Evaluation of the Mechanical and Corrosion Behavior of Twin Wire Arc Sprayed Ni-Al Coatings with Different Al and Mo Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials Preparation
2.2. Heat Exposure at High-Temperature
2.3. Microstructural Characterization of Coating Layers
2.4. Mechanical Properties of the Coating Layers
2.5. Chlorine-Induced Corrosion Test
3. Results and Discussion
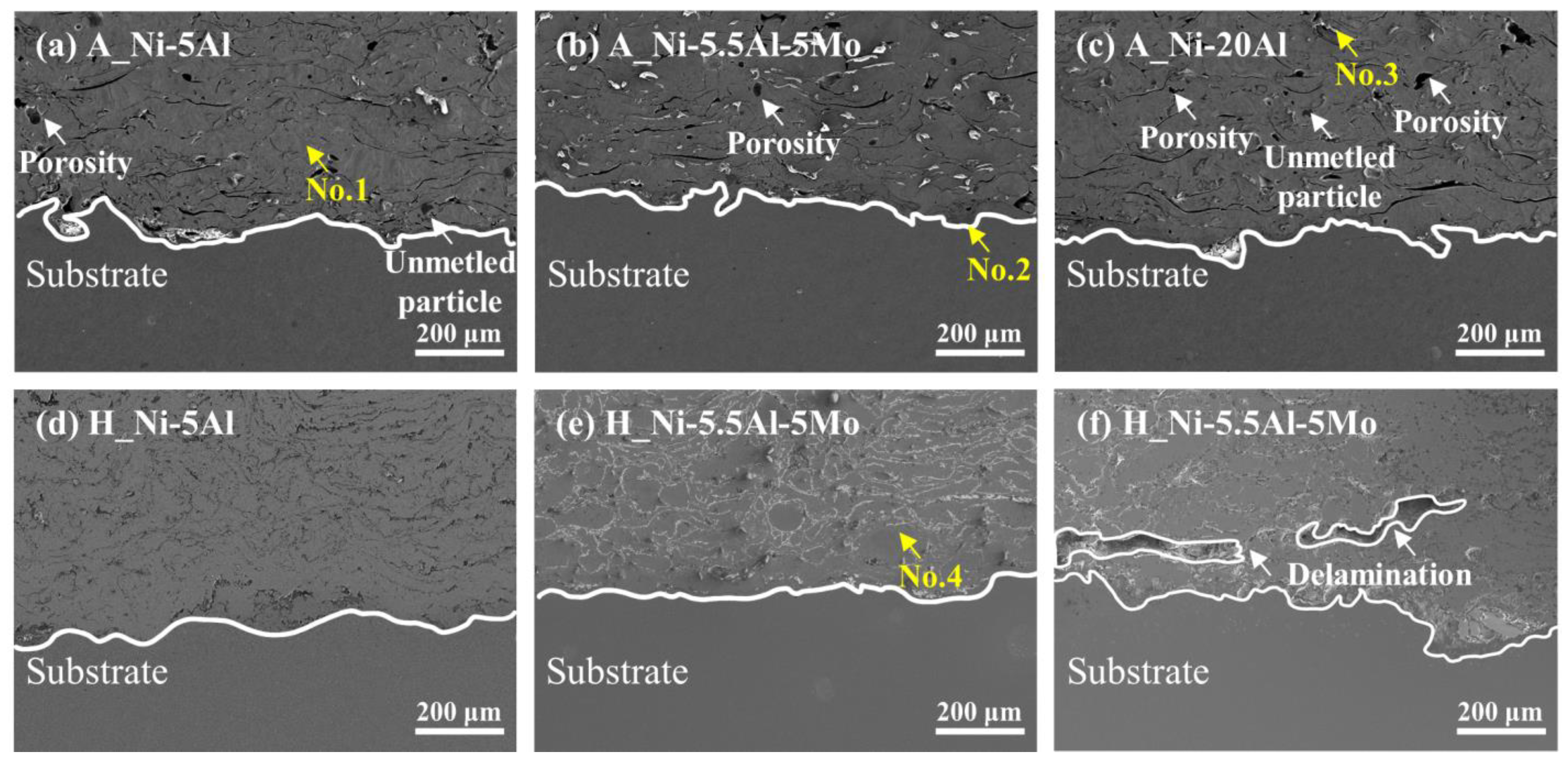
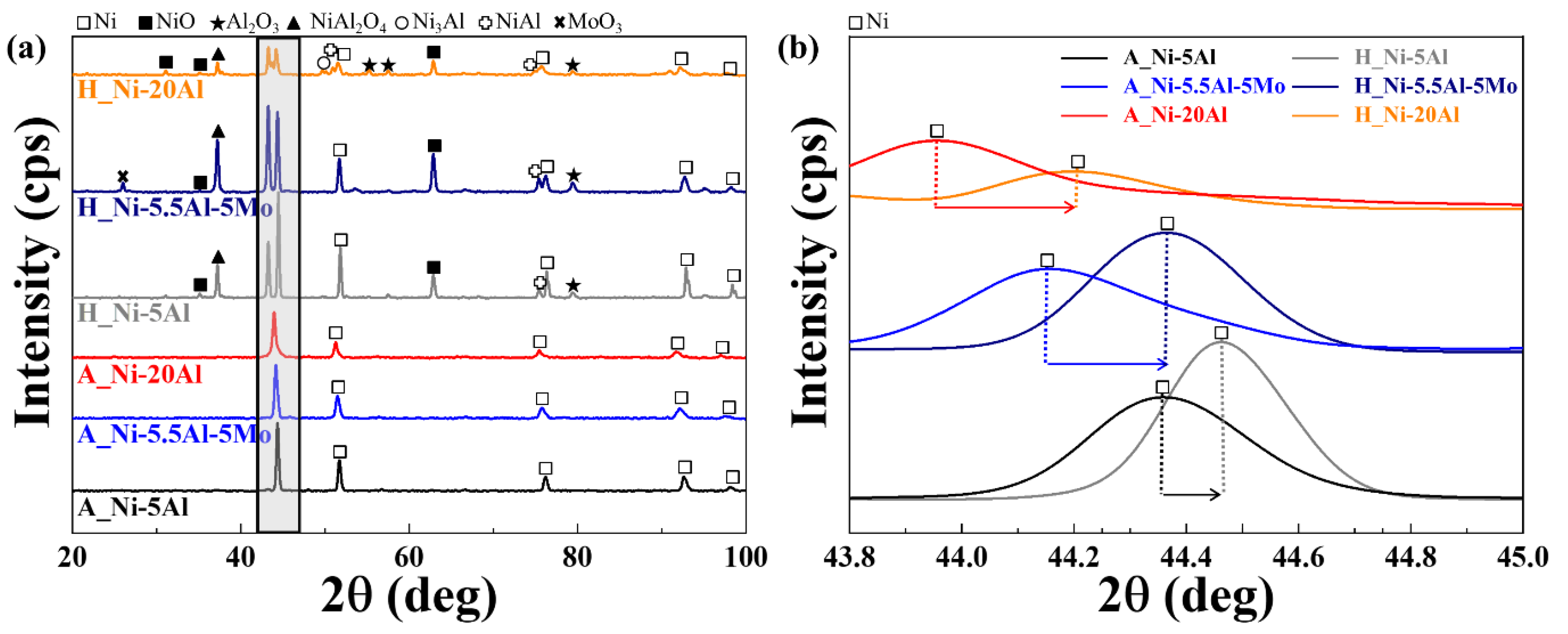
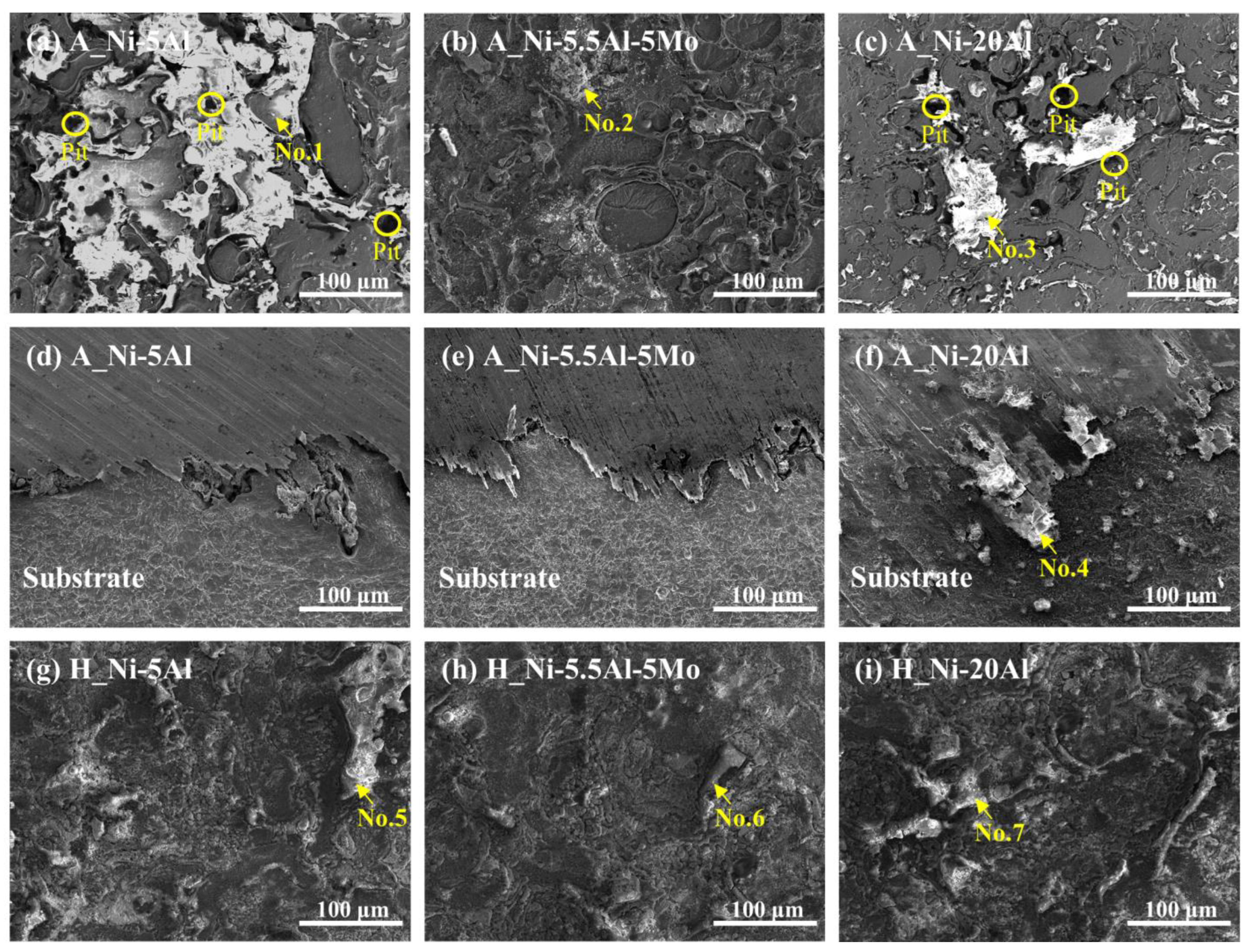
3.1. Characterizations of the as-Sprayed Coating Layers and after the High-Temperature Heat Exposure
3.2. Mechanical Properties of as-Sprayed and Heat-Exposed Ni-Al Coating Layers
3.3. Electrochemical Properties of Ni-Al Coatings before and after the High-Temperature Exposure in 3.5% NaCl Solution
3.3.1. Galvanic Corrosion Test
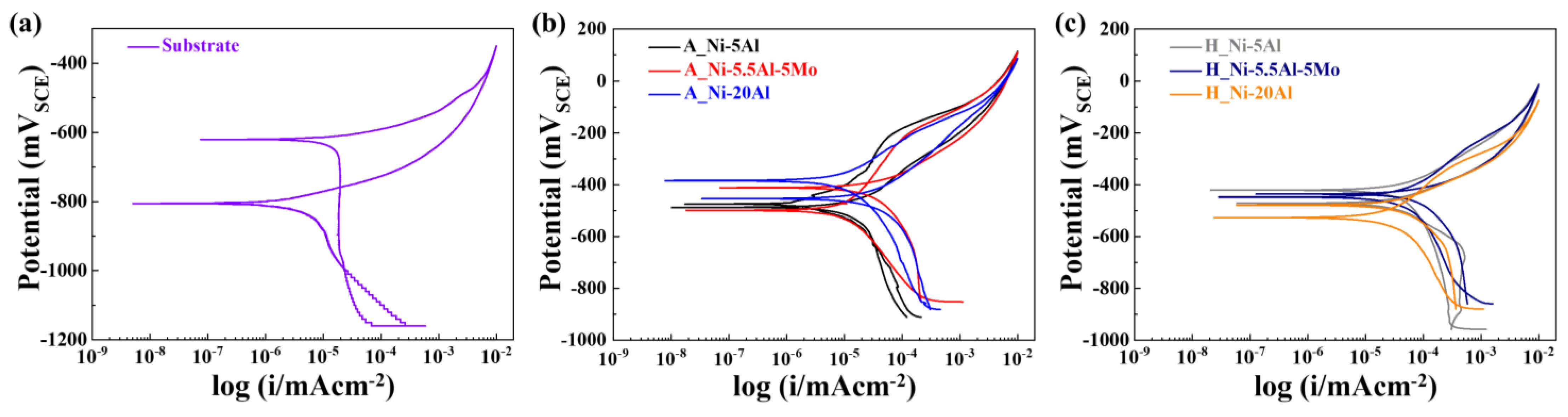
3.3.2. Cyclic Potentiodynamic Polarization
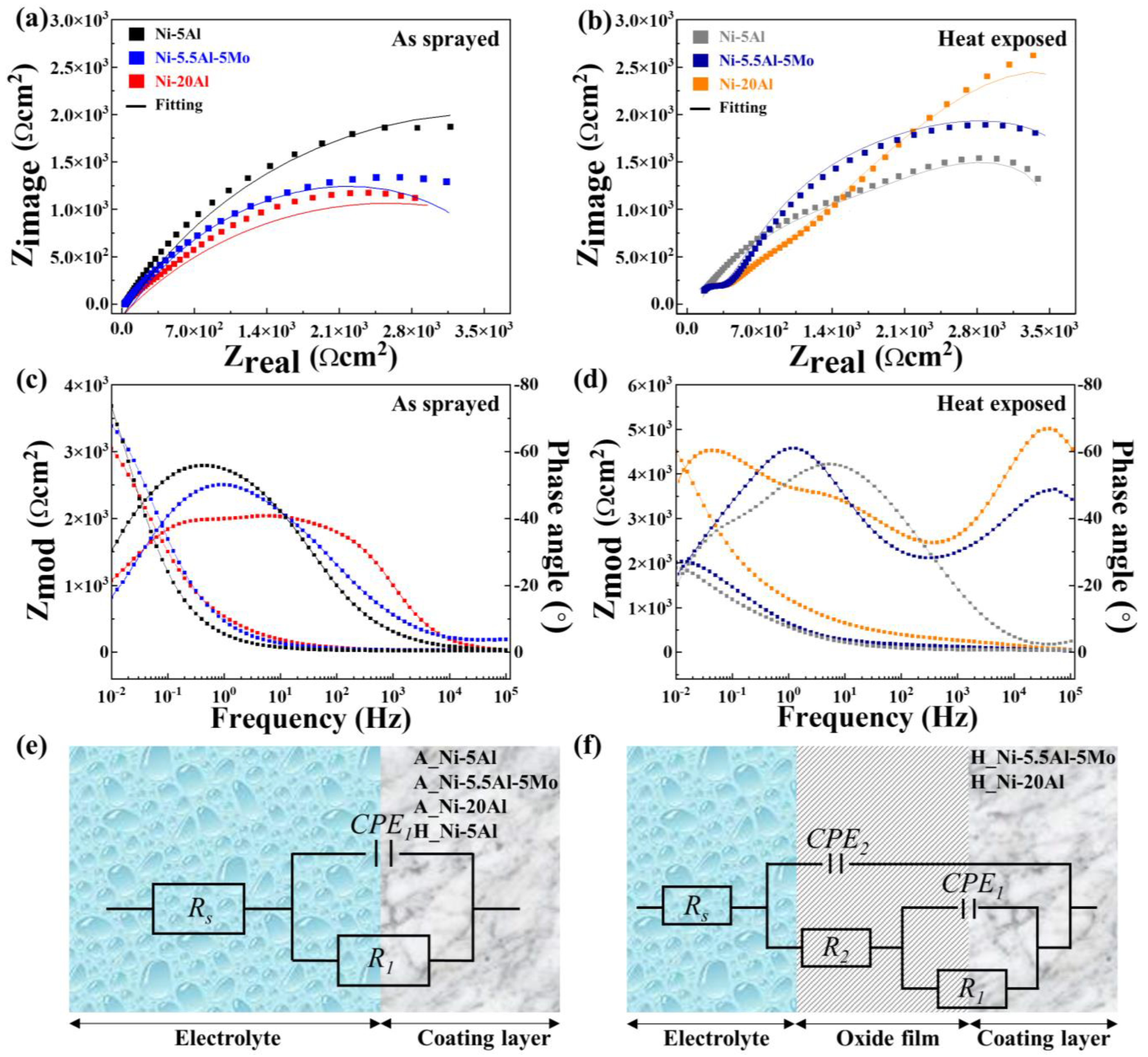
3.3.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.3.4. Immersion Test
4. Conclusions
- The Ni-Al and Ni-Al-Mo coating layers exhibited typical lamellar microstructures resulting from the twin wire arc spray, with increasing porosity and oxide content as the Al content increased. Delamination was observed in the Ni-20Al coating layer after thermal exposure. The addition of Al elements resulted in the miniaturization of the grain size and various oxides after high-temperature exposure. Ni-20Al exhibited the excellent mechanical properties among the coatings, under both as-sprayed and high-temperature heat exposure.
- Following the corrosion tests, the galvanic corrosion potential difference between the substrate and the coating layers decreased with increasing Al content. Ni-5Al and Ni-20Al exhibited localized galvanic corrosion around the intermetallic compounds and oxides, whereas Ni-5.5Al-5Mo showed uniform corrosion. However, the formation of an oxide layer resulting from the phase transformation of intermetallic compounds after exposure to high temperatures improved the corrosion resistance, demonstrating the superior corrosion properties of Ni-20Al. These results emphasize the correlation between the corrosion behavior and the composition of the passivation film and support the potential application of the Ni-5.5Al-5Mo coating as a protective layer against the pitting corrosion of the substrate.