Magnetron Deposition of Cr Coatings with RF-ICP Assistance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
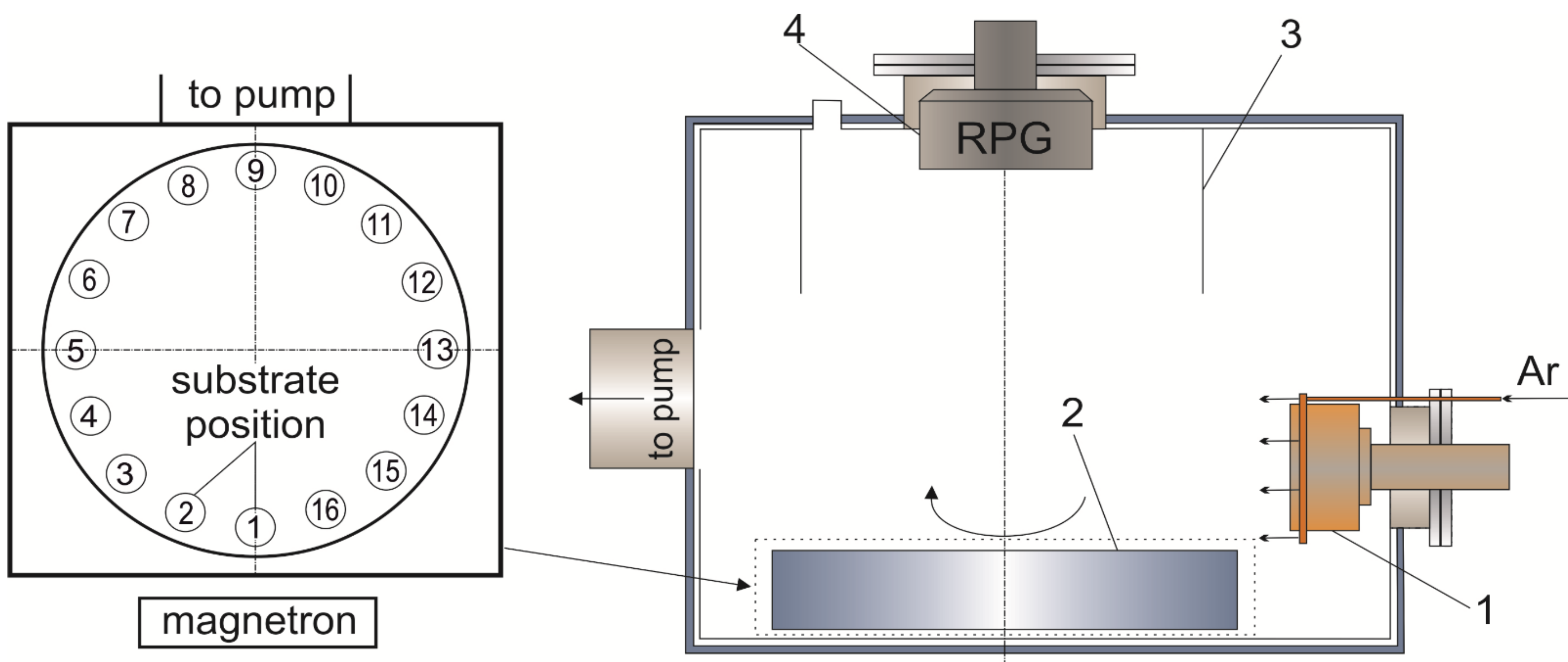
2.1. Sample Preparation
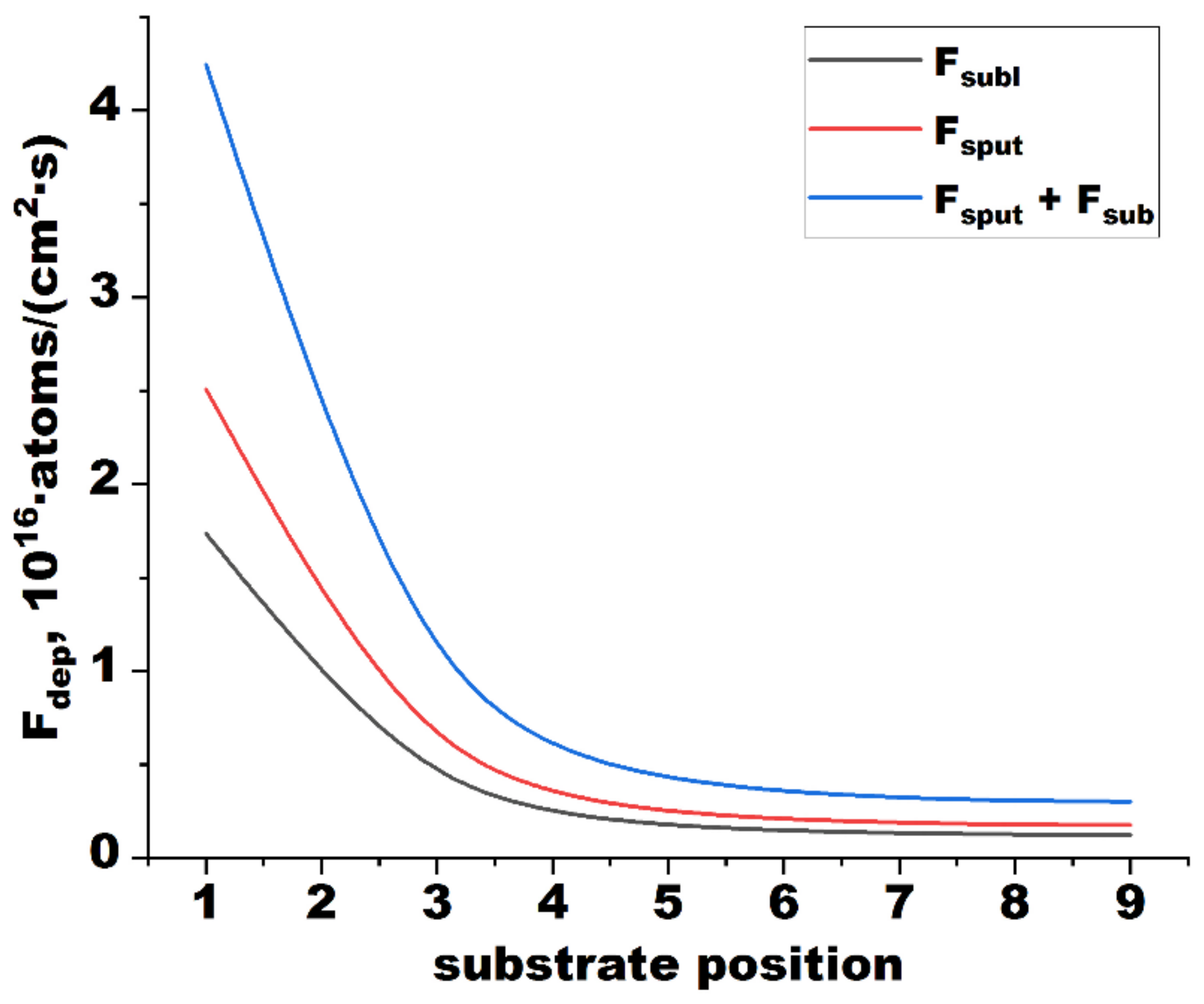
2.2. Calculation of Particle Flux and Ion Current Density to A Substrate
2.3. Sample Characterization
3. Results
3.1. Process Parameters
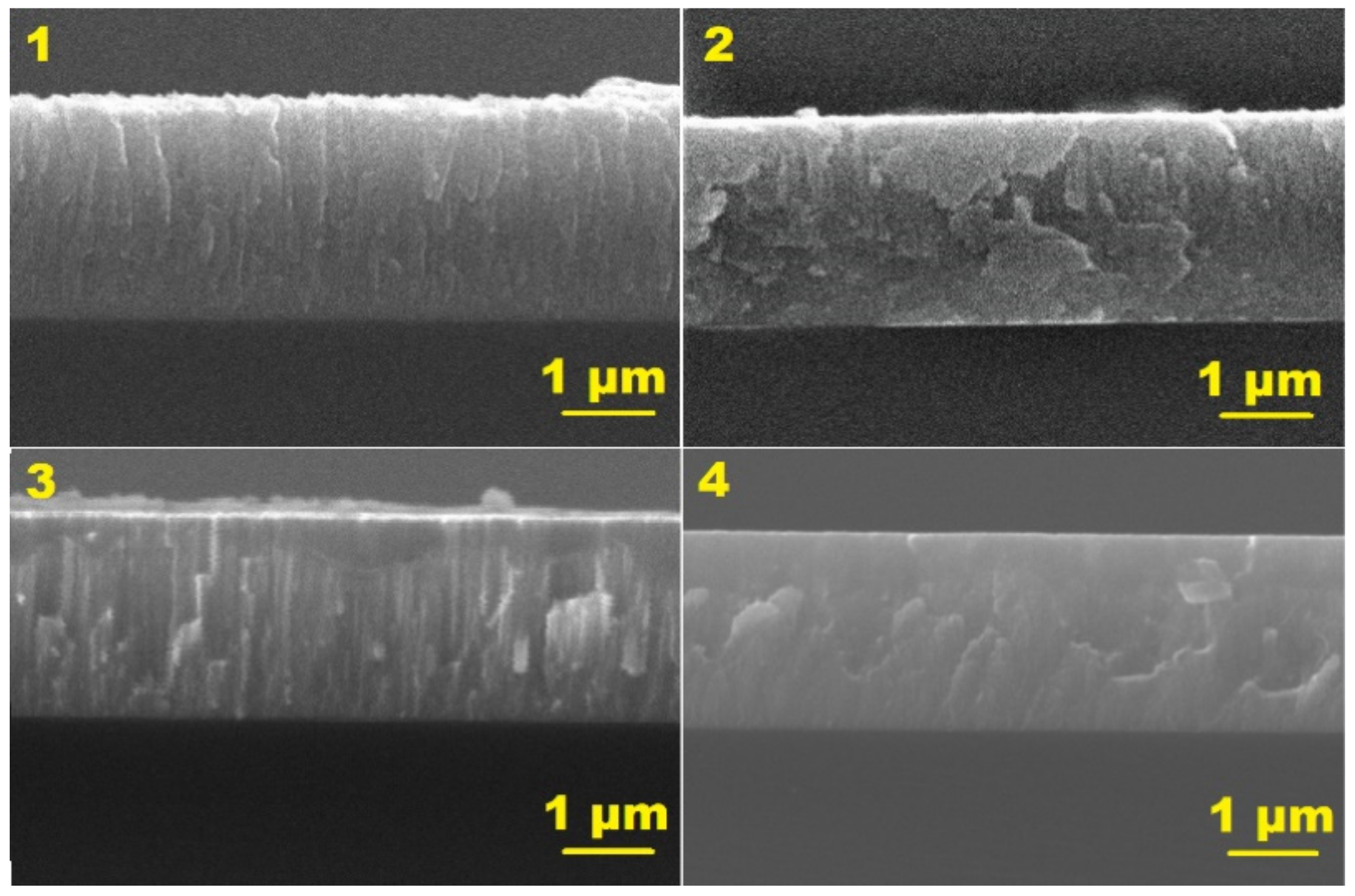
