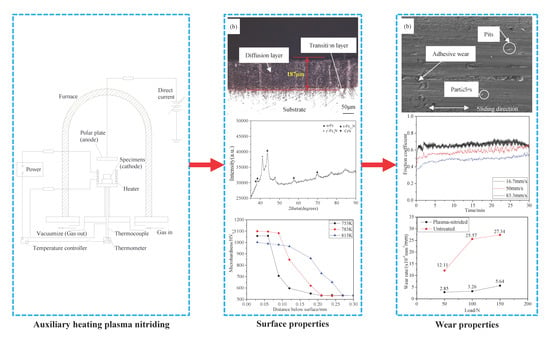
Investigation of the Surface Properties and Wear Properties of AISI H11 Steel Treated by Auxiliary Heating Plasma Nitriding
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Plasma Nitriding Treatment
1.2. Wear Properties
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Heat Treatment
2.3. Plasma Nitriding
2.4. Testing Methods
2.4.1. Surface Morphology
2.4.2. Cross-Sectional Morphology
2.4.3. Phase Analysis
2.4.4. Microhardness
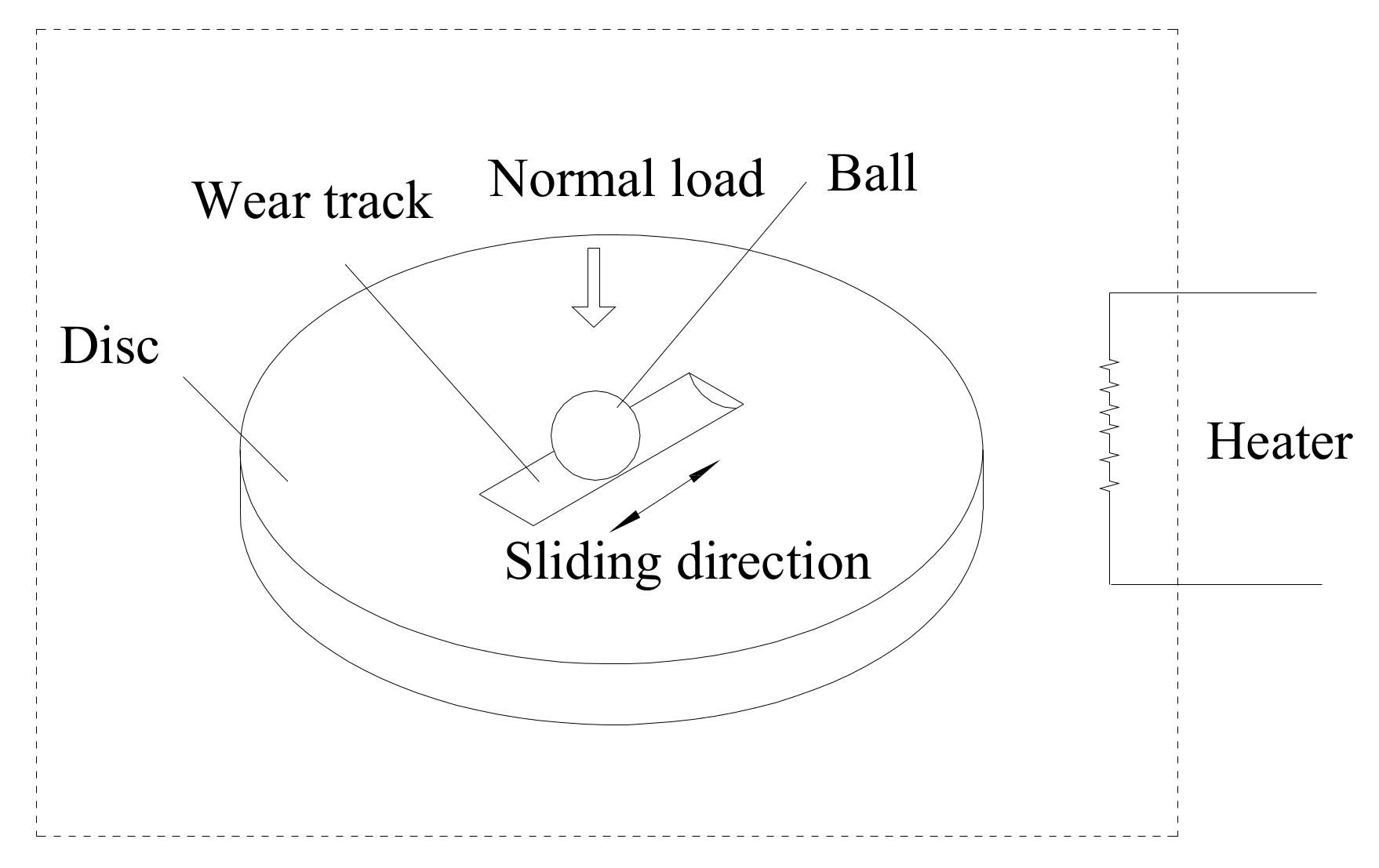
2.4.5. Friction Test
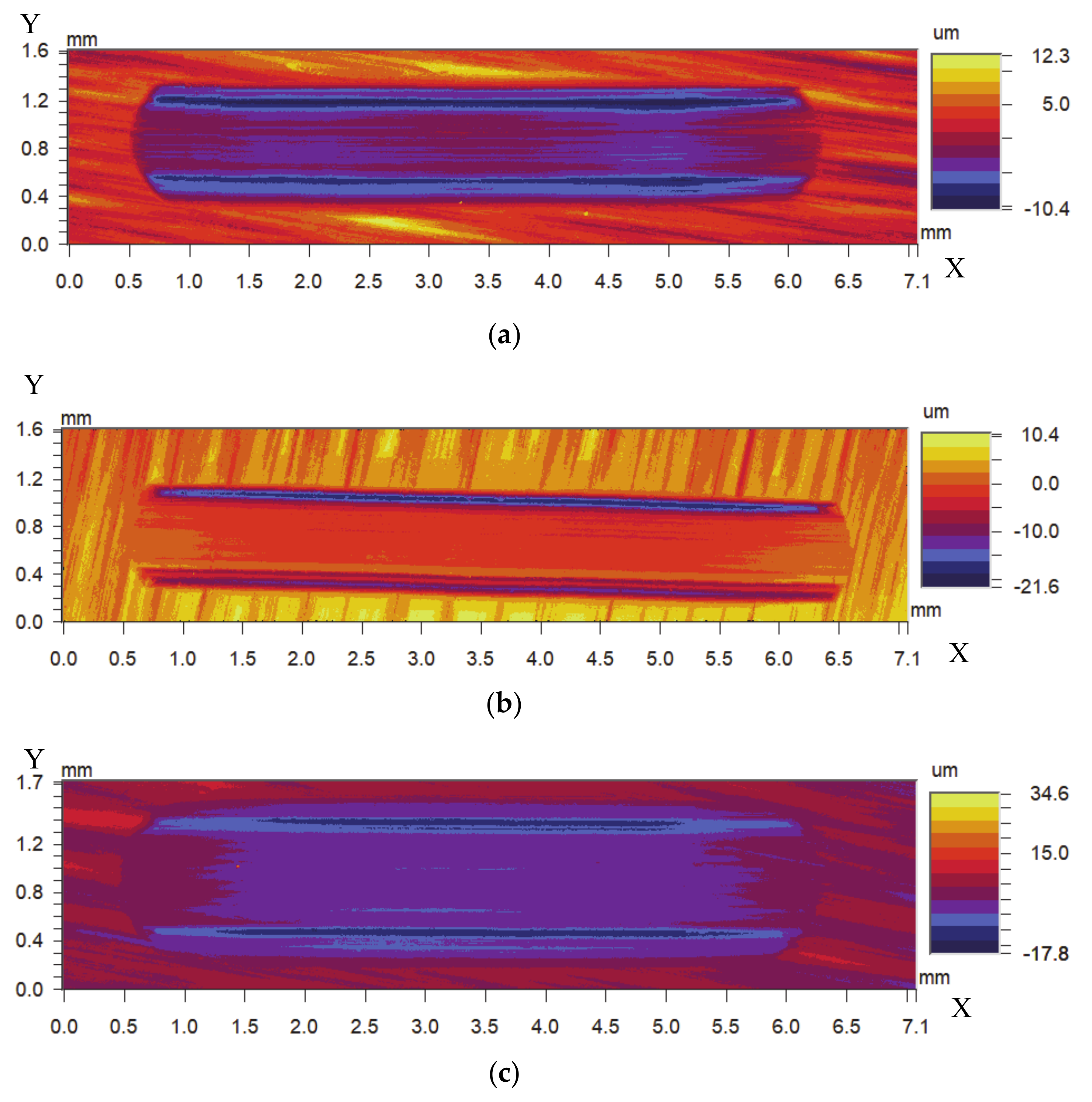
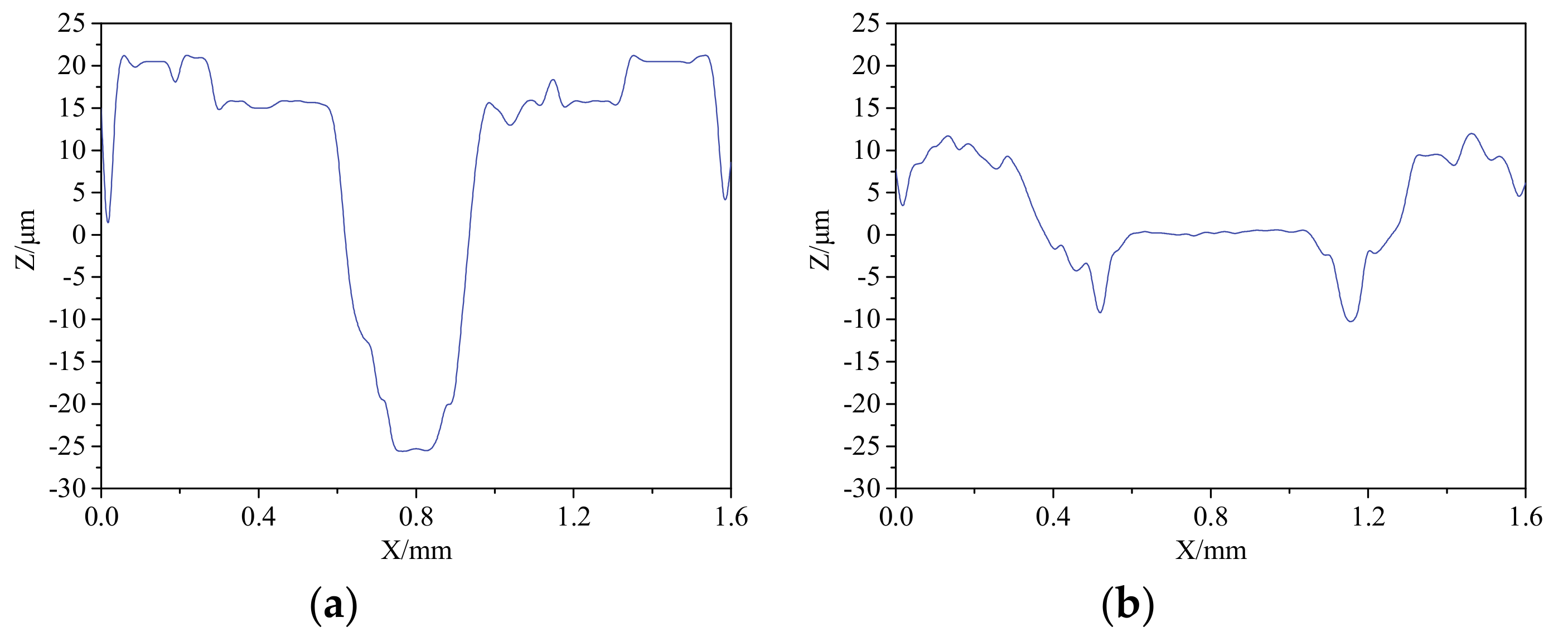
2.4.6. Wear Trace
3. Surface Properties
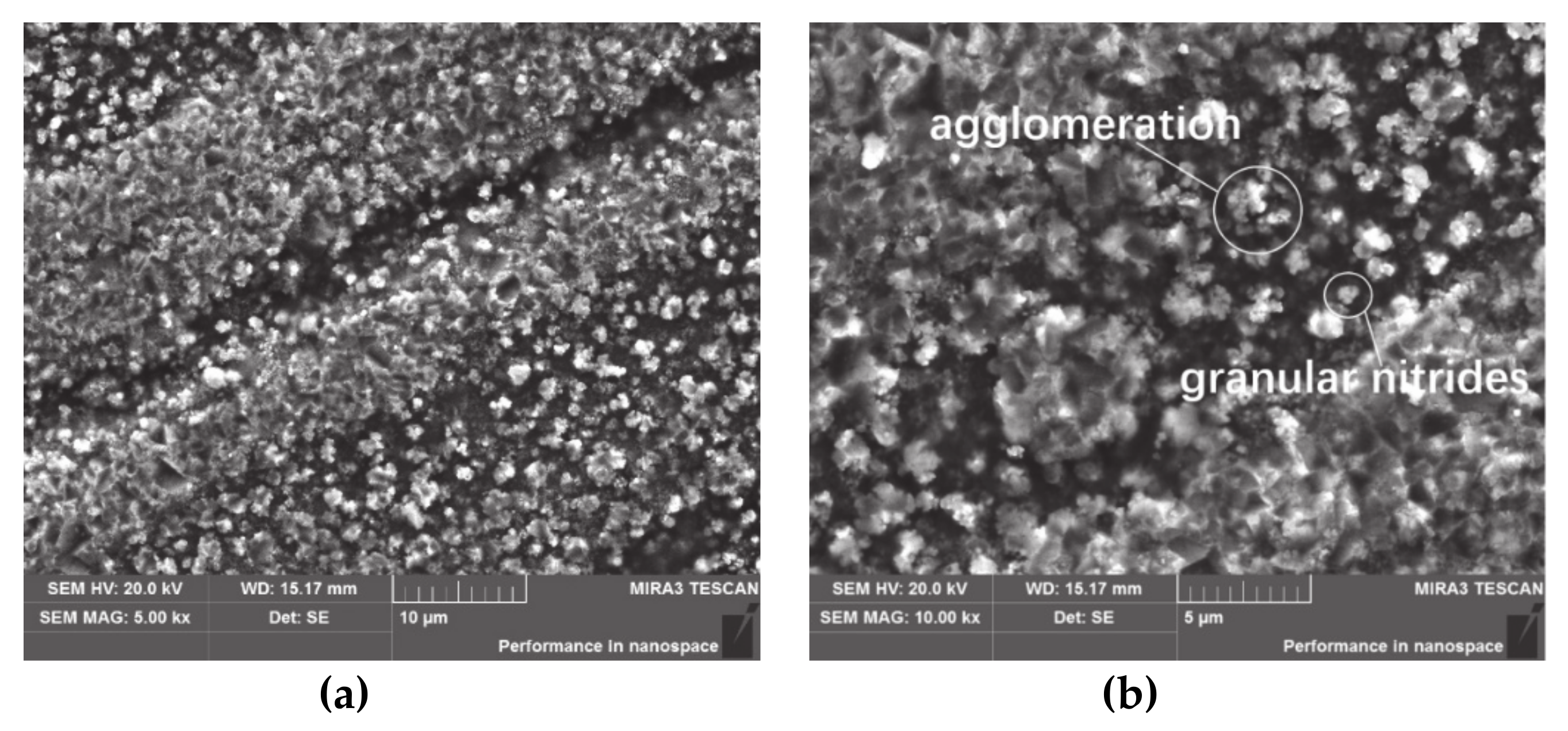
3.1. Surface Morphology
3.2. Cross-Sectional Morphology
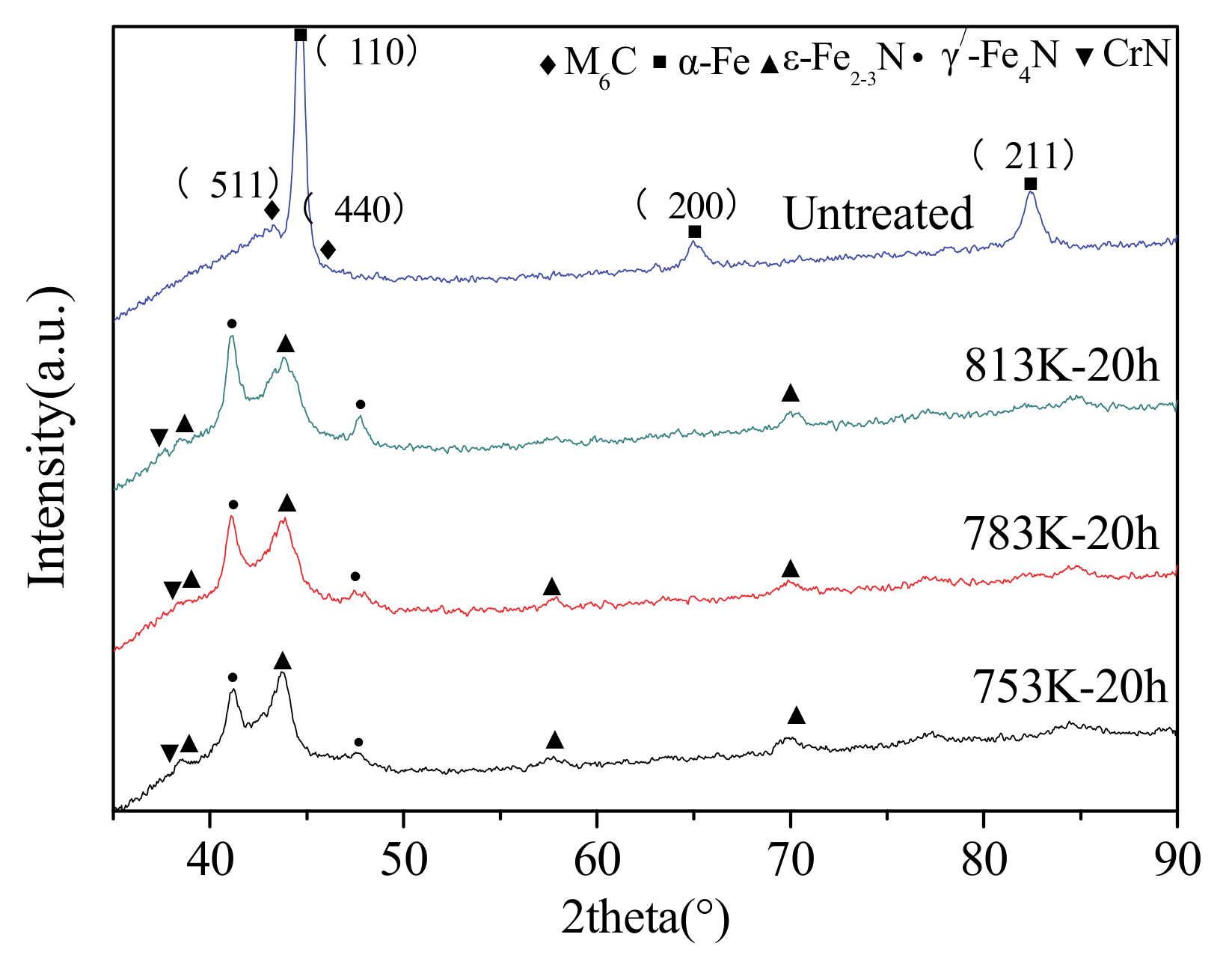
3.3. Phase Analysis
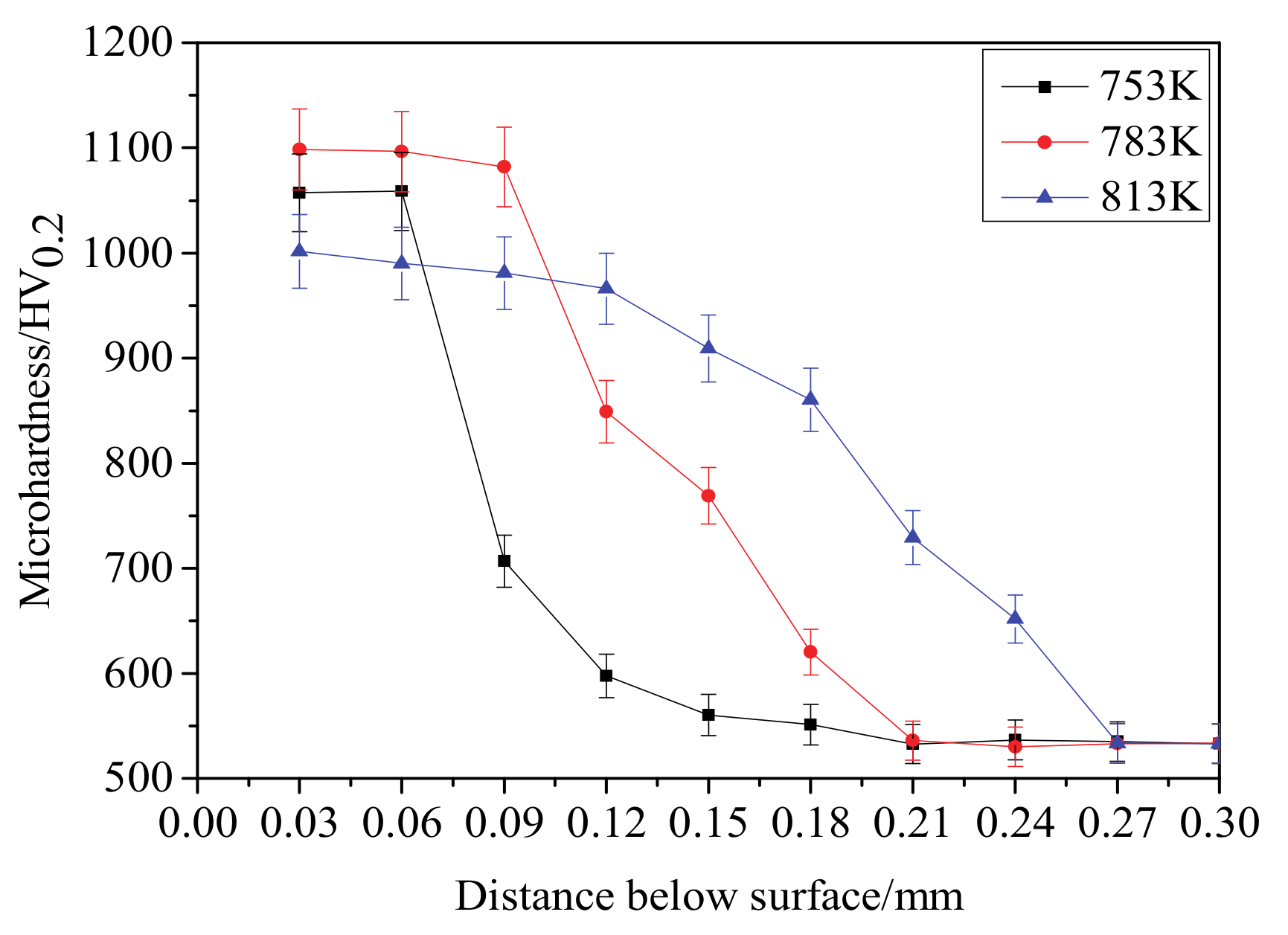
3.4. Microhardness
