Abstract
Structural damage identification has become an important topic in the field of civil engineering in recent years. The shear-type structure, such as shear frame structure, is a common type used in civil engineering. In this paper, a damage identification method based on the change of generalized shear energy is proposed for shear-type structures. The main steps of the proposed method are as follows. Firstly, the element stiffness matrix in the structural finite element model is decomposed to obtain the elementary shear force vector. Secondly, the elementary generalized shear energy is calculated by the dot product of the vibration mode shape vector and the elementary shear force vector. Thirdly, structural damage locations can be determined by the changes of elementary generalized shear energy. Finally, more accurate damage localization and quantification are achieved by solving the mode shape sensitivity equation. A 20-storey numerical example and a three-storey experimental model are used to demonstrate the proposed damage identification algorithm. From the numerical and experimental results, it was found that the proposed approach can accurately identify the location and extent of the damage in the shear structures even if the data contain noise. It has been shown that the presented algorithm may be useful in the damage identification of shear-type structures.
1. Introduction
With an increase in the service life of a structure, various damage conditions will inevitably appear in the structure. The local damages of structural members may lead to the rapid destruction of the whole structure and cause serious disasters. Therefore, it is very necessary to detect structural damages in time to ensure the safety of use. To this end, many research studies have been performed over the years in the area of damage identification, by using structural static or dynamic response data [1,2,3]. Common methods of structural damage identification include static displacement method [4,5], strain mode method [6,7], modal sensitivity method [8,9,10], residual force vector method [11,12], intelligent optimization algorithm [13,14], strain energy method [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36], etc. Among them, strain energy method has attracted extensive attention because of its clear physical meaning. The earliest contribution to the development of strain energy method is the application of modal strain energy change ratio [15], whose sensitivity to damage location was theoretically proved and verified by a laboratory 2-D structure. Cornwell et al. [16] used the modal strain energy method to determine the damage locations of plate-like structures. Shi et al. [17] extended modal strain energy method to size damage on the basis of preliminary damage localization. With practical considerations, Shi et al. [18] further developed an improved structural damage quantification algorithm, by which the truncation and modeling errors in higher modes were reduced significantly. Hu et al. [19,20,21] used the differential quadrature method to calculate modal strain energy for identifying the surface crack location of the aluminum plate. They found that, as the second-order derivatives, modal strain energy is much more sensitive to the small change of structural response than frequencies and mode shapes. Yan et al. [22] proposed a statistic structural-damage detection algorithm based on the closed form of element modal strain energy sensitivity. Their method is oriented to the ambient vibration measurements where only the operational mode shapes are available. Entezami and Shariatmadar [23] used the direct changes of modal strain energy to identify structural damage locations. Subsequently, an improved sensitivity of modal strain energy is generated to determine damage severities. Moradi et al. [24] improved the modal strain energy method to detect and quantify the damage in complex structures at an early stage of formation. Cha and Buyukozturk [25] developed a novel damage detection approach using hybrid multi-objective optimization algorithms based on modal strain energy to detect damages in various three-dimensional steel structures. Vo-Duy et al. [26,27] combined modal strain energy with the improved differential evolution algorithm to locate and quantify damage on the laminated composite plate. Li et al. [28] developed an improved modal strain energy method for detecting damage in offshore platform structures, based on the traditional modal strain energy method. The most significant difference from the traditional method was the application of modal frequencies. Liu et al. [29] proposed a novel method to detect structural damages of offshore platforms based on grouping modal strain energy. Their method divides the unit modal strain energy into axial tension/compression and bending. This operation can overcome the problem of the incomplete modal parameters under natural load excitation. Xu and Wang [30] summarized the cross-modal strain energy method and developed a two-stage methodology for damage assessment. The wholeness strain energy approach is first utilized for roughly localizing the potentially damaged members, and then the final damage locations and associated extents are exactly estimated with the locality strain energy approach. Wu et al. [31] presented a modal strain energy based on strain modes for structural damage detection. Only strain data are adopted in their proposed method and no rotational information of the structure is required. Kaveh and Zolghadr [32] combined the cyclical parthenogenesis algorithm with the guided modal strain energy to detect structural damages. The generalized flexibility matrix of the structure is used in their method to define the objective function of the optimization problem. Ghasemi et al. [33] used the modal strain energy and a modified genetic algorithm to determine structural damage location and extent. Ashory et al. [34] developed a new objective function based on weighted strain energy for damage assessment using genetic algorithm. It is shown that the accuracy of damage location and intensity identification is improved using their method. Teng et al. [35,36] proposed a structural-damage detection method based on the convolutional neural network and modal strain energy. Two cases were considered for the input of the neural network; the first used the modal strain energy only and the second used the combination of modal strain