Abstract
Iranian white cheese has a dynamic microbial load and moisture content of about 50%–60% and a short shelf-life (about 10 days). As a result, this research aimed to prolong the shelf-life of Iranian white cheese using an antimicrobial whey protein concentrate (WPC) edible coating enriched with 1 and 2% of cumin essential oil (CEO). The microbiological (total bacteria, lactic acid bacteria, and dairy-related pathogen risk), physicochemical (fat, protein, pH, titratable acidity, moisture, and total solid content), color, texture, organoleptic, and sensorial properties of the cheese samples were assessed during 28 days of storage at 4–5 °C. The integration of the WPC and the CEO reduced the moisture content of the films and improved their durability. The presence of the CEO significantly enhanced the mechanical attributes of the films, i.e., Young’s modulus and tensile strength. Cheese samples coated with WPC containing 1 and 2% CEO maintained the moisture content of the cheese samples, decreased the counts of Listeria monocytogenes, Staphylococcus aureus, and Escherichia coli (EHEC) by 2 log after 28 days of storage. The yeast and mold count decreased from 4.6 log CFU·g−1 to 2.1 and 2 log CFU·g−1. The edible coating did not affect the color or texture of samples during the 28 days of storage. The sensory qualities of all samples were identical, demonstrating that the coating did not influence the curd cheese flavor. This study demonstrated that an edible coating made of WPC with the addition of CEO could effectively improve the shelf-life of Iranian white cheese, contribute to the development of a more sustainable manufacturing process, and increase its functional value.
1. Introduction
Traditional Iranian white cheese has a soft texture and sour taste. This type of cheese is produced without dry curd salting or slime development on the curd surface [1]. However, cheeses created from raw milk in artisan manufacturing may be matured for up to nine months, but cheeses made in industrial settings are ripened from 45 to 90 days [2,3]. Due to the possibility of cross-contamination from manual manufacturing procedures, the moisture content (50%–60%), the dynamic microbiological and suitable acidity conditions, and the long ripening times, Iranian white cheese has a limited shelf-life of around ten days [4]. As a result, appropriate cheese packaging is regarded as one of the most effective methods of preventing the physicochemical, biochemical, and microbial degradation of the cheese, extending its shelf-life, and improving its overall quality [5].
The production of edible coatings as a viable replacement for vacuum packaging provides a thin layer around the cheese to limit moisture loss and contamination while keeping the quality and freshness of the final product [6]. Film made from biopolymers, such as protein- and chitosan-based, have been used to preserve the quality of cheeses, including Eastern European curd cheese [7] and Karish cheese [8]. Whey protein-based coatings showed transparency, high UV light, and oxygen barrier properties, resulting in the preservation of lipids and flavor of products [9,10].
Aromatic oils have increased color stability, inhibited lipid oxidation, and prevented alterations in food [11]. Further research into the discovery of essential oil compounds and their antibacterial activity is required to control food-borne infections while minimizing any negative impacts on the sensory and nutritional aspects of the controlled goods. Cumin (Cuminum cyminum) is a culinary spice in the food industry due to its aromatic, flavoring, and antimicrobial effects [12]. Cumin essential oil (CEO) was chosen because of its good flavor and taste by local customers who used it solely with Iranian white cheese.
The dairy industry needs to discover innovative methods to improve safety and functionality of traditional dairy products which might deliver important organoleptic qualities for consumers. As a result of a high demand on the market for edible coatings, this work aimed to (1) produce an antimicrobial whey protein concentrate (WPC) edible coating enriched with 1 and 2% of cumin essential oil (CEO); (2) assess the thickness, mechanical properties, and moisture content of the prepared film; (3) produce and coat Iranian white cheese with WPC film; (4) during 28 days of storage at 4°C, asses total bacterial count as well as lactic acid bacteria (LAB) count; (5) evaluate the effect of film in preserving the cheese from Listeria (L.) monocytogenes, Staphylococcus (S.) aureus, Escherichia (E.) coli (EHEC), yeast, and mold contamination; (6) assess the effect of the coating on the physicochemical properties (fat, protein, pH, titratable acidity, moisture, and total solid content), color, texture, and organoleptic and sensorial properties of the cheese samples.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
The WPC (80%) was received from Nasr Dalya Development and Investment Food Industry Co. (Mashhad, Iran). Glycerol was used as an emulsifier and was purchased from the Raha Group (Istanbul, Turkey).
2.2. Extraction and Analysis of CEO
In general, C. cyminum plants were collected in the fall of 2022 from Ramsar, Mazandaran province (northern Iran). The accuracy of the collected botanical information was verified by the Botanical Department, Gorgan University of Agricultural Sciences and Natural Resources, Gorgan, Iran. The volatile oil of C. cyminum was extracted using distillation with water for 3 h and a Clevenger apparatus. The extracted essential oil was stored refrigerated until used for a GC-MS analysis (Agilent, Santa Clara, CA, USA) via HP-5MS column with head pressure 74,359.9574 Pa (10.785 psi) and helium gas as the carrier gas). Components were discovered by comparing relative retention durations to data [12].
2.3. Cheese Preparation
Batch pasteurization of fresh raw milk received from the Iran Dairy Industries corporation (Isfahan, Iran) was performed at 65 °C for 5 min in a container. Then, it was placed in a water bath and cooled to 37 °C before being carried to a cheese vat (WSNL, China) for further processing. For starter maturation, milk was treated with 0.20 g CaCl2 for 1 kg of milk. The starter culture was inoculated into the milk and kept at 35 °C for 60 min, then rennet was added. After the curd became firm, it was sliced into 3 cm cubes followed by resting from 3 to 5 min. Then, it was softly agitated at a progressively rising pace for 12–15 min to prevent fusion of the freshly cut curd cubes and assist whey outflow. Curds were transferred into mold blocks for 2.5 h under increasing pressure up to 2.9 MPa at the first hour to facilitate whey draining. Then, the curds were sliced into blocks of 5 cm × 5 cm × 7 cm, placed in containers, covered with 15% pasteurized brine, and stored at 25 °C for 20–24 h. Afterwards, they were moved to 5–6 °C for the 90-day ripening phase [1].