4. Wear Properties
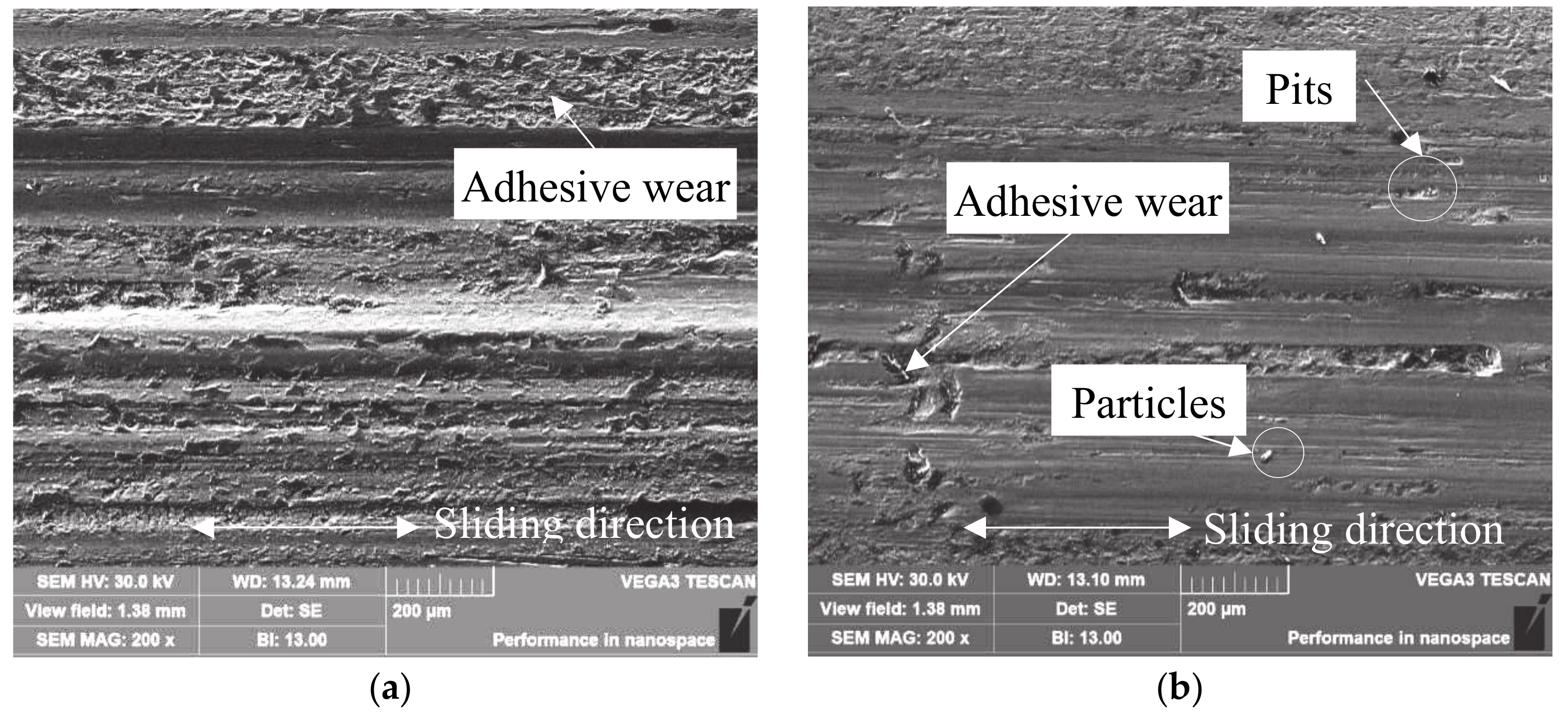
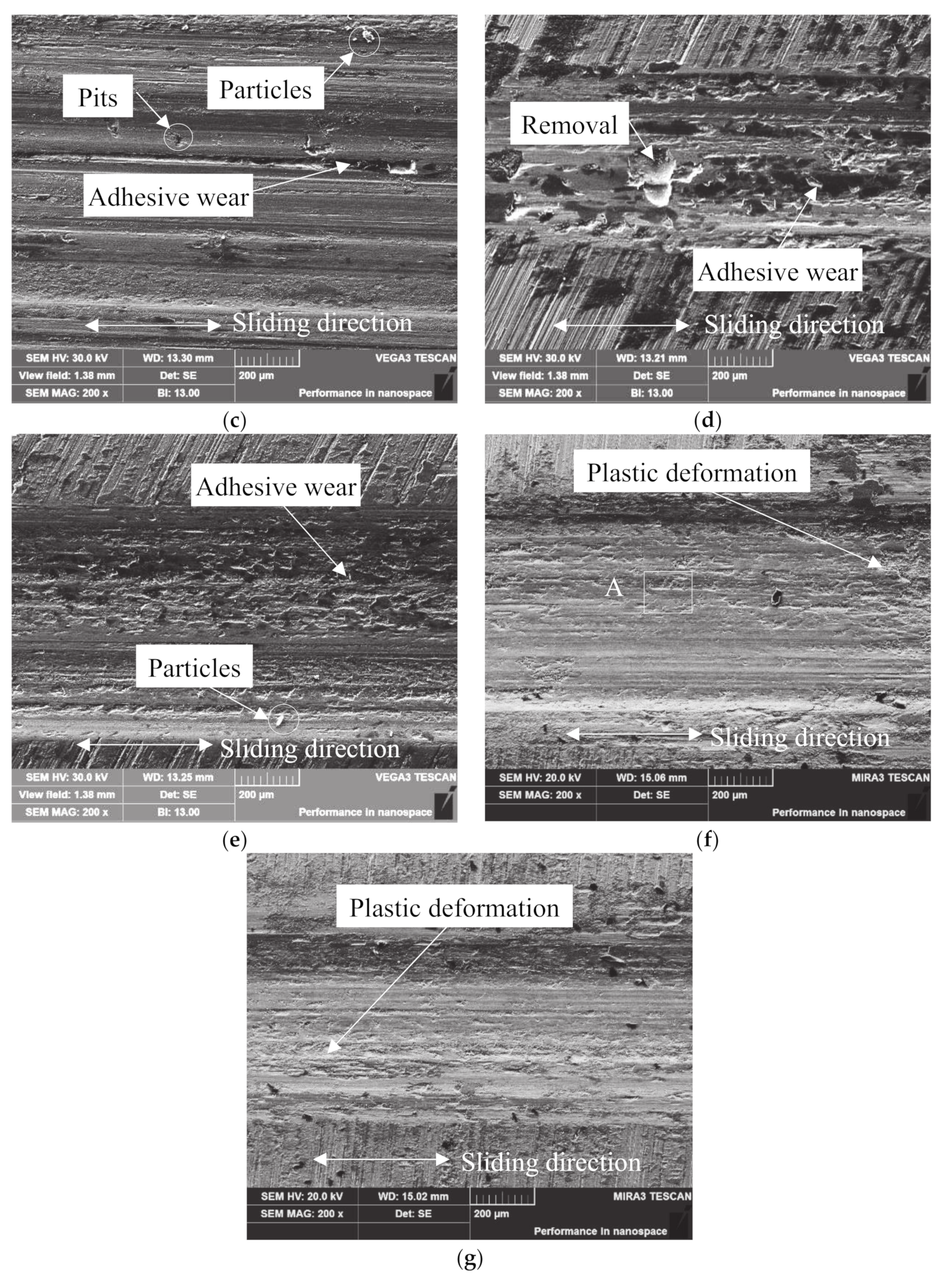
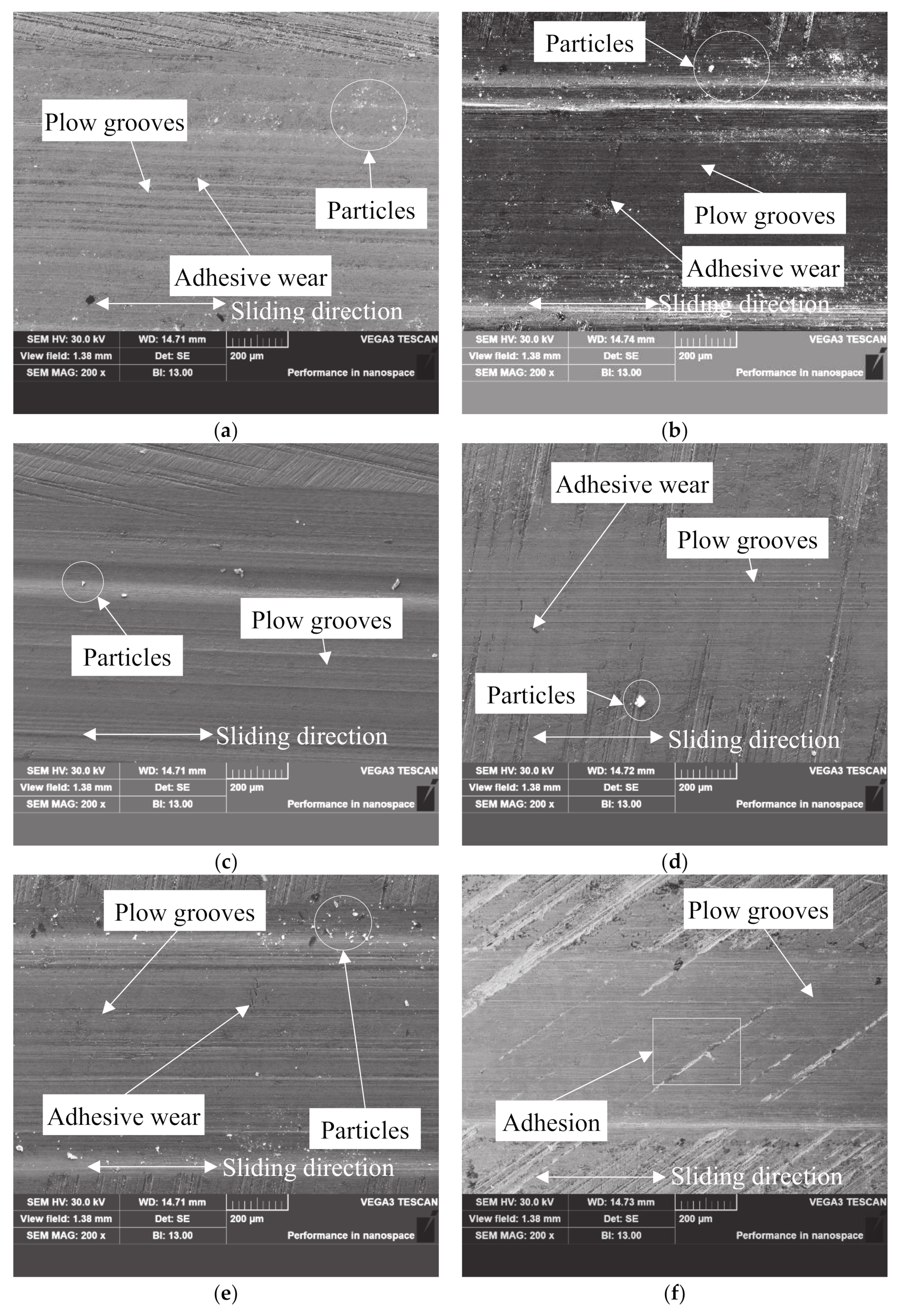
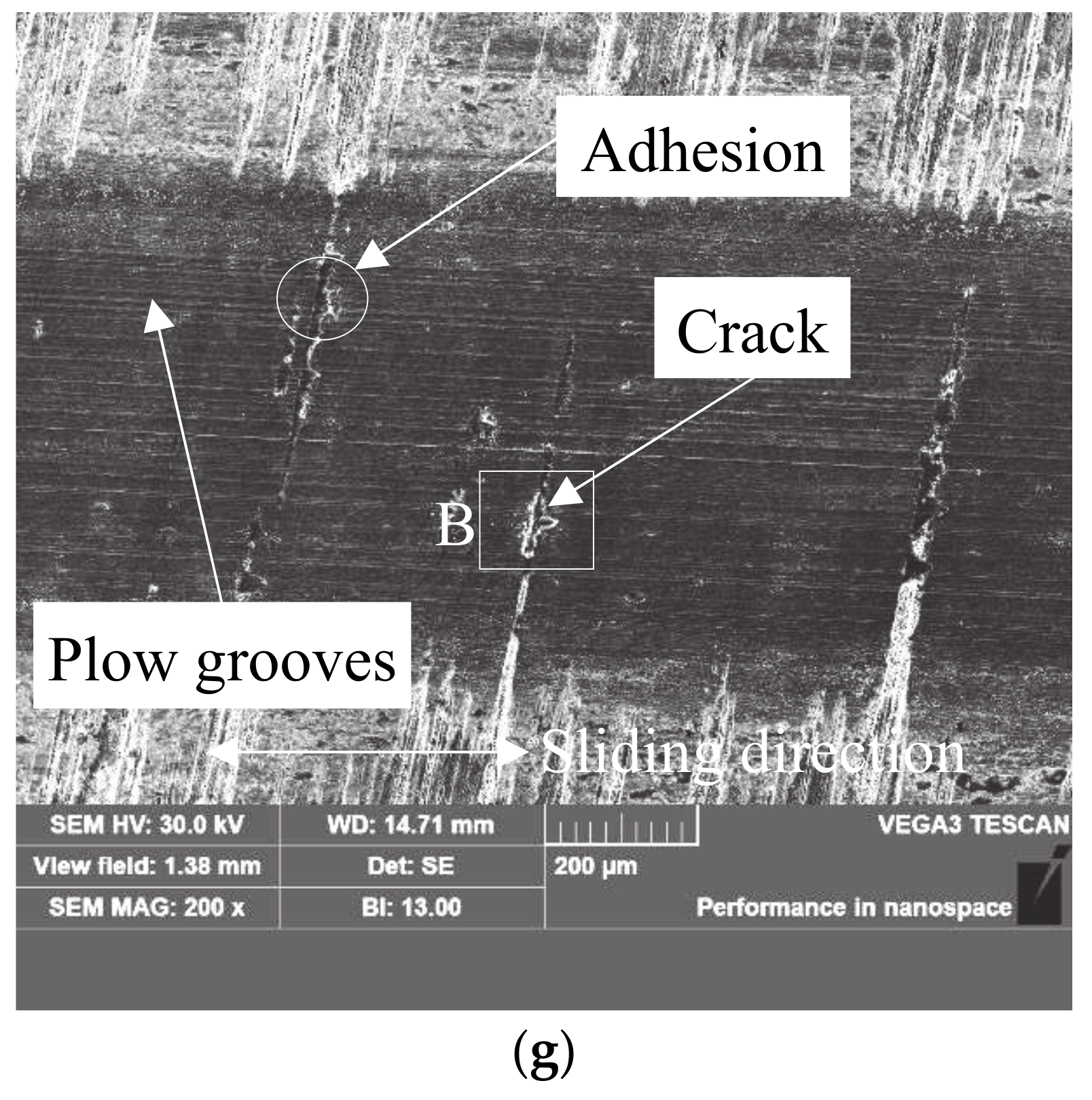
4.1. Wear Mechanism
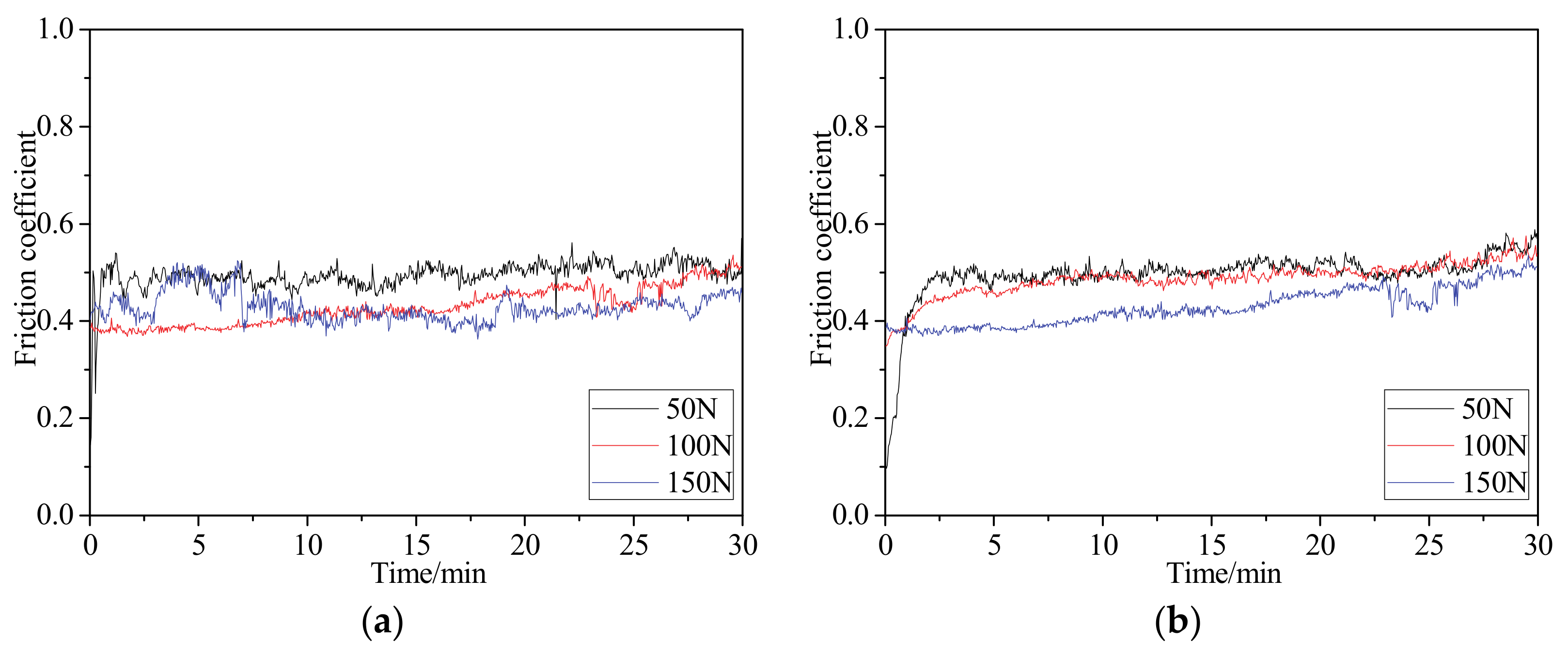
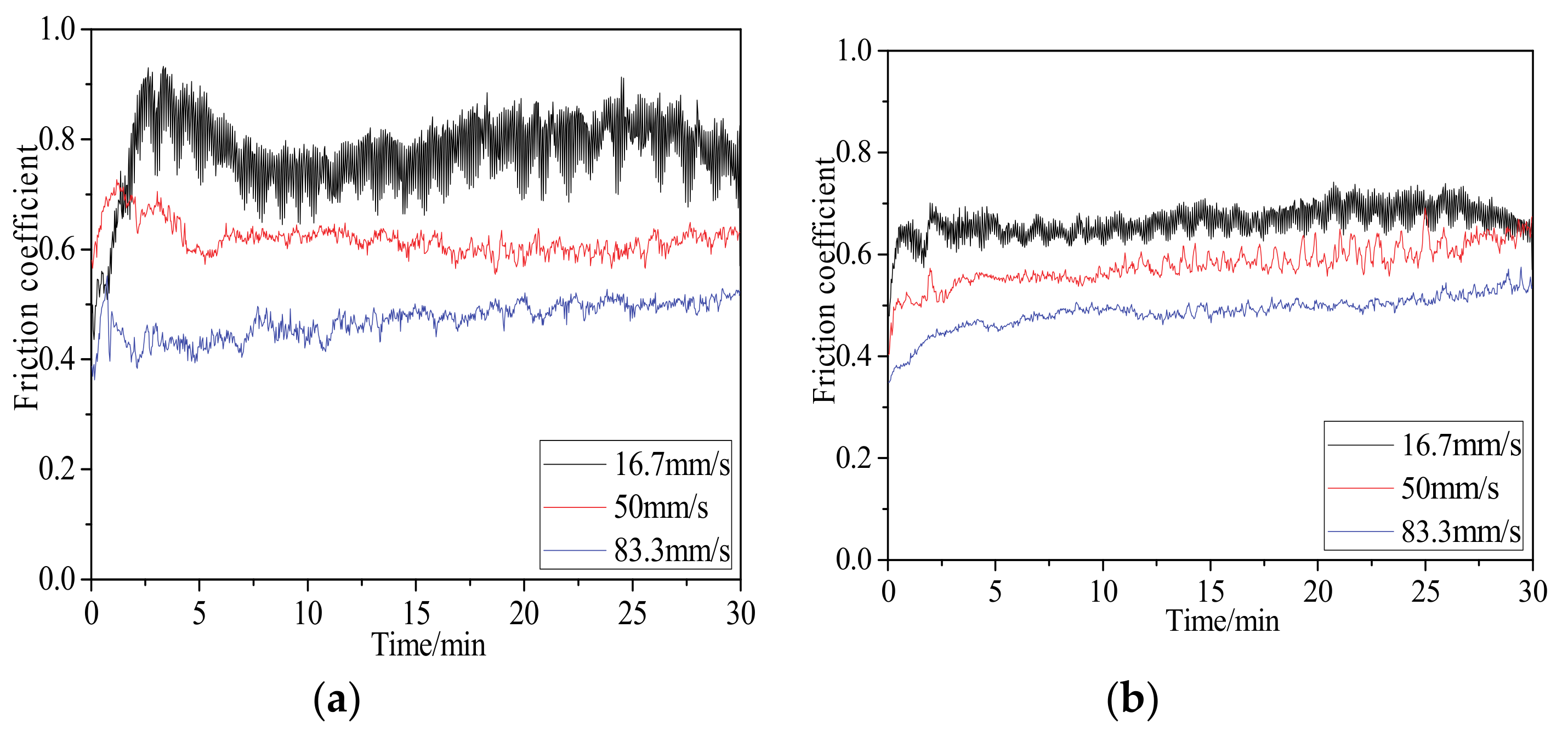
4.2. Friction Coefficient
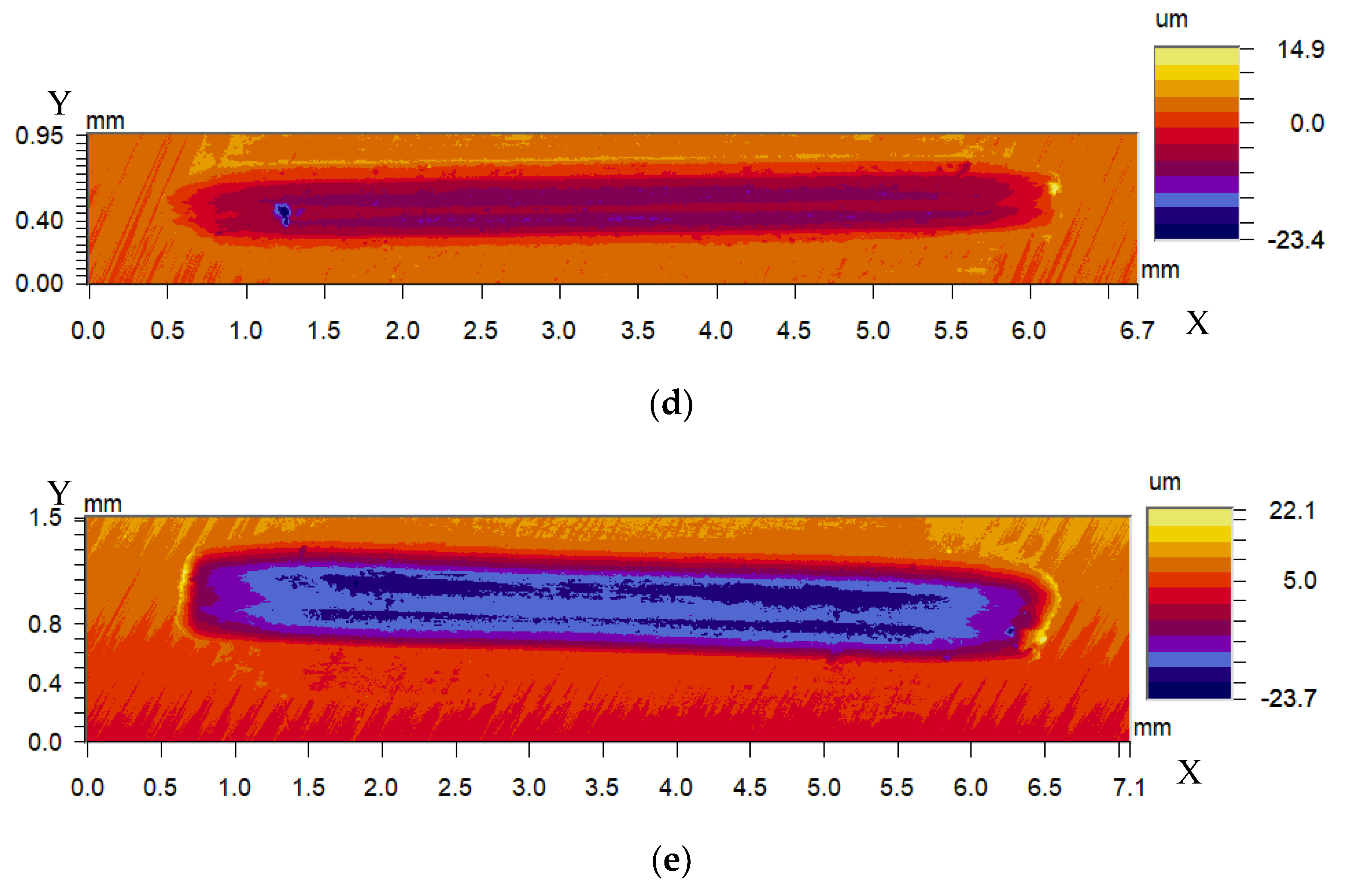
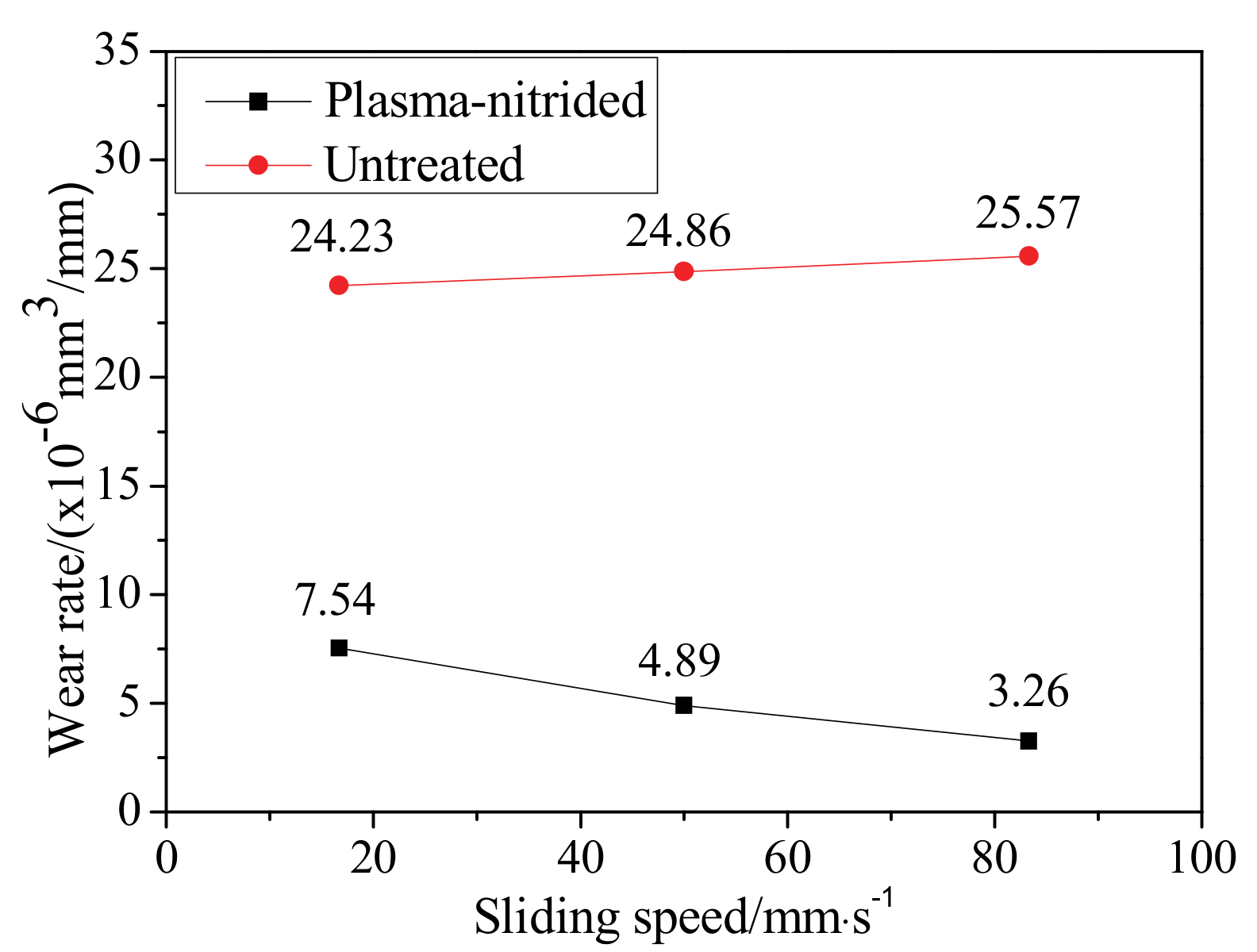
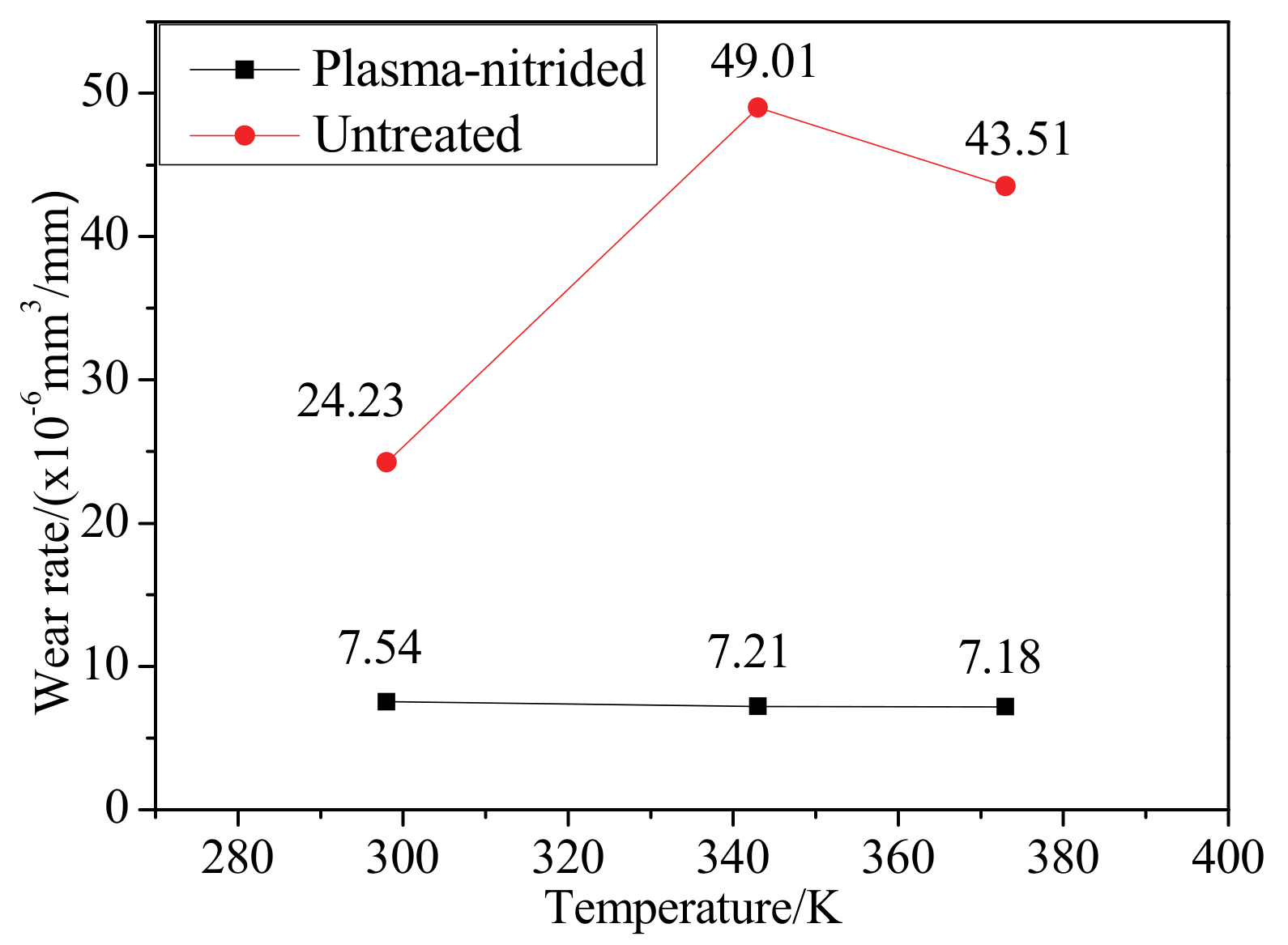
4.3. Wear Rate
