Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Laser Cladding + Ultrasonic Rolling High-Entropy Alloy Composite Coating on H13 Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Laser Cladding and Ultrasonic Rolling Experiments
2.3. Microstructure and Performance Characterization
2.3.1. Microstructure Characterization
2.3.2. Property Characterization
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
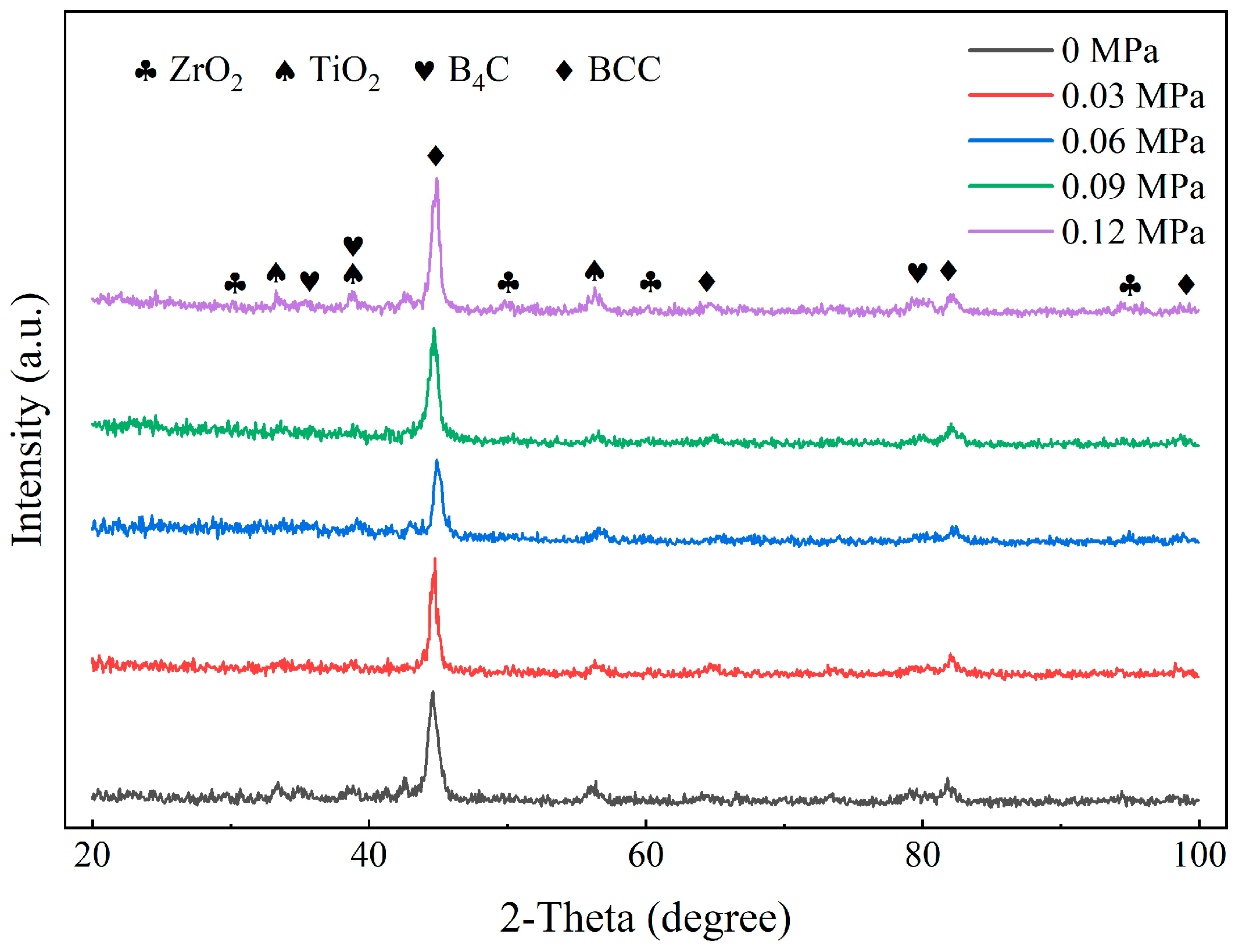
3.1. Effect of Static Load on Phase Composition of the Composite Coatings
3.2. Effect of Static Load on the Microstructure of the Composite Coatings
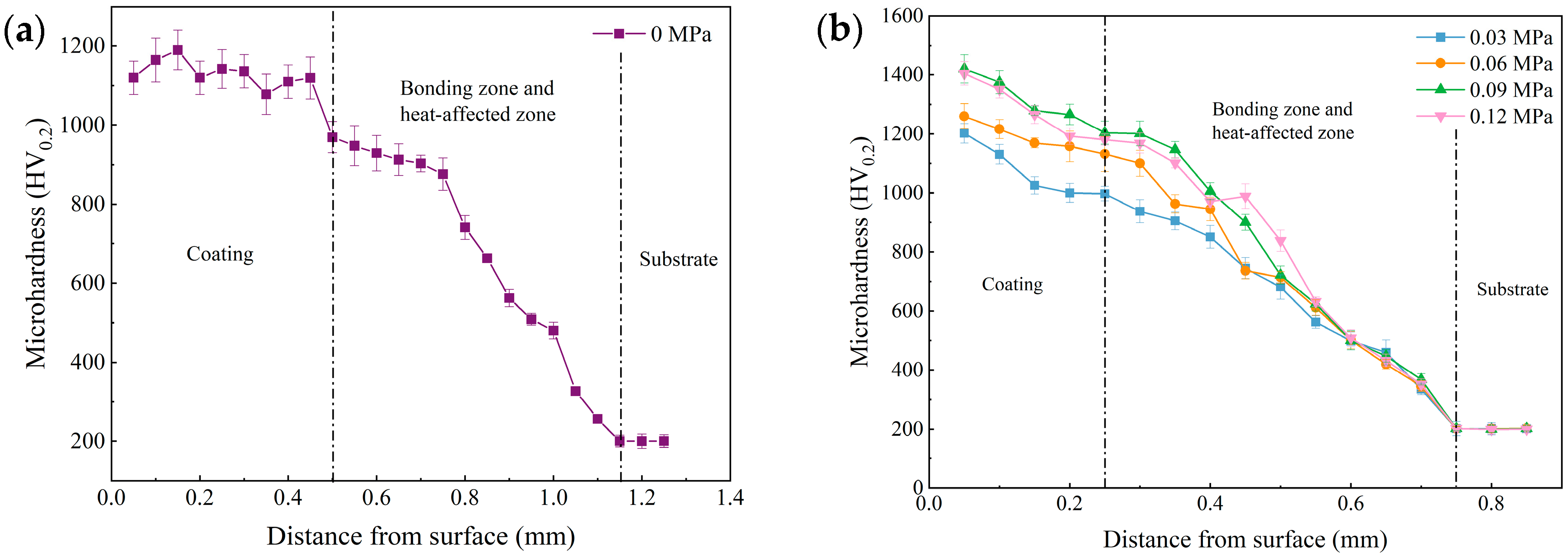
3.3. Effect of Static Load on the Microhardness of the Composite Coatings
