Comparison of Tribological Characteristics of AA2024 Coated by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) Sealed by Different sol–gel Layers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
- (a)
- 2.5 N load, 1200 s (20 min) sliding duration, 60 m distance;
- (b)
- 3 N load, 2400 s sliding duration, 120 m distance.
3. Results and Discussion
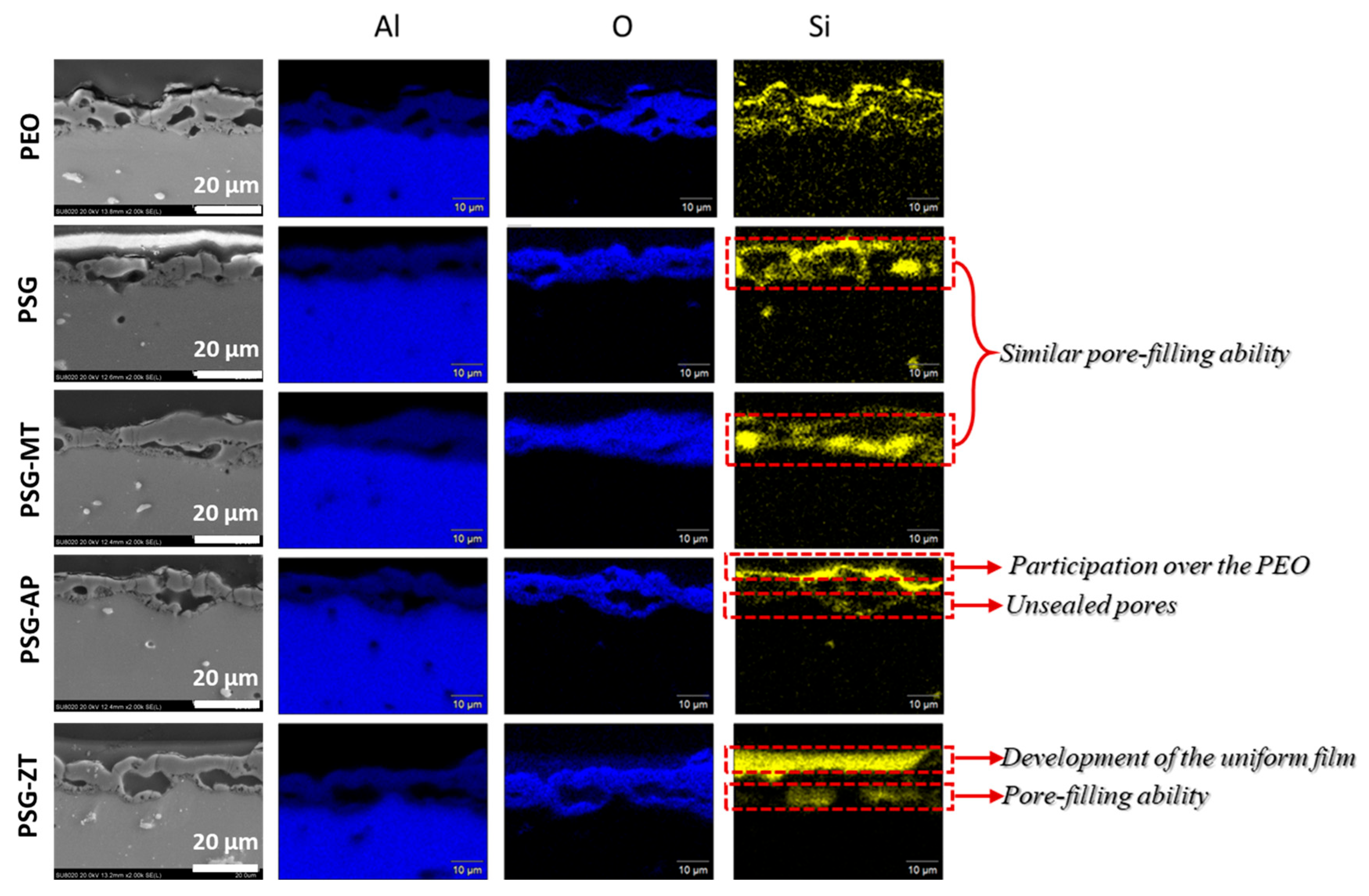
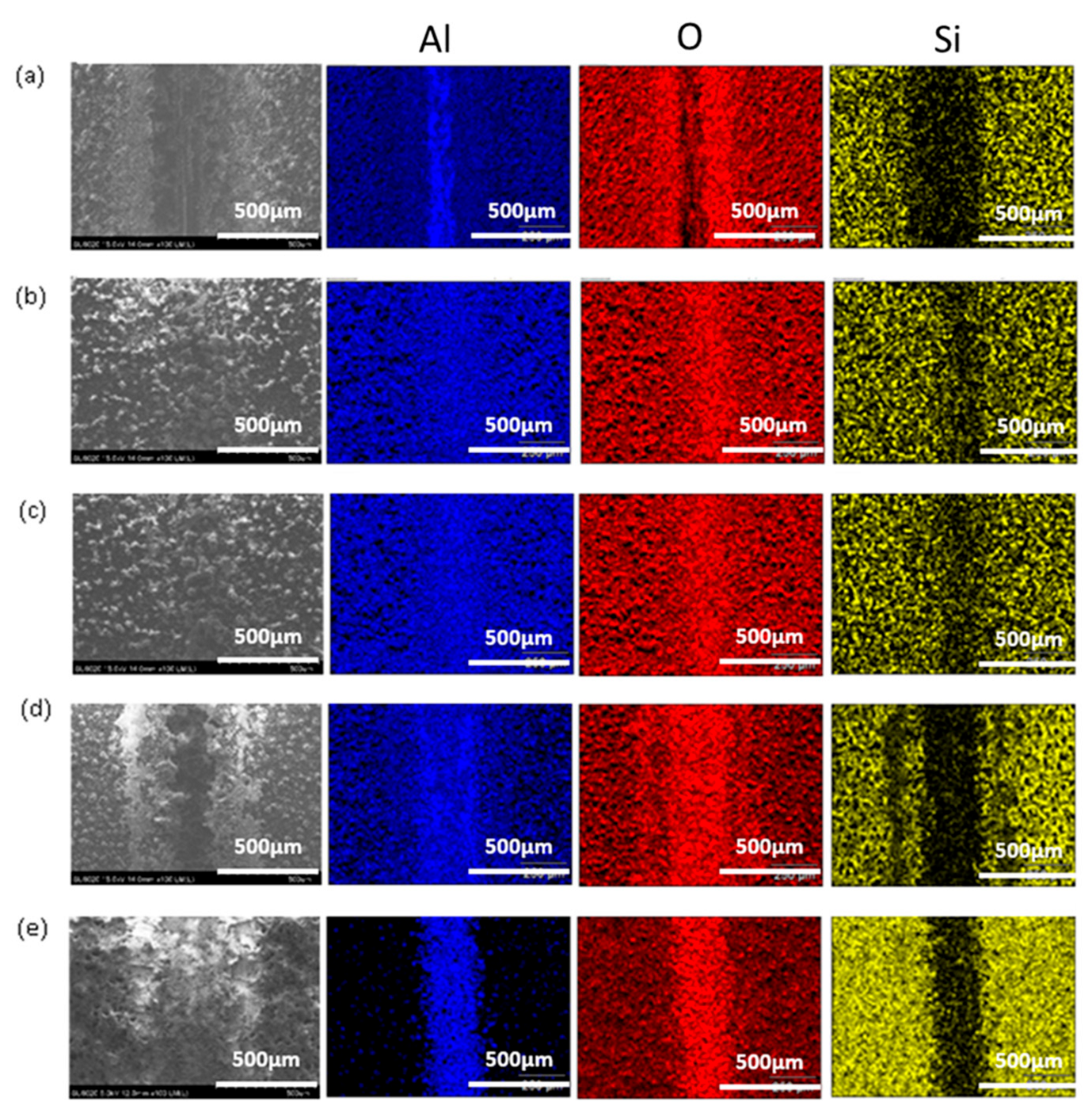
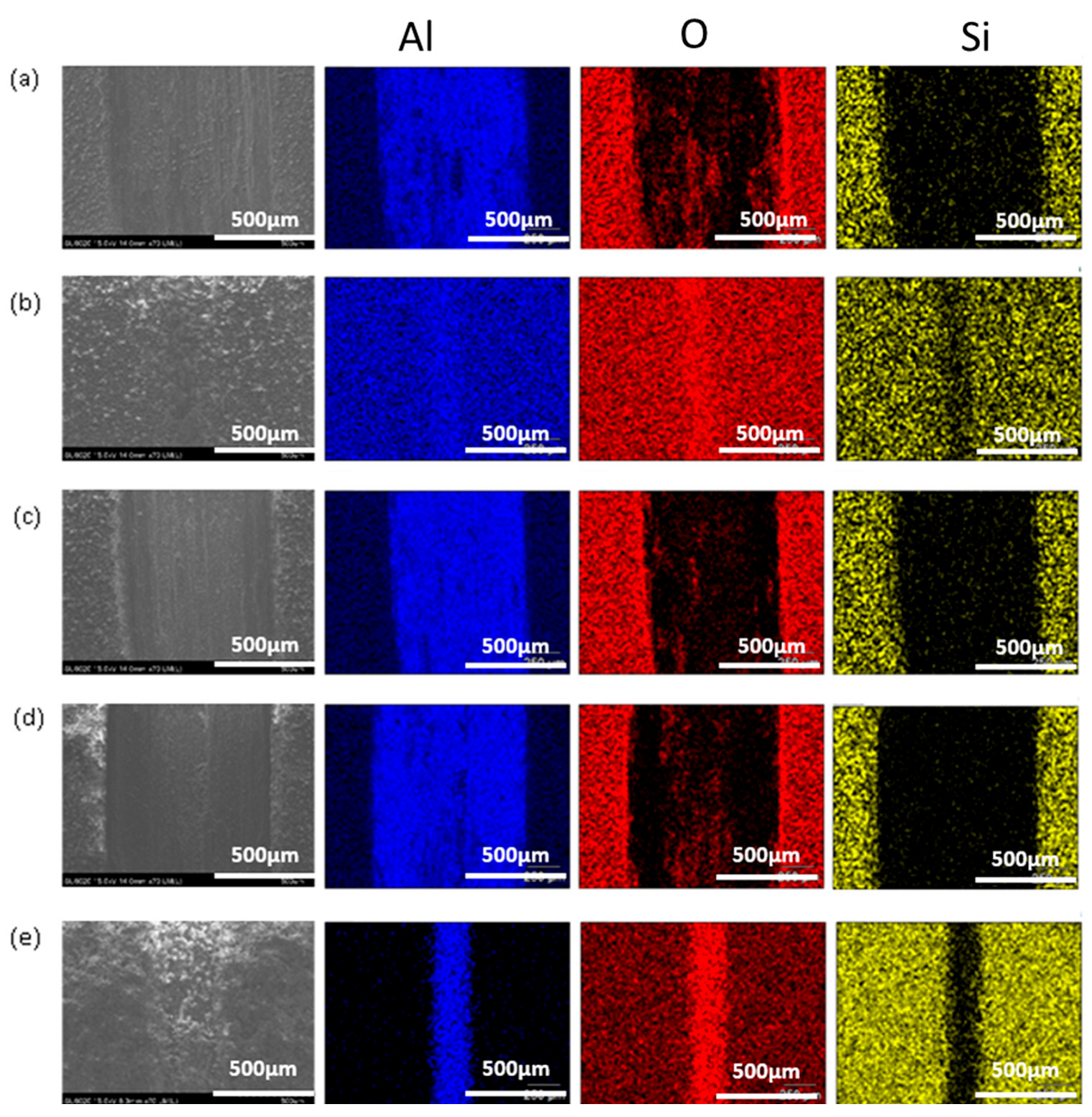
3.1. SEM Analysis
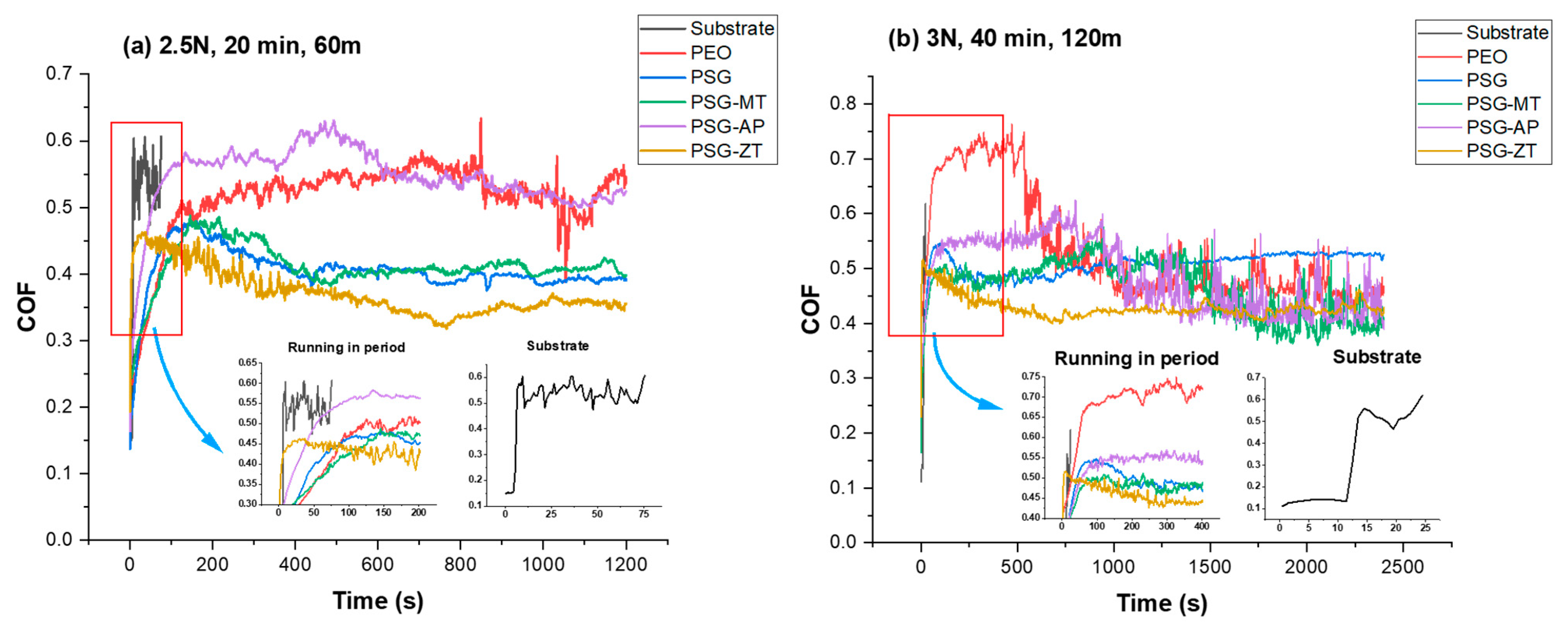
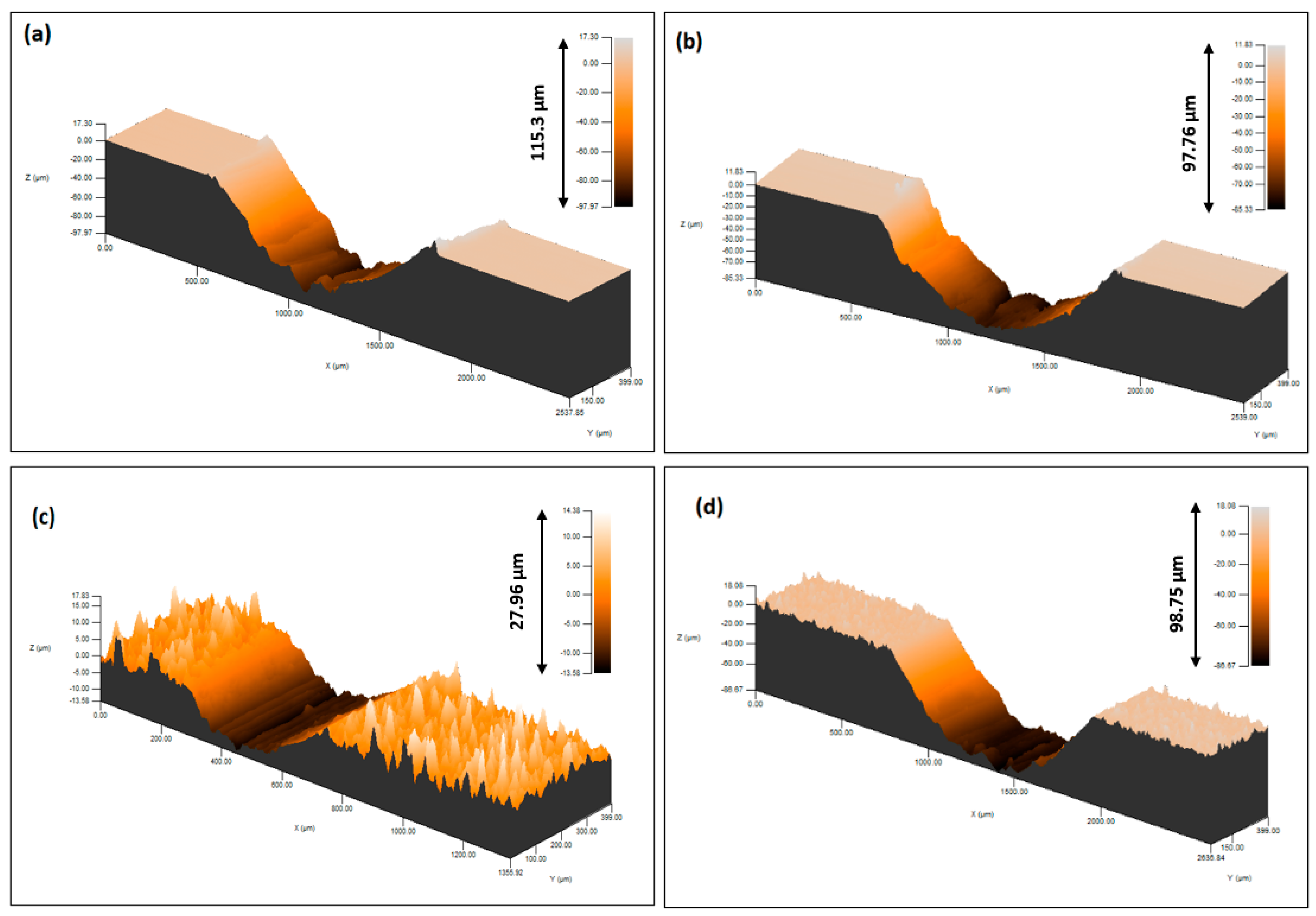
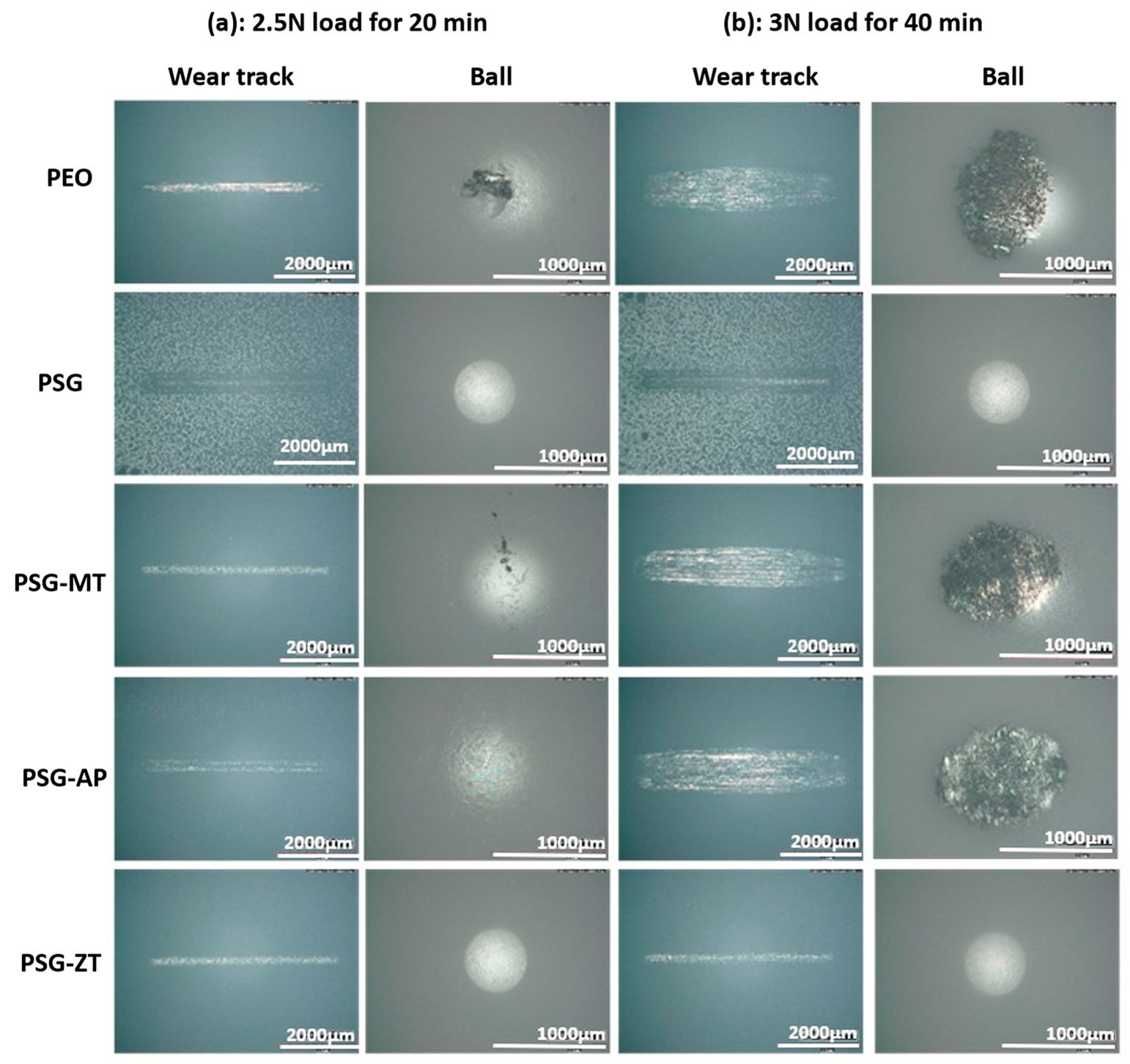
3.2. Tribological Evaluation
4. Conclusions
- -
- The average COF values in the steady-state range for Case (a) (2.5 N and 20 min) and Case (b) (3 N and 40 min) are, respectively, followed as 0.53 and NA for PEO, 0.41 and 0.49 for PSG, 0.40 and 0.50 for PSG−MT, 0.55 and 0.55 for PSG−AP, and 0.34 and 0.43 for PSG−ZT.
- -
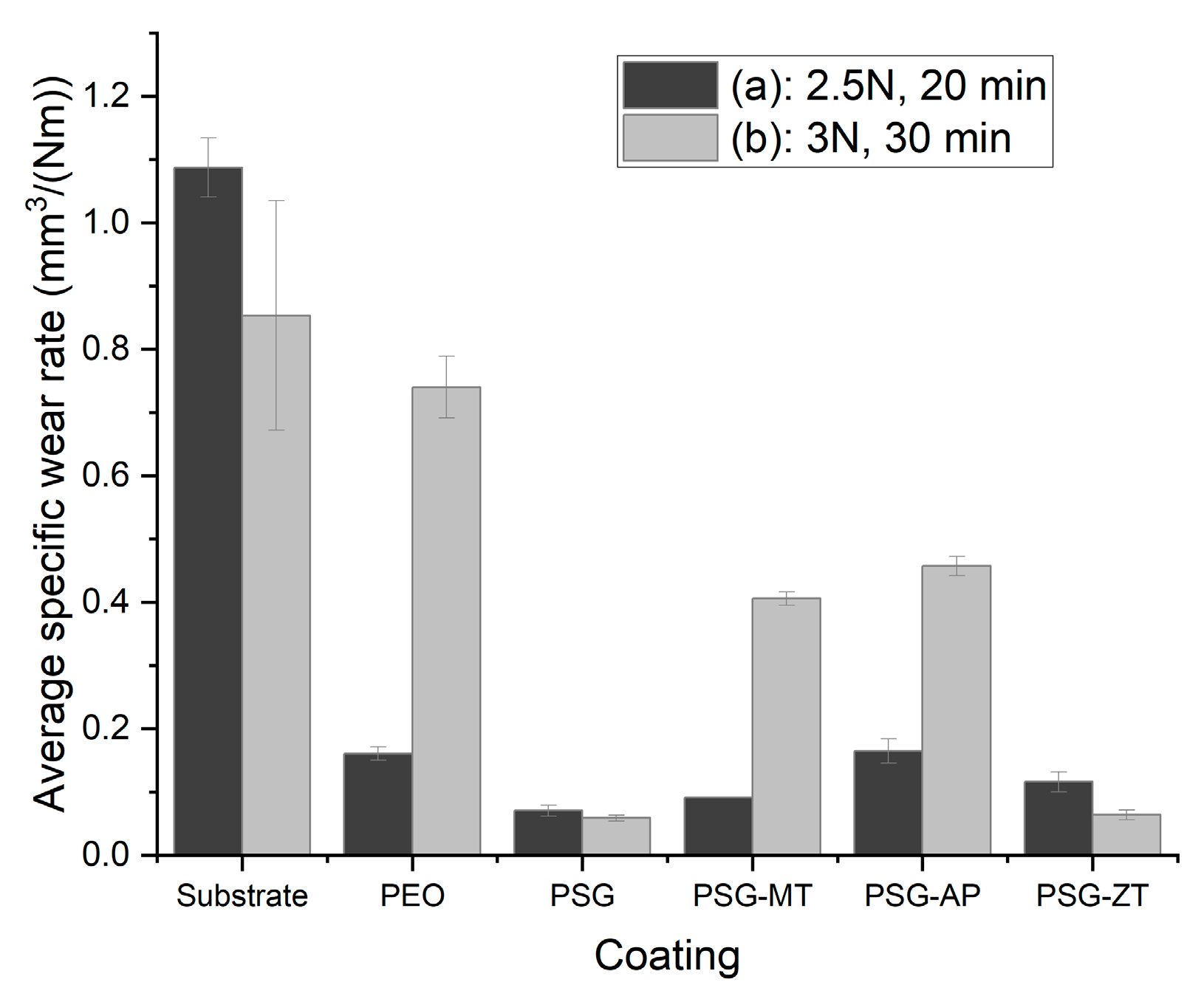
- The average specific wear rate in 3 N load for the 40 min condition was 0.74016, 0.05883, 0.40587, 0.45725, and 0.06379 mm3/(Nm), for PEO, PSG, PSG−MT, PSG−AP, and PSG−ZT, respectively.
- -
- The presence of GPTMS along with TEOS in PSG has created a dense sol–gel network in the PEO structure that has a good penetrative ability to seal the PEO layer resulting in a low COF and wear loss volume. Similarly, PSG−ZT, due to a higher sol–gel content, exhibited the same behavior. In fact, the more the hydrolyzed groups inside of a sol–gel network, the more opportunity for either the network formation or chemical adsorption of a sol–gel cluster to the PEO layer. The addition of MTES to the sol–gel formulation brought about a lower number of hydrolyzed groups possessing an un-hydrolyzed methyl functional group. Not only was the compactness of the PSG coating higher than that of PSG−MT but also its wettability, leading to the creation of more chemical bonds to the oxide groups over the PEO sample. For the PSG−ZT formulation, a high content of sol–gel precursors were utilized, which, interestingly, resulted in the formation of a dense layer over the PEO along with pore-filling ability. Hence, one could expect that, even though a high content of organic compounds was employed to obtain PSG−ZT, the wettability could be comparable with PSG.