3.2. Structural Parameters
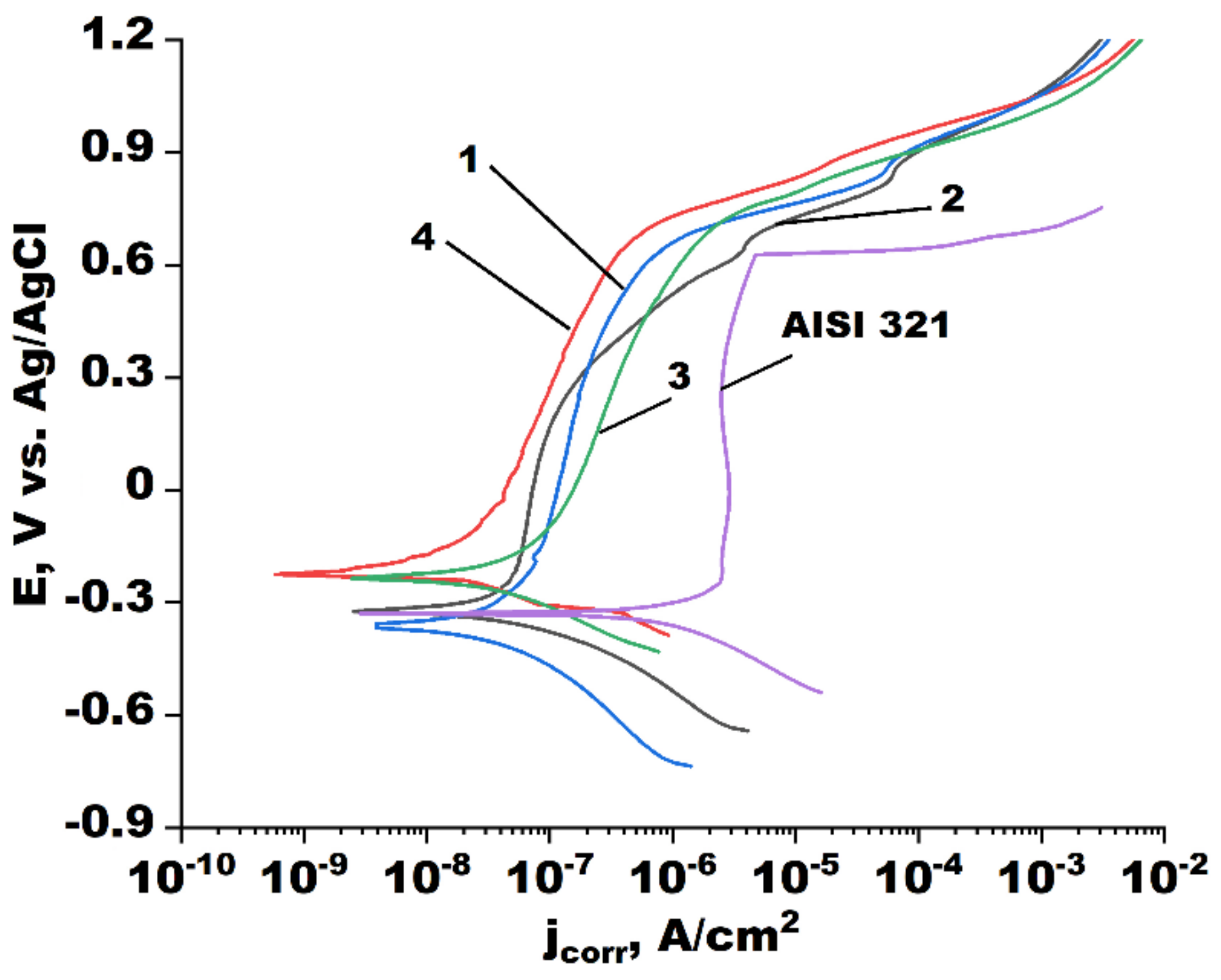
3.3. Corrosion Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
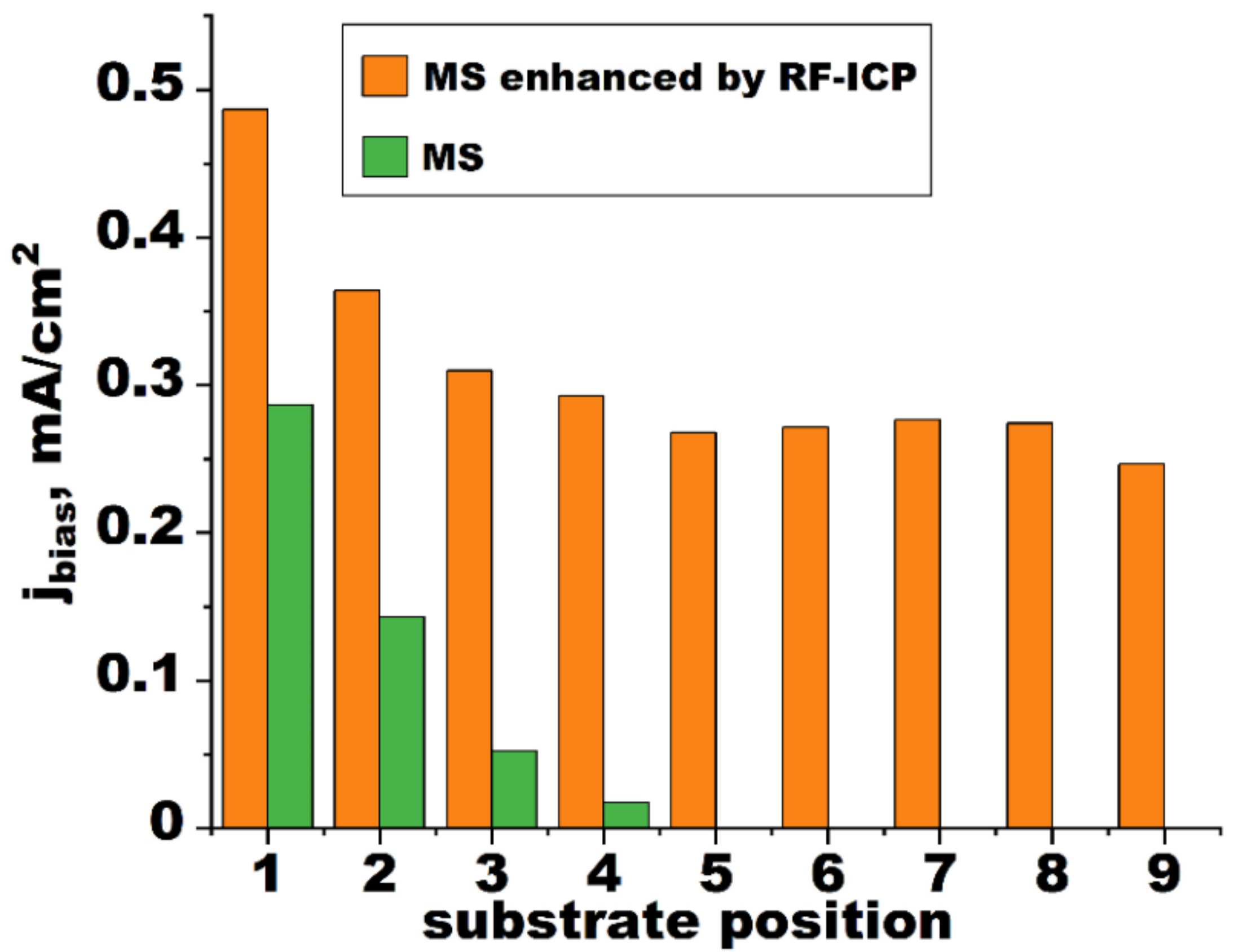
- RF-ICP assistance can increase the ion current density of a substrate by almost twofold when magnetron sputtering is applied in the coating process. It causes an increase in ion-to-atom ratio in the flux of a substrate.
- Calculations of particle and ion flux densities showed a change in the dependence of ion-to-atom ratio on substrate position, when planetary rotation of substrates was used. Magnetron deposition enhanced by an RF-ICP source became a two-step process including stages with relatively low (0.11–0.18) and high (0.84–1.43) ion-to-atom ratios in particle flux entering a substrate.
- Intensive ion bombardment during the coating process induced by RF-ICP assistance can result in modification of the crystal structure of Cr coatings from Cr (110) to Cr (211) orientations and coating densification. Due to the two-stage deposition process, Cr coating can have a layered structure caused by ion bombardment in positions distant from the magnetron sputtering system.
