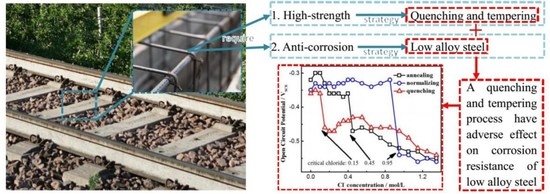
Effect of Heat Treatment on the Passive Film and Depassivation Behavior of Cr-Bearing Steel Reinforcement in an Alkaline Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedures
2.1. Material and Heat Treatment
2.2. Microstructure
2.3. Passive Film
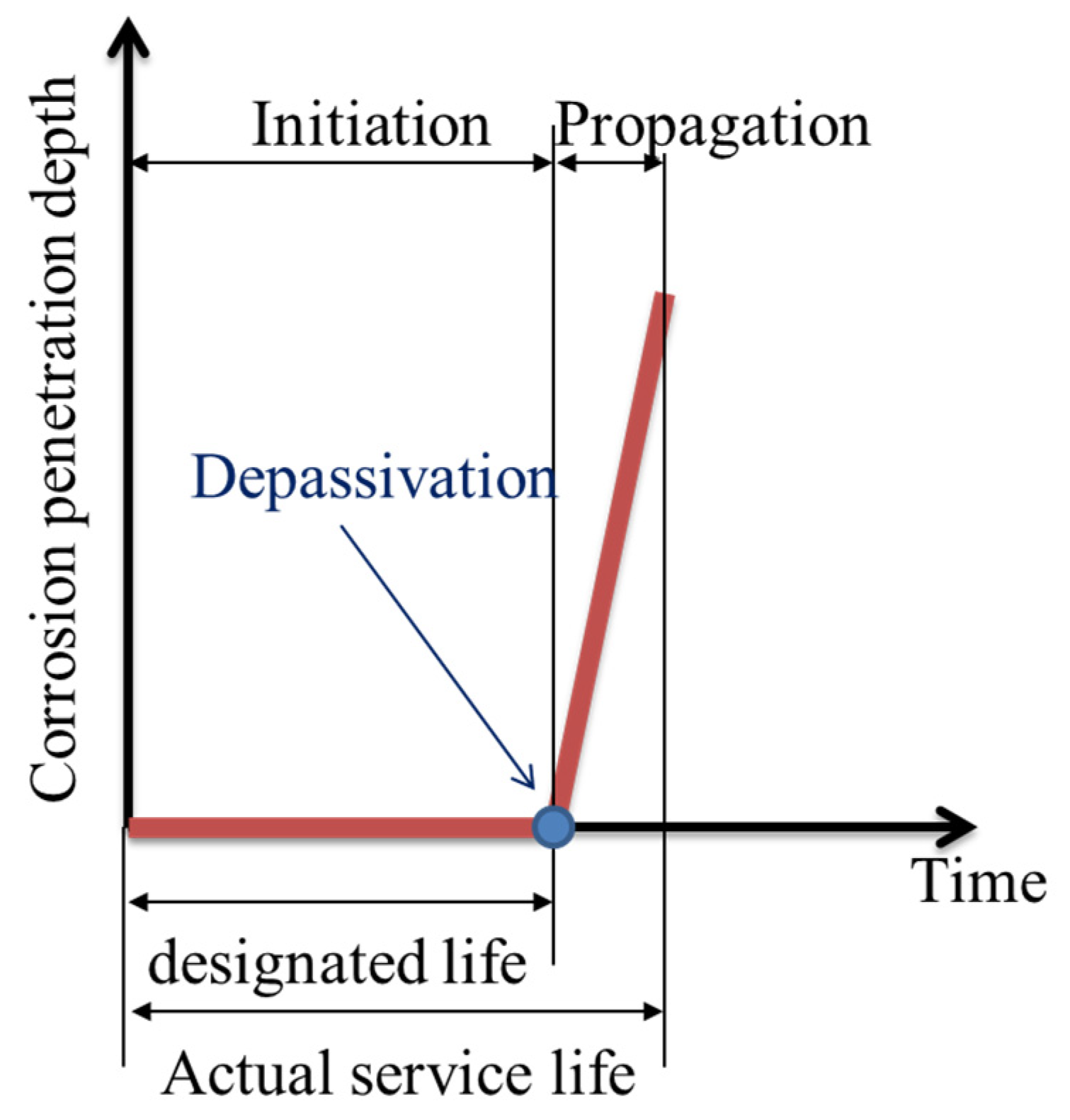
2.4. Depassivation
3. Results
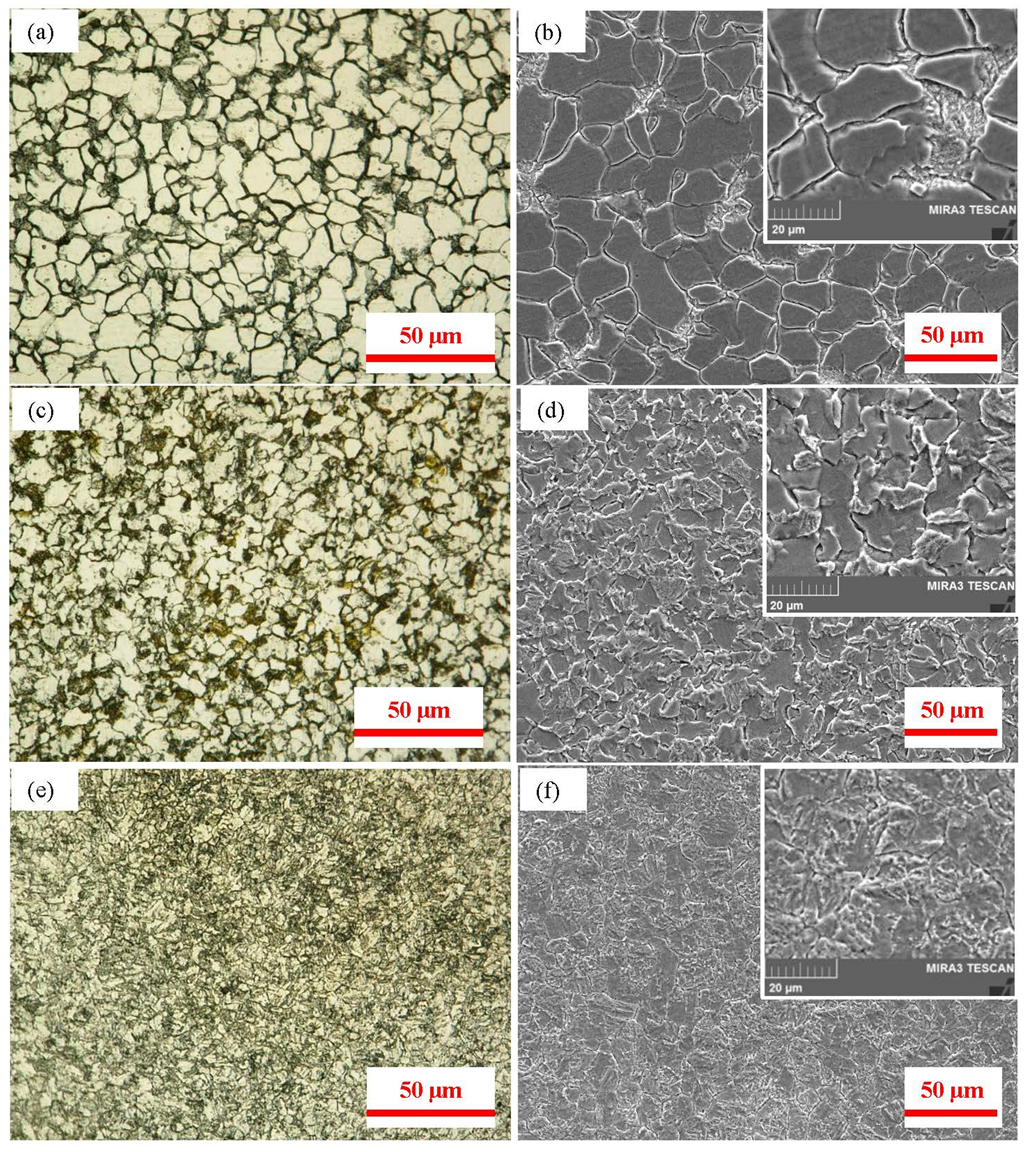
3.1. Microstructure and Phase Distribution
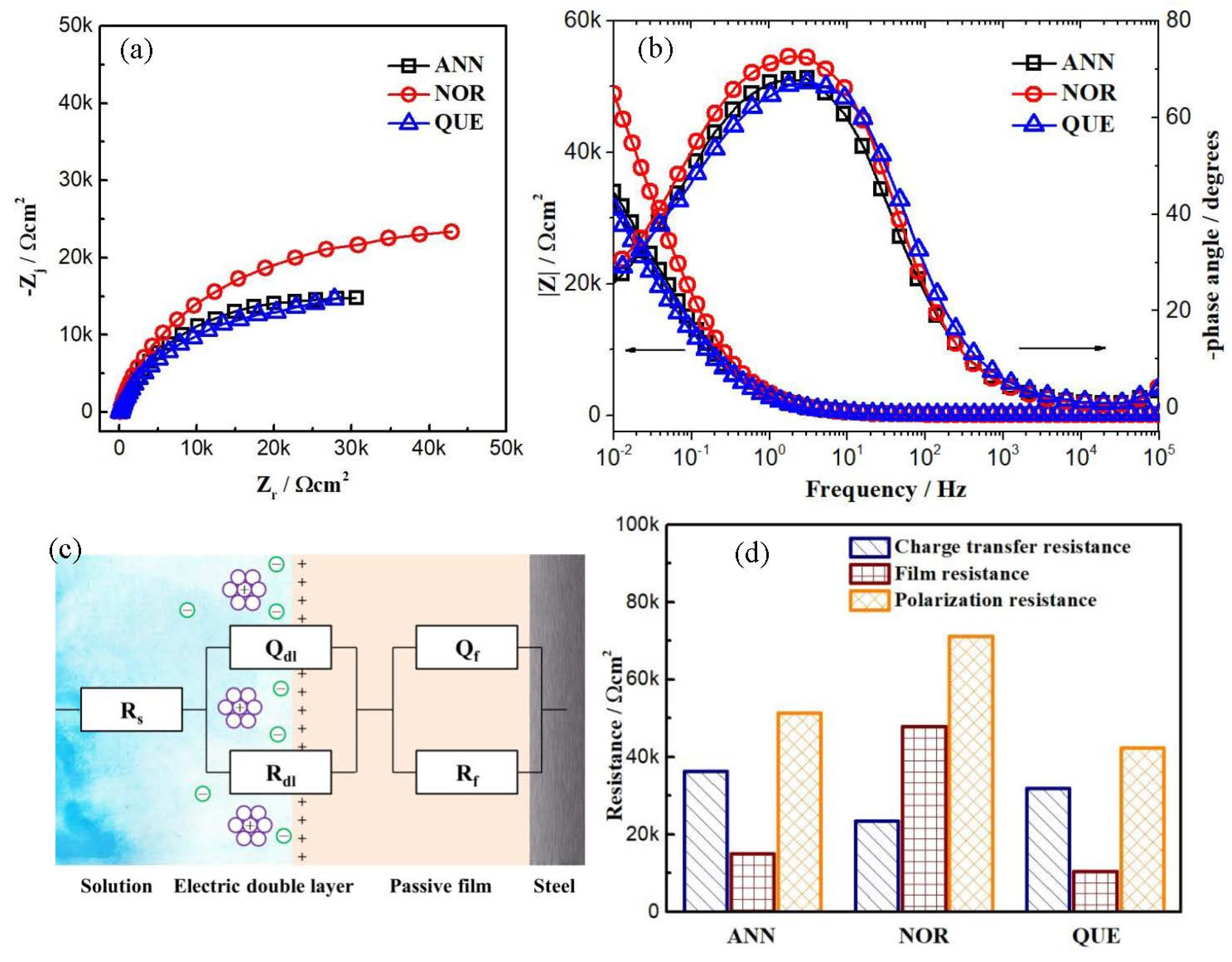
3.2. Passive Film
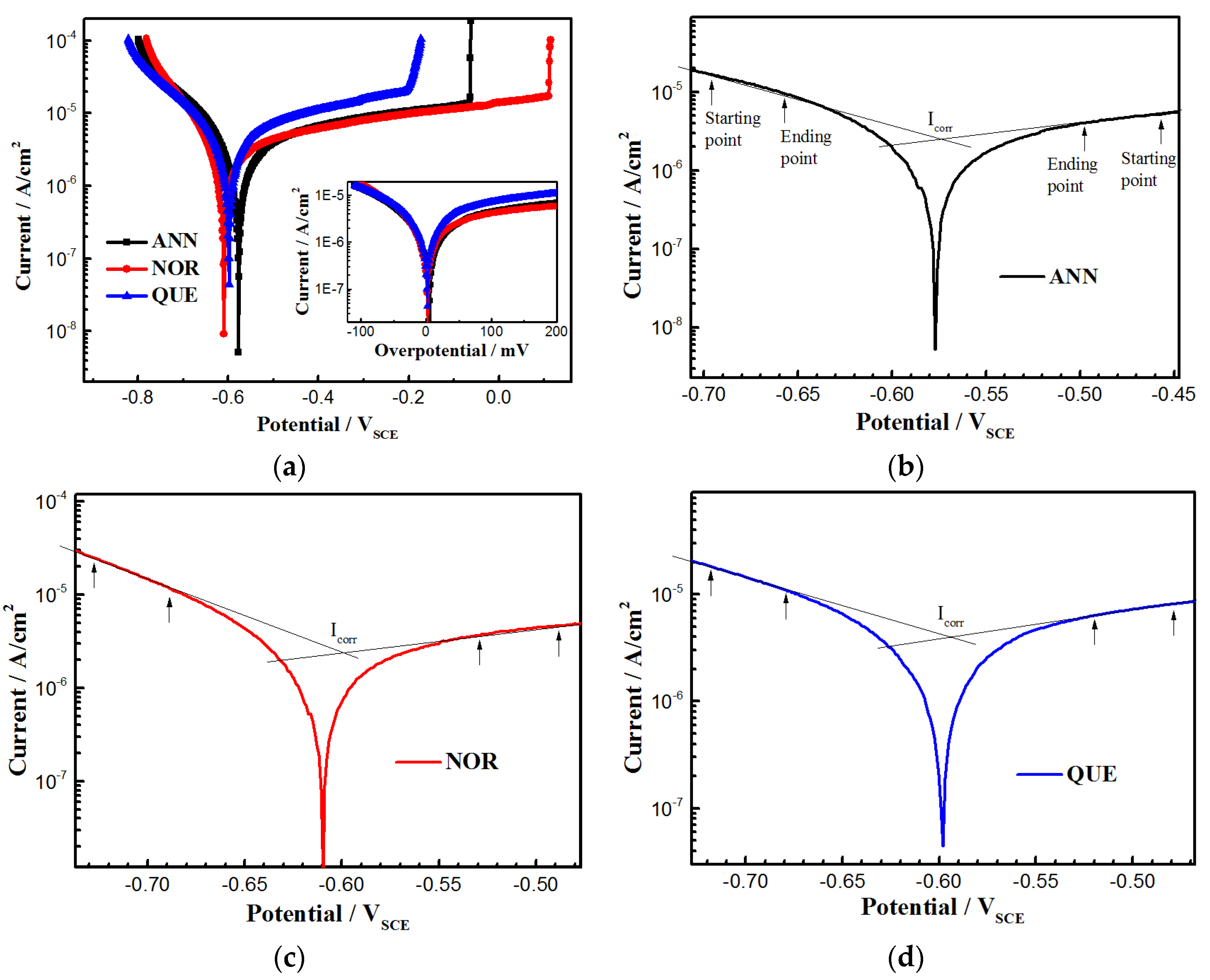
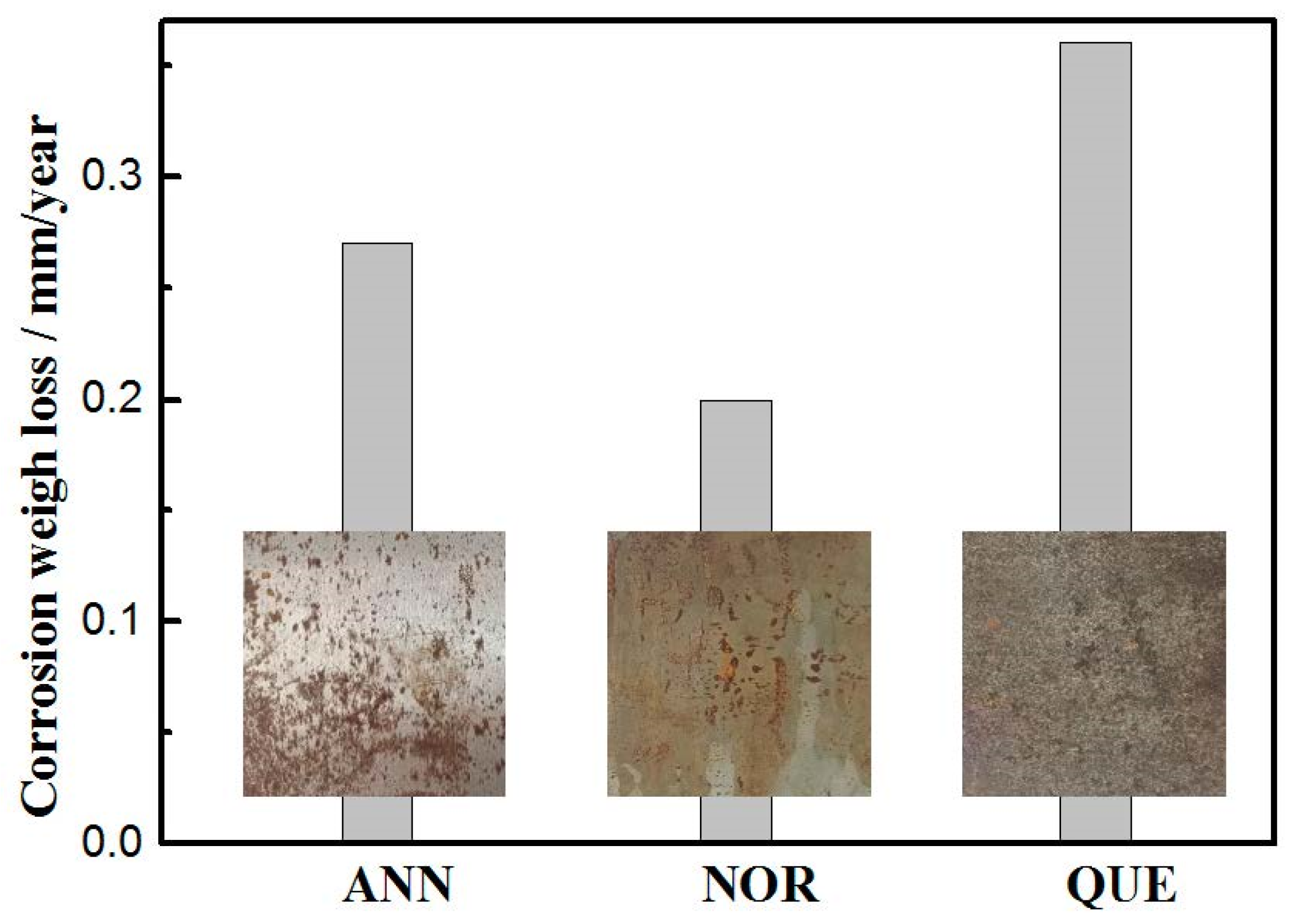
3.3. Depassivation and Corrosion
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Winslow, D.N. High-strength low-alloy, weathering, steel as reinforcement in the presence of chloride ions. Cem. Concr. Res. 1986, 16, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolini, L.; Elsener, B.; Pedeferri, P.; Redaelli, E.; Polder, R.B. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete; WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH and Co. KgaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Ming, J.; Wu, M.; Shi, J. Passive film modification by concrete carbonation: Re-visiting a corrosion-resistant steel with Cr and Mo. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2021, 123, 104178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ming, J.; Wu, M. Electrochemical behavior and corrosion products of Cr-modified reinforcing steels in saturated Ca (OH)2 solution with chlorides. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2020, 110, 103587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Pan, Y.; Li, J. Effect of Cr on the passive film formation mechanism of steel rebar in saturated calcium hydroxide solution. