Plasma-Polymerized Aniline–Diphenylamine Thin Film Semiconductors
Abstract
1. Introduction
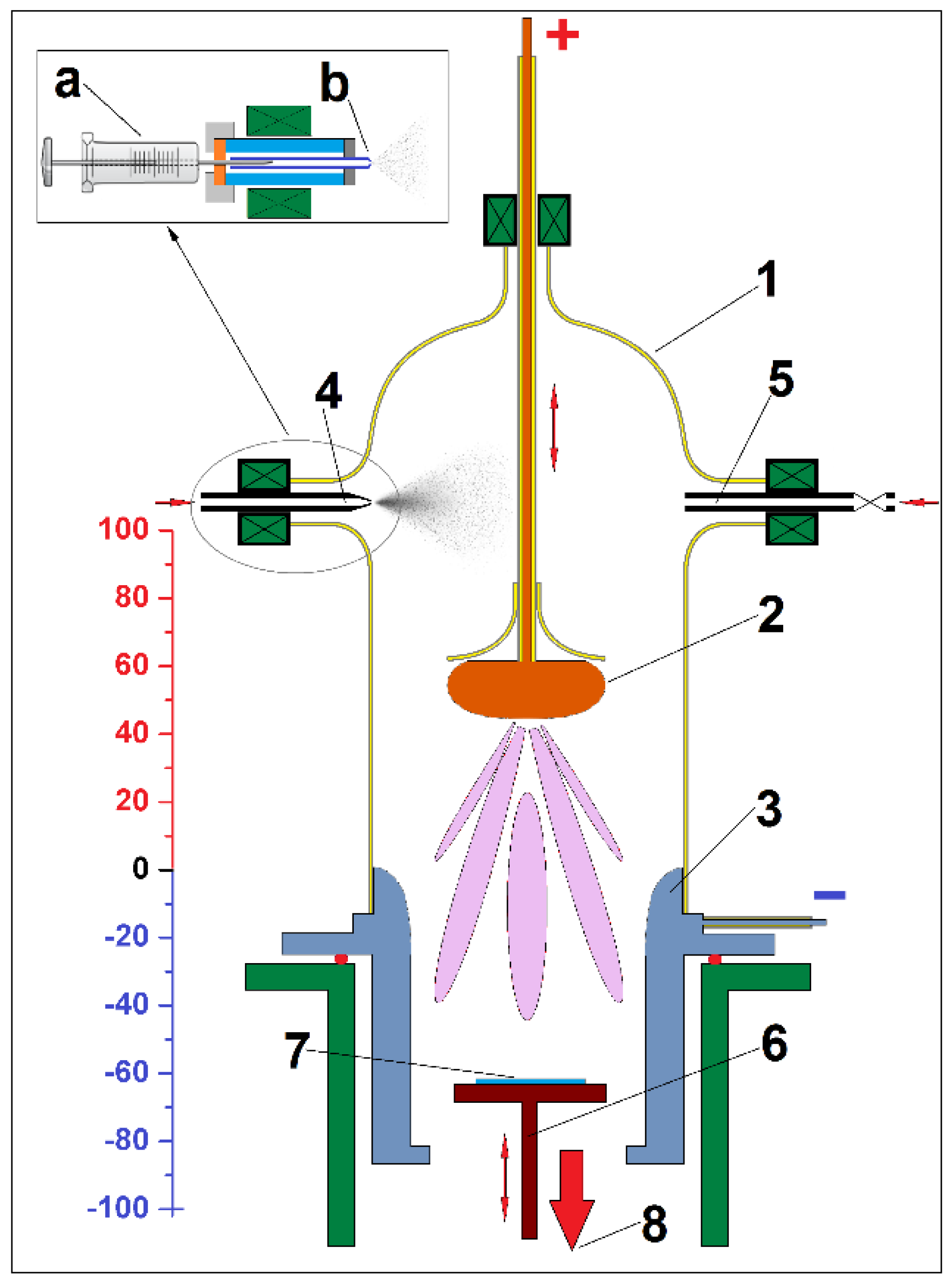
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
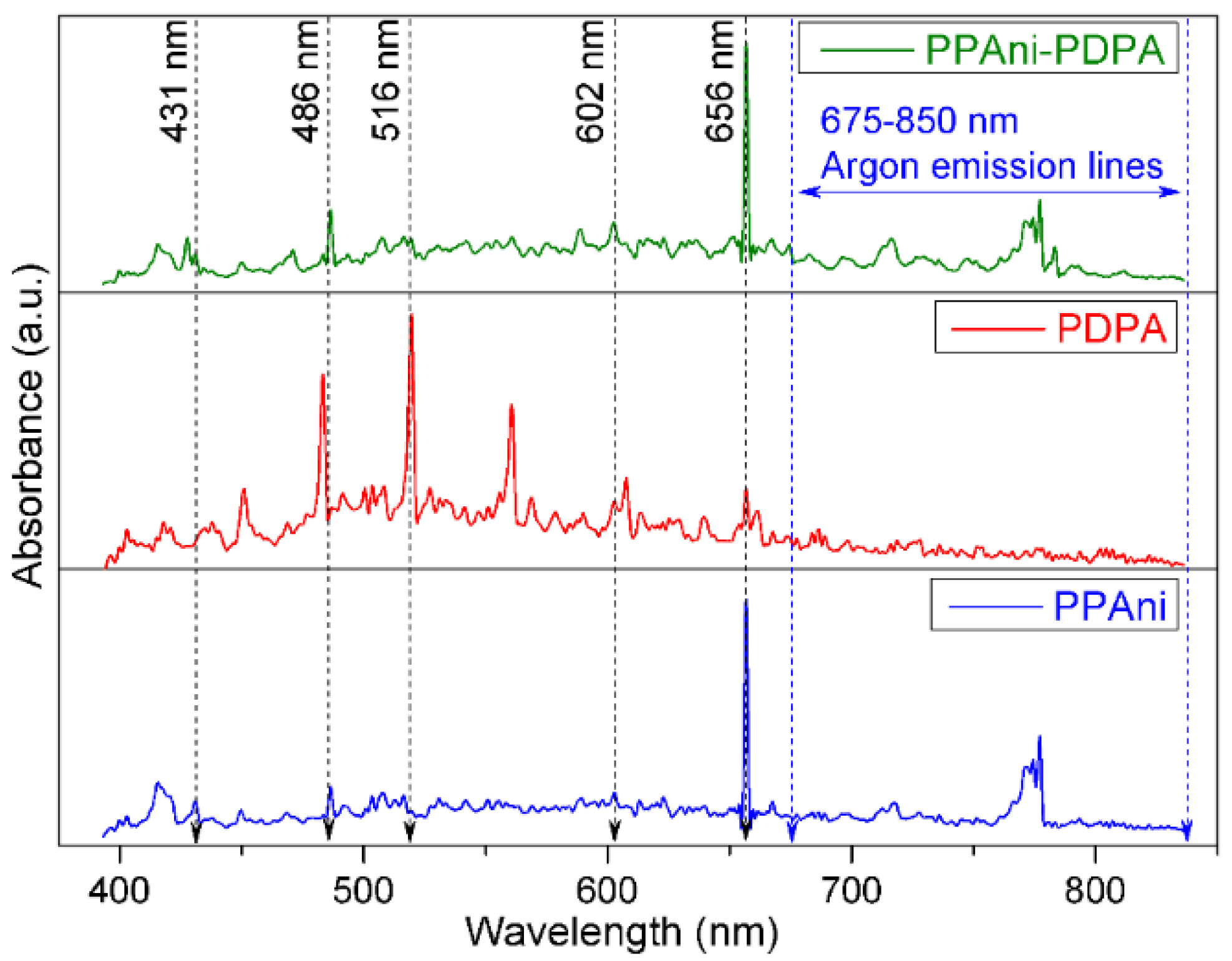
3.1. Optical Emission Spectroscopy of Plasmas
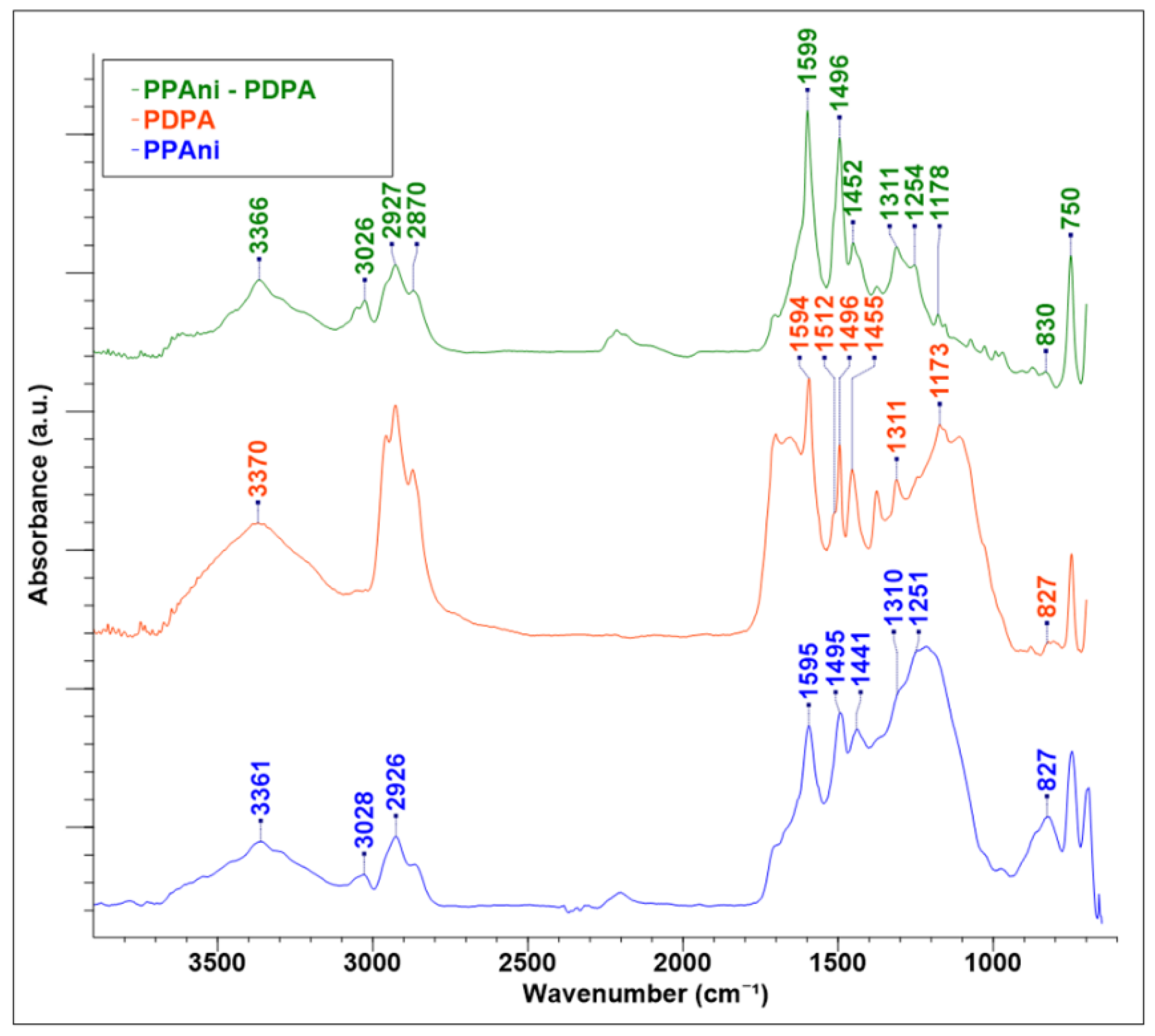
3.2. FT-IR Analyses
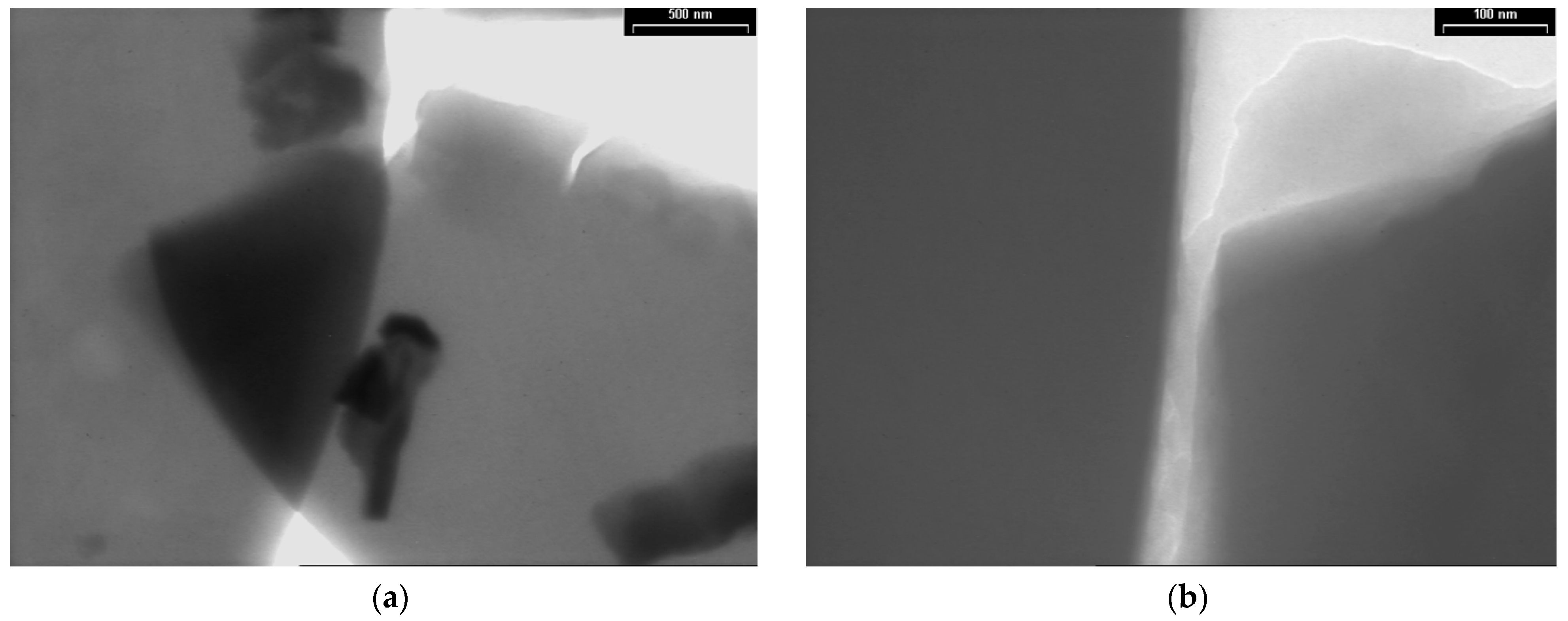
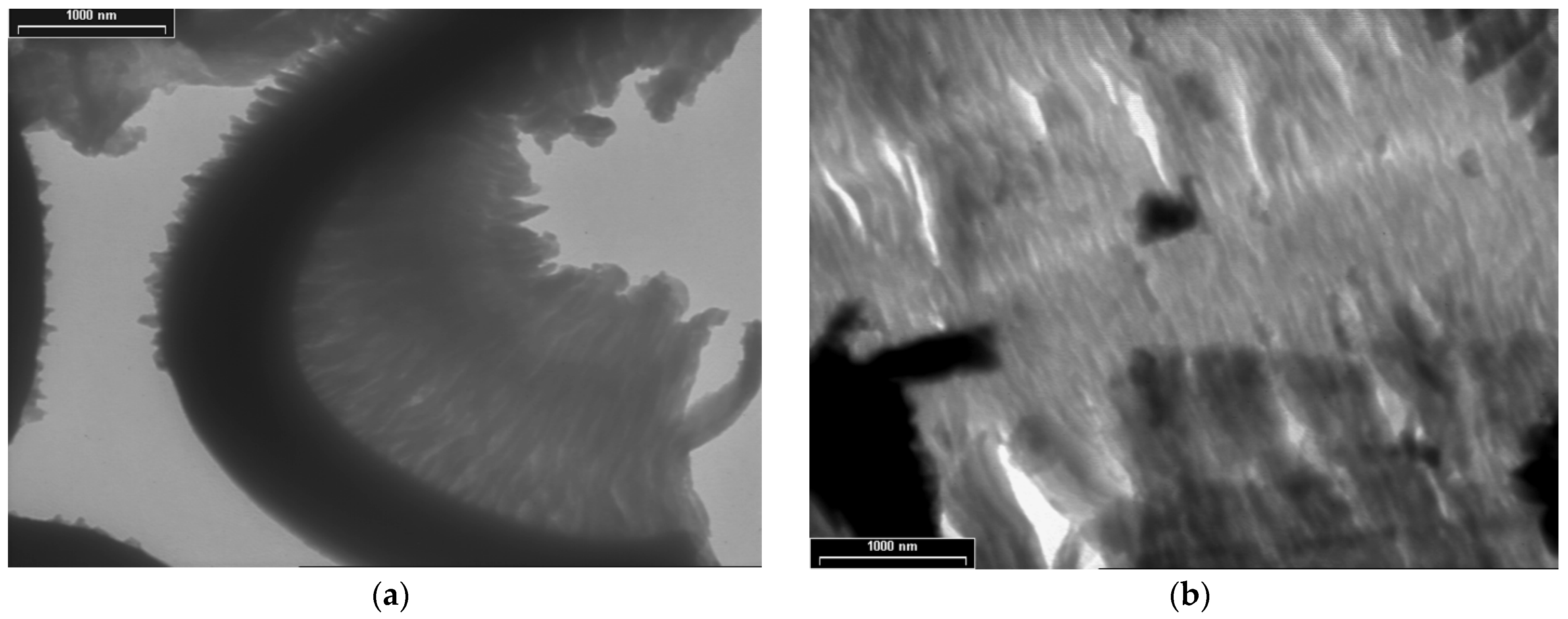
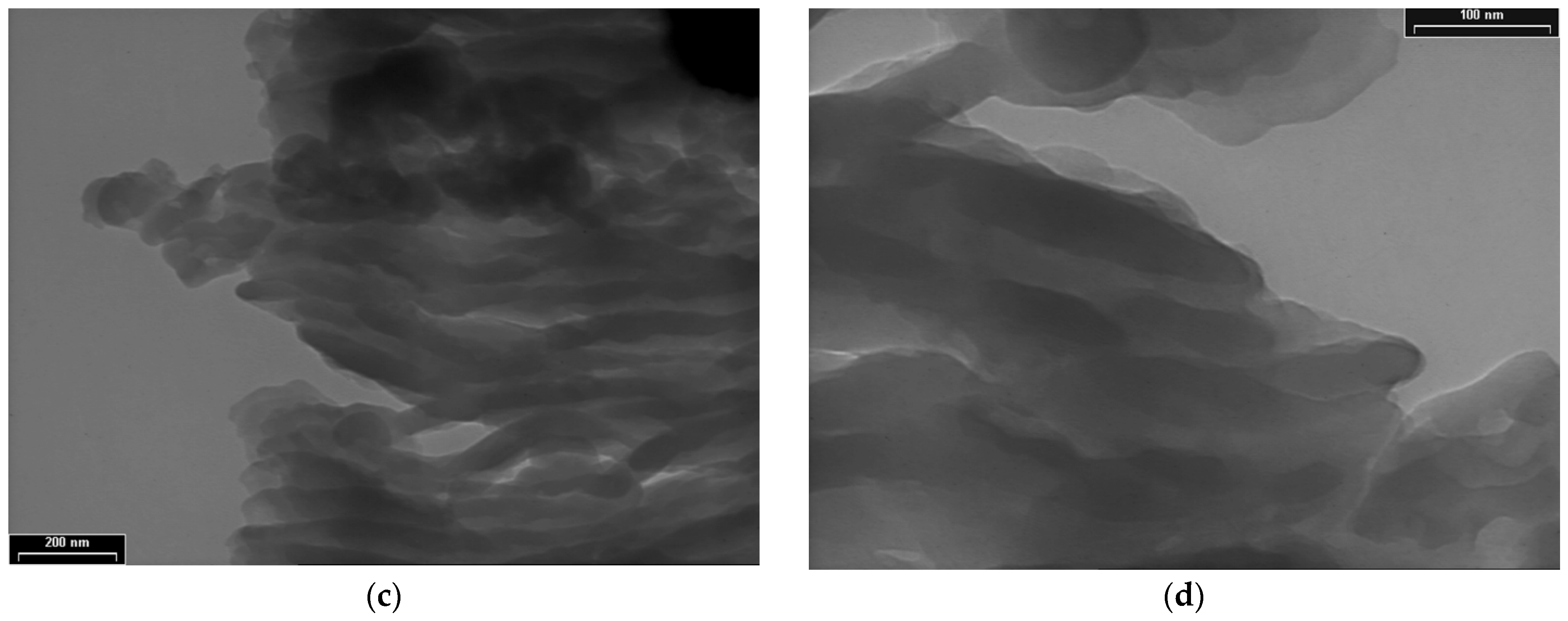
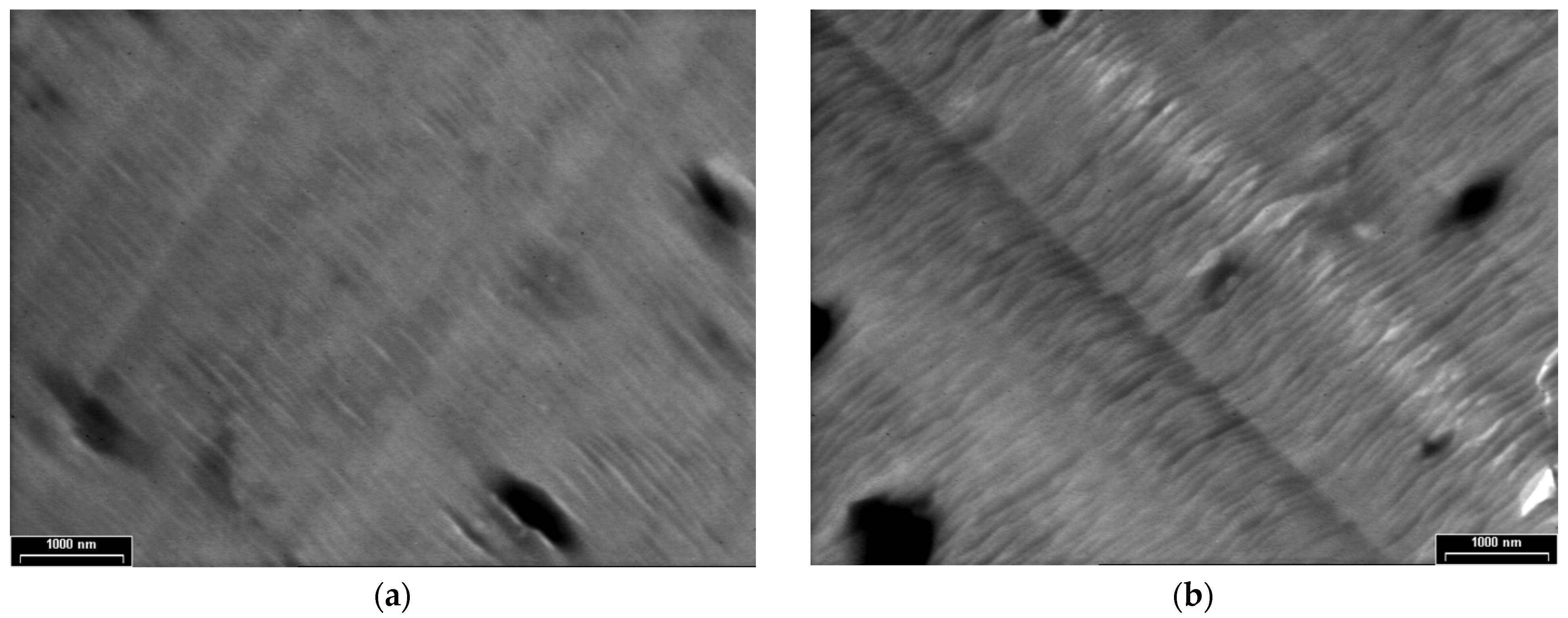
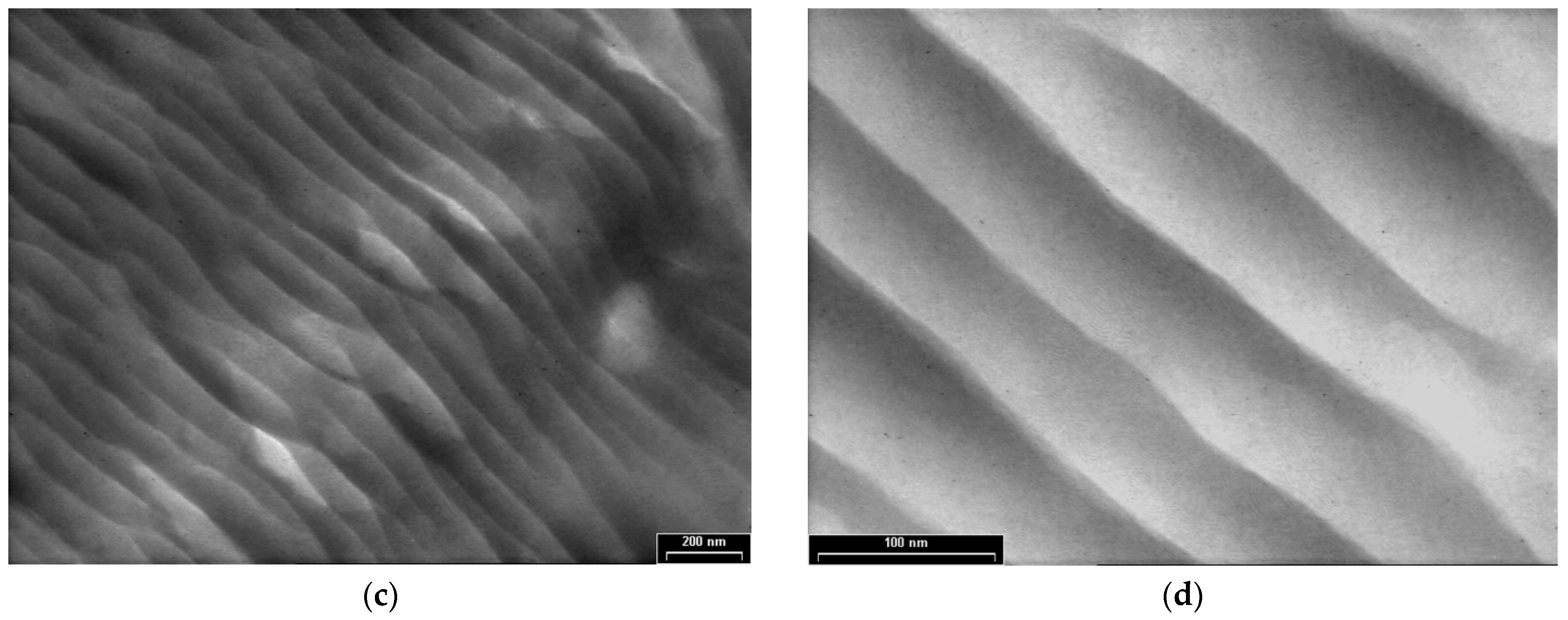
3.3. TEM Analyses
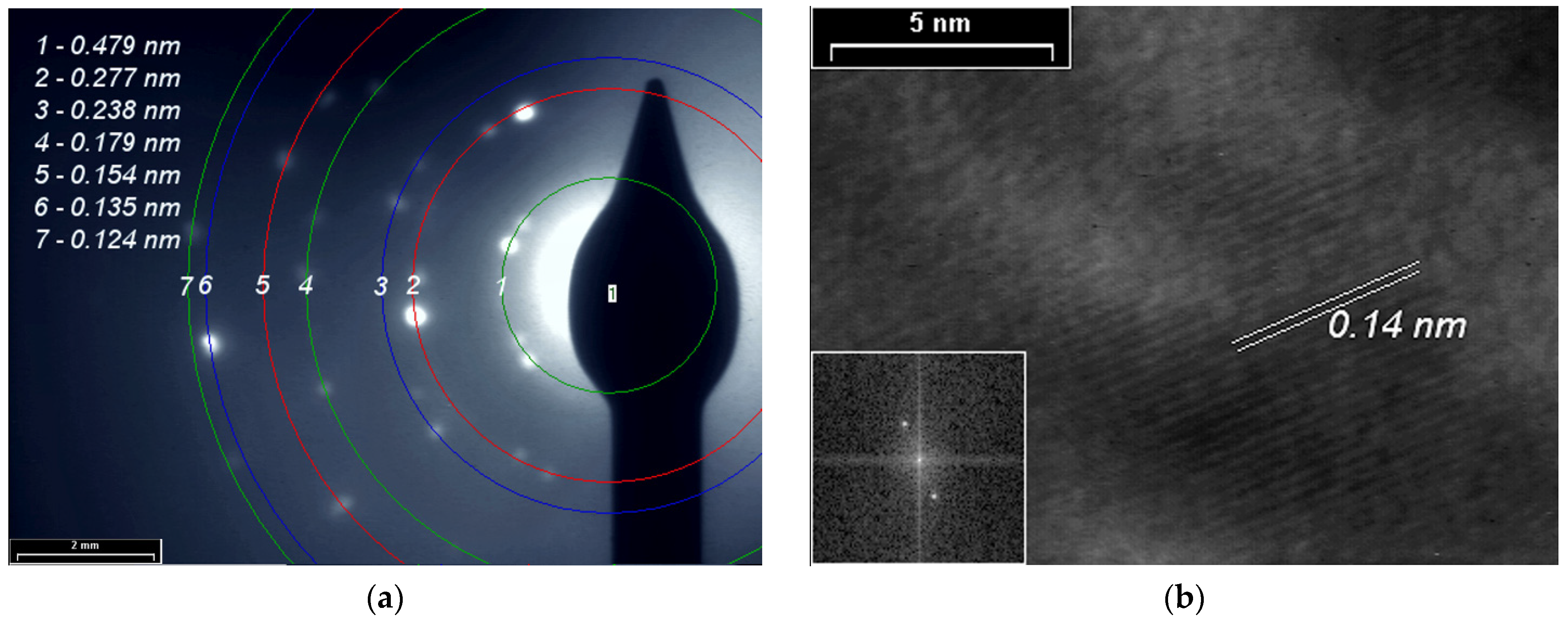
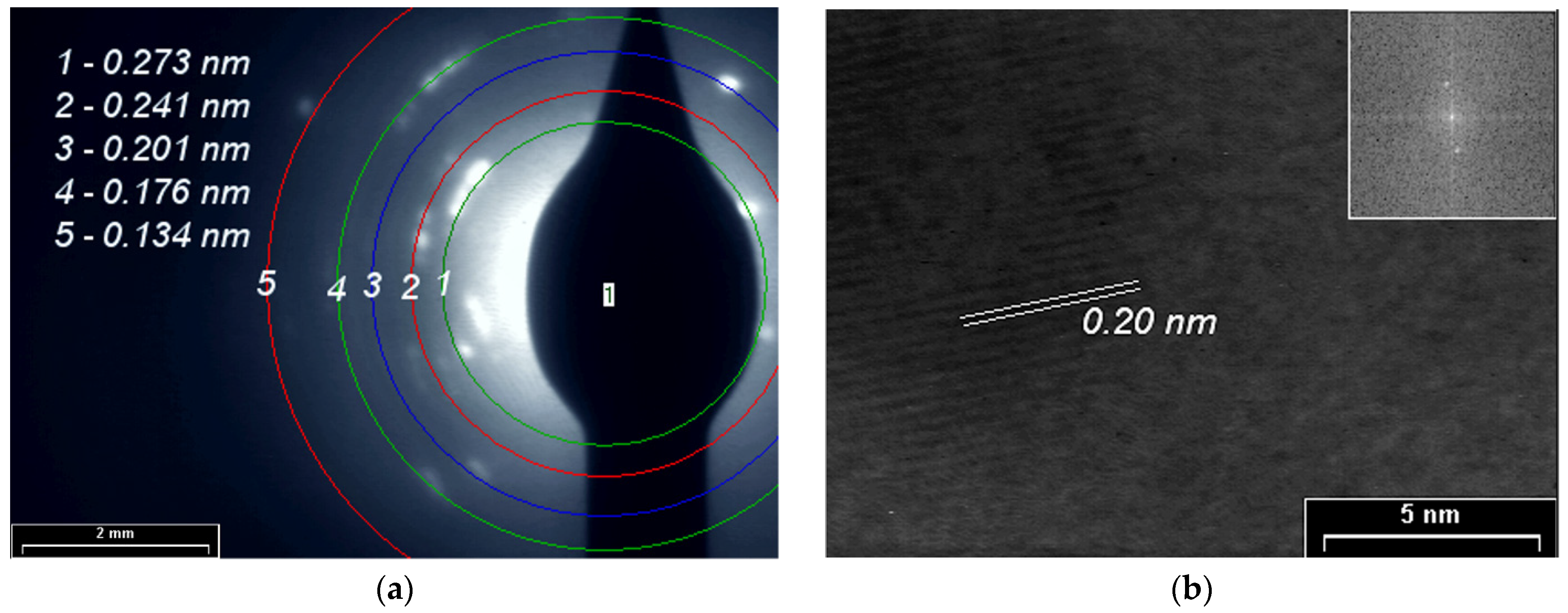
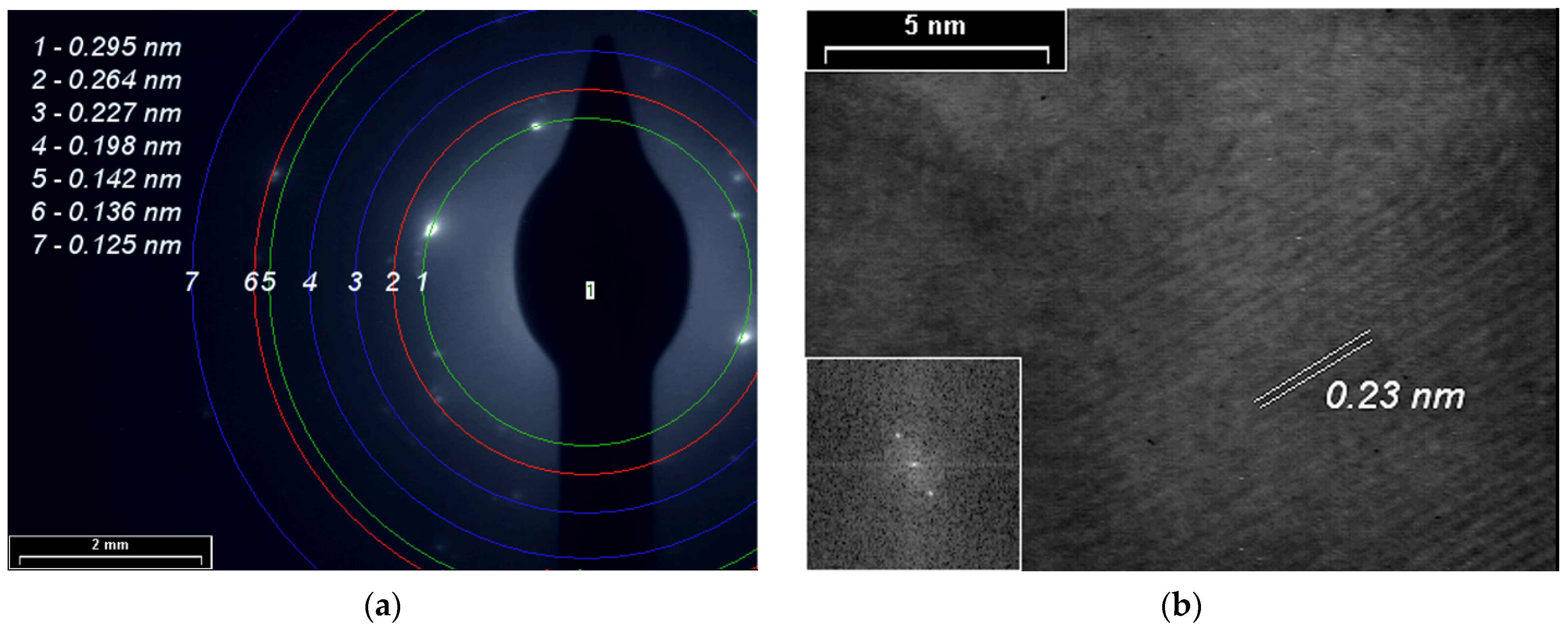
3.4. XRD, SAED and HR-TEM Analyses
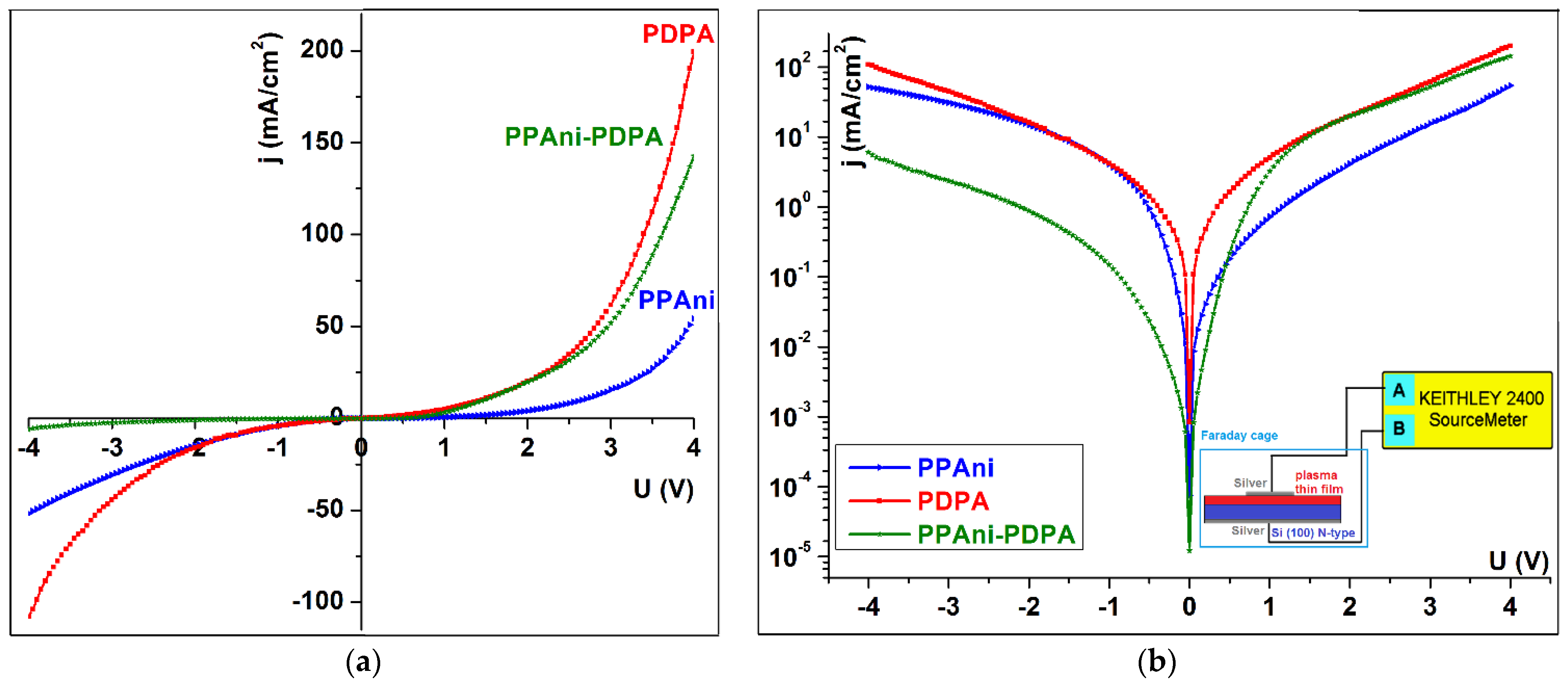
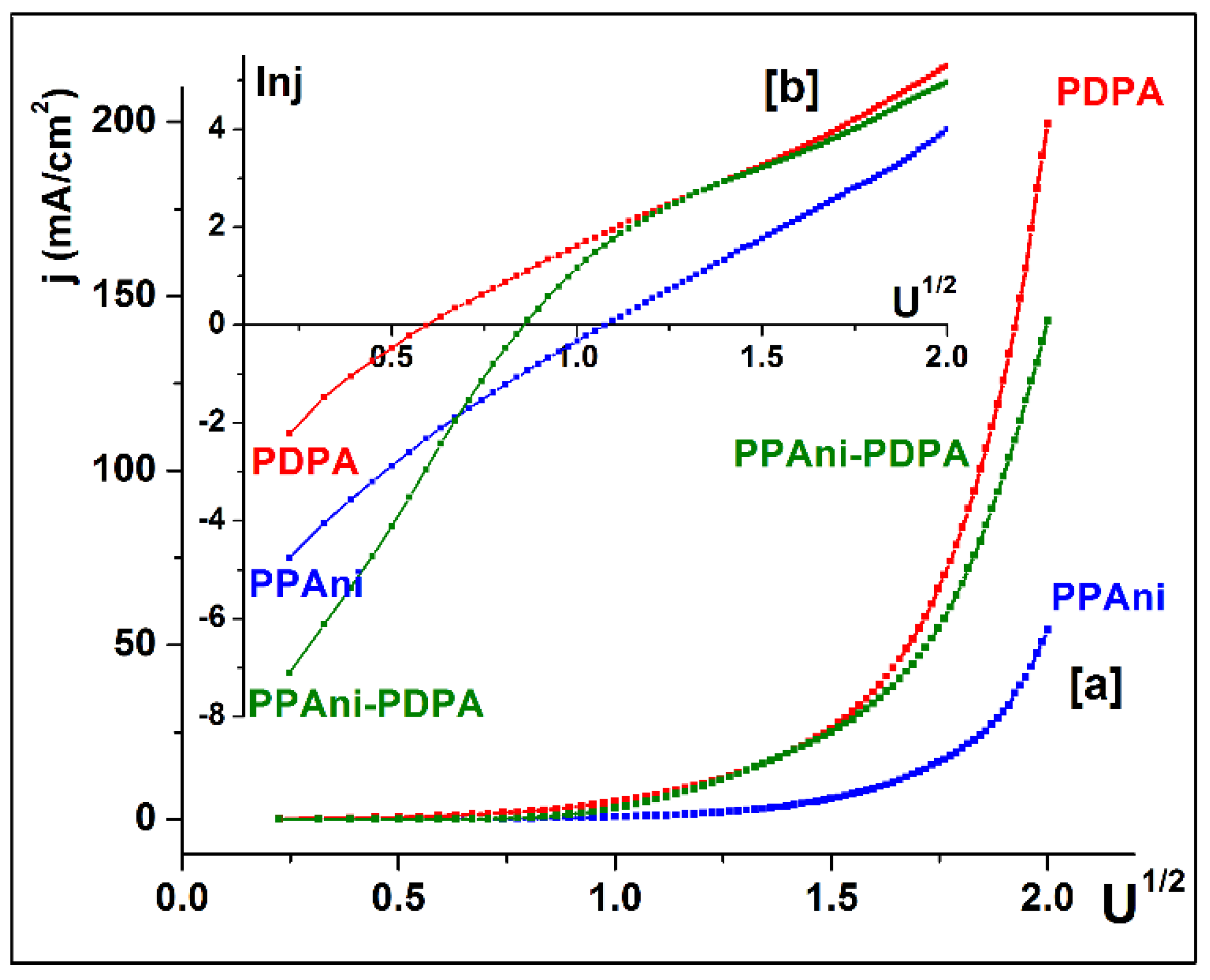
3.5. I–V Characteristics
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chiang, J.-C.; MacDiarmid, A.G. Polyaniline: Protonic acid doping of the emeraldine form to the metallic regime. Synth. Met. 1986, 13, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Kumar, H.; Sharma, R.; Kumari, R.; Thakur, M. Quantum dot decorated polyaniline plastic as a multifunctional nanocomposite: Experimental and theoretical approach. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 24063–24076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camelet, J.L.; Lacorix, J.C.; Aeiyach, S.; Chaneching, K.; Lacaze, P.C. Electrosynthesis of adherent polyaniline films on iron and mild steel in aqueous oxalic acid medium. Synth. Met. 1998, 93, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Niu, Q.; Fan, S.; Zhang, Y. Highly oriented lamellar polyaniline with short-range disorder for enhanced electrochromic performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 417, 128126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Ren, Y.; Yang, H.; Xu, Q. Fabrication of 3D Hierarchical MoS2/Polyaniline and MoS2/C Architectures for Lithium-Ion Battery Applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14644–14652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, J.