The Influence of H Content on the Properties of a-C(W):H Coatings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
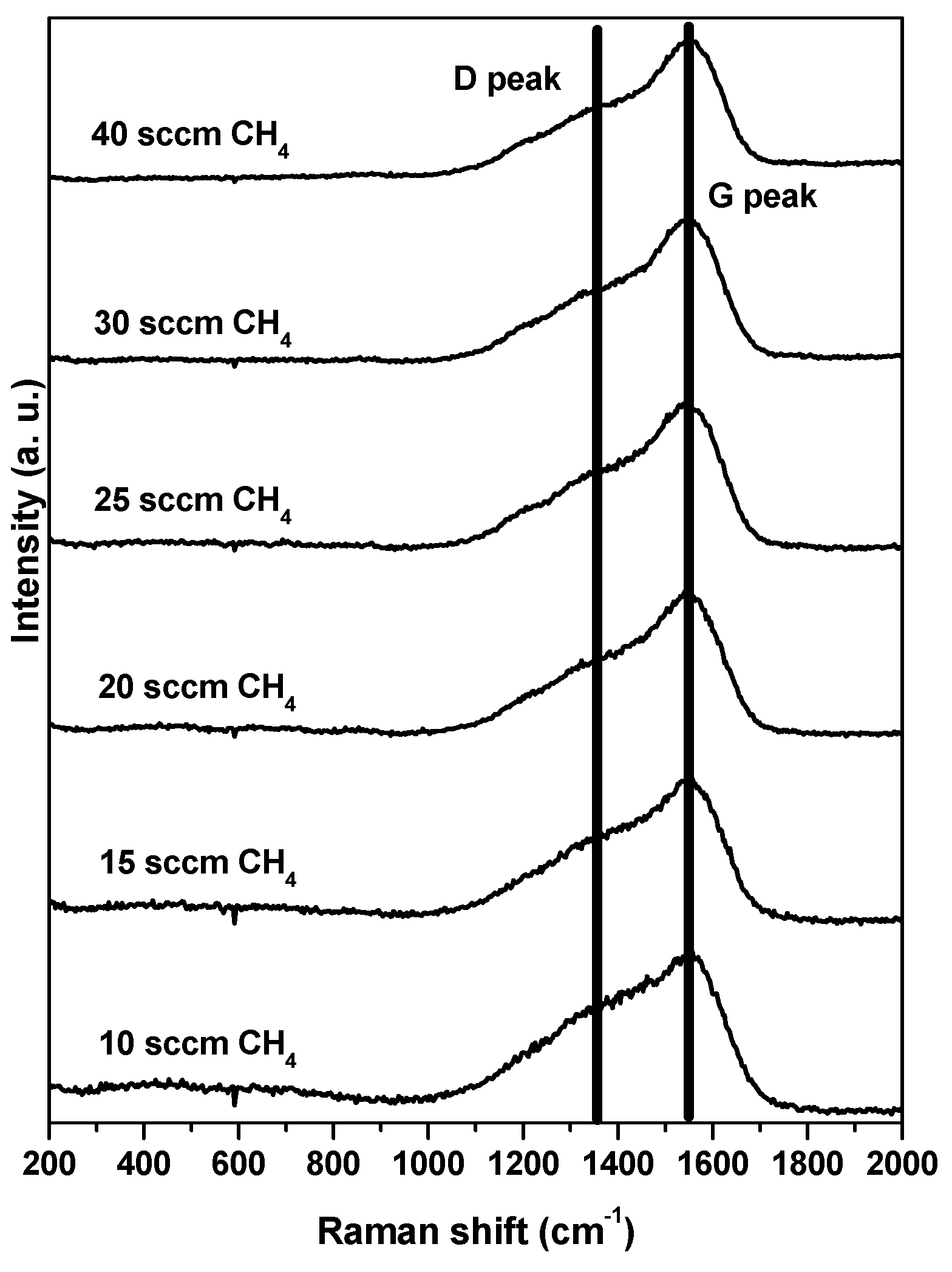
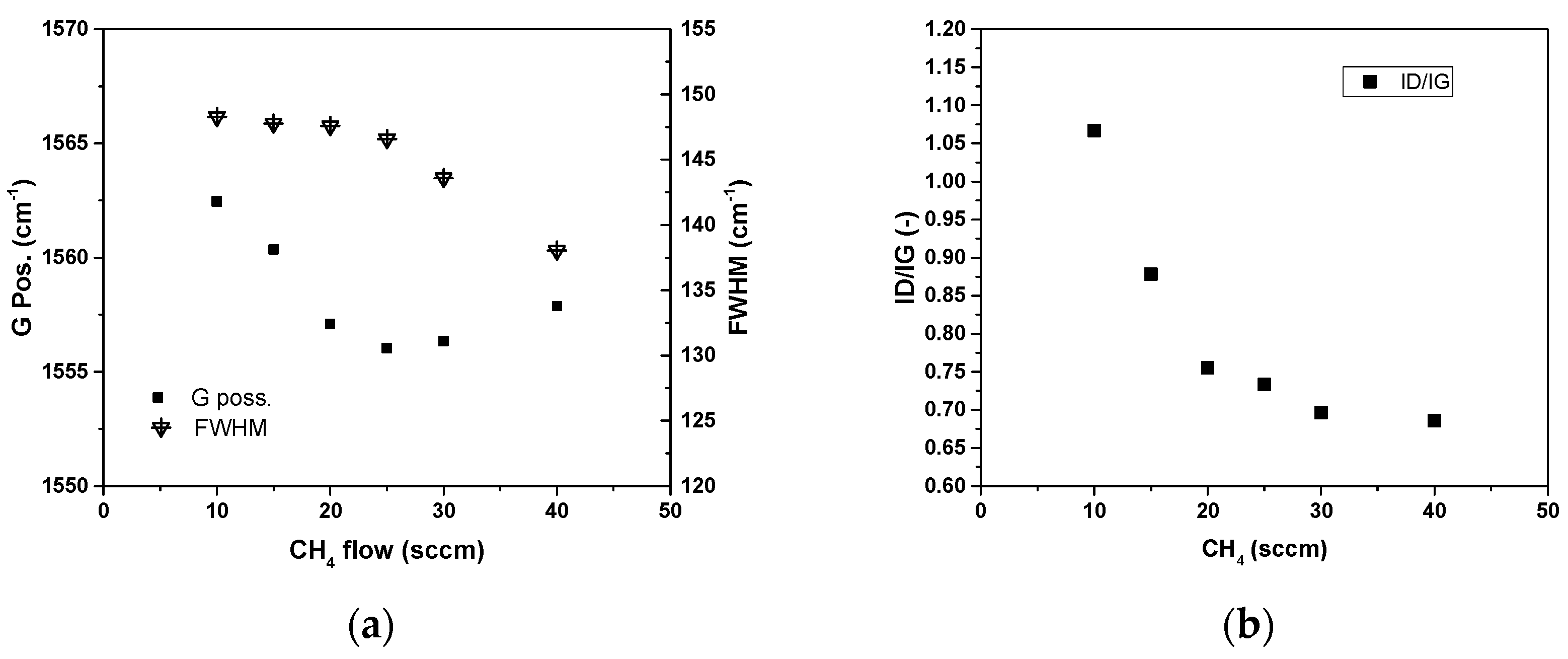
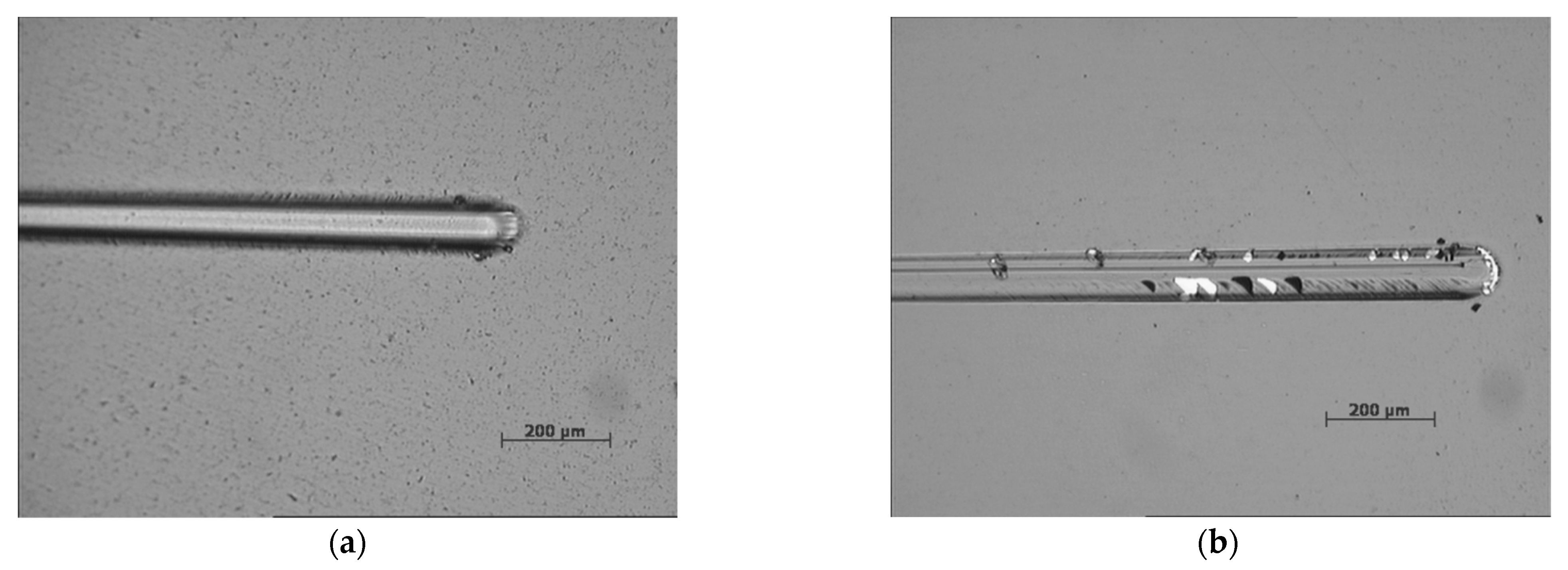
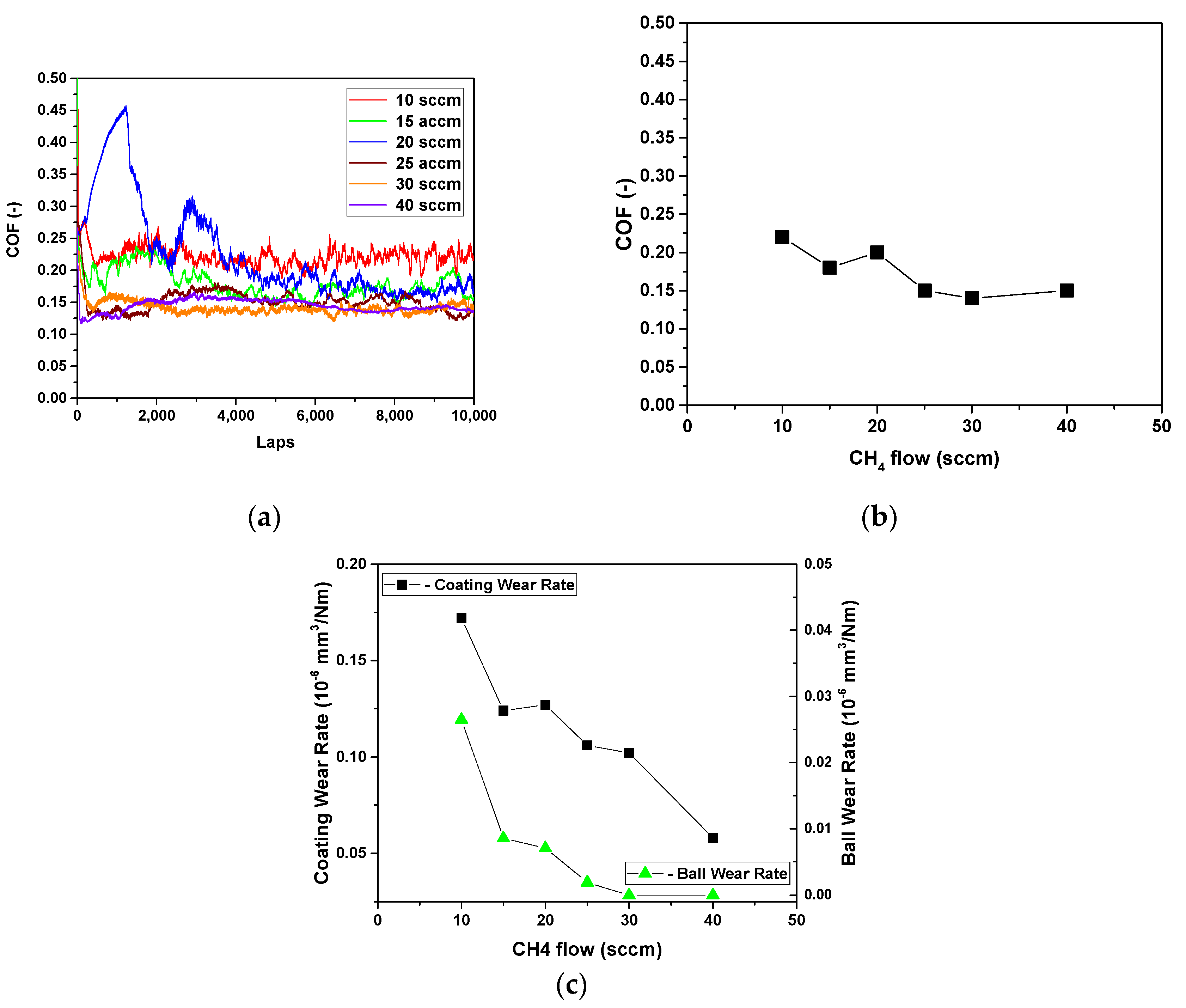
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Matthews, A.; Eskildsen, S.S. Engineering applications for diamond-like carbon. Diam. Relat. Mater. 1994, 3, 902–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyzniewski, A. Optimising deposition parameters of W-DLC coatings for tool materials of high speed steel and cemented carbide. Vacuum 2012, 86, 2140–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czyzniewski, A. The effect of air humidity on tribological behaviours of W–C:H coatings with different tungsten contents sliding against bearing steel. Wear 2012, 296, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voevodin, A.A.; Prasad, S.V.; Zabinski, J.S. Nanocrystalline carbide/amorphous carbon composites. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 82, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbella, C.; Oncins, G.; Gómez, M.; Polo, M.; Pascual, E.; García-Céspedes, J.; Andújar, J.; Bertran, E. Structure of diamond-like carbon films containing transition metals deposited by reactive magnetron sputtering. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 1103–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, D.; Svahn, F.; Wiklund, U.; Hogmark, S. Low-friction carbon-rich carbide coatings deposited by co-sputtering. Wear 2003, 254, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, W.J.; Gillispie, B.A. Mechanical properties of Ti-containing and W-containing diamond-like carbon coatings. J. Appl. Phys. 1998, 84, 4314–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Ohana, T.; Tanaka, A. Tribological properties of DLC films with different hydrogen contents in water environment. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2004, 13, 2216–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, C.; Piazza, F.; Ferrari, A.; Grambole, D.; Robertson, J. Bonding in hydrogenated diamond-like carbon by Raman spectroscopy. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 1098–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofaj, F.; Kabátová, M.; Kvetková, L.; Dobrovodský, J. The effects of deposition conditions on hydrogenation, hardness and elastic modulus of W-C:H coatings. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 40, 2721–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lofaj, F.; Kabátová, M.; Dobrovodský, J.; Cempura, G. Hydrogenation and hybridization in hard W-C:H coatings prepared by hybrid PVD-PECVD method with methane and acetylene. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2020, 88, 105211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libardi, J.; Grigorov, K.; Massi, M.; Otani, C.; Ravagnani, S.; Maciel, H.; Guerino, M.; Ocampo, J. Comparative studies of the feed gas composition effects on the characteristics of DLC films deposited by magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2004, 459, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. Requirements of ultrathin carbon coatings for magnetic storage technology. Tribol. Int. 2003, 36, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, M.; Paskvale, S.; Čekada, M.; Schöberl, T.; Waldhauser, W.; Mitterer, C.; Pelicon, P.; Brandstätter, E. The relationship between structure and mechanical properties of hydrogenated amorphous carbon films. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2010, 19, 1245–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2000, 61, 14095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Resonant Raman spectroscopy of disordered, amorphous, and diamondlike carbon. Phys. Rev. B 2001, 64, 075414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, J. Daimond–Like amorphous carbon. Mat. Sci. Eng. 2002, R37, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Wu, G.; Wang, A. Structure and elastic recovery of Cr–C:H films deposited by a reactive magnetron sputtering technique. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 257, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeynes, C.; Colaux, J.L. Thin film depth profiling by ion beam analysis. Analyst 2016, 141, 5944–5985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, J.; Trindade, A.; Menezes, L.; Cavaleiro, A. A model for coated surface hardness. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2000, 131, 457–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gurbich, A. Evaluated differential cross-sections for IBA. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2010, 268, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeynes, C.; Palitsin, V.; Grime, G.; Pascual-Izarra, C.; Taborda, A.; Reis, M.; Barradas, N. External beam Total-IBA using DataFurnace. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2020, 481, 47–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, N.P.; Jeynes, C. Advanced physics and algorithms in the IBA DataFurnace. Nucl. Instruments Methods B 2008, 266, 1875–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casiraghi, C.; Ferrari, A.C.; Robertson, J. Raman spectroscopy of hydrogenated amorphous carbons. Phys. Rev. B 2005, 72, 085401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henley, S.J.; Carey, J.D.; Silva, S.R.P. Room temperature photoluminescence from nanostructured amorphous carbon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 6236–6238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodil, S.E.; Muhl, S.; Maca, S.; Ferrari, A.C. Optical gap in carbon nitride films. Thin Solid Film 2003, 433, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanchini, G.; Ray, S.; Tagliaferro, A. Photoluminescence investigation of carbon nitride-based films deposited by reactive sputtering. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2003, 12, 1084–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wu, W.; Gong, C.; Wang, W.; He, Z.; Li, J.; Ju, X.; Tang, Y.; Xie, E. Structural and optical properties of Fe-doped hydrogenated amorphous carbon films prepared from trans-2-butene by plasma enhanced metal organic chemical vapor deposition. Appl. Phys. A 2010, 98, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, A.; Gómez-Aleixandre, C.; Orwa, J.; Cimmino, A.; Prawer, S. Modification of characteristics of diamond-like carbon thin films by low chromium content addition. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2012, 26, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugo, D.; Silva, P.; Ramirez, M.; Pillaca, E.; Rodrigues, C.; Fukumasu, N.; Corat, E.; Tabacniks, M.; Trava-Airoldi, V. Characterization and tribologic study in high vacuum of hydrogenated DLC films deposited using pulsed DC PECVD system for space applications. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 332, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreault, G.; Elliman, R.G.; Grötzschel, R.; Gujrathi, S.C.; Jeynes, C.; Lennard, W.N.; Rauhala, E.; Sajavaara, T.; Timmers, H.; Wang, Y.Q.; et al. Round Robin: Measurement of H implantation distributions in Si by elastic recoil detection. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2004, 222, 547–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abriola, D.; Barradas, N.P.; Bogdanović-Radović, I.; Chiari, M.; Gurbich, A.F.; Jeynes, C.; Kokkoris, M.; Mayer, M.; Ramos, A.R.; Shi, L.; et al. Development of a reference database for Ion Beam Analysis and future perspectives. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2011, 269, 2972–2978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegler, J.F. SRIM-2003. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2004, 219, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wielopolski, L.; Gardner, R.P. Prediction of the pulse-height spectral distortion caused by the peak pile-up effect. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 1976, 133, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molodtsov, S.L.; Gurbich, A.F. Simulation of the pulse pile-up effect on the pulse-height spectrum. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2009, 267, 3484–3487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Izarra, C.; Barradas, N.P. Introducing routine pulse height defect corrections in IBA. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2008, 266, 266–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, N.P. Rutherford backscattering analysis of thin films and superlattices with roughness. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2001, 34, 2109–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Simon, A.; Jeynes, C.; Webb, R.P.; Finnis, R.; Tabatabaian, Z.; Sellin, P.J.; Breese, M.B.H.; Fellows, D.F.; van den Broek, R.; Gwilliam, R.M. The new Surrey ion beam analysis facility. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2004, 219, 405–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grime, G.W.; Dawson, M. Recent developments in data acquisition and processing on the Oxford scanning proton microprobe. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 1995, 104, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blaauw, M.; Campbell, J.L.; Fazinić, S.; Jakšić, M.; Orlic, I.; van Espen, P. The 2000 IAEA intercomparison of PIXE spectrum analysis software. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2002, 189, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeynes, C.; Barradas, N.P.; Marriott, P.K.; Boudreault, G.; Jenkin, M.; Wendler, E.; Webb, R.P. Elemental thin film depth profiles by ion beam analysis using simulated annealing-a new tool. J. Phys. D 2003, 36, R97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudreault, G.; Jeynes, C.; Wendler, E.; Nejim, A.; Webb, R.P.; Wätjen, U. Accurate RBS measurement of ion implant doses in silicon. Surf. Interface Anal. 2002, 33, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barradas, N.P.; Arstila, K.; Battistig, G.; Bianconi, M.; Dytlewski, N.; Jeynes, C.; Kótai, E.; Lulli, G.; Mayer, M.; Rauhala, E.; et al. Summary of “IAEA intercomparison of IBA software”. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2008, 266, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Izarra, C.; Barradas, N.P.; Reis, M.A.; Jeynes, C.; Menu, M.; Lavedrine, B.; Ezrati, J.J.; Röhrs, S. Towards truly simultaneous PIXE and RBS analysis of layered objects in cultural heritage. Nucl. Instrum. Methods B 2007, 261, 426–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| CH4 (sccm) | H (at.%) | C (at.%) | W (at.%) | Ar (at.%) | O (at.%) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 26.4 ± 1.3 | 65.6 ± 3.3 | 5.0 ±0.25 | 1.58 ± 0.08 | 1.40 ± 0.07 | 3.9 ± 0.20 |
| 15 | 26.6 ± 1.3 | 65.8 ± 3.3 | 4.6 ±0.23 | 1.50 ± 0.08 | 1.50 ± 0.08 | 3.6 ± 0.18 |
| 20 | 28.3 ± 1.4 | 64.9 ± 3.2 | 4.3 ±0.22 | 1.00 ± 0.05 | 1.50 ± 0.08 | 3.2 ± 0.16 |
| 25 | 29.1 ± 1.5 | 65.5 ± 3.3 | 4.0 ± 0.20 | 0.45 ± 0.02 | 0.90 ± 0.05 | 3.4 ± 0.17 |
| 30 | 30.8 ± 1.5 | 64.3 ± 3.2 | 3.5 ± 0.13 | 0.20 ± 0.01 | 1.30 ± 0.07 | 3.0 ± 0.15 |
| 40 | 30.5 ± 1.5 | 65.1 ± 3.3 | 2.9 ± 0.15 | 0.04 ± 0.00 | 1.40 ± 0.07 | 2.1 ± 0.11 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Evaristo, M.; Fernandes, F.; Jeynes, C.; Cavaleiro, A. The Influence of H Content on the Properties of a-C(W):H Coatings. Coatings 2023, 13, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13010092
Evaristo M, Fernandes F, Jeynes C, Cavaleiro A. The Influence of H Content on the Properties of a-C(W):H Coatings. Coatings. 2023; 13(1):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13010092
Chicago/Turabian StyleEvaristo, Manuel, Filipe Fernandes, Chris Jeynes, and Albano Cavaleiro. 2023. "The Influence of H Content on the Properties of a-C(W):H Coatings" Coatings 13, no. 1: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13010092
APA StyleEvaristo, M., Fernandes, F., Jeynes, C., & Cavaleiro, A. (2023). The Influence of H Content on the Properties of a-C(W):H Coatings. Coatings, 13(1), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings13010092