energy and dynamic response. The comparison results show that the inclusion of dynamic responses in the damage index significantly improves the correctness rate of structural damage detection and enhances the convergence of the network. For shear buildings, Zhu et al. [37] developed a damage detection method by using the changes in the first mode shape slopes. The validity of their method is demonstrated using an eight-storey numerical example and a three-storey experimental model. Xing and Mita [38] proposed a substructure approach that allows for the local damage detection of a shear structure. Simulations and experiments on five-storey buildings were conducted to test the feasibility of their method. Aloisio et al. [39] carried out the covariance-based sensitivity analysis on a spatial truss structure to evaluate the sensitivity of damage indicators for ambient excitation covariance, damage severity, and damage location. A methodological Bayesian approach, based on the results of the sensitivity analysis, is proposed for the development of a structural reliability analysis driven by damage indicators. Their method has been successfully applied in the health monitoring system of the basilica of Santa Maria di Collemaggio in L’Aquila, Italy [40]. Niu [41] developed a damage detection method for shear frame structures by using frequency response function measurements before and after damage. The effect of noise on damage detection was greatly suppressed by simultaneously increasing the number of equations and reducing the unknown coefficients. Nguyen-Ngoc [42] proposed a damage identification approach using Particle Swarm Optimization (PSO) combined with Artificial neural network (ANN). The numerical and experimental results show that ANN–PSO not only significantly reduces computational time compared to PSO but also possibly identifies damages in the considered structures more accurately than ANN and PSO separately.
Although great progress has been made in strain energy methods in the past few decades, it is still necessary to develop a new strain energy method for damage identification according to the particularity of various structures. The shear-type structure, such as shear frame structure, is a common type used in civil engineering. In this work, a damage identification method based on the change of generalized shear energy is proposed for shear-type structures. The proposed method makes full use of the mechanical characteristics of shear-type structures. The proposed method is mainly divided into the following steps to achieve the goal of structural damage identification. Firstly, the element stiffness matrix in the structural finite element model is decomposed to obtain the elementary shear force vector. Secondly, the elementary generalized shear energy is calculated by the dot product of the vibration mode shape vector and the elementary shear force vector. Thirdly, structural damage locations are determined by the changes of elementary generalized shear energy. Finally, more accurate damage localization and quantification can be achieved by solving the mode shape sensitivity equation. The main innovations of the proposed method are as follows. (1) The generalized shear energy can be directly and quickly calculated for damage localization even if structural FEM is not constructed in advance. This is the outstanding advantage of the proposed method over the previous modal strain energy methods. (2) Compared with the pure sensitivity-based method, the proposed method has higher calculation accuracy because many undamaged elements are removed according to the shear energy changes. (3) To solve the incomplete measurement problem, mode shape expansion based on the NSE (Neumann series expansion) condensation model is proposed in this work to achieve the complete mode shape. A 20-storey shear frame structure and a three-storey experimental model are used to verify the feasibility of the proposed method. From numerical and experimental results, it was found that the proposed approach can accurately identify the location and extent of the damage in the shear structures even if the data contain noise. The proposed method provides a new way to realize the damage identification goal of shear-type structures. The remainder of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the basic principles and main formulas of the proposed generalized shear energy method. Section 3 provides the verification of the proposed method by a 20-storey shear frame structure. In Section 4, the proposed method is further verified by a three-storey experimental model. Finally, the conclusions of this work are summarized in Section 5. The assumption is made that (1) the shear-type structure is linear before and after damage occurs, (2) structural damage only reduces the system stiffness matrix, and (3) the structural refined finite element model has been developed before damage occurrence.
2. Theoretical Development
2.1. Modal Strain Energy
In this section, the damage localization principle based on modal strain energy [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] is briefly illustrated. From the structural finite element model (FEM), the free-vibration modes of a structure with degrees of freedom (DOFs) can be computed by solving the following generalized eigenvalue equation as:
where and are the mass and stiffness matrices, and are the th eigenvalue (i.e., square of frequency) and mass-normalized eigenvector (i.e., mode shape), is the th natural frequency of free-vibration. Correspondingly, the free-vibration modes of a damaged structure can also be obtained as:
where is the damaged stiffness matrix, is the stiffness change due to damage, and are the th eigenvalue and eigenvector for the damaged structure. Note that the global stiffness matrix of the undamaged structure equals the sum of all the elementary stiffness matrices, i.e.,
where is the th elementary stiffness matrix in global co-ordinates, is the th elementary stiffness matrix in local co-ordinates ( is the number of elementary DOFs), is the transformation matrix from elementary degree of freedom (DOF) to global DOF, is the total number of elements. Therefore, the stiffness change can also be expressed as the sum of the elementary stiffness matrices multiplied by the damage parameters, i.e.,
where is the damage parameter of the th element. denotes the th element is undamaged and denotes the th element is completely damaged.
