The Effects of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Property of Duplex Stainless Steel Layer Obtained by Plasma Arc Cladding Technology
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Experimental Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Macro-Morphology Analysis of 2205 DSS Cladding Layer
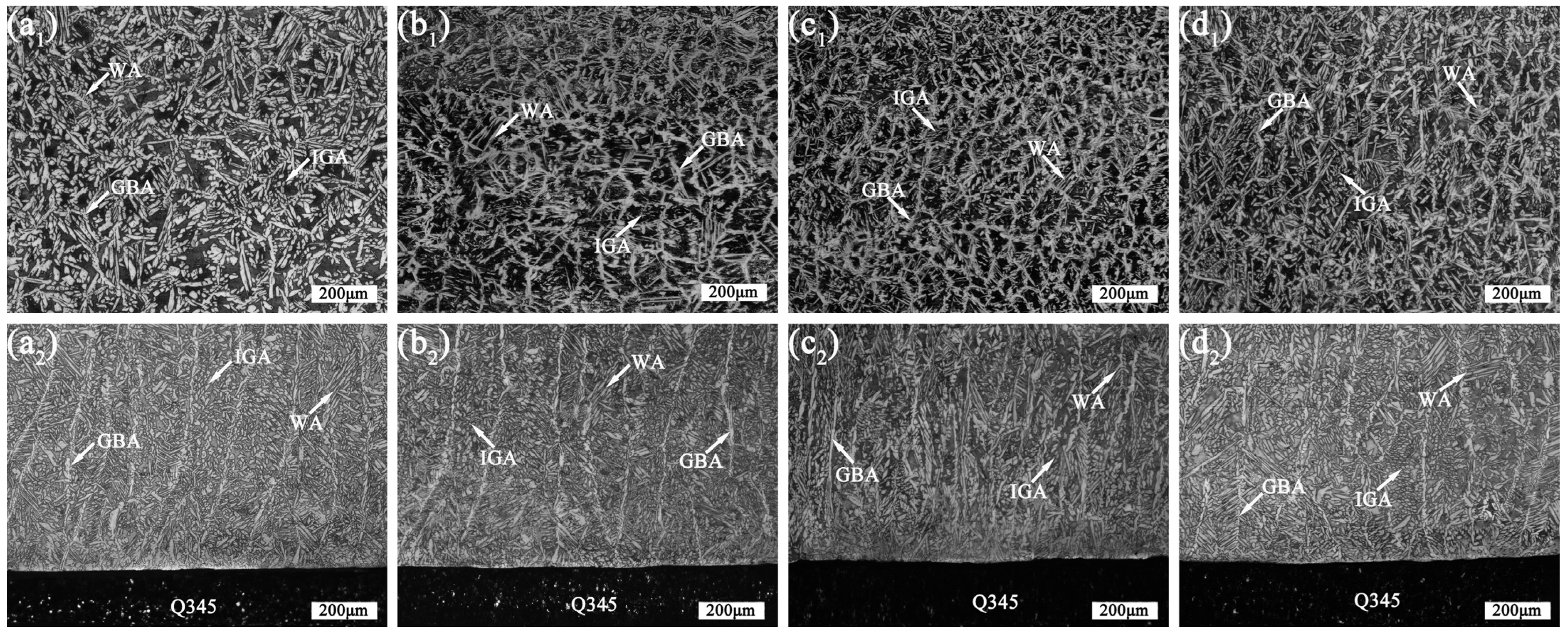
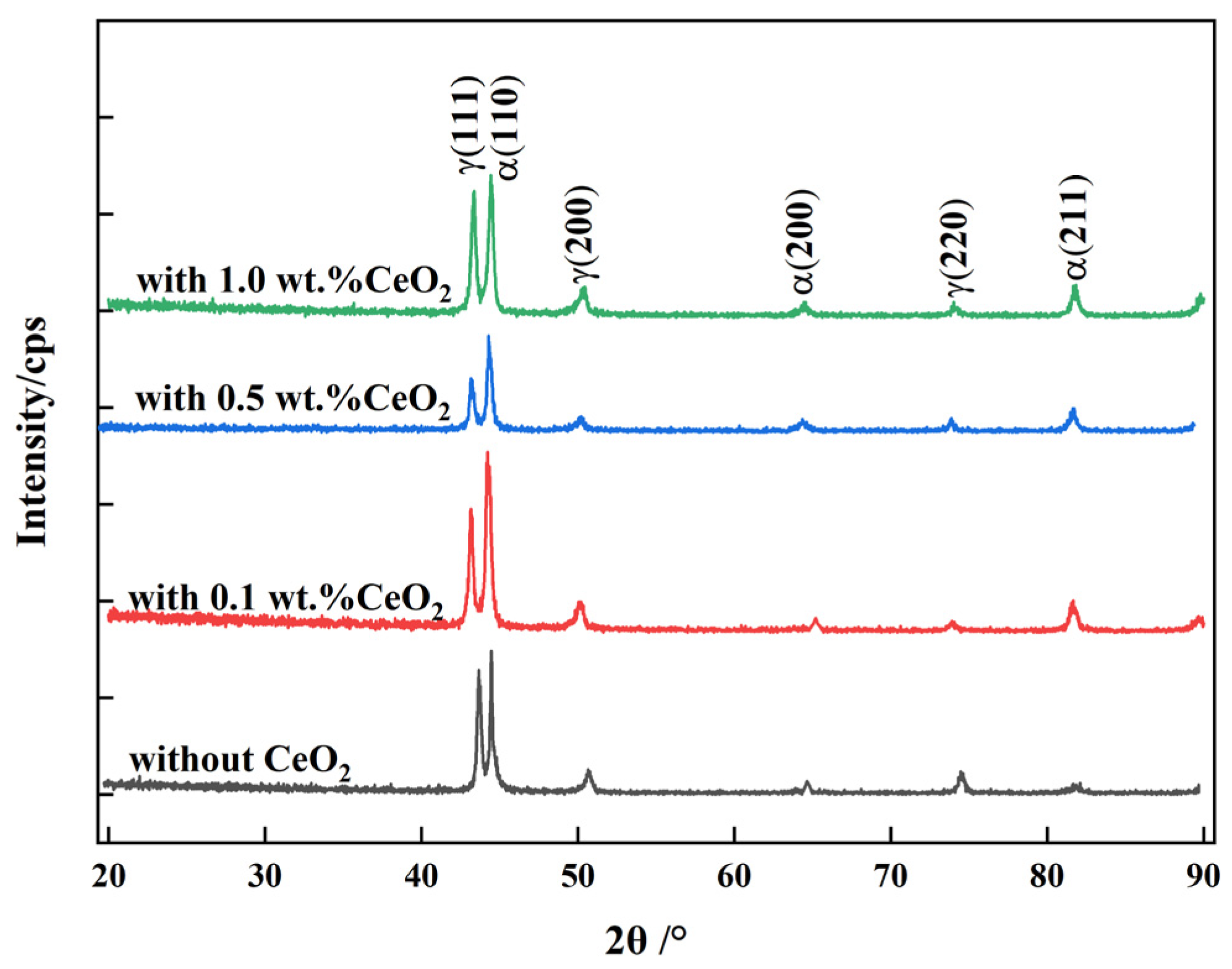
3.2. Microstructure Analysis of 2205 DSS Cladding Layer
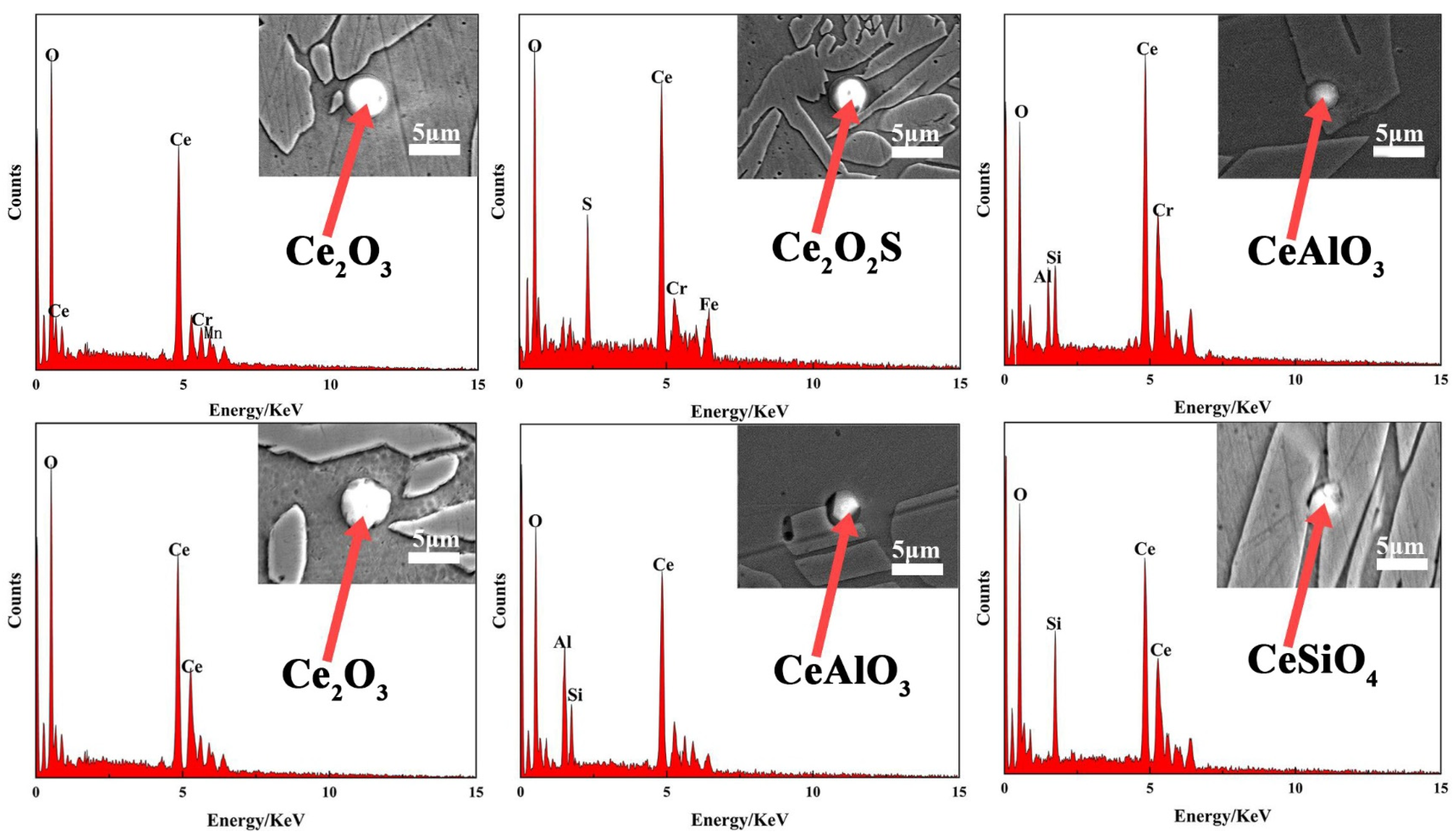
