Induced Codeposition of Tungsten with Zinc from Aqueous Citrate Electrolytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Development of Stable Baths for Electrodeposition of Zn–W Alloys
3.2. Steady-State Behavior
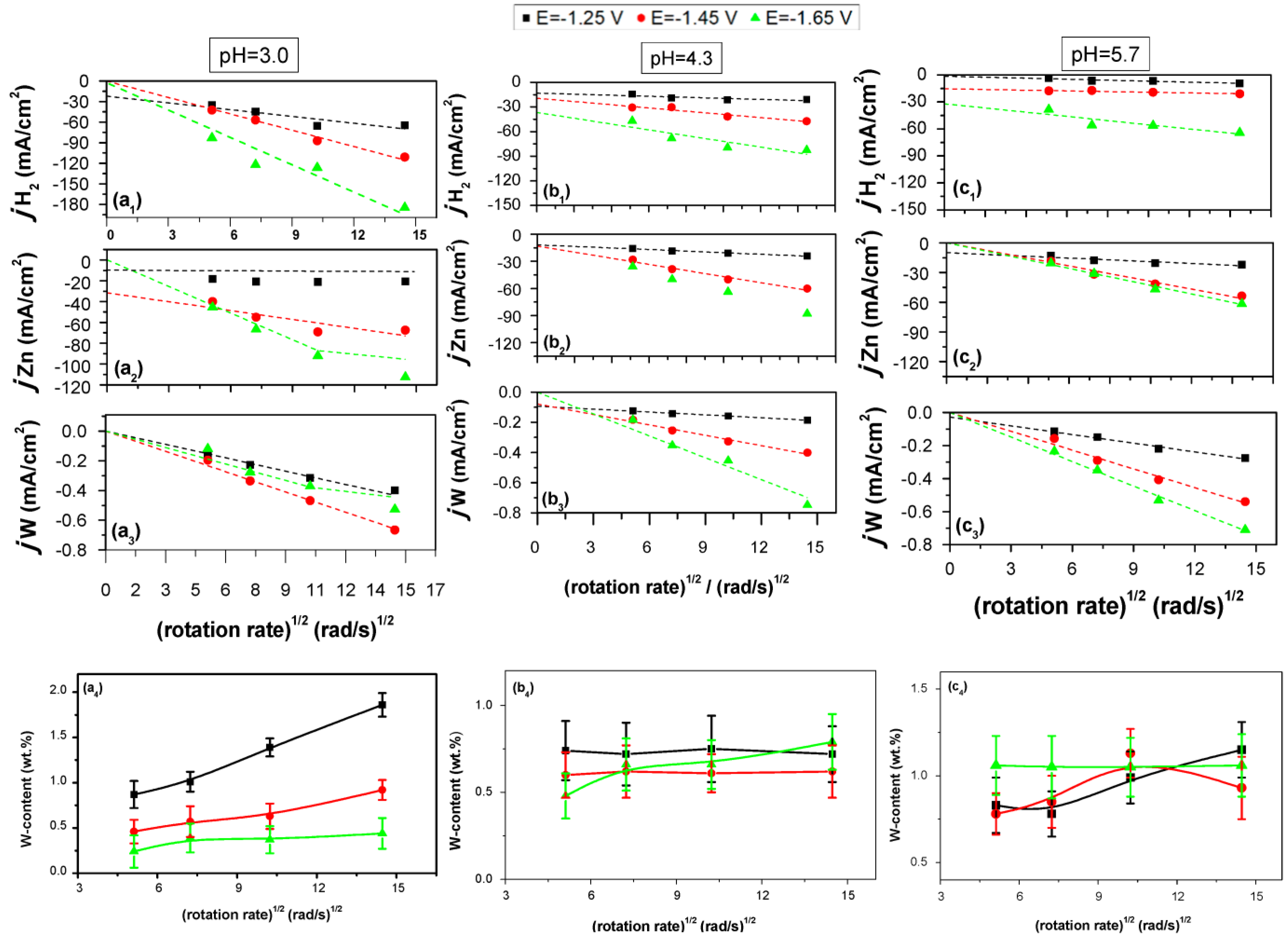
3.3. The Effect of Hydrodynamic Conditions
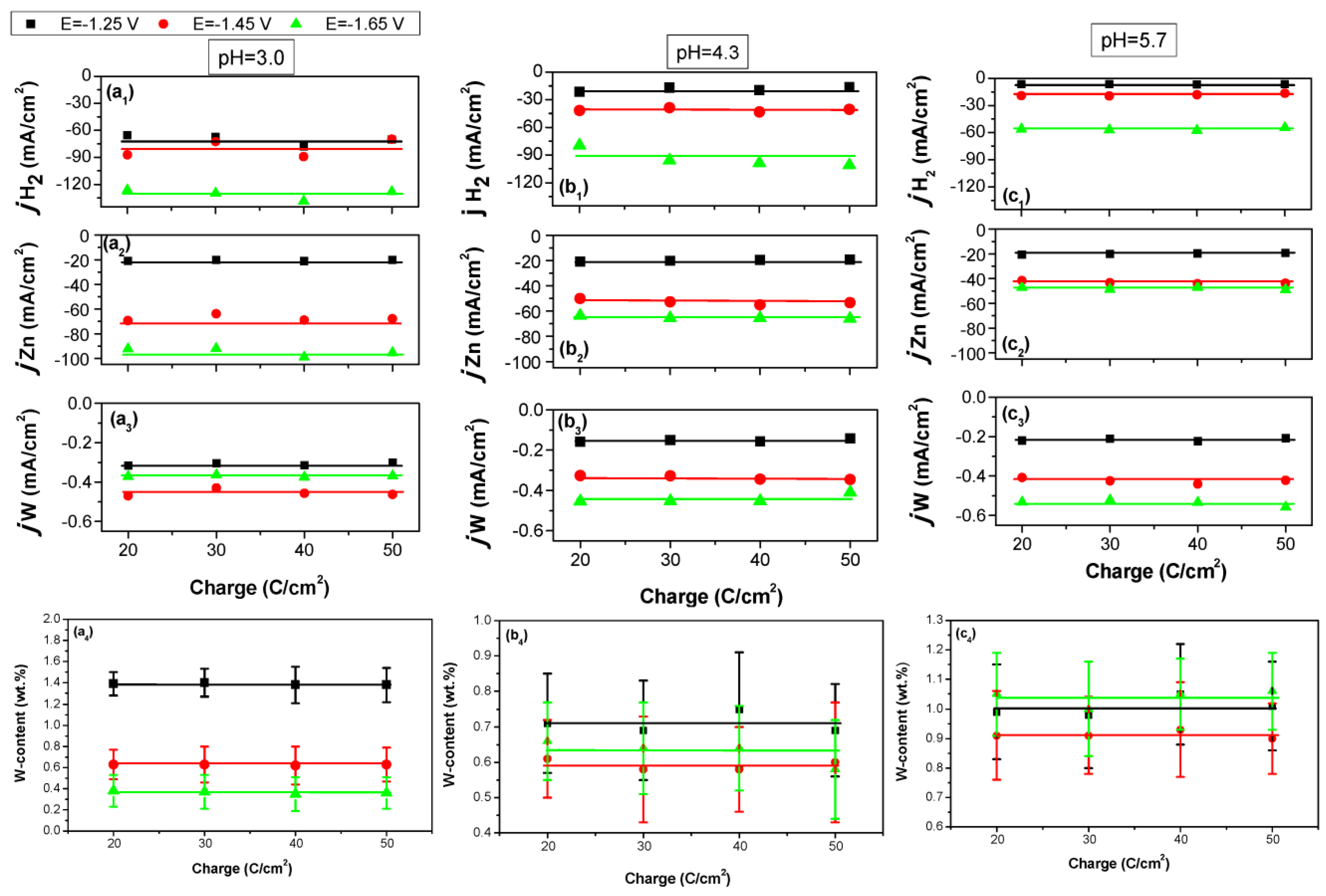
3.4. The Effect of Passed Charge
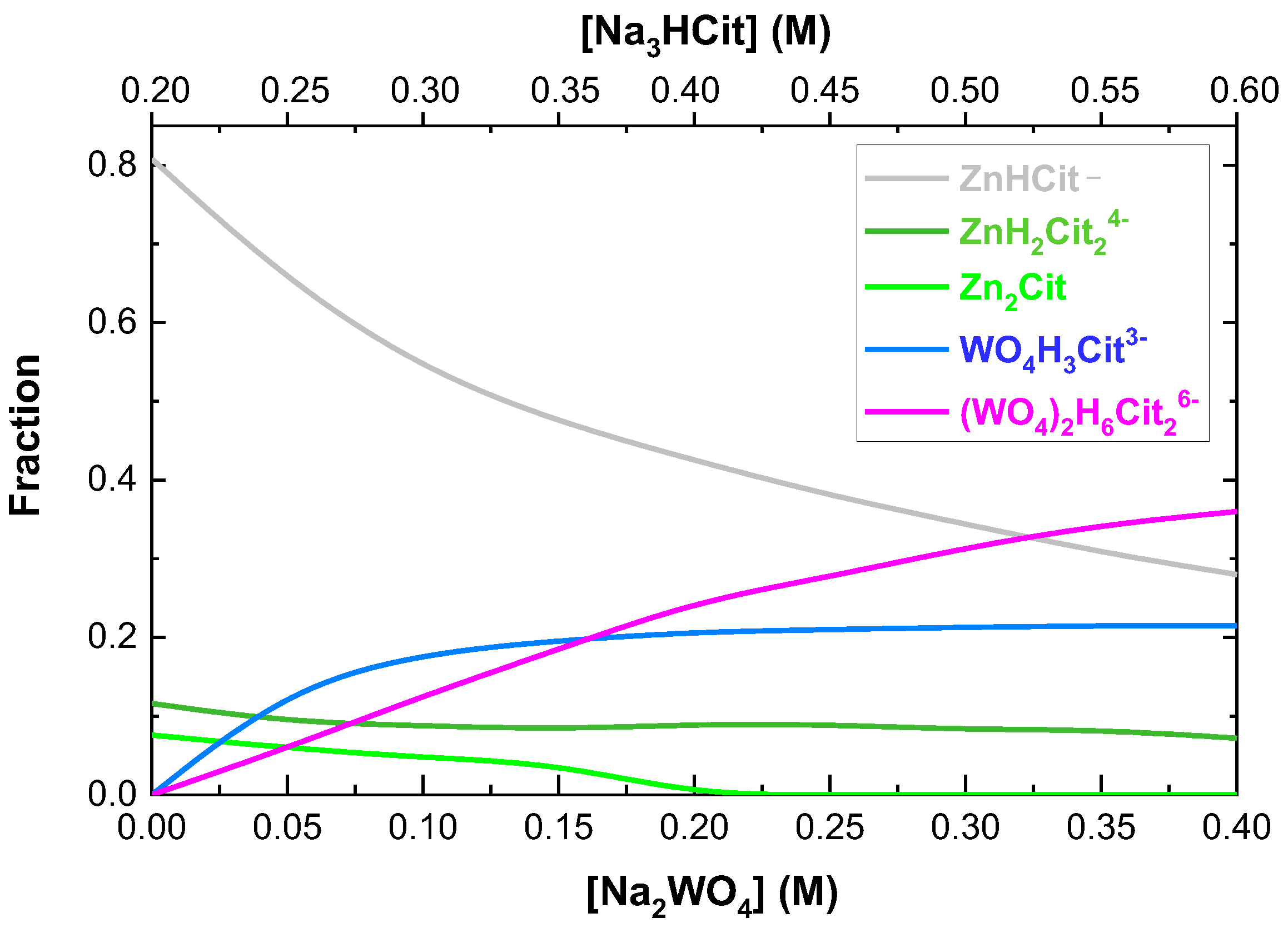
3.5. The Effect of Bath Composition
3.6. Characterization of the Zn–W Deposits
3.7. The Mechanism of Zn–W Codeposition
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McCain, W.C.; Crouse, L.C.B.; Bazar, M.A.; Roszell, L.E.; Leach, G.J.; Middleton, J.R.; Reddy, G. Subchronic oral toxicity of sodium tungstate in Sprague-Dawley rats. Int. J. Toxicol. 2015, 34, 336–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.E.; Wilcox, G.D. Molybdate based conversion coatings for zinc and zinc alloy surfaces: A review. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2008, 86, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keith, S.; Moffett, D.B.; Rosemond, Z.A.; Wohlers, D.W.; Amata, R.J.; Diamond, G.L.; Swarts, S.G. Toxicological Profile for Tungsten; Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rashmi, S.; Elias, L.; Hegde, A.C. Multilayered Zn-Ni alloy coatings for better corrosion protection of mild steel. Eng. Sci. Technol. Int. J. 2017, 20, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, F.; Kahoul, A. Electrodeposition and corrosion behaviour of Zn/Co coating produced from a sulphate bath. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2016, 94, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Report on Carcinogens, 14th ed.; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Triangle Park, NC, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Eichinger, E.; Osborne, J.; Van Cleave, T. Hexavalent chromium elimination: An aerospace industry progress report. Met. Finish. 1997, 95, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, A. Electrodeposition of Alloys: Principles and Practice; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963; Volume II. [Google Scholar]
- Eliaz, N.; Gileadi, E. Physical Electrochemistry: Fundamentals, Techniques, and Applications, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Koster, W.; Schmid, H. Über die Legierungsfähigkeit von Zink mit Wolfram und Molybdän. Z. Metallkd. 1955, 46, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodge, W.; Evans, R.M.; Haskins, A.F. Metallic Materials Resistant to Molten Zinc. JOM 1955, 7, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, W.; Koch, E. Gmelin handbook of inorganic chemistry. In Metal, Chemical Reactions with Metals Zinc to Lawrencium; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1988. [Google Scholar]