From Equation (1), the mode shape can be seen as a displacement vector of the structure under the load of . As a result, the work done by the load vector can be readily calculated by
It is known that the work done by the load is transformed into the strain energy stored in the structure. Thus Equation (9) is also the definition of structural modal strain energy, that is
where is the th modal strain energy. Substituting Equation (5) into (10) yields
where is the strain energy of the th element for the th mode shape. For the damaged structure, the corresponding strain energy can be defined as
From Equations (12) and (13), the strain energy change can be calculated by
where is the strain energy change of the th element for the th mode shape. As is well known, the strain energy at the damage location will be greatly released when structural damage occurs. Therefore, the relatively large values in () will indicate the locations of the damages. This is the principle of damage localization based on modal strain energy. The previous studies [15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36] have shown that this principle can be successfully used in structural damage detection.
2.2. Generalized Shear Energy
For the shear-type structure, the rank of the elementary stiffness matrix is usually equal to 1. This means that the elementary stiffness matrix can be decomposed as
where is the unique nonzero eigenvalue of the matrix and is the corresponding eigenvector of , is also called the elementary shear force vector. Substituting Equation (15) into (12) and (13), one has
Based on Equations (16) and (17), the generalized shear energy for the intact and damaged structure can be defined as
where is the generalized shear strain energy of the th element for the undamaged structure, is the generalized shear strain energy of the th element for the damaged structure. Obviously, the generalized shear energy will have the same variation law as the strain energy for the shear-type structure before and after damage. Therefore, the change of the generalized shear energy before and after damage can also be used to determine the damage locations. Similarly, the change of the generalized shear energy can be calculated as
where is the generalized shear energy change of the th element. The relatively large values in all the () indicate the possible damage locations. For convenience, the relative rate of generalized shear energy change is defined as the new index to indicate damage location, that is
where is the relative rate of generalized shear energy change of the th element. The relatively large values in all correspond to the most possible damage locations.
According to the above derivation process, the elementary shear force vector is an important part of calculating the generalized shear energy. Next, the fast computing method on and is described as follows. For the shear-type structure, as shown in Figure 1, the node displacement vector and the node shear force vector in local co-ordinates can be expressed as
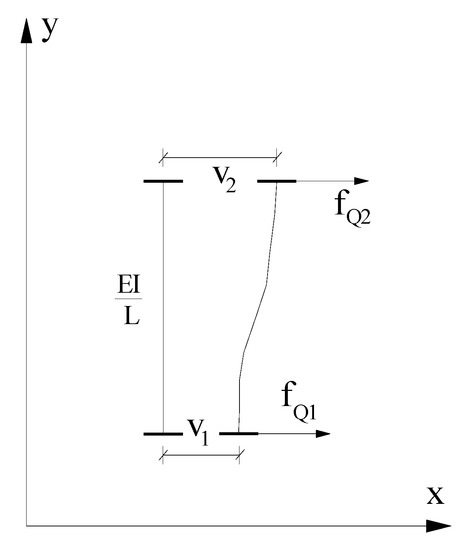
Figure 1.
Shear element with two DOFs.
According to structural mechanics, the node shear forces can be calculated by
where denotes the elastic modulus, denotes the moment of inertia, is the shear element length, and is also called the storey stiffness. From Equations (24) and (25), the elementary stiffness matrix in local co-ordinates can be obtained as
Equation (27) can be easily decomposed as
Substituting Equation (28) into (6) yields
Compared Equation (29) with (15), one can obtain
From Equations (30) and (31), it was found that and can be quickly obtained as long as , , , and are given. In especial, is independent of the material physical parameters and can be directly obtained by the DOF relation. For example, for the shear structures with two, three, and four storeys (shown in Figure 2) are listed in Table 1. This also means that the generalized shear energy can be directly calculated by Equation (18) or (19) even if structural FEM is not constructed in advance. Thus, damage localization using the proposed method for shear-type structures will be very simple and fast. This is the advantage of the proposed method over the previous modal strain energy methods.
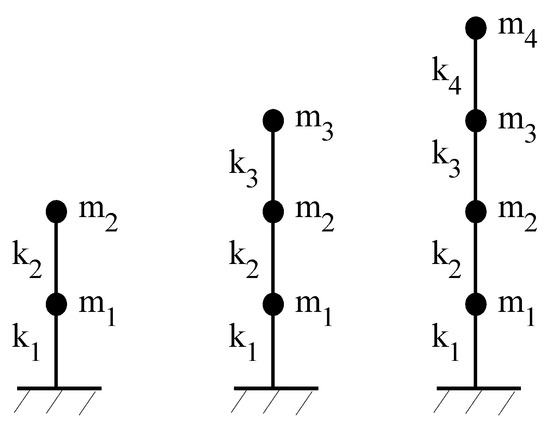
Figure 2.