2.4. Preparation of Whey Protein Concentrate-CEO Coating
A quantity of 5 g of WPC was dispersed in 100 mL sterilized water and allowed to dissolve. In the next step, 2.5 g glycerol was added to the solution, and then the magnetic stirring of the mixture for 15 min was completed. A water bath was used to heat the solution for 30 min at 90 °C before homogenizing it with a homogenizer for 5 min at 2000 rpm. The solution was degassed for 60 min using a Bransonic CPXH (Emerson, St. Louis, MO, USA) with ultrasonic energy [13]. The CEO was added to the solution in 1 and 2% v/v concentrations and then homogenized (OSHengwin, Changzhou, China) at 10,000 rpm for 8–10 s. A quantity of 25 mL of film solution was inserted into the surface of a 16 cm circular Teflon and dried for 12 h at 36 °C and 40% relative humidity [14].
2.5. Characterization of WPC Films
2.5.1. Thickness, Moisture Content, and Solubility
An electronic digital caliper (OSHengwin, Changzhou, China) with 0.01 mm of precision was used to measure the thickness of the film. The measurements were obtained the moment that the micrometer contacted the film, which is referred to as the first instant of contact. Eight points were assessed for each film sample, with one in the middle and the other seven at random locations throughout the sample. First, square samples of each film measuring 25 mm were heated to 105 °C and dried for 24 h to assess the film’s moisture content [15]. A total of five replications were carried out. Five square samples of each film measuring 25 mm were dried at 105 °C for 24 h to determine initial dry matter, and then placed in a 50-mL sealed beaker containing 30 mL of distilled water in an environmental chamber at 25 °C for 24 h with occasional gentle stirring. The film pieces from the beakers were rinsed with distilled water and then dried at 105 °C for 24 h. The amount of dry matter dispersed in water after 24 h of immersion was obtained using the following equation [15]:
Water solubility (%) = the mass of undispersed dry matter − the mass of the initial dry matter.
2.5.2. Determination of Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties of films were analyzed with the method used by [15] and a texture profile analyzer (Mecmesin, Sterling, VA, USA). The films (25 mm × 100 mm diameter) were placed in the testing machine’s self-tightening roller grips and stretched at a rate of 1 mm/s until they broke. The separation distance was initially specified at 50 mm. The experiment was carried out at room temperature with an approximate humidity of 50%. Each film’s mechanical properties were tested in at least 10 diverse ways. The slope of the first linear section of stress–strain curves was used to calculate Young’s modulus (YM). The following equations were used to compute the tensile strength (TS) and elongation at break (EB):
TS = F/Ai, TS is the tensile stress, F is the force acting, and A (2 mm²) is the area;
EB = (ΔL/L) × 100, EB is the elongation at break, ΔL is the final length, and L is the initial length.
2.6. Cheese Coating
Samples of Iranian white cheese and prepared films were sliced into 5 cm × 5 cm squares, aseptically. Film squares weighed 0.504 g and had an average thickness of 0.18 mm. The dried films contained a final concentration of 145.2 mg/g antimicrobials in every case of use. The ultimate concentration of essential oils in the film samples was calculated by multiplying the average weight of the determining area by the final essential oil concentration [16]. Essential oils were added at a 2% (w/v) concentration to the WPC film-forming solutions, resulting in a concentration of 145.2 mg/g. Sterile cabin with UV light (OSHengwin, Changzhou, China) used to sterilize films for 30 min. Cheese samples were dipped in a 108 CFU/mL bacteria culture to inoculate them, and any extra liquid was wiped away using a sterile cotton pad. The low-density polyethylene film (45 µm), with an oxygen permeability rate of 10 mL O2/m2/day at 1 atm, 25 °C, and 0% relative humidity, was used to package each cheese slice after it had been sandwiched between two WPC films with antimicrobial additives and then packaged using a heat seal (OSHengwin, Changzhou, China). Uncoated cheese cubes were used as a control (C). The cheese cubes were then coated with WPC (5% w/v) alone, with 1% (v/v) CEO (WCEO1), and with 2% (v/v) CEO (WCEO2). For the coating of the cheese samples, two milliliters of various coating solutions were used. The samples were then kept at 4–5 °C during the experiment [17].
2.7. Microbiological Analysis of Cheese during Storage
The microbiological examination was performed on the Iranian cheese samples stored for 28 days at 7 °C. Samples of 10 g were dipped in 1 mL of 108 CFU/mL microbial suspension and inserted in a stomacher bag containing 90 mL of sterile peptone water (0.1% w/v). The stomacher bag was stirred for 5 min under aseptic conditions, and, after incubation at 30 °C for 24 h, a serial dilution in sterilized physiological water was made. The LAB was counted on De Man, Rogosa, and Sharpe (MRS) agar incubated at 37 °C for 72 h. The plate count agar (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) was utilized to analyze the change in the overall number of bacteria in cheese samples. L. monocytogenes, S. aureus, and E. coli (EHEC) were enumerated on CHROM agar, Listeria (CHROMagar, Paris, France), CHROM agar, Staphylococcus (CHROMagar, France), and ECC agar (CHROMagar, France), respectively. On potato dextrose agar (PDA), yeast and mold were counted after a 72 h incubation at 25 °C.
2.8. Physicochemical Analysis of Cheese during Storage
Iranian white cheese samples were assessed for their physical, chemical, color, and textural properties in triplicate at 28 days of storage. A portable pH meter (HI9025, Hanna Instruments, Woonsocket, RI, USA) was used to determine the pH by inserting the electrode (FC 200B, designed for solids) inside the cheese sample. For each triplicate, three measurements were made. The ISO:11869 standard procedure is used to evaluate the titratable acidity of cheese [18]. Following the recommendations of the manufacturer, the FoodScan (Foss, Hillerd, Denmark) instrument was used for a routine analysis of cheese to determine the amounts of fat and protein present. Each duplicate received three readings. After TS was determined, moisture content was calculated using the ISO:5534 technique [19]. Cheese samples were desiccated in an oven dryer for 5 h at 100 °C to determine their total solid content [20].
Samples of Iranian cheese were analyzed using a texture analyzer (TA.XT Plus model, Stable Micro Systems, Surrey, UK). A cylindrical plunger with a diameter of 6.3 mm was utilized to conduct three double compression tests for each cheese triplicate at random locations with a constant penetration speed of 2 mm/s and a trigger force of 0.1 g per test [3]. The texture expert (Windows version 1.20, Stable Microsystems, Godalming, UK) calculated the textural properties (hardness, adhesiveness, springiness, chewiness, cohesiveness, and resilience) based on force deformation readings.