- Cr coating deposition led to a decrease in the corrosion rate of AISI 321 steel from 6.2 × 10−6 to 2.8 × 10−7 mm/year in a 3.5 wt.% NaCl solution. The corrosion rate of Cr-coated steel substrates can be reduced up to 4.0 × 10−8 mm/year by applying RF-ICP assistance for magneton sputtering.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lin, J.; Dahan, I. Nanostructured chromium coatings with enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 265, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diniasi, D.; Golgovici, F.; Anghel, A.; Fulger, M.; Surdu-Bob, C.C.; Demetrescu, I. Corrosion Behavior of Chromium Coated Zy-4 Cladding under CANDU Primary Circuit Conditions. Coatings 2021, 11, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinuzzi, S.M.; Donati, L.; Giurlani, W.; Pizzetti, F.; Galvanetto, E.; Calisi, N.; Innocenti, M.; Caporali, S. A Comparative Research on Corrosion Behavior of Electroplated and Magnetron Sputtered Chromium Coatings. Coatings 2022, 12, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashkarov, E.B.; Sidelev, D.V.; Rombaeva, M.; Syrtanov, M.S.; Bleykher, G.A. Chromium coatings deposited by cooled and hot target magnetron sputtering for accident tolerant nuclear fuel claddings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 389, 125618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachet, J.-C.; Idarraga-Trujillo, I.; Le Flem, M.; Le Saux, M.; Vandenberghe, V.; Urvoy, S.; Rouesne, E.; Guilbert, T.; Toffolon-Masclet, C.; Tupin, M.; et al. Early studies on Cr-Coated Zircaloy-4 as enhanced accident tolerant nuclear fuel claddings for light water reactors. J. Nucl. Mater. 2019, 517, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, D.V.; Kashkarov, E.B.; Syrtanov, M.S.; Krivobokov, V.P. Nickel-chromium (Ni–Cr) coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering for accident tolerant nuclear fuel claddings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 369, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachet, J.-C.; Rouesne, E.; Ribis, J.; Guilbert, T.; Urvoy, S.; Nony, G.; Toffolon-Masclet, C.; Le Saux, M.; Chaabane, N.; Palancher, H.; et al. High temperature steam oxidation of chromium-coated zirconium-based alloys: Kinetics and process. Corr. Sci. 2020, 167, 108537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miretzky, P.; Fernandez Cirelli, A. Cr(VI) and Cr(III) removal from aqueous solution by raw and modified lignocellulosic materials: A review. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 180, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini, J.W.; Johnson, H.A.; Jonas, A. Plating on Some Difficult-to-Plate Metals and Alloys; Materials Development Division/Sandia Laboratories: Livermore, CA, USA, 1980; pp. 21–23.
- Sidelev, D.V.; Poltronieri, C.; Bestetti, M.; Krinitcyn, M.G.; Grudinin, V.A.; Kashkarov, E.B. A comparative study on high-temperature air oxidation of Cr-coated E110 zirconium alloy deposited by magnetron sputtering and electroplating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2022, 433, 128134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; Li, Y.; Ran, G.; Yang, Z.; Wang, P. Cr-coated Zr-4 alloy prepared by electroplating and its in situ He+ irradiation behavior. J. Nucl. Mater. 2020, 538, 152240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bräuer, G.; Szyszka, B.; Vergöhl, M.; Bandorf, R. Magnetron sputtering—Milestones of 30 years. Vacuum 2010, 84, 1354–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, D.V.; Bleykher, G.A.; Bestetti, M.; Krivobokov, V.P.; Vicenzo, A.; Franz, S.; Brunella, M.F. A comparative study on the properties of chromium coatings deposited by magnetron sputtering with hot and cooled target. Vacuum 2017, 143, 479–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thornton, J.A. Influence of apparatus geometry and deposition conditions on the structure and topography of thick sputtered coatings. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. 1974, 11, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barna, P.B.; Adamik, M.; Pauleau, Y. Protective Coatings and Thin Films; Kluwer Academic Publishers: Alphen aan den Rijn, The Netherlands, 1997; p. 279. [Google Scholar]
- Eichenhofer, G.; Fernandez, I.; Wennberg, A. Industrial use of HiPIMS and the hiP-V hiPlus technology: A review by a manufacturer. Vak. Forsch. Prax. 2017, 29, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarakinos, K.; Alami, J.; Konstantinidis, S. High power pulsed magnetron sputtering: A review on scientific and engineering state of the art. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2010, 204, 1661–1684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, P.J.; Arnell, R.D. Magnetron sputtering: A review of recent developments and applications. Vacuum 2000, 56, 159–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laing, K.; Hampshire, J.; Teer, D.; Chester, G. The effect of ion current density on the adhesion and structure of coatings deposited by magnetron sputter ion plating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 112, 177–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, D.V.; Voronina, E.D.; Grudinin, V.A. High-rate magnetron deposition of CuOx films in the metallic mode enhanced by radiofrequency inductively coupled plasma source. Vacuum 2022, 207, 111551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, T.; Okimura, K. Ti ion density in inductively coupled plasma enhanced dc magnetron sputtering. Vacuum 2004, 74, 391–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlin, E.V.; Grigoryev, V.J. Plasma Generator. U.S. Patent 9,704,691, 11 July 2017. Available online: https://patentimages.storage.googleapis.com/a1/1e/7c/744db9db1b29c8/US9704691.pdf (accessed on 28 September 2022).
