Controlling the Surface Roughness of Surface-Electrode Ion Trap Based on Micro-Nano Fabrication
Abstract
1. Introduction
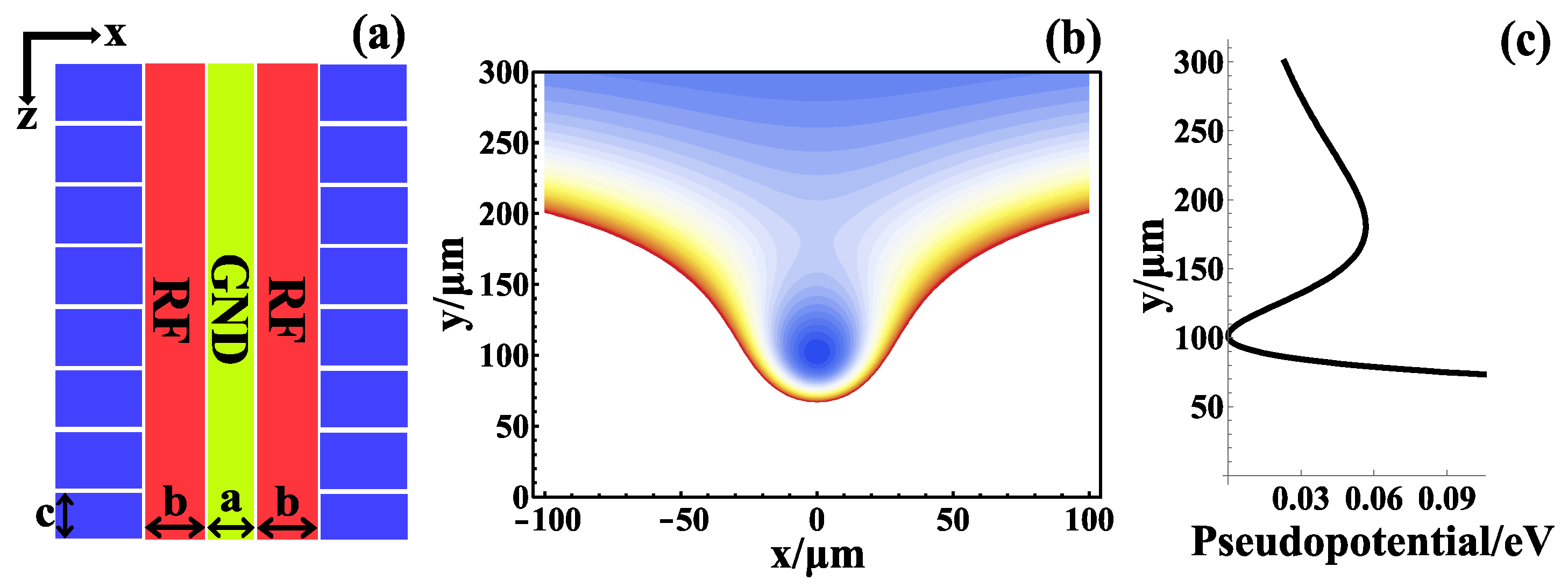
2. Method and Fabrication
2.1. Thick Film Micro-Nano Fabrication Process with Controllable Surface Roughness
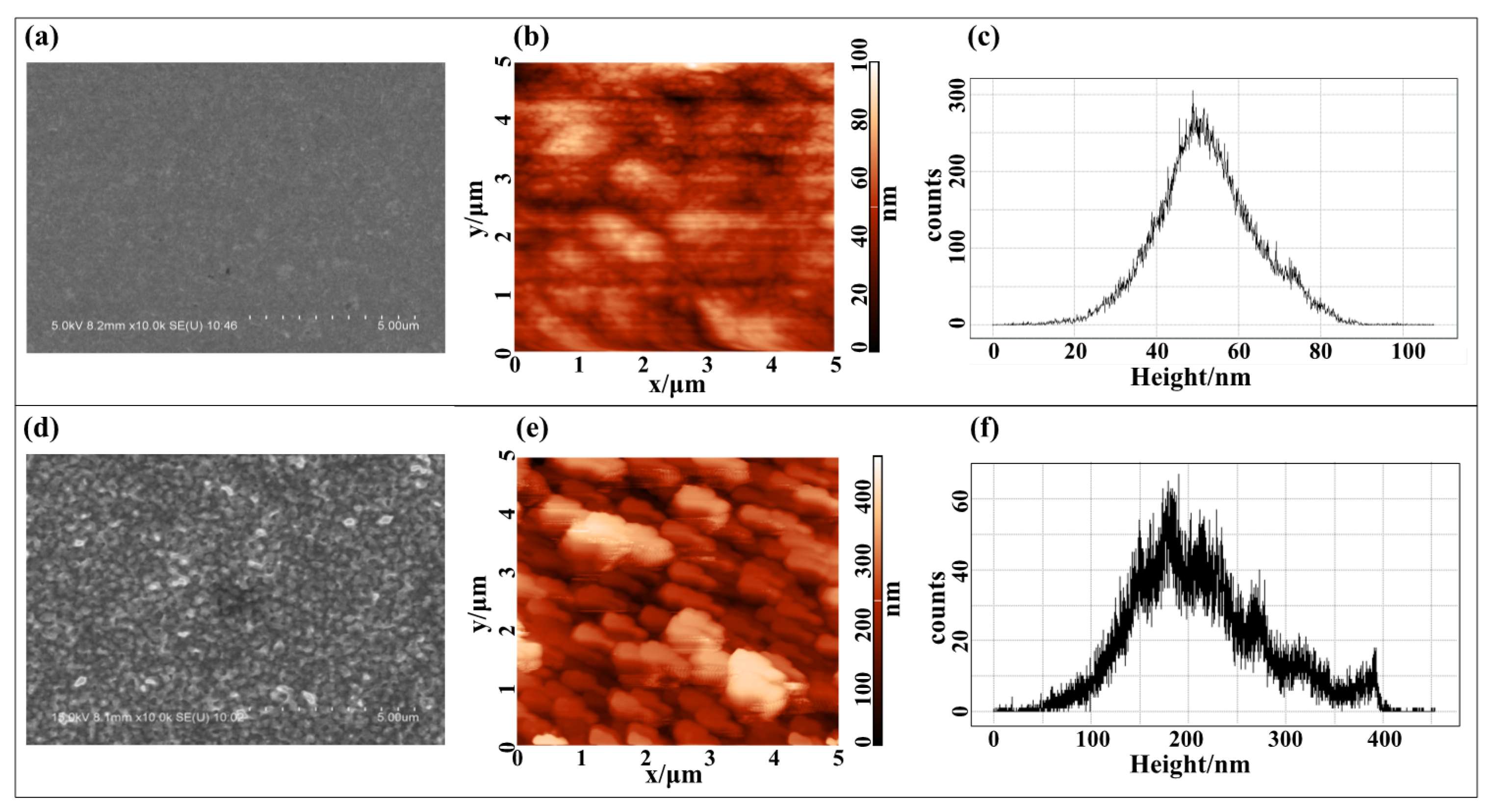
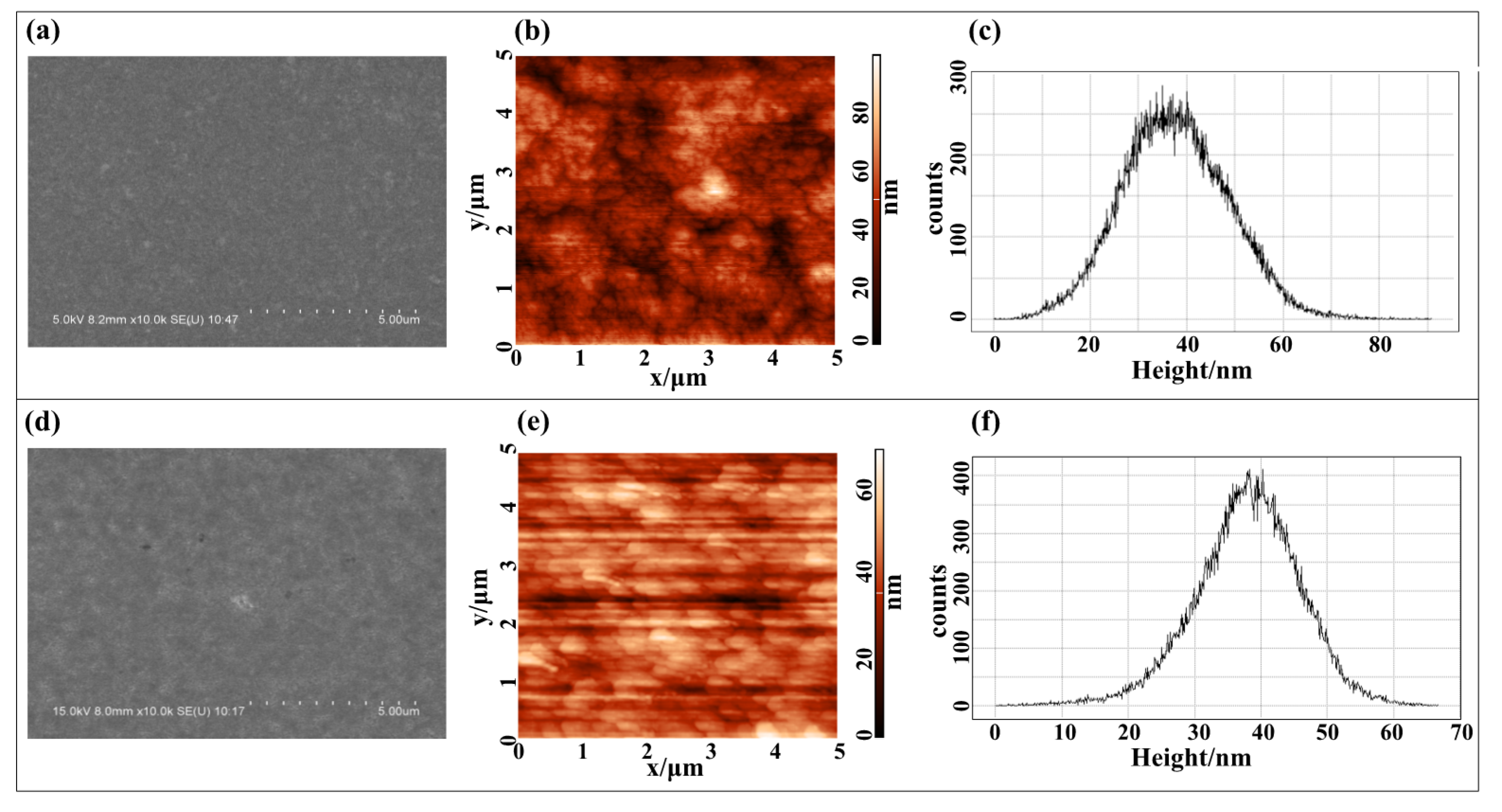
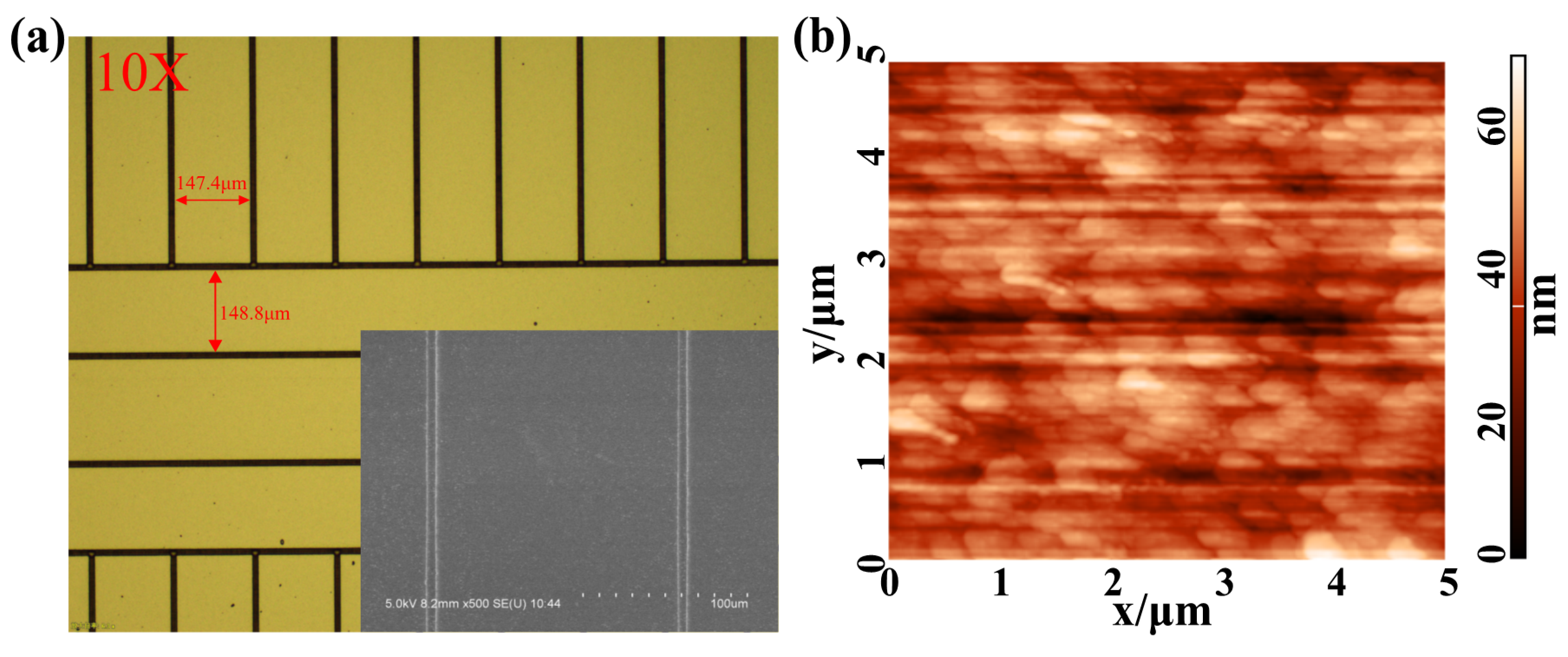
2.2. Fabrication of Thick Film Surface-Electrode Ion Trap with Different Roughness
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blatt, R.; Wineland, D. Entangled states of trapped atomic ions. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 453, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, H.; Roos, C.; Becher, C.; Hansel, W.; Körber, T.; Schmidt-Kaler, F.; Riebe, M.; Benhelm, J.; Lancaster, G.; Chek-Al-Kar, D.; et al. Quantum computing with trapped ions. In Proceedings of the EQEC’05. European Quantum Electronics Conference, Munich, Germany, 12–17 June 2005; Volume 469, pp. 155–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amini, J.M.; Uys, H.; Wesenberg, J.H.; Seidelin, S.; Britton, J.; Bollinger, J.J.; Leibfried, D.; Ospelkaus, C.; VanDevender, A.P.; Wineland, D.J. Toward scalable ion traps for quantum information processing. New J. Phys. 2010, 12, 033031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Herskind, P.F.; Chuang, I.L. Surface-electrode ion trap with integrated light source. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 214103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakestad, R.B.; Ospelkaus, C.; VanDevender, A.P.; Amini, J.M.; Britton, J.; Leibfried, D.; Wineland, D.J. High-Fidelity Transport of Trapped-Ion Qubits through anX-Junction Trap Array. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009, 102, 153002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesenberg, J.H. Electrostatics of surface-electrode ion traps. