Abstract
We report the successful synthesis of amorphous titanium-engineered tungsten oxide (WTi) films via a facile and cost-effective electrodeposition method. Unlike conventional high-temperature or vacuum-based techniques, our approach enables a scalable, all-solution process, ensuring efficiency and sustainability. X-ray diffraction (XRD) confirmed the amorphous nature of all films, a key factor in enhancing ion diffusion for superior electrochromic (EC) performance. Field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FESEM) revealed that an optimized nanoparticle network facilitates rapid charge transport and ion intercalation, while uncontrolled nucleation and grain growth hinder EC efficiency. By precisely tuning the Ti concentration, the optimized 3 at% WTi-3 film achieved outstanding EC properties, including an impressive optical modulation of 85% at 600 nm, exceptional reversibility of 95.61%, and a high coloration efficiency of 51.55 cm2/C. This study underscores the pivotal role of amorphous engineering and dopant concentrations in advancing high-performance EC materials, paving the way for next-generation smart windows and energy-efficient displays. Our findings highlight a transformative strategy for low-cost, high-efficiency EC devices, demonstrating unprecedented performance through precision-engineered material design.
1. Introduction
In recent decades, rapid population growth and economic expansion have led to a surge in global energy demand, largely driven by fossil fuels. However, the depletion of coal, oil, and natural gas reserves now threatens the future of human development. To mitigate the effects of resource scarcity and environmental challenges, it is crucial to prioritize the development of clean, safe, and sustainable energy sources. One promising avenue is the EC effect, a phenomenon where the optical properties of materials change in response to electrochemical redox reactions [1,2,3]. EC effect involves the reversible injection or withdrawal of ions and electrons when subjected to an electric field. This process has garnered considerable attention, leading to the development of electrochromic devices (ECDs). ECDs have been widely explored for applications across various fields, such as smart windows for energy efficiency, adaptive rearview mirrors, thermal management in spacecrafts, and sensing technologies, offering significant potential to address both energy and environmental challenges [4,5,6]. EC materials are typically classified into three main categories: metal oxides, conductive polymers, and inorganic non-oxides. Among these, metal oxides stand out as one of the most widely studied and utilized groups, with well-known examples including niobium pentoxide (Nb2O5), titanium dioxide (TiO2), tungsten trioxide (WO3), nickel oxide (NiO), manganese dioxide (MnO2), and vanadium pentoxide (V2O5) [7,8,9]. These metal oxide materials are highly regarded for their stability, electrochemical properties, and effectiveness in various EC applications [10,11].
Among the various materials studied for EC applications, tungsten oxide (WO3) has garnered significant interest due to its exceptional EC properties, making it a promising material for a wide array of applications [12,13]. However, conventional WO3 films face several challenges that limit their practical deployment, such as insufficient EC performance, characterized by low optical contrast, and sluggish ion diffusion rates. These issues hinder the material’s ability to achieve fast, reversible switching and stable performance. To address these challenges, researchers have focused on developing strategies to enhance the EC properties of WO3, including optimizing its structural characteristics, improving ion diffusion kinetics, and increasing optical modulation through various modifications, such as doping, composite formation, and nanostructuring techniques [14,15,16].
One highly effective strategy to improve the EC performance of WO3 is by doping the material with a range of metal atoms. This approach enhances the electrical conductivity of the material while introducing charge barriers within its crystal lattice, which in turn optimizes charge transport and significantly enhances its EC properties. Various metal atoms, including titanium (Ti), zinc (Zn), molybdenum (Mo), europium (Eu), iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), and niobium (Nb), have been successfully incorporated into WO3 through different studies. These dopants not only modify the electronic structure but also influence ion diffusion and redox kinetics, leading to improvements in optical contrast, stability, and overall EC performance [17,18].
Cai et al. synthesized Ti-doped WO3 films using a template-free hydrothermal method. The low Ti doping improved EC performance with a transmittance modulation of 49.1% at 750 nm, 64.6% at 2000 nm, and 59.3% at 10 μm; fast switching speeds of 1.7 s and 1.6 s; and a coloration efficiency of 68 cm2 C−1 at 750 nm. This enhancement was attributed to reduced crystallization, a star-like structure, and improved conductivity and reaction kinetics [19]. Peng et al. prepared pure and Ti-doped WO3 films using magnetron sputtering. Ti doping had no impact on the surface morphology or the optical band gap but improved EC stability by reducing ion residues. The 5% Ti-doped WO3 film showed the best EC performance, with better charge cycling and optical transmittance [20]. Ming-Dong et al. found that Ti doping in WO3 films improved ion reversibility, cycling stability, and EC performance. While it had little effect on the morphology and optical properties, Ti increased the crystallization temperature and reduced the switching times from 9.8 s to 8.4 s (colored) and 3.5 s to 2.7 s (bleached) [21]. Zhan et al. synthesized Ti-doped WO3 nanomaterials (5 nm) via the wet bath method. Ti doping improved EC performance by increasing the surface area, enhancing the transmittance contrast, and boosting coloration efficiency due to reduced crystallite size and stable Ti–O bonding. However, proton diffusion was reduced, slowing coloring/bleaching kinetics. The optimized Ti-doped WO3 achieved a high coloration efficiency of 106.6 cm2 C−1 and an optical contrast of ~67.6% at 633 nm [22]. Xie et al. developed Mo-doped WO3 films via the electrodeposition method, achieving 83.3% optical modulation at 633 nm and 117.1 mF cm−2 pseudocapacitance. The case of 2 at% Mo doping improved EC and energy-storage properties due to the amorphous state and structural distortion. These films showed strong performance in bifunctional devices, demonstrating their potential for energy-saving and energy-storage applications [23]. Luo et al. doped Eu ions into WO3 films using the hydrothermal method, enhancing both EC and photoluminescence properties. The 10% Eu-doped WO3 film showed a significantly improved optical contrast of 80.7% at 680 nm, a faster coloration response (7.2 s), and over three times higher coloration efficiency (57.85 cm2 C−1) compared to undoped WO3. Additionally, it exhibited tunable red emission under UV light (260 nm) in response to an electric field, demonstrating potential for smart windows [24]. Wang et al. deposited Nb-doped WO3 films using e-beam co-evaporation. The as-deposited films were amorphous and lacked EC effects. Post-annealing at 350–450 °C improved the films, making them crystalline and transparent, and enhancing their optical modulation, energy band gap, and coloration efficiency [25].
