A Simple Method to Prepare Superhydrophobic Surfaces Based on Bamboo Cellulose, and an Investigation of Surface Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis of Materials
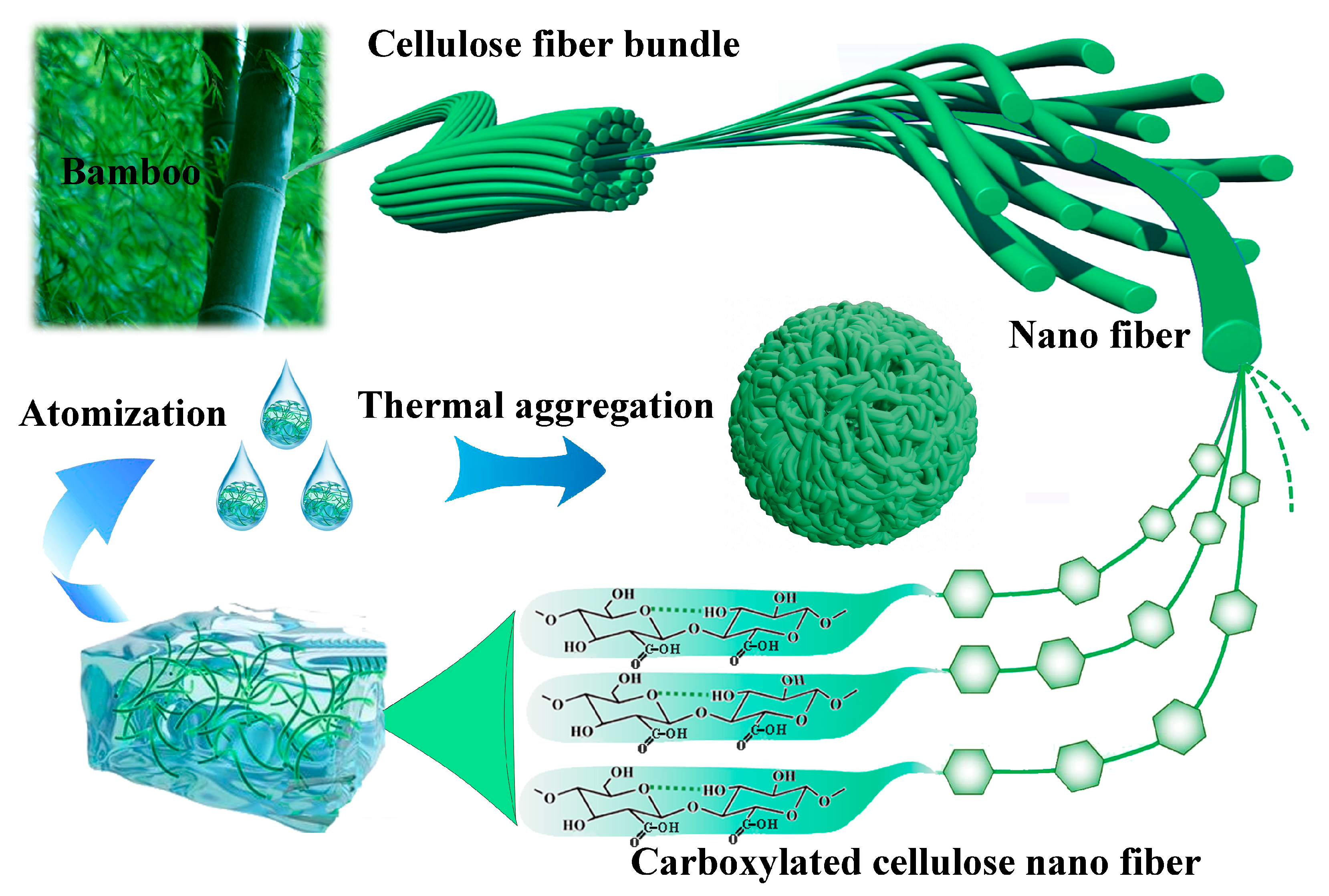
2.1.1. Fabrication of TOC Particles
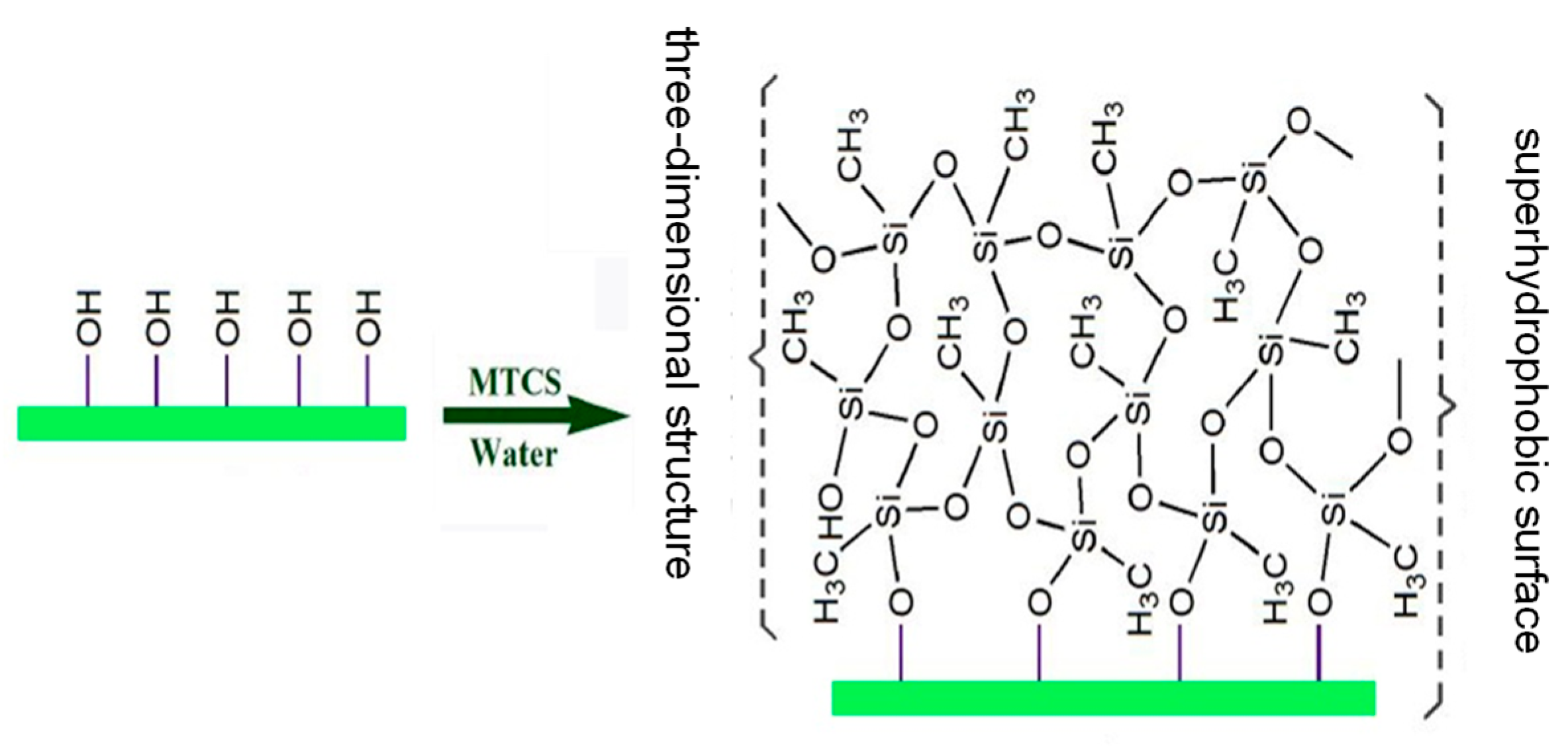
2.1.2. Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surface
2.2. Measurements and Characterizations
2.3. Mechanical Durability and Chemical Stability Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
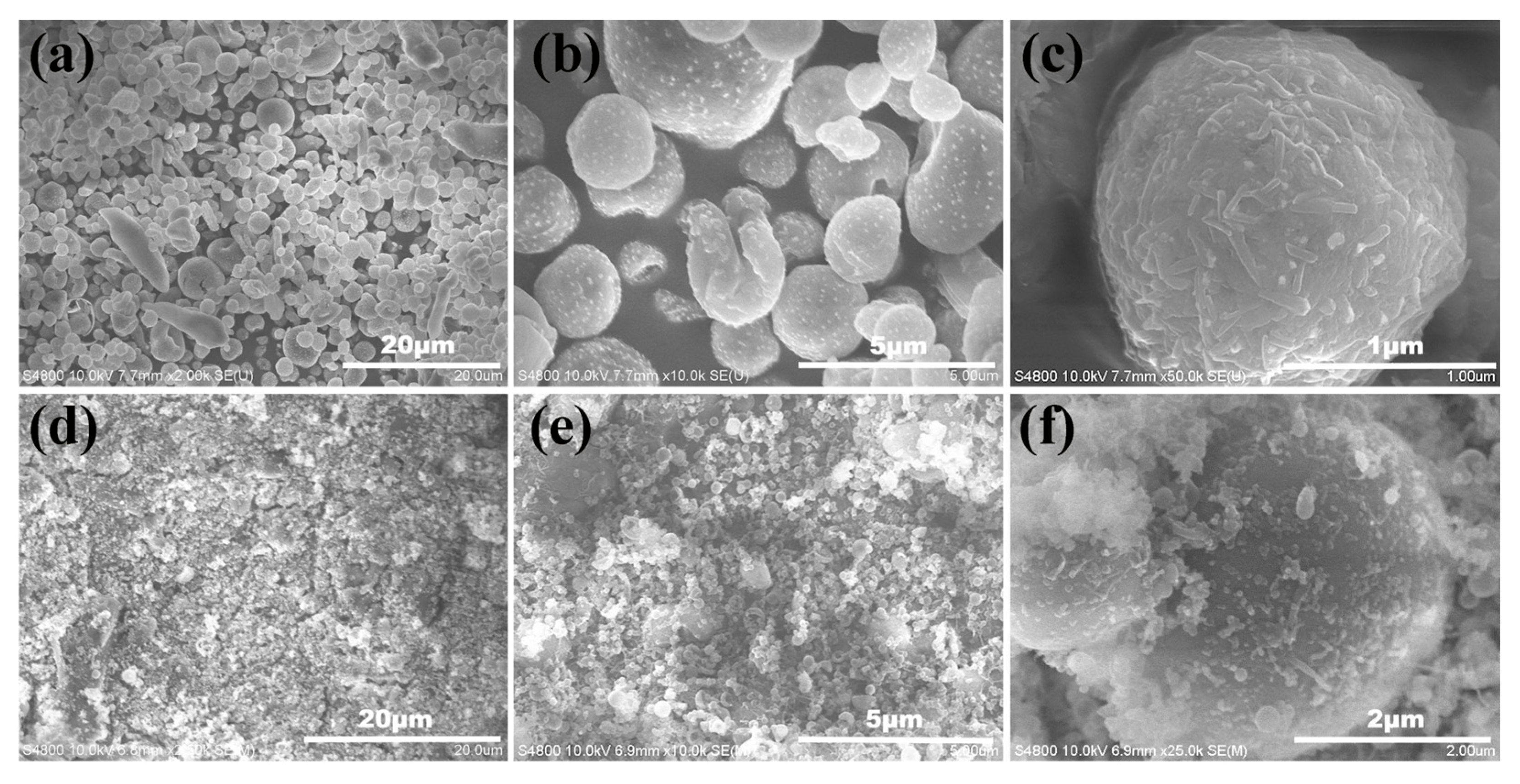
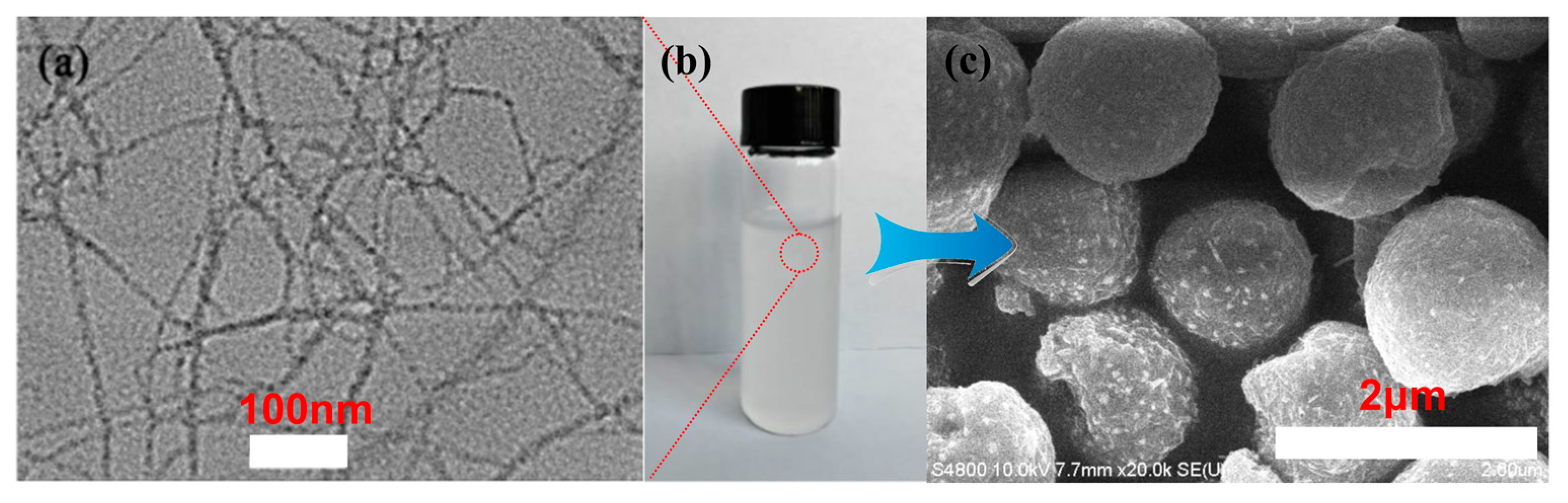
3.1. Fabrication of the TOC Particles and Superhydrophobic Surface
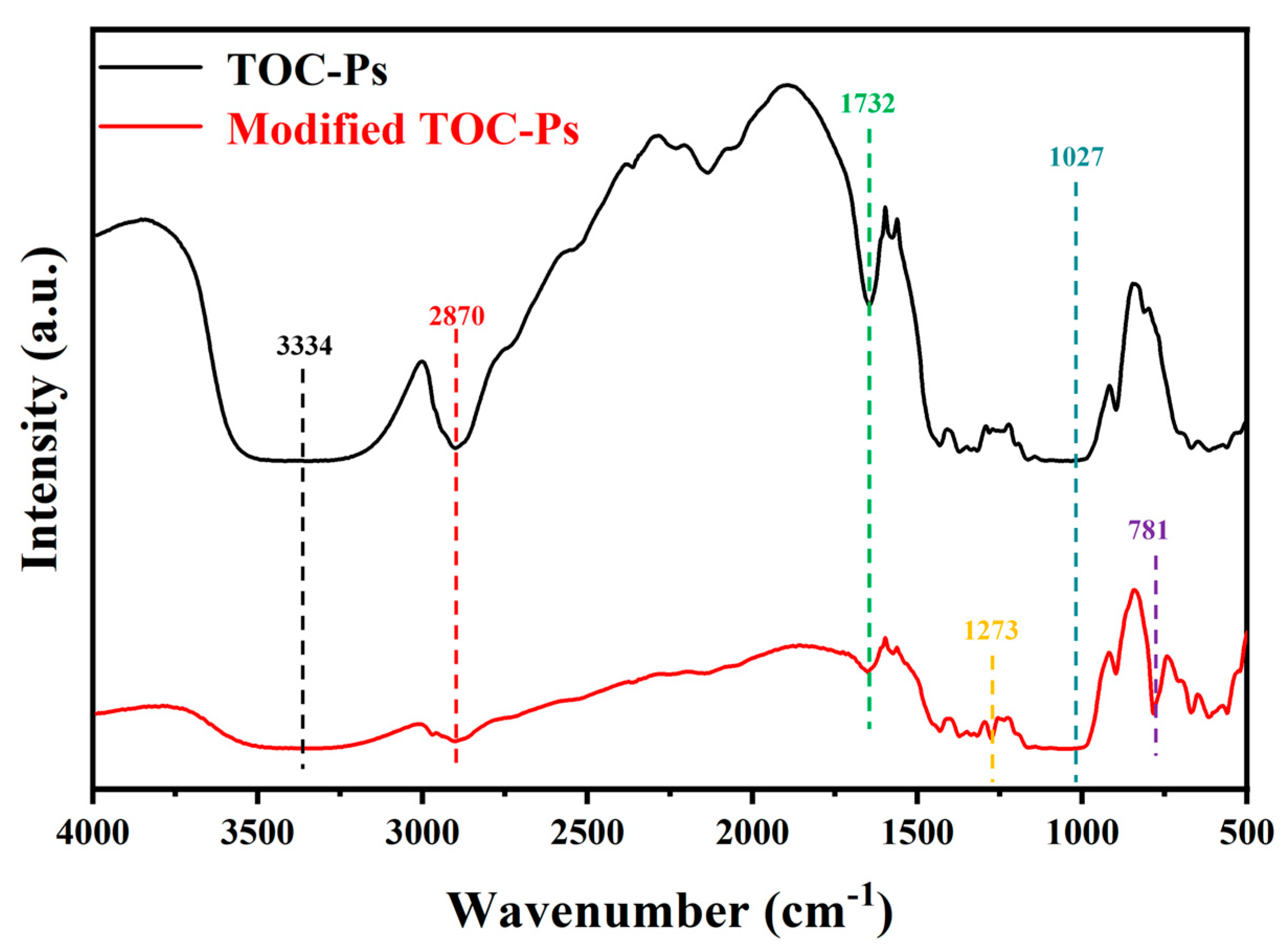
3.2. Chemical Analysis and Surface Characterization
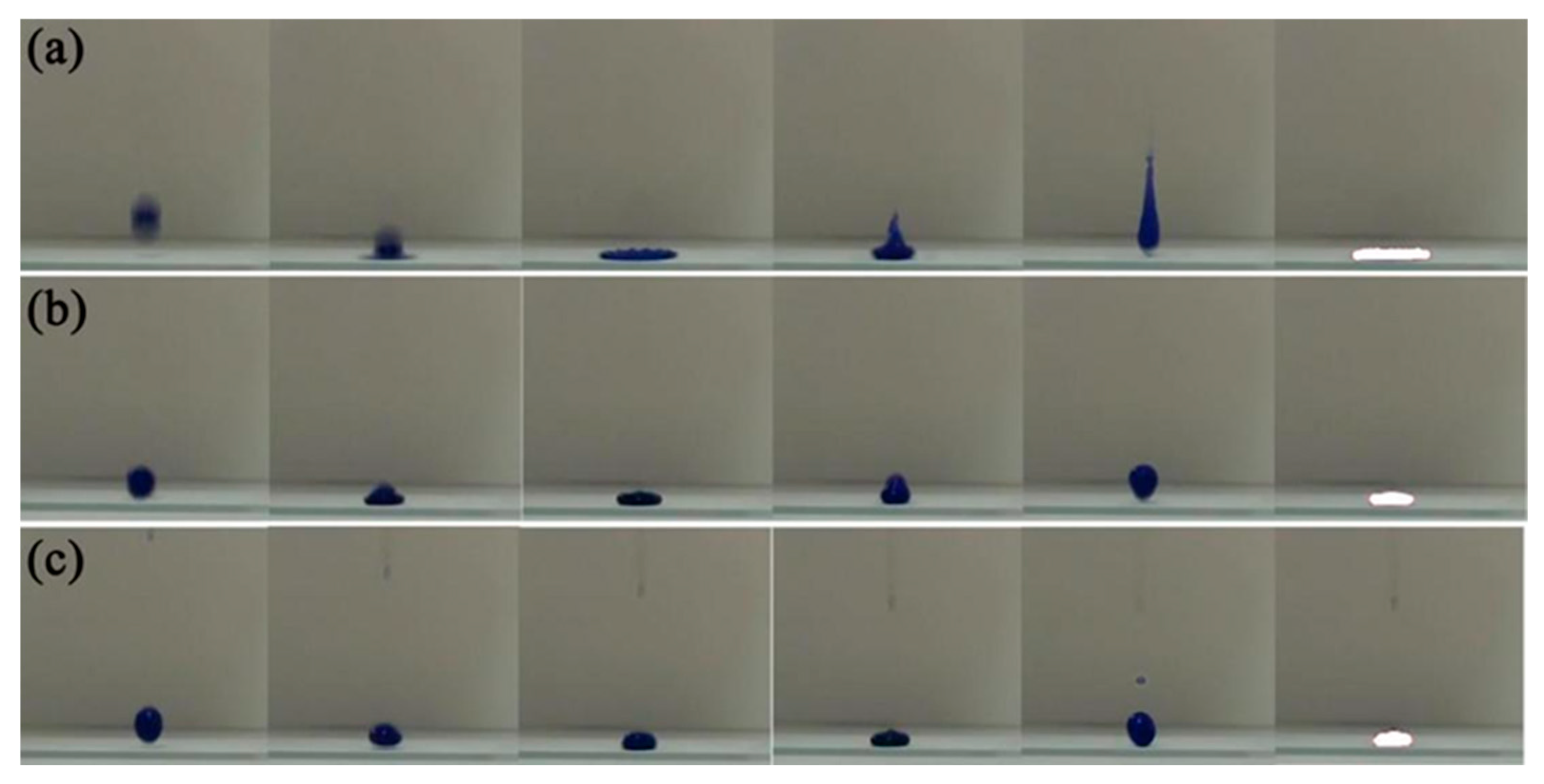
3.3. Wettability of TOC-P Superhydrophobic Surface
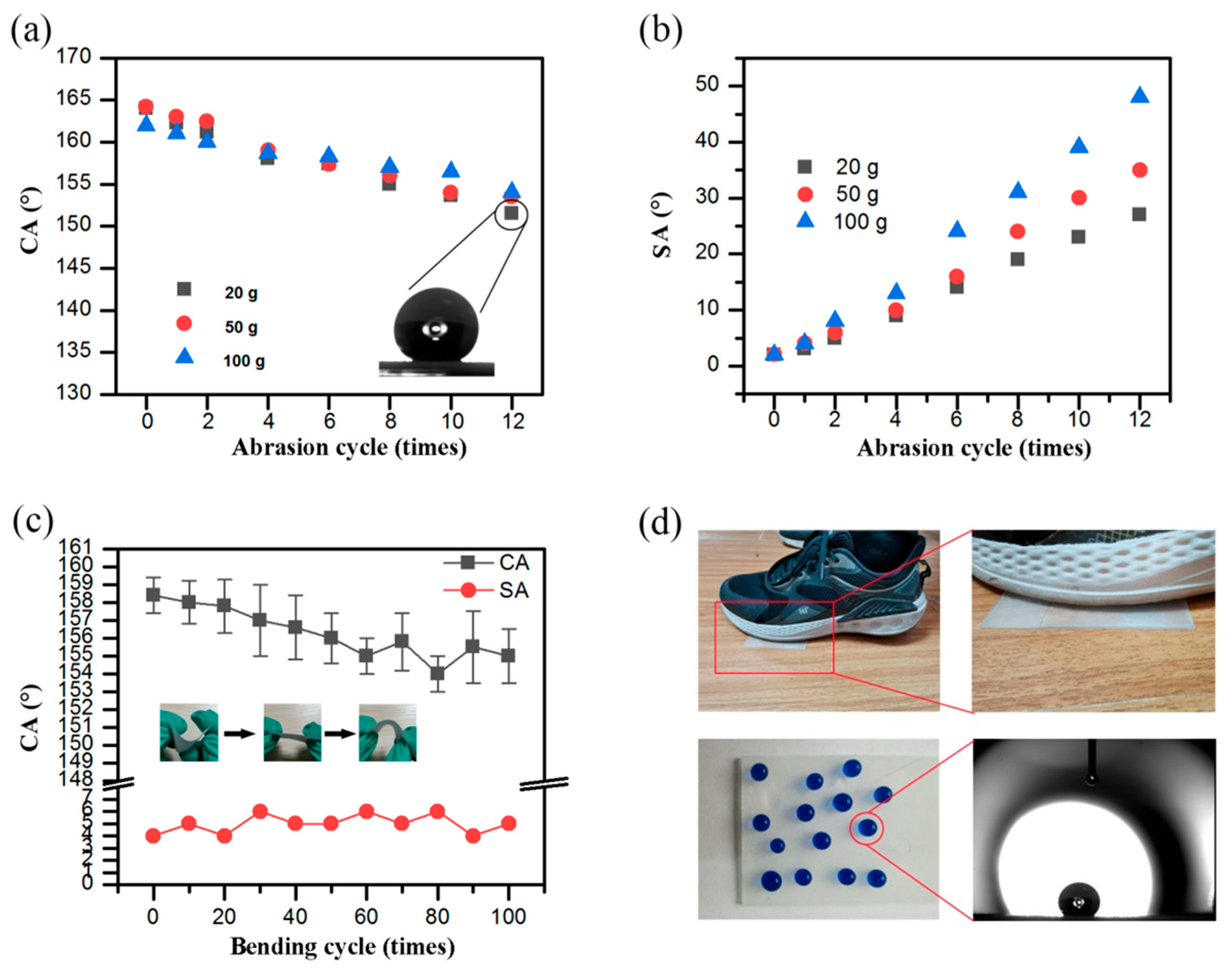
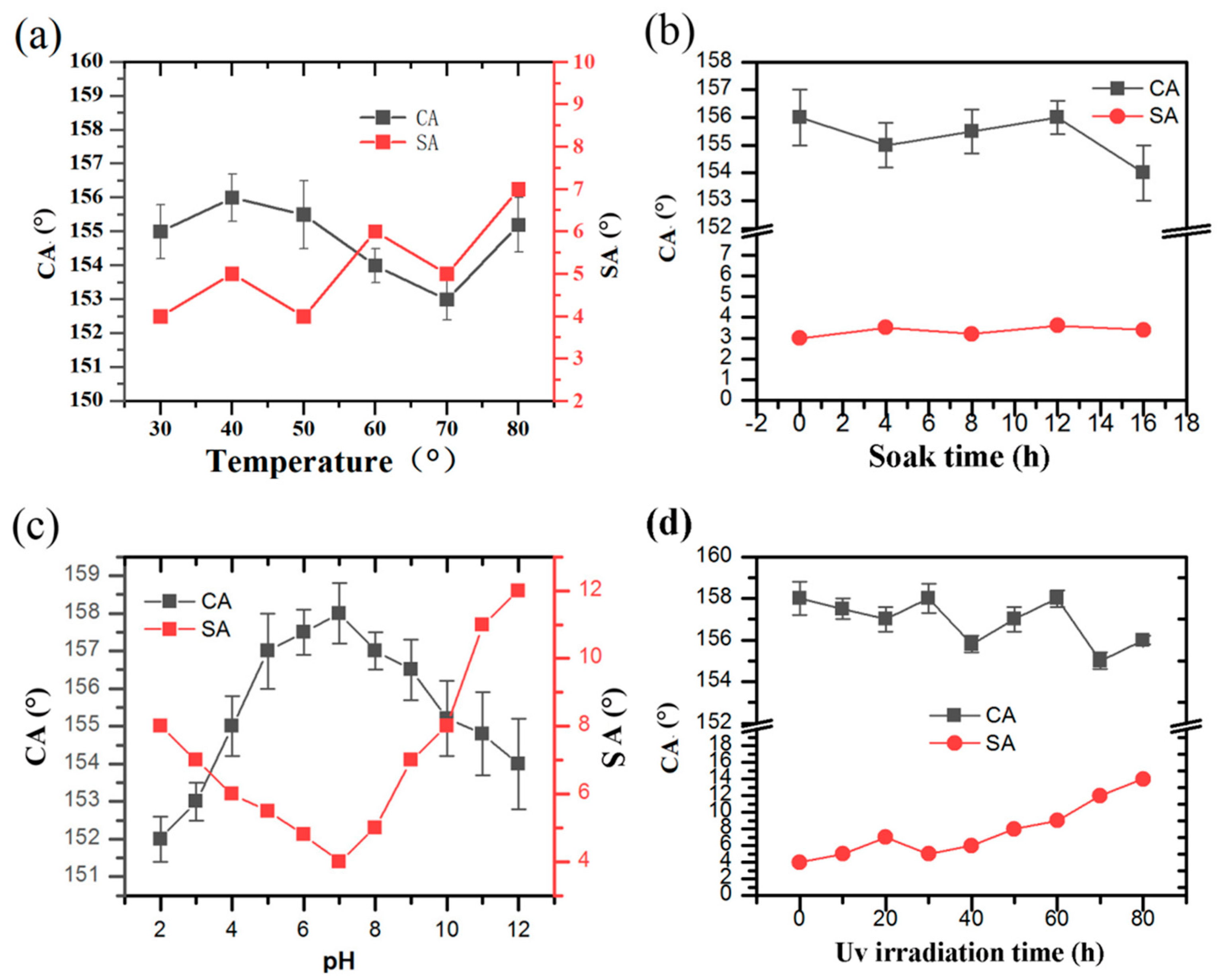
3.4. Mechanical and Chemical Stability and Durability
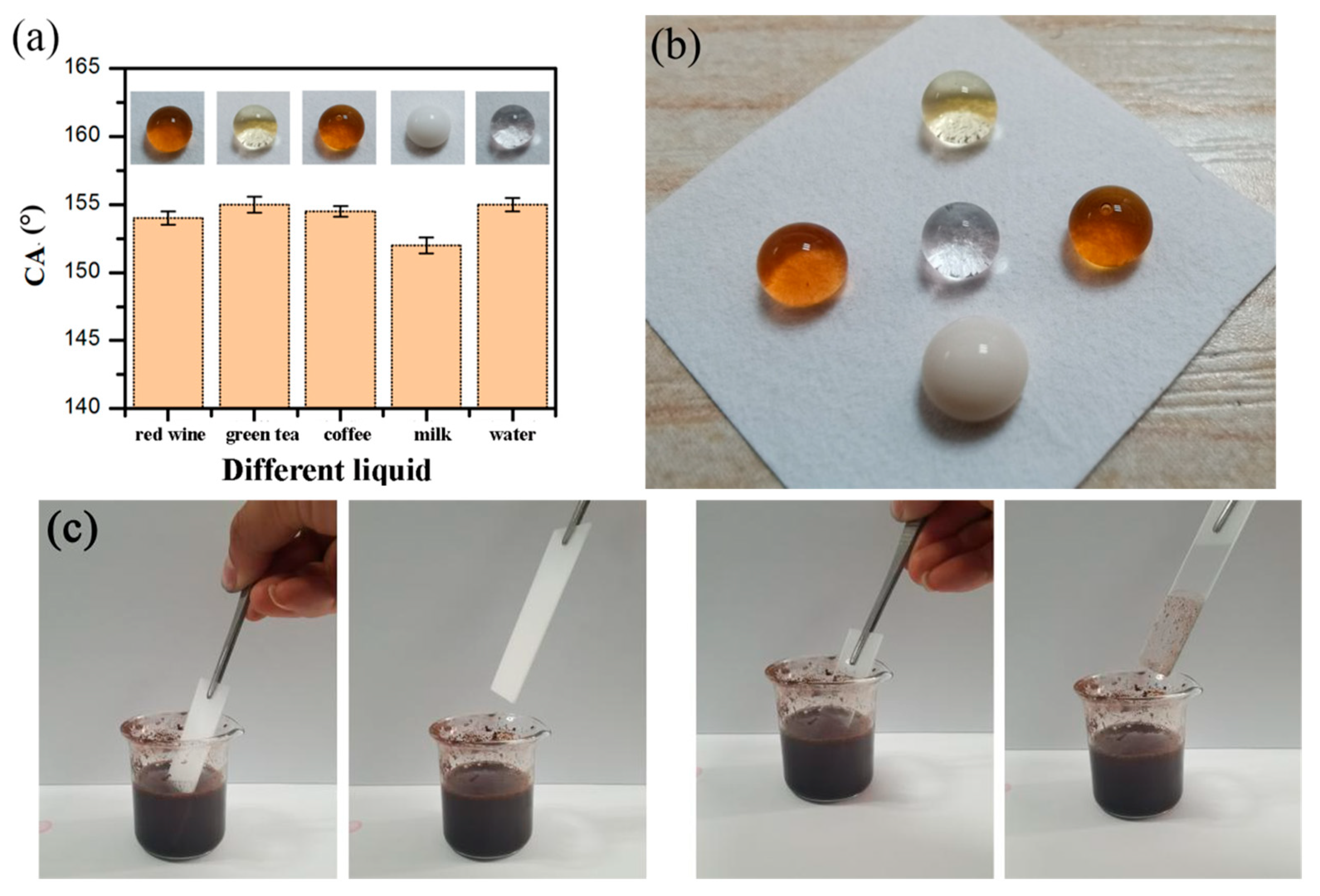
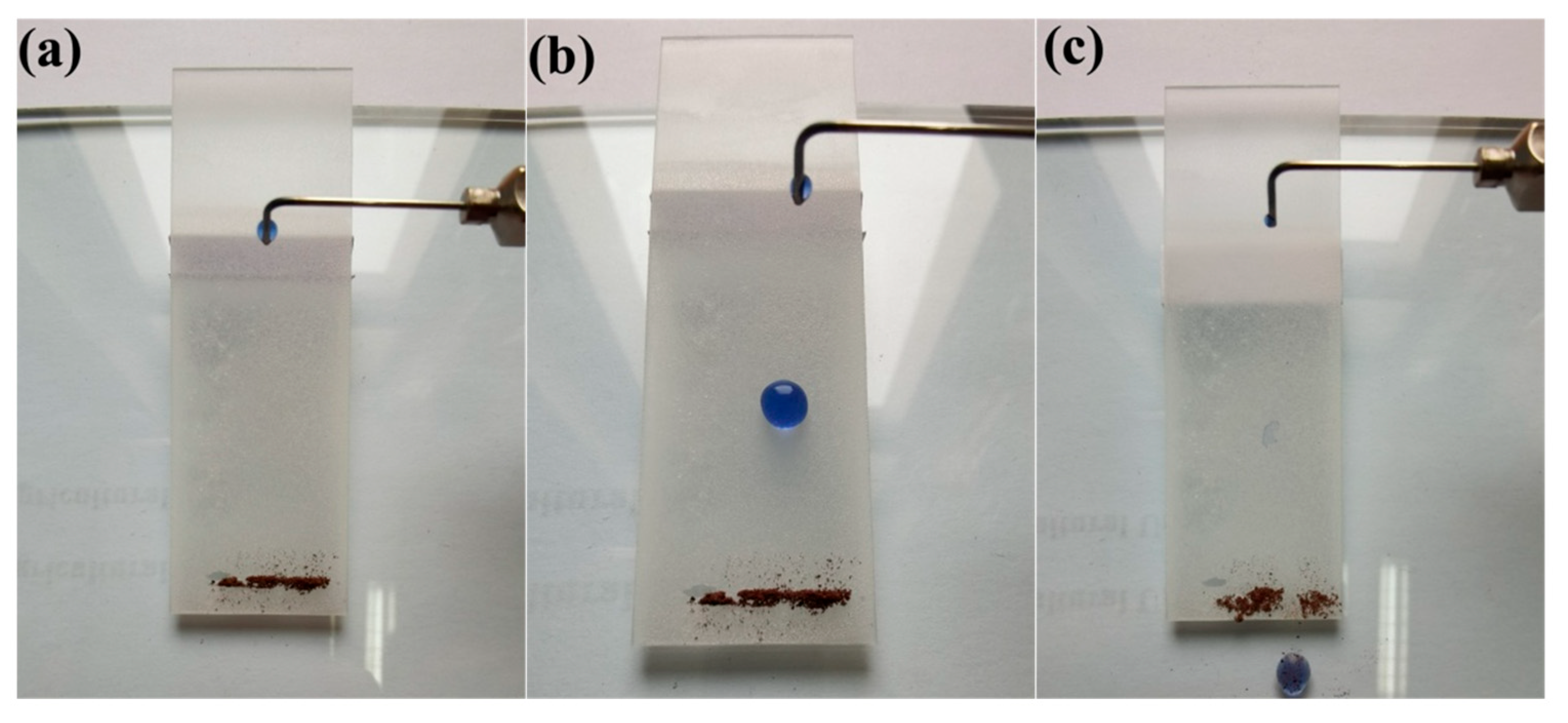
3.5. Self-Cleaning Properties and Mechanism
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Du, J.; Yang, K.L.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, S.J.; Li, C.C.; Meng, S.T. Preparation of a robust and stable superhydrophobic coating with self-cleaning and mold resistance properties on natural bamboo substrate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 411, 134454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Gan, M.; Xie, Y.; Yu, Y.; Feng, Q. Facile fabrication of biometric cellulose-based films with superhydrophobicity and tunable optical performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 637, 157924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Lin, J.; Yu, Y.; Yu, W.; Lai, C.