- -
- On the higher loads for PSG and PSG−ZT, they showed lesser wear due to the structure of the sol–gel layer being pushed together and aligning in the direction of sliding, giving lubricating characteristics to the surface.
- -
- Moreover, the relatively low amount of wear debris in PSG and PSG−ZT with no material transfer to the counter body is indicative of the improved compactness of the coating and adhesion of the coating. Supporting EDS color maps through the SEM analysis shows the presence of sol–gel constituents in the wear tracks after the test.
- -
- PSG−MT and PSG−AP are rendered inefficient to enhance the mechanical properties of the coatings, especially in severe conditions (Case (b)). In the case of PSG−AP, the insufficient sealing ability and the configuration of the hydrophilic amine group over the PEO sample could be the reason for such behavior. In any case, sol–gel-treated PEO layers have shown tremendous improvement in tribological properties compared to untreated samples.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tlili, B.; Barkaoui, A.; Walock, M. Tribology and Wear Resistance of the Stainless Steel. The sol–gel Coating Impact on the Friction and Damage. Tribol. Int. 2016, 102, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çam, S.; Demir, V.; Özyürek, D. Wear Behaviour of A356/TiAl3 in Situ Composites Produced by Mechanical Alloying. Metals 2016, 6, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, R.G. Mechanical and Textured Finishes in Surface Treatment and Finishing of Aluminium; Chapter 1; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1988; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Mora-Sanchez, H.; del Olmo, R.; Rams, J.; Torres, B.; Mohedano, M.; Matykina, E.; Arrabal, R. Hard Anodizing and Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of an Additively Manufactured Al-Si Alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 420, 127339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Nie, X.