The CIE L*a*b* color system was used to assess the color properties of Iranian cheese samples using a chroma meter CR-400 (Tokyo, Japan, Konica Minolta). L indicates the intensity of color lightness and obtains values of between 0 and 100 with 0 indicating the darkest black and 100 indicating the brightest white. The “a” indicates red–green colors and “b” indicates yellow–blue colors. Each triplicate was tested three times and the total color difference (∆E) was calculated as follows:
∆E = √(L2 − L1)2 + (a2 − a1)2 + (b2 − b1)2;
L*: lightness difference between the initial and final measurement.
a*: redness or greyness difference between the sample and standard colors.
b*: denotes the blueness-yellowness difference between the initial and final measurement.
2.9. Sensory Analysis of Cheese during Storage
Sensory analysis of untreated and treated cheese samples was completed by 12 trained people (seven men and five women) who were familiar with Iranian traditional cheese; they assessed the impact of storage duration on the sensory qualities of cheese. Samples were served on plastic dishes and coded with random three-digit numbers and served at room temperature. Sensory analysis of cheese samples was carried out based on ISO 11136:2014 [21] and using the 10-40-50-point CU (contractual unit) scale at the sensory laboratory of the Pegah dairy company. Treated and controlled samples were assessed at day zero (fresh), 14, and 28 days of storage. A flavor and odor evaluation (0–50 scale, 25 as the limit of acceptability), a body and texture evaluation (0–40 scale, 20 as the limit of acceptability), and an appearance evaluation (0–10 scale, 5 as the limit of acceptability) were conducted on the samples [22].
2.10. Statistical Analyses
SAS version 9.1 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA) was used to perform the analysis of the collected data, and one-way ANOVA methods and variations between effects were examined using the Duncan test (p < 0.05). The least significant differences (LSD) were chosen to differentiate means at p < 0.05.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemical Composition of CEO
The GC–MS analysis of the CEO is mentioned in Table 1. The main volatile components of CEO were γ-terpinene, propanal, geranyl acetate, p-cymene, and sabinene. The primary components of CEO, according to other investigations, were p-cymene, pinene, terpinene, cuminal, and terpinen-7 [23]. The researchers also looked at 20 different varieties of Iranian cumin and discovered that terpinene, cumin aldehyde, cumin alcohol, and p-cymene were the principal constituents in the cumin plants [24]. There could be differences in the chemical compositions of EOs between the current study and other studies because of differences in geographical areas of plantation and planting seasons, climatic conditions, various parts of the plants used for EO extraction, different extraction methodologies, and different periods for EO extractions and evaluations [25]. Some of the major compounds of CEO, like γ-terpinene, geranyl acetate, and p-cymene, showed synergic antioxidant, antibacterial, and antifungal activities [26,27,28]. The antibacterial characteristics of CEO could prolong the shelf-life of coated cheeses.

Table 1.
Major chemical compositions of the cumin essential oil.
3.2. Moisture Content, Water Solubility, Thickness, and Mechanical Properties
Table 2 shows the impact of adding CEO on the moisture content, water solubility, thickness, and the mechanical properties of WPC films. The WPC films, either solely or enriched with CEO, were uniform, clear, and smooth in appearance and texture. The plant extract’s active film had a yellowish tint and smelled strongly of cumin, an herb associated with healing. With or without CEO, the film was not found to cause changes in film thickness, showing that plant extracts high in phenolic compounds might be dispersed throughout the film matrix without influencing the thickness of the film due to their presence.

Table 2.
The influence of the addition of cumin essential oil on the moisture content and mechanical properties of WPC films.
The integration of WPC and CEO lowered the moisture content of the films (control: 23.28 ± 1.08%, 1 and 2% CEO: 19.32 ± 0.84%, and 19.87 ± 1.18%, respectively), and the films were more durable than the control. Adding phenolic compounds from CEO results in significant contact between the phenolic compounds of the CEO and the whey protein group, which reduces the available water for building the matrix with the WPC polymer chain. As a result, using plant EO in the current study makes the film more durable. The same results were found by [29] when a whey protein-based film containing rosemary and sage extracts extended the shelf-life of soft cheese. Active packaging material for soft cheese with furcellaran–whey protein isolate and yerba mate extract has been successfully developed. The yerba mate extract made the biopolymer film more water vapor-permeable, water-rich, soluble, and elastic, and thus more durable. It also improved the film’s puncture strength and thermal stability [30]. Moreover, similar to the present investigation, ref. [7] discovered that the control film had a greater moisture content than WPC-based films.
A film’s solubility and water content impact its water-resistance qualities, determining its further uses. It is possible to utilize significantly soluble films as edible coatings. However, if the film is intended to protect intermediate- or high-moisture foods, it is not recommended; it must be resistant to water as a protective coating. After 24 h of preservation in water, all the tested films remained intact, indicating a very stable protein network. No significant difference (p > 0.05) in solubility was seen when cumin infusions were included in the WPC-based film. These findings may be explained by the interactions between the proteins of the WPC-based films and the polyphenols that exist in CEO. The protein content of the WPC made a stable network with polyphenols present in the EO, so the films showed resistance to water and remained intact during the solubility test. According to the same research by [30], a similar tendency was seen when furcellaran–whey protein isolates and yerba mate extract were combined.
As asserted in Table 2, the addition of extracts containing 1% CEO (WCEO1) and 2% CEO (WCEO2) reduced the amount of moisture that is included in the film. The addition of phenolic compounds from the CEO makes it more difficult for water to interact with the protein polymer chain. This phenomenon makes it less likely to allow water into the protein polymer chain. This could explain the reason for an increase in tensile strength from 1.32 ± 0.24 to 1.43 ± 0.26 and 1.41 ± 0.09 when 1 and 2% CEO was added, respectively, which indicates a slight improvement in strength. The modulus of elasticity and tensile strength of the 2% CEO because of more EO and more polyphenol content strengthen the network with the protein content of the WPC; as a result, the reinforced films were more significant than the control films.
The mechanical attributes of the control film were considerably different (p < 0.05) from the relevant values of the WCEO2 film. The elongation at break values was reduced by increasing the CEO’s percentage which could be due to the lower mobility of the chain. The lower mobility of the protein chain can be described due to the higher interactions of the polyphenolic chemicals with the protein polymer chain after the addition of 2% CEO. This behavior has been described by other writers who have used active films made from biopolymers in conjunction with essential oils containing polyphenolic chemicals [30,31]. Similarly, ref. [29] stated that when compared to the control, whey protein films enriched with a sage infusion significantly improved the mechanical characteristics of the coatings.
The more phenolic component in the cumin with 2% EO has a more significant impact on how the protein polymer chain and the polyphenolic chemicals in the infusion work together. In the case of plants, the EO is a complicated combination of numerous components, and it is a time-consuming effort to identify the interactions between the EO compounds and the polymer units. Ref. [32] stated that the N-terminal protein end of WPC and the hydroxyl group (-OH) of the aromatic hydrocarbon of EO polyphenols bond together as an intermolecular hydrogen bonding.