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y. Multifunctional bamboo-based fiber composites fabricated by assembling 3D network structures of bamboo and spatial distribution of silver nanoparticles. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2024, 255, 110739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Wang, B.; Jiang, H.; Lu, Q.; Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Cheng, R.; Gao, Q.; Yang, L.; Duan, G.; et al. Optimization of durable superhydrophobic wood with superstrong ultraviolet resistance and chemical stability. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 480, 148164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, W.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Chai, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, J. Nacre-like graphene oxide–calcium carbonate coated membrane with underwater superoleophobic property for highly efficient oil/water separation. J. Water Process Eng. 2023, 55, 104095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, B.; Liu, H.; Huang, C.; Huang, J.; Cui, X. A supramolecular polydimethysiloxane-based coating with tunable surface topography for photothermal-enhanced sterilization, self-healing and anti/de-icing. Chem. Eng. J. 2025, 504, 158709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, X.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J. A robust superhydrophobic anti-icing/de-icing composite coating with electrothermal and auxiliary photothermal performances. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2022, 227, 109578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Si, Y.; Yu, C.; Jiang, L.; Dong, Z. Bioinspired superwetting oil–water separation strategy: Toward the era of openness. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 10012–10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zeng, H.; Yuan, Y.; Shi, N.; Wen, L.; Rong, H.; Zhu, D.; Hu, L.; Ji, L.; Zhao, L.; et al. Constructing superhydrophobicity by self-assembly of SiO2@ polydopamine core-shell nanospheres with robust oil-water separation efficiency and anti-corrosion performance. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2213042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazirinasab, E.; Jafari, R.; Momen, G. Application of superhydrophobic coatings as a corrosion barrier: A review. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 341, 40–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Q.; Liang, J.; Hao, J. Facile fabrication of a robust super-hydrophobic surface on magnesium alloy. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2014, 443, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayer, I.S. Superhydrophobic coatings from ecofriendly materials and processes: A review. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 7, 2000095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Xie, H.; Yao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Brozena, A.; Li, J.; Ding, Y.; Zhao, X.; Hong, M.; et al. Sustainable high-strength macrofibres extracted from natural bamboo. Nat. Sustain. 