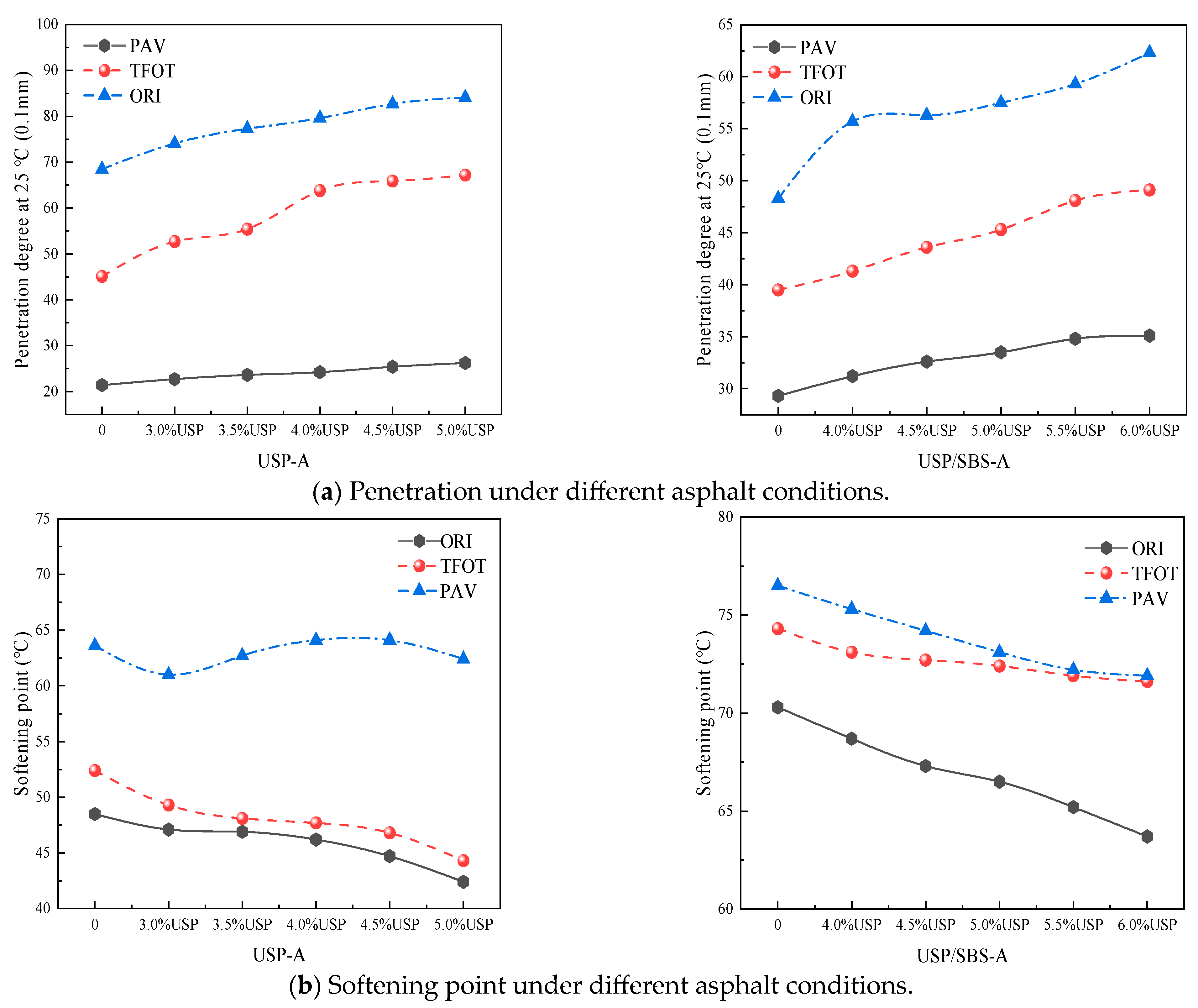
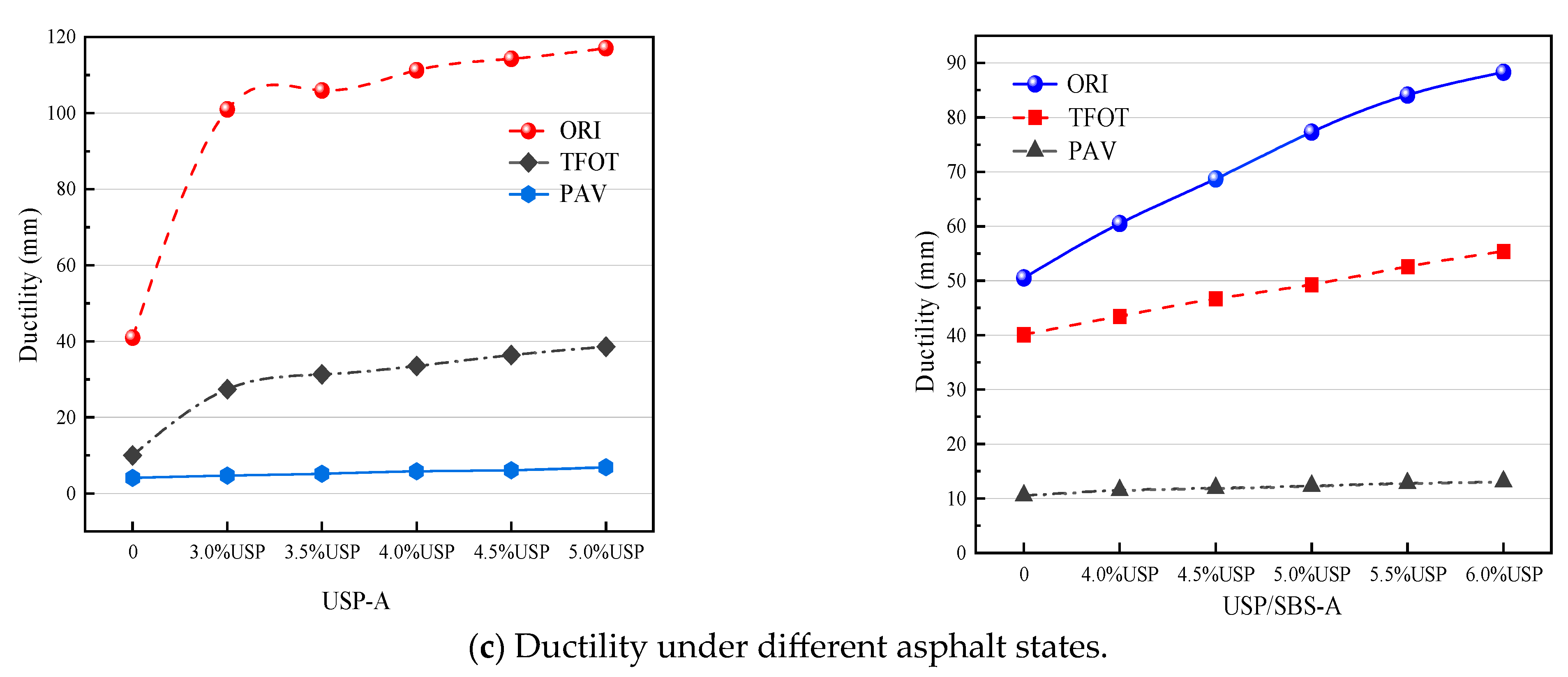
2.4.1. Basic Performance Testing
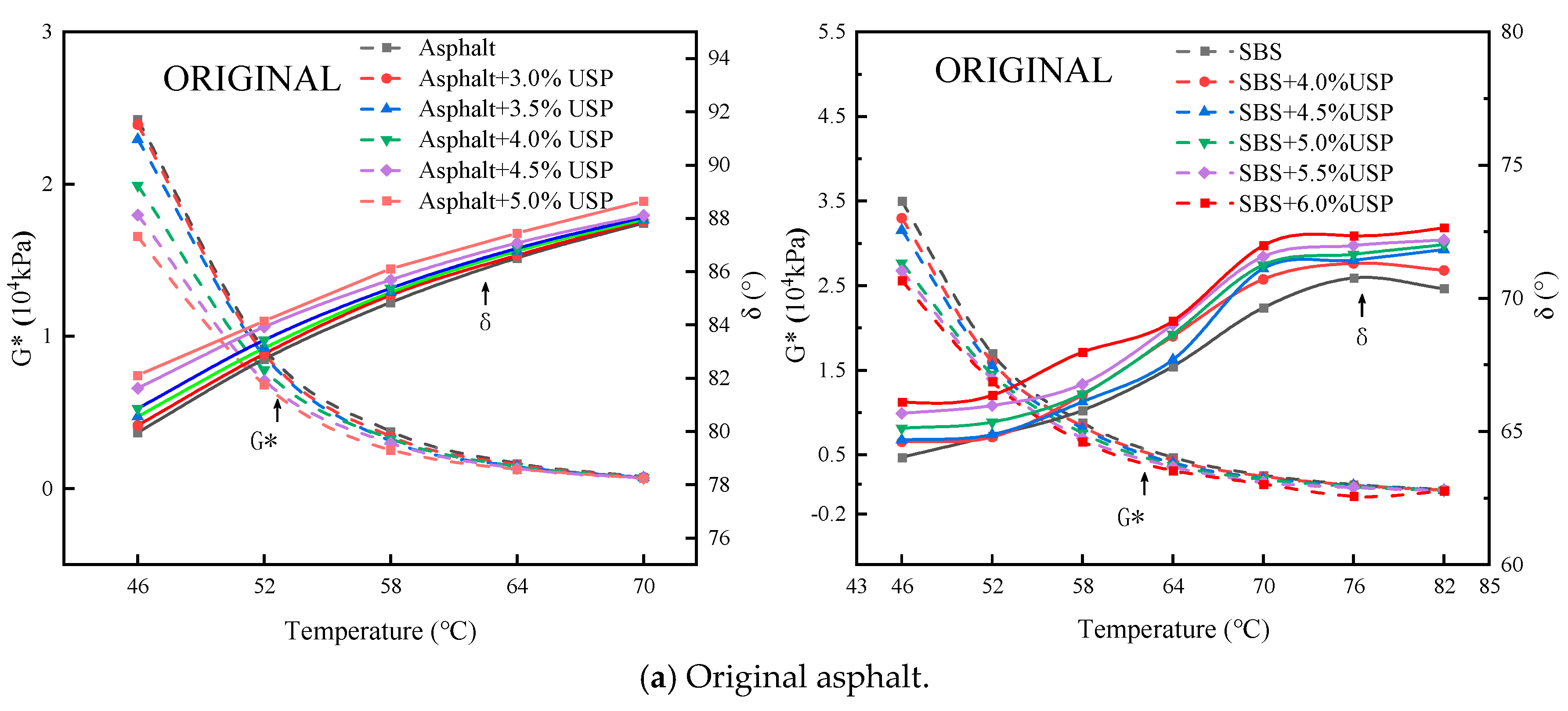
2.4.2. Temperature Sweep Test