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A.; Dowey, S.J. Plasma Electrolysis for Surface Engineering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 122, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakoch, A.G.; Bardin, I.V.; Kovalev, V.L.; Avanesyan, T.G. Microarc Oxidation of Light Constructional Alloys: Part 1. Main Notions on the Microarc Oxidation of Light Constructional Alloys. Russ. J. Non-Ferr. Met. 2013, 54, 341–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielage, B.; Alisch, G.; Lampke, T.; Nickel, D. Anodizing—A Key for Surface Treatment of Aluminium. Key Eng. Mater. 2008, 384, 263–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohedano, M.; Lu, X.; Matykina, E.; Blawert, C.; Arrabal, R.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) of Metals and Alloys. In Encyclopedia of Interfacial Chemistry-Surface Science and Electrochemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 6, pp. 423–438. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, M.H.; Cai, Z.B.; Lin, X.Z.; Ren, P.D.; Tan, J.; Zhou, Z.R. Fretting Wear Behaviour of Ceramic Coating Prepared by Micro-Arc Oxidation on Al–Si Alloy. Wear 2007, 263, 472–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treviño, M.; Mercado-Solis, R.D.; Colás, R.; Pérez, A.; Talamantes, J.; Velasco, A. Erosive Wear of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Layers on Aluminium Alloy 6061. Wear 2013, 301, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curran, J.A.; Clyne, T.W. Thermo-Physical Properties of Plasma Electrolytic Oxide Coatings on Aluminium. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 199, 168–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, B.L.; Wang, Y.M. Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Treatment of Aluminium and Titanium Alloys. In Surface Engineering of Light Alloys; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2010; pp. 110–154. [Google Scholar]