- Martinz, H.; Nigg, B.; Hoffmann, A. The corrosion behaviour of refractory metals against molten and evaporated zinc. In Proceedings of the 17th Plansee Seminar, Reutte, Austria, 25–29 May 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Shabalin, I.L. Ultra-High Temperature Materials I: Carbon (Graphene/Graphite) and Refractory Metals; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Massalski, T.B.; Okamoto, H.; Subramanian, P.R.; Kacprzak, L. Binary Alloy Phase Diagrams, 2nd ed.; ASM International: Metals Park, OH, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallotti, P.L.; Nobili, L.; Vicenzo, A. Phase structure of electrodeposited alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 4557–4565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sridhar, T.M.; Eliaz, N.; Gileadi, E. Electroplating of Ni4W. ECS Solid-State Lett. 2005, 8, C58–C61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegde, A.C.; Venkatakrishna, K.; Eliaz, N. Electrodeposition of Zn–Ni, Zn–Fe and Zn–Ni–Fe alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 205, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagiv, M.C.; Eliaz, N.; Gileadi, E. Incorporation of iridium into electrodeposited rhenium–nickel alloys. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 88, 240–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baik, S.I.; Duhin, A.; Phillips, P.J.; Klie, R.F.; Gileadi, E.; Seidman, D.N.; Eliaz, N. Atomic-scale structural and chemical study of columnar and multilayer Re–Ni electrodeposited thermal barrier coating. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 1133–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliaz, N.; Gileadi, E. Induced codeposition of alloys of tungsten, molybdenum and rhenium with transition metals. In Modern Aspects of Electrochemistry; Vayenas, C.G., White, R.E., Gamboa-Aldeco, M.E., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 42, Chapter 4; pp. 191–301. [Google Scholar]