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, B. The performance of a 12% chromium steel in concrete in severe marine environments. Corros. Sci. 1993, 35, 1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, B. The use of 3CR12 as reinforcing in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 1993, 7, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Ming, J.; Wang, D.; Wu, M. Improved corrosion resistance of a new 6% Cr steel in simulated concrete pore solution contaminated by chlorides. Corros. Sci. 2020, 174, 108851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.J.; Zou, Y.; Ming, J.; Wu, M. Effect of DC stray current on electrochemical behavior of low-carbon steel and 10%Cr steel in saturated Ca(OH)2 solution. Corros. Sci. 2020, 169, 108610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammarullah, M.I.; Santoso, G.; Sugiharto, S.; Supriyono, T.; Kurdi, O.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Winarni, T.; Jamari, J. Tresca stress study of CoCrMo-on-CoCrMo bearings based on body mass index using 2D computational model. J. Tribol. 2022, 33, 31. [Google Scholar]
- Clover, D.; Kinsella, B.; Pejcic, B.; De Marco, R. The influence of microstructure on the corrosion rate of various carbon steels. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2005, 35, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Zhou, Y.; Dong, J.; He, X.; Ke, W. Effect of cementite spheroidization on improving corrosion resistance of pearlitic steel under simulated bottom plate environment of cargo oil tank. Materialia 2019, 6, 100316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.B.; Zhang, G.A.; Liu, W.; Lu, M.X. The formation mechanism of corrosion scale and electrochemical characteristic of low alloy steel in carbon dioxide-saturated solution. Corros. Sci. 2012, 57, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, B.; Li, W.; Luo, J.; Chiovelli, S. Pitting susceptibility of induction-quenched pipeline with microstructural heterogeneity. Mater. Sci. 2012, 47, 6823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.H.; Dong, J.H.; Etim, I.N.; Wei, J.; Ke, W. Sustained effect of remaining cementite on the corrosion behavior of ferrite-pearlite steel under the simulated bottom plate environment of cargo oil tank. Corros. Sci. 2016, 110, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.G.; Liu, W.; Fan, Y.M.; Fan, E.D.; Dong, B.J.; Zhang, T.Y.; Li, X.G. Effect of Cr content on the passivation behavior of Cr alloy steel in a CO2 aqueous environment containing silty sand. Corros. Sci. 2020, 168, 108591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralston, K.D.; Birbilis, N.; Davies, C.H.J. Revealing the relationship between grain size and corrosion rate of metals. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argade, G.R.; Panigrahi, S.K.; Mishra, R.S. Effects of grain size on the corrosion resistance of wrought magnesium alloys containing neodymium. Corros. Sci. 2012, 58, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzima, B.; Janeček, M.; Estrin, Y.; Kim, H.S. Microstructure and corrosion properties of ultrafine-grained interstitial free steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2007, 462, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.G.; Shen, C.B.; Long, K.; Zhang, T.; Wang, F.H.; Zhang, Z.D. The electrochemical corrosion of bulk nanocrystalline ingot iron in acidic sulfate solution. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Ma, L.; Cheng, X.; Li, X. Effect of grain size and crystallographic orientation on the corrosion behaviors of low alloy steel. Alloys Compd. 