-Z.; Yang, Y.-C.; Tuan, H.-Y. Interface engineering of high entropy Oxide@Polyaniline heterojunction enables highly stable and excellent lithium ion storage performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 450, 137924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Feng, X.; Ren, L.; Piao, Q.; Zhong, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Chen, Y.; Wang, B. Flexible Solid-State Supercapacitor Based on a Metal–Organic Framework Interwoven by Electrochemically-Deposited PANI. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 4920–4923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Hu, W.; Qiu, J.; Geng, B.; Du, M.; Zheng, Q. Solvent-assisted self-assembly to fabricate a ternary flexible free-standing polyaniline@MXene-CNTs electrode for high-performance supercapacitors. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 921, 166062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ye, B.; Hu, X.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Deng, Y. Facile electropolymerized-PANI as counter electrode for low cost dye-sensitized solar cell. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 1768–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawo, C.; Chaturvedi, H. High performance PANI-PSSNa doped counter electrode for dye-sensitized solar cells. Appl. Phys. A-Mater. Sci. Process. 2022, 128, 640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.; Voiry, D.; Chhowalla, M.; Asefa, T. Efficient Metal-Free Electrocatalysts for Oxygen Reduction: Polyaniline-Derived N- and O-Doped Mesoporous Carbons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 7823–7826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, D.; Zhu, C.; He, Y.; Xing, C.C.; Xie, K.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y. Polyaniline-MXene-coated carbon cloth as an anode for microbial fuel cells. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2022, 26, 2435–2443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comisso, N.; Daolio, S.; Mengoli, G.; Salmaso, R.; Zecchin, S.; Zotti, G. Chemical and electrochemical synthesis and characterization of polydiphenylamine and poly-N-methylaniline. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1988, 255, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Heeger, A.J. A new architecture for polymer transistors. Nature 1994, 372, 344–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, E.W.; Ricco, A.J.; Wrighton, W.S. Resistance of polyaniline films as a function of electrochemical potential and the fabrication of polyaniline-based microelectronic devices. J. Phys. Chem. 1985, 89, 1441–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athawale, A.A.; Deore, B.A.; Chobukswar, V.V. Studies on poly(diphenylamine) synthesized electrochemically in nonaqueous media. Mater. Chem. Phys. 1999, 58, 94–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dao, L.H.; Guay, J.; Leclerc, M. Poly(n-arylanilines), synthesis and spectroelectrochemistry. Synth. Met. 1989, 29, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, J.; Paynter, R.; Dao, L.H. Synthesis and characterization of poly(diarylamines): A new class of electrochromic conducting polymers. Macromolecules 1990, 23, 3598–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-Y.; Wen, T.-C.; Gopalan, A. Identification of electrochromic sites in poly(diphenylamine) using a novel absorbance–potential–wavelength profile. Electrochim. Acta 2001, 47, 423–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.-C.; Chen, J.-B.; Gopalan, A. Soluble and methane sulfonic acid doped poly(diphenylamine)—Synthesis and characterization. Mater. Lett. 2002, 57, 280–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Santhosh, P.; Sankarasubramanian, M.; Vasudevan, T.; Gopalan, A.; Lee, K.-P. UV–vis spectroscopy for following the kinetics of homogeneous polymerization of diphenylamine in p-toluene sulphonic acid. Spectrochim. Acta Part A-Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2005, 62, 420–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Aragón, A.; Hernández-Escobar, C.A.; Vega-Rios, A.; Zaragoza, E.A. Contreras Poly(diphenylamine-co-aniline) copolymers for supercapacitor electrodes. J. Mater. Sci.