Among various metal dopants, Ti has proven to be a particularly effective enhancer of WO3 EC properties. Ti doping improves the electrical conductivity, optical characteristics, and ion diffusion capabilities of WO3, resulting in faster charge transfer and increased EC contrast. These enhancements make Ti-doped WO3 a promising candidate for advanced, high-performance EC applications. This study aims to optimize the fabrication of WTi thin films on FTO glass substrates using the electrodeposition technique with varying Ti concentrations. The research systematically explores how different Ti concentrations affect the structural, morphological, and EC properties of the WTi thin films, as well as their performance in EC devices. The impact of the Ti concentration on both material characteristics and device functionality is discussed in detail.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Reagents and Materials
All chemicals and solvents used in this study were of analytical-grade (AR) quality, eliminating the need for further purification. Fluorine-doped tin oxide (FTO) glass, obtained from MTI Co., Ltd., Gyeonggi, Republic of Korea (FTO thickness 200 nm), served as the conductive electrode substrate. Prior to use, the FTO glass was meticulously cleaned through sequential ultrasonication in ethanol, acetone, and deionized water for 15 min each, ensuring a pristine surface. The primary reagents, including sodium tungstate dihydrate (Na2WO4·2H2O) (St. Louis, MO, USA), 30% hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) (St. Louis, MO, USA), nitric acid (HNO3), titanium butoxide (Ti (OC4H9)4) (St. Louis, MO, USA), lithium perchlorate (LiClO4), and propylene carbonate (PC), were sourced from Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA. These high-purity chemicals were selected to maintain consistency and reliability across all experiments.
2.2. Preparation of Ti-Integrated WO3 Films
WTi thin films were fabricated using a straightforward and effective electrodeposition technique. The process began with the preparation of a 50 mM Na2WO4·2H2O solution in 150 mL of deionized water. To this solution, 2.5 mL of 30% H2O2 was added, resulting in a deep yellow color. The pH of the solution was adjusted using HNO3, and the mixture was gently heated at 45 °C to promote the formation of peroxo-tungstic acid (PTA). The solution was then allowed to cool to room temperature. Electrodeposition was conducted on thoroughly cleaned FTO substrates using the prepared PTA solution. To achieve different Ti concentrations, 1, 3, and 5 wt.% of Ti precursor (Ti (OC4H9)4) were introduced into the PTA solution and stirred for 20 min. A battery cycler (Biologic Instrument WBCS3000) in the conventional three-electrode configuration was used for the entire electrochemical deposition process. The cyclic voltammetry deposition process was carried out in the potential range from ±1 V with a sweep rate of 50 mV/s for electrodeposition cycles. The deposition process was carried out under controlled conditions, maintaining a fixed cycle count of 20. The films were labeled as WTi-1, WTi-3, and WTi-5 based on the corresponding Ti concentrations. A schematic of the WTi synthesis process, illustrating each step of preparation and fabrication, is shown in Figure 1.
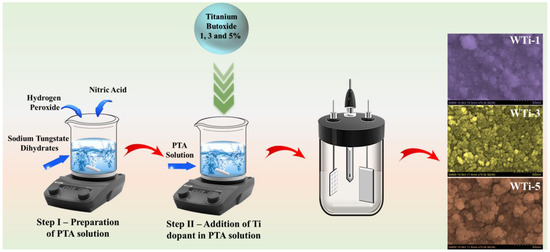
Figure 1.
A schematic illustration of the synthesis process for WTi thin films via electrodeposition.
2.3. Electrochromic Device Fabrication
An EC device was fabricated using a simple electrodeposition method to deposit the WTi thin films. The device structure consisted of glass/FTO/WTi-3/LiClO4+PC/FTO/glass, with dimensions of 4 × 3 cm2. FTO glass acted as the conductive electrode, while the WTi-3 thin film, electrodeposited onto the FTO substrate, functioned as the active layer. The electrolyte, comprising LiClO4 dissolved in PC, was sandwiched between the active layer and the bare FTO/glass electrode. To ensure the device’s stability and to prevent leakage, the entire EC setup was sealed using transparent double-sided adhesive tape (Scotch Brand Tape, 3M, Osaka, Japan).
3. Sample Characterization and Electrochemical Measurements
The structural properties of the W-Nb thin films were examined using X-ray diffraction (XRD, Bruker PAN Analytical, Almelo, The Netherlands, CuKα, ~1.54 Å, Model: D2 Phaser). The surface morphology and elemental composition were analyzed using field-emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM, S-4800 HITACHI, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) coupled with Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS, S-4800 HITACHI, Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The chemical composition at the surface was determined through X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS, K-alpha, Thermo Scientific, Cheshire, UK). The electrochemical performance was evaluated using a battery cycler (Biologic Instrument-WBCS3000, Gières, France) in a three-electrode setup, with the WTi thin film as the working electrode, platinum as the counter electrode, and Ag/AgCl as the reference electrode. The electrolyte used was a 1M LiClO4 solution in PC. Optical transmittance measurements were carried out using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer (S-3100, SCINCO, Seoul, Republic of Korea), integrated with an electrochemical workstation (IVIUM Technologies, COMPACTSTAT, Capelle aan den IJssel, The Netherlands).
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. XRD Elucidation
The XRD patterns of the WTi thin films (WTi-1, WTi-3, and WTi-5) are presented in Figure 2. All samples exhibit a broad hump in the lower 2θ region, with no additional diffraction peaks corresponding to crystalline WO3 or WTi phases, indicating their amorphous nature. The diffraction peaks observed in the XRD patterns correspond to the underlying FTO substrate, as expected. The absence of distinct peaks for WO3 suggests that the electrodeposited films remain amorphous, which is consistent with previous reports on electrodeposited tungsten oxide films without post-deposition annealing. Although no crystalline phases of WTi are detected, slight variations in the intensity and position of the amorphous hump can be observed across different Ti concentrations. This structural characteristic may facilitate better ion intercalation and charge transport, which are critical for EC performance. The WTi-5 sample shows a broader hump, indicating increased disorder within the amorphous matrix. Such structural irregularities may influence ion diffusion kinetics, thereby affecting the EC switching speed and cycling stability [6,25].