3.3. The Action Mechanism of CeO2 in the Cladding Layer
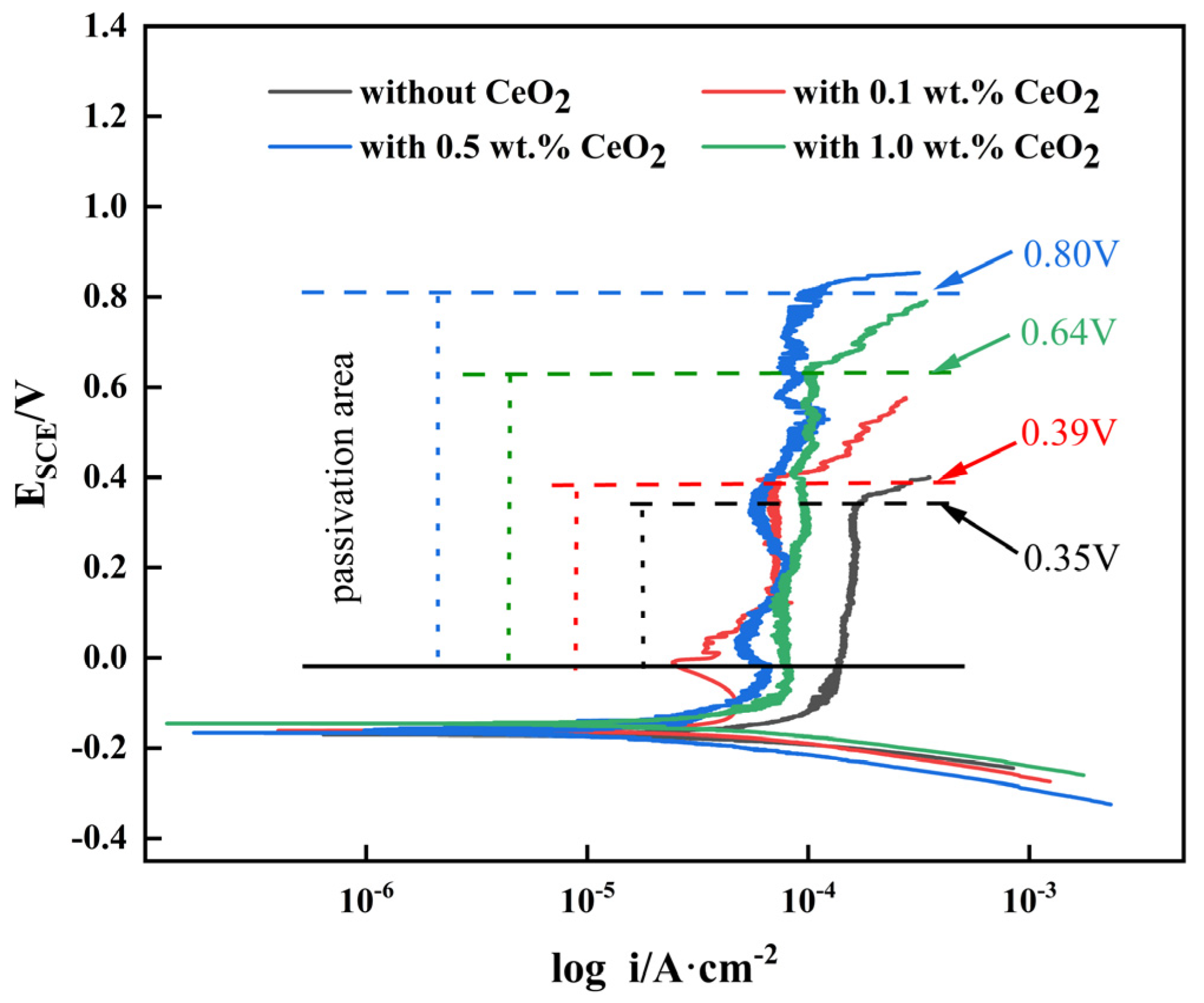
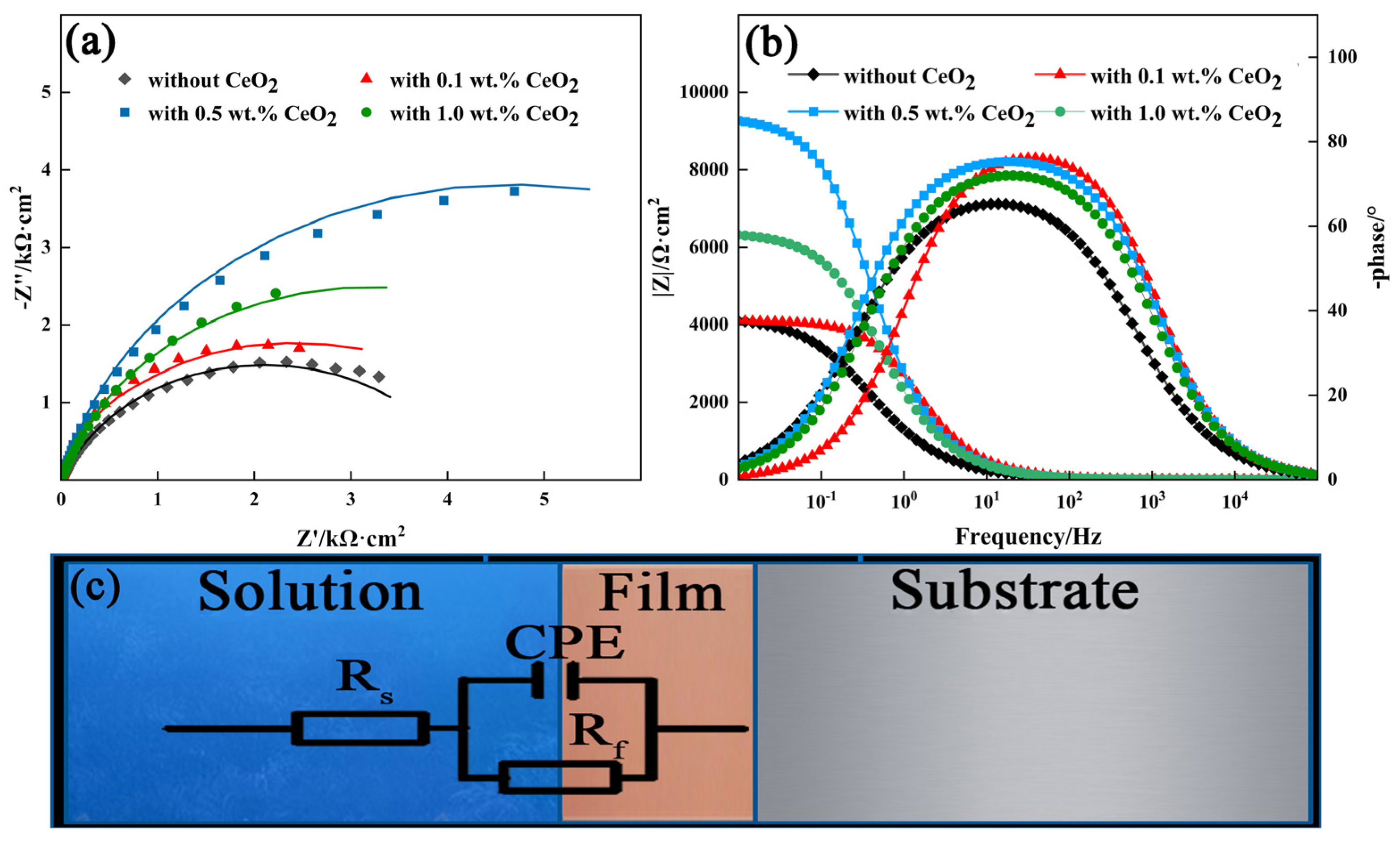
3.4. Corrosion Resistance of 2205 DSS Cladding Layer
3.4.1. Potentiodynamic Polarization Curve
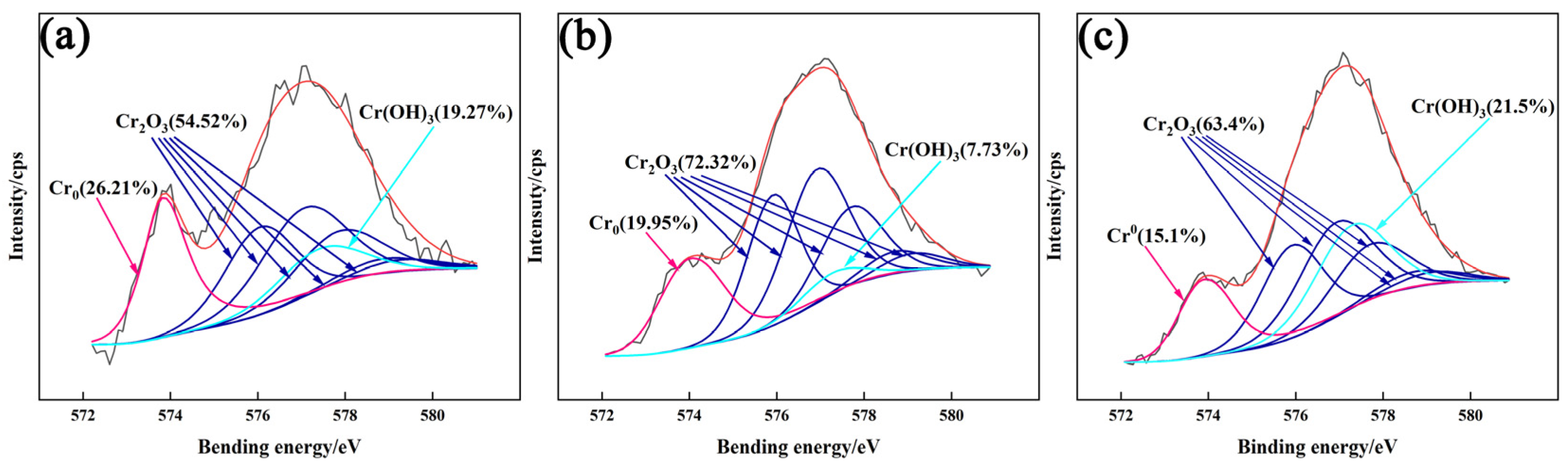
