Effects of Heat Treatment on Interfacial Properties of Pinus Massoniana Wood
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Melamine-Urea-Formaldehyde Resin
2.3. Preparation of Pinus Massoniana Heat-Treated Wood
2.4. Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
2.5. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
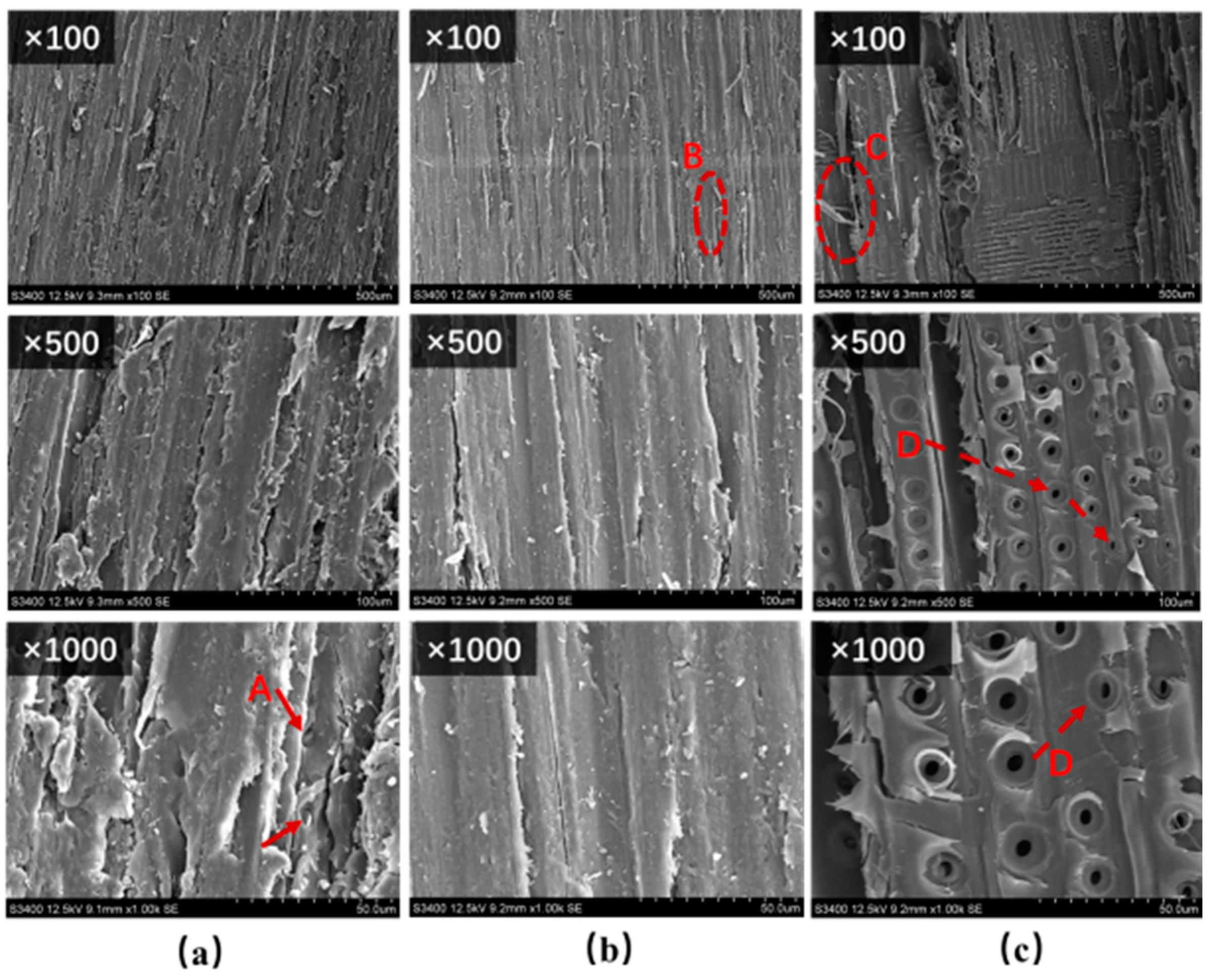
2.6. Scanning ElectronMicroscopy(SEM)
2.7. Contact Angle Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effects of Heat Treatment on Contents of Pinus Massoniana Wood
3.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR)Spectroscopy Analysis
3.3. XRD Analysis
3.4. Color Change of Pinus Massoniana Wood
3.5. SEM Analysis
3.6. Contact Angle Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kržišnik, D.; Lesar, B.; Thaler, N.; Humar, M. Influence of natural and artificial weathering on the colour change of different wood and wood-based materials. Forests 2018, 9, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramage, M.H.; Burridge, H.; Busse-Wicher, M.; Fereday, G.; Reynolds, T.; Shah, D.U.; Wu, G.; Yu, L.; Fleming, P.; Densley-Tingley, D.; et al. The wood from the trees: The use of timber in construction. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017, 68, 333–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Z.; Zhou, P.; Xu, M.; Xu, L. Development and characterization of chloroplast microsatellite markers for Pinus massoniana and their application in Pinus (Pinaceae) species. J. Genet. 2018, 97, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Xie, Y.; Wei, Q.; Wang, X.; Hagman, O.; Karlsson, O.; Liu, J. Effect of refining on physical properties and paper strength of Pinus massoniana and China fir cellulose fibers. BioRes 2016, 11, 7839–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteves, B.; Pereira, H. Wood modification by heat treatment: A review. BioRes 2009, 4, 370–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nhacila, F.; Sitoe, E.; Uetimane, E.; Manhica, A.; Egas, A.; Möttönen, V. Effects of thermal modification on physical and mechanical properties of Mozambican Brachystegia spiciformis and Julbernardia globiflora wood. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2020, 78, 871–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkut, S.; Alma, M.; Elyildirim, Y. The effects of heat treatment on physical and technological properties and surface roughness of European Hophornbeam (Ostrya carpinifolia Scop.) wood. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 820, 5316–5327. [Google Scholar]
- Wikberg, H.; Liisamaunu, S. Characterisation of thermally modified hard- and softwoods by 13C CPMAS NMR. Carbohydr. Polym. 2004, 58, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Lu, J.; Huang, R.; Jiang, J. Increased dimensional stability of Chinese fir through steam-heat treatment. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2011, 70, 441–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Wang, X.; Yu, Q. New research progress of functional wood. J. For. Eng. 2019, 4, 10–18. [Google Scholar]
