Recent Advances in Magnetocaloric Effect of High-Entropy Alloys
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Magnetocaloric Effect in Materials
2.1. Magnetocaloric Effect
2.2. Classification of Magnetocaloric Materials
2.3. Efficiency Metrics
3. Definition and Characteristics of HEAs
3.1. Component Definition
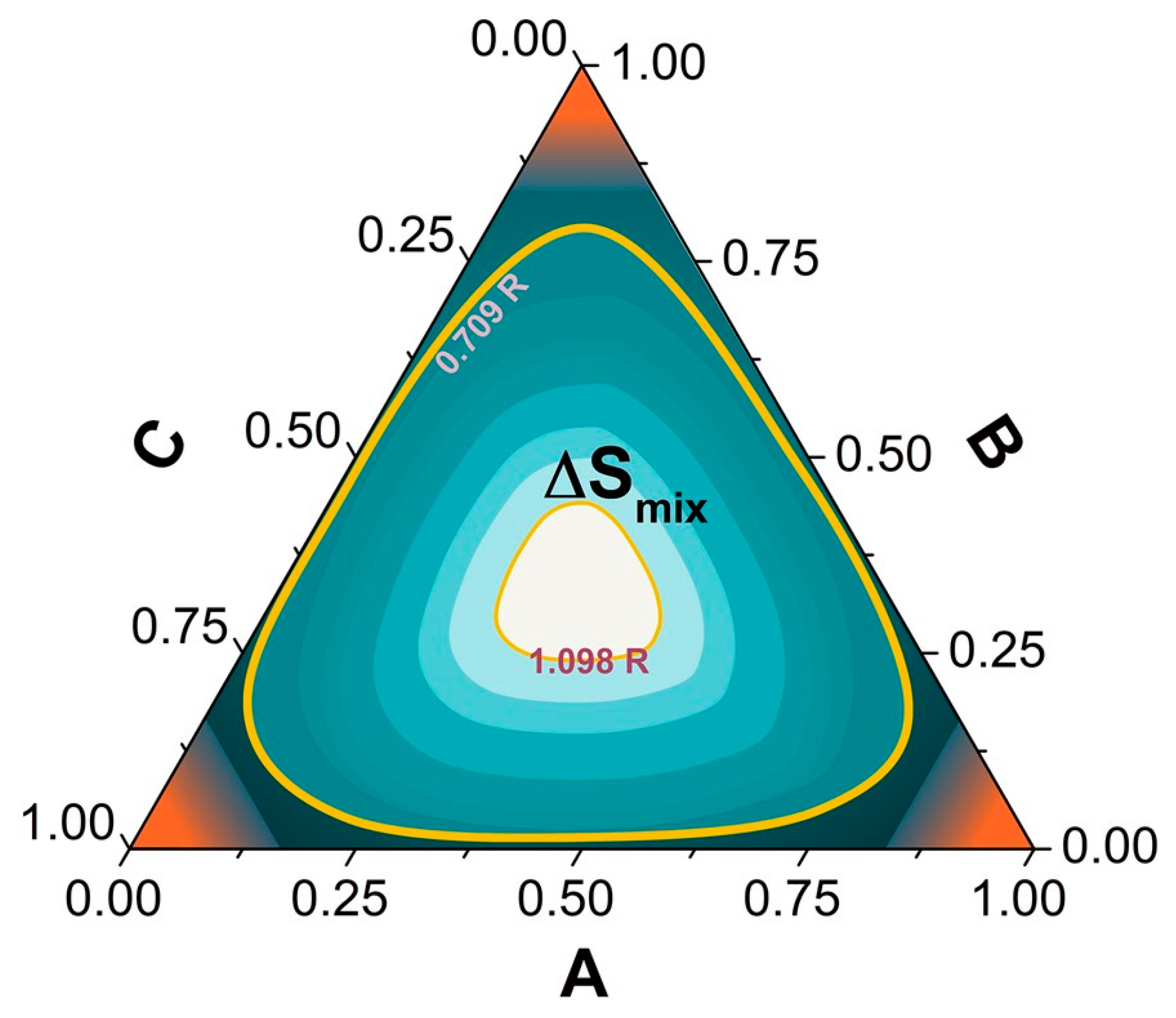
3.2. Configurational Entropy in HEAs
3.3. Design Strategies
4. Magnetic HEAs Research Status
4.1. Rare-Earth HEAs
4.2. Non-Rare Earth HEAs
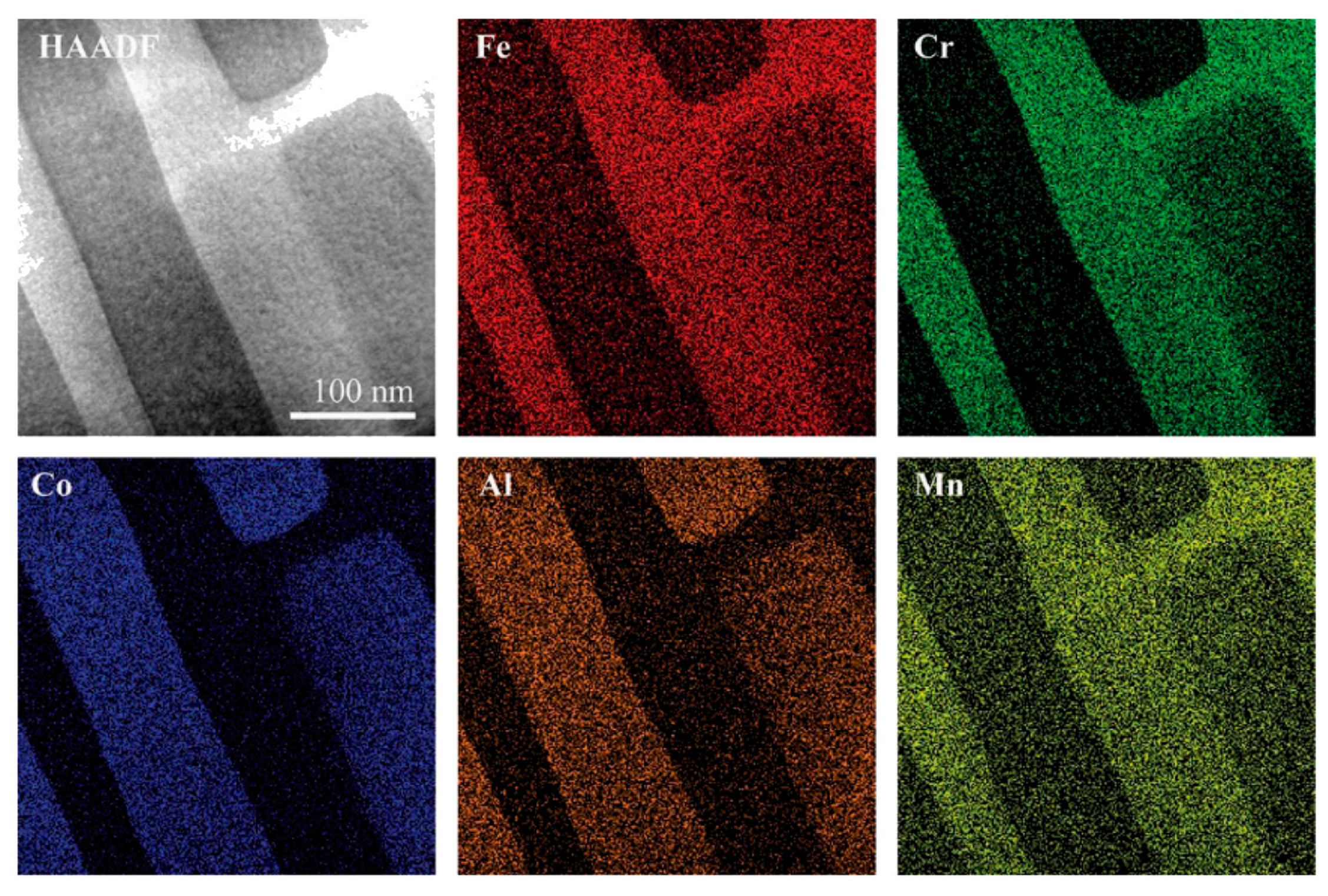
4.2.1. Transition Metal-Based HEAs
4.2.2. HEAs Containing Ga and Ge Elements
4.2.3. Other HEAs
4.3. Transition Metal and Rare-Earth Composite HEAs
5. Summary and Outlook
- Further optimization of alloy composition and design.