- Hussein, R.O.; Zhang, P.; Nie, X.; Xia, Y.; Northwood, D.O. The Effect of Current Mode and Discharge Type on the Corrosion Resistance of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) Coated Magnesium Alloy AJ62. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 1990–1997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molaeipour, P.; Allahkaram, S.R.; Akbarzadeh, S. Corrosion Inhibition of Ti6Al4V Alloy by a Protective Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Coating Modified with Boron Carbide Nanoparticles. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 430, 127987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matykina, E.; Arrabal, R.; Skeldon, P.; Thompson, G.E.; Belenguer, P. AC PEO of Aluminium with Porous Alumina Precursor Films. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Deng, Z.; Chen, R.; Zhang, T. Growth Regularity of Ceramic Coatings Formed by Microarc Oxidation on Al–Cu–Mg Alloy. Thin Solid Films 2000, 372, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, R.H.U.; Yerokhin, A.L.; Pilkington, T.; Leyland, A.; Matthews, A. Residual Stresses in Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Coatings on Al Alloy Produced by Pulsed Unipolar Current. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2005, 200, 1580–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guangliang, Y.; Xianyi, L.; Yizhen, B.; Haifeng, C.; Zengsun, J. The Effects of Current Density on the Phase Composition and Microstructure Properties of Micro-Arc Oxidation Coating. J. Alloys Compd. 2002, 345, 196–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerokhin, A.L.; Snizhko, L.O.; Gurevina, N.L.; Leyland, A.; Pilkington, A.; Matthews, A. Discharge Characterization in Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of Aluminium. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2003, 36, 2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehnavi, V.; Liu, X.Y.; Luan, B.L.; Shoesmith, D.W.; Rohani, S. Phase Transformation in Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Coatings on 6061 Aluminum Alloy. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 251, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutsaylyuk, V.; Student, M.; Posuvailo, V.; Student, O.; Hvozdets’kyi, V.; Maruschak, P.; Zakiev, V. The Role of Hydrogen in the Formation of Oxide-Ceramic Layers on Aluminum Alloys during Their Plasma-Electrolytic Oxidation. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2021, 14, 1682–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troughton, S.C.; Nominé, A.; Dean, J.; Clyne, T.W. Effect of Individual Discharge Cascades on the Microstructure of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 260–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, L.; Qi, J.; Chen, F. Corrosion Protection of Ti6Al4V by a Composite Coating with a Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Layer and sol–gel Layer Filled with Graphene Oxide. Prog. Org. Coat. 2020, 144, 105632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toorani, M.; Aliofkhazraei, M. Review of Electrochemical Properties of Hybrid Coating Systems on Mg with Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation Process as Pretreatment. Surf. Interfaces 2019, 14, 262–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javidi, M.; Fadaee, H. Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of 2024-T3 Aluminum Alloy and Investigation on Microstructure and Wear Behavior. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 286, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasconcelos, D.C.L.; Carvalho, J.A.N.; Mantel, M.; Vasconcelos, W.L. Corrosion Resistance of Stainless Steel Coated with sol–gel Silica. J. Non. Cryst. Solids 2000, 273, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenzi, P.; Esposto, M.; Maddalena, A. Mechanical Properties of 3-Glycidoxypropyltrimethoxysilane Based Hybrid Organic-Inorganic Materials. J. sol–gel Sci. Technol. 