5. Conclusions
- A large number of granular nitrides are generated on the surface of the plasma-nitrided specimens. The diameter of the granular nitrides ranges from 0.1 to 1 μm. A portion of the granular nitrides is agglomerated to coralloid granular nitrides.
- The thickness of the diffusion layer increases with the increase of the nitriding temperature. More specifically, the thicknesses of the diffusion layer are 144, 187 and 244 μm when the plasma nitriding temperatures are 753, 783 and 813 K, respectively.
- The phase composition of plasma-nitrided specimens mainly consists of γ/-Fe4N, ε-Fe2-3N and CrN. The relative content of ε-Fe2–3N reduces with the increase of nitriding temperature. However, the relatively content of γ/-Fe4N rises with the increase of nitriding temperature.
- The surface hardness of the plasma-nitrided specimen is almost twice as high as that of untreated specimen. The surface hardness of the specimen first increases and then reduces with the increase of nitriding temperature. In addition, the microhardness of the specimen material at 0.1 mm depth is higher than 1000 HV0.2 when the nitriding temperature is 783 K.
- The fluctuations of the friction coefficients of plasma-nitrided specimens are all lower than those of untreated specimens. The coefficient of friction reduces with the increase of load as well as with the increase of the speed.
- The plasma nitriding method can significantly reduce the wear rate of AISI H11 steel. The wear rate of the plasma-nitrided specimen was only 12.7%~31.11% of the untreated specimen.
- The wear rates of plasma-nitrided specimens rise with the increase of load, while, the wear rates of plasma-nitrided specimens reduce with the increase of sliding speed and friction temperature.