2022, 5, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Lin, Q.; Wang, X.; Yu, Y.; Yu, W.; Huang, Y. Bamboo cellulose fibers prepared by different drying methods: Structure-property relationships. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 296, 119926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, G.; Hou, G.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, X. Critical role of degree of polymerization of cellulose in super-strong nanocellulose films. Matter 2020, 2, 1000–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lyu, S.; Fu, F.; Chang, H.; Wang, S. Preparation of superhydrophobic coating with excellent abrasion resistance and durability using nanofibrillated cellulose. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 106194–106200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherian, R.M.; Tharayil, A.; Varghese, R.T.; Antony, T.; Kargarzadeh, H.; Chirayil, C.J.; Thomas, S. A review on the emerging applications of nano-cellulose as advanced coatings. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 282, 119123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teisala, H.; Tuominen, M.; Kuusipalo, J. Superhydrophobic coatings on cellulose-based materials: Fabrication, properties, and applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 1, 1300026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, H.A.; Bhat, I.U.H.; Jawaid, M.; Zaidon, A.; Hermawan, D.; Hadi, Y.S. Bamboo fibre reinforced biocomposites: A review. Mater. Des. 2012, 42, 353–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Meng, Y.; Chen, X.; Chang, L.; Guo, W.; Wang, Y.; Tang, Q. Aligned