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bandgar, S.; Gupta, C.; Rao, G.; Malik, P.; Singh, R.N.; Sridhar, K. Fatigue Crack Growth Rate Behaviour of HSLA Steel at Varying Load Amplitudes. Procedia Struct. Integr. 2019, 14, 330–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Wang, Q.; Yang, L.; Liu, Z.; Li, X.; Li, Y. Corrosion and SCC initiation behavior of low-alloy high-strength steels microalloyed with Nb and Sb in a simulated polluted marine atmosphere. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2020, 9, 12976–12995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yuming, H.; Yucheng, L. Microstructure and properties of 700 MPa grade HSLA steel during high temperature deformation. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 631, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Jeong, Y.; Shim, D.; Lee, E. Microstructural evolution and martensitic transformation in FeCrV alloy fabricated via additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 809, 140943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, Y.; Lee, J.; Lee, E.; Shim, D. Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Deposited Fe-8Cr-3V-2Mo-2W on SCM420 Substrate Using Directed Energy Deposition and Effect of Post-Heat Treatment. Materials 2021, 14, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, S.; Panchal, H. A review on thermal spray coating processes. Transfer 2016, 2, 556–563. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.; Du, Y.; Chen, S.; Ren, Y.; Ma, Y. Effect of secondary passivation on corrosion behavior and semiconducting properties of passive film of 2205 duplex stainless steel. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 15, 6828–6840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, G.