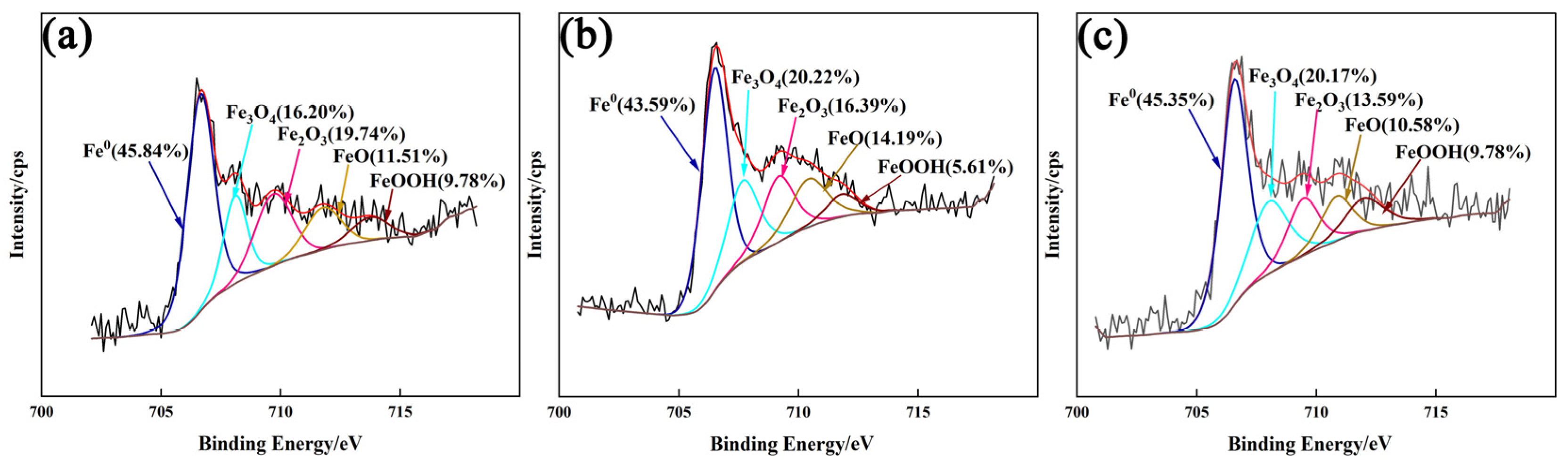
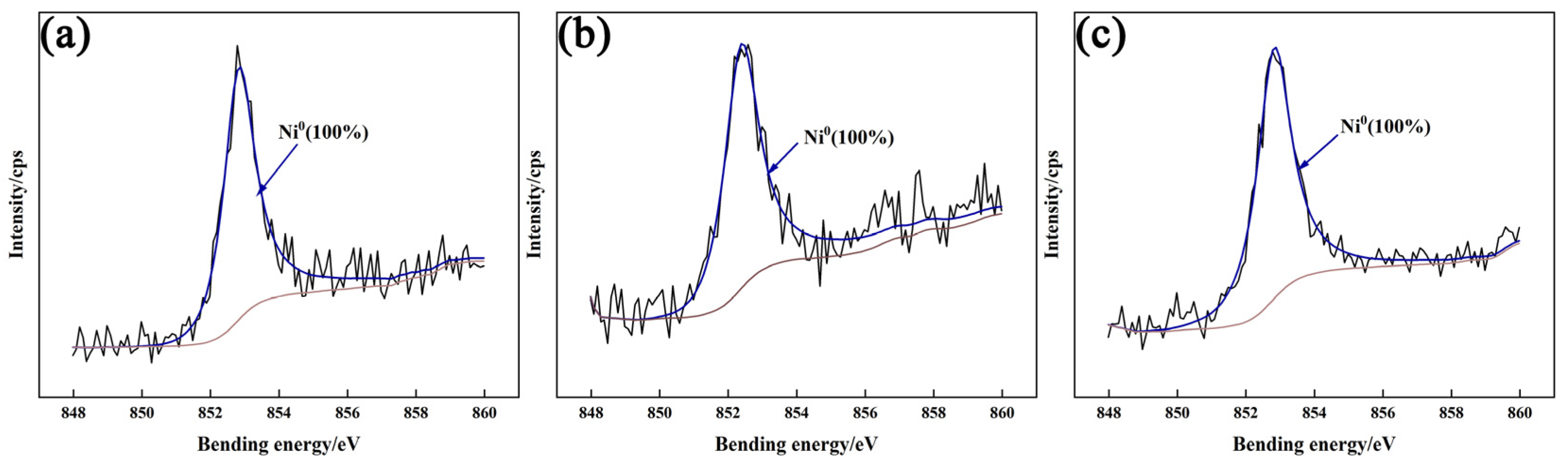
3.4.2. XPS Analysis of Passivation Film
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The addition of CeO2 modified the appearance of the 2205 DSS cladding layer and decreased the dilution ratio of the substrate to the cladding layer; when the content of CeO2 was 0.5 wt.%, the appearance of cladding layer was optimal. The content of CeO2 increased from 0 wt.% to 1.0 wt.%, while the dilution rate decreased from 11.2% to 8.3%.