-Mater. Electron. 2018, 29, 15329–15338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, M.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Alothman, Z.A.; Dhanusuraman, R.; Ponnusamy, V.K. Improved cyclic retention and high-performance supercapacitive behavior of poly(diphenylamine-co-aniline)/phosphotungstic acid nanohybrid electrode. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 8180–8188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madaswamy, S.L.; Alfakeer, M.; Bahajjaj, A.A.A.; Ouladsmane, M.; Wabaidur, S.M.; Chen, C.-X.; Dhanusuraman, R. Remarkable electrocatalytic activity of Pd nanoparticles dispersed on polyaniline-polydiphenylamine copolymer nanocomposite for methanol and ethanol oxidation reaction. Synth. Met. 2021, 281, 116925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, A.A.; Pal, A.R.; Bailung, H.; Chutia, J.; Patil, D.S. Fabrication of a heterostructure device with Au/PPani–TiO2/ITO configuration and study of device parameters including current conduction mechanism. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 2013, 46, 325301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.Y.; Iqbal, S.; Jang, H.J.; Jung, E.Y.; Bae, G.T.; Park, C.S.; Shin, B.J.; Tae, H.S. Transparent Polyaniline Thin Film Synthesized Using a Low-Voltage-Driven Atmospheric Pressure Plasma Reactor. Materials 2021, 14, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattyn, C.; Kovacevic, E.; Strunskus, T.; Lecas, T.; Berndt, J. Formation and behavior of negative ions in low pressure aniline-containing RF plasmas. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chermisinoff, N.P. Handbook of Polymer Science and Technology; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1989; Volume 4. [Google Scholar]