2021, 857, 158258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, P.K.; Shekhar, S.; Mondal, K. Development of gradient microstructure in mild steel and grain size dependence of its electrochemical response. Corros. Sci. 2018, 138, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Ma, A.; Jiang, J.; Jie, X. Effect of processing methods on microhardness and acid corrosion behavior of low-carbon steel. Mater. Des. 2015, 65, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novikov, V.F.; Sokolov, R.A.; Muratov, K.R.; Venediktov, A.N. Determination of influence of grain size factor on the corrosion speed of structural steel. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 38, 1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmezim, M.J.; Simoes, A.M.; Montemor, M.F.; Belo, M.D.C. Capacitance behaviour of passive films on ferritic and austenitic stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2005, 47, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hakiki, N.E.; Montemor, M.F.; Ferreira MG, S.; da Cunha Belo, M. Semiconducting properties of thermally grown oxide films on AISI 304 stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2000, 42, 687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, P.; Isgor, O.B.; Bensebaa, F.; Kingston, D. Angle-resolved XPS study of carbon steel passivity and chloride-induced depassivation in simulated concrete pore solution. Corros. Sci. 2012, 58, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Q.L.; Rondot, B.; Belo, M.D.C. Relations entre la structure electronique des films de passivation formes sur les aciers inoxydables et la susceptibilite de ces derniers a la corrosion par piqures. Chim. Sci. Mater. 1998, 23, 607. [Google Scholar]