3.4. Effect of Static Load on the Wear Resistance of the Composite Coatings
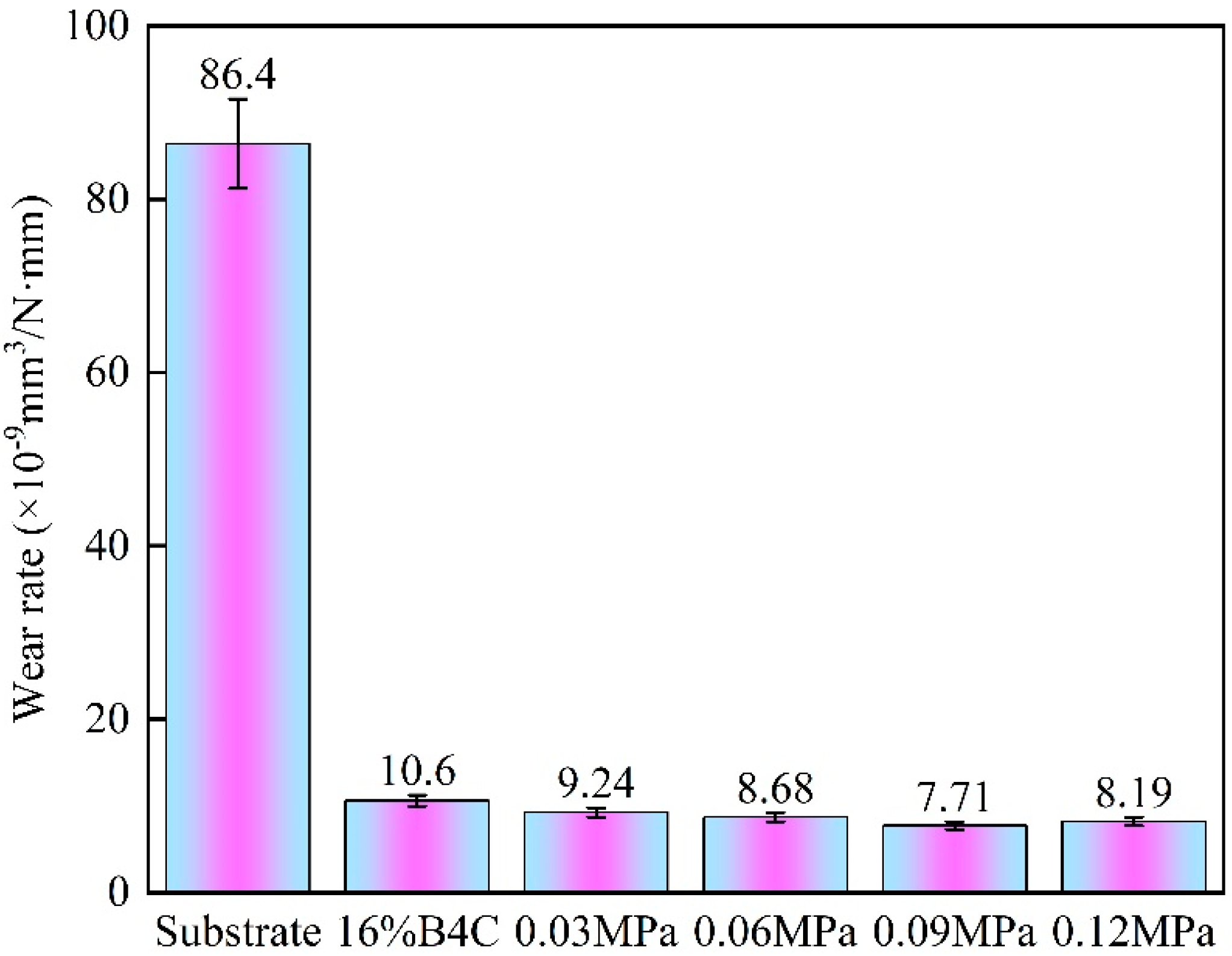
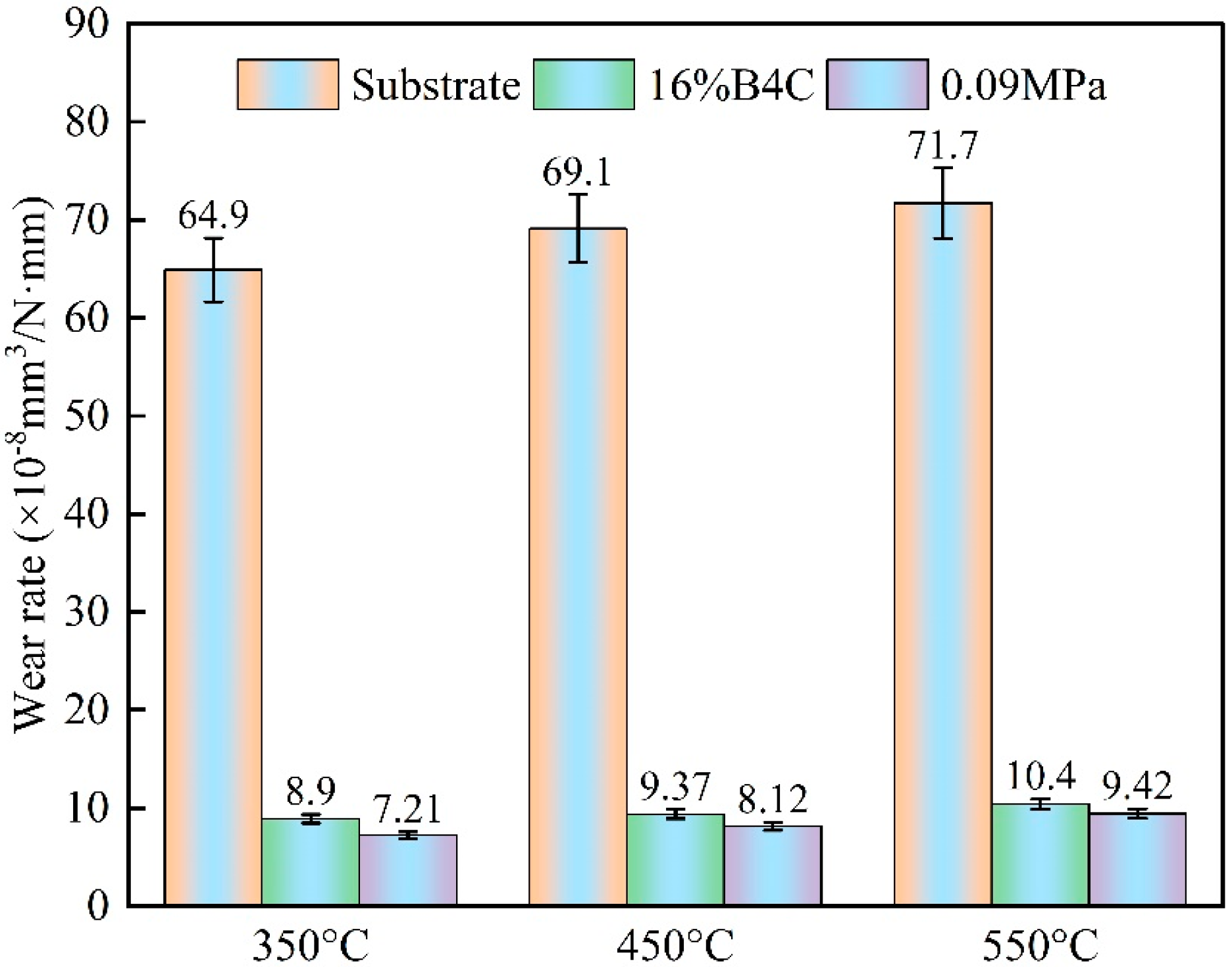
3.4.1. Effect of Static Load on the Wear Rate of the Composite Coatings
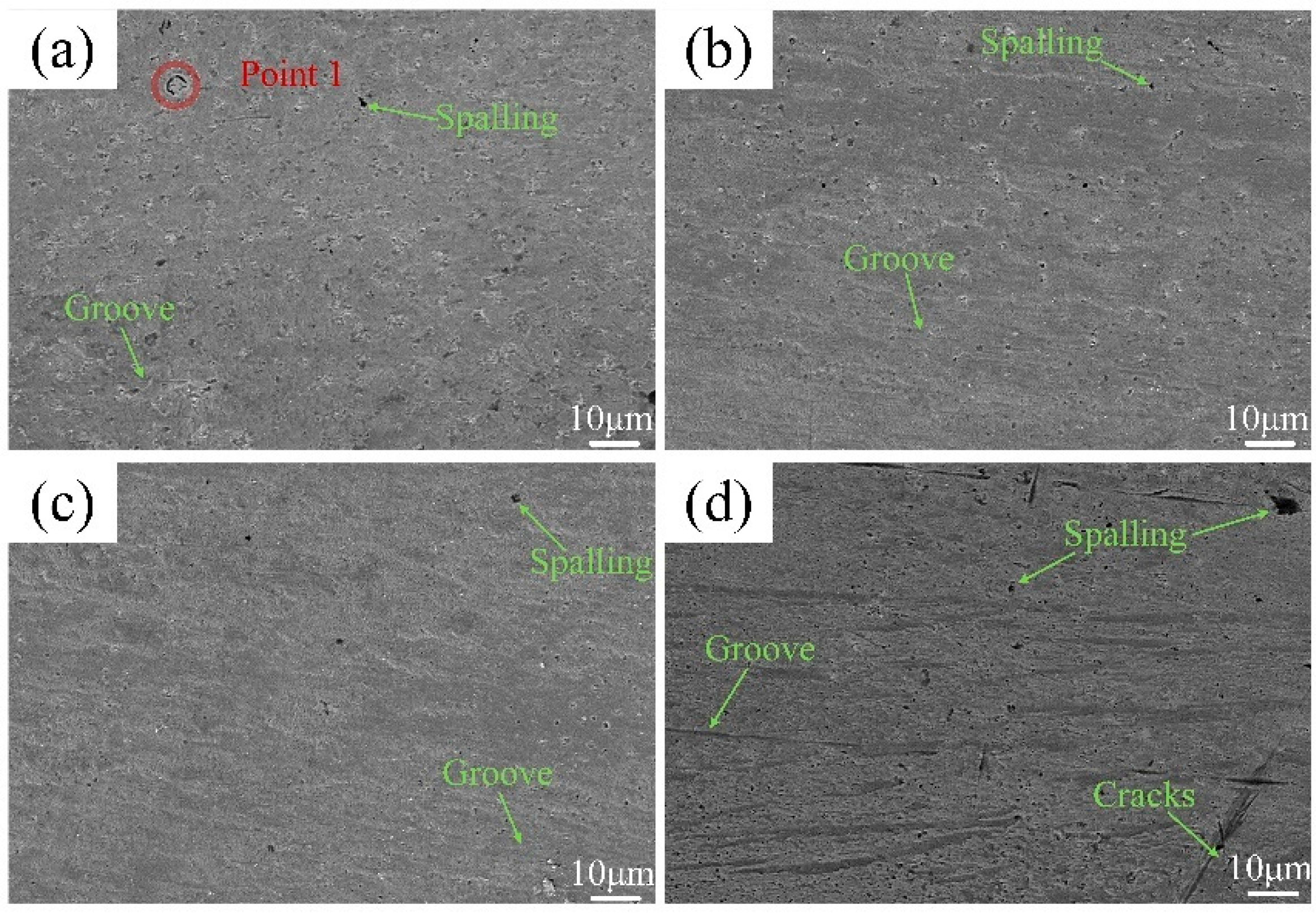
3.4.2. Effect of Static Load on Wear Morphologies of the Composite Coatings
4. Conclusions
- The phase composition of the composite coatings still composed of BCC phase, TiO2, ZrO2, and B4C. The plastic deformation induced by ultrasonic rolling increased the dislocation density of the coatings.
- After ultrasonic rolling, columnar grains and equiaxed grains of laser cladding composite coatings turn into equiaxed crystals. With the increase in the static load, the size of the grains decreased, and the hard phase particles became more refined and uniformly distributed.
- Under the combined effects of work hardening and fine grain strengthening, the coating treated at 0.09 MPa exhibited a hardness 18.7% higher than that of the laser cladding coating and 534.9% higher than that of H13.