- Through comparison of the literature results regarding traditional plasma nitriding with our results, the proposed auxiliary heating plasma nitriding can acquire thicker nitrided layers and better wear resistance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russell, A.M.; Cook, B. Wear-resistant boride nanocomposite coating exhibits low friction. MRS Bull. 2009, 34, 792. [Google Scholar]
- Podgrajsek, M.; Glodez, S.; Ren, Z. Failure analysis of forging die insert protected with diffusion layer and PVD coating. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2015, 276, 521–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podgornik, B.; Majdic, F.; Leskovsek, V.; Vizintin, J. Improving tribological properties of tool steels through combination of deep-cryogenic treatment and plasma nitriding. Wear 2012, 288, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghajani, H.; Torshizi, M.; Soltanieh, M. A new model for growth mechanism of nitride layers in plasma nitriding of AISI H11 hot work tool steel. Vacuum 2017, 141, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, M.; Belzunce, F.J. A comparative study of salt-bath nitrocarburizing and gas nitriding followed by post-oxidation used as surface treatments of H13 hot forging dies. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 305, 146–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; He, Y.; Xiu, J.J.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.J.; Hu, B.G. Wear and corrosion properties of AISI 420 martensitic stainless steel treated by active screen plasma nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 329, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathallah, B.B.; Dakhli, C.E.; Terres, M.A. The effect of grinding parameters and gas nitriding depth on the grindability and surface integrity of AISI D2 tool steel. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2019, 104, 1449–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.Z.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.N.; Dargusch, M. Development in plasma surface diffusion techniques of Ti-6Al-4V alloy: A review. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 92, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawryluk, M.; Gronostajski, Z.; Kaszuba, M.; Polak, S.; Widomski, P.; Ziemba, J.; Smolik, J. Application of selected surface engineering methods to improve the durability of tools used in precision forging. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2017, 93, 2183–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, H.F.; Amadeh, A.; Moradi, H. Wear assessment of plasma nitrided AISI H11 steel. Mater. Des. 2011, 32, 2635–2643. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.R.; Yan, H.Z.; Li, S.; Tian, H.; Qin, J. Effect of ion nitriding process parameters on surface properties of 4Cr5MoSiV steel. Surf. Technol. 2019, 48, 199–205. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto, J.; Abraha, P. The effect of plasma nitriding treatment time on the tribological properties of the AISI H13 tool steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 375, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Joseph, A.; Ghosh, M.; Mukherjee, S. Microstructure and wear behaviour of pulsed plasma nitrided AISI H13 tool steel. Can. Metall. Q. 2016, 55, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zlatanovic, M.; Popovic, N.; Mitric, M. Plasma processing in carbon containing atmosphere for possible treatment of wind turbine components. Thin Solid Film 2007, 516, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobsen, S.D.; Hinrichs, R.; Aguzzoli, C.; Figueroa, C.A.; Baumvol, I.J.R.; Vasconcellos, M.A.Z. Influence of current density on phase formation and tribological behavior of plasma nitrided AISI H13 steel. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 286, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamis, M.B.; Gercekcioglu, E. Wear behaviour of plasma nitrided steels at ambient and elevated temperatures. Wear 2000, 243, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, M.R.; Staia, M.H. Ion nitrided AlSl H-13 tool steel—Part 2—High temperature performance under sliding wear conditions. Surf. Eng. 2007, 23, 223–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhu, S.X.; Wang, S.Q. Effect of sliding speed and hardness on wear behavior and mechanism of AISI H13 steel. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part J J. Eng. Tribol. 2019, 0, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, M.V.; Figueroa, C.A.; Gallo, S.C.; Rovani, A.C.; Basso, R.L.O.; Mei, P.R.; Baumvol, I.J.R.; Sinatora, A. Wear mechanisms and microstructure of pulsed plasma nitrided AISI H13 tool steel. Wear 2010, 269, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karamis, M.B.; Yildizli, K.; Aydin, G.C. Sliding/rolling wear performance of plasma nitrided H11 hot working steel. Tribol. Int. 2012, 51, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshy, S.; Jayadevan, K.R.; Ramesh, A.; Mahipal, D. Influence of loading conditions on wear behaviour of H11 tool steel. World J. Eng. 2019, 16, 614–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.M.; Wang, L.; Wang, S.Q.; Wei, M.X. Oxidative wear behavior of H13 steel. Tribology 2011, 31, 317–322. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Kaur, M.; Singh, S.; Josep, A.; Jhala, G.; Bhandari, S. High-temperature tribological studies of plasma-nitrided tool steels. Surf. Eng. 2018, 34, 620–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, R.H.; Tian, L.H.; Bao, M.D.; Yong, M.; Bin, T. Wear properties of plasma nitrided H13 steel at room and elevated temperature. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2012, 41, 203–206. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.W.; Zuo, P.P.; He, X.J.; Sheng, Z.D.; Wu, X.C. Influence of Al on mechanical properties and carbides of quenched and tempered H11 steel. Chin. J. Eng. 2018, 40, 208–216. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H. Periodic responses of a pulley−belt system with one-way clutch under inertia excitation. J. Sound Vib. 2015, 353, 308–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.Z.; Ye, H.; Chen, X.Y.; Wang, Y.W.; Zhao, P. Analysis of friction and wear characteristics of overrunning spring clutch. Mech. Sci. Technol. 2016, 35, 630–635. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Du, S. Development of ion nitriding technology and equipment modification. Met. Process. Hot Work. 2018, 6, 16–23. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Szala, M.; Winiarski, G.; Wójcik, Ł.; Bulzak, T. Effect of annealing time and temperature parameters on the microstructure, hardness, and strain-hardening coefficients of 42CrMo4 steel. Materials 2020, 13, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadzadeh, R.; Akbari, A.; Drouet, M. Microstructure and wear properties of AISI M2 tool steel on RF plasma nitriding at different N2–H2 gas compositions. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 258, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Nitta, S.; Nagamatsu, K.; Fujimoto, N.; Kushimoto, M.; Deki, M.; Tanaka, A.; Honda, Y.; Pristovsek, M.; Amano, H. Ammonia decomposition and reaction by high-resolution mass spectrometry for group III—Nitride epitaxial growth. J. Cryst. Growth 2019, 516, 63–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conci, M.D.; Bozzi, A.C.; Franco, A.R. Effect of plasma nitriding potential on tribological behaviour of AISI D2 cold-worked tool steel. Wear 2014, 317, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, F.A.P.; Heck, S.C.; Picone, C.A.; Casteletti, L.C. On the wear and corrosion of plasma nitrided AISI H13. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2020, 381, 125216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordonez, M.F.C.; Amorim, C.L.G.; Krindges, I.; Aguzzoli, C.; Baumvol, I.J.; Figueroa, C.A.; Sinatora, A.; Souza, R.M.; Farias, M.C.M. Microstructure and micro-abrasive wear of sintered yttria-containing 316L stainless steel treated by plasma nitriding. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2019, 374, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suh, N.P. An overview of the delamination theroy of wear. Wear 1977, 44, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanafi-Benghalem, N.; Felder, E.; Loucif, K.; Montmitonnet, P. Plastic deformation of 25CrMo4 steel during wear: Effect of the temperature, the normal force, the sliding velocity and the structural state. Wear 2010, 268, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Element | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Mo | V | P | S | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (wt %) | 0.4 | 0.85 | 0.42 | 4.96 | 1.18 | 0.45 | 0.002 | 0.014 | Balance |
| Factor | Specimens | Load (N) | Temperature (K) | Sliding Speed (mm·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal load | Untreated/Nitrided | 50/100/150 | 298 | 83.3 |
| Sliding speed | Untreated/ Nitrided | 100 | 298 | 16.7/50/83.3 |
| Temperature | Untreated/ Nitrided | 100 | 298/343/373 | 16.7 |
| Element | Weight % | Atomic % |
|---|---|---|
| O | 13.45 | 33.47 |
| Si | 0.81 | 1.14 |
| V | 0.69 | 0.53 |
| Cr | 4.61 | 3.53 |
| Fe | 79.16 | 56.40 |
| Mo | 1.28 | 0.53 |
| Totals | 100 | - |
| Element | Weight % | Atomic % |
|---|---|---|
| O | 4.74 | 14.93 |
| N | 4.76 | 13.02 |
| Si | 1.12 | 1.76 |
| V | 0.88 | 0.76 |
| Cr | 4.72 | 3.99 |
| Fe | 82.73 | 65.07 |
| Mo | 1.04 | 0.48 |
| Totals | 100 | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, H.; Zhao, L.; Chen, Z.; Hu, X.; Yan, Z. Investigation of the Surface Properties and Wear Properties of AISI H11 Steel Treated by Auxiliary Heating Plasma Nitriding. Coatings 2020, 10, 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10060528
Yan H, Zhao L, Chen Z, Hu X, Yan Z. Investigation of the Surface Properties and Wear Properties of AISI H11 Steel Treated by Auxiliary Heating Plasma Nitriding. Coatings. 2020; 10(6):528. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10060528
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Hongzhi, Linhe Zhao, Zhi Chen, Xuan Hu, and Zhaojun Yan. 2020. "Investigation of the Surface Properties and Wear Properties of AISI H11 Steel Treated by Auxiliary Heating Plasma Nitriding" Coatings 10, no. 6: 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10060528
APA StyleYan, H., Zhao, L., Chen, Z., Hu, X., & Yan, Z. (2020). Investigation of the Surface Properties and Wear Properties of AISI H11 Steel Treated by Auxiliary Heating Plasma Nitriding. Coatings, 10(6), 528. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10060528