3.3. Microbial Analysis of Cheese during Storage
Because cheeses fall into the category of unstable foods, both physiologically and biochemically, they are subjected to various microbiological and chemical deteriorations throughout the production, processing, and storage processes. Iranian white cheese spoils quickly. This is caused by the high moisture and dynamic microbial load. The surface of this type of cheese rots because of microbial growth that spreads through the whole surface and core.
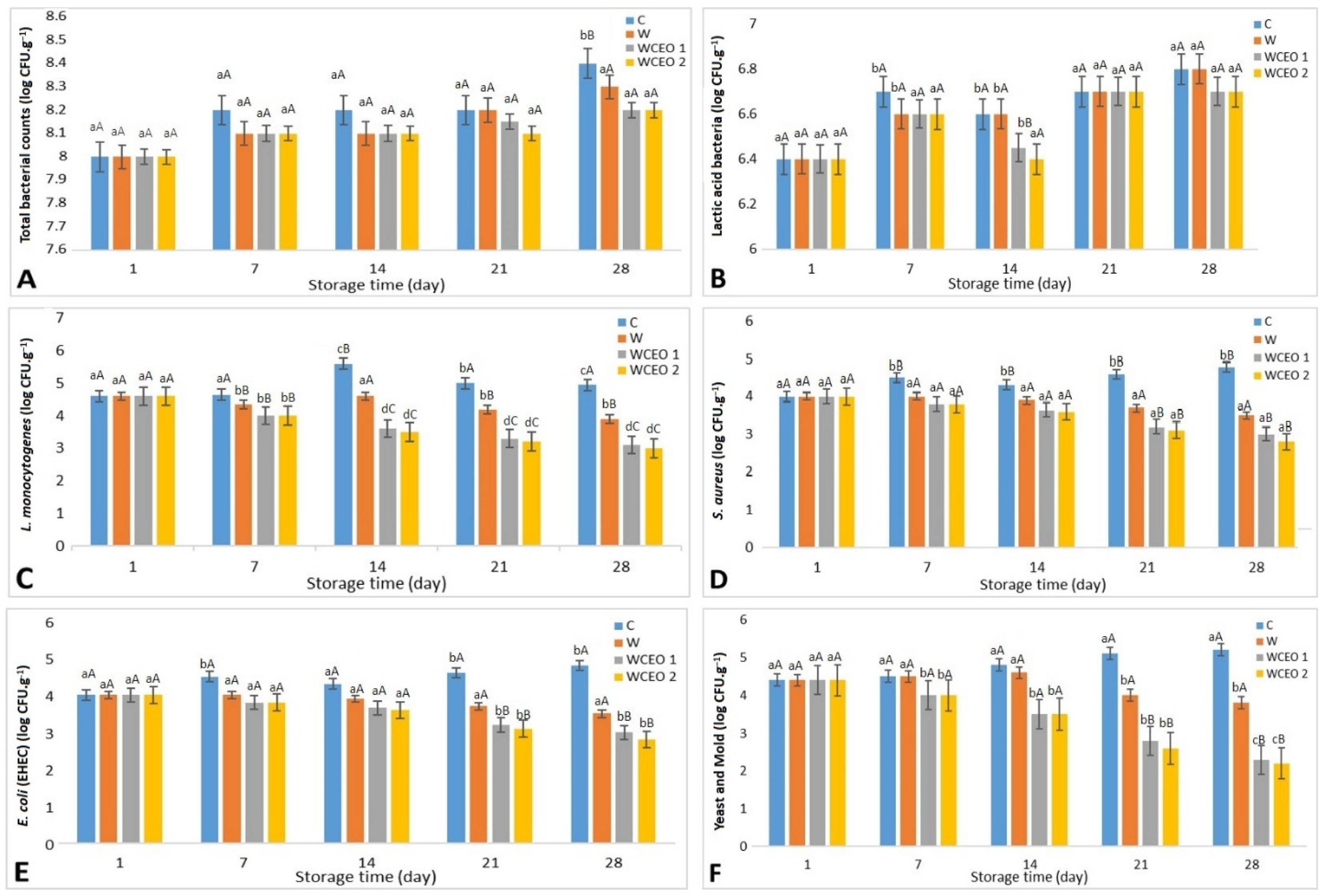
Figure 1 shows that in the cold storage of cheese, the total bacterial and LAB count rose in all Iranian cheese samples. This concurrent increase in the total bacterial count and the LAB population is because the LAB count is the most significant element of the total bacteria, which is the most significant constituent of the injected starting culture. The addition of WCEO1 and WCEO2 had no significant change (p > 0.05) on the whole bacterial count or lactic acid bacteria count compared to WPC and C.
Figure 1.
Microbial changes were obtained from un/treated Iranian white cheese samples stored at 4 °C for 28 days of storage. C: uncoated sample, W: whey protein concentrate coating, WCEO1: whey protein concentrate containing 1 percent v/v CEO, and WCEO2: whey protein concentrate containing 2 percent v/v CEO. ((A) Changes in the total bacterial count counts (log CFU·g−1) of cheese slices. (B) Changes in Lactic acid bacteria counts (log CFU·g−1) of cheese slices. (C) Changes in L. monocytogenes counts (log CFU·g−1) of cheese slices after inoculation. (D) Changes in S. aureus counts (log CFU·g−1) of cheese slices after inoculation. (E) Changes in E. coli O157:H7 counts (log CFU·g−1) of cheese slices after inoculation. (F) Changes in yeast and mold counts (log CFU·g−1) of cheese slices after inoculated with yeast and mold).
In this case, the antibacterial activity of the CEO against the LAB was shown to be the least effective compared to other microorganisms since the LAB’s inoculum level was high (around 6 log CFU·g−1) after the cheese preparation [7]. The findings of this research have been approved by [33] when using liquid WPC coating enriched with cinnamon extract to extend the shelf-life of Eastern European soft cheese. They mentioned that WPC coating enriched with cinnamon extract did not affect the total bacteria and LAB counts after 31 days of storage.
As represented in Figure 1, L. monocytogenes, E. coli (EHEC), S. aureus, and yeast and mold colonies were determined in all cheese samples during the experiment.