2.4.3. Multiple Stress Creep Recovery
2.4.4. Bending Beam Rheometer (BBR) Test
2.4.5. Micro Performance Test
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Basic Performance Analysis
3.2. Analysis of Temperature Scanning Test Results
3.2.1. G* and δ
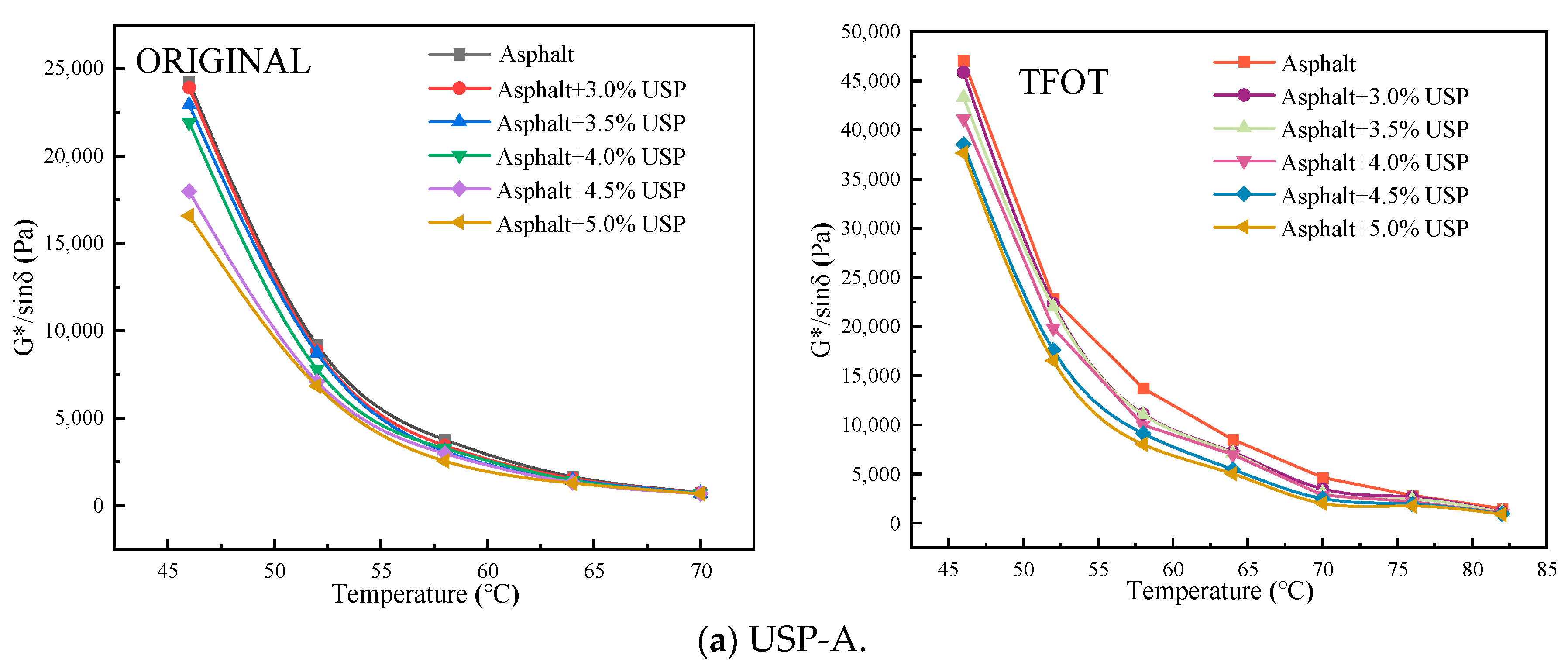
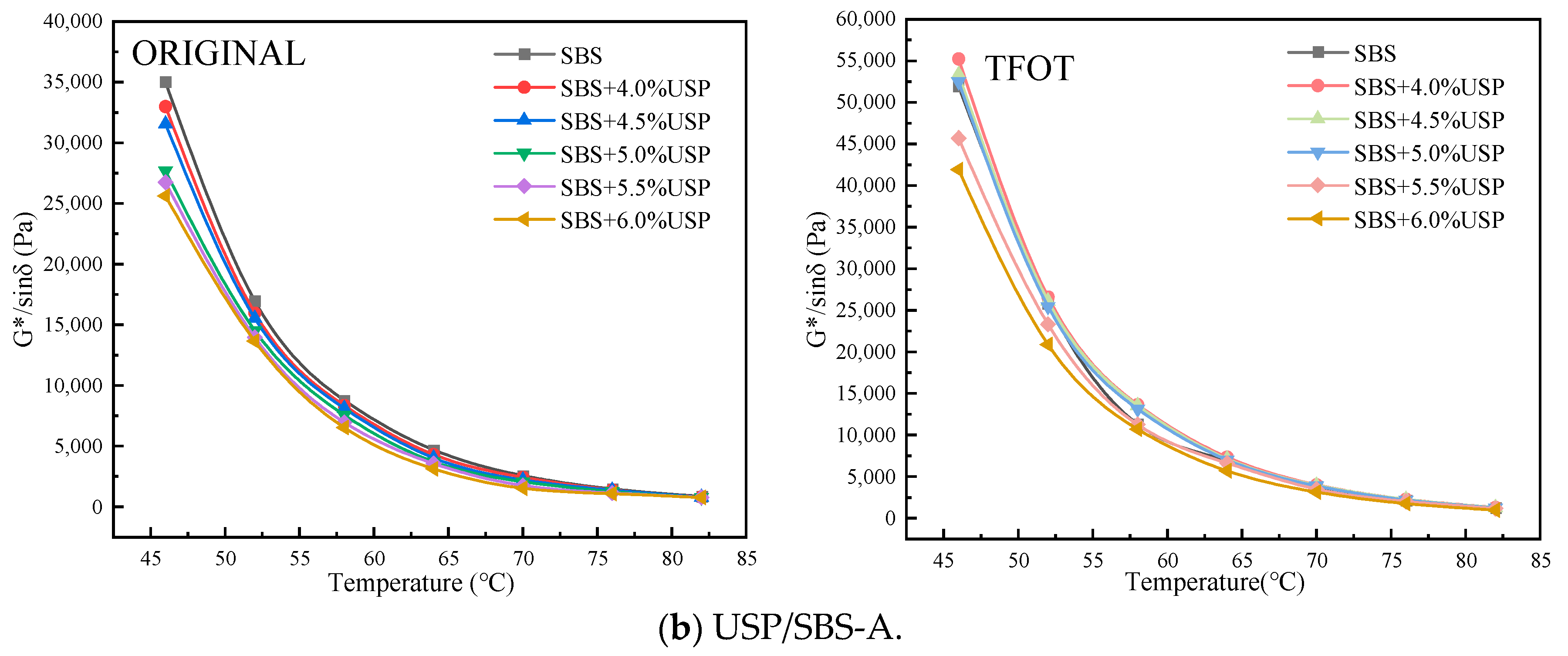
3.2.2. G*/sin δ
3.3. Analysis of Creep Recovery Test Results
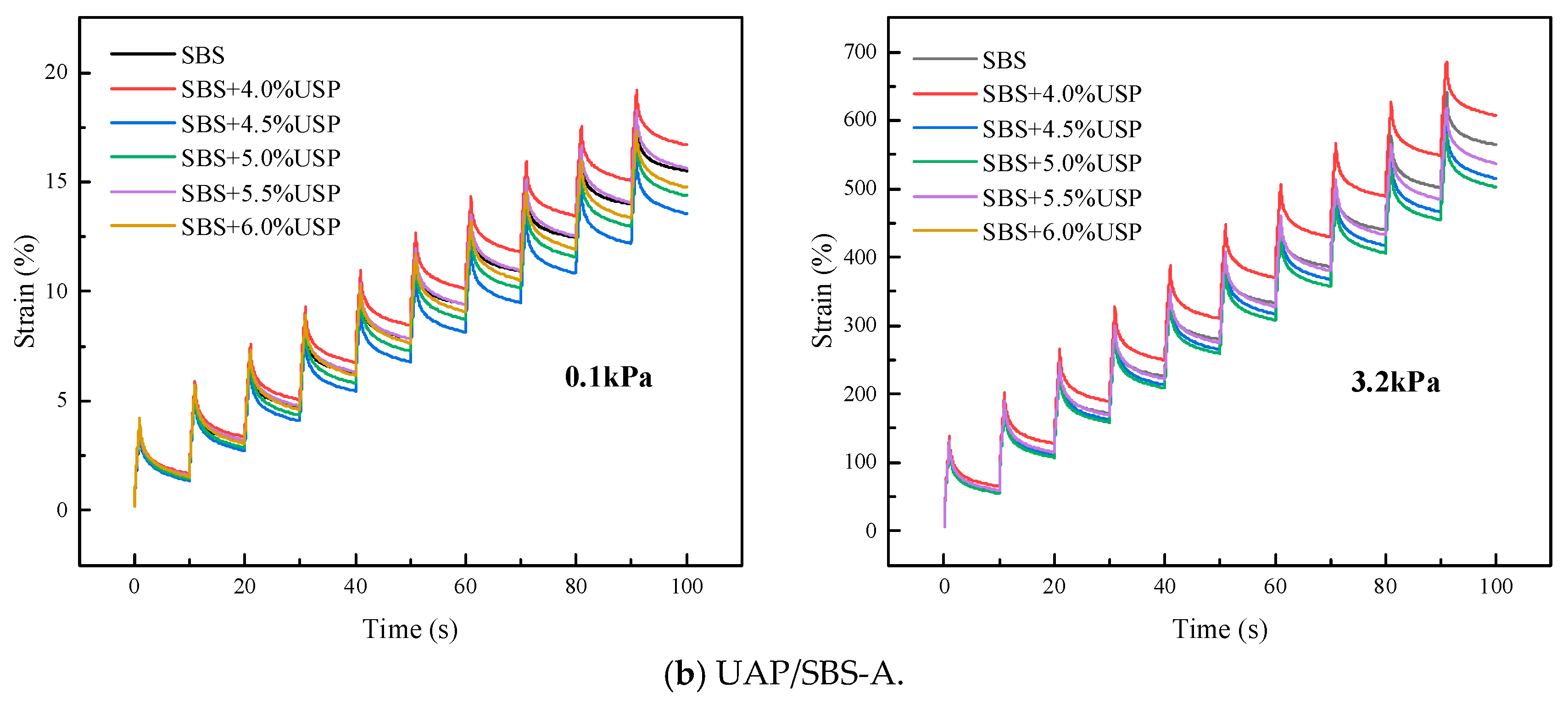