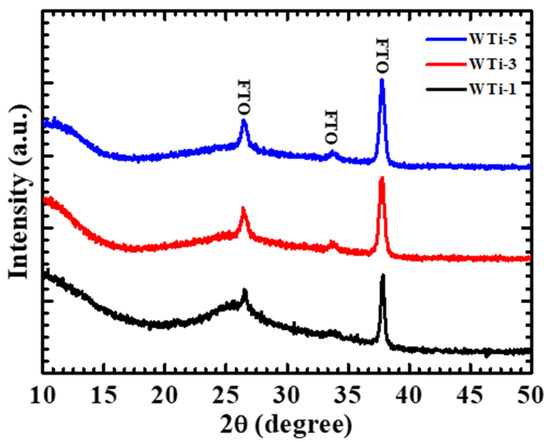
Figure 2.
XRD patterns of WTi-1, WTi-3, and WTi-5 samples.
4.2. XPS Elucidation
XPS analysis was performed on Ti-incorporated WO3 thin films to elucidate their chemical composition and oxidation states. Given that the WTi-3% sample demonstrated the most favorable EC performance, it was selected for an in-depth XPS investigation to gain precise insights into its surface chemistry and electronic structure. The XPS survey spectrum (Figure 3a) confirmed the presence of W, Ti, and O as the primary elements, with no detectable impurities, verifying the high purity of the synthesized film. High-resolution spectra of the W 4f region (Figure 3b) exhibited two well-defined peaks at approximately 35.68 eV and 37.73 eV, corresponding to W 4f7/2 and W 4f5/2, respectively. These binding energy positions indicate the dominance of the W6+ oxidation state, signifying the fully oxidized WO3 phase. The absence of lower-valence tungsten species suggests minimal oxygen vacancies, which is essential for maintaining EC reversibility and long-term stability [15,22]. Similarly, the Ti 2p spectrum (Figure 3c) displayed two distinct peaks at 458.7 eV (Ti 2p3/2) and 462.3 eV (Ti 2p1/2), confirming the presence of Ti4+. The incorporation of Ti4+ into the WO3 lattice is expected to subtly alter the local electronic environment, potentially enhancing charge transfer dynamics and improving the material’s EC efficiency by facilitating ion diffusion. The O 1s spectrum (Figure 3d) exhibited a predominant peak at 529.5 eV, attributed to lattice oxygen in WO3, along with a secondary peak at 531.5 eV, which is typically associated with surface hydroxyl groups or minor oxygen vacancies. The presence of hydroxyl groups can contribute to enhanced ion intercalation kinetics by increasing the number of active sites available for electrochemical reactions, further improving the EC response of the WTi-3% thin film. Overall, these XPS results confirm the successful incorporation of Ti into the WO3 framework, demonstrating its role in modulating the electronic structure and defect chemistry of the material. The well-defined oxidation states and uniform elemental distribution highlight the beneficial impact of Ti incorporation in optimizing charge transport, improving electrochemical stability, and ultimately enhancing the EC performance of WO3 thin films [19].
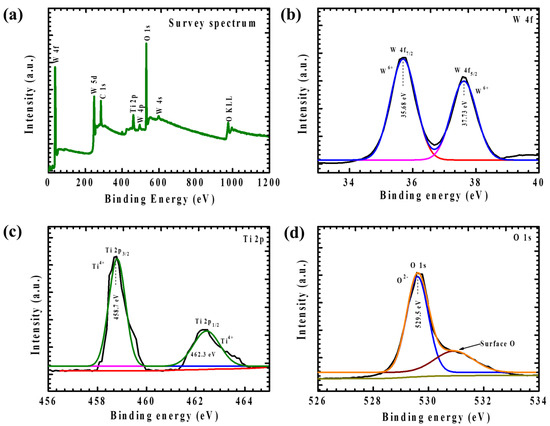
Figure 3.
(a) High-resolution XPS survey spectrum, (b) W 4f spectrum, (c) Ti 2p spectrum, and (d) O 1s core-level XPS spectra of WTi-3 thin films.
4.3. Morphological and Elemental Compositional Characteristics
The morphological evolution of Ti-incorporated WO3 thin films synthesized via electrodeposition was meticulously analyzed to elucidate their structural attributes and EC performance. FE-SEM revealed a pronounced influence of Ti incorporation on the distribution, connectivity, and growth behavior of nanogranules, directly impacting EC functionality. At a low Ti concentration (WTi-1%, Figure 4(a1)), the nanogranules were sparsely distributed and exhibited an extremely fine size, suggesting inhibited nucleation and constrained grain growth during electrodeposition. The inadequate structural cohesion resulted in a non-uniform morphology, which is likely detrimental to EC activity due to a reduced number of electrochemically active sites and restricted ion diffusion pathways. Consequently, this morphology compromises the charge storage capability and limits the films’ EC efficiency. In contrast, the WTi-3% sample (Figure 4(b1)) exhibited a well-defined, highly interconnected nanogranular network with uniform distribution across the substrate. This optimized morphology is particularly advantageous for EC applications as it strikes a critical balance between a high surface area and structural stability. The interconnected granules promote efficient ion intercalation/deintercalation kinetics, enhance charge transport dynamics, and facilitate rapid EC switching. Additionally, the uniformity in grain distribution ensures homogeneous coloration kinetics, leading to superior optical modulation and long-term electrochemical durability [26]. However, at an excessive Ti concentration of 5% (WTi-5%, Figure 4(c1)), the nanogranules underwent uncontrolled growth and subsequent agglomeration, forming a dense, compact structure. This morphological transformation likely introduces increased interfacial resistance, impeding charge transfer and restricting electrolyte penetration. The loss of porosity and active EC sites in this agglomerated framework leads to sluggish ion kinetics and diminished EC efficiency, ultimately compromising the film’s practical applicability. Among the studied compositions, WTi-3% demonstrated the most favorable EC characteristics, attributed to its finely tuned, interconnected nanogranular architecture. This morphology maximizes charge storage capacity, ensures rapid Li+ ion transport, and enhances EC contrast, enabling fast switching speeds, high optical modulation, and prolonged cycling stability. These findings underscore the pivotal role of Ti incorporation in tailoring the morphological landscape of WO3 thin films, offering a promising strategy for optimizing EC materials in next-generation smart window and energy storage applications [27].