Shear structures with two, three, and four storeys.

Table 1.
For the shear structures with two, three, and four storeys.
With the possible damaged elements determined by the above principle, more accurate damage localization and quantification can be achieved by solving the mode shape sensitivity equation as
where is the th mode shape change, is the damage parameter vector for the possible damaged elements, is the corresponding sensitivity matrix of the th mode shape. The mode shape sensitivity can be calculated by the following formula [43] as
where
where
From Equation (32), the desired damage parameters can be obtained as
where the superscript “+” denotes the generalized inverse of matrix. According to the resulting , the locations and extents of structural damages can be accurately evaluated again.
2.3. Mode Shape Expansion
In structural dynamic testing, it is hard to acquire a full measurement for the mode shapes due to the limitation of sensors. To solve this problem, mode shape expansion based on the NSE (Neumann series expansion) condensation model is proposed in this work to achieve the complete mode shape. The NSE condensation model, proposed by Yang in reference [44], is a succession-level approximate reduction method for obtaining a highly accurate condensation FEM for large-scale structures. Without loss of generality, the mode shape can be partitioned as
where the superscripts “” and “” denote the measured and unmeasured DOFs, respectively. Correspondingly, Equation (1) can be rewritten as
Let
Then the formula of mode shape expansion based on the first-order NSE condensation model can be obtained as
Similarly, the formula of mode shape expansion for the damaged structure is
where is the incomplete mode shape associated with measured DOFs. Using the extended mode shapes by Equations (47) and (48), the generalized shear strain energy can also be calculated by Equations (18) and (19) for structural damage localization.
In the end, a step-by-step summary of the whole technique is described as follows. Step 1: Establish the FEM of the shear-type structure. Step 2: Calculate the shear force vector using Equation (15) or (31). Step 3: Perform the modal testing of the structure to obtain the mode shapes and for the intact and damaged structures. Calculate the expanded mode shapes by Equations (47) and (48) if necessary. Step 4: Calculate the generalized shear strain energy and using Equations (18) and (19). Step 5: Calculate the relative rate of generalized shear energy change using Equation (21). Step 6: Determine the possible damaged elements according to the relatively large values in all the . Step 7: Evaluate the locations and extents of structural damages again using Equation (41). Accordingly, the flow chart of the whole technology is shown in Figure 3.
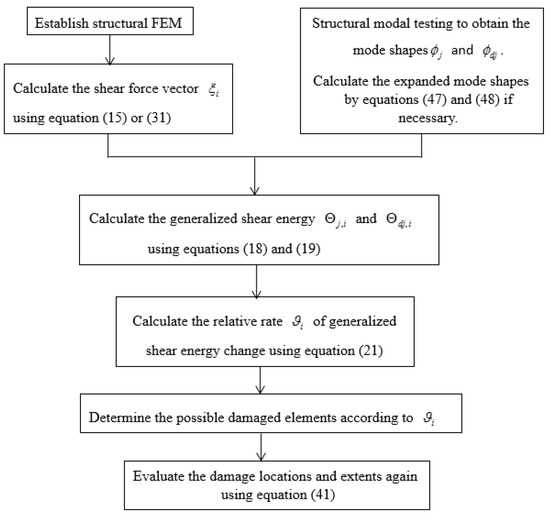
Figure 3.
The flowchart of the whole technique.
3. Numerical Verification
As shown in Figure 4, a shear frame structure with twenty floors is used to verify the feasibility of the proposed method. The storey stiffness and mass of each floor in Figure 4 are: , , , and . Four damage cases as shown in Table 2 are studied in the example. Case 1: The stiffness of the fifth floor is reduced by 20%. Case 2: The stiffness of the third and twelfth floors are reduced by 10% and 15%. Case 3: The stiffness of the seventh and eighth floors are both reduced by 20%. Case 4: The stiffness of the fourth and tenth floors are reduced by 15% and 12%. Theoretically, any mode shape of the structure can be used to calculate the generalized shear energy for damage detection. However, in practice, only the low-frequency mode modes can be measured in the structural modal test. In view of this, the first-order mode shape (i.e., the mode shape with the fundamental frequency) is used to calculate the generalized shear energy for damage identification in this example. The choose of the first-order mode shape will have the following two outstanding advantages. (1) The first-order mode shape is usually the easiest to measure and has the highest measurement accuracy. (2) If only partial DOFs are measured, the first-order extended mode shape obtained by the above mode shape expansion approach will also have the highest computation accuracy. Using the first-order mode shape, the values of all for damage case 1 obtained by the proposed method are shown in Figure 5. Note that 3% random noise is added to the mode shape data to simulate the measurement error. From Figure 5, one can find that fifth floor corresponds to the maximum shear energy change rate. When the data without noise is used, the proposed method can clearly indicate that the fifth floor is the only place where damage occurs. When 3% noise is considered, elements 5, 10, 14 and 18 can be determined as the possible damaged elements since their corresponding shear energy change rates are relatively large. Subsequently, the mode shape sensitivity equation is further used for accurate damage location and quantification. Using Equation (41), the damage parameters of elements 5, 10, 14, and 18 can be obtained as , , , and . According to the above results, element 5 can be finally judged as the real damaged location, while other elements are excluded.