Fiber Induced Laser-Driven Bamboo Diffuser Enabling Highly Directional Illumination Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2024, 2419025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Zhang, R.; Jin, X.; Zhang, X.; Bao, G.; Qin, D. Bamboo-derived phase change material with hierarchical structure for thermal energy storage of building. J. Energy Storage 2023, 62, 106911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.H.; Shang, J.P.; Su, X.; Zhao, S.; Peng, Y.; Li, Y.B. Fabrication of superhydrophobic/superoleophilic bamboo cellulose foam for oil/water separation. Polymers 2022, 14, 5162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhao, W.; Wu, X.; Gan, J.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Y. A superhydrophobic moso bamboo cellulose nano-fibril film modified by dopamine hydrochloride. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 756839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kan, L.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tian, M.; Huang, Q.; Wei, W.; Zhang, F.; Wang, X. Fabrication of cellulose-based and fluorine/silane free superhydrophobic paper by a green and sustainable approach. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 203, 117226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Ding, Q.; Han, W.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Z.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Wang, S. Preparation of durable and multifunctional superhydrophobic cellulose paper-based materials using the phase change properties of carnauba waxes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2025, 310, 143007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, B.M.; Mekonnen, T. Hydrophobic esterification of cellulose nanocrystals for epoxy reinforcement. Polymer 2018, 155, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehaqui, H.; Zimmermann, T.; Tingaut, P. Hydrophobic cellulose nanopaper through a mild esterification procedure. Cellulose 2014, 21, 367–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, A.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Y.; Yang, Z. Polydimethylsiloxane-decorated magnetic cellulose nanofiber composite for highly efficient oil-water separation. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 277, 118787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.Y.; Liu, M.C.; Li, Y.D.; Zhu, J.; Du, A.K.; Zeng, J.B. Biobased super-hydrophobic coating on cotton fabric fabricated by spray-coating for efficient oil/water separation. Polym. Test. 2018, 66, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilmour, K.A.; Dell’Agnese, B.M.; Bonney, G.; Unthank, M.; White, N.; Scott, J.; Sherry, A.; James, P.; Jiang, Y.; Dade-Robertson, M.; et al. Environmentally Conscious Hydrophobic Spray Coatings on Bacterial Cellulose for Sustainable and Reusable Textiles. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 514, 145775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Wang, S.; Lyu, S.; Fu, F. Preparation of a robust cellulose nanocrystal superhydrophobic coating for self-cleaning and oil-water separation only by spraying. Ind. Crops Prod. 2018, 122, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Lyu, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S.; Fu, F. A facile method for fabricating robust cellulose nanocrystal/SiO2 superhydrophobic coatings. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 536, 349–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Wang, L.; Xu, L.; Pan, H.; Hao, H.; Guo, F. Preparation of peanut shell cellulose nanofibrils and their superhydrophobic aerogels and their application on cotton fabrics. J. Porous Mater. 2023, 30, 471–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, A.; Huh, J.W.; Lim, W.; Joshi, B.; Aldalbahi, A.; Rahaman, M.; Lim, J.; Yoon, S.S. Water-repelling, vapor-resisting, self-cleaning, oil–water-separating, water-purifying, antibacterial Hanji cellulose papers coated with Teflon and ZnO particles via supersonic spraying. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 634, 157551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitbanyong, K.; Pitiphatharaworachot, S.; Pisutpiched, S.; Khantayanuwong, S.; Puangsin, B. Characterization of bamboo nanocellulose prepared by TEMPO-mediated oxidation. BioResources 2018, 13, 4440–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huinink, H.P.; Pel, L.; Michels, M.V.A. How ions distribute in a drying porous medium: A simple model. Phys. Fluids. 2002, 14, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; Lee, M.; Choe, E.K. Characterization of cotton fabric scouring by FT-IR ATR spectroscopy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 417–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeong, Y.H.; Burton, J.; Loth, E.; Bayer, I.S. Drop impact and rebound dynamics on an inclined superhydrophobic surface. Langmuir 2014, 30, 12027–12038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| TOC-P Concentration (wt%) | Static Contact Angle/CA (°) | Rolling Contact Angle/SA (°) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 wt% | 113.4 (±2.1)° | - |
| 2 wt% | 126.6 (±1.7)° | 46 (±5)° |
| 4 wt% | 143.8 (±0.9)° | 25 (±3)° |
| 6 wt% | 156.2 (±1.9)° | 7 (±2)° |
| 8 wt% | 151.3 (±1.1)° | 8 (±3)° |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Y.; Li, J.; Guo, J.; Yuan, T.; Li, Y. A Simple Method to Prepare Superhydrophobic Surfaces Based on Bamboo Cellulose, and an Investigation of Surface Properties. Coatings 2025, 15, 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070740
Wang Y, Li J, Guo J, Yuan T, Li Y. A Simple Method to Prepare Superhydrophobic Surfaces Based on Bamboo Cellulose, and an Investigation of Surface Properties. Coatings. 2025; 15(7):740. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070740
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Yu, Junting Li, JingHai Guo, Tiancheng Yuan, and Yanjun Li. 2025. "A Simple Method to Prepare Superhydrophobic Surfaces Based on Bamboo Cellulose, and an Investigation of Surface Properties" Coatings 15, no. 7: 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070740
APA StyleWang, Y., Li, J., Guo, J., Yuan, T., & Li, Y. (2025). A Simple Method to Prepare Superhydrophobic Surfaces Based on Bamboo Cellulose, and an Investigation of Surface Properties. Coatings, 15(7), 740. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15070740