- Mantanis, G.I. Chemical modification of wood by acetylation or furfurylation: A review of the present scaled-up technologies. BioRes 2017, 12, 4478–4489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, F.; Nemeth, R.; Lankveld, C.; Hofmann, T. Effect of acetylation on the chemical composition of hornbeam (Carpinus betulus L.) in relation with the physical and mechanical properties. Wood Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 13, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Iida, I.; Guo, J. Studies on pre-treatment by compression for wood impregnation I: Effects of compression ratio, compression direction, compression speed and compression-unloading place on the liquid impregnation of wood. J. Wood Sci. 2018, 64, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Iida, I.; Guo, J. Studies on pre-treatment by compression for wood impregnation II: The impregnation of wood compressed at different moisture content conditions. J. Wood Sci. 2019, 65, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Deng, X.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, B.; Xi, X.; Yu, L.; Li, L. Improvements in fire resistance, decay resistance, anti-mold property and bonding performance in plywood treated with manganese chloride, phosphoric acid, boric acid and ammonium chloride. Coatings 2021, 11, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bytner, O.; Laskowska, A.; Drożdżek, M.; Kozakiewicz, P.; Zawadzki, J. Evaluation of the dimensional stability of black poplar wood modified thermally in nitrogen atmosphere. Materials 2021, 14, 1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozakiewicz, P.; Drożdżek, M.; Laskowska, A.; Grześkiewicz, M.; Bytner, O.; Radomski, A.; Zawadzki, J. Effects of thermal modification on the selected physical properties of sapwood and heartwood of black poplar (Populusnigra). BioRes 2019, 14, 8391–8404. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Sun, W. New perspective on wood thermal modification: Relevance between the evolution of chemical structure and physical-mechanical properties, and online analysis of release of VOCs. Polymers 2019, 11, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čabalová, I.; Kačík, F.; Lagaňa, R.; Výbohová, E.; Bubeníková, T.; Čaňová, I.; Ďurkovič, J. Effect of thermal treatment on the chemical, physical, and mechanical properties of pedunculate oak (Quercus robur) wood. BioRes 2018, 13, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bremer, M.; Fischer, S.; Nguyen, T.C.; Wagenführ, A.; Phuong, L.X.; Dai, V.H. Effects of thermal modification on the properties of two vietnamese bamboo species. Part II: Effects on chemical composition. BioRes 2013, 8, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Windeisen, E.; Strobel, C.; Wegener, G. Chemical changes during the production of thermo-treated beech wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 523–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundqvist, B.; Karlsson, O.; Westermark, U. Determination of formic-acid and acetic acid concentrations formed during hydrothermal treatment of birch wood and its relation to colour, strength and hardness. Wood Sci. Technol. 2006, 40, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokhan, G.; Suleyman, K.; Deniz, A.; Llter, B. The density, compression strength and surface hardness of heat treated Hornbeam (Carpinusbetulus L.) wood. Cienc. Tecnol. 2009, 11, 61–70. [Google Scholar]