On day 1, in cheese samples, L. monocytogenes, E. coli (EHEC), and S. aureus counts were around 4.6, 4, and 4 Log CFU·g−1, respectively, in all cheese samples with no significant difference (p > 0.05) with the control. The total L. monocytogenes count in the C treatment increased throughout the 7-day analysis period. E. coli (EHEC) and S. aureus counts also increased to 4.4 and 4.5 after a week of storage. However, the L. monocytogenes, E. coli, and S. aureus count in the W, WCEO1, and WCEO2 treatments significantly decreased. Also, after the 28-day storage period at 4 °C, all bacterium species counts declined considerably (p < 0.05) for W, WCEO1, and WCEO2; these findings are due to the preservation action of the plant metabolites that are encapsulated inside the edible film’s matrix. This result agrees with [34], who made edible films with whey protein and black CEOs and found that they decreased the L. monocytogenes, E. coli (EHEC), Penicillium spp., S. Enteritidis, S. aureus counts in slices of Kasar cheese.
Figure 1 illustrates the change in the counts of yeast and mold in cheese samples stored at 4 °C for 4 weeks. On day 1, the counts of yeast and mold were recorded as 4.4 Log CFU·g−1 for C, W, WCEO1, and WCEO2. A significant reduction (p < 0.05) in the count of yeast and mold was seen in the WCEO1 and WCEO2 treatments after 14 days of storage when compared to the other treatments on day 7. A clean appearance was detected in just two samples after 28 days. For WCEO1 and WCEO2, and for WCEO1 and WCEO2, respectively, the average counts of yeast and mold were 2.3 and 2.2. After 28 days, only two samples were observed to have a clean appearance, with no apparent contamination development. WCEO1 and WCEO2 had significant reductions (p < 0.05) in the counts of yeast and mold, whereas the latter had a higher reduction in the counts of yeast and mold when compared to day 1 for the same treatments. According to an investigation carried out by [31], identical results were found when a WPC film infused with cinnamon carbon dioxide extract decreased yeasts, molds, and coliform counts in Eastern European curd cheese.
Based on the results of this study, coating Iranian white cheese with a WPC coating containing CEOs (WCEO1 and WCEO2) lowered the counts of L. monocytogenes, E. coli (EHEC), S. aureus, and total yeast and mold. According to the researchers, these findings are due to the preservation action of the plant extracts encapsulated inside the edible film’s matrix. In addition, the coating had a superior effect on preventing the rotting of the cheese samples caused by bacteria, yeast, and molds even without the addition of a plant extract. The bioactive compounds of the CEO inhibited bacterial, mold, and yeast growth in cheese samples. The biological activity of the bioactive compounds of CEO was comprehensively studied in the literature [35,36]. Besides the biological activity of γ-terpinene, geranyl acetate, and p-cymene, all the components of CEO have been determined by [26,28].
The shelf-life of Iranian white cheese extended more effectively when coated with WPC than the uncoated sample (control). This finding agreed with [31] who found that an edible coating made of liquid WPC and cinnamon extract could effectively increase the shelf-life of fresh curd cheese, simultaneously increase its functional properties, and make the process more sustainable.
Other investigations have not been conducted into using WPC-containing CEO as a bio-preservation agent for the protection of cheese. A few studies investigated the impact of adding CEO directly to the cheese matrix on the antibacterial actions of the cheese against spoilage and/or pathogenic microorganisms. A study [37] stated that for a cheese preserved in 1% CEO nanoemulsion for 60 days, no yeasts, molds, or psychotropic counts were found. Moreover, according to [7], when CEO is introduced into cheese samples directly it has the same antibacterial effect on L. monocytogenes, E. coli, S. aureus, and S. enteritidis.
3.4. Physicochemical Properties of Cheese during Storage
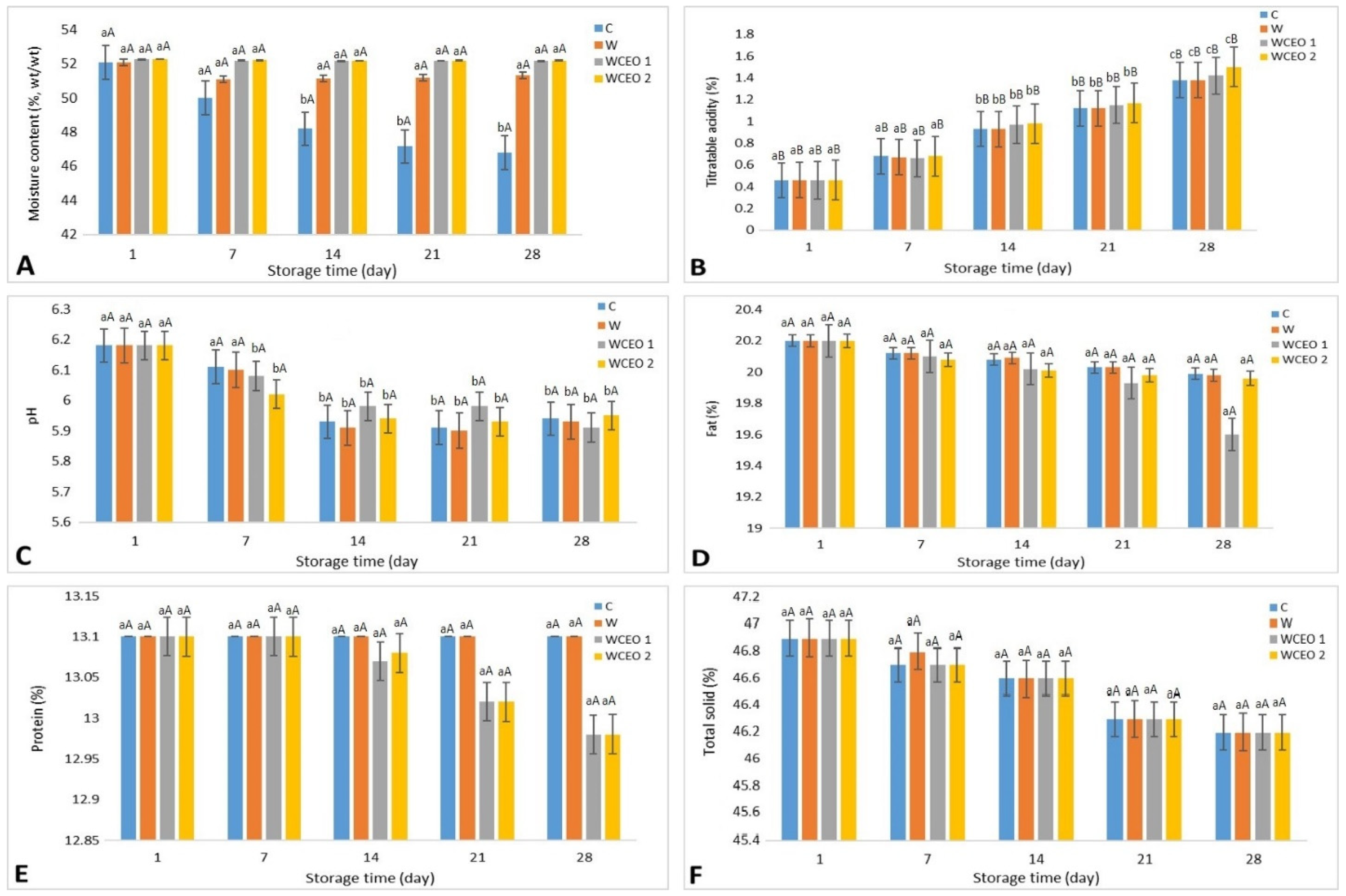
The following percentages were found in the chemical composition of fresh cheese: moisture content = 52.13 ± 0.11%; fat = 20.18 ± 0.12%; protein = 13.1 ± 0.13%; T. S = 47.02 ± 0.11%. Various chemical parameters of various treatments are given in Figure 2. The analysis was carried out at 4 °C in a cold storage room for four weeks. The coating of the cheese had no noticeable impact on the moisture content of the cheese among the various treatments. However, during storage within the same treatment, the moisture content of all samples reduced considerably (p < 0.05) in a linear pattern. Additionally, titratable acidity did not vary across the four treatments, although acidity rose considerably (p < 0.05) while all treatments were being stored. However, pH levels had no significant (p > 0.05) change throughout cold storage.