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Sun, J. Microstructure of Ni-Al powder and Ni-Al composite coatings prepared by twin-wire arc spraying. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 810–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Du, L.; Yang, B.; Zhang, W. The effect of Al content on the galvanic corrosion behaviour of coupled Ni/graphite and Ni–Al coatings. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 2066–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuwarda, N.; Lopez, A.J.; Lopez, M.D.; Utrilla, M.V. High temperature corrosion and wear behavior of HVOF-sprayed coating of Al2O3-NiAl on AISI 304 stainless steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 359, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saladi, S.; Menghani, J.; Prakash, S. A study on the cyclic oxidation behavior of detonation-gun-sprayed Ni-5Al coatings on Inconel-718 at 900 °C. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 4394–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgiel, J.; Poliarus, O.; Pomorska, M.; Maj, L.; Szlezynger, M. Thermal stability of plasma-sprayed NiAl/CrB2 composite coatings investigated through in-situ TEM heating experiment. Mater. Charact. 2020, 159, 110068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, G.; Lee, E. Combined effects of optimized heat treatment and nickel coating for the improvement of interfacial bonding in aluminum–iron alloys hybrid structures. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabani, A.; Nahvi, S.M.; Raeissi, K. Effect of heat treatment on structure and oxidation resistance of flame-sprayed Ni-20 wt.% Al on carbon steel. J. Therm. Spray Technol. 2021, 30, 739–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Byon, E.; Lee, E. Effects of Na2B4O7·10H2O on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlSi7Mg0.3 and AlSi10MnMgAlSi10MnMg alloys. J. Adv. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2021, 45, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xanthopoulou, G.; Marinou, A.; Vekinis, G.; Lekatou, A.; Vardavoulias, M. Ni-Al and NiO-Al composite coatings by combustion-assisted flame spraying. Coatings 2014, 4, 231–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafari, R.; Sadeghi, E. High-temperature corrosion performance of HVAF-sprayed NiCr, NiAl, and NiCrAlY coatings with alkali sulfate/chloride exposed to ambient air. Corros. Sci. 2019, 160, 108066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, R.A.; Jayaganthan, R.; Prakash, S. Microstructure characterization and hardness evaluation of HOVF sprayed Ni–5Al coatings on Ni- and Fe-based superalloys. J. Mater. Process. Tech. 2009, 209, 3501–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.C.; Pfender, E. Microstructure of plasma-sprayed Ni–Al alloy coating on mild steel. Thin Solid Films. 1996, 280, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugimoto, K.; Sawada, Y. The role of molybdenum additions to austenitic stainless steels in the inhibition of pitting in acid chloride solutions. Corros. Sci. 1977, 17, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, C.R.; Lu, Y.C. A Bipolar Model of the Passivity of Stainless Steel: The Role of Mo Addition. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1986, 133, 2465–2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landolt, D.; Mischler, S.; Vogel, A.; Mathieu, H.J. Chloride Ion Effects on Passive Films on FeCr and FeCrMo Studied by AES, XPS and SIMS. Corros. Sci. 1990, 31, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannur, K.H.; Yaqub, T.B.; Huminiuc, T.; Polcar, T.; Pupier, C.; Héau, C.; Cavaleiro, A. Synthesis and structural properties of Mo-SN sputtered coatings. Appl. Sci. 2020, 527, 146790. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, J.J.; Yao, S.W.; Luo, X.T.; Li, C.X.; Li, C.J. An effective approach for creating metallurgical self-bonding in plasma-spraying of NiCr-Mo coating by designing shell-core-structured powders. Acta Mater. 