- Percin, O.; Hüseyin, P.; Atlgan, A. The effect of heat treatment on the some physical and mechanical properties of beech (Fagus orientalislipsky) wood. Wood Res. 2016, 61, 443–456. [Google Scholar]
- Borůvka, V.; Dudík, R.; Zeidler, A.; Holeček, T. Influence of site conditions and quality of birch wood on its properties and utilization after heat treatment. Part I—Elastic and strength properties, relationship to water and dimensional stability. Forests 2019, 10, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obataya, E.; Shibutani, S.; Hanata, K.; Doi, S. Effects of high temperature kiln drying on the practical performances of Japanese cedar wood (Cryptomeria japonica) II: Changes in mechanical properties due to heating. J. Wood. Sci. 2006, 52, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildiz, S.; Gezer, E.D.; Yildiz, U.C. Mechanical and chemical behavior of spruce wood modified by heat. Build. Environ. 2006, 41, 1762–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamdem, D.P.; Pizzi, A.; Jermannaud, A. Durability of heat-treated wood. Holzalsroh. Werkst. 2002, 60, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simdqvist, B. Colour changes and acid formation in wood during heating. Ph.D. Thesis, Université de Lorraine, Nancy, France, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Suleyman, K.; Budakci, M. The effects of high-temperature heat-treatment on physical properties and surface roughness of rowan (Sorbus aucuparial.) wood. Wood Res. 2010, 55, 67–78. [Google Scholar]
- Chu, D.; Xue, L.; Zhang, Y.; Kang, L. Surface characteristics of poplar wood with high-temperature heat treatment: Wettability and surface brittleness. BioRes 2016, 11, 6948–6967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gérardin, P.; Petrič, M.; Petrissans, M.; Lambert, J.; Ehrhrardt, J. Evolution of wood surface free energy after heat treatment. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2007, 92, 653–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, S.; Li, X.; Luo, T.; Li, M. Anisotropic propagation of acoustic emission signal on surface of Pinus massoniana Lamb. glulam. J. For. Eng. 2019, 4, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Meng, J.; Cheng, Z.; Guan, H. Research progress of durable superhydrophobic wood surface. J. For. Eng. 2020, 5, 13–20. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Chen, S.; Tian, M.; Li, L.; Yu, L.; Xi, X.; Liang, J.; Zhang, B.; Lei, H.; Zhang, J.; et al. Effects of heat-treatment on bonding performance of Betula alnoides. Wood Res. 2019, 64, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, F.; Zhao, X.; Hu, Y. Lignocellulosic biomass delignification using aqueous alcohol solutions with the catalysis of acidic ionic liquids: A comparison study of solvents. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 969–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Ding, T.; Jiang, N. Development of wood heat treatment research and industrialization. J. For. Eng. 2019, 4, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Mehnet, A.; Esat, G.; Suleyman, K. Crystalline structure of heat- treated Scots pine (Pinus sylvestris L.) and Uludag fir (Abies nordmanniana (Stev.) subsp. Bornmuelleriana (Mattf.)) wood. Wood Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 281–289. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Gao, J.; Wu, Y.; Yi, S.; Wu, Z. Characteristics of FTIR and XRD for wood with high-temperature heating treatment. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2009, 31, 104–107. [Google Scholar]
- Boonstra, M.J.; van Acker, J.; Kegel, E.; Stevens, M. Optimisation of a two-stage heat treatment process: Durability aspects. Wood Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 31–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tang, R.; Bao, B.; Sun, H. Mechanical properties and dimensional stability of heat-treated Chinese fir. J. Beijing For. Univ. 2010, 32, 232–236. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, G.; Li, L.; Li, X. Study on the surface characteristics of Pinus massoniana heat-treated wood. For. Environ. Sci. 2018, 34, 12–17. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Jiang, P.; Chen, Z.; Li, L. Characteristic analysis of flame retardant particleboard using three methods of combustion performance evaluation. J. For. Eng. 2020, 5, 28–34. [Google Scholar]







| Treatment Temperature | Cellulose/% | Hemicelluloses/% | Lignin/% |
|---|---|---|---|
| control | 42.6 (3.3) | 13.1 (1.2) | 21.1 (3.2) |
| 160 °C | 41.2 (2.5) | 11.4 (0.9) | 25.1 (3.9) |
| 180 °C | 39.0 (3.7) | 8.8 (0.8) | 26.3 (3.6) |
| 200 °C | 33.5 (2.5) | 4.5 (0.5) | 33.4 (3.5) |
| 220 °C | 29.4 (3.1) | 1.1 (0.3) | 37.7 (3.3) |
| Treatment Temperature | 2θ/° | Relative Degree of Crystallinity/% |
|---|---|---|
| control | 22.5 | 45.8% |
| 160 °C | 22.3 | 46.5% |
| 180 °C | 22.0 | 47.3% |
| 200 °C | 22.1 | 43.8% |
| 220 °C | 22.1 | 50.5% |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wu, Z.; Deng, X.; Li, L.; Xi, X.; Tian, M.; Yu, L.; Zhang, B. Effects of Heat Treatment on Interfacial Properties of Pinus Massoniana Wood. Coatings 2021, 11, 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050543
Wu Z, Deng X, Li L, Xi X, Tian M, Yu L, Zhang B. Effects of Heat Treatment on Interfacial Properties of Pinus Massoniana Wood. Coatings. 2021; 11(5):543. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050543
Chicago/Turabian StyleWu, Zhigang, Xue Deng, Lifen Li, Xuedong Xi, Meifen Tian, Liping Yu, and Bengang Zhang. 2021. "Effects of Heat Treatment on Interfacial Properties of Pinus Massoniana Wood" Coatings 11, no. 5: 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050543
APA StyleWu, Z., Deng, X., Li, L., Xi, X., Tian, M., Yu, L., & Zhang, B. (2021). Effects of Heat Treatment on Interfacial Properties of Pinus Massoniana Wood. Coatings, 11(5), 543. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11050543