- (2)
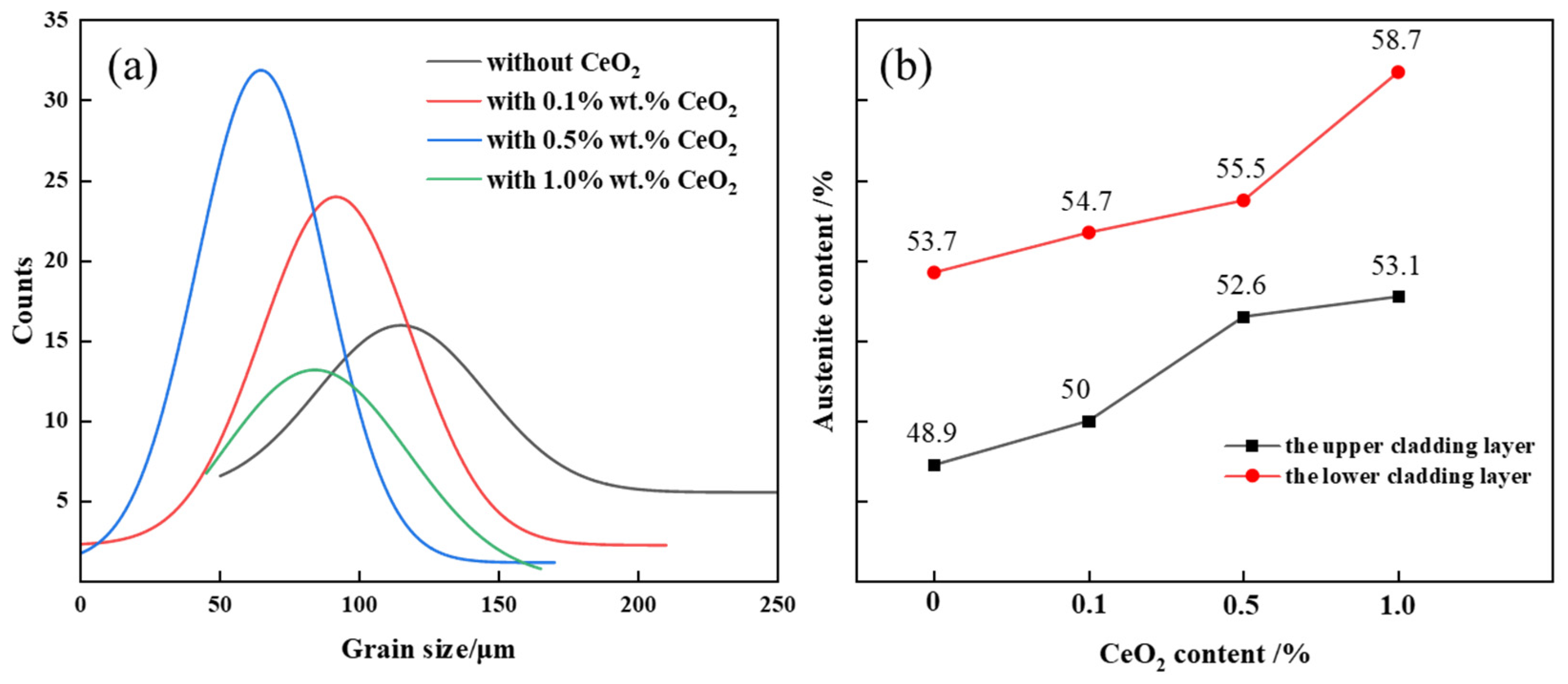
- The 2205 DSS cladding layer was composed of the ferrite and the austenite including GBA, IGA, and WA. The addition of CeO2 affected the morphology of the columnar crystal near the matrix, and when the CeO2 content was 0.5 wt.% and 1.0 wt.%, the austenite in the cladding layer was refined and grew in a columnar shape no longer and began to form equiaxed crystals.
- (3)
- The austenite proportion in the cladding layer increased with the increasing of the CeO2 content. When the CeO2 content was 0.5 wt.%, the austenite proportion in the upper cladding layer and the lower one reached up to 52.6% and 55.5%, respectively. Meanwhile, the austenite proportion in the lower cladding layer was higher than that in the upper one under the action of plasma arc heat cycle.
- (4)
- The addition of CeO2 improves the corrosion resistance of the DSS cladding layer, and it was optimum with the CeO2 content of 0.5 wt.%. Ce element promoted the formation of Cr2O3 to improve the corrosion resistance through changing the element distribution of the cladding layer.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Parker, M.E.; Horton, D.J.; Wahl, K.J. Tribocorrosion behavior of 2205 duplex stainless steel in sodium chloride and sodium sulfate environments. Tribol. Lett. 2022, 70, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H.; Ha, H.Y.; Kim, S.D.; Lee, T.H.; Jang, J.H.; Moon, J.; Kang, N. Effects of carbon substitution for nitrogen on the pitting corrosion resistance of type UNS S32205 duplex stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2020, 164, 108308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.X.; Du, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, G.S.; Ma, L. Effect of hydrogen on pitting corrosion of 2205 duplex stainless steel under alternating dry/wet marine environment. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2023, 48, 17983–17994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, Q.G.; Fang, Y.; Li, X.P.; Luo, J.H.; Song, C.L.; Wang, S. Failure analysis of 2205 duplex stainless steel connecting pipe for composite plate pressure vessel in a high pressure gas field. Int. J. Press. Vessel. Pip. 2023, 202, 104921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varavallo, R.; Moreira, V.D.M.; Paes, V.; Brito, P.; Olivas, J.; Pinto, H.C. Residual stresses of explosion cladded composite plates of ZERON 100 superduplex stainless steel and ASTM SA516-70 carbon steel. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 996, 500–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.Q.; Wang, D.P.; Hu, W.B.; Cui, L.; Gao, Z.M.; Zhou, L.J. Effect of interlayers on microstructure and properties of 2205/Q235B duplex stainless steel clad plate. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2020, 33, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Fang, W.P.; Yi, Y.Y.; Deng, Y.L. Study on microstructure and properties of flux cored twin-wire CMT welded joint of 2205 duplex stainless steel. Hot Work. Technol. 2020, 49, 16–19+24. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Q.L.; Long, W.M.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, H.W. A review on ceramic coatings prepared by laser cladding technology. Opt. Laser Technol. 2024, 176, 110993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, E.; Huang, F.F.; Bao, F.H.; Xue, Y.P.; Wang, H.M.; Jin, Y. Microstructure and electrochemical corrosion behaviors of laser-cladded 2205 duplex stainless steel. Steel Res. Int. 2020, 91, 1900456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Zhu, X.B.; Cheng, J.Q.; Liu, Z.H.; Han, S.S. Microstructure and Properties of Fe-Based/WC-10Co-4Cr Coatings by Plasma Cladding. Surf. Technol. 2023, 52, 167–176+230. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, X.Z.; Zhao, M.; Cao, M.Q. Study on Microstructure and Properties of Fe Based ZrB2-ZrC Compound Coating on Q235 SteeI by PIasma CIadding. Hot Work. Technol. 2019, 48, 106–110+115. [Google Scholar]
- Pu, J.; Sun, Y.B.; Wu, L.; He, P.; Long, W.M. Effect of CeO2 Content on Microstructure and Properties of Ni-Based Tungsten Carbide Layer by Plasma Arc Cladding. Coatings 2022, 12, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, P.J.; Mooraj, S.; Champagne, V.K.; Siopis, M.J.; Liaw, P.K.; Gerasimidis, S. Effect of Build Height on Temperature Evolution and Thermally Induced Residual Stresses in Plasma Arc Additively Manufactured Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2022, 53, 627–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, J.; Xie, P.; Long, W.M.; Wu, M.F.; Sheng, Y.W.; Jie, S. Effect of current on corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steel layer obtained by plasma arc cladding. Crystals 2022, 12, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, W.; Wang, P.F.; Zhang, L.; Jiang, Z.H. Effects of Ce on microstructure and mechanical properties of LDX2101 duplex stainless steel. Metals 2020, 10, 1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, S.I.; Park, Y.S.; Kim, S.T.; Song, C.B. Effects of rare earth metal addition on the cavitation erosion-corrosion resistance of super duplex stainless steels. Met. Mater. Int. 2002, 8, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, T. The effect and mechanism of rare earth elements in metals. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 1996, 6, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, S.H.; Kim, S.T.; Choi, M.S.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, K.T.; Park, Y.S. Effects of cerium on the compositional variations in and around inclusions and the initiation and propagation of pitting corrosion in hyperduplex stainless steels. Corros. Sci. 2013, 75, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Chen, J.; Qiao, Y.X.; Zhang, J.W.; Huang, Y.M. Effect of rare earth oxides on microstructure and corrosion behavior of laser-cladding coating on 316L stainless steel. Coatings 2019, 9, 636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S. Effect of Rare Earth Ce on Inclusions in Q345 Steel. Acad. J. Mater. Chem. 2023, 4, 59–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Lu, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.Q.; Zhu, Z.H.; Xiang, L.; Qiu, S.T. Effect of Ce on inclusions modification in 2.9%Si–0.8%Al non-oriented electrical steel. J. Iron Steel Res. 2017, 29, 570–576. [Google Scholar]
- Hemmati, I.; Ocelik, V.; De-Hosson, J.T.M. Dilution effects in laser cladding of Ni-Cr-B-Si-C hardfacing alloys. Mater. Lett. 2012, 84, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, D.; Dai, S.C.; Wang, G.; Si, W.D.; Xiao, P.; Cui, X.X.; Chen, X. Influence of CeO2 content on WC morphology and mechanical properties of WC/Ni matrix composites coating prepared by laser in-situ synthesis method. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 11111–11120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Jiang, C.N.; Fu, T.L.; Lin, T.; Guo, W.M.; Liu, N.N. Effect of CeO2 on the microstructure and properties of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 laser cladding coatings. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 976, 172948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.H.; Yu, Y.C.; Wang, S.B.; Li, H. Effects of cerium addition on solidification structure and mechanical properties of 434 ferritic stainless steel. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Q.Q.; Wu, C.C.; Cheng, G.G.; Li, F.W. Characteristic and formation mechanism of inclusions in 2205 duplex stainless steel containing rare earth elements. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, S300–S305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, A.Q.; Li, C.Y.; Yu, X.S.; Xie, J.P.; Liang, T.T.; Liu, C.L. Effects of rare earth metals on microstructure, mechanical properties, and pitting corrosion of 27% Cr hyper duplex stainless steel. Rev. Adv. Mater. Sci. 2022, 61, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.M.; Liang, G.F.; Guan, Q.F.; Jiang, Q.H. TiC as heterogeneous nuclei of the (Fe, Mn)3C and austenite intergrowth eutectic in austenite steel matrix wear resistant composite. Mater. Res. Bull. 2004, 39, 457–463. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, J.F.; Fang, H.S.; Yu, G.C.; Zheng, Y.K. Study of Re-Ti Multi-modification on Grain Refinement of Bainitic Cast Steel. Heat Treat. Met. 1999, 9, 5–9. [Google Scholar]
- Zang, Q.Y.; Jin, Y.F.; Zhang, T.; Yang, Y.T. Effect of yttrium addition on microstructure, mechanical and corrosion properties of 20Cr13 martensitic stainless steel. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2020, 27, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Liu, D.T.; Cheng, Y.H.; Wan, Y.X.; Ren, H.W.; Jeyaprakash, N.; Wang, H.N.; Yang, J.Y. Investigation of corrosion resistance offered by the Fe-based clad layer under salt spray and electrochemical workstations. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 494, 131482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.Y.; He, C.L.; Chen, L.Q.; Wei, L.L.; Misra, R.D.K. Effect of W and Ce additions on the electrochemical corrosion behaviour of 444-type ferritic stainless steel. Corros. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.B.; Chang, P.F.; Zhang, B.B.; Jiang, Z.H.; Li, H.B. Effect of Ce on inclusion modification in a new type super duplex stainless steel 2707HD. Iron Steel 2018, 53, 37–44. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Wang, L.M. Effects of rare earth addition on the inclusions and mechanical properties of 2205 duplex stainless steel. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 503, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, S.K.; Zhang, L.F. Effect of rare earth element yttrium modified inclusion on corrosion properties of stainless steel. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 39, 109185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.K.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, B.Y.; Hwang, S.K. Effect of inclusion size on the nucleation of acicular ferrite in welds. ISIJ Int. 2000, 40, 1260–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ju, D.C.; Chen, L. Effect of rare earth metals on passivation behavior of UNS S31803 duplex stainless steel in sulfuric acid solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 421, 135644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ming, J.; Zhou, X.C.; Shi, J.J. Feasibility of using 2304 duplex stainless steel in seawater-mixed concrete pore solutions: A preliminary passivation consideration. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 438, 137037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souto, R.M.; Rosca, I.C.M.; González, S. Resistance to localized corrosion of passive films on a duplex stainless. Corrosion 2001, 57, 300–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, S.; Newman, R.C.; Smith, G.S.; Kaye, S.P.; Kheyrandish, H.; Colligon, J.S. Passivation thresholds in iron-chromium alloys prepared by ion-beam sputtering. Corros. Sci. 1993, 35, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.E.; Newman, R.C.; Song, Q.; Kelly, R.G. Passivity breakdown and pitting corrosion of binary alloys. Nature 1991, 350, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wei, X.X.; Wu, B.; Wang, J.; Shao, X.H.; Yang, L.X.; Zheng, S.J.; Zhou, Y.T.; Jin, Q.Q.; Oguzie, E.E.; et al. Chloride attack on the passive film of duplex alloy. Corros. Sci. 2019, 154, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.Q.; Peng, K.; Chen, X.Z. Duplex stainless steel 2209 with excellent properties deposited by plasma arc additive manufacturing without post heat-treatment: Favorable phase ratio and no σ-phase. Arch. Civ. Mech. Eng. 2024, 24, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.X.; Chi, R.T.; Chen, Q.C.; Wang, B.; Liu, W.; He, Y.L. Microstructural evolution and coarsening behavior of the precipitates in 2205 duplex stainless steel aged at 850 °C. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 2560–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Ma, L.F.; Li, Y.G. Effect of La and Ce on corrosion resistance of duplex stainless steel. Trans. Mater. Heat Treat. 2016, 37, 112–118. [Google Scholar]



| Cr | Ni | Mo | Mn | Si | C | Cu | V | Al | N | P | S | Fe | CeO2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2205 | 22.5 | 5.9 | 3.2 | 1.5 | 0.8 | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 | 0.004 | 0.2 | 0.02 | 0.015 | Bal | 0 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 1.0 |
| Q345 | ≤0.3 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.1 | ≤1.7 | ≤0.5 | ≤0.2 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | Bal | ||||||||
| Welding Current | Cladding Speed | Powder Feeding Speed | Ionic Gas Flow | Shielding Gas Flow | Sending Powder Flow | Height of Nozzle |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90 A | 5 mm/s | 25 cm3/min | 1.5 L/min | 15 L/min | 4 L/min | 8 mm |
| Reaction | ΔG/J·mol−1 (1873k) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| CeO2 Content | |||
| 0.1 wt.% | 0.5 wt.% | 1.0 wt.% | |
| [Ce] + 2[O] = CeO2 | −59,328 | −90,472 | −137,189 |
| [Ce] + 3/2[O] = 1/2Ce2O3 | −81,930 | −128,647 | −144,219 |
| [Ce] + [O] + 1/2[S] = 1/2Ce2O2S | −69,767 | −100,064 | −137,228 |
| [Ce] + [Al] + 3[O] = CeAlO3 | −185,818 | −232,534 | −279,250 |
| [Al] + 3/2[O] = 1/2Al2O3 | −37,850 | −39,251 | −46,882 |
| CASE | [hkl]s | [hkl]n | d [uvw]s/nm | d [uvw]n/nm | θ/° | δ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [] | [] | 0.3889 | 0.41457 | 0 | ||
| Ce2O3(0001)//δ-Fe(111) | [] | [] | 0.6736 | 0.71806 | 0 | 6.19% |
| [] | [] | 0.3889 | 0.41457 | 0 | ||
| [1] | [] | 0.4 | 0.41457 | 0 | ||
| Ce2O2S(0001)//δ-Fe(111) | [] | [] | 0.6929 | 0.71806 | 0 | 3.52% |
| [] | [] | 0.4 | 0.41457 | 0 |
| CeO2/wt.% | Self-Corrosion Potential/V | Self-Corrosion Current Density/A·cm−2 |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | −0.178 | 7.79 × 10−5 |
| 0.1 | −0.165 | 4.22 × 10−5 |
| 0.5 | −0.153 | 3.18 × 10−5 |
| 1.0 | −0.173 | 5.42 × 10−5 |
| DSS | Rs (Ω·cm−2) | Cdl (F·cm−2) | Rf (Ω·cm−2) | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without CeO2 | 9.55 | 1.57 × 10−4 | 4208 | 0.81 |
| 0.1 wt.% CeO2 | 6.75 | 4.71 × 10−5 | 4100 | 0.89 |
| 0.5 wt.% CeO2 | 6.41 | 6.62 × 10−5 | 9379 | 0.96 |
| 1.0 wt.% CeO2 | 7.56 | 7.91 × 10−5 | 6394 | 0.90 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pu, J.; Wu, D.; Shi, X.; Long, F.; Sun, H. The Effects of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Property of Duplex Stainless Steel Layer Obtained by Plasma Arc Cladding Technology. Coatings 2025, 15, 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050590
Pu J, Wu D, Shi X, Long F, Sun H. The Effects of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Property of Duplex Stainless Steel Layer Obtained by Plasma Arc Cladding Technology. Coatings. 2025; 15(5):590. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050590
Chicago/Turabian StylePu, Juan, Di Wu, Xiaohui Shi, Fei Long, and Huawei Sun. 2025. "The Effects of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Property of Duplex Stainless Steel Layer Obtained by Plasma Arc Cladding Technology" Coatings 15, no. 5: 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050590
APA StylePu, J., Wu, D., Shi, X., Long, F., & Sun, H. (2025). The Effects of CeO2 Content on the Microstructure and Property of Duplex Stainless Steel Layer Obtained by Plasma Arc Cladding Technology. Coatings, 15(5), 590. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15050590