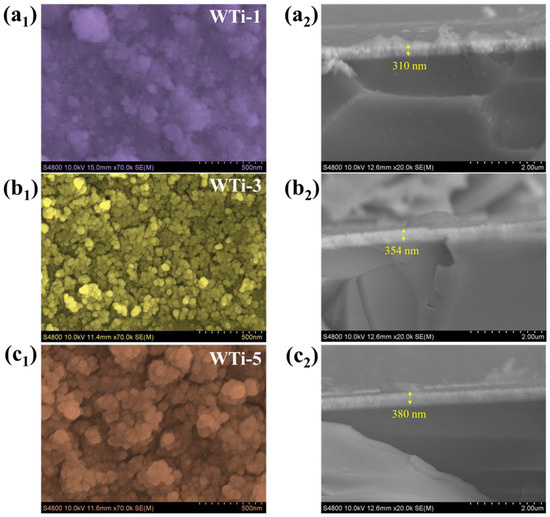
Figure 4.
FE-SEM and cross-section images of (a1,a2) WTi-1, (b1,b2) WTi-3, and (c1,c2) WTi-5 samples.
The cross-sectional FE-SEM images (Figure 4(a1–c1)) clearly demonstrate the successful deposition of Ti-WO3 thin films on the FTO substrate. The measured thickness values for WTi-1, WTi-3, and WTi-5 are 310 nm, 354 nm, and 380 nm, respectively, indicating a slight increase in film thickness with the increasing Ti concentration. This trend suggests that Ti incorporation may have a minor influence on electrodeposition kinetics, possibly enhancing the film growth rate due to changes in the nucleation density or conductivity of the deposition solution. However, the overall uniformity and adherence of the films remain consistent across all doping levels, confirming the successful development of high-quality Ti-WO3 thin films.
EDS analysis was performed on the WTi thin films to confirm the elemental composition and distribution of W, Ti, and O in the as-deposited samples, as illustrated in Figure 5A–C. The EDS spectra exhibited distinct peaks corresponding to these elements, validating the successful incorporation of Ti into the WO3 matrix. The elemental atomic percentages for films deposited with different Ti concentrations are presented in Figure 5A–C. Additionally, the EDS elemental mapping images depicted in Figure 5(a1–a3) for WTi-1, Figure 5(b1–b3) WTi-3, and Figure 5(c1–c3) WTi-5 demonstrate the uniform spatial distribution of W, Ti, and O across the FTO substrate. The arrangement of these elements aligns well with their respective atomic percentage values, further confirming the homogeneous dispersion of Ti within the WO3 structure.
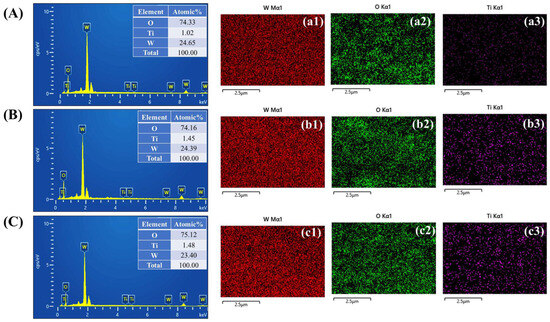
Figure 5.
(A–C) EDS spectra and mapping analysis images of (a1–a3) WTi-1, (b1–b3) WTi-3, and (c1–c3) WTi-5 thin films.
5. Electrochromic Analysis
The electrochemical properties of the W-Ti thin film electrodes were systematically investigated using cyclic voltammetry (CV) to evaluate charge storage behavior and ion transport dynamics at the electrode–electrolyte interface. A three-electrode configuration was employed, with measurements conducted in a 1 M LiClO4+PC electrolyte over a potential window of +1 V to −1 V vs. Ag/AgCl. The scan rates varied from 10 to 100 mV/s to assess the electrochemical kinetics and diffusion-controlled charge storage mechanisms in the system. The CV profiles of W-Ti thin films, presented in Figure 6a–d, exhibit distinct redox peaks, indicative of efficient and reversible faradaic reactions. Figure 6a compares the CV responses of WTi-1, WTi-3, and WTi-5 at 10 mV/s, while the individual CV curves of WTi-1, WTi-3, and WTi-5 are separately illustrated in Figure 6b–d, respectively. The nearly symmetrical nature of the redox peaks confirms excellent electrochemical reversibility, ensuring minimal energy loss during oxidation–reduction transitions. Furthermore, an increase in the current response and a progressive broadening of the hysteresis loop with increasing scan rates suggest enhanced charge storage capability, attributed to improved ion diffusion kinetics and rapid Li+ intercalation/deintercalation processes [28]. Among the studied compositions, the WTi-3 electrode exhibited significantly higher peak currents compared to WTi-1 and WTi-5, highlighting its superior electrochemical activity. This enhancement is primarily attributed to its well-defined, highly interconnected nanogranular structure, which facilitates efficient ion diffusion and charge transfer. In contrast, both WTi-1 and WTi-5 exhibited lower current densities, likely due to morphological limitations. The WTi-1 film, characterized by sparsely distributed and extremely small nanogranules, provided insufficient electroactive sites for Li+ ion diffusion, leading to a restricted charge storage capacity. Conversely, WTi-5 suffered from excessive grain growth and agglomeration, forming a densely packed structure that hindered electrolyte penetration and ion transport. The superior electrochemical performance of the WTi-3 thin film can be directly correlated with its uniformly distributed and highly interconnected nanogranular network, which optimizes Li+ ion accessibility and diffusion pathways. This well-balanced morphology enhances charge storage capability, ensures efficient electrochemical switching, and supports rapid redox kinetics, making WTi-3 the most promising candidate for EC applications [29].
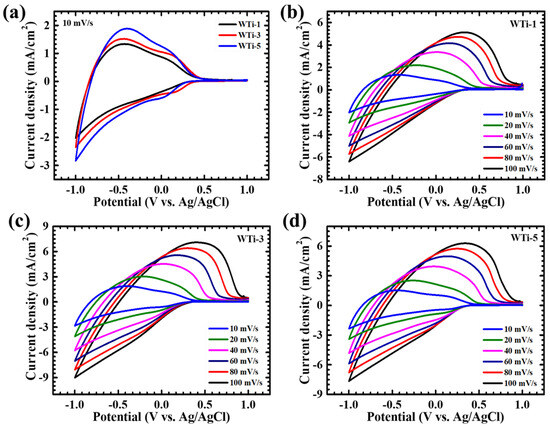
Figure 6.