- Betova, I.; Bojinov, M.; Karastoyanov, V.; Kinnunen, P.; Saario, T. Estimation of kinetic and transport parameters by quantitative evaluation of EIS and XPS data. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanna, S.; Seyeux, A.; Allion-Maurer, A.; Marcus, P. Escherichia coli siderophore-induced modification of passive films on stainless steel. Corros. Sci. 2020, 175, 108872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Feng, Z.; Zhang, L. Effect of high temperature on the corrosion behavior and passive film composition of 316 L stainless steel in high H2S-containing environments. Corros. Sci. 2020, 174, 108844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan-Rosado, G.; Pech-Canul, M.A. Influence of native oxide film age on the passivation of carbon steel in neutral aqueous solutions with a dicarboxylic acid. Corros. Sci. 2019, 153, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hu, J.; Ma, Y.W.; Guo, W.H.; Huang, H.L.; Wei, J.X.; Yin, S.H.; Yu, Q.J. Characterization of the passive film formed on the reinforcement surface in alkali activated fly ash: Surface analysis and electrochemical evaluation. Corros. Sci. 2020, 163, 108393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, B.; Neupane, S.; Wiame, F.; Seyeux, A.; Maurice, V.; Marcus, P. An XPS and ToF-SIMS study of the passive film formed on a model FeCrNiMo stainless steel surface in aqueous media after thermal pre-oxidation at ultra-low oxygen pressure. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 554, 149435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, M.; Gregori, J.; Alonso, C.; García-Jareño, J.J.; Takenouti, H.; Vicente, F. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy for studying passive layers on steel rebars immersed in alkaline solutions simulating concrete pores. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 7634. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.R.; Lu, M.X. Combined effect of pH and H2S on the structure of passive film formed on type 316L stainless steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 458, 686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, J.; Isgor, O.B. The effect of simulated concrete pore solution composition and chlorides on the electronic properties of passive films on carbon steel rebar. Corros. Sci. 2016, 106, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghods, P.; Isgor, O.B.; Carpenter GJ, C.; Li, J.; McRae, G.A.; Gu, G.P. Nano-scale study of passive films and chloride-induced depassivation of carbon steel rebar in simulated concrete pore solutions using FIB/TEM. Cem. Concr. Res. 2013, 47, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, G.; Bautista, A.; Takenouti, H. EIS study of passivation of austenitic and duplex stainless steels reinforcements in simulated pore solutions. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2006, 28, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freire, L.; Carmezim, M.J.; Ferreira, M.A.; Montemor, M.F. The passive behaviour of AISI 316 in alkaline media and the effect of pH: A combined electrochemical and analytical study. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 6174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joiret, S.; Keddam, M.; Nóvoa, X.R.; Pérez, M.C.; Rangel, C.; Takenouti, H. Use of EIS, ring-disk electrode, EQCM and Raman spectroscopy to study the film of oxides formed on iron in 1 M NaOH. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2002, 24, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.Z.; Jiang, L.H.; Li, S.S. Effect of limestone powder addition on threshold chloride concentration for steel corrosion in reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2020, 131, 106018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammarullah, M.I.; Afif, I.Y.; Maula, M.I.; Winarni, T.I.; Tauviqirrahman, M.; Akbar, I.; Basri, H.; van der Heide, E.; Jamari, J. Tresca stress simulation of metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty during normal walking activity. Materials 2021, 14, 7554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, R.C.; Miller, M.K. Carbide precipitation in martensite during the early stages of tempering Cr- andMo-containing low alloy steels. Acta Mater. 1998, 46, 2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


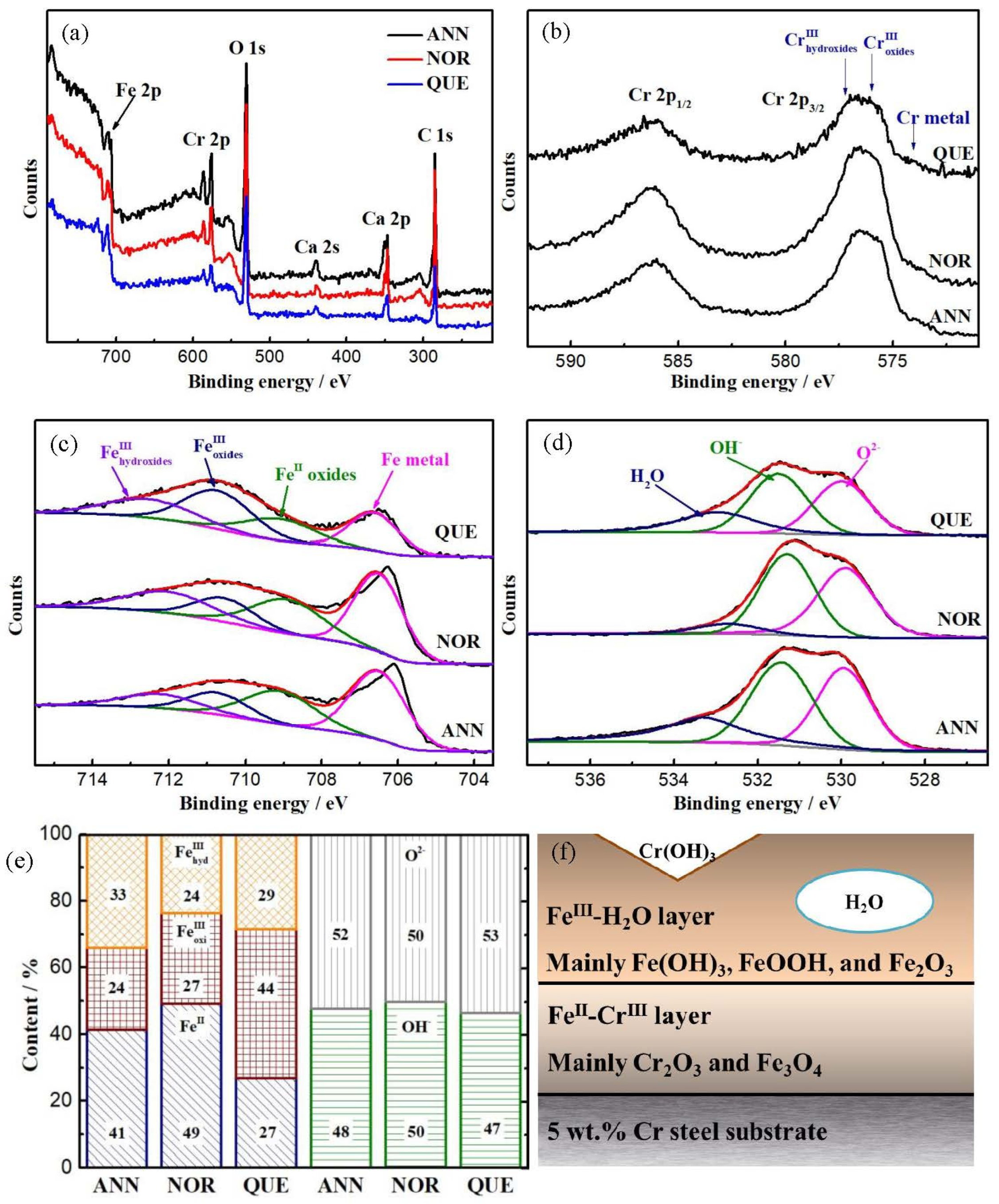


| Fe 2p | Assignment | Fe Metal | FeII | FeIII in Oxides | FeIII in Hydroxides |
| Binding energy/eV | 706.9 ± 0.3 | 709.2 ± 0.3 | 711.0 ± 0.3 | 712.7 ± 0.3 | |
| FWHM/eV | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 2 ± 0.2 | 2 ± 0.2 | 2.5 ± 0.2 | |
| O 1s | Assignment | O2− | OH− | H2O | -- |
| Binding energy/eV | 530.2 ± 0.3 | 531.4 ± 0.3 | 533 ± 0.3 | -- | |
| FWHM/eV | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 1.5 ± 0.2 | 2 ± 0.2 | -- |
| Sample | Slope1 | Slope2 | Donor Density, cm−3 | Flatband Potential, mVSCE | Thickness, nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANN | 5.02 ± 0.09 × 109 | 9.87 ± 0.04 × 109 | 1.15 ± 0.01 × 1021 | −608 ± 3 | 0.869 ± 0.08 |
| NOR | 13.5 ± 0.03 × 109 | 33.0 ± 0.04 × 109 | 0.51 ± 0.01 × 1021 | −773 ± 8 | 1.553 ± 0.03 |
| QUE | 5.74 ± 0.10 × 109 | 11.3 ± 0.11 × 109 | 1.00 ± 0.06 × 1021 | −638 ± 17 | 0.926 ± 0.09 |
| Sample | Rs Ωcm2 | Qdl Fcm−2sn−1 | ndl sn | Rdl Ωcm2 | Qf Fcm−2sn−1 | nf sn | Rf Ωcm2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANN | 118 ± 23 | 2.50 ± 0.08 × 10−4 | 0.77 | 3.64 ± 0.07 × 106 | 1.12 ± 0.02 × 10−4 | 0.85 | 1.50 ± 0.09 × 104 |