- At room temperature, the wear rate of the 0.09 MPa coating decreased by 91% compared with H13 and by 27% compared with the laser cladding coating. At 350 °C, 450 °C, and 550 °C, the wear rates of the 0.09 MPa coating were reduced by approximately 89%, 88%, and 87% compared with H13, and by approximately 19%, 13%, and 9% compared with the laser cladding coating, respectively.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Telasang, G.; Majumdar, J.D.; Wasekar, N.; Padamanabham, G.; Manna, I. Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Laser Clad and Post-cladding Tempered AISI H13 Tool Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2015, 46, 2309–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, B.; Chen, T.; Chen, L.; Yu, T.; Zhao, J. The microstructure and mechanical properties analysis of H13/Ni60 functionally gradient coating fabricated by laser cladding method. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 190, 113024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Sun, S.; Xia, J.; Liu, Z.; Deng, W.; Li, J.; Wu, T.; Zhu, X.; Lv, Z.; Gao, J.; et al. Effect of WC content on microstructure, mechanical properties, and tribo-corrosion behavior of laser-cladded Ni40A/WC composite coatings on H13 steel. Mater. Charact. 2025, 224, 115072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Jing, C.; Fu, T.; Lin, T.; Guo, W.; Liu, N. Effect of TiC addition on the microstructure and properties of laser cladding Ni60A coatings on H13 steel surface. Mater. Today Commun. 2024, 38, 107904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, D.P.; Muvvala, G.; Nath, A.K. High-temperature abrasive wear characteristics of H13 steel modified by laser remelting and cladded with Stellite 6 and Stellite 6/30% WC. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 422, 127498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.Z.; Xue, K.N.; Lu, H.F.; Xing, F.; Luo, K.Y. Laser shock wave-induced wear property improvement and formation mechanism of laser cladding Ni25 coating on H13 tool steel. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2021, 296, 117202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, D.; He, L.; Ye, X.; Ouyang, W.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhou, X. Microstructure and elevated temperature wear behavior of laser-cladded AlCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy coating. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 149, 107845. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Gao, W.; Du, X.; Hao, J. Microstructural evolution and properties of dual-layer CoCrFeMnTi0.2 high-entropy alloy coating fabricated by laser cladding. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 134, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Han, B.; Li, M.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y. Investigation on microstructure and properties of laser cladded AlCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy coating by ultrasonic impact treatment. Intermetallics 2021, 128, 107017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, G.; Yue, T.; Lin, X.; Yang, H.; Xie, H.; Ding, X. Laser surface forming of AlCoCrCuFeNi particle reinforced AZ91D matrix composites. Opt. Laser Technol. 2015, 70, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, S.; Xu, G.; Yan, S.; Ren, J. Study on laser cladding system of the high-entropy alloy layer on the AZ91D magnesium. J. Laser Appl. 2022, 34, 032007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, T.M.; Xie, H.; Lin, X.; Yang, H.O.; Meng, G.H. Solidification behavior in laser cladding of AlCoCrCuFeNi high entropy alloy on magnesium substrates. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 587, 588–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Ge, F.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, X.; Han, J.; Cai, Y. Study on the Strengthening Mechanism of AlCoCrFeNi2.1 Eutectic High Entropy Alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 171878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Duan, H.; Li, J.; Zhan, S.; Jia, D.; Tu, J.; Li, Y. Effect of ultrasonic surface rolling on dry sliding tribological behavior of ductile iron under different normal loads. Met. Mater. Int. 2022, 28, 988–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, D.P.; Liu, G.; Gong, B.; Song, N. Investigations on the nanocrystallization of 40Cr using ultrasonic surface rolling processing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2008, 255, 1824–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Lin, G.; Dang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Peng, L.; Zheng, H. The study on surface strengthening technology of Ti-6Al-4V alloy used in Power Plants. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Conference on Power System Technology (Powercon), Guangzhou, China, 6–8 September 2018; pp. 4077–4082. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, M.; Yin, H.; Zhang, Q.; Long, J. Effect of ultrasonic surface rolling process on the high temperature fretting wear behavior of Inconel 690 alloy. Wear 2022, 500–501, 204347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Z.; Chiang, R.; Qin, H.; Vasudevan, V.K.; Doll, G.L.; Dong, Y.; Ye, C. Tribological performance of 52, 100 steel subjected to boron doped DLC coating and ultrasonic nanocrystal surface modification. Wear 2020, 458–459, 203398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, H.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, W.; Wang, D. Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser cladded Cr Ni alloy by hard turning (HT) and ultrasonic surface rolling (USR). Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 393, 125806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, D.; Wang, R.; Chen, P.; Zhu, R.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Effect of ultrasonic surface rolling extrusion on microstructural evolution and wear resistance of laser-clad CoCrFeMnNi high-entropy alloy with low stacking fault energy. J. Alloys Compd. 2025, 1010, 177832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanbariha, M.; Farvizi, M.; Ebadzadeh, T. Microstructural development in nanostructured AlCoCrFeNi-ZrO2 high-entropy alloy composite prepared with mechanical alloying and spark plasma sintering methods. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 1265b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Elements | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | P | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt.% | 0.32~0.45 | 0.80~1.20 | 0.20~0.50 | 4.75~5.50 | 1.10~1.75 | 0.80~1.20 | ≤0.03 | ≤0.03 | Bal. |
| Elements | Melting Points (°C) | Atomic Radius (a/Å) | Crystal Structure | Molar Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fe | 1535 | 1.30 | BCC/FCC | 55.85 |
| Ni | 1452 | 1.26 | FCC | 58.69 |
| Ti | 1668 | 1.40 | HCP | 47.86 |
| Zr | 1852 | 1.55 | HCP | 91.22 |
| Cr | 1890 | 1.32 | BCC | 51.99 |
| Elements | Fe | Cr | Ni | Ti | Zr | B4C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wt.% | 15.4 | 14.3 | 16.1 | 13.2 | 25.0 | 16.0 |
| Laser Power (W) | Scanning Speed (mm/min) | Spot Diameter (mm) | Overlap Ratio (%) | Ar Gas Flow Rate (L/h) | Coating Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1400 | 480 | 3 | 30 | 5 | 0.5 |
| Spindle Speed (r/min) | Indenter Diameter (mm) | Ultrasonic Power (W) | Amplitude (2 μm) | Oscillation Frequency (Hz) | Static Load (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | 12 | 1200 | 0.12 | ||
| 2 μm | 28,000 | 0.9 | |||
| 0.06 | |||||
| 0.03 |
| Static Load (MPa) | Lattice Constant (Å) | Lattice Distortion | Microstrain (με) | Dislocation Density (cm−2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.867 | 3.13 × 10−3 | 2.48 × 10−3 | 2.97 × 1011 |
| 0.03 | 2.869 | 2.43 × 10−3 | 2.90 × 10−3 | 3.53 × 1011 |
| 0.06 | 2.859 | 5.91 × 10−3 | 2.94 × 10−3 | 3.91 × 1011 |
| 0.09 | 2.852 | 8.34 × 10−3 | 3.35 × 10−3 | 4.23 × 1011 |
| 0.12 | 2.847 | 1.01 × 10−2 | 4.19 × 10−3 | 5.16 × 1011 |
| Fe | Cr | Ni | Ti | Zr | B | C | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.03 | 0.27 | 0.31 | 0.98 | 67.87 | 1.16 | 7.36 | 19.41 |
| Samples | Fe | Cr | Ni | Ti | Zr | B | C | O |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.03 MPa | 57.44 | 7.77 | 5.31 | 2.18 | 10.19 | 3.60 | 6.69 | 6.82 |
| 0.06 MPa | 60.44 | 6.67 | 3.24 | 1.92 | 11.70 | 2.75 | 6.77 | 6.50 |
| 0.09 MPa | 60.24 | 6.91 | 3.32 | 1.79 | 11.39 | 3.77 | 6.55 | 6.03 |
| 0.12 MPa | 63.49 | 7.21 | 4.08 | 2.47 | 8.69 | 2.33 | 6.12 | 5.60 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jie, M.; Jiang, D.; Qi, Z.; Cai, L.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, F.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, S. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Laser Cladding + Ultrasonic Rolling High-Entropy Alloy Composite Coating on H13 Steel. Coatings 2025, 15, 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101162
Jie M, Jiang D, Qi Z, Cai L, Zhao Y, Sun Z, Zhang F, Gao Y, Zhang S. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Laser Cladding + Ultrasonic Rolling High-Entropy Alloy Composite Coating on H13 Steel. Coatings. 2025; 15(10):1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101162
Chicago/Turabian StyleJie, Meng, Delong Jiang, Zhenxiang Qi, Lutong Cai, Yejing Zhao, Zhi Sun, Fei Zhang, Yali Gao, and Shuai Zhang. 2025. "Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Laser Cladding + Ultrasonic Rolling High-Entropy Alloy Composite Coating on H13 Steel" Coatings 15, no. 10: 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101162
APA StyleJie, M., Jiang, D., Qi, Z., Cai, L., Zhao, Y., Sun, Z., Zhang, F., Gao, Y., & Zhang, S. (2025). Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Laser Cladding + Ultrasonic Rolling High-Entropy Alloy Composite Coating on H13 Steel. Coatings, 15(10), 1162. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings15101162