- 2.
- Improving stability and cyclic performance.
- 3.
- Promoting industrial applications and reducing costs.
- 4.
- In-depth research combining theory and experiments.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ajay, P.; Dabhade, V.V. Heat treatments of Inconel 718 nickel-based superalloy: A review. Met. Mater. Int. 2025, 31, 1204–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.-Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B.; Chang, I.T.H.; Knight, P.; Vincent, A.J.B. Microstructural development in equiatomic multicomponent alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2004, 375–377, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Guo, E. Effect of annealing temperature on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiNb0.2Mo0.2 high entropy alloy. Materials 2023, 16, 3987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufanets, M.; Sklyarchuk, V.; Plevachuk, Y.; Kulyk, Y.; Mudry, S. The structural and thermodynamic analysis of phase formation processes in equiatomic AlCoCuFeNiCr high-entropy alloys. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 7321–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Bai, S.; Chong, K.; Liu, C.; Cao, Y.; Zou, Y. Machine learning accelerated design of non-equiatomic refractory high entropy alloys based on first principles calculation. Vacuum 2023, 207, 111608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, Y.J.; Won, Y.J.; Cho, K.S. Thermodynamic evaluation of the phase stability in mechanically alloyed AlCuxNiCoTi high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 948, 169772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, U.S.; Hung, U.D.; Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Huang, Y.S.; Yang, C.C. Alloying behavior of iron, gold and silver in AlCoCrCuNi-based equimolar high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 460–461, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, L.; Qin, G.; Yang, X.; Ren, H.; Chen, R. Influence of aging heat treatment on the microstructure and mechanical properties of Co29Cr31Cu4Mn15Ni21 high-entropy alloys strengthened by nano-precipitates. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 920, 147508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, H.; Li, X. Architecture design and strengthening-toughening mechanisms in heterogeneous-structured medium/high entropy alloys. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2024, 69, 3864–3886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, W.; Lin, S.; Liu, C.; Qin, J.; Qu, P.; Zhang, J.; Liu, L. A novel L12-strengthened single crystal high entropy alloy with excellent high-temperature mechanical properties. Mater. Charact. 2024, 212, 113958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.X.; Kang, K.W.; Yu, S.B.; Zhang, J.S.; Xu, M.K.; Huang, D.; Che, C.N.; Liu, S.K.; Jiang, Y.T.; Li, G. Heterogeneous structure and dual precipitates induced excellent strength-ductility combination in CoCrNiTi0.1 medium entropy alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 912, 146992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, F.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Yang, G.; Xu, M.; Xu, W.; Tang, C.; Yi, J. An excellent synergy in yield strength and plasticity of NbTiZrTa0.25Cr0.4 refractory high entropy alloy through the regulation of cooling rates. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2023, 117, 106409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Huang, Y.; Sun, J.; Lu, Y. The relationship between thermo-mechanical history, microstructure and mechanical properties in additively manufactured CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2021, 77, 187–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, R.; Guo, E.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Zhao, S.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Cui, B. Multi-scale microstructure strengthening strategy in CoCrFeNiNb0.1Mo0.3 high entropy alloy overcoming strength-ductility trade-off. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 882, 145446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, R.; Rao, Y.; Liu, C.; Xie, X.; Yu, D.; Chen, Y.; Ghazisaeidi, M.; Ungar, T.; Wang, H.; An, K.; et al. Enhancing fatigue life by ductile-transformable multicomponent B2 precipitates in a high-entropy alloy. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Xue, J.; Lin, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Zhang, G.; Jiang, H.; et al. The Mo-14Re alloy, a promising candidate material for bioresorbable vascular scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2025, 204, 657–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, M.; Mohd Najib, A.S.; Fadil, N.A.; Abu Bakar, T.A. Microstructure and phase chemistry of vacuum induction melting fabricated-equimolar AlCoCrFeNi HEA during spinodal dissolution annealing. Int. J. Integr. Eng. 2024, 16, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajilou, N.; Javaheri, M.; Ebadzadeh, T.; Farvizi, M. Investigation of the electrochemical behavior of AlCoCrFeNi–ZrO2 high entropy alloy composites prepared with mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2024, 54, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da, Q.; Kang, J.; Ma, G.; Zhou, Y.; Fu, Z.; Zhu, L.; She, D.; Wang, H. Research on microstructure, mechanical property and wear mechanism of AlCoCrFeNi/WC composite coating fabricated by HVOF. Tribol. Int. 2024, 200, 110149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charkhchian, J.; Zarei-Hanzaki, A.; Schwarz, T.M.; Lawitzki, R.; Schmitz, G.; Schell, N.; Shen, J.; Oliveira, J.P.; Waryoba, D.; Abedi, H.R. Unleashing the microstructural evolutions during hot deformation of as-cast AlCoCrFeNi2.1 eutectic high entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2024, 168, 108253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemanate, A.M.; Jorge Júnior, A.M.; Andreani, G.F.D.L.; Roche, V.; Cardoso, K.R. Corrosion behavior of AlCoCrFeNix high entropy alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 441, 141844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhao, W.; Li, Z.; Guo, N.; Xiao, G.; Zhang, H. High-temperature oxidation behavior and corrosion resistance of in-situ TiC and Mo reinforced AlCoCrFeNi-based high entropy alloy coatings by laser cladding. Ceram. Int. 2023, 49, 10151–10164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Choi, Y.T.; Yang, J.; He, J.; Zeng, Z.; Zhou, N.; Baptista, A.C.; Kim, H.S.; Oliveira, J.P. Fabrication of spatially-variable heterostructured CoCrFeMnNi high entropy alloy by laser processing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 896, 146272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Han, Y.; Li, H.-B.; Tian, Y.-Z.; Zhu, H.-C.; Jiang, Z.-H.; He, T.; Zhou, G. Enhancement in impact toughness of CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy via nitrogen addition. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 932, 167615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Gonçalves, R.; Choi, Y.T.; Lopes, J.G.; Yang, J.; Schell, N.; Kim, H.S.; Oliveira, J.P. Microstructure and mechanical properties of gas metal arc welded CoCrFeMnNi joints using a 410 stainless steel filler metal. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 857, 144025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shangguan, Z.; Ma, S.; Li, J.; Liu, P.; Wang, Z. Study on high-temperature oxidation of TiZrHfNbTaV high-entropy alloy. Mater. Lett. 2024, 360, 135907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.; Shu, D.; Zhu, G.; Wang, D.; Sun, B. Mechanical instability and tensile properties of TiZrHfNbTa high entropy alloy at cryogenic temperatures. Acta Mater. 2020, 201, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Yu, Q.; Tang, Y.T.; Xu, M.; Wang, H.; Zhu, C.; Ell, J.; Zhao, S.; MacDonald, B.E.; Cao, P.; et al. Strong and ductile FeNiCoAl-based high-entropy alloys for cryogenic to elevated temperature multifunctional applications. Acta Mater. 2023, 242, 118449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Dong, H.; Sun, W.; Lv, L.; Yang, C.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, F.; Wang, Y.; et al. Progress and perspective of high-entropy strategy applied in layered transition metal oxide cathode materials for high-energy and long cycle life sodium-ion batteries. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2417258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, M.; Gao, L.; Ma, Z.; Cao, M. High entropy ceramics for electromagnetic functional materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2416673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Miao, X.; Van Dijk, N.; Brück, E.; Ren, Y. Advanced magnetocaloric materials for energy conversion: Recent progress, opportunities, and perspective. Adv. Energy Mater. 2024, 14, 2400369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, V.; Blázquez, J.S.; Ipus, J.J.; Law, J.Y.; Moreno-Ramírez, L.M.; Conde, A. Magnetocaloric effect: From materials research to refrigeration devices. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2018, 93, 112–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.-Y.; Han, Y.-Q.; Cheng, J.; Gao, L.; Jin, X.; Sun, Z.-B.; Huang, J.-H. Effect of Al doping on magnetocaloric effect and mechanical properties of La(FeSi)13-based alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 990, 174398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarkevich, N.A.; Zverev, V.I. Viable materials with a giant magnetocaloric effect. Crystals 2020, 10, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.-Q.; Shen, J.; Hu, F.-X.; Sun, J.-R.; Shen, B.