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 063410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stick, D.; Hensinger, W.K.; Olmschenk, S.; Madsen, M.J.; Schwab, K.; Monroe, C. Ion trap in a semiconductor chip. Nat. Phys. 2005, 2, 36–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.J.; Lin, Z.; Diab, K.S.; Chuang, I.L. A cryogenic surface-electrode elliptical ion trap for quantum simulation. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 109, 76103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Home, J.P.; Hanneke, D.; Jost, J.D.; Amini, J.M.; Leibfried, D.; Wineland, D.J. Complete Methods Set for Scalable Ion Trap Quantum Information Processing. Science 2009, 325, 1227–1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- House, M.G. Analytic model for electrostatic fields in surface-electrode ion traps. Phys. Rev. A 2008, 78, 033402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Ou, B.; Chen, T.; Xie, Y.; Wu, W.; Chen, P. Versatile surface ion trap with fork junction for effective cooling. Phys. Scr. 2019, 95, 045103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.-Y.; Low, G.H.; Chuang, I.L. Effects of electrode surface roughness on motional heating of trapped ions. Phys. Rev. A 2016, 94, 013418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niedermayr, M.; Lakhmanskiy, K.; Kumph, M.; Partel, S.; Edlinger, J.; Brownnutt, M.; Blatt, R. Cryogenic surface ion trap based on intrinsic silicon. New J. Phys. 2014, 16, 113068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seidelin, S.; Chiaverini, J.; Reichle, R.; Bollinger, J.J.; Leibfried, D.; Britton, J.; Wesenberg, J.H.; Blakestad, R.B.; Epstein, R.J.; Hume, D.B.; et al. Microfabricated Surface-Electrode Ion Trap for Scalable Quantum Information Processing. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006, 96, 253003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, B.