Research on the Interaction Capability and Microscopic Interfacial Mechanism between Asphalt-Binder and Steel Slag Aggregate-Filler
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Experimental Test Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of the Asphalt Mortar
2.2.2. Physical Property Testing
2.2.3. Rheological Property Testing
2.2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectrometer Testing
2.2.5. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) Testing
3. Laboratory Test Results and Analysis
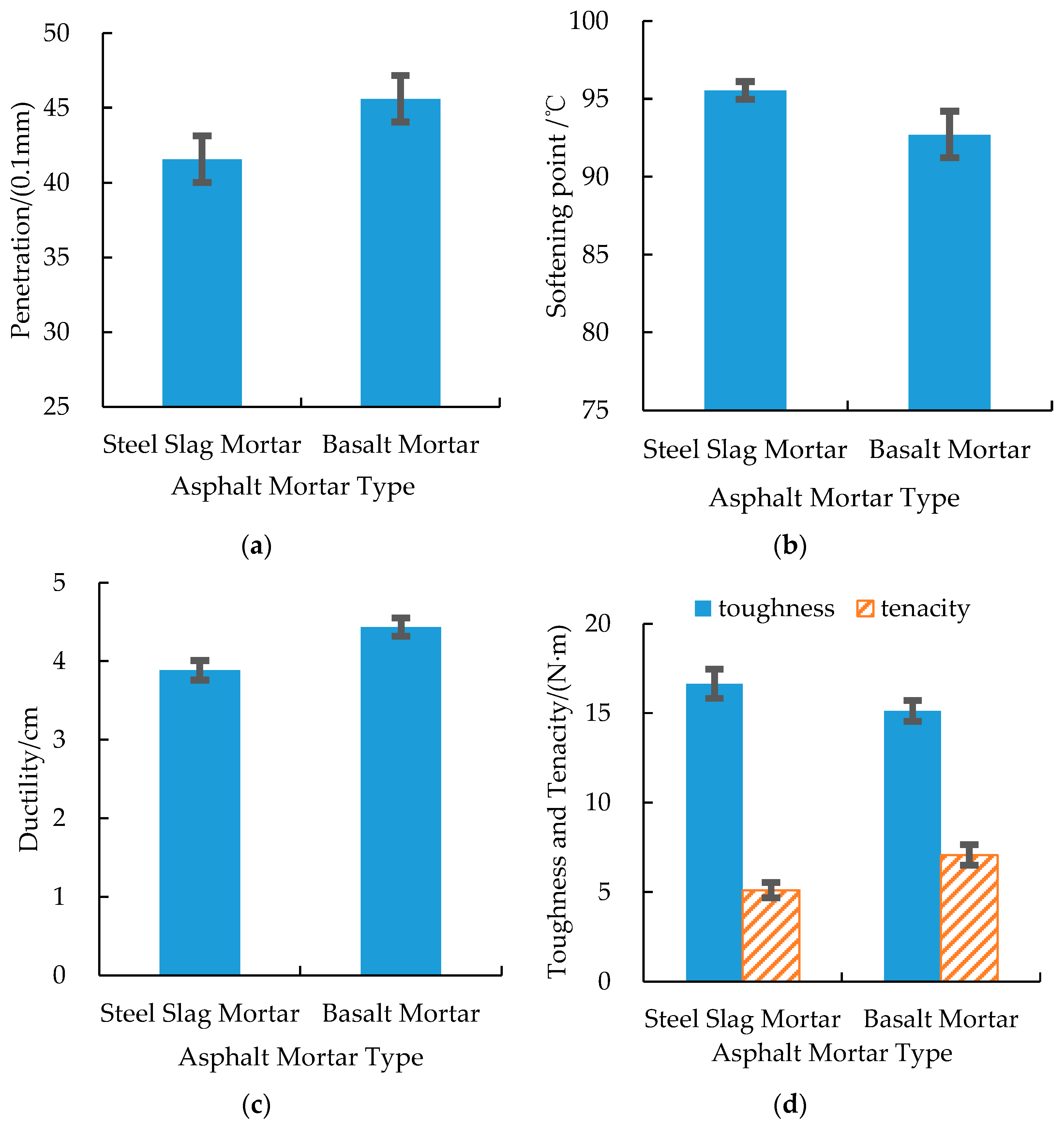
3.1. Physical Properties of the Asphalt Mortar
3.2. Rheological Properties of the Asphalt Mortar
3.3. Asphalt-Binder-Filler Interaction Capability
3.3.1. Parametric Index Formulation
- The dispersed phase presented a spherical distribution when in a continuous matrix phase.