-G. Research progress in magnetocaloric effect materials. Acta Phys. Sin. 2016, 65, 217502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheibel, F.; Gottschall, T.; Taubel, A.; Fries, M.; Skokov, K.P.; Terwey, A.; Keune, W.; Ollefs, K.; Wende, H.; Farle, M.; et al. Hysteresis design of magnetocaloric materials—From basic mechanisms to applications. Energy Technol. 2018, 6, 1397–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, S.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z. Achievement of giant cryogenic refrigerant capacity in quinary rare-earths based high-entropy amorphous alloy. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 102, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.-W. Review of magnetic properties and magnetocaloric effect in the intermetallic compounds of rare earth with low boiling point metals. Chin. Phys. B 2016, 25, 37502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y. Review of the structural, magnetic and magnetocaloric properties in ternary rare earth RE2T2X type intermetallic compounds. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 787, 1173–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Man, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, G.; Xiao, S.; Dong, N. Effect of nano WC on wear and corrosion resistances of CoCrFeNiTi high entropy alloy coating. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2025, 34, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Liang, H.; Li, Y. Effect of Si content on phase structure, microstructure, and corrosion resistance of FeCrNiAl0.7Cu0.3Six high-entropy alloys in 3.5% NaCl solution. Coatings 2025, 15, 342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Shahi, R.R.; Singh, A.R.; Sahay, P.P. Synthesis, characterizations, and magnetic properties of FeCoNiTi-based high-entropy alloys. Emergent Mater. 2020, 3, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Law, J.Y.; Franco, V. Review on magnetocaloric high-entropy alloys: Design and analysis methods. J. Mater. Res. 2023, 38, 37–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantor, B. Multicomponent and high entropy alloys. Entropy 2014, 16, 4749–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, R.; Li, Y. Influence of Si content on the microstructure, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of FeCoNiCrAl0.7Cu0.3Six high entropy alloy. Coatings 2024, 14, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y.; Lin, H.; Ji, X. Corrosion behavior of as-cladding Al0.8CrFeCoNiCu0.5Six high entropy alloys in 3.5% NaCl solution. Mater. Res. 2024, 27, e20230221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, J.; Fu, H.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, S.; Xiang, X.; Xu, B.; Lu, W.; Zhang, Y.; Weber, W.J.; et al. Irradiation performance of high entropy ceramics: A comprehensive comparison with conventional ceramics and high entropy alloys. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2024, 143, 101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ALMisned, G.; Güler, Ö.; Özkul, İ.; Sen Baykal, D.; Alkarrani, H.; Kilic, G.; Mesbahi, A.; Tekin, H.O. Exploring thermodynamic, physical and radiative interaction properties of quinary FeNiCoCr high entropy alloys (HEAs): A multi-directional characterization study. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 115303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhan, Z.; Liu, J.; Liao, X.; Deng, J.; Wei, L.; Li, X. Effect of Al addition on the corrosion behavior of Al CoCrFeNi high entropy alloys in supercritical water. Corros. Sci. 2023, 216, 111089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.-T.; Liu, S.-W.; Zheng, H.-L.; Huang, W.-J.; Zhao, W.; Liao, W.-B. Effects of transient thermal shock on the microstructure and mechanical properties of CoCrFeNiMn high-entropy alloy coatings. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 805296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Li, T.; Lu, Y. A novel Co-free high-entropy alloy with excellent antimicrobial and mechanical properties. Rare Met. 2025, 44, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aizenshtein, M.; Ungarish, Z.; Woller, K.B.; Hayun, S.; Short, M.P. Mechanical and microstructural response of the Al0.5CoCrFeNi high entropy alloy to Si and Ni ion irradiation. Nucl. Mater. Energy 2020, 25, 100813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, J.; Qiao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.-W.; Li, T.; Wang, H.-Y.; Dai, L.-H. A high-entropy alloy syntactic foam with exceptional cryogenic and dynamic properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2023, 876, 145146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusenko, K.V.; Riva, S.; Crichton, W.A.; Spektor, K.; Bykova, E.; Pakhomova, A.; Tudball, A.; Kupenko, I.; Rohrbach, A.; Klemme, S.; et al. High-pressure high-temperature tailoring of high entropy alloys for extreme environments. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 738, 491–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonal, S.; Lee, J. Recent advances in additive manufacturing of high entropy alloys and their nuclear and wear-resistant applications. Metals 2021, 11, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Inoue, A.; Wang, F.; Chang, C. The influence of boron and carbon addition on the glass formation and mechanical properties of high entropy (Fe, Co, Ni, Cr, Mo)-(B, C) glassy alloys. Coatings 2024, 14, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sfikas, A.K.; Kamnis, S.; Tse, M.C.H.; Christofidou, K.A.; Gonzalez, S.; Karantzalis, A.E.; Georgatis, E. Microstructural evaluation of thermal-sprayed CoCrFeMnNi0.8V high-entropy alloy coatings. Coatings 2023, 13, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, R.; Lei, Z. Influences of synthetic parameters on morphology and growth of high entropy oxide nanotube arrays. Coatings 2022, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Ni, X.; Tian, F. Ab initio predicted alloying effects on the elastic properties of AlxHf1−xNbTaTiZr high entropy alloys. Coatings 2015, 5, 366–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, K.; Zhang, Y. High-entropy alloy films. Coatings 2023, 13, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Liu, C.T. Phase stability in high entropy alloys: Formation of solid-solution phase or amorphous phase. Prog. Nat. Sci. Mater. Int. 2011, 21, 433–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaladurgam, N.R.; Lozinko, A.; Guo, S.; Harjo, S.; Colliander, M.H. Load redistribution in eutectic high entropy alloy AlCoCrFeNi2.1 during high temperature deformation. Materialia 2022, 22, 101392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Lü, S.; Wu, S.; Chen, X.; Guo, W. Development of MoNbVTax refractory high entropy alloy with high strength at elevated temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2022, 850, 143554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, D.; Jiang, W.; Wang, X.; Ma, T.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Huo, J. Enhanced mechanical properties of high pressure solidified CoCrFeNiMo0.3 high entropy alloy via nano-precipitated phase. Intermetallics 2024, 166, 108192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Ren, Y.; Sun, D.; Wang, B.; Wu, H.; Bian, H.; Cao, J.; Cao, X.; Ding, F.; Lu, J.; et al. High entropy alloy nanoparticles dual-decorated with nitrogen-doped carbon and carbon nanotubes as promising electrocatalysts for lithium–sulfur batteries. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2024, 188, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, T.Z.; Wilkerson, R.P.; Musicó, B.L.; Foley, A.; Brahlek, M.; Weber, W.J.; Sickafus, K.E.; Mazza, A.R. High entropy ceramics for applications in extreme environments. J. Phys. Mater. 2024, 7, 21001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hua, K.; Cao, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, H. Microstructures and properties of FeCrAlMoSi high entropy alloy coatings prepared by laser cladding on a titanium alloy substrate. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2024, 478, 130437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Kruk, R.; Hahn, H. Magnetic properties of high entropy oxides. Dalton Trans. 2021, 50, 1973–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Wen, Z.; Ma, B.; Wu, Z.; Yu, J.; Tang, L.; Lu, T.; Zhao, Y. Effect of A-site rare-earth ions on structure and magnetic properties of novel (Ln0.2Gd0.2La0.2Nd0.2Sm0.2)MnO3 (Ln = Eu, Ho, Yb) high-entropy perovskite ceramics. Ceram. Int. 2024, 50, 26040–26048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, P.; Kiran Kumar Yadav Nartu, M.S. Additive manufacturing of soft magnetic high entropy alloys: A review. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2025, 627, 173148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Zhong, Z.; Liang, Z.; Wang, S.; Du, Y.; Yan, C. High-entropy rare earth materials: Synthesis, application and outlook. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 2211–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, P.; Gupta, A.K.; Mishra, R.K.; Ahmad, M.S.; Shahi, R.R. A comprehensive review: Recent progress on magnetic high entropy alloys and oxides. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2022, 554, 169142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.C.; Miracle, D.B.; Maurice, D.; Yan, X.; Zhang, Y.; Hawk, J.A. High-entropy functional materials. J. Mater. Res. 2018, 33, 3138–3155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yayla, N.; Güler, Ö. A short review of structural, mechanical and magnetic properties of high and medium entropy alloys added rare earth elements. Mater. Today Commun. 2025, 47, 113264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.; Gong, M.; Zhang, D.; Sun, W.; Liu, F.; Bai, J.