Figure 2.
The change in moisture content (A), titratable acidity (B), pH (C), fat content (D), protein content (E), and total solids content (F) of Iranian white cheese at different treatments during 28 days of storage at 4 °C. C: uncoated sample, W: whey protein concentrate coating, WCEO1: whey protein concentrate containing 1 percent v/v CEO, and WCEO2: whey protein concentrate containing 2 percent v/v CEO.
Finally, the active coating did not have any influence on the physicochemical characteristics of Iranian white cheese samples. In the same trend, ref. [31] reported that the cinnamon carbon dioxide extract-enhanced, liquid, WPC-based edible coating showed no influence on the pH, lactic acid concentration, protein, or fat contents of the coating. Identical results were found by [8] who worked on chitosan-based emulsions consisting of liposomes loaded with thyme EO and tested them to find whether they could be used to extend the shelf-life of Karish cheese. The results indicated that coatings did not affect their moisture content, pH, or titratable acidity.
The obtained values of hardness, adhesiveness, springiness, cohesiveness, chewiness, and resilience are presented in Table 3. Hardness is the maximum peak force during compression (first bite). The significant differences (p ≤ 0.05) in hardness and chewiness in group 1 appeared only on day 7 of storage; the cheese C sample had less moisture content, resulting in higher hardness and chewiness values (r = −0.92, p ≤ 0.001). The applied coating in W, WCEO1, and WCEO2 did not affect the hardness, cohesiveness, springiness, chewiness, adhesiveness, and resilience values (p > 0.05).

Table 3.
Hardness, adhesiveness, chewiness, cohesiveness, springiness, and resilience of Iranian white cheese uncoated and coated with different concentrations of CEO during 28 days of storage at 7 °C.
Color is a crucial aspect of cheese; customers avoid cheese that is discolored. yellow color is a result of moisture loss in cheese curds, due to surface drying on the curds [38]. Instrumental color determination results are illustrated in Table 4. The control sample indicated the highest changes in color during all storage. In the C sample, increasing the b* value during storage represented the drying-off process (increasing yellowness). The lowering of a* (increasing greenness) values indicated the intensity of mold growth in the C sample. Significant color values change in the C sample because of lost moisture content, yeast, and mold growth. At storage day 7, the coated sample was shown to be significantly (p ≤ 0.05) whiter (L*) than the control (C). However, the W cheese sample kept the moisture, but the decrease in the b* (increasing blueness) and a* (increasing greenness) indicated mold growth. In the control sample, this change occurs faster (p ≤ 0.05) in C (on d 7) than in W (on d 14). The variations in the means and the expanding standard deviation of L*a*b* coordinates are observed because of moisture loss and inconsistent mold growth on the cheese surface.

Table 4.
Color coordinate (L*, a*, b*) values during 28 d of storage at 7 °C and 90% relative humidity.
Coated samples (W, WCEO1, WCEO2) on days 1 and 28 had no difference (p ≤ 0.05) on b* coordinates, which means that coated samples had the same yellowness and kept the moisture content of cheese throughout the 28 days of storage.
The overall color change (∆E) in cheese samples during storage is shown in Table 4. WCEO1 and WCEO2 had remarkably lower (p ≤ 0.05) ∆E values than the W and C samples. These results allow us to conclude that WPC coating infused with CEO can potentially enhance the cheese’s shelf life. There were no significant color changes or differences during storage because the color changes were likely to be caused by less moisture loss (r = −0.90, p ≤ 0.001) as mentioned in moisture content analysis section and Figure 2; there was no growth of yeasts or molds (Y/M; r = 0.85, p ≤ 0.001), as shown in the microbial analysis section and Figure 1.
3.5. Sensory Analysis of Cheese during Storage
As mentioned in Table 5, all sensory metrics were changed in control and treated samples with a WCEO1 and a WCEO2 over the storage period. The texture of samples coated with WPC film enhanced with 1% and 2% CEO obtained an acceptable grade. The sensory qualities of Iranian white cheese samples coated with WPC films containing 1% CEO did not alter appreciably throughout storage; they had a better acceptability score at the end of the period than all other treatments.

Table 5.
Sensory characteristics of uncoated and coated Iranian white cheese during 28 days of storage at 7 °C.
The sensory assessment of flavor and odor scores demonstrated that panelists gave a lower score to the cheese samples treated with the films containing 2% CEO owing to the overpowering taste and odor created by the CEO, as opposed to the sample of cheese incorporated with the films containing 1% CEO. Because CEO keeps coming out while it is in storage, lactic acid bacteria might not be able to make the food more acidic. The formation of lactic acid and other organic acids throughout storage imparts a sour flavor and leads to the development of brittle tissue [39]. The sensory evaluation indicates no difference between cheese sample flavors. Samples coated with WPC and enriched with 1% CEO, on the other hand, improved the texture and appearance of treated samples. Another study executed by Cakir et al., 2016, introduced cumin to improve the sensory scores and proteolysis in Erzincan Tulum (Savak) cheese prepared from raw Akkaraman sheep’s milk. Also, ref. [7] stated that using CEO could restrict the increase in titratable acidity and limit the changes in flavor components and ripening indices while maintaining important physical, chemical, and sensory qualities in the cheese. The sensorial analysis of control (C) and cheese coated with only WPC without CEO (W) stopped from day 14 because of contamination with yeast and mold.