- Hopwood, J. Review of inductively coupled plasmas for plasma processing. Plasm. Sourc. Sci. Technol. 1992, 1, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bleykher, G.A.; Borduleva, A.O.; Krivobokov, V.P.; Sidelev, D.V. Evaporation factor in productivity increase of hot target magnetron sputtering systems. Vacuum 2016, 132, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glangm, R. Vacuum Evaporation Handbook of Thin Film Technology; McGraw-Hill Book Company: New York, NY, USA, 1970; p. 130. [Google Scholar]
- Depla, D. Magnetrons, Reactive Gases and Sputtering. Available online: http://hdl.handle.net/1854/LU-4239033 (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Ziegler, J.; Biersack, J.P.; Ziegler, M.D. TRIM (the Transport of Ions in Matter). Available online: www.srim.org (accessed on 30 July 2022).
- Abadias, G.; Chason, E.; Keckes, J.; Sebastiani, M.; Thompson, G.B.; Barthel, E.; Doll, G.L.; Murray, C.E.; Stoessel, C.H.; Martuni, L. Review Article: Stress in thin films and coatings: Current status, challenges, and prospects. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. A 2018, 36, 020801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.L. The scherrer formula for X-ray particle size determination. Phys. Rev. 1939, 56, 978–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kutz, M. Handbook of Environmental Degradation of Materials, 2nd ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM G102-89; Standard Practice for Calculation of Corrosion Rates and Related Information From Electrochemical Measurements. 2004. Available online: https://www.astm.org/g0102-89r04e01.html (accessed on 6 October 2022).
- Stockemer, J.; Winand, R.; Vanden Brande, P. Comparison of wear and corrosion behaviors of Cr and CrN sputtered coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 1999, 115, 230–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diesselberg, M.; Stock, H.-R.; Mayr, P. Corrosion protection of magnetron sputtered TiN coatings deposited on high strength aluminium alloys. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2004, 177–178, 399–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidelev, D.V.; Bestetti, M.; Bleykher, G.A.; Krivobokov, V.P.; Grudinin, V.A.; Franz, S.; Vicenzo, A.; Shanenkova, Y.L. Deposition of Cr films by hot target magnetron sputtering on biased substrates. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 350, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wang, G.; Yu, S.; Zhang, G. Microstructure and mechanical properties of nano-multilayer structured (AlCrMoTaTi)Nx coatings deposited by closed field unbalanced magnetron sputtering. J. All. Comp. 2022, 924, 166592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Li, B.; Jiang, B.; Yan, F.; Chen, D. Microstructure and tribological properties of TiN, TiC and Ti(C, N) thin films prepared by closed-field unbalanced magnetron sputtering ion plating. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 8788–8793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarakinos, K.; Wördenweber, J.; Uslu, F.; Schulz, P.; Alami, J.; Wuttig, M. The effect of the microstructure and the surface topography on the electrical properties of thin Ag films deposited by high power pulsed magnetron sputtering. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2008, 202, 2323–2327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.C.; Laughlin, D.E.; Lambeth, D.N. Formation of crystallographic texture in rf sputter-deposited Cr thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1994, 76, 7311–7316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, S.L.; Artman, J.O.; Wong, B.; Laughlin, D.E. Study of the growth characteristics of sputtered Cr thin films. J. Appl. Phys. 1990, 67, 4913–4915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudinin, V.A.; Bleykher, G.A.; Krivobokov, V.P.; Semyonov, O.V.; Obrosov, A.; Weiβ, S.; Sidelev, D.V. Hot target magnetron sputtering enhanced by RF-ICP source: Microstructure and functional properties of CrNx coatings. Vacuum 2022, 200, 111020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.J.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, J.J.; Joo, J.H. Study of chromium and chromium nitride coatings deposited by inductively coupled plasma-assisted evaporation. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2003, 169–170, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, K.; Li, Z. Effect of microstructure of TiN film on properties as bipolar plate coatings in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell prepared by inductively coupled plasma assisted magnetron sputtering. Thin Solid Films 2013, 544, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foord, J.S.; Lambert, R.M. Oxygen chemisorption and corrosion on Cr(100) and Cr(110) single crystal surfaces. Surf. Sci. 1985, 161, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokcekaya, O.; Hayashi, N.; Ishimoto, T.; Ueda, K.; Narushima, T.; Nakano, T. Crystallographic orientation control of pure chromium via laser powder bed fusion and improved high temperature oxidation resistance. Add. Manuf. 2020, 36, 101624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