The cyclic voltammetry of (a) WTi samples at a scan rate of 10 mV/s; (b) WTi-1, (c) WTi-3, and (d) WTi-5 samples at varying scan rates (10–100 mV/s).
The impact of varying Ti incorporation on EC performance was systematically evaluated through in-situ transmittance measurements of WTi-1, WTi-3, and WTi-5 thin films in both their colored and bleached states over the 350–1100 nm wavelength range, as shown in Figure 7a–c. Upon applying a −1 V external voltage to the working and counter electrodes, a distinct blue shift was observed, suggesting the formation of Ti3+ and W5+ oxidation states. For these measurements, FTO glass was used as a reference baseline to monitor transmittance variations throughout the EC process. After electrochemical cycling, the electrodes were exposed to a reverse bias of +1 V vs. Ag/AgCl to assess their transmittance in the bleached state. Table 1 presents the integrated transmittance percentages for both the bleached (Tb%) and colored (Tc%) states of the WTi thin films, along with the total optical modulation (ΔT = Tb − Tc) at 600 nm within the visible spectrum. Initially, all electrodes exhibited high optical transmittance in their pristine, uncolored state. During the EC coloration process, the WTi-3 electrode maintained a relatively high level of transmittance, while the WTi-1 and WTi-5 electrodes showed a significant reduction in transmittance. Specifically, the WTi-3 electrode exhibited a 9.22% decrease in transmittance at 600 nm, while the WTi-1 and WTi-5 electrodes experienced reductions of 22.40% and 11.24%, respectively. The observed variations in transmittance, as well as the underperformance of certain electrodes, can be attributed to differences in their structural composition, surface morphology, and electrochemical behavior. Notably, the WTi-3 electrode exhibited superior EC efficiency across both the visible and infrared regions of the spectrum. Figure 7d illustrates the WTi-3 films in their bleached and colored states, highlighting their pronounced EC response. With an optical modulation (ΔT) of 85% at 600 nm, the WTi-3 electrode outperformed both WTi-1 (70.50%) and WTi-5 (74.57%). A lower ΔT reflects reduced charge transfer efficiency, resulting in diminished EC performance [30,31,32].
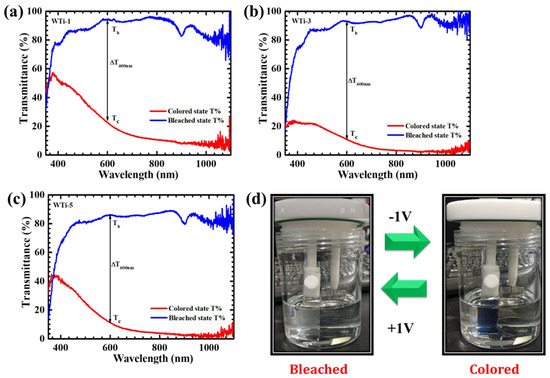
Figure 7.
The optical transmittance spectra of (a) WTi-1, (b) WTi-3, and (c) WTi-5 thin films in both colored and bleached states within the 350 to 1100 nm range, and (d) images of the colored and bleached states of the WTi-3 thin film.

Table 1.
Evaluation of electrochromic measurements of WTi thin films.
The intercalation and deintercalation processes of Li+ ions in Ti-incorporated WO3 thin films were systematically investigated using chronocoulometry (CC) analysis. The results for the WTi-1, WTi-3, and WTi-5 electrodes are shown in Figure 8a–c. Upon cathodic polarization, Li+ ions were intercalated into the films, causing a transition from the transparent to the colored state. This was accompanied by the reduction from Ti4+ to Ti3+ and W6+ to W5+. During anodic polarization, the reverse process occurred, restoring the films to their bleached state by oxidizing Ti3+ to Ti4+ and W5+ to W6+ while expelling the intercalated Li+ ions. A key parameter for evaluating the EC performance of these films is their electrochemical reversibility, which was quantitatively assessed through the ratio of the deintercalation charge (Qdi) to the intercalation charge (Qi) [19,33]. This ratio, as defined in the equation, provides an indication of the efficiency and reversibility of the ion insertion and extraction processes, which are essential for the long-term performance and durability of EC materials [6].
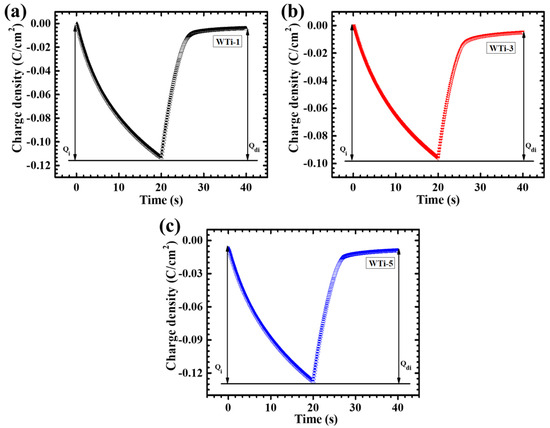
Figure 8.
Chronocoulometry profiles of (a) WTi-1, (b) WTi-3, and (c) WTi-5 thin films.
Table 1 outlines the electrochemical reversibility percentages for the WTi thin films. Reversibility is predominantly influenced by the efficiency of the ion intercalation and deintercalation processes. Among the different Ti incorporation levels, the WTi-3 film demonstrated the highest reversibility, achieving a value of 95.61%. This enhanced performance is attributed to the optimized Ti content in WTi-3, which increased the material’s surface area and created more active sites for ion interaction. This structural improvement promotes efficient Li+ ion diffusion, leading to more effective intercalation and deintercalation, thereby enhancing electrochemical reversibility and overall EC performance.