4. Conclusions
It was shown that antibacterial activity in Iranian white cheese kept under edible coatings comprised of WPC infused with CEO lasted for over four weeks of cold storage since, as opposed to control samples, the cheese treated with film infused with EO kept the physicochemical and sensorial properties of samples during the experiment. GC–MS determined the chemical composition of cumin seed oil, and the results revealed that γ-terpinene, propanal, geranyl acetate, p-cymene, and sabinene were the primary constituents. Based on antimicrobial activity, coating Iranian white cheese with concentrated WPC containing CEO at concentrations of 1 and 2% did not affect the total bacterial count and LAB count. It also reduced L. monocytogenes, E. coli (EHEC), S. aureus, and the yeast/mold count. The physicochemical properties of cheese samples were unaffected by the films, as were the sensory properties and overall acceptability of the samples treated with 1% CEO, which outperformed the other samples, including the control sample. Consequently, the shelf-life of Iranian white cheese extended from about 10–15 days to 28 days while keeping its characteristics. Current research results indicate that upcoming studies could be carried out with higher concentrations of cumin EO in the coating, aiming for higher antimicrobial efficiency against foodborne pathogens in soft cheese. Generally, the integration of WPC as a cheese byproduct back into dairy products in the form of edible coating is quite advantageous for dairy industry manufacturers. The WPC-based coating could be prepared immediately with minimal investments after curd cheese production by reusing whey leftovers. This type of active edible coating with an antimicrobial effect could be an exceptional addition to both package-free cheeses produced by manufacturers aiming for sustainability and functional product value.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.N.; Data curation, V.N.; Formal analysis, V.N.; Funding acquisition, V.N.; Investigation, F.H.-B., L.M.J. and A.M.A.; Methodology, V.N. and A.M.A.; Project administration, V.N.; Supervision, L.M.J. and A.M.A.; Validation, A.M.A.; Writing—original draft, V.N., F.H.-B., M.S.G.-N., E.F., L.M.J. and A.M.A.; Writing—review and editing, V.N., F.H.-B. and M.S.G.-N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Iran Dairy Industries Co. (Pegah) for research and development [2023/12-1] and São Paulo Research Foundation (FAPESP) for the postdoctoral fellowship of L. Marangoni Júnior [2021/04043-2].
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The Research and Development (R&D) management of Iran Dairy Industries Co. (Pegah) supported this research. The authors would like to thank Pegah Dairy for their financial and technical support and valuable assistance in the production of Iranian white cheese.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Madadlou, A.; Khosroshahi, A.; Mousavi, S.M.; Djome, Z.E. Microstructure and Rheological Properties of Iranian White Cheese Coagulated at Various Temperatures. J. Dairy. Sci. 2006, 89, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.M.; Mashayekh, M.; Banikhademi, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Heidary, R.H.; Mousavi, M.M.; Pilevar, Z. Microbial and Chemical Parameters of Traditional Siahmazgi Cheese Produced in Zanjan Province, Iran. Adv. Anim. Vet. Sci. 2019, 7, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khosrowshahi, A.; Madadlou, A.; Mousavi, M.E.Z.; Emam-Djomeh, Z. Monitoring the Chemical and Textural Changes during Ripening of Iranian White Cheese Made with Different Concentrations of Starter. J. Dairy Sci. 2006, 89, 3318–3325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proulx, J.; Sullivan, G.; Marostegan, L.F.; VanWees, S.; Hsu, L.C.; Moraru, C.I. Pulsed Light and Antimicrobial Combination Treatments for Surface Decontamination of Cheese: Favorable and Antagonistic Effects. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 1664–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kandasamy, S.; Yoo, J.; Yun, J.; Kang, H.B.; Seol, K.H.; Kim, H.W.; Ham, J.S. Application of Whey Protein-Based Edible Films and Coatings in Food Industries: An Updated Overview. Coatings 2021, 11, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Xie, Y.; Guo, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Qian, H.; Yao, W. Application of Edible Coating with Essential Oil in Food Preservation. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 59, 2467–2480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mileriene, J.; Serniene, L.; Henriques, M.; Gomes, D.; Pereira, C.; Kondrotiene, K.; Kasetiene, N.; Lauciene, L.; Sekmokiene, D.; Malakauskas, M. Effect of Liquid Whey Protein Concentrate–Based Edible Coating Enriched with Cinnamon Carbon Dioxide Extract on the Quality and Shelf Life of Eastern European Curd Cheese. J. Dairy Sci. 2021, 104, 1504–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Moghazy, M.; El-sayed, H.S.; Salama, H.H.; Nada, A.A. Edible Packaging Coating of Encapsulated Thyme Essential Oil in Liposomal Chitosan Emulsions to Improve the Shelf Life of Karish Cheese. Food Biosci. 2021, 43, 101230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ket-on, A.; Pongmongkol, N.; Somwangthanaroj, A.; Janjarasskul, T.; Tananuwong, K. Properties and Storage Stability of Whey Protein Edible Film with Spice Powders. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 53, 2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osés, J.; Fernández-Pan, I.; Mendoza, M.; Maté, J.I. Stability of the Mechanical Properties of Edible Films Based on Whey Protein Isolate during Storage at Different Relative Humidity. Food Hydrocoll. 2009, 23, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bettaieb, I.; Bourgou, S.; Wannes, W.A.; Hamrouni, I.; Limam, F.; Marzouk, B. Essential Oils, Phenolics, and Antioxidant Activities of Different Parts of Cumin (Cuminum Cyminum L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10410–10418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemati, V.; Khomeiri, M.; Moayedi, A.; Mahoonak, A.S.; Sadeghi, A.; Yamchi, A. Use of Cuminum cyminum Essential Oil and Biarum Carduchcorum Water Extract on Shelf-Life Extension of Lambs at Cold Storage. Nutr. Food Sci. Res. 2019, 6, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soazo, M.; Pérez, L.M.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Verdini, R.A. Effect of Freezing on Physical Properties of Whey Protein Emulsion Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 31, 256–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yu, H.; Tian, B.; Jiang, B.; Xu, J.; Li, D.; Feng, Z.; Liu, C. Novel Edible Coating with Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activities Based on Whey Protein Isolate Nanofibrils and Carvacrol and Its Application on Fresh-Cut Cheese. Coatings 2019, 9, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galus, S.; Kadzińska, J. Moisture Sensitivity, Optical, Mechanical and Structural Properties of Whey Protein-Based Edible Films Incorporated with Rapeseed Oil. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2016, 54, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedro, S.; Pereira, L.; Domingues, F.; Ramos, A.; Luís, Â. Optimization of Whey Protein-Based Films Incorporating Foeniculum vulgare Mill. Essential Oil. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferraz, A.R.; Goulão, M.; Santo, C.E.; Anjos, O.; Serralheiro, M.L.; Pintado, C.M.B.S. Novel, Edible Melanin-Protein-Based Bioactive Films for Cheeses: Antimicrobial, Mechanical and Chemical Characteristics. Foods 2023, 12, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO/TS 11869:2012; Fermented Milks—Determination of Titratable Acidity—Potentiometric Method. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2012. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/56875.html (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- ISO 5534:2004/Cor 1:2013; Cheese and Processed Cheese—Determination of the Total Solids Content (Reference Method)—Technical Corrigendum 1. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2013. Available online: https://www.iso.org/standard/63977.html (accessed on 8 August 2023).