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, T.; Wu, C.; Wu, W.; Chen, P. Optimization of parameters of a surface-electrode ion trap and experimental study of influences of surface on ion lifetime. Sci. China Ser. G Phys. Mech. Astron. 2016, 59, 123011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Low, G.H.; Lachenmyer, N.S.; Ge, Y.; Herskind, P.F.; Chuang, I.L. Laser-induced charging of microfabricated ion traps. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 104901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Lau, Y.Y.; Gilgenbach, R.M. Analysis of radio-frequency absorption and electric and magnetic field enhancements due to surface roughness. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 114908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hite, D.; Colombe, Y.; Wilson, A.; Allcock, D.; Leibfried, D.; Wineland, D.; Pappas, D. Surface science for improved ion traps. MRS Bull. 2013, 38, 826–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labaziewicz, J.; Ge, Y.; Antohi, P.; Leibrandt, D.; Brown, K.R.; Chuang, I.L. Suppression of Heating Rates in Cryogenic Surface-Electrode Ion Traps. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2008, 100, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T. Characterization of surface roughness. Precis. Eng. 1981, 3, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, D.T.C.; Sherman, J.A.; Stacey, D.N.; Burrell, A.H.; Curtis, M.J.; Imreh, G.; Linke, N.M.; Szwer, D.J.; Webster, S.C.; Steane, A.M.; et al. Implementation of a symmetric surface electrode ion trap with field com-pensation using a modulated Raman effect. New. J. Phys. 2009, 12, 053026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, Y.; Maebara, M.; Tashiro, K.; Honma, H.; Yamashita, T. Surface Morphology and Characteristics of Electroplated Au/Ni Films for Connector Contact Materials. Trans. Jpn. Inst. Electron. Packag. 2013, 6, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Yoshiba, M.; Nagoshi, T.; Chang, T.