2016, 110, 19–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, H.Y.; Lee, T.H.; Bae, J.H.; Chun, D.W. Molybdenum effects on pitting corrosion resistance of FeCrMnMoNC austenitic stainless steels. Metals 2018, 8, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, K.; Asami, K.; Teramoto, K. An X-ray photo-electron spectroscopic study on the role of molybdenum in increasing the corrosion resistance of ferritic stainless steels in HCl. Corros. Sci. 1979, 19, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Kwon, H.; Byon, E.; Lee, E. Understanding of microstructures and mechanical properties of thermal sprayed Ni-based coatings with Al and Mo addition. J. Adv. Mar. Eng. Technol. 2022, 46, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamed, K.N.; El-Mahallawy, N.; Mokhtar, M.O.A. An investigation of plasma sprayed nickel-based and pure aluminum coatings on austenitic stainless steel AISI 304. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 1172, 012025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Sun, J.F.; Wang, Z.P. Effect of Heat Treatment to Ni-20 wt.% Al Coating Diffusion. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 621, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornienko, E.; Gulyaev, I.; Smirnov, A.; Nikulina, A.; Ruktuev, A.; Kuzmin, V.; Tuezov, A. Microstructure and properties of Ni-Al coatings obtained by conventional and high-velocity atmospheric plasma spraying. Results Surf. Interfaces 2022, 6, 100038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrdak, M.R. Mechanical properties and metallographic analysis of plasma spray APS-Ni5. 5 wt.% Al5 wt.% Mo coatings. Vojnoteh. Glas. 2019, 67, 573–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumar, M.; Handa, A. Comparative study of high temperature oxidation behavior and mechanical properties of wire arc sprayed NiCr and NiAl coatings. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2019, 106, 104173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yan, M.F. Microstructures, hardness and erosion behavior of thermal sprayed and heat treated NiAl coatings with different ceria. Wear 2007, 263, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, T.; Hu, C.; Lu, H.; Chen, Y.; Lin, Y.; Dong, H. Effect of annealing temperature on microstructure and hardness of Ni-Co alloy coating. Mater. Today Commun. 