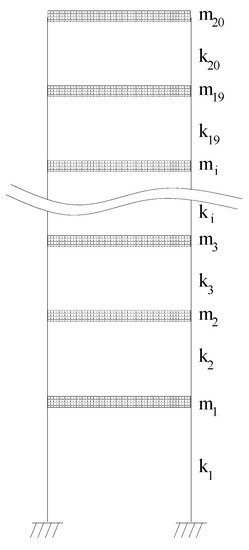
Figure 4.
A shear frame structure with twenty floors.

Table 2.
Damage cases in the example.
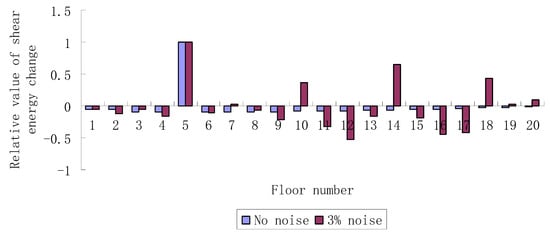
Figure 5.
Relative rates of shear energy changes when the fifth floor is damaged.
For damage case 2, the values of all obtained from steps 1-5 of the proposed method are shown in Figure 6. According to Figure 6, it was found that the third and twelfth floors correspond to the relatively large rates of shear energy changes. When the data without noise is used, the proposed method can clearly indicate that the third and twelfth floors are the locations where damage occurs. When 3% noise is considered, elements 3, 8, 12, and 18 can be determined as the possible damaged elements since their corresponding shear energy change rates are relatively large. Again, the mode shape sensitivity equation is further used for accurate damage location and quantification. The damage parameters of elements 3, 8, 12, and 18 can be computed using Equation (41) as , , , and . From the above results, elements 3 and 12 can be finally judged as the real damaged locations, while other elements are excluded.
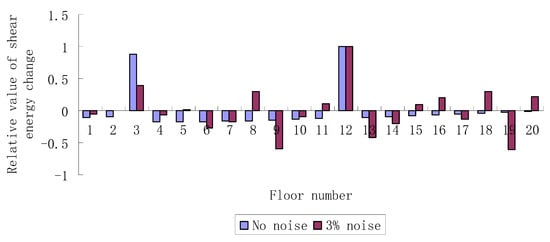
Figure 6.
Relative rates of shear energy changes when the third and twelfth floors are damaged.
Damage case 3 is used to investigate the feasibility of the proposed method for identifying the damages of adjacent elements in the structure. Figure 7 presents the values of all obtained by the proposed method. It is clear from Figure 7 that the seventh and eighth floors can be determined as the damaged elements if noise free data is used. When noisy data is used, elements 7, 8, 15, 17, and 19 can be selected as the possible damaged elements since their corresponding rates of shear energy changes are relatively large. Using Equation (41), the damage parameters of these possible damaged elements can be calculated as , , , , and . Apparently, elements 7 and 8 can be finally determined to be the true damaged elements and the other elements can be excluded. The above results show that the proposed method can successfully identify the damages in the shear-type structure even if the contaminated data is used.
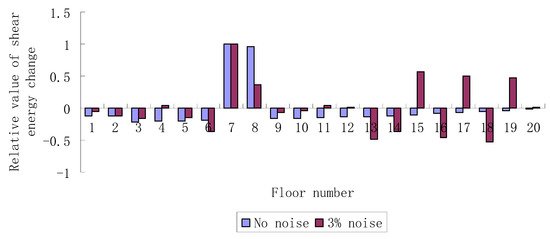
Figure 7.
Relative rates of shear energy changes when the seventh and eighth floors are damaged.