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, X. Effect of heat treatment time on the microstructure and properties of FeCoNiCuTi high-entropy alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 24, 4510–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, A.; Eivani, A.R.; Abbasi, S.M.; Jafarian, H.R.; Ghosh, M.; Anijdan, S.H.M. Al-Co-Cr-Fe-Ni-Ti high entropy alloys: A review of microstructural and mechanical properties at elevated temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 178216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, M.; Qu, H.; Xu, C.; Guo, W.; Wang, K.; Liu, F.; Bai, J.; Gao, Q.; Zhao, X.; Li, S. Effect of heat treatment temperature on microstructure and properties of FeCoNiCuTi high–entropy alloy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2022, 75, 1951–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, H.; Li, K.; Shi, L.; Zhao, W.; Bu, H.; Gong, P.; Yao, K.-F. Recent progress in high-entropy metallic glasses. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2023, 161, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Shi, Y. Microhardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance of AlxCrFeCoNiCu high-entropy alloy coatings on aluminum by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 134, 106632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.-L.; Tsai, C.-W.; Yeh, A.-C.; Yeh, J.-W. Clarifying the four core effects of high-entropy materials. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2024, 8, 471–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, W.; Yuan, X.; Zhang, Z.; Cheng, C.; Liu, H.; Qiu, H.; Cheng, X. Effect of volumetric energy density on the mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of laser-additive-manufactured AlCoCrFeNi2.1 high-entropy alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 178032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Zhang, Q.; Yao, K. Composition design strategy for high entropy amorphous alloys. Materials 2024, 17, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fruhling, K.; Yao, X.; Streeter, A.; Tafti, F. Characterization of the magnetocaloric effect in RMn6Sn6 including high-entropy forms. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 319, 129230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirayama, Y.; Nakagawa, T.; Kusunose, T.; Yamamoto, T.A. Magnetocaloric effect of rare earth nitrides. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2008, 44, 2997–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Shen, B.G.; Li, D.X.; Gao, Z.X. New magnetic refrigeration materials for temperature range from 165 K to 235 K. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 311, 22–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Wu, Y.; Tong, X.; Zhang, H.; Wang, H.; Liu, X.J.; Ma, L.; Suo, H.L.; Lu, Z.P. Rare-earth high-entropy alloys with giant magnetocaloric effect. Acta Mater. 2017, 125, 481–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, R.; Jiang, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, H.; Ma, D.; Lu, Z. Effect of Sc addition on magnetocaloric properties of GdTbDyHo high-entropy alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2024, 26, 2300616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, G.V. Magnetic heat pumping near room temperature. J. Appl. Phys. 1976, 47, 3673–3680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecharsky, V.K.; Gschneidner, K.A., Jr. Giant magnetocaloric effect in Gd5(Si2Ge2). Phys. Rev. Lett. 1997, 78, 4494–4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Provenzano, V.; Shapiro, A.J.; Shull, R.D. Reduction of hysteresis losses in the magnetic refrigerant Gd5Ge2Si2 by the addition of iron. Nature 2004, 429, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Hui, X.; Wu, Y.; Chen, G.L. Large magnetocaloric effect in Gd36Y20Al24Co20 bulk metallic glass. J. Alloys Compd. 2008, 457, 541–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Liu, C.; Lu, W.; Sun, Y.; Zhu, W.; Nie, X.; Sang, X.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, Q. Effect of Gd doping on the microstructure and magnetocaloric properties of LaFe11.5Si1.5 alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 910, 164858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fries, M.; Pfeuffer, L.; Bruder, E.; Gottschall, T.; Ener, S.; Diop, L.V.B.; Gröb, T.; Skokov, K.P.; Gutfleisch, O. Microstructural and magnetic properties of Mn-Fe-P-Si (Fe2P-type) magnetocaloric compounds. Acta Mater. 2017, 132, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.F.; Ma, Y.Y.; Tan, X. Structural and magnetic properties of Mn1.25Fe0.7P0.5Si0.5 alloys prepared by spark plasma sintering using raw materials milled with different lengths of time. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1007, 176378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.G.; Huang, P.Y.; Wang, H.Y.; Qiu, Z.G.; Zeng, D.C. Physical mechanisms of large magnetocaloric effects in Mn1.95-FeP0.5Si0.5 alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1026, 180345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, K.H.; Lee, A.-Y.; Ahn, H.; Lee, W.; Kim, J.-W. Multi-phase transition behavior over a wide temperature range in magnetocaloric (Mn, Fe, Ni)2(P, Si) alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 1005, 176140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.Q.; Li, B.; Du, J.; Deng, Y.F.; Zhang, Z.D. Large reversible high-temperature magnetocaloric effect in alloys. Solid State Commun. 2010, 150, 949–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelen, A.; Koželj, P.; Gačnik, D.; Vrtnik, S.; Krnel, M.; Dražić, G.; Wencka, M.; Jagličić, Z.; Feuerbacher, M.; Dolinšek, J. Collective magnetism of a single-crystalline nanocomposite FeCoCrMnAl high-entropy alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 864, 158115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
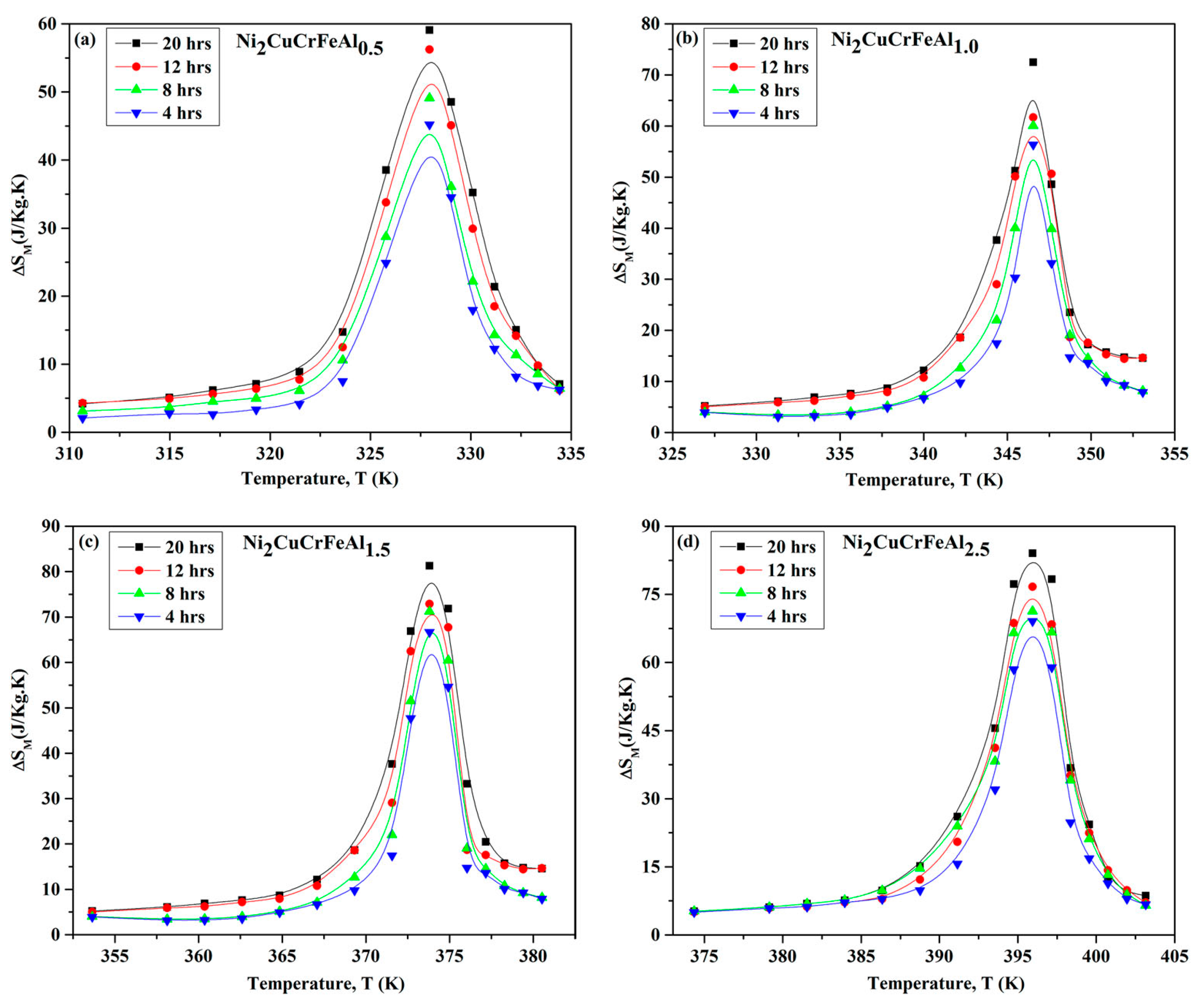
- Kush, L.; Srivastava, S. Effect of mechanical milling and sintering on magnetic entropy of Ni-based Ni2CuCrFeAlx (x = 0.5, 1.0, 1.5 and 2.5) high entropy alloys. Phase Transit. 2022, 95, 406–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
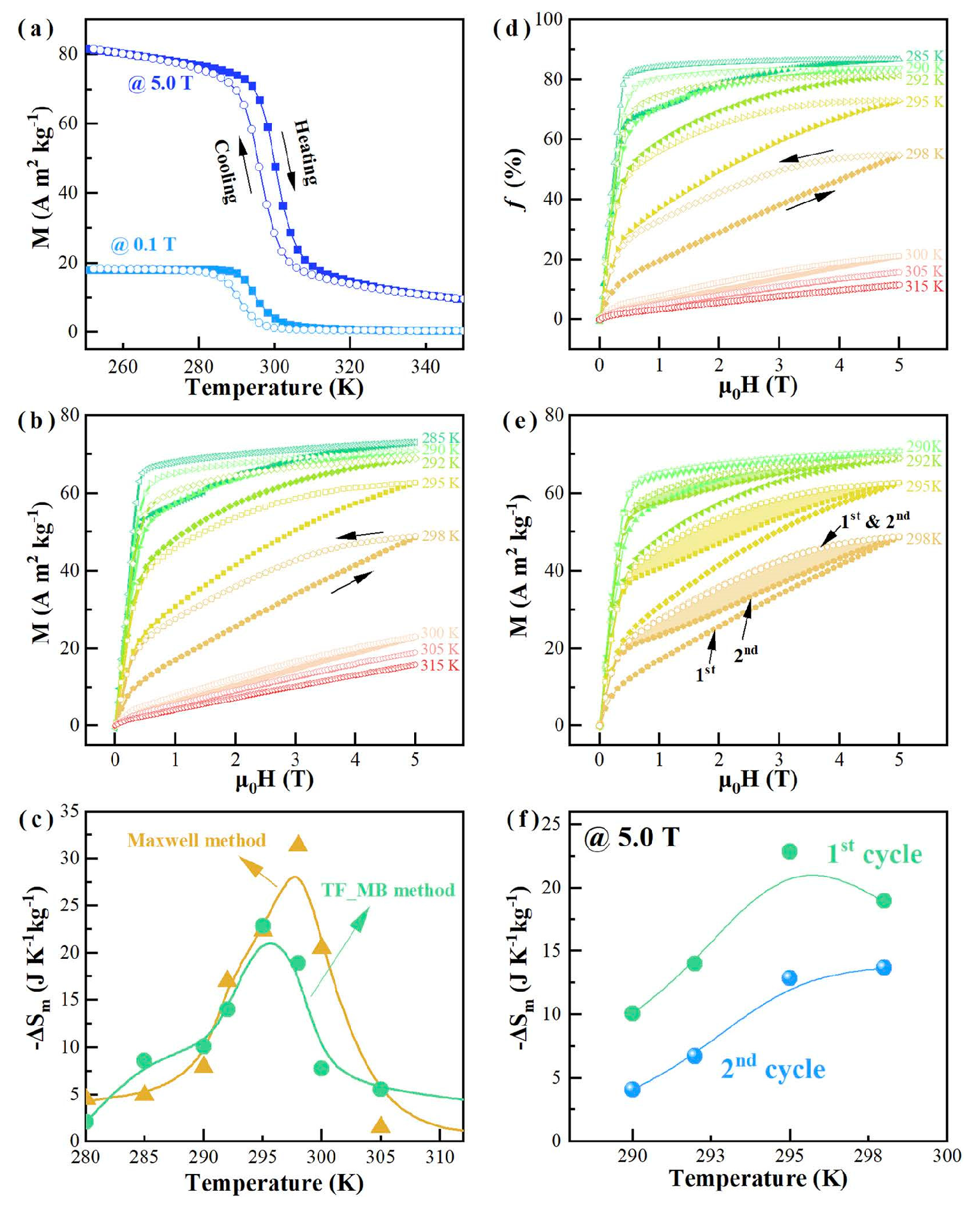
- Zheng, Z.G.; Chen, X.L.; Wang, H.Y.; Da, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, Z.G.; Zeng, D.C.; Xia, Q.B. Giant magnetocaloric effects of MnNiSi-based high-entropy alloys near room temperature. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 966, 171483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, B.; Guo, W.; Pan, S.; Gong, Y.; Bai, Y.; Gong, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. Large reversible magnetocaloric effect in high-entropy MnFeCoNiGeSi system with low-hysteresis magnetostructural transformation. APL Mater. 2022, 10, 91107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Huang, P.; Chen, X.; Wang, H.; Da, S.; Wang, G.; Qiu, Z.; Zeng, D. Enhanced magnetocaloric properties of the (MnNi)0.6Si0.62(FeCo)0.4Ge0.38 high-entropy alloy obtained by Co substitution. Entropy 2024, 26, 799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlar, K.; Tekgül, A.; Kucuk, I. Magnetocaloric properties in a FeNiGaMnSi high entropy alloy. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2020, 20, 18–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlar, K.; Tekgül, A.; Küçük, N.; Etemoğlu, A.B. Structural and magnetocaloric properties of FeNi high entropy alloys. Phys. Scr. 2021, 96, 125847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggert, B.G.F.; Delczeg-Czirjak, E.K.; Hauback, B.C.; Frommen, C. Magnetic transitions in V-Fe-Co-Ni-Cu-based high entropy alloys. Mater. Today Phys. 2023, 35, 101116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa Rocha, V.; Cesare, J.-P.; Messina, T.C. Searching for magnetic high entropy alloy treasure in CoCrFeNiQ. Intermetallics 2022, 146, 107581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, C.; Zheng, X.; Wang, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, J.; Xi, L.; Liu, H.; Zhen, S.; et al. Enhancement of magnetocaloric effect by amorphous engineering in Er-Tm-Al-Cu-Ni-Ga high-entropy alloy. Intermetallics 2025, 179, 108682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zong, S.; Zhang, Y.; Mo, Z.; Qiao, J.; Liaw, P.K. The large magnetocaloric effect in GdErHoCoM (M = Cr and Mn) high-entropy alloy ingots with orthorhombic structures. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2024, 124, 122412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, G.; Huaijin, M.; Pengyu, W.; Juan, C.; Yingde, Z.; Huiqin, Y.; Fei, G.; Pengchao, Z.; Boyu, S.; Jiaohong, H.; et al. Cryogenic temperature magnetocaloric effect and critical behavior of GdDyErAlM (M = Fe, Co, Ni) high entropy amorphous alloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 32, 1493–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Shen, H.; Zhang, L.; Luo, L.; Tang, X.; Sun, J.; Li, X. Microstructure and magnetocaloric properties of melt-extracted SmGdDyCoAl high-entropy amorphous microwires. Rare Met. 2024, 43, 1234–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Materials | TN | TC | Appliedfield (T) | ΔSM (J·kg−1·K−1) | RC (J·kg−1) | TEC (J·kg−1·K−1) | Other Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gd [89] | 293 | 5 | 9.8 | - | |||
| Gd5Si2Ge2 [90,91] | 276 | 5 | 18.6 | 306 | |||
| Gd5Si2Ge1.9Fe0.1 [90] | 320 | 5 | 7 | 360 | |||
| Gd36Y20Al24Co20 [92] | 53 | 5 | 7.76 | 457 | |||
| LaFe11.5Si1.5 [93] | 195 | 2 | 9.3 | 140 | |||
| Mn1.32Fe0.71P0.5Si0.56 [94] | 1 | 8.5 | - | ||||
| Mn1.25Fe0.7P0.5Si0.5 [95] | 1.5 | 9.6 | 114 | ||||
| Mn0.95FeP0.5Si0.5 [96] | 255 | 2 | 16.8 | - | |||