- The interfacial tension between the dispersed phase and matrix phase had no relationship with the partial area change.
3.3.2. Parametric Index Results and Evaluation
3.4. Chemical Bonding between the Asphalt-Binder and Aggregate
3.5. SEM Imaging Results
4. Conclusions
- The physical properties of the steel slag and basalt asphalt mortars were quantitatively similar and did not significantly differ from each other.
- The rheological properties of the steel slag asphalt mortar exhibited superiority over the basalt asphalt mortar, with the latter being more temperature sensitive and less rutting resistant. At intermediate temperatures, however, the difference in the rheological properties between the steel slag and basalt asphalt mortar was quantitatively insignificant.
- The parametric indices obtained from DSR rheological testing were found to be satisfactory for use as indicative measures to characterize and quantify the asphalt-binder-aggregate (filler) interaction capability. The corresponding results and findings indicated better interaction capability and interfacial bonding potential between the asphalt-binder and steel slag aggregate-filler than that between the asphalt-binder and the basalt aggregate-filler.
- Based on the FTIR analysis, the main action between the asphalt-binder and basalt aggregates was predominantly physical. By contrast, the chemical bonding action between the asphalt-binder and steel slag aggregates that generated organic silicon compounds significantly contributed to enhancing the interfacial bond strength within the steel slag asphalt mortar.
- From SEM imaging analysis, the micro-surface texture of the steel slag aggregates was observed to be more overgrown and rougher than that of the basalt aggregates, which alluded to the improved adhesion between the asphalt-binder and steel slag aggregates. In addition to the chemical bonding force generated from the chemical reactions, there was also a strong mechanical bonding force that greatly enhanced the interfacial bond strength between the asphalt-binder and steel slag aggregate-fillers.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Diab, A.; Enieb, M. Investigating influence of mineral filler at asphalt mixture and mastic scales. Int. J. Pavement Res. Technol. 2018, 11, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Su, P.; Li, M.; You, Z.; Zhao, M. Review on evolution and evaluation of asphalt pavement structures and materials. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. Engl. Ed. 2020, 7, 573–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Qiu, X.; Xiao, S.; Hong, H.; Wang, F.; Yuan, J. Characteristics and Mechanisms of Asphalt–Filler Interactions from a Multi-Scale Perspective. Materials 2020, 13, 2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Faruk, A.N.M.; Fuentes, L.; Prakoso, A.; Dessouky, S.; Naik, B.; Nyamuhokya, T. Using the Simple Punching Shear Test (SPST) for evaluating the HMA shear properties and predicting field rutting performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 224, 920–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xu, S.; Tebaldi, G.; Romeo, E. Role of mineral filler in asphalt mixture. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2022, 23, 247–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhtar, N.; Mohd Hasan, M.R.; Mohd Ghazali, M.F.H.; Mohd Zin, Z.; Shariff, K.A.; Sani, A. Influence of concentration and packing of filler particles on the stiffening effect and shearing behaviour of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 295, 123660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Y.; Wei, R.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Pei, J. Evaluation of rheological master curves of asphalt mastics and asphalt-filler interaction indices. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 265, 120046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Lee, S.I.; Faruk, A.N.M.; Scullion, T.; Nazarian, S.; Abdallah, I. Texas Flexible Pavements and Overlays: Year 5 Report-Complete Data Documentation; Texas A&M Transportation Institute: Bryan, TX, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- John, I.; Bangi, M.R.; Lawrence, M. Effect of Filler and Binder Contents on Air Voids in Hot-Mix Asphalt for Road Pavement Construction. Open J. Civ. Eng. 2021, 11, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lyv, Y.; Fan, L.; Zhang, Y. Effects of Cement and Emulsified Asphalt on Properties of Mastics and 100% Cold Recycled Asphalt Mixtures. Materials 2019, 12, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, K.H.; Falchetto, A.C.; Wang, D.; Riccardi, C.; Wistuba, M.P. Mechanical Performance of Asphalt Mortar Containing Hydrated Lime and EAFSS at Low and High Temperatures. Materials 2017, 10, 743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büchner, J.; Wistuba, M.P. Relating Asphalt Mixture Performance to Asphalt Mastic Rheology. In Lecture Notes in Civil Engineering; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; Volume 76, pp. 639–649. [Google Scholar]