- Vasilev, K.; Michelmore, A.; Griesser, H.J.; Short, R.D. Substrate influence on the initial growth phase of plasma-deposite polymer films. Chem. Commun. 2009, 24, 3600–3602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, G.J.; Morales, J.; Castillo-Ortega, M.M.; Olayo, R. Synthesis of polyaniline films by plasma polymerization. Synth. Met. 1997, 88, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajeev, U.S.; Mathai, C.J.; Saravanan, S.; Ashokan, R.R.; Venkatachalam, S.; Anantharaman, M.R. On the optical and electrical properties of rf and a.c. plasma polymerized aniline thin films. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2006, 29, 159–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debarnot, D.; Mérian, T.; Poncin-Epaillard, F. Film Chemistry Control and Growth Kinetics of Pulsed Plasma-Polymerized Aniline. Plasma Chem. Plasma Process. 2011, 31, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tristant, P.; Ding, Z.; Trang Vinh, Q.B.; Hidalgo, H.; Jauberteau, J.L.; Desmaison, J.; Dong, C. Microwave plasma enhanced CVD of aluminum oxide films: OES diagnostics and influence of the RF bias. Thin Solid Films 2001, 390, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koidl, P.; Wild, C.; Dischler, B.; Wagner, J.; Ramsteiner, M. Plasma Deposition, Properties and Structure of Amorphous Hydrogenated Carbon Films. Mater. Sci. Forum 1990, 52–53, 41–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larijani, M.M.; Le Normand, F.; Crégut, O. An optical emission spectroscopy study of the plasma generated in the DC HF CVD nucleation of diamond. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2007, 253, 4051–4059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, S.; Ahner, N.; Blaschta, F.; Schaller, M.; Rülke, H.; Schulz, S.E.; Gessner, T. Analysis of the impact of different additives during etch processes of dense and porous low-k with OES and QMS. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blinova, N.V.; Stejskal, J.; Trchová, M.; Prokeš, J.; Omastová, M. Polyaniline and polypyrrole: A comparative study of the preparation. Eur. Polym. J. 2007, 43, 2331–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Bae, D.H.; Choi, H.J.; Seo, Y. Synthesis of semiconducting poly(diphenylamine) particles and analysis of their electrorheological properties. Polymer 2017, 119, 40–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guay, J.; Dao, L.H. Formation of poly(4-phenylaniline) by electropolymerization of 4-aminobiphenyl or diphenylamine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1989, 274, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, X.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, L.; Bai, Y.; Zhu, J.; Mao, S. Polyaniline with high crystallinity degree: Synthesis, structure, and electrochemical properties. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2014, 131, 40827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coates, J. Interpretation of Infrared Spectra, A Practical Approach. In Encyclopedia of Analytical Chemistry; Meyers, R.A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2000; pp. 10815–10837. [Google Scholar]
- Nalwa, H.S. Handbook of Organic Conductive Molecules and Polymers, Volume 2 Conductive Polymers: Synthesis and Electrical Properties, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1997; pp. 505–572. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, J.; Wang, Z.H.; Cromack, K.R.; Epstein, A.J.; Macdiarmid, A.G. Effect of sulfonic acid group on polyaniline backbone. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991, 113, 2665–2671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamirisa, P.A.; Liddell, K.C.; Pedrow, P.D.; Osman, M.A. Pulsed-Plasma-Polymerized Aniline Thin Films. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 93, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Socrates, G. Infrared Characteristic Group Frequencies, Tables and Charts, 2nd ed.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Furukawa, Y.; Kawagoe, T.; Hyodo, Y.; Harada, I.; Ueda, F.; Nakajima, T. Vibrational spectra and structure of polyaniline. Macromolecules 1988, 21, 1297–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, L.E. X-ray Diffraction Methods in Polymer Science, 1st ed.; Wiley-Interscience: New York, NY, USA, 1969. [Google Scholar]