Note that, in essence, the proposed method is a two-stage damage assessment algorithm. The first stage is to determine the possible damaged locations by the generalized shear energy change. The second stage is to calculate the damage parameters of those possible damaged elements by the mode shape sensitivity method. Compared with the pure sensitivity-based method, the proposed method has higher calculation accuracy because many undamaged elements are removed in the first stage. Damage case 4 is used for the comparative study on the proposed method and the pure sensitivity-based method. When data with 3% random noise is used, Table 3 presents the calculation results obtained by the pure sensitivity-based method. From Table 3, it has been shown that the true damaged elements 4 and 10 cannot be clearly identified according to the results obtained by the pure sensitivity-based method. Using the proposed method, Figure 8 presents the values of all obtained by the first-order mode shape. It is clear from Figure 8 that elements 4, 10, 14, 16, and 18 can be selected as the possible damaged elements since their corresponding rates of shear energy changes are relatively large. Using Equation (41), the damage parameters of these possible damaged elements can be calculated as , , , , and . Apparently, elements 4 and 10 can be finally determined to be the true damaged elements and the other elements can be excluded. The above results show that the identification accuracy of the proposed method is higher than that of the pure sensitivity-based method.

Table 3.
Calculation results by the pure sensitivity-based method.
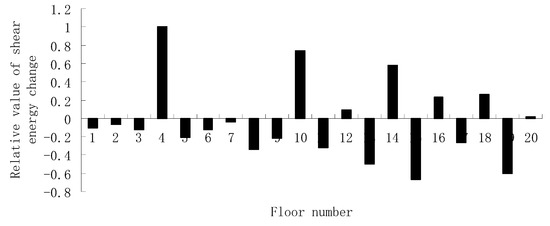
Figure 8.
Relative rates of shear energy changes when the fourth and tenth floors are damaged (3% noise).
Next, damage case 4 is further used to demonstrate the proposed method by using the extended mode shape when only partial DOFs are measured. It is assumed that floors 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, and 20 are measured and the other floors are unmeasured. Using the corresponding partial DOF data, the extended mode shapes are firstly calculated by Equations (47) and (48) and then used for computing the generalized shear energy. Figure 9 presents the values of all obtained by the proposed method using the first-order extended mode shape. From Figure 9, elements 4, 9, 10, 13 and 15 can be determined as the possible damaged elements since their corresponding shear energy-change rates are relatively large. Subsequently, the damage parameters of these possible damaged elements can be further computed using Equation (41) as , , , , and . From the above results, elements 4 and 10 can be finally judged as the real damaged locations, while other elements are excluded. It has been shown that the proposed method is also applicable for the situation when the amplitudes in some of the stories are missed.
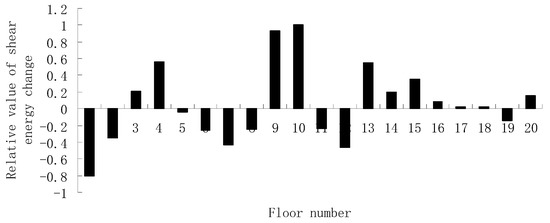
Figure 9.
Relative rates of shear energy changes using the incomplete mode shape.
4. Experimental Verification
In this section, the proposed generalized shear energy method is further verified by the experimental data obtained from a three-storey steel frame model in reference [45]. This test model is composed of three steel plates and four rectangular columns, as shown in Figure 10. The plates and columns were welded to form rigid connections. Detailed instructions of material physical parameters and test processes are shown in reference [45]. The damage situation was implemented by cutting part of the columns on the first floor, and the corresponding damage extent was about 11.6%. The first-order frequency and mode shape for the undamaged experimental model are: and . The first-order frequency and mode shape for the damaged experimental model are: and . Using the proposed method, the values of all calculated by the first-order mode shape are shown in Figure 11. From Figure 11, one can find that the first floor corresponds to the maximum shear energy change rate. This means that the first floor is the location where damage occurs. Using Equation (41), the damage parameter of the first floor can be obtained as . It has been shown that the proposed method can successfully identify the damage in this experimental structure. Note that the proposed method may also be suitable for detecting other damage types such as loose connection and material fatigue, as long as there is observable shear deformation before and after damage. More numerical and experimental studies should be carried out to popularize the proposed method in the future.
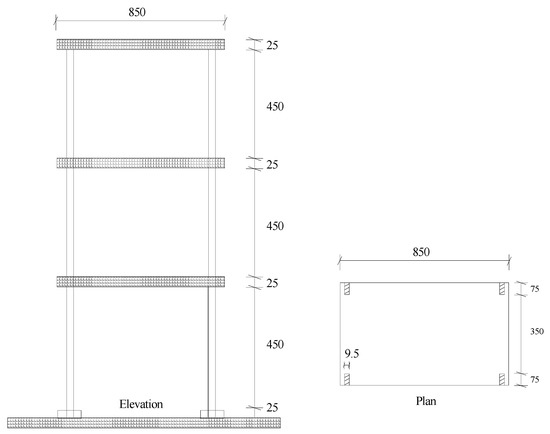
Figure 10.
Steel frame test model.
