SiO2/Ladder-Like Polysilsesquioxanes Nanocomposite Coatings: Playing with the Hybrid Interface for Tuning Thermal Properties and Wettability
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Materials