2022, 31, 103244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmailzadeh, S.; Aliofkhazraei, M.; Sarlak, H. Interpretation of cyclic potentiodynamic polarization test results for study of corrosion behavior of metals: A review. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2018, 54, 976–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekatou, A.G.; Sfikas, A.K.; Karantzalis, A.E. The influence of the fabrication route on the microstructure and surface degradation properties of Al reinforced by Al9Co2. Materials Chem. Phys. 2017, 200, 33–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lekatou, A.; Sfikas, A.K.; Petsa, C.; Karantzalis, A.E. Al-Co alloys prepared by vacuum arc melting: Correlating microstructure evolution and aqueous corrosion behavior with Co content. Metals 2016, 6, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Min, X.; Wan, S.; Liu, J.; Liao, B.; Guo, X. A novel green corrosion inhibitor extracted from waste feverfew root for carbon steel in H2SO4 solution. Results Eng. 2023, 17, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Ma, S.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Quan, R.; Wan, S.; Guo, X. Fructus cannabis protein extract powder as a green and high effective corrosion inhibitor for Q235 carbon steel in 1 M HCl solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 239, 124358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajideh, M.R.; Farahani, M.; Pakravan, M.; Shahmirzalo, A. Corrosion resistance and hydrophilic properties of plasma sprayed Ni + 5% Al coatings. Heliyon 2019, 5, e01920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popczyk, M.; Kubisztal, J.; Swinarew, A.S.; Waśkiewicz, Z.; Stanula, A.; Knechtle, B. Corrosion resistance of heat-treated Ni-W alloy coatings. Materials 2020, 13, 1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.H. Oxidation and sulfidation of Ni3Al. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2002, 76, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, F.; Randkle, E.; Felten, E. Formation of NiAl2O4 by solid state reaction. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1966, 49, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Spray Parameters (Units) | Settings | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Coating materials | Ni-5Al | Ni-5.5Al-5Mo | Ni-20Al |