2001, 20, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sopchenski, L.; Robert, J.; Touzin, M.; Tricoteaux, A.; Olivier, M.G. Improvement of Wear and Corrosion Protection of PEO on AA2024 via sol–gel Sealing. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2021, 417, 127195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, S.; Sopchenski Santos, L.; Vitry, V.; Paint, Y.; Olivier, M.G. Improvement of the Corrosion Performance of AA2024 Alloy by a Duplex PEO/Clay Modified sol–gel Nanocomposite Coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 434, 128168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balgude, D.; Sabnis, A. sol–gel Derived Hybrid Coatings as an Environment Friendly Surface Treatment for Corrosion Protection of Metals and Their Alloys. J. sol–gel Sci. Technol. 2012, 64, 124–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Ooij, W.J.; Zhu, D.; Stacy, M.; Seth, A.; Mugada, T.; Gandhi, J.; Puomi, P. Corrosion Protection Properties of Organofunctional Silanes—An Overview. Tsinghua Sci. Technol. 2005, 10, 639–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, S.; Paint, Y.; Olivier, M.-G. A Comparative Study of Different sol–gel Coatings for Sealing the Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) Layer on AA2024 Alloy. Electrochim. Acta 2023, 443, 141930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deflorian, F.; Rossi, S.; Fedrizzi, L. Silane Pre-Treatments on Copper and Aluminium. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 6097–6103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Innocenzi, P.; Abdirashid, M.O.; Guglielmi, M. Structure and Properties of sol–gel Coatings from Methyltriethoxysilane and Tetraethoxysilane. J. sol–gel Sci. Technol. 1994, 3, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.J.; Damron, M.; Tang, G.; Zheng, H.; Chu, C.J.; Osborne, J.H. Inorganic/Organic Hybrid Coatings for Aircraft Aluminum Alloy Substrates. Prog. Org. Coatings 2001, 41, 226–232. [Google Scholar]