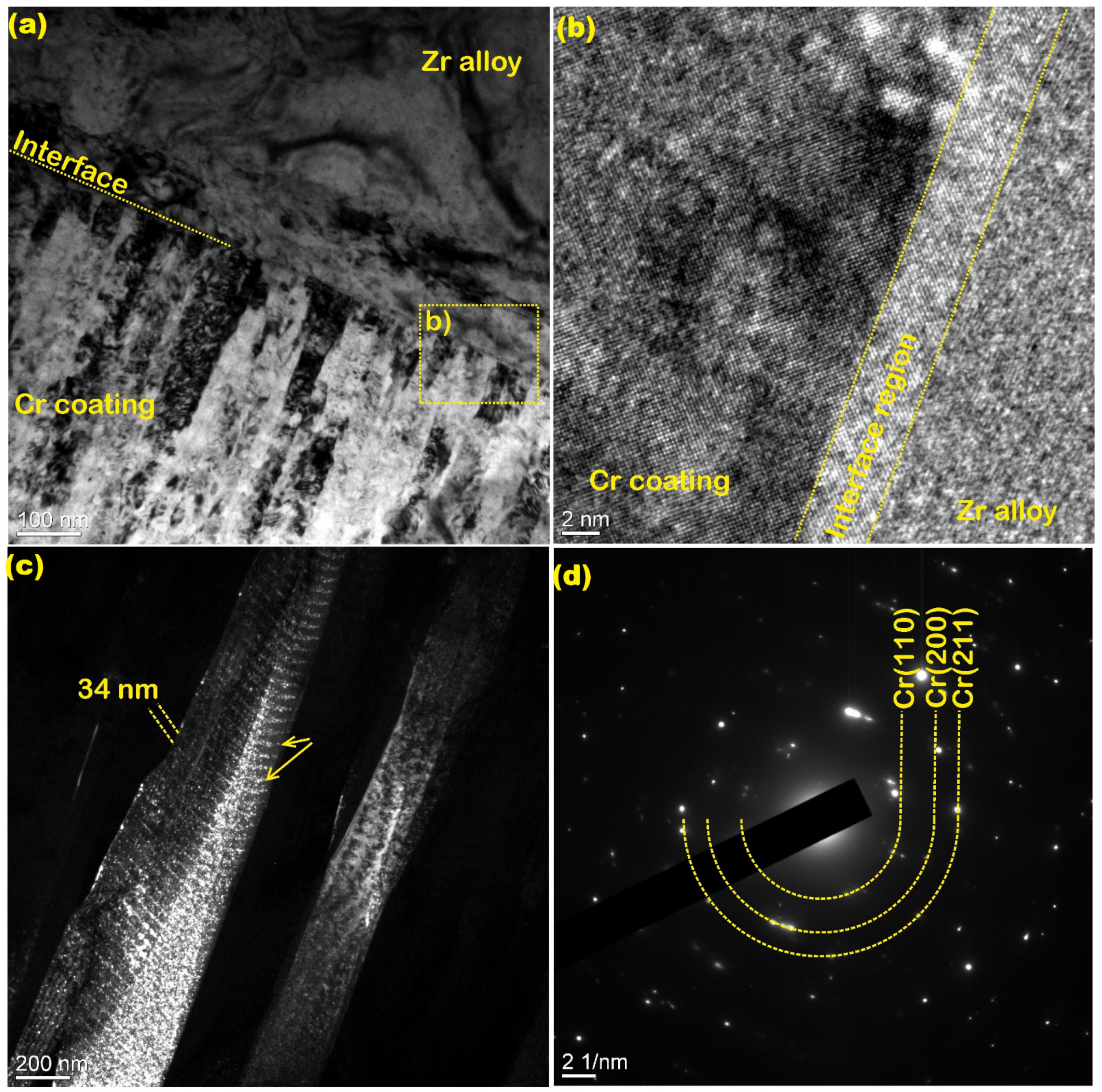
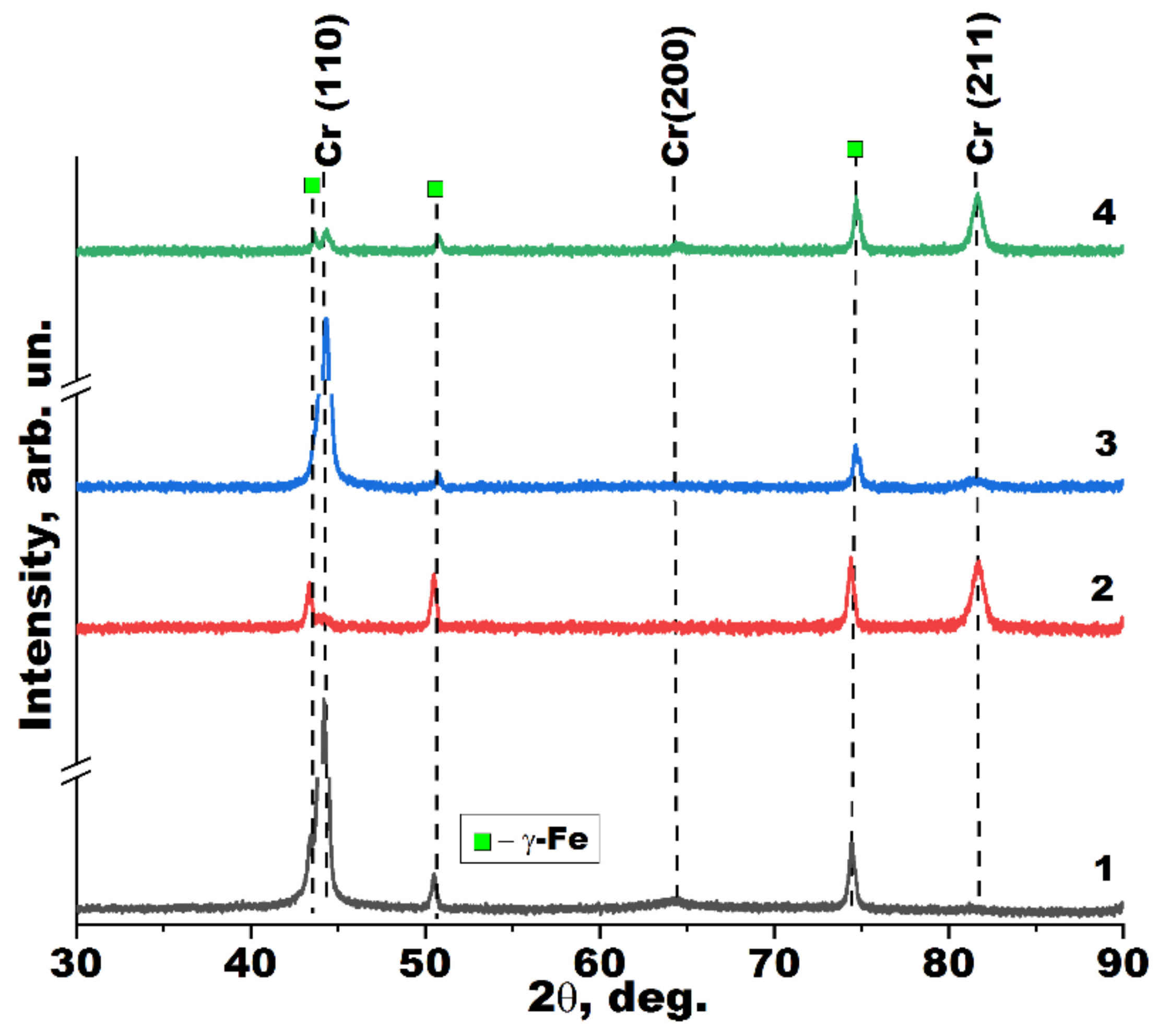

| Deposition Mode | Target Type | RPG-128 | t, min | p, Pa | Ibias, mA/cm2 | h, µm | T, K |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | conventional | no use | 108 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 2.0 | 375 |
| 2 | applied | 120 | 1.9 | 422 | |||
| 3 | hot | no use | 70 | 2.3 | 568 | ||
| 4 | applied | 80 | 3.7 | 635 |
| Deposition Mode | a, Å | D, nm | TC(110) | TC(200) | TC(211) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2.866 | 23 | 2.6 | 0.3 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 2.855 | 10 | 0.2 | 0 | 2.8 |
| 3 | 2.880 | 19 | 2.6 | 0 | 0.4 |
| 4 | 2.879 | 12 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 1.7 |
| Deposition Mode | Ecorr, mV | jcorr,·10−9 A/cm2 | βa, mV | βc, mV | Rp, MΩ·cm2 | CR, 10−6 mm/year |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AISI 321 | −328 | 621.0 | −155 | 149 | 3.2 | 6.23 |
| 1 | −359 | 27.5 | −140 | 223 | 5.9 | 0.28 |
| 2 | −323 | 17.7 | −141 | 204 | 11.2 | 0.18 |
| 3 | −234 | 24.5 | −89 | 296 | 2.2 | 0.25 |
| 4 | −225 | 3.6 | −53 | 126 | 10.6 | 0.04 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sidelev, D.V.; Grudinin, V.A.; Zinkovskii, K.A.; Alkenova, K.; Bleykher, G.A. Magnetron Deposition of Cr Coatings with RF-ICP Assistance. Coatings 2022, 12, 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101587
Sidelev DV, Grudinin VA, Zinkovskii KA, Alkenova K, Bleykher GA. Magnetron Deposition of Cr Coatings with RF-ICP Assistance. Coatings. 2022; 12(10):1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101587
Chicago/Turabian StyleSidelev, Dmitrii V., Vladislav A. Grudinin, Konstantin A. Zinkovskii, Kamila Alkenova, and Galina A. Bleykher. 2022. "Magnetron Deposition of Cr Coatings with RF-ICP Assistance" Coatings 12, no. 10: 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101587
APA StyleSidelev, D. V., Grudinin, V. A., Zinkovskii, K. A., Alkenova, K., & Bleykher, G. A. (2022). Magnetron Deposition of Cr Coatings with RF-ICP Assistance. Coatings, 12(10), 1587. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101587