- Lucas, B.; El Amrani, A.; Moliton, A.; Skaiky, A.; El Hajj, A.; Aldissi, M. Charge transport properties in pentacene films: Evaluation of carrier mobility by different techniques. Solid State Electron. 2012, 69, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Plasma Polymer | Plasma Power (W) | Plasma Potential (V) | Pressure (Pa) | Deposition Time (s) | Film Thickness (nm) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Initial | Final | Initial | Final | Initial | Final | |||
| PPAni | 3.5 | 7.1 | 350 | 710 | 1.33 | 18.33 | 600 | ~165 |
| PDPA | 3.5 | 5.4 | 350 | 540 | 1.33 | 13.66 | 600 | ~155 |
| PPAni-PDPA | 3.5 | 6.8 | 350 | 680 | 1.33 | 16.33 | 600 | ~160 |
| Wave Number (cm−1) | Assignment | Plasma Polymer | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PPAni | PDPA | PAni-PDPA | ||
| 747 (ortho) | aromatic ring substitutions, out-of-plane (C–H) bending vibration [39,40] | 746 | 748 | 750 |
| 830 (para) | aromatic ring substitution [30,39] | 827 | 827 | 830 |
| 873, 692 | meta substitutions, 1,3 disubstitution in benzene ring [41] | 692 | 878 | 875 |
| 995, 971, 909 | C–H out-of-plane bending vibrations [41] | 973 | - | 970 |
| 1070 | quinoid ring –NH+– benzoid ring stretching vibrations [40] | - | - | 1072 |
| 1173 | C–H bending vibration in quinoid ring [38,42] | 1177 | 1173 | 1178 |
| 1255 | C–N+ stretching vibrations in aromatic primary amine [40] | 1251 | 1248 | 1254 |
| 1285–1315 (aromatic) 1290–1300 (quinone) | C=C, or aromatic (C–N) stretching vibrations of aromatic ring, CH bending [42,43] | 1310 | 1311 | 1311 |
| 1373 | C–H symmetric deformation vibrations in –CH3 [44] | 1373 | 1376 | 1376 |
| 1450 | C=C stretching vibrations of benzenoid ring [40] | 1441 | 1455 | 1452 |
| 1498 | NH bending of aromatic secondary amines [39] | 1495 | 1496 | 1496 |
| 1505 | C=C stretching of benzene ring [38] | - | 1510 | 1512 |