- ISIRI. Cheese Production Safety and Standard Criteria; ISIRI: Karaj, Iran, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Pappas, C.P.; Kondyli, E.; Voutsinas, L.P.; Mallatou, H. Effects of Starter Level, Draining Time and Aging on the Physicochemical, Organoleptic and Rheological Properties of Feta Cheese. Int. J. Dairy Technol. 1996, 49, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petretto, G.L.; Fancello, F.; Bakhy, K.; Al Faiz, C.; Sibawayh, Z.; Chessa, M.; Zara, S.; Sanna, M.L.; Maldini, M.; Rourke, J.P.; et al. Chemical Composition and Antimicrobial Activity of Essential Oils from Cuminum cyminum L. Collected in Different Areas of Morocco. Food Biosci. 2018, 22, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaddam, M.; Pirbalouti, A.G. Agro-Morphological and Phytochemical Diversity of Iranian Cuminum cyminum Accessions. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 99, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burt, S. Essential Oils: Their Antibacterial Properties and Potential Applications in Foods—A Review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2004, 94, 223–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Baschieri, A.; Amorati, R.; Valgimigli, L. Synergic Antioxidant Activity of γ-Terpinene with Phenols and Polyphenols Enabled by Hydroperoxyl Radicals. Food Chem. 2021, 345, 128468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshitomi, K.; Taniguchi, S.; Tanaka, K.; Uji, Y.; Akimitsu, K.; Gomi, K. Rice Terpene Synthase 24 (OsTPS24) Encodes a Jasmonate-Responsive Monoterpene Synthase That Produces an Antibacterial γ-Terpinene against Rice Pathogen. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 191, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonçalves, M.J.; Cruz, M.T.; Tavares, A.C.; Cavaleiro, C.; Lopes, M.C.; Canhoto, J.; Salgueiro, L. Composition and Biological Activity of the Essential Oil from Thapsia Minor, a New Source of Geranyl Acetate. Ind. Crops Prod. 2012, 35, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogianni, V.G.; Kasapidou, E.; Mitlianga, P.; Mataragas, M.; Pappa, E.; Kondyli, E.; Bosnea, L. Production, Characteristics and Application of Whey Protein Films Activated with Rosemary and Sage Extract in Preserving Soft Cheese. LWT 2022, 155, 112996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pluta-Kubica, A.; Jamróz, E.; Kawecka, A.; Juszczak, L.; Krzyściak, P. Active Edible Furcellaran/Whey Protein Films with Yerba Mate and White Tea Extracts: Preparation, Characterization and Its Application to Fresh Soft Rennet-Curd Cheese. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 155, 1307–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, L.M.; Piccirilli, G.N.; Delorenzi, N.J.; Verdini, R.A. Effect of Different Combinations of Glycerol and/or Trehalose on Physical and Structural Properties of Whey Protein Concentrate-Based Edible Films. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccirilli, G.N.; Soazo, M.; Pérez, L.M.; Delorenzi, N.J.; Verdini, R.A. Effect of Storage Conditions on the Physicochemical Characteristics of Edible Films Based on Whey Protein Concentrate and Liquid Smoke. Food Hydrocoll. 2019, 87, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassanien, M.F.R.; Mahgoub, S.A.; El-Zahar, K.M. Soft Cheese Supplemented with Black Cumin Oil: Impact on Food Borne Pathogens and Quality during Storage. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 21, 280–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seydim, A.C.; Sarikus-Tutal, G.; Sogut, E. Effect of Whey Protein Edible Films Containing Plant Essential Oils on Microbial Inactivation of Sliced Kasar Cheese. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2020, 26, 100567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proestos, C.; Zoumpoulakis, P.; Sinanoglou, V.J. Isolation and Characterization of Phenolic Compounds from Selected Foods of Plant Origin Using Modern Spectroscopic Approaches. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2018, 57, 203–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, H.; Hosseini-Ghazvini, S.M.B.; Khodarahmi, R. Therapeutic Potentials of the Most Studied Flavonoids: Highlighting Antibacterial and Antidiabetic Functionalities. Stud. Nat. Prod. Chem. 2019, 60, 85–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sayed, H.S.; El-Sayed, S.M. A Modern Trend to Preserve White Soft Cheese Using Nano-Emulsified Solutions Containing Cumin Essential Oil. Environ. Nanotechnol. Monit. Manag. 2021, 16, 100499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayaloglu, A.A.; Guven, M.; Fox, P.F. Microbiological, Biochemical and Technological Properties of Turkish White Cheese “Beyaz Peynir”. Int. Dairy J. 2002, 12, 635–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buriti, F.C.A.; da Rocha, J.S.; Saad, S.M.I. Incorporation of Lactobacillus Acidophilus in Minas Fresh Cheese and Its Implications for Textural and Sensorial Properties during Storage. Int. Dairy J. 2005, 15, 1279–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cakir, Y.; Cakmakci, S.; Hayaloglu, A.A. The Effect of Addition of Black Cumin (Nigella Sativa L.) and Ripening Period on Proteolysis, Sensory Properties and Volatile Profiles of Erzincan Tulum (Şavak) Cheese Made from Raw Akkaraman Sheep’s Milk. Small Rumin. Res. 2016, 134, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).