- Eliaz, N.; Sridhar, T.M.; Gileadi, E. Synthesis and characterization of nickel tungsten alloys by electrodeposition. Electrochim. Acta 2005, 50, 2893–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gileadi, E.; Eliaz, N. The mechanism of induced codeposition of Ni-W alloys. ECS Trans. 2007, 2, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, C.G.; Jones, F.L. The electrodeposition of tungsten from aqueous solutions. Trans. Electrochem. Soc. 1931, 59, 461–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.L. The co-deposition of tungsten and iron from aqueous solutions. Trans. Electrochem. Soc. 1934, 66, 453–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.L. Metals codeposited with tungsten from the alkaline tungsten plating bath. Trans. Electrochem. Soc. 1937, 71, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.L.; Nielsen, M.L. Electrodeposition of iron-tungsten alloys from an acid plating bath. Trans. Electrochem. Soc. 1942, 82, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brenner, A.; Burkhead, P.; Seegmiller, E. Electrodeposition of tungsten alloys containing iron, nickel, and cobalt. J. Res. Natl. Bur. Stand. 1947, 39, 351–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lietzke, M.H.; Holt, M.L. Codeposition of tungsten and iron from an aqueous ammoniacal citrate bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1948, 94, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, M.L.; Vaaler, L.E. Electrolytic reduction of aqueous tungstate solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1948, 94, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akiyama, T.; Fukushima, H. Recent study on the mechanism of the electrodeposition of iron-group metal alloys. ISIJ Int. 1992, 32, 787–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silkin, S.A.; Gotelyak, A.V.; Tsyntsaru, N.I.; Dikusar, A.I. Electrodeposition of alloys of the iron group metals with tungsten from citrate and gluconate solutions: Size effect of microhardness. Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 2017, 53, 7–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsyntsaru, N.; Cesiulis, H.; Donten, M.; Sort, J.; Pellicer, E.; Podlaha-Murphy, E.J. Modern trends in tungsten alloys electrodeposition with iron group metals. Surf. Eng. Appl. Electrochem. 2012, 48, 491–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernickaite, E.; Tsyntsaru, N.; Cesiulis, H. Electrodeposited Co-W alloys and their prospects as effective anode for methanol oxidation in acidic media. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 1322–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yar-Mukhamedova, G.; Ved, M.; Sakhnenko, N.; Nenastina, T. Electrodeposition and properties of binary and ternary cobalt alloys with molybdenum and tungsten. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernickaite, E.; Tsyntsaru, N.; Sobczak, K.; Cesiulis, H. Electrodeposited tungsten-rich Ni-W, Co-W and Fe-W cathodes for efficient hydrogen evolution in alkaline medium. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 318, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Boraei, N.F.; Ibrahim, M.A.M. Preparation, characterisation and electrochemical study of crack-free nanocrystalline electrodeposited Co-W alloy coating of high hardness. Trans. Inst. Met. Finish. 2020, 98, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, D.G.; Burr, A.A. Electrodeposition of chromium-tungsten alloy plates. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1950, 97, 67–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, W.E.; Lietzke, M.H. The mechanism of the tungsten alloy plating process. J. Electrochem. Soc. 1952, 99, 245–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacal, P.; Indyka, P.; Stojek, Z.; Donten, M. Unusual example of induced codeposition of tungsten. Galvanic formation of Cu-W alloy. Electrochem. Commun. 2015, 54, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bacal, P.; Stojek, Z.; Donten, M. Optimization of CuW alloy electrodeposition towards high-tungsten content. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2016, 20, 3143–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vernickaite, E.; Tsyntsaru, N.; Cesiulis, H. Electrochemical co-deposition of tungsten with cobalt and copper: Peculiarities of binary and ternary alloys coatings formation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 307, 1341–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saitou, M. Cu–W thin film electrodeposited in an aqueous solution. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2017, 12, 4714–4723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Nakano, H.; Oue, S.; Taniguchi, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Fukushima, H. Effect of a small amount of Mo, W and Sn additives on the morphology and orientation of electrodeposited Zn. Tetsu-To-Hagane/J. Iron Steel Inst. Japan 2007, 93, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Sadjadi, S.A.S.; Bohlooli, F.; Zare-Dorabei, R. Electroless deposition of novel ternary Zn-W-B alloy coating. Anal. Bioanal. Electrochem. 