| Wire diameter (mm) | 1.6 | 1.6 | 1.6 |
| Voltage (V) | 36 | 36 | 36 |
| Current (A) | 250 | 250 | 200 |
| Air pressure (psi) | 70 | 70 | 70 |
| Spray Distance (mm) | 200 | 200 | 200 |
| Gun spraying angle (°) | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| Number | Chemical Compositions (at. %) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Al | O | |
| No. 1 | 30.33 | 69.67 | - |
| No. 2 | 72.61 | 27.39 | - |
| No. 3 | - | 43.56 | 56.44 |
| No. 4 | 28.78 | 71.22 | - |
| Coating Materials | Ni-5Al | Ni-5.5Al-5Mo | Ni-20Al | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area Fraction (%) | As Sprayed | Heat Exposed | As Sprayed | Heat Exposed | As Sprayed | Heat Exposed | |
| Porosity | 1.48 | 1.14 | 1.51 | 1.15 | 1.97 | 1.17 | |
| (±0.14) | (±0.17) | (±0.15) | (±0.11) | (±0.11) | (±0.16) | ||
| Oxide | 1.92 | 1.42 | 1.91 | 1.57 | 2.25 | 2.01 | |
| (±0.16) | (±0.12) | (±0.18) | (±0.23) | (±0.16) | (±0.21) | ||
| Intermetallic phase | 0.62 | 0.60 | 0.63 | 0.61 | 0.68 | 0.64 | |
| (±0.15) | (±0.10) | (±0.14) | (±0.12) | (±0.12) | (±0.11) | ||
| Mechanical Properties | Hardness (HV) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement Location | As Sprayed | Heat Exposed | |
| Matrix of coating layer | Ni-5Al | 182.5 (±11.8) | 141 (±15.1) |
| Ni-5.5Al-5Mo | 217.7 (±7.8) | 157.8 (±18.8) | |
| Ni-20Al | 404.5 (±15) | 270.2 (±22.2) | |
| Materials | As Sprayed | Heat Exposed | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr (mVSCE) | Icorr (mA/m2) | Erep (mVSCE) | Ecorr (mVSCE) | Icorr (mA/m2) | Erep (mVSCE) | |
| Substrate | −620 | 118 | −806 | - | - | - |
| Ni-5Al | −467 | 177 | −482 | −445 | 550 | −465 |
| Ni-5.5Al-5Mo | −502 | 113 | −390 | −448 | 483 | −426 |
| Ni-20Al | −384 | 199 | −439 | −531 | 108 | −436 |