- Steineder, M.; Peyer, M.J.; Hofko, B.; Chaudhary, M.; Saboo, N.; Gupta, A. Comparing different fatigue test methods at asphalt mastic level. Mater. Struct. Mater. Et. Constr. 2022, 55, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Pei, Z.; Luo, C.; Xia, J.; Chen, C.; Kang, A. Effect of different basalt fibers on the rheological behavior of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 125718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Fuentes, L.; Tanvir, H.; Chunduri, H.R.; Dessouky, S. Correlating the Asphalt-Binder BBR Test Data to the HMA (ML-OT) Fracture Properties. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2021, 33, 04021230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Gonzalez-Hernandez, J.G.; Martinez-Arguelles, G.; Tanvir, H.; Fuentes, L.; Tahami, S.A. Statistical Evaluation of the Material-Source Effects on the DSR Rheological Properties of Plant-Mix Extracted Asphalt-Binders. Materials 2021, 14, 1931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Mohammedawi, A.; Mollenhauer, K. A Study on the Influence of the Chemical Nature of Fillers on Rheological and Fatigue Behavior of Bitumen Emulsion Mastic. Materials 2020, 13, 4627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arulrajah, A.; Mohammadinia, A.; D’Amico, A.; Horpibulsuk, S. Cement kiln dust and fly ash blends as an alternative binder for the stabilization of demolition aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 218–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Qian, Z.; Huang, W.; Li, H.; Liu, Y. Low-temperature thermal cracking performance of waterborne epoxy asphalt emulsion mastic based on bending beam rheometer (BBR). Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 334, 127461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, Y. The interfacial effect of mineral filler to asphalt binder and its influence on asphalt aging behavior. Mater. Struct. Mater. Et Constr. 2021, 54, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zhou, S.; Peng, A. Comparison of performance characterization of asphalt mastic prepared by foamed and unfoamed asphalt binders. J. Therm. Anal. 2021, 144, 657–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Yang, Y. Experimental investigation on the influence of interfacial effects of limestone and fly ash filler particles in asphalt binder on mastic aging behaviors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 290, 123184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Xie, J.; Yang, C.; Wan, P.; Guo, S.; Ma, W. Characteristics of calcareous sand filler and its influence on physical and rheological properties of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-Y.; Tan, Y.-Q.; Liu, K.; Xu, H.-N. Preparation and electrical properties of conductive asphalt concretes containing graphene and carbon fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 318, 125875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Sun, G.; Sun, D.; Lu, T.; Ma, J.; Deng, Y. Survival and activation behavior of microcapsules in self-healing asphalt mixture. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Wei, J.; Chen, Z.; Wang, F.; Zhao, J. Evaluation of the Effects of Filler Fineness on the Properties of an Epoxy Asphalt Mixture. Materials 2021, 14, 2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marath, A.; Singh, D.; Rajan, B. Stiffness Behavior and Micromechanical Modeling of Asphalt Mastic Composed of Different Fillers. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2022, 34, 04022179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, A.; Lesueur, D. Impact of Different Fillers on the Properties of Asphalt Mixtures. In Proceedings of the RILEM International Symposium on Bituminous Materials, Lyon, France, 14–16 December 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1007–1013. [Google Scholar]
- Choudhary, J.; Kumar, B.; Gupta, A. Effect of Filler Type and Content on the Rheological Properties of Asphalt Mastics. In Proceedings of the RILEM International Symposium on Bituminous Materials, Lyon, France, 14–16 December 2020; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 591–597. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Chen, Z.; Wu, S.; Li, B.; Xie, J.; Xiao, Y. Effects of steel slag fillers on the rheological properties of asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Wu, S.; Xu, H.; Li, H.; Yang, C. Characterization of Steel Slag Filler and Its Effect on Aging Resistance of Asphalt Mastic with Various Aging Methods. Materials 2021, 14, 869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Victory, W. A review on the utilization of waste material in asphalt pavements. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 27279–27282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, P. Properties of a Steel Slag–Permeable Asphalt Mixture and the Reaction of the Steel Slag–Asphalt Interface. Materials 2019, 12, 3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, W.; Jiang, W.; Yuan, D.; Lu, R.; Shan, J.; Xiao, J.; Ogbon, A.W. A review of asphalt-filler interaction: Mechanisms, evaluation methods, and influencing factors. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 124279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JTG E20-2011; Standard Test Methods of Bitumen and Bituminous Mixtures for Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2011.