2015, 7, 118–128. [Google Scholar]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Ozga, P. Electrodeposition of Sn-Zn and Sn-Zn-Mo layers from citrate solutions. Surf. Sci. 2013, 607, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Ozga, P.; Socha, R.P. Investigation of electrochemical co-deposition of zinc and molybdenum from citrate solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 104, 378–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Hara, A.; Bigos, A.; Ozga, P. Electrodeposition of Zn-Mn-Mo layers from citrate-based aqueous electrolytes. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 202, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, E.; Pellicer, E.; Duch, M.; Esteve, J.; Vallés, E. Molybdenum alloy electrodeposits for magnetic actuation. Electrochim. Acta 2006, 51, 3214–3222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Ozga, P.; Świa, Z.; Bielańska, E. Characterisation of Zn-Mo alloy layers electrodeposited from aqueous citrate solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2013, 578, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Ozga, P.; Berent, K.; Kot, M. Microstructure and micromechanical properties of electrodeposited Zn-Mo coatings on steel. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 636, 156–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Morgiel, J.; Swiatek, Z.; Vega, J.M.; García-Lecina, E. Effect of Mo addition on corrosion of Zn coatings electrodeposited on steel. Corros. Sci. 2018, 135, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervilla, A.; Ramirez, J.A.; Llopis, E. Compounds of tungsten(VI) with citric acid: A spectrophotometric; polarimetric; hydrogen-1, carbon-13 N.M.R. study of the formation and interconversion equilibria in aqueous solution. Transit. Met. Chem. 1986, 11, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruywagen, J.J.; Saayman, L.J.; Niven, M.L. Complexation between tungsten(VI) and citrate: The crystal and molecular structure of a dinuclear complex, Na6[W2O5(cit)2]·10H2O. J. Crystallogr. Spectrosc. Res. 1992, 22, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Ozga, P.; Jałowiec, A.; Kowalik, R. Tin-zinc alloy electrodeposition from aqueous citrate baths. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 240, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H.; Szymkiewicz, K.; Rogal, Ł.; Gileadi, E.; Eliaz, N. Direct current electrodeposition of Zn-SiC nanocomposite coatings from citrate bath. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2018, 165, D526–D535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettit, L.D.; Powell, K.J. The IUPAC Stability Constants Database, SC-Database for Windows; Academic Software: Yorks, UK, 2012; Release 5. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, W.R.; Missen, R.W. Chemical Reactions Equilibrium Analysis: Theory and Algorithms; John Wiley & Sons: Toronto, Canada, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Ozga, P. The thermodynamic models of complex electrolytic baths for electrodepostion of zinc and tin alloys. In Polska Metalurgia w Latach 2006–2010; Akapit: Krakow, Poland, 2010. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Puigdomenech, I. MEDUSA (Make Equilibrium Diagrams Using Sophisticated Algorithms) Program, Ver. 26; Royal Institute of Technology: Stockholm, Sweden, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Hamada, Y.Z.; Bayakly, N.; George, D.; Greer, T. Speciation of molybdenum(VI)-citric acid complexes in aqueous solutions. Synth. React. Inorg. Met. Nano-Met. Chem. 2008, 38, 664–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, A.; Barkleit, A.; Foerstendorf, H.; Tsushima, S.; Heim, K.; Bernhard, G. Curium(III) citrate speciation in biological systems: A europium(III) assisted spectroscopic and quantum chemical study. Dalt. Trans. 2012, 41, 13969–13983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazimierczak, H. Electrodeposition of Zn-Mo Layers from Aqueous Citrate Solutions; Institute of Metallurgy and Materials Science PAS: Kraków, Poland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hreid, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Spratt, H.J.; Wang, H.; Will, G. Effects of metal ion concentration on electrodeposited CuZnSn film and its application in kesterite Cu2ZnSnS4 solar cells. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 65114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozga, P.; Swiatek, Z.; Dębski, A.; Bonarski, J.; Tarkowski, L.; Bielanska, E.; Onderka, B.; Michalec, M. Modern Technologies and Advanced Materials and Products in Balanced Development of Non-Ferrous Metals Industry; IMN: Gliwice, Poland, 2010; Volume 295. (In Polish) [Google Scholar]