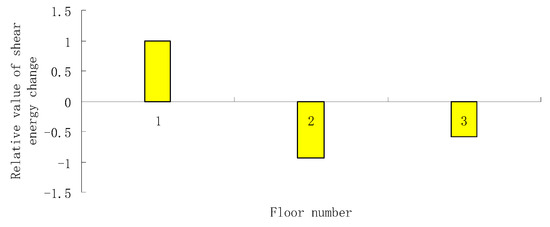
Figure 11.
Relative rates of shear energy changes for the experimental model when the first floor is damaged.
5. Conclusions
A generalized shear energy method is proposed in this work for damage identification in shear-type structures. The proposed method makes use of the decomposition of elementary stiffness matrix and the vibration mode shape of the shear-type structure. Due to energy release after damage, the generalized shear energy of the structure will be redistributed in each shear element. As a result, the generalized shear energy of the damaged element will have a larger change when damage occurs. Thus, the change of the generalized shear energy can be served as the indexes of the damage locations in the shear-type structure. The proposed damage detection method is demonstrated by a 20-storey shear frame structure and a three-story experimental model. From the numerical and experimental results, it was found that the relatively large values in the shear energy changes indicate the possible damage locations. With damage locations determined by the generalized shear energy method, more accurate damage localization and quantification can be achieved by solving the mode shape sensitivity equation even if the mode shape data used contain random noise. The proposed method provides a simple and effective way of damage identification of shear-type structures.
Author Contributions
Methodology, Y.S. and Q.Y.; Software, X.P.; Validation, Y.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work is supported by the public welfare technology application research project of Zhejiang Province, China (LGF22E080021), Natural Science Foundation of China (52008215), the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province, China (LQ20E080013), the major special science and technology project (2019B10076) of” Ningbo science and technology innovation 2025”, and Ningbo natural science foundation project (202003N4169).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are included within the article and also available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
References
- Fan, W.; Qiao, P. Vibration-based damage identification methods: A review and comparative study. Struct. Health Monit. 2011, 10, 83–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvandi, A.; Cremona, C. Assessment of vibration-based damage identification techniques. J. Sound Vib. 2006, 292, 179–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ierimonti, L.; Cavalagli, N.; Venanzi, I.; García-Macías, E.; Ubertini, F. A transfer Bayesian learning methodology for structural health monitoring of monumental structures. Eng. Struct. 2021, 247, 113089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.W.; Sun, B.X. Structural damage localization and quantification using static test data. Struct. Health Monit. 2011, 10, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.T.; Eun, H.C. Damage detection of damaged beam by constrained displacement curvature. J. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2008, 22, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, H.; Xu, X.; Peng, W.; Zhou, Z.; Hong, M. A damage detection method based on strain modes for structures under ambient excitation. Measurement 2018, 125, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Mu, H.; Pommerenke, D.; Drewniak, J.L. Damage detection of reinforced concrete beams with novel distributed crack/strain sensors. Struct. Health Monit. 2004, 3, 225–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yang, Q.W. Sensor Placement and Structural Damage Evaluation by Improved Generalized Flexibility. IEEE Sens. J. 2021, 21, 11654–11664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Peng, X. Sensitivity Analysis Using a Reduced Finite Element Model for Structural Damage Identification. Materials 2021, 14, 5514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.R.; Wang, L. An enhanced response sensitivity approach for structural damage identification: Convergence and performance. Int. J. Numer. Methods Eng. 2017, 111, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.W.; Liu, J.K. Structural damage identification based on residual force vector. J. Sound Vib. 2007, 305, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, A.Z.; Amiri, G.G.; Abyaneh, M.J.; Razzaghi, S.A.S.; Hamzehkolaei, A.G. Baseline updating method for structural damage identification using modal residual force and grey wolf optimization. Eng. Optim. 2019, 52, 549–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lian, J.; Ma, B. Intelligent damage identification method for large structures based on strain modal parameters. J. Vib. Control 2014, 20, 1783–1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Gu, X.; Li, J. A novel deep learning-based method for damage identification of smart building structures. Struct. Health Monit. 2019, 18, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doebling, S.W.; Farrar, C.R.; Prime, M.B. A summary review of vibration-based damage identification methods. Shock Vib. Dig. 1998, 30, 91–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cornwell, P.; Doebling, S.W.; Farrar, C.R. Application of the strain energy damage detection method to plate-like structures. J. Sound Vib. 1999, 224, 359–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Law, S.S.; Zhang, L.M. Structural damage detection from modal strain energy change. J. Eng. Mech. 2000, 126, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.Y.; Law, S.S.; Zhang, L.M. Improved damage quantification from elementary modal strain energy change. J Eng Mech-Asce 2002, 128, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, B.-T.; Lee, C.-H.; Su, J.-S. Damage detection of surface cracks in composite laminates using modal analysis and strain energy method. Compos. Struct. 