3.3.1. Stress and Strain
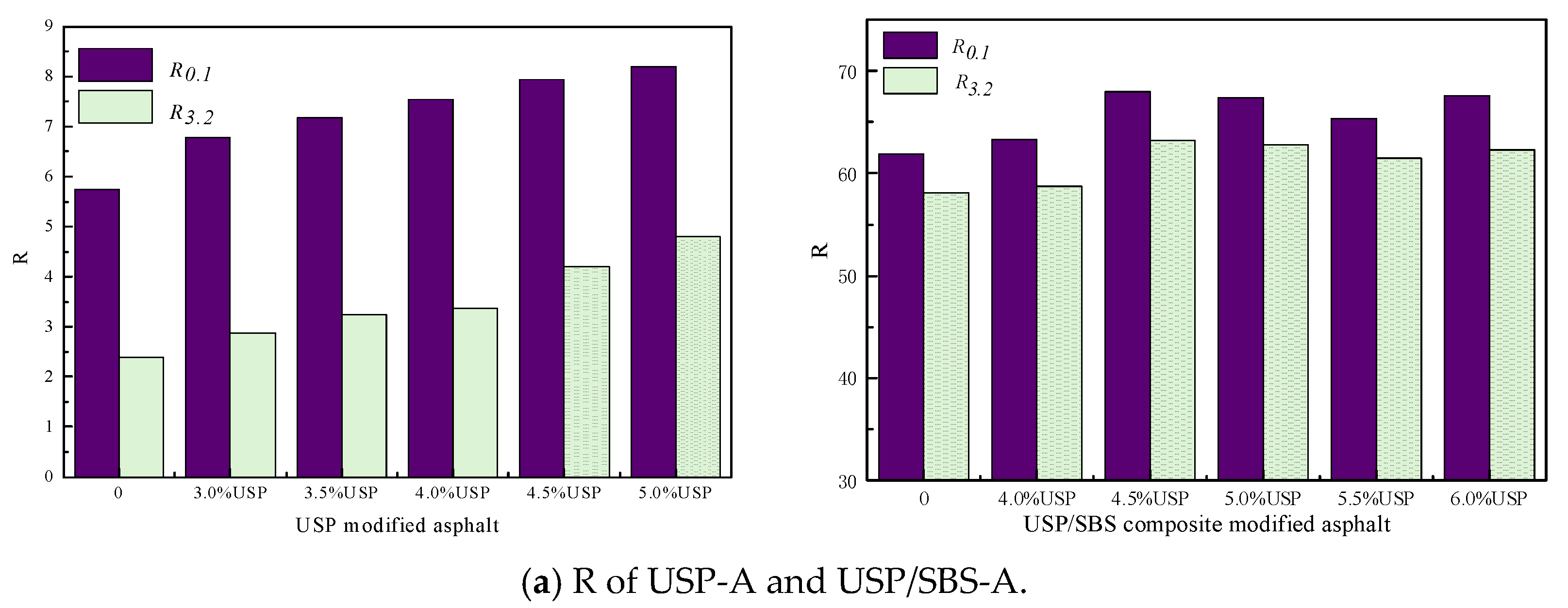
3.3.2. R and Jnr
3.4. Analysis of Low-Temperature Bending Creep Test Results
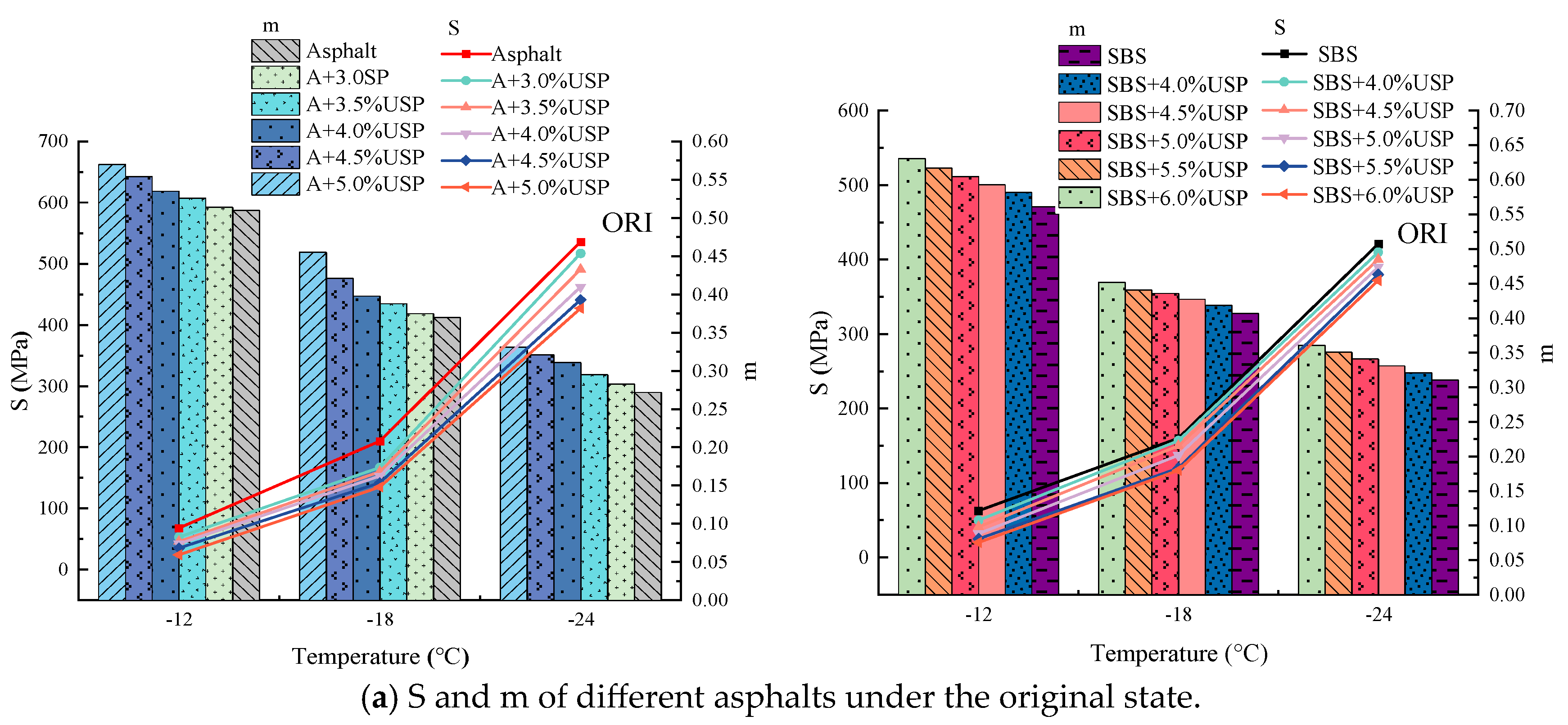