- Rodič, P.; Mertelj, A.; Borovšak, M.; Benčan, A.; Mihailović, D.; Malič, B.; Milošev, I. Composition, Structure and Morphology of Hybrid Acrylate-Based sol–gel Coatings Containing Si and Zr Composed for Protective Applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 286, 388–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sieber, M.; Simchen, F.; Morgenstern, R.; Scharf, I.; Lampke, T. Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation of High-Strength Aluminium Alloys—Substrate Effect on Wear and Corrosion Performance. Metals 2018, 8, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasirivatan, H.; Kahrizsangi, R.E.; Asgarani, M.K. Tribological Performance of PEO-WC Nanocomposite Coating on Mg Alloys Deposited by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation. Tribol. Int. 2016, 98, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdechnova, M.; Mohedano, M.; Kuznetsov, B.; Mendis, C.L.; Starykevich, M.; Karpushenkov, S.; Tedim, J.; Ferreira, M.G.S.; Blawert, C.; Zheludkevich, M.L. PEO Coatings with Active Protection Based on In-Situ Formed LDH-Nanocontainers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2017, 164, C36–C45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Jiancheng, D.U.; Xiaoling, W.U.; Lai, Y. Tribological Behavior of Microarc Oxidation Coatings on Aluminum Alloy. ISIJ Int. 2006, 46, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzato, L.; Rigon, M.; Martucci, A.; Brunelli, K.; Dabalà, M. Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) as Pre-Treatment for sol–gel Coating on Aluminum and Magnesium Alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 366, 114–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhopadhyay, A.K.; Chakraborty, D.; Swain, M.V.; Mai, Y.W. Scratch Deformation Behaviour of Alumina under a Sharp Indenter. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 1997, 17, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Untreated AA2024 | PEO Treated | PEO + SG (TEOS + GPTMS) | PEO + SG-MT (TEOS + GPTMS + MTES) | PEO + SG-AP (TEOS + APTES) | PEO + SG-ZT (ZTP + MAPTMS + TEOS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Substrate | PEO | PSG | PSG-MT | PSG-AP | PSG-ZT |