| 1596, 1580–1615 | HN=quinoid=NH imine, N–H deformation vibrations of primary aromatic amine [45], quinone ring stretching [20] | 1595 | 1594 | 1599 |
| 1650 | C=N stretching vibrations of quinoid ring [40] | - | 1654 | - |
| 2862 | C–H vibrations in CH2 [40] | 2862 | 2872 | 2870 |
| 2750–3000 (aromatic) | NH2 stretching and C–H stretching vibrations in CH3 [38,42] | 2926 | 2927 | 2927 |
| 3027 | 3028 | - | 3026 | |
| 3100–3400 (aromatic) | N–H stretching vibrations [41,42,46] | 3361 | 3370 | 3366 |
| Plasma Polymer | Diffraction Line | 2θ | d (nm) | t (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 37.74 | 0.238 | 37.72 | |
| 2 | 43.98 | 0.205 | 35.29 | |
| PPAni | 3 | 64.34 | 0.144 | 34.36 |
| 4 | 69.12 | 0.135 | 35.32 | |
| 5 | 77.46 | 0.123 | 33.56 | |
| 1 | 37.86 | 0.237 | 34.59 | |
| PDPA | 2 | 44.08 | 0.205 | 36.84 |
| 3 | 64.42 | 0.144 | 34.38 | |
| 4 | 69.20 | 0.136 | 47.71 | |
| 5 | 77.54 | 0.122 | 29.62 | |
| 1 | 11.68 | 0.756 | 56.39 | |
| 2 | 37.80 | 0.237 | 34.59 | |
| 3 | 44.02 | 0.205 | 35.29 | |
| PPAni-PDPA | 4 | 64.38 | 0.144 | 34.37 |
| 5 | 69.22 | 0.135 | 73.40 | |
| 6 | 69.44 | 0.135 | 50.29 | |
| 7 | 69.70 | 0.134 | 47.85 | |
| 8 | 77.48 | 0.123 | 29.61 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nastase, C.; Prodan, G.; Nastase, F. Plasma-Polymerized Aniline–Diphenylamine Thin Film Semiconductors. Coatings 2022, 12, 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101441
Nastase C, Prodan G, Nastase F. Plasma-Polymerized Aniline–Diphenylamine Thin Film Semiconductors. Coatings. 2022; 12(10):1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101441
Chicago/Turabian StyleNastase, Claudia, Gabriel Prodan, and Florin Nastase. 2022. "Plasma-Polymerized Aniline–Diphenylamine Thin Film Semiconductors" Coatings 12, no. 10: 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101441
APA StyleNastase, C., Prodan, G., & Nastase, F. (2022). Plasma-Polymerized Aniline–Diphenylamine Thin Film Semiconductors. Coatings, 12(10), 1441. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings12101441