- Trasatti, S. Work function; electronegativity, and electrochemical behaviour of metals. III. Electrolytic hydrogen evolution in acid solutions. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1972, 39, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiarski, J.; Tylus, W.; Krawczyk, M.S.; Szczygieł, B. The influence of molybdenum on the electrodeposition and properties of ternary Zn-Fe-Mo alloy coatings. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 196, 708–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khyzhun, O.Y.; Zaulychny, Y.V.; Zhurakovsky, E.A. Electronic structure of tungsten and molybdenum germanides synthesized at high pressures. J. Alloys Compd. 1996, 244, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gassman, P.G.; Macomber, D.W.; Willging, S.M. Isolation and characterization of reactive intermediates and active catalysts in homogeneous catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, K.T.; Hercules, D.M. Studies of nickel-tungsten-alumina catalysts by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. 1976, 80, 2094–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clementi, E.; Raimondi, D.L.; Reinhardt, W.P. Atomic screening constants from SCF functions. II. Atoms with 37 to 86 electrons. J. Chem. Phys. 1967, 47, 1300–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanauskas, R.; Gudavičiute, L.; Juškenas, R.; Ščit, O. Structural and corrosion characterization of pulse plated nanocrystalline zinc coatings. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 53, 1801–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, A.M.N.; Kong, X.; Hider, R.C. Determination of the pKa value of the hydroxyl group in the α-hydroxycarboxylates citrate, malate and lactate by 13C NMR: Implications for metal coordination in biological systems. BioMetals 2009, 22, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younes, O.; Gileadi, E. Electroplating of Ni/W Alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2002, 149, C100–C111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oue, S.; Nakano, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Fukushima, H. Structure and codeposition behavior of Ni–W alloys electrodeposited from ammoniacal citrate solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2009, 156, D17–D22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chassaing, E.; Quang, K.V.; Wiart, R. Mechanism of nickel-molybdenum alloy electrodeposition in citrate electrolytes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1989, 19, 839–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, E.; Pellicer, E.; Vallés, E. Detection and characterization of molybdenum oxides formed during the initial stages of cobalt-molybdenum electrodeposition. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2003, 33, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