| NOR | 112 ± 10 | 7.97 ± 0.01 × 10−4 | 0.87 | 2.35 ± 0.01 × 106 | 2.54 ± 0.05 × 10−4 | 0.88 | 4.78 ± 0.03 × 104 |
| QUE | 90 ± 17 | 2.42 ± 0.14 × 10−4 | 0.83 | 3.19 ± 0.10 × 106 | 1.07 ± 0.02 × 10−4 | 0.83 | 1.05 ± 0.11 × 104 |
| Sample | Ecorr mVSCE | Epit mVSCE | βc mV/dec | βa mV/dec | Icorr μAcm−2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANN | −580 ± 5 | −70 ± 21 | 161.85 ± 6.38 | 386.86 ± 1.02 | 2.72 ± 0.05 |
| NOR | −610 ± 10 | 110 ± 6 | 120.77 ± 9.51 | 410.9 ± 7.55 | 2.44 ± 0.10 |
| QUE | −600 ± 8 | −200 ± 37 | 176.46 ± 9.77 | 376.19 ± 6.90 | 3.92 ± 0.07 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, Y.; Wen, C.; Xi, X.; Yang, D.; Deng, P. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Passive Film and Depassivation Behavior of Cr-Bearing Steel Reinforcement in an Alkaline Environment. Coatings 2023, 13, 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050964
Tian Y, Wen C, Xi X, Yang D, Deng P. Effect of Heat Treatment on the Passive Film and Depassivation Behavior of Cr-Bearing Steel Reinforcement in an Alkaline Environment. Coatings. 2023; 13(5):964. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050964
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Yuwan, Cheng Wen, Xiaohui Xi, Deyue Yang, and Peichang Deng. 2023. "Effect of Heat Treatment on the Passive Film and Depassivation Behavior of Cr-Bearing Steel Reinforcement in an Alkaline Environment" Coatings 13, no. 5: 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050964
APA StyleTian, Y., Wen, C., Xi, X., Yang, D., & Deng, P. (2023). Effect of Heat Treatment on the Passive Film and Depassivation Behavior of Cr-Bearing Steel Reinforcement in an Alkaline Environment. Coatings, 13(5), 964. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050964