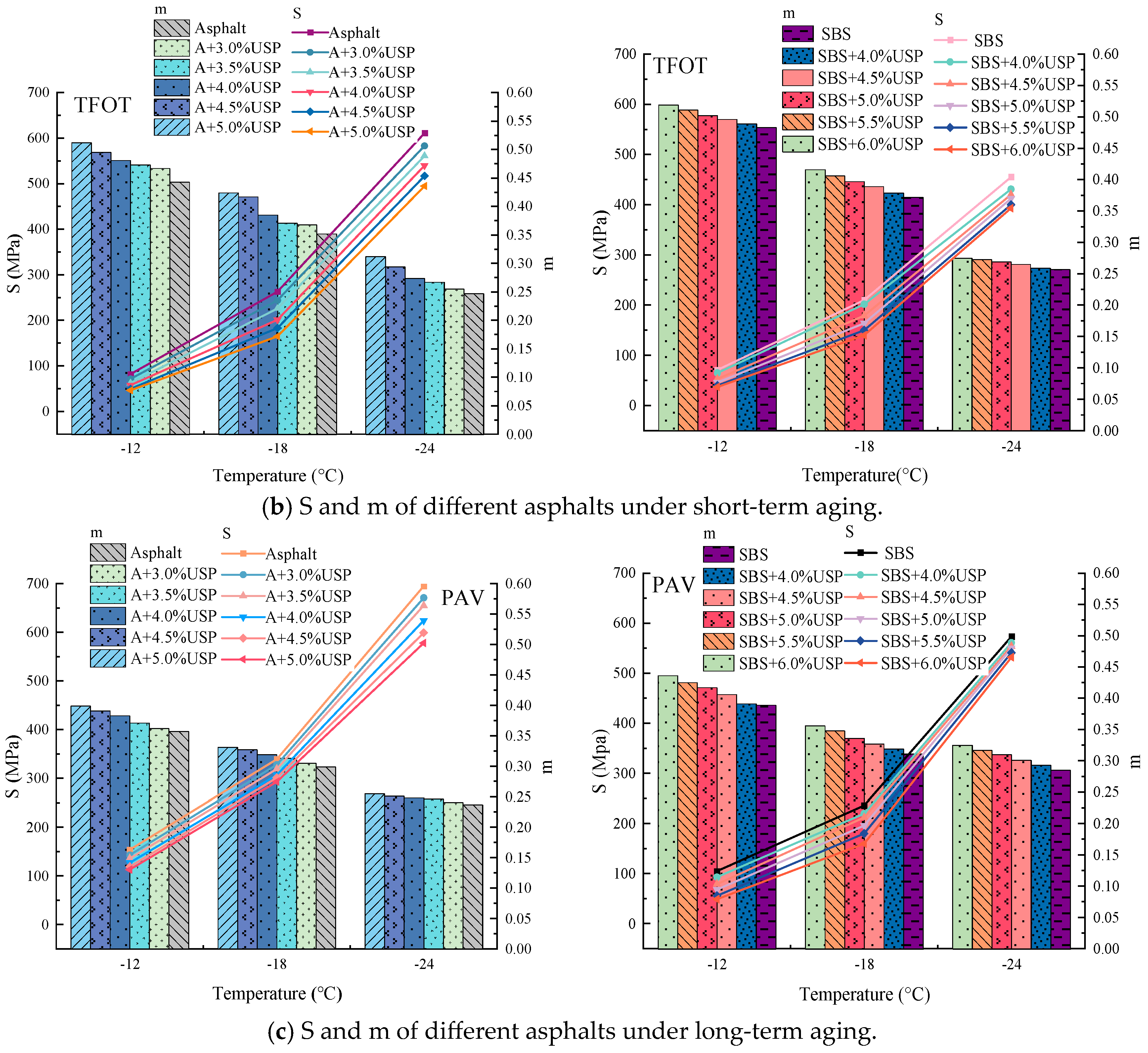
3.4.1. S and m
3.4.2. S/m
3.5. Analysis of Microscopic Test Results
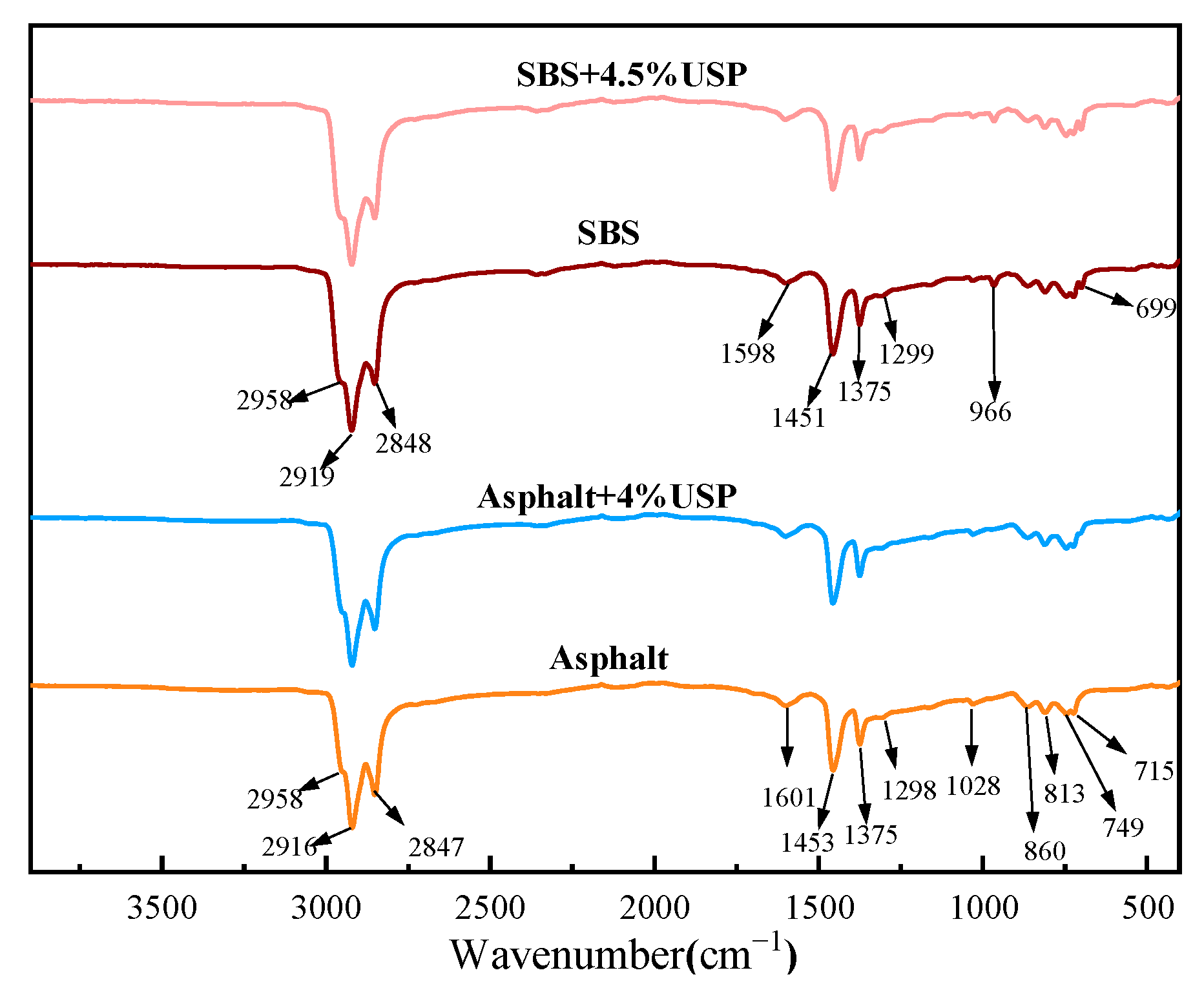
3.5.1. Analysis of Infrared Spectrum Results