Coloration efficiency (CE) is a critical metric for assessing the EC performance of materials, quantifying the change in optical density (ΔOD) per unit charge injected or extracted from an EC film at a specific wavelength. This parameter is essential for determining the effectiveness of EC materials, as higher CE indicates a more pronounced optical change for a given charge density. A film with higher CE demonstrates a greater variation in transmittance between its colored and bleached states, signifying a more efficient utilization of charge for inducing color change [34]. The relationship between coloration efficiency and the charge density is typically expressed by the following equation [10],
The CC plot can be used to figure out Q/A, which is the amount of charge introduced per unit of the electrode working area. The charge-dependent function is the amount of charge in the sample that can cause a change in ΔOD, and it is computed using the following equation [19],
To calculate the ΔOD and the CE for the WTi thin films, the transmittance values at 600 nm in both the Tb and Tc states were analyzed. The CE values, as shown in Table 1, indicate that the WTi-3 film achieved the highest coloration efficiency of approximately 51.55 cm2/C at 600 nm. This high CE is a direct result of the films’ well-defined nanograin structure and interconnected morphology, which contribute to a larger available surface area for charge interaction, thereby enhancing charge transfer during the EC process. These structural advantages promote efficient ion intercalation and deintercalation, improving the overall EC response.
Coloration and bleaching times are critical factors for evaluating the real-world applicability of EC films. The coloration time refers to the period required for the film to change from its bleached to its fully colored state under an applied electrical field, while the bleaching time measures how long it takes for the material to return to its transparent state once the voltage is removed. These time parameters are essential for determining the operational efficiency of EC devices in practical applications like smart windows, adaptive displays, and other dynamic optical systems, where quick and reversible transitions between optical states are necessary for seamless functionality. To assess the optical switching properties of WTi thin films (WTi-1, WTi-3, and WTi-5), in situ transmittance cycling experiments were performed, as shown in Figure 9a–c. The switching time, defined as the duration required to achieve 95% of the maximum optical contrast during both coloration and bleaching processes, was evaluated. Based on the data summarized in Table 1, the WTi-3 film exhibited the fastest response, with a coloration time of 15.1 s and a bleaching time of 11.4 s. These results suggest that WTi-3 optimizes ion diffusion and charge transfer kinetics, leading to faster optical switching and enhanced EC performance [6,10,35].
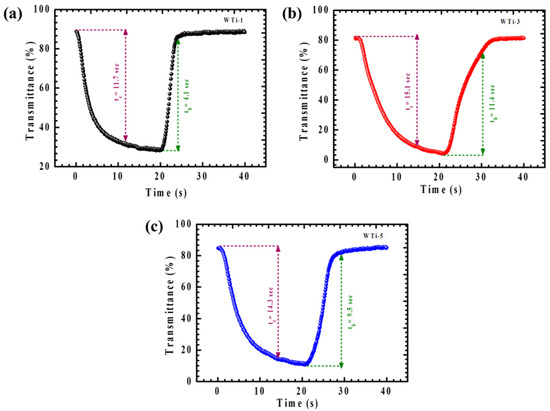
Figure 9.
Chronoamperometric response time with in situ transmittance measurements at 600 nm of (a) WTi-1, (b) WTi-3, and (c) WTi-5 thin films in both colored and bleached states for 40 s.
The long-term cycling stability of the films is critical for practical applications, such as for smart windows, where sustained optical modulation is required. To examine this, the stability of WTi thin films was investigated through in situ transmittance measurements at 600 nm using a UV-Vis spectrophotometer in combination with an electrochemical cyclic tester. The cycling stability, presented in Figure 10a–c, was tested over different durations: WTi-1 and WTi-5 films were tested for 2000 s, while the WTi-3 film was evaluated for 3000 s. A 20 s cycling interval was employed, alternating between the colored state at −1 V and the bleached state at +1 V. The WTi-3 film demonstrated the highest cycling stability, with minimal transmittance degradation after 3000 s of continuous switching. This excellent stability is attributed to its well-structured, interconnected nanograin network, which facilitates efficient charge transport and rapid ion intercalation and deintercalation. The interconnected structure minimizes ion-trapping sites and enhances the adhesion of the film to the substrate, contributing to its prolonged electrochemical stability. In contrast, the WTi-1 and WTi-5 films exhibited higher degradation, likely due to larger ion-trapping sites that hinder ion diffusion and reduce cycling performance [36,37].
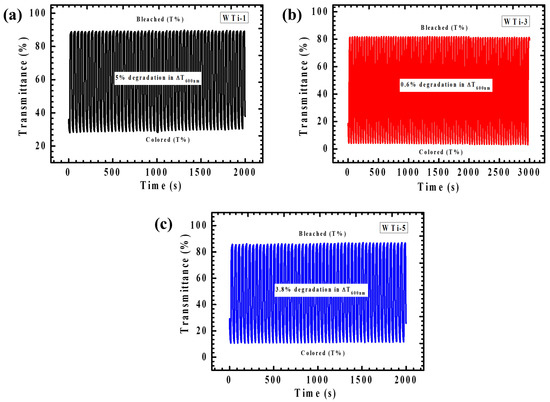
Figure 10.
The long-term in situ optical response (at 600 nm) as a function of time for (a) WTi-1, (b) WTi-3, and (c) WTi-5 thin films.
6. Electrochromic Device Performance
To assess the practical feasibility of EC materials for applications like smart windows, it is crucial to develop and optimize a functioning prototype EC device. In this investigation, WTi thin films were synthesized with varying electrodeposition cycles, and WTi-3 was selected as the optimal candidate for large-scale device fabrication. The EC device was constructed using a traditional sandwich-type structure, comprising an EC working electrode, an electrolyte layer, and a counter electrode. As shown in Figure 11a, the device demonstrated impressive EC performance, exhibiting a clear transition from a colorless (bleached) state to a deep blue (colored) state upon the application of an external voltage, confirming the effective EC switching of the WTi-3 material. In-situ transmittance measurements were conducted over a wavelength range of 350–1100 nm (Figure 11b), showing a notable optical modulation of 70.45% at 600 nm. This result demonstrates that the large-area device replicates the EC behavior observed in the laboratory-scale three-electrode system, effectively regulating light transmission within the visible spectrum. To assess the device’s long-term durability, continuous coloration and bleaching cycles were performed for 1000 s within the visible range (Figure 11c). While the optical modulation remained stable initially, a slight decline of 3.2% was observed after prolonged cycling. Despite this minor degradation, the results validate the scalability of the WTi-3 thin film, highlighting its ability to maintain its EC properties when scaled up for practical applications. This successful demonstration of material scalability provides a solid foundation for the integration of W-Ti-based EC materials in future commercial technologies [19].