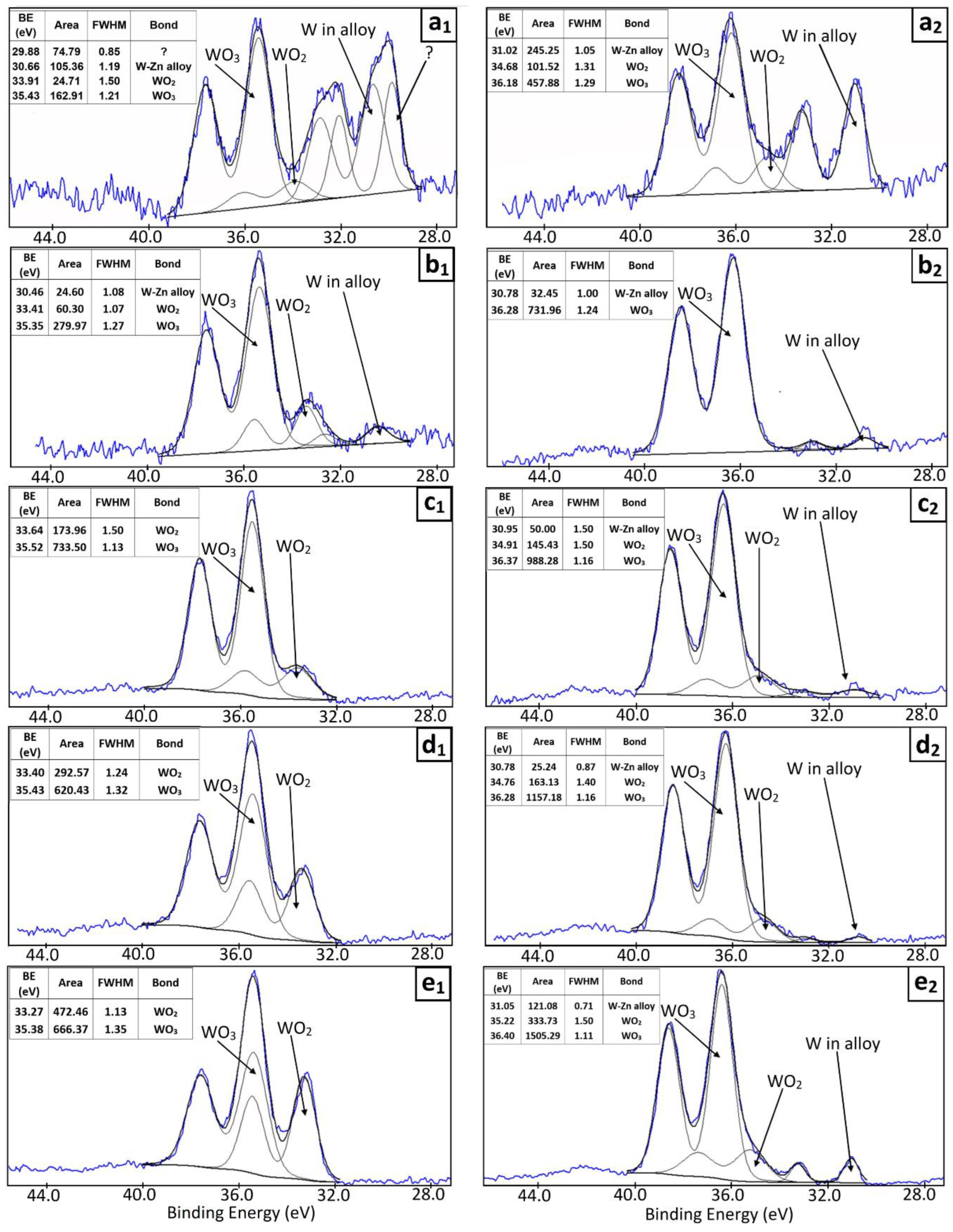
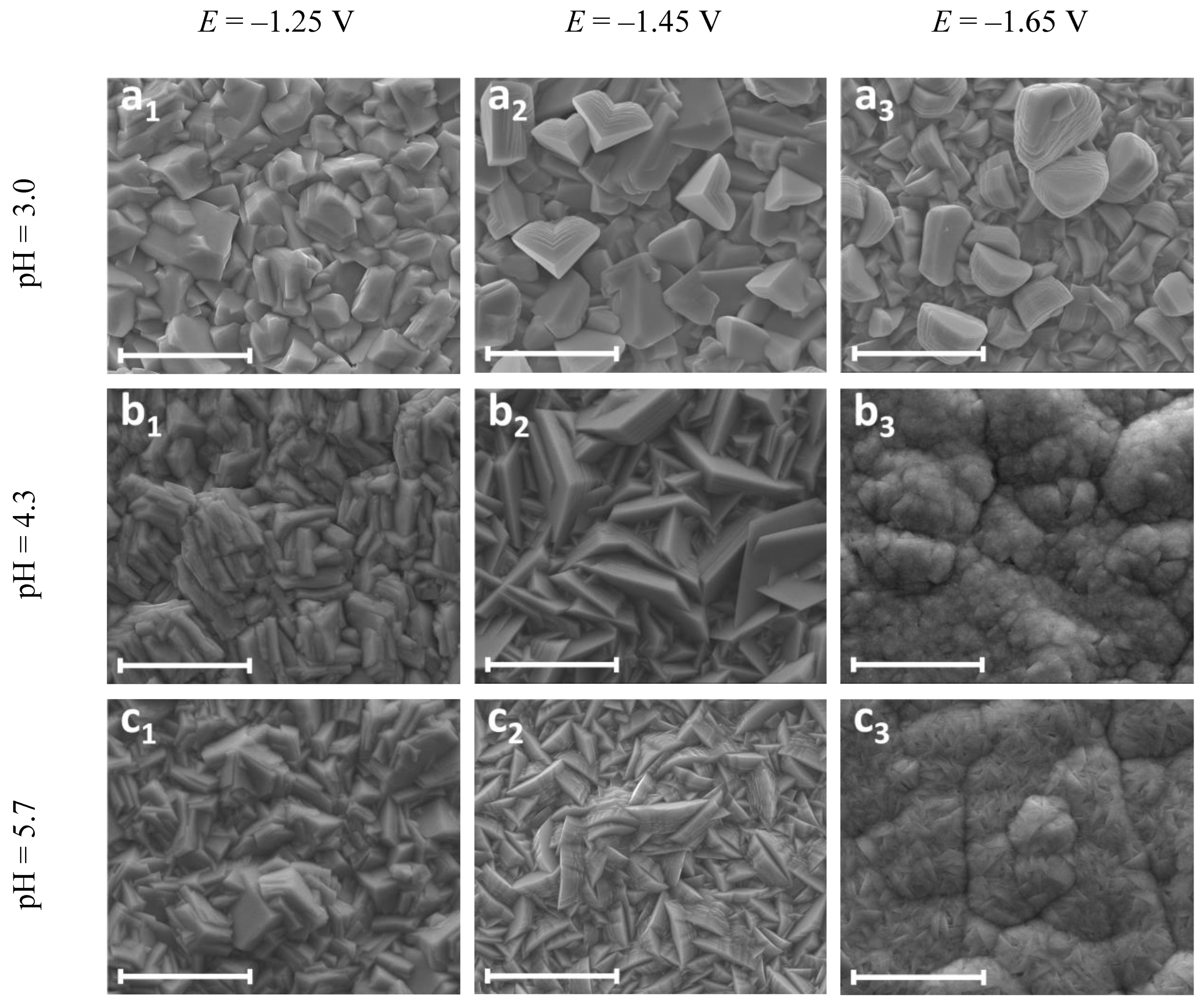
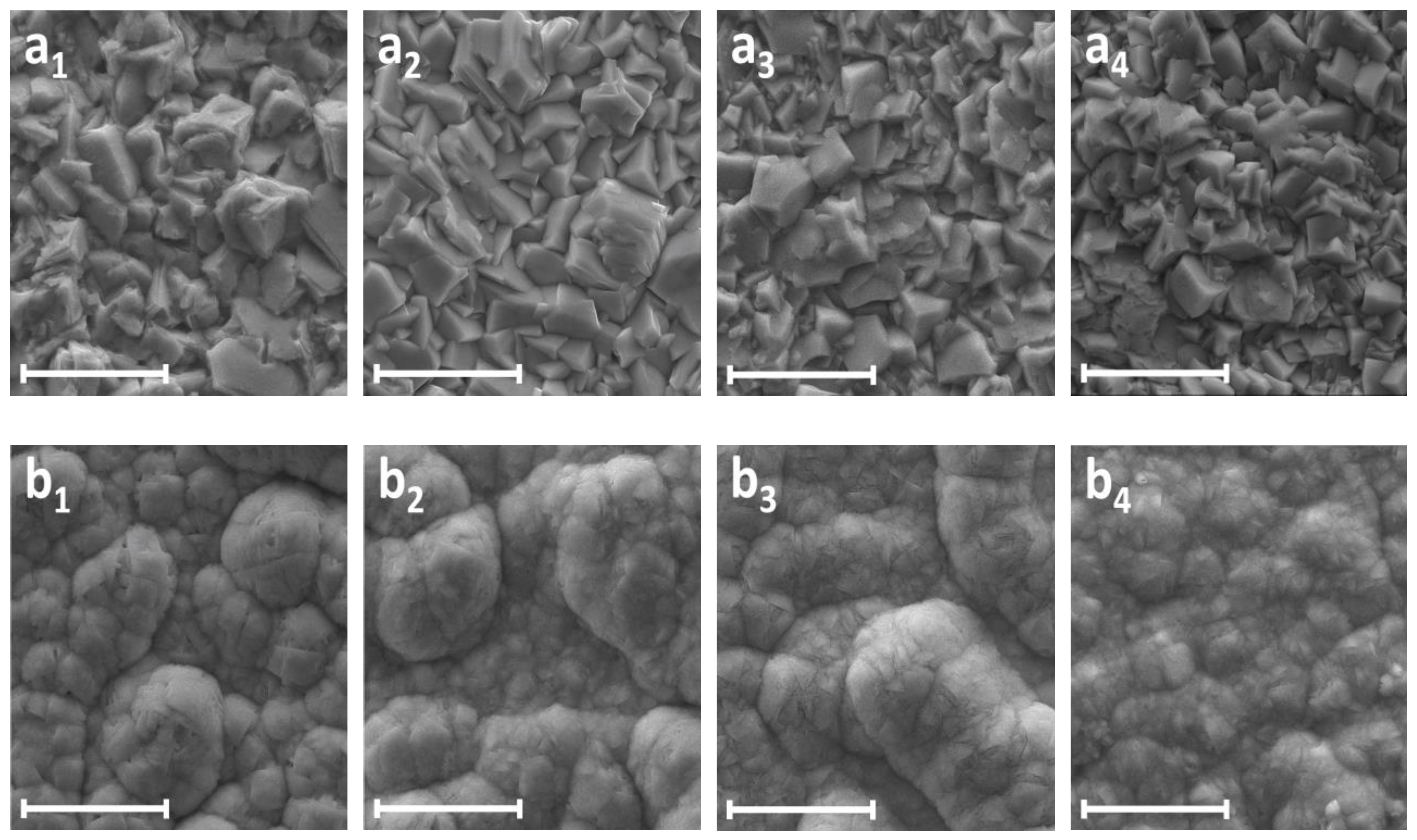

| Electrodeposition Conditions | Location | Zn (at.%) | W (at.%) | O (at.%) | C (at.%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E = −1.25 V pH = 3.0 | a1 | 14.81 | 0.31 | 36.26 | 48.62 |
| a2 | 84.18 | 0.95 | 13.06 | 1.82 | |
| E = −1.25 V pH = 4.3 | b1 | 18.22 | 0.26 | 37.69 | 43.84 |
| b2 | 62.87 | 0.80 | 31.02 | 5.31 | |
| E = −1.25 V pH = 5.7 | c1 | 21.01 | 0.90 | 37.88 | 40.21 |
| c2 | 69.48 | 1.41 | 26.60 | 2.50 | |
| E = −1.45 V pH = 5.7 | d1 | 23.87 | 1.13 | 41.86 | 33.14 |
| d2 | 58.78 | 1.88 | 35.65 | 3.70 | |
| E = −1.65 V pH = 5.7 | e1 | 13.42 | 1.19 | 33.40 | 51.99 |
| e2 | 68.47 | 2.23 | 27.39 | 1.94 |
| Electrodeposition Conditions | Location | WO3 (% Area) | WO2 (% Area) | Zn–W Alloy (% Area) | Unknown Spectral Line (% Area) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| E = −1.25 V pH = 3.0 | a1 | 44.30 | 6.72 | 28.65 | 20.34 |
| a2 | 56.90 | 12.62 | 30.48 | 0.00 | |
| E = −1.25 V pH = 4.3 | b1 | 76.73 | 16.53 | 6.74 | 0.00 |
| b2 | 95.75 | 0.00 | 4.25 | 0.00 | |
| E = −1.25 V pH = 5.7 | c1 | 80.83 | 19.17 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| c2 | 83.49 | 12.29 | 4.22 | 0.00 | |
| E = −1.45 V pH = 5.7 | d1 | 67.96 | 32.04 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| d2 | 86.00 | 12.12 | 1.88 | 0.00 | |
| E = −1.65 V pH = 5.7 | e1 | 58.51 | 41.49 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| e2 | 76.80 | 17.03 | 6.18 | 0.00 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kazimierczak, H.; Eliaz, N. Induced Codeposition of Tungsten with Zinc from Aqueous Citrate Electrolytes. Coatings 2023, 13, 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13122001
Kazimierczak H, Eliaz N. Induced Codeposition of Tungsten with Zinc from Aqueous Citrate Electrolytes. Coatings. 2023; 13(12):2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13122001
Chicago/Turabian StyleKazimierczak, Honorata, and Noam Eliaz. 2023. "Induced Codeposition of Tungsten with Zinc from Aqueous Citrate Electrolytes" Coatings 13, no. 12: 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13122001
APA StyleKazimierczak, H., & Eliaz, N. (2023). Induced Codeposition of Tungsten with Zinc from Aqueous Citrate Electrolytes. Coatings, 13(12), 2001. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13122001