| Condition | Rs (Ωcm2) | R1 (Ωcm2) | R2 (Ωcm2) | CPE1 (Ω−1sncm 2) | CPE2 (Ω−1sncm 2) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Samples | ||||||
| As sprayed | Ni-5Al | 20.76 | 4.23 × 104 | - | 1.28 × 10−4 | - |
| Ni-5.5Al-5Mo | 19.81 | 3.78 × 104 | - | 1.42 × 10−4 | - | |
| Ni-20Al | 16.84 | 3.07 × 104 | - | 1.06 × 10−4 | - | |
| Heat exposed | Ni-5Al | 17.55 | 3.77 × 104 | 3.17 × 103 | 1.86 × 10−4 | 1.21 × 10−4 |
| Ni-5.5Al-5Mo | 18.38 | 4.10 × 104 | 5.47× 103 | 1.23 × 10−4 | 1.37 × 10−4 | |
| Ni-20Al | 22.28 | 5.18 × 104 | 7.05 × 103 | 2.09 × 10−4 | 2.36 × 10−4 | |
| Coating Layers | As Sprayed (mm/y) | Heat Exposed (mm/y) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface | Cross Section | Surface | |
| Ni-5Al | 13.23 | 14.76 | 12.64 |
| Ni-5.5Al-5Mo | 12.72 | 10.89 | 12.54 |
| Ni-20Al | 14.52 | 8.77 | 11.48 |
| Number | Chemical Compositions (at.%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Al | Mo | O | |
| No. 1 | 32.18 | - | 67.82 |
| No. 2 | - | 64.67 | 35.33 |
| No. 3 | 40.02 | - | 59.98 |
| No. 4 | 38.56 | - | 32.87 |
| No. 5 | 35.78 | - | 64.22 |
| No. 6 | 37.82 | - | 62.18 |
| No. 7 | 29.77 | - | 70.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bang, J.; Lee, E. Evaluation of the Mechanical and Corrosion Behavior of Twin Wire Arc Sprayed Ni-Al Coatings with Different Al and Mo Content. Coatings 2023, 13, 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13061069
Bang J, Lee E. Evaluation of the Mechanical and Corrosion Behavior of Twin Wire Arc Sprayed Ni-Al Coatings with Different Al and Mo Content. Coatings. 2023; 13(6):1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13061069
Chicago/Turabian StyleBang, Jaehui, and Eunkyung Lee. 2023. "Evaluation of the Mechanical and Corrosion Behavior of Twin Wire Arc Sprayed Ni-Al Coatings with Different Al and Mo Content" Coatings 13, no. 6: 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13061069
APA StyleBang, J., & Lee, E. (2023). Evaluation of the Mechanical and Corrosion Behavior of Twin Wire Arc Sprayed Ni-Al Coatings with Different Al and Mo Content. Coatings, 13(6), 1069. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13061069