| Average COF | PEO | PSG | PSG-MT | PSG-AP | PSG-ZT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ra | 1.7 | 1.3 | 1.3 | 1.2 | 0.2 |
| Rz | 11.3 | 8.9 | 9.2 | 6.4 | 0.9 |
| Average COF | Substrate | PEO | PSG | PSG-MT | PSG-AP | PSG-ZT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case (a) 2.5 N, 20 min | NA | 0.53 | 0.41 | 0.40 | 0.55 | 0.34 |
| Case (b) 3 N, 40 min | NA | NA | 0.49 | 0.50 | 0.55 | 0.43 |
| Average Specific Wear Rate mm3/(Nm) | Substrate | PEO | PSG | PSG-MT | PSG-AP | PSG-ZT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Case (a) | 1.08728 | 0.16073 | 0.07049 | 0.09131 | 0.16482 | 0.11602 |
| Case (b) | 0.85314 | 0.74016 | 0.05883 | 0.40587 | 0.45725 | 0.06379 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Khalid, H.A.; Akbarzadeh, S.; Paint, Y.; Vitry, V.; Olivier, M.-G. Comparison of Tribological Characteristics of AA2024 Coated by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) Sealed by Different sol–gel Layers. Coatings 2023, 13, 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050871
Khalid HA, Akbarzadeh S, Paint Y, Vitry V, Olivier M-G. Comparison of Tribological Characteristics of AA2024 Coated by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) Sealed by Different sol–gel Layers. Coatings. 2023; 13(5):871. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050871
Chicago/Turabian StyleKhalid, Hafiza Ayesha, Sajjad Akbarzadeh, Yoann Paint, Véronique Vitry, and Marie-Georges Olivier. 2023. "Comparison of Tribological Characteristics of AA2024 Coated by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) Sealed by Different sol–gel Layers" Coatings 13, no. 5: 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050871
APA StyleKhalid, H. A., Akbarzadeh, S., Paint, Y., Vitry, V., & Olivier, M.-G. (2023). Comparison of Tribological Characteristics of AA2024 Coated by Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) Sealed by Different sol–gel Layers. Coatings, 13(5), 871. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13050871