2006, 74, 399–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, J. Damage detection of a woven fabric composite laminate using a modal strain energy method. Eng. Struct. 2009, 31, 1042–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wu, C. Development of scanning damage index for the damage detection of plate structures using modal strain energy method. Mech. Syst. Signal Processing 2009, 23, 274–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.J.; Ren, W.X.; Huang, T.L. Statistic structural damage detection based on the closed-form of element modal strain energy sensitivity. Mech. Syst. Signal Processing 2012, 28, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Entezami, A.; Shariatmadar, H. Damage detection in structural systems by improved sensitivity of modal strain energy and Tikhonov regularization method. Int. J. Dyn. Control 2014, 2, 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moradi Pour, P.; Chan, T.; Gallage, C. An improved modal strain energy method for structural damage detection, 2D simulation. Struct. Eng. Mech. 2015, 54, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cha, Y.J.; Buyukozturk, O. Structural damage detection using modal strain energy and hybrid multiobjective optimization. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2015, 30, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo-Duy, T.; Ho-Huu, V.; Dang-Trung, H.; Dinh-Cong, D.; Nguyen-Thoi, T. Damage detection in laminated composite plates using modal strain energy and improved differential evolution algorithm. Procedia Eng. 2016, 142, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vo-Duy, T.; Ho-Huu, V.; Dang-Trung, H.; Nguyen-Thoi, T. A two-step approach for damage detection in laminated composite structures using modal strain energy method and an improved differential evolution algorithm. Compos. Struct. 2016, 147, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Zheng, C. An improved modal strain energy method for damage detection in offshore platform structures. J. Mar. Sci. Appl. 2016, 15, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhai, Y.; Leng, D.; Tian, X.; Mu, W. Research on structural damage detection of offshore platforms based on grouping modal strain energy. Ocean Eng. 2017, 140, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, S. Cross modal strain energy–based structural damage detection in the presence of noise effects. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9, 1687814017744122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Zhou, J.; Rui, S.; Fei, Q. Reformulation of elementary modal strain energy method based on strain modes for structural damage detection. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2017, 20, 896–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaveh, A.; Zolghadr, A. Cyclical parthenogenesis algorithm for guided modal strain energy based structural damage detection. Appl. Soft Comput. 2017, 57, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, M.R.; Nobahari, M.; Shabakhty, N. Enhanced optimization-based structural damage detection method using modal strain energy and modal frequencies. Eng. Comput. 2018, 34, 637–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashory, M.R.; Ghasemi-Ghalebahman, A.; Kokabi, M.J. An efficient modal strain energy-based damage detection for laminated composite plates. Adv. Compos. Mater. 2018, 27, 147–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, S.; Chen, G.; Liu, G.; Lv, J.; Cui, F. Modal strain energy-based structural damage detection using convolutional neural networks. Appl. Sci. 2019, 9, 3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teng, S.; Chen, G.; Gong, P.; Liu, G.; Cui, F. Structural damage detection using convolutional neural networks combining strain energy and dynamic response. Meccanica 2020, 55, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Li, L.; He, X.Q. Damage detection method for shear buildings using the changes in the first mode shape slopes. Comput. Struct. 2011, 89, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.H.; Mita, A. A substructure approach to local damage detection of shear structure. Struct. Control Health Monit. 2012, 19, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisio, A.; Di Battista, L.; Alaggio, R.; Fragiacomo, M. Sensitivity analysis of subspace-based damage indicators under changes in ambient excitation covariance, severity and location of damage. Eng. Struct. 2020, 208, 110235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloisio, A.; Di Battista, L.; Alaggio, R.; Antonacci, E.; Fragiacomo, M. Assessment of structural interventions using Bayesian updating and subspace-based fault detection methods: The case study of S. Maria di Collemaggio basilica, L’Aquila, Italy. Struct. Infrastruct. Eng. 2021, 17, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Z. Two-step structural damage detection method for shear frame structures using FRF and Neumann series expansion. Mech. Syst. Signal Processing 2021, 149, 107185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngoc, L.; Tran, H.; Bui-Tien, T.; Mai-Duc, A.; Wahab, M.A.; Nguyen, H.X.; De Roeck, G. Damage detection in structures using particle swarm optimization combined with artificial neural network. Smart Struct. Syst. 2021, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.W.; Peng, X. An exact method for calculating the eigenvector sensitivities. Appl. Sci. 2020, 4, 2577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Q.W. Model reduction by Neumann series expansion. Appl. Math. Model. 2009, 33, 4431–4434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, L. Numerical and Experimental Studies of Damage Detection for Shear Buildings. Ph.D Thesis, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China, 2005. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).