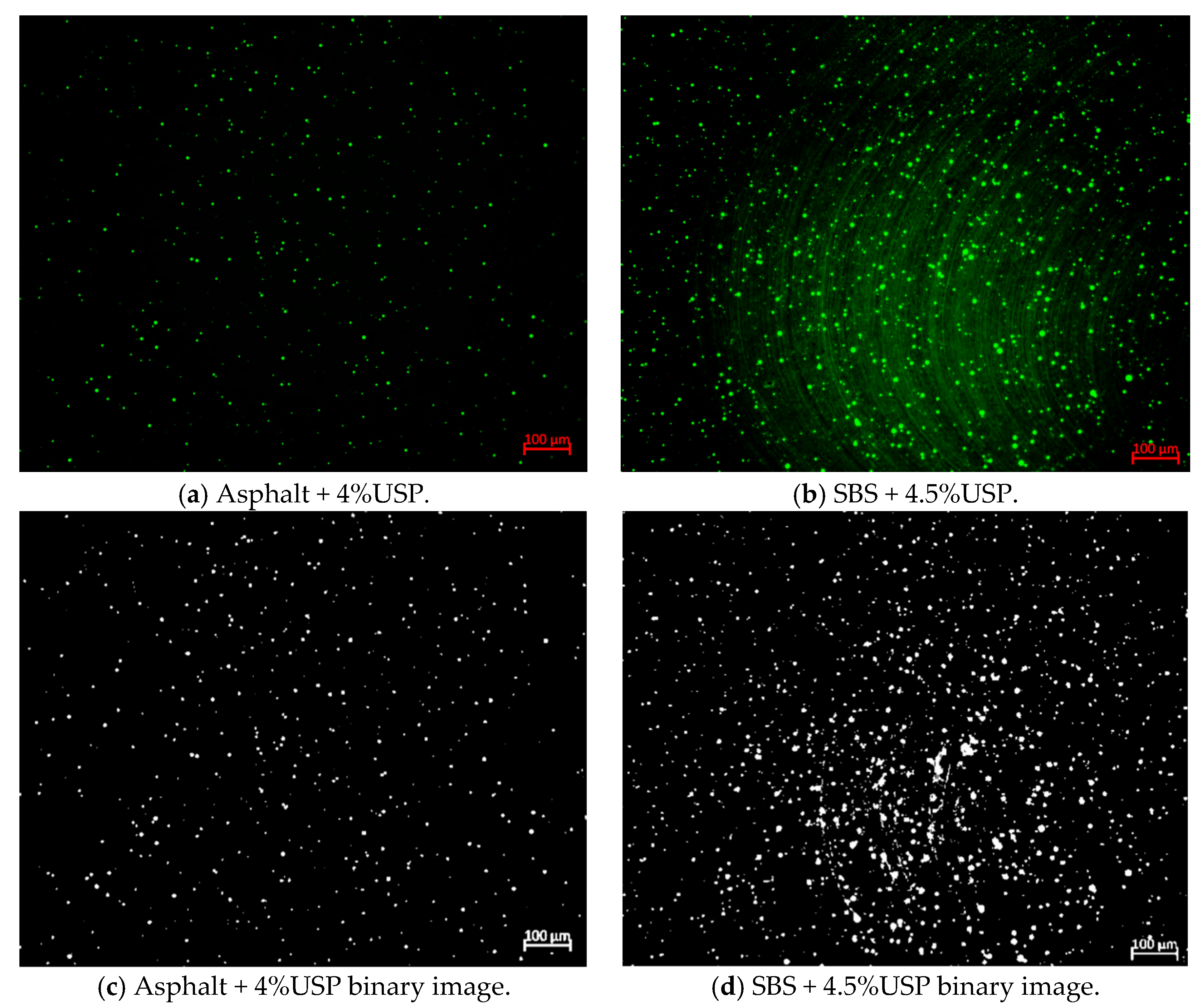
3.5.2. Analysis of Fluorescence Microscopy Results
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The optimal dosage of USP warm-mixed modifier in asphalt is 4.0% to 4.5%.