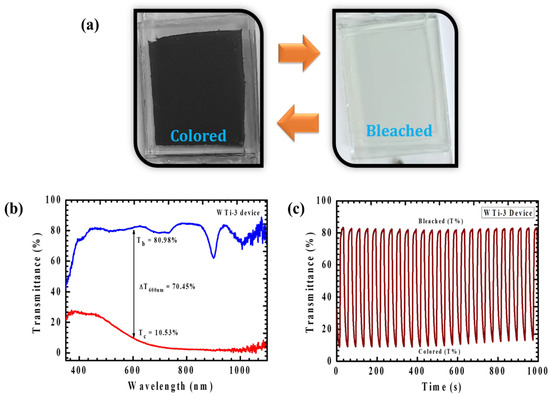
Figure 11.
(a) A digital image of the WTi-3 device in the bleached and colored states, (b) the optical transmittance spectrum, and (c) a plot of the in situ optical response as a function of time for the WTi-3 device (all measured at 600 nm wavelength).
7. Conclusions
This study demonstrated successfully synthesized amorphous titanium-engineered tungsten oxide (WTi) thin films via a scalable and cost-effective electrodeposition method. Unlike conventional high-temperature or vacuum-based techniques, this all-solution process provides a sustainable and efficient route for EC material fabrication. XRD analysis confirmed the amorphous nature of the films, a crucial characteristic for enhanced ion transport. Surface morphology revealed that an optimized nanoparticle network in WTi-3 facilitates efficient charge transport and ion intercalation, whereas excessive Ti incorporation in WTi-5 leads to structural disorder, affecting EC performance. By precisely tuning the Ti concentration, the WTi-3 film demonstrated superior EC properties, achieving 85% optical modulation at 600 nm, 95.61% EC reversibility, and a high coloration efficiency of 51.55 cm2/C. The optimized structure enhances ion diffusion kinetics, ensuring fast switching speeds and long-term cycling stability. These findings emphasize the critical role of dopant engineering in tailoring material properties for next-generation smart windows and energy-efficient display technologies. The optimized WTi-3 film exhibited excellent EC device performance, demonstrating fast high optical contrast and outstanding cycling stability. These superior properties make it a promising candidate for next-generation smart windows and energy-efficient display technologies. Overall, this work highlights a transformative approach to high-performance EC materials through precise engineering and dopant control. The demonstrated low-cost and scalable fabrication strategy paves the way for practical applications in energy-efficient and sustainable electrochromic devices.
Author Contributions
R.U.A.: Writing—original draft, Methodology, Investigation. P.J.M.: Review and editing, Software. N.A.A.: Software. C.-W.J.: Supervision, Writing—review and editing, Project administration. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Korean Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) grant funded by the Korean government (MOTIE) (No. 20204010600100, Hydrogen Education and Research Consortium).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to restrictions.
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Korean Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP) grant funded by the Korean government (MOTIE) (No. 20204010600100, Hydrogen Education and Research Consortium).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kodam, P.M.; Ghadage, P.A.; Nadargi, D.Y.; Shinde, K.; Mulla, I.S.; Park, J.; Suryavanshi, S.S. Ru, Pd doped WO3 nanomaterials: A synergistic effect of noble metals to enhance the acetone response properties. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 17923–17933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Cong, S.; Su, W.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Geng, F.; Zhao, Z. Synergy of W18O49 and polyaniline for smart supercapacitor electrode integrated with energy level indicating functionality. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 2150–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, V.; Singh, R.S.; Blackwood, D.J.; Zhili, D. A review on recent advances in electrochromic devices: A material approach. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2020, 22, 2000082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, A.I.; Kim, Y.; Jang, B.; Im, H.; Jung, W.; Kim, D.-Y.; Kim, H. Effects of oxygen stoichiometry on electrochromic properties in amorphous tungsten oxide films. Thin Solid Films 2012, 520, 5367–5371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, R.-T.; Granqvist, C.G.; Niklasson, G.A. Eliminating degradation and uncovering ion-trapping dynamics in electrochromic WO3 thin films. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 996–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morankar, P.J.; Amate, R.U.; Chavan, G.T.; Teli, A.M.; Dalavi, D.S.; Jeon, C.-W. Improved electrochromic performance of potentiostatically electrodeposited nanogranular WO3 thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 945, 169363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, H.S.; Hou, B.; Ahmed, A.T.A.; Kim, J.; Jo, Y.; Cho, S.; Park, Y.; Pawar, S.M.; Inamdar, A.I.; Cha, S.N.; et al. Ultrathin Ni-Mo oxide nanoflakes for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 767, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, S.; Zhang, T.; Fisher, A.; Lee, J.Y. Al3+ intercalation/de-intercalation-enabled dual-band electrochromic smart windows with a high optical modulation, quick response, and long cycle life. Energy Environ. Sci. 2018, 11, 2884–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teli, A.M.; Beknalkar, S.A.; Satale, V.V.; Morankar, P.J.; Yewale, M.A.; Shin, J.C. Exploring the synergistic effect of palladium-doped molybdenum phosphate as an electrode material for high-performance asymmetric supercapacitor device. Surf. Interfaces 2023, 40, 103149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morankar, P.J.; Amate, R.U.; Teli, A.M.; Chavan, G.T.; Beknalkar, S.A.; Dalavi, D.S.; Ahir, N.A.; Jeon, C.-W. Surfactant integrated nanoarchitectonics for controlled morphology and enhanced functionality of tungsten oxide thin films in electrochromic supercapacitors. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 109095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.; Ma, D.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Guo, H.; Zhu, X.; Wang, J. Solvothermal growth of Nb2O5 films on FTO coated glasses and their electrochromic properties. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 9651–9658. [Google Scholar]
- Ouendi, S.; Arico, C.; Blanchard, F.; Codron, J.-L.; Wallart, X.; Taberna, P.-L.; Roussel, P.; Clavier, L.; Simon, P.; Lethien, C. Synthesis of T-Nb2O5 thin-films deposited by atomic layer deposition for miniaturized electrochemical energy storage devices. Energy Storage Mater. 2019, 16, 581–588. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, H.-C.; Zydlewski, B.Z.; Tandon, B.; Shubert-Zuleta, S.A.; Milliron, D.J. Understanding the role of charge storage mechanisms in the electrochromic switching kinetics of metal oxide nanocrystals. Chem. Mater. 2022, 34, 5621–5633. [Google Scholar]