- JTG F40-2004; Technical Specification for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2004.
- JTG E42-2005; Test Methods of Aggregate for Highway Engineering. China Communications Press: Beijing, China, 2005.
- Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Zhu, C.; Pei, J. Evaluation indices of asphalt–filler interaction ability and the filler critical volume fraction based on the complex modulus. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 1338–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faheem, A.F.; Bahia, H. Conceptual Phenomenological Model for Interaction of Asphalt Binders with Mineral Fillers. Asph. Paving Technol. Proc. 2009, 28, 679. [Google Scholar]
- Walubita, L.F.; Martinez-Arguelles, G.; Chunduri, H.R.; Gonzalez Hernandez, J.G.; Fuentes, L. Statistical Evaluation of the Material-Source Effect on the Ductility and Elastic Recovery (ER) of Plant-Mix Extracted Asphalt-Binders. Adv. Civ. Eng. 2020, 2020, 8851691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Ji, G.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, J. Research on High- and Low-Temperature Characteristics of Bitumen Blended with Waste Eggshell Powder. Materials 2021, 14, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polo-Mendoza, R.; Martinez-Arguelles, G.; Walubita, L.F.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Giustozzi, F.; Fuentes, L.; Navarro-Donado, T. Ultraviolet ageing of bituminous materials: A comprehensive literature review from 2011 to 2022. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 350, 128889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ressler, T. WinXAS: A New Software Package not only for the Analysis of Energy-Dispersive XAS Data. J. Phys. IV Fr. 1997, 7, C2-269–C262-270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louanate, A.; Otmani, R.E.; Kandoussi, K.; Boutaous, M.H. Characterization of the rheological behavior of a paraffin-based phase change material under steady and oscillatory shear. Thermochim. Acta 2021, 704, 179018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, T.; Hu, Z.-A.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Fuentes, L.; Walubita, L.F. Rejuvenation of short-term aged asphalt-binder using waste engine oil. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2020, 47, 822–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krotova, S.Y.; Ilin, A.E.; Chirgin, A.V. Analysis of software products for processing the results of spectroscopy. Int. J. Mech. Eng. Technol. 2019, 10, 1823–1832. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Huang, Z. Investigation of the Microcharacteristics of Asphalt Mastics under Dry–Wet and Freeze–Thaw Cycles in a Coastal Salt Environment. Materials 2019, 12, 2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wei, H.; Bai, X.; Qian, G.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y. Aging Mechanism and Properties of SBS Modified Bitumen under Complex Environmental Conditions. Materials 2019, 12, 1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, S.; Fan, Y.; Feng, Z.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, C.; Huang, H. Comparison of quantitative determination for SBS content in SBS modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 282, 122733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, H.; Wu, S. Aging Mechanism and Rejuvenating Possibility of SBS Copolymers in Asphalt Binders. Polymers 2020, 12, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walubita, L.F.; Mahmoud, E.; Fuentes, L.; Prakoso, A.; Lee, S.I.; Souliman, M.; Komba, J.J. Correlating the asphalt-binder high-temperature properties (DSR) to HMA permanent deformation (RLPD) and field rutting: A laboratory-field study. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 262, 120761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Zhang, J.; Alvarez, A.E.; Hi, X. Exploring the flow number (FN) index as a means to characterise the HMA permanent deformation response under FN testing. J. South Afr. Inst. Civ. Eng. 2013, 55, 103–112. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, T.; Cheng, Z.; Hu, X.; Fuentes, L.; Walubita, L.F. Viscoelastic modelling of an asphalt pavement based on actual tire-pavement contact pressure. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 22, 2458–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varma, R.; Narayan, A.; Krishnan, M. Quantification of Viscous and Fatigue Dissipation of Asphalt Concrete in Four-Point Bending Tests. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Martin, A.E.; Cleveland, G.S.; Lytton, R.L. Computation of pseudo strain energy and Paris law fracture coefficients from surface energy and uniaxial strain-controlled tension test data. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2006, 7, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Simate, G.S.; Ofori-Abebresse, E.; Martin, A.E.; Lytton, R.L.; Sanabria, L.E. Mathematical formulation of HMA crack initiation and crack propagation models based on continuum fracture-mechanics and work-potential theory. Int. J. Fatigue 2012, 40, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walubita, L.F.; Martin, A.E.; Glover, C.; Jung, S.H.; Cleveland, G.; Lytton, R.L. Fatigue Characterization of HMAC Mixtures Using Mechanistic Empirical and Calibrated Mechanistic Approaches Including the Effects of Aging. In Asphalt Concrete: Simulation, Modeling, and Experimental Characterization; American Society of Civil Engineers: Reston, VA, USA, 2005; pp. 103–114. [Google Scholar]
- Bahia, H.; Anderson, D.A. Strategic highway research program binder rheological parameters: Background and comparison with conventional properties. Transp. Res. Rec. 1995, 1488, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Fan, S.; Li, X.; Pan, P.; Fuentes, L.; Walubita, L.F. Exploring the feasibility of using reclaimed paper-based asphalt felt waste as a modifier in asphalt-binders. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 234, 117379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ge, D.; Wang, J.; Wu, D.; Liu, J. The Performance Evaluation of Asphalt Mortar and Asphalt Mixture Containing Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Fly Ash. Materials 2022, 15, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, Y.; Hossiney, N.; Tebaldi, G. Low temperature performance evaluation of asphalt binders and mastics based on relaxation characteristics. Mater. Struct. 2022, 55, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, X.; Apostolidis, P.; Scarpas, T. Non-Newtonian Behaviors of Crumb Rubber-Modified Bituminous Binders. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sybilski, D. Non-newtonian viscosity of polymer-modified bitumens. Mater. Struct. 1993, 26, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diab, A.; You, Z.; Li, X.; Pais, J.C.; Yang, X.; Chen, S. Rheological models for non-newtonian viscosity of modified asphalt binders and mastics. Egypt. J. Pet. 2020, 29, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipińska, M. The Effect of Various Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes on Viscoelastic, Thermal Properties and Crystallization of Poly(ε-caprolactone) Nanocomposites. Polymers 2022, 14, 5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Jia, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yang, T.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J. Quantitative comparison of evaluation indices for asphalt–filler interaction ability within filler critical volume fraction. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2020, 21, 906–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibarra, L.; Paños, D. Dynamic properties of thermoplastic butadiene-styrene (SBS) and oxidized short carbon fiber composite materials. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 67, 1819–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, J.; Yang, T.; Zhang, J. Applicability of evaluation indices for asphalt and filler interaction ability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 148, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziegel, K.D.; Romanov, A. Modulus reinforcement in elastomer composites. I. Inorganic fillers. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1973, 17, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Hu, Z.; Zhu, C.; Pei, J.; Jin, L. Effects of temperature and loading frequency on asphalt and filler interaction ability. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 124, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palierne, J.F. Linear rheology of viscoelastic emulsions with interfacial tension. Rheol. Acta 1990, 29, 204–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, T.; Zhao, K.; Wang, L. Reinforcement Effect of Different Fibers on Asphalt Mastic. Materials 2022, 15, 8304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fan, Z.; Hu, D.; Hu, Z.; Pei, J.; Kong, W. Evaluation of asphalt–aggregate interaction based on the rheological properties. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2018, 19, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, J. Internal Influence Factors of Asphalt-Aggregate Filler Interactions Based on Rheological Characteristics. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2012, 24, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Chen, H.; Kuang, D.; Song, L.; Wang, L. Effect of chemical composition of aggregate on interfacial adhesion property between aggregate and asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, P. Effects of Steel-Slag Components on Interfacial-Reaction Characteristics of Permeable Steel-Slag–Bitumen Mixture. Materials 2020, 13, 3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Li, H.; Zhu, H.; Xu, P. The Interfacial Adhesion Performance and Mechanism of a Modified Asphalt–Steel Slag Aggregate. Materials 2020, 13, 1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, A.M.; Suhandri, H.F.; Realini, E.; Reguzzoni, M.; de Lacy, M.C. goGPS: Open-source MATLAB software. GPS Solutions 2015, 20, 595–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knight, A. Basics of MatLab® and Beyond; Chapman and Hall/CRC: London, UK, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- So, G.-B.; So, H.-R.; Jin, G.-G. Enhancement of the Box-Counting Algorithm for fractal dimension estimation. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 98, 53–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, G.; Xiao, Y.; Yang, L.; Cui, P.; Kong, D.; Xue, Y. Characteristics of steel slag filler and its influence on rheological properties of asphalt mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 201, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Zhao, G.; Tighe, S.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Adhikari, S.; Gao, Y. Quantitative comparison of surface and interface adhesive properties of fine aggregate asphalt mixtures composed of basalt, steel slag, and andesite. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 246, 118507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, A.; Zhai, C.; Guo, Y.; Yang, X. Mechanism of adhesion property between steel slag aggregate and rubber asphalt. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2018, 32, 2727–2740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Yu, B.; Hong, Q. Molecular dynamics simulation of distribution and adhesion of asphalt components on steel slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 255, 119332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Index | Units | Test Results | Spec Requirement [36] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Penetration (25 °C, 100 g, 5 s) | 0.1 mm | 55.9 | 40~60 | |
| Penetration index (PI) | - | 0.2 | −0.2~+1.0 | |
| Ductility (5 cm/min, 5 °C) | cm | 34.6 | ≥20 | |
| Softening point (ring and ball method) | °C | 82.5 | ≥70 | |
| Density | g/cm3 | 1.029 | - | |
| After TFOT 1 | Mass variation | % | 0.14 | ≤±1.0 |
| Softening point difference (After-before) | °C | −4 | −12~+10 | |
| Penetration ratio (25 °C) | % | 80 | ≥65 | |
| Ductility (5 °C) | cm | 22.6 | ≥15 | |
| Index | Units | Basalt | Steel Slag | Spec Requirement [36] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apparent specific gravity | - | 2.900 | 3.549 | ≥2.60 |
| Water absorption | % | 0.47 | 1.59 | ≤2.0 |
| Crush value | % | 10.4 | 13.4 | 13.4 |
| Los Angeles abrasion value | % | 14.6 | 10.7 | 10.7 |
| Flat elongated particles content | % | 9.8 | 10.1 | 10.1 |
| Water washing method (<0.075 mm particle Content) | % | 0.47 | 0.47 | 0.47 |
| Adhesion | - | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Polishing value | - | 49 | 52 | 52 |
| Aggregate Type | Steel Slag | Basalt |
|---|---|---|
| Fractal dimension | 2.54 | 2.47 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Wen, W.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, X.; Ning, Y.; Liang, Z.; Ma, Z. Research on the Interaction Capability and Microscopic Interfacial Mechanism between Asphalt-Binder and Steel Slag Aggregate-Filler. Coatings 2022, 12, 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121871
Chen X, Wen W, Zhou J, Zhou X, Ning Y, Liang Z, Ma Z. Research on the Interaction Capability and Microscopic Interfacial Mechanism between Asphalt-Binder and Steel Slag Aggregate-Filler. Coatings. 2022; 12(12):1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121871
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xiaobing, Wei Wen, Jianguang Zhou, Xiaolong Zhou, Yunfeng Ning, Zhongshan Liang, and Zhenyu Ma. 2022. "Research on the Interaction Capability and Microscopic Interfacial Mechanism between Asphalt-Binder and Steel Slag Aggregate-Filler" Coatings 12, no. 12: 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121871
APA StyleChen, X., Wen, W., Zhou, J., Zhou, X., Ning, Y., Liang, Z., & Ma, Z. (2022). Research on the Interaction Capability and Microscopic Interfacial Mechanism between Asphalt-Binder and Steel Slag Aggregate-Filler. Coatings, 12(12), 1871. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12121871