- (2)
- The experiments indicate that, with the addition of USP, the low-temperature flexibility of asphalt has significantly improved. At −12 °C, the creep stiffness of USP-A decreases by 38%. The creep stiffness of USP/SBS-A decreased by 35%.
- (3)
- The addition of the USP warm-mixing modifier can enhance the deformation resistance of asphalt. Furthermore, it can also enhance the creep recovery capability of asphalt. With the incorporation of USP, the deformability resistance of asphalt increased. At 0.1 kPa and 0.3 kPa, the modified asphalt R increases, while the Jnr decreases.
- (4)
- From a microscopic perspective, the incorporation of USP into the two types of asphalt did not result in any chemical reaction. Under a fluorescence microscope, USP is uniformly distributed within the asphalt. Furthermore, inclusion of USP will lead to collapse of the asphalt spatial network structure, which is the reason for the decreased high-temperature stability of asphalt.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, X.; Zhang, J.J.; Gong, B.; Wu, Y. Study on Low-carbon Evaluation Indicator System for Highway Traffic Safety Facilities. J. Highw. Transp. Res. Dev. 2022, 39, 202–208. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Yang, J. Study on Carbon Emission of Epoxy Recycled Pavement Based on LCA. Mater. Rep. 2022, 36, 121–128. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.; Zhang, C.; Li, R.; Zheng, L.; Xu, J. Effect of temperature and humidity environment on the microstructure and physicochemical properties of SBS modified asphalt. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2025, 22, e04192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Hu, S.; Zhang, M. Development of Intelligent Motorway Traffic Application Technologies: A Review. China J. Highw. Transp. 2023, 36, 142–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Tian, Z. Research on the Path of Transportation Decarbonization under the Vision of Carbon Neutrality in China. Energy China 2021, 43, 6–12+37. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Q.; Song, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Zhang, S. A review of the development of asphalt foaming technology. J. Road Eng. 2024, 4, 334–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Hao, P.; Zhang, Q.; Li, R. Analysis of Environmenta and Economic Benefits of Warm Mix Asphalt. Environ. Eng. 2012, 30, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Liu, F.; Wang, L. Automated, economical, and environmentally-friendly asphalt mix design based on machine learning and multi-objective grey wolf optimization. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 11, 381–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, L.; Zefeng, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xiang, L.; Wenfu, W.; Hao, L.; Chuanjun, T.; Qichen, C.; Guofeng, Y.; Guangning, W. Improving carbon/carbon composites mechanical and thermal properties by the co-carbonization of pre-oxidized carbon fiber and pitch. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 139, e51846. [Google Scholar]
- Nithinchary, J.; Dhandapani, B.P.; Mullapudi, R.S. Application of warm mix technology—Design and performance characteristics: Review and way forward. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 414, 134915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratap, W.V.; Nikhil, S.; Ankit, G. Tribology as emerging science for warm mix technology: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 359, 129445. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, X.; Hettiarachchi, C.; Xiao, F.; Zhao, Z.; Xiang, Q.; Yong, D. Blending efficiency improvement and energy investigation of recycled asphalt mixture involved warm mix technology. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 279, 123732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Zhang, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zheng, J. Review on Warm mixing asphalt technology. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2023, 23, 24–46. [Google Scholar]
- Eltwati, A.; Hainin, M.R.; Tarhuni, F.; Jusli, E.; Alamri, M. Effect of waste engine oil and warm mix additive on the physical, rheological, and short-term aging attributes of Styrene–Butadiene Rubber-modified asphalt binders. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 21, e03433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, M.; Yue, J.; Wang, R.; Xiong, Y. Evaluating the fatigue characteristics and healing potential of asphalt binder modified with Sasobit® and polymers using linear amplitude sweep test. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 289, 123054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; You, Z.; Hasan, M.R.M.; Diab, A.; Shao, H.; Chen, S.; Ge, D. Environmental and mechanical performance of crumb rubber modified warm mix asphalt using Evotherm. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 159, 346–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suleiman, A.; Fayez, A.; Rosli, H.M.; Mohammed, A.; Hani, A.; Musa, A.; Abdelhalim, A. Rheological and Morphological Characterization of Cup Lump Rubber-Modified Bitumen with Evotherm Additive. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2023, 48, 13195–13209. [Google Scholar]
- Tao, Z.; Shen, S.; Yu, H.; Sun, Y.; Zou, Y. Rejuvenating aged asphalt using surfactant-foaming warm recycling technology. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 384, 131297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, J.; Chen, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, H.; Yan, Y.; Hossiney, N. Experimental Study on Warm Mix Asphalt Binders with a Focus on Rheological Performance. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2025, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.A.; Zheng, N.; Wang, Y.; Su, H.; Ren, X.; Zhao, F. Rheological properties of warm mixed high viscosity asphalt at high and low temperatures. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0301138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z.; Sun, Q.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Li, X. Rheological Properties of Desulfurized Crumb Rubber Modified Warm Mix Asphalt. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2023, 2553, 012011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adwani, D.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, A.; Naga, G.R.R. Comprehensive rheological and mechanistic evaluation of an asphalt binder and mixture modified with warm mix additives. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 51633–51646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, J.; Dong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Suo, Z.; Zheng, W. Effect of different warm additives on rubber asphalt performance. J. China Univ. Pet. (Ed. Nat. Sci.) 2020, 44, 133–140. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, L.; Hu, M.; Ni, H.; Sun, D.; Tian, Y. Thermal Oxidative Aging Effect on Chemo-Rheological and Morphological Evolution of Crumb Rubber Modified Asphalt Binders with Wax-Based Warm Mix Additives. Transp. Res. Rec. 2024, 2678, 942–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, W.; Li, L.; Lan, W. Selection of Optimal Warm-Mix Additive for Recycled Crumb-Rubber Modified Asphalt Binder Based on Rheological Tests and Viscoelastic Models. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, e04602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, J.; Ding, H.; Xie, Q.; Qiu, Y. Evaluation of physical hardening of wax-based warm mix asphalt binders from low-temperature rheological properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 419, 135496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saberi, K.F.; Fakhri, M.; Azami, A. Evaluation of warm mix asphalt mixtures containing reclaimed asphalt pavement and crumb rubber. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1125–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diyar, K.; Rawid, K.; Tariq, K.M.; Muhammad, A.; Tanveer, H. Performance of hot-mix asphalt using polymer-modified bitumen and marble dust as a filler. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2023, 10, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kök, B.V.; Yılmaz, M.; Akpolat, M. Performance Evaluation of Using Evotherm in SBS Modified Binder. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Punith, V.S.; Putman, B.J. Effect of Compaction Temperature on Rutting and Moisture Resistance of Foamed Warm-Mix-Asphalt Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cui, Y.N.; Du, C.; Liu, L.; Chen, Q. Low-temperature performance and micro-structure of warm mix recycled composite aged asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 440, 137443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Wu, C.; Jing, H.; Tang, B. Evaluation on performances restoration and warm-mix effect of rejuvenated SBS modified bitumen incorporating a compound rejuvenator. Mater. Struct. 2024, 58, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, D.; Diao, H.; Li, B.; Liang, Y.; Ling, T.; Kuang, W. Rheological properties and microscopic characterization of high viscosity asphalt with different warm mixing agents. Clean. Mater. 2025, 16, 100308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wei, H.; Lei, Z.; Xiaodong, L.; Yaseen, M. Preparation and properties evaluation of shape memory epoxy asphalt composites with high toughness and damping. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 53117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Su, Q.; Li, G.; Cao, D.; Yao, Y.; Yang, S.; Wang, S. Enhancing Reutilization of Waste Tires and Sustainability of Environment: Analysis of the Performance and Emission Reduction Mechanism of High Content Rubber Modified Asphalt. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 508, 160917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Lu, T.; Chen, Z.; Ni, H.; Sun, D.; Tian, Y. A review of polyurethane as an alternative to asphalt binder for more sustainable roads: Performance, environment, and economy. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 11, 1268–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, K.; Xu, W.; Yu, D.; Zhu, L.; Xie, H.; Cheng, R. Thermal, mechanical properties, and low-temperature performance of fibrous nanoclay-reinforced epoxy asphalt composites and their concretes. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132, 41694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Yan, X.; Pu, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Kang, K.; Hu, J.; Yang, Y. Quantitative evaluation on the energy saving and emission reduction characteristics of warm mix asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 407, 133465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.Y.; Hao, Y.; Ye, Y.L.; Guo, J.K. Research on strength formation mechanism and noise reduction characteristics of waste rubber powder micro-surfacing. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 19, e02293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, C.; Guo, H.; Zhao, S.; Shu, S.; Ye, Y.; Xing, B. Study on fatigue performance of asphalt mixture in service life based on accelerated loading test. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2024, 20, e03055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, M.; Li, G.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Cao, Z.; Li, Z.; Chen, H. Investigation of the Properties of High-Viscosity Modified Asphalt Binder under Hygrothermal Environments. Materials 2024, 17, 2869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Rong, L.; Li, J.; Wang, L. Evaluation on the influence of dynamic water pressure environment on viscoelastic mechanical performance of asphalt mixture using the bending beam rheometer method. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 321, 126428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Liang, P.; Luo, T.; Yan, Y. Influence of Different Warm Mix Agents on Rheological and Microscopic Properties of High-viscosity Asphalt. Mater. Rep. 2023, 37, 104–109. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, Z.; Xu, S.; Liu, J.; Qi, Z.; Ma, S.; Fu, D. Effect of different types of warm mix agents on asphalt properties. J. Shandong Univ. (Eng. Sci.) 2023, 53, 18–24. [Google Scholar]




| Technical Indexes | Results | Requirements | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 70# | SBS | ||
| Penetration (0.1 mm) | 67.5 | 51 | 40~60 |
| Ductility (cm) | 40 | 28.3 | ≥20 |
| Softening point (°C) | 48.4 | 67.6 | ≥60 |
| Density (g/cm−3) | 1.021 | 1.030 | / |
| Solubility (%) | 99.6 | 99.3 | ≥99 |
| Boiling point (°C) | 289 | 312 | ≥230 |
| Technical Index | Unit | Result | Test Procedure |
|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | / | black | Visual estimation |
| Density (20 °C) | g/cm3 | 0.98 | T 0603 |
| Water content | % | 0.2 | GB/T 260 |
| Boiling point | °C | 256 | T 0611 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Ping, J.; Guo, H.; Kang, Y.; Ye, Y. Investigating the Rheological Impact of USP Warm Mix Modifier on Asphalt Binder. Coatings 2025, 15, 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070784
Liu Y, Ping J, Guo H, Kang Y, Ye Y. Investigating the Rheological Impact of USP Warm Mix Modifier on Asphalt Binder. Coatings. 2025; 15(7):784. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070784
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yali, Jingfei Ping, Hao Guo, Yikai Kang, and Yali Ye. 2025. "Investigating the Rheological Impact of USP Warm Mix Modifier on Asphalt Binder" Coatings 15, no. 7: 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070784
APA StyleLiu, Y., Ping, J., Guo, H., Kang, Y., & Ye, Y. (2025). Investigating the Rheological Impact of USP Warm Mix Modifier on Asphalt Binder. Coatings, 15(7), 784. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070784