-F.M.; Yamane, D.; Machida, K.; Masu, K.; Sone, M. Pulse electroplating of ultra-fine grained Au films with high compressive strength. Electrochem. Commun. 2016, 67, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binnig, G.; Rohrer, H.; Gerber, C.; Weibel, E. Surface studies by scanning tunneling microscopy. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1982, 49, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Staffier, P.A.; Blawzdziewicz, J.; Schwarz, U.D.; Schroers, J. Atomically smooth surfaces through thermoplastic forming of metallic glass. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 101907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Luo, L.; Thadasina, K.; Qian, K.; Cui, J.; Huang, Y. Fabrication of ion-trap electrodes by self-terminated electrochemical etching. EPJ Tech. Instrum. 2016, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hite, D.A.; Colombe, Y.; Wilson, A.C.; Brown, K.R.; Warring, U.; Jördens, R.; Jost, J.D.; McKay, K.S.; Pappas, D.P.; Leibfried, D.; et al. 100-fold reduction of electric-field noise in an ion trap cleaned with in situ ar-gon-ion-beam bombardment. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2012, 109, 103001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allcock, D.; Guidoni, L.; Harty, T.; Ballance, C.J.; Blain, M.G.; Steane, A.M.; Lucas, D.M. Reduction of heating rate in a microfabricated ion trap by pulsed-laser cleaning. New J. Phys. 2011, 13, 123023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.X.; Labaziewicz, J.; Ge, Y.; Shewmon, R.; Chuang, I.L. Individual addressing of ions using magnetic field gradients in a surface-electrode ion trap. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 94103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.; Amini, J.M.; Faircloth, D.L.; Volin, C.; Doret, S.C.; Hayden, H.; Pai, C.