- Come, J.; Augustyn, V.; Kim, J.W.; Rozier, P.; Taberna, P.-L.; Gogotsi, P.; Long, J.W.; Dunn, B.; Simon, P. Electrochemical kinetics of nanostructured Nb2O5 electrodes. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2014, 161, A718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, W.; Lv, Y.; Xiao, L.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, N.; Liu, X. Bifunctional MoO3–WO3/Ag/MoO3–WO3 films for efficient ITO-free electrochromic devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 33842–33847. [Google Scholar]
- Morankar, P.J.; Amate, R.U.; Teli, A.M.; Beknalkar, S.A.; Jeon, C.-W. Unveiling nanogranular advancements in nickel-doped tungsten oxide for superior electrochromic performance. Coatings 2024, 14, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.; Wang, X.; Cui, M.; Darmawan, P.; Wang, J.; Eh, A.L.-S.; Lee, P.S. Electrochromo-supercapacitor based on direct growth of NiO nanoparticles. Nano Energy 2015, 12, 258–267. [Google Scholar]
- Amate, R.U.; Morankar, P.J.; Chavan, G.T.; Teli, A.M.; Desai, R.S.; Dalavi, D.S.; Jeon, C.-W. Bi-functional electrochromic supercapacitor based on hydrothermal-grown 3D Nb2O5 nanospheres. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 459, 142522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, G.-F.; Wang, X.-L.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, J.-H.; Xiong, Q.-Q.; Gu, C.-D.; Tu, J.-P. Hierarchical structure Ti-doped WO3 film with improved electrochromism in visible-infrared region. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 6896–6905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.-D.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Song, L.-X.; Wu, L.-N.; Zhang, Y.-L.; Hu, X.-F. Electrochemical stability properties of titanium-doped WO3 electrochromic thin films. Surf. Eng. 2017, 33, 305–309. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, M.-D.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Song, L.-X.; Yin, X.-F.; Wang, P.-P.; Wu, L.-N.; Hu, X.-F. Structure and electrochromic properties of titanium-doped WO3 thin film by sputtering. J. Inorg. Mater. 2017, 32, 287–292. [Google Scholar]
- Zhan, Y.; Tan, M.R.J.; Cheng, X.; Tan, W.M.A.; Cai, G.-F.; Chen, J.W.; Kumar, V.; Magdassi, S.; Lee, P.S. Ti-doped WO3 synthesized by a facile wet bath method for improved electrochromism. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 9995–10000. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, S.; Bi, Z.; Chen, Y.; He, X.; Guo, X.; Gao, X.; Li, X. Electrodeposited Mo-doped WO3 film with large optical modulation and high areal capacitance toward electrochromic energy-storage applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 459, 774–781. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, G.; Shen, L.; Zheng, J.; Xu, C. A europium ion doped WO3 film with the bi-functionality of enhanced electrochromic switching and tunable red emission. J. Mater. Chem. C 2017, 5, 3488–3494. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.-K.; Sahu, D.; Wang, S.-C.; Huang, J.-L. Electrochromic Nb-doped WO3 films: Effects of post annealing. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 2829–2833. [Google Scholar]
- Houweling, Z.S.; Geus, J.W.; Schropp, R.E. Synthesis of WO3 nanogranular thin films by hot-wire CVD. Chem. Vap. Depos. 2010, 16, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- More, A.; Patil, R.; Dalavi, D.; Mali, S.; Hong, C.; Gang, M.; Kim, J.; Patil, P. Electrodeposition of nano-granular tungsten oxide thin films for smart window application. Mater. Lett. 2014, 134, 298–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poongodi, S.; Kumar, P.S.; Mangalaraj, D.; Ponpandian, N.; Meena, P.; Masuda, Y.; Lee, C. Electrodeposition of WO3 nanostructured thin films for electrochromic and H2S gas sensor applications. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 719, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalavi, D.S.; Devan, R.S.; Patil, R.A.; Patil, R.S.; Ma, Y.-R.; Sadale, S.B.; Kim, I.; Kim, J.-H.; Patil, P.S. Efficient electrochromic performance of nanoparticulate WO3 thin films. J. Mater. Chem. C 2013, 1, 3722–3728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalavi, D.S.; Devan, R.S.; Patil, R.S.; Ma, Y.-R.; Kang, M.-G.; Kim, J.-H.; Patil, P.S. Electrochromic properties of dandelion flower-like nickel oxide thin films. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.H.; Deshpande, R.; Parilla, P.A.; Jones, K.M.; To, B.; Mahan, A.H.; Dillon, A.C. Crystalline WO3 nanoparticles for highly improved electrochromic applications. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 763–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shim, H.-S.; Kim, J.W.; Sung, Y.-E.; Kim, W.B. Electrochromic properties of tungsten oxide nanowires fabricated by electrospinning method. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 2062–2068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deepa, M.; Srivastava, A.; Sood, K.; Agnihotry, S. Nanostructured mesoporous tungsten oxide films with fast kinetics for electrochromic smart windows. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 2625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venugopal, R.; Dinakaran, A.; Nair, M.C.; Balachandran, A.C.; Madhavan, N.D.; Deb, B. Electrochromic properties of MnO2/WO3 bilayered electrodes for enhanced charge storage and superior stability. RSC Appl. Interfaces 2024, 1, 1382–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Tan, M.; Wang, T.; Sun, J.; Du, J.; Ma, R.; Wang, W.; Hu, D. Boosting the electrochromic performance of P-doped WO3 films via electrodeposition for smart window applications. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 10298–10303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Jia, H.; Shao, Z.; Jin, P.; Cao, X. Fast-switching WO3-based electrochromic devices: Design, fabrication, and applications. Acc. Mater. Res. 2023, 4, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y. A novel method for performance rejuvenation of WO3//NiO electrochromic devices: Lithium ion kinetic behavior with variable cycling temperature and switching voltage. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2023, 11, 13566–13573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).