| Mn1.32Fe0.71P0.5Si0.56 [94] | 1 | 8.5 | - | ||||
| MnFe0.91Ni0.04P0.6Si0.4 [97] | 268 | 2 | 7.76 | 183 | |||
| Ni49Mn39Sb12 [98] | 185 | 5 | 5.21 | ||||
| Gd20Dy20Er20Ho20Tb20 [87] | 186 | 5 | 8.6 | 627 | YS > 250 MPa PL > 20% | ||
| Gd25Er25Ho25Tb25 [87] | 139 | 3 | 4.8 | 137 | |||
| Dy25Er25Ho25Tb25 [87] | 52 | 3 | 0.65 | 27.3 | |||
| Er33.33Ho33.33Tb33.34 [87] | 88 | 3 | 3 | 150 | |||
| GdTbDyHo [88] | 198 | 5 | 8.2 | 634.4 | 8.11 | ||
| GdTbDyHoSc0.3 [88] | 181 | 5 | 7.4 | 802.4 | 7.19 |
| Material | Price (USD/Kg) | Sample | Estimated Price (USD/Kg) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gd (Gadolinium iron) | 19.5 | Gd5Si2Ge2 | 380.5 |
| Tb (Terbium) | 1015.5 | Gd36Y20Al24Co20 | 18.2 |
| Dy (Dy-Iron) | 183.8 | LaFe11.5Si1.5 | 1.36 |
| Ho (Holmium Oxide) | 61.4 | Mn1.32Fe0.71P0.5Si0.56 | 1.41 |
| Er (Erbium Oxide) | 42.8 | Ni49Mn39Sb12 | 10.02 |
| Y (Yttrium) | 29.19 | Gd20Dy20Er20Ho20Tb20 | 264.6 |
| La (Lanthanum) | 2.6 | GdTbDyHo | 319.0 |
| Sc (5N High Purity Scandium) | 3292.0 | FeCoCrMnAl | 7.7 |
| Ga (Gallium) | 206.8 | Ni2CuCrFeAl | 8.73 |
| Ge (Germanium Ingot) | 1662.6 | (MnNi)0.6Si0.62(FeCo)0.4Ge0.38 | 321.0 |
| Sb (Antimony Ingot) | 19.72 | Mn1.75Fe0.25CoNiGe1.6Si0.4 | 449.0 |
| Al (SMM A00 Aluminum Ingot) | 2.6 | Fe26.7Ni26.7Ga15.6Mn20Si11 | 36.6 |
| Cu (Standard-Grade Copper) | 10.6 | Er20Ho20Gd20Ni20Co20 | 264.6 |
| Ni (SMM #1 Nickel) | 14.3 | Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa | 63.2 |
| Cr (Chromium 99A) | 10.2 | ||
| Fe (Billet) | 0.4 | ||
| Co (Cobalt Metal) | 23.6 | ||
| Mn (Electrolytic Manganese) | 1.7 | ||
| Si (Recycled Silicon Metal) | 1.2 |
| Ni2CuCrFeAlx | ΔSM (J·kg−1·K−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4 h | 8 h | 12 h | 20 h | |
| x = 0.5 | 42.23 | 49.13 | 56.60 | 59.07 |
| x = 1 | 56.37 | 59.75 | 61.67 | 72.25 |
| x = 1.5 | 66.71 | 70.68 | 73.45 | 81.02 |
| x = 2.5 | 69.90 | 71.47 | 78.23 | 84.03 |
| Materials | Tc (K) | Appliedfield (T) | ΔSM (J·kg−1·K−1) | RC (J·kg−1) | Other Properties |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (MnNiSi)0.6(FeCoGe)0.4 [101] | 273.3 | 5 | 44.9 | - | 552.7 HV0.2 CS = 383 MPa |
| (MnNiSi)0.58(FeCoGe)0.42 [101] | 224.7 | 5 | 29.2 | 306 | CS = 321 MPa |
| (MnNiSi)0.55(FeCoGe)0.45 [101] | 232.5 | 5 | 1.9 | 360 | |
| (MnNiSi)0.53(FeCoGe)0.47 [101] | 235.0 | 5 | 2.4 | 457 | 708.7 HV0.2 |
| (MnNi)0.6Si0.64(FeCo)0.4Ge0.36 [101] | 327.6 | 5 | 55.3 | 140 | |
| (MnNi)0.6Si0.62(FeCo)0.4Ge0.38 [101] | 308.8 | 5 | 48.5 | - | 580.6 HV0.2 CS = 267 MPa |
| (MnNi)0.6Si0.6(FeCo)0.4Ge0.4 [101] | 271.3 | 5 | 44.9 | 114 | |
| (MnNi)0.6Si0.58(FeCo)0.4Ge0.42 [101] | 295.5 | 5 | 41.5 | - | |
| Mn1.75Fe0.25CoNiGe1.6Si0.4 [102] | 5 | 22.83 | |||
| Mn0.6Ni0.6Si0.62Fe0.4Co0.4Ge0.38 [103] | 309 | 2 | 48.5 | 183 | 552 V0.2 CS = 78 MPa |
| Fe26.7Ni26.7Ga15.6Mn20Si11 [104] (annealed at 700 K) | 334 | 2 | 1.59 | 75.6 | |
| Fe30.7Ni25.7Ga14.6Mn19Si10 [105] (annealed at 500 K) | 462 | 2 | 0.9 | 178.4 |
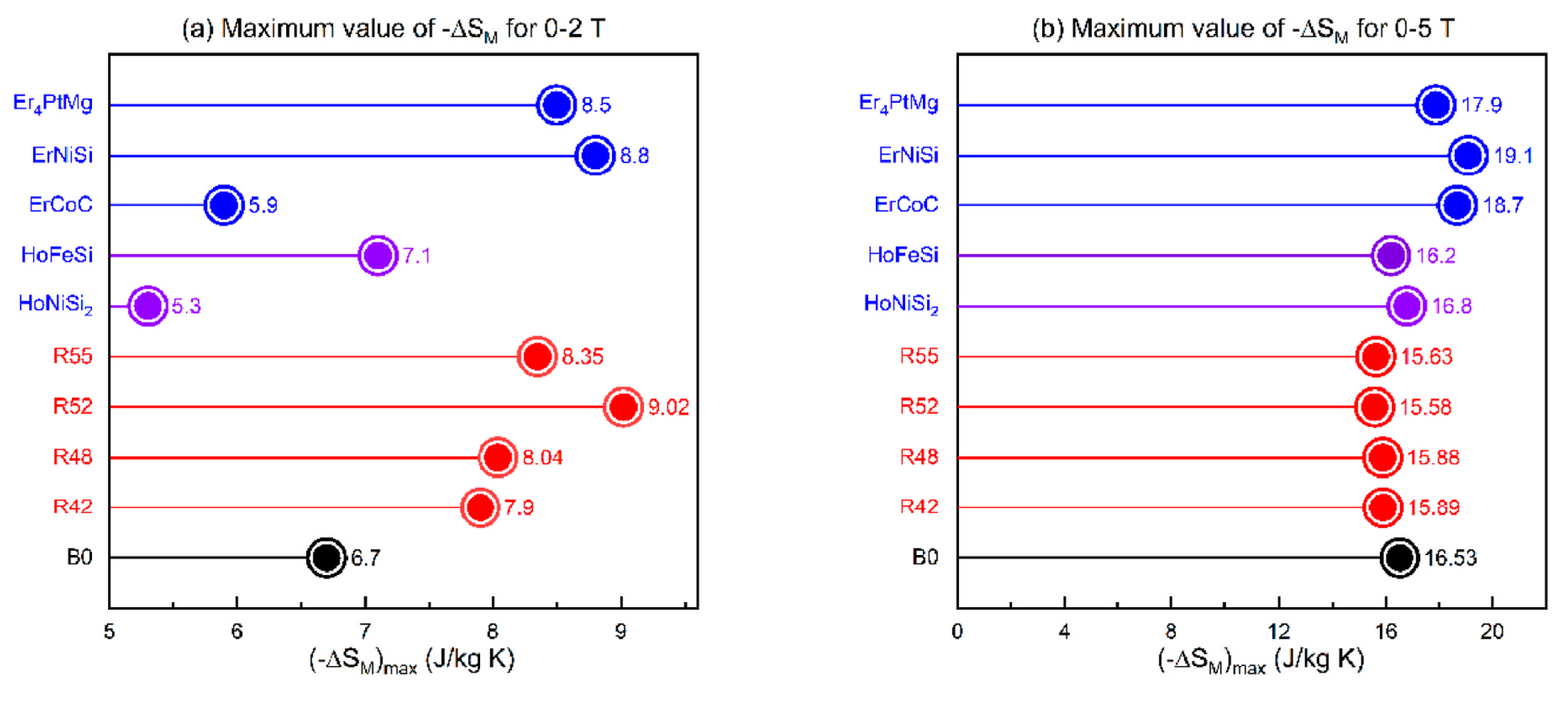
| Materials | Tc | Appliedfield (T) | ΔSm (J·kg−1·K−1) | RC (J·kg−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Er20Ho20Gd20Ni20Co20 [38] | 5 | 13.7 | 759 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B0) [108] | 4.5 | 2 | 6.7 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B0) [108] | 4.5 | 5 | 16.7 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B42) [108] | 3.3 | 2 | 7.8 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B42) [108] | 3.3 | 5 | 15.9 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B48) [108] | 3.3 | 2 | 8.0 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B48) [108] | 3.3 | 5 | 15.9 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B52) [108] | 3.0 | 2 | 9.0 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B52) [108] | 3.0 | 5 | 15.4 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B55) [108] | 3.0 | 2 | 8.3 | |
| Er2Tm2Al4CuNiGa(B55) [108] | 3.0 | 5 | 15.6 | |
| GdErHoCoCr [109] | 5 | 12.2 | ||
| GdErHoCoMn [110] | 5 | 10.1 | ||
| Gd20Dy20Er20Al20Co20 [111] | 5 | 6.34 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Recent Advances in Magnetocaloric Effect of High-Entropy Alloys. Coatings 2025, 15, 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121425
Zhang X, Guo Z, Zhang F, Li Y. Recent Advances in Magnetocaloric Effect of High-Entropy Alloys. Coatings. 2025; 15(12):1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121425
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xiaoli, Ziwei Guo, Fulong Zhang, and Yanzhou Li. 2025. "Recent Advances in Magnetocaloric Effect of High-Entropy Alloys" Coatings 15, no. 12: 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121425
APA StyleZhang, X., Guo, Z., Zhang, F., & Li, Y. (2025). Recent Advances in Magnetocaloric Effect of High-Entropy Alloys. Coatings, 15(12), 1425. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15121425