-S.; Landgren, D.W.; Denison, D.; Killian, T.; et al. Reliable transport through a microfabricatedX-junction surface-electrode ion trap. New J. Phys. 2013, 15, 367–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobe, K.A. Electroplating engineering handbook. J. Chem. Educ. 1955, 32, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ojo, A.A.; Dharmadasa, I.M. Electroplating of Semiconductor Materials for Applications in Large Area Electronics: A Review. Coatings 2018, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, M.Z. Electrodeposition Theory and Technique, 1st ed.; Harbin Institute of Technology Press: Harbin, China, 2004; pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar]




| Parameter Name | Value |
|---|---|
| Pulse peak current density | 5 |
| Duty ratio | 1:9 |
| Pulse frequency | 200 |
| Electroplating solution temperature | 40 °C |
| Pulse electroplating time | 366 |
| Distance between cathode and anode | 80 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wu, W.; Zhang, T.; Chen, P.; Deng, Z. Controlling the Surface Roughness of Surface-Electrode Ion Trap Based on Micro-Nano Fabrication. Coatings 2021, 11, 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11040406
Hou Y, Zhang X, Wu W, Zhang T, Chen P, Deng Z. Controlling the Surface Roughness of Surface-Electrode Ion Trap Based on Micro-Nano Fabrication. Coatings. 2021; 11(4):406. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11040406
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Yizhu, Xinfang Zhang, Wei Wu, Ting Zhang, Pingxing Chen, and Zhijiao Deng. 2021. "Controlling the Surface Roughness of Surface-Electrode Ion Trap Based on Micro-Nano Fabrication" Coatings 11, no. 4: 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11040406
APA StyleHou, Y., Zhang, X., Wu, W., Zhang, T., Chen, P., & Deng, Z. (2021). Controlling the Surface Roughness of Surface-Electrode Ion Trap Based on Micro-Nano Fabrication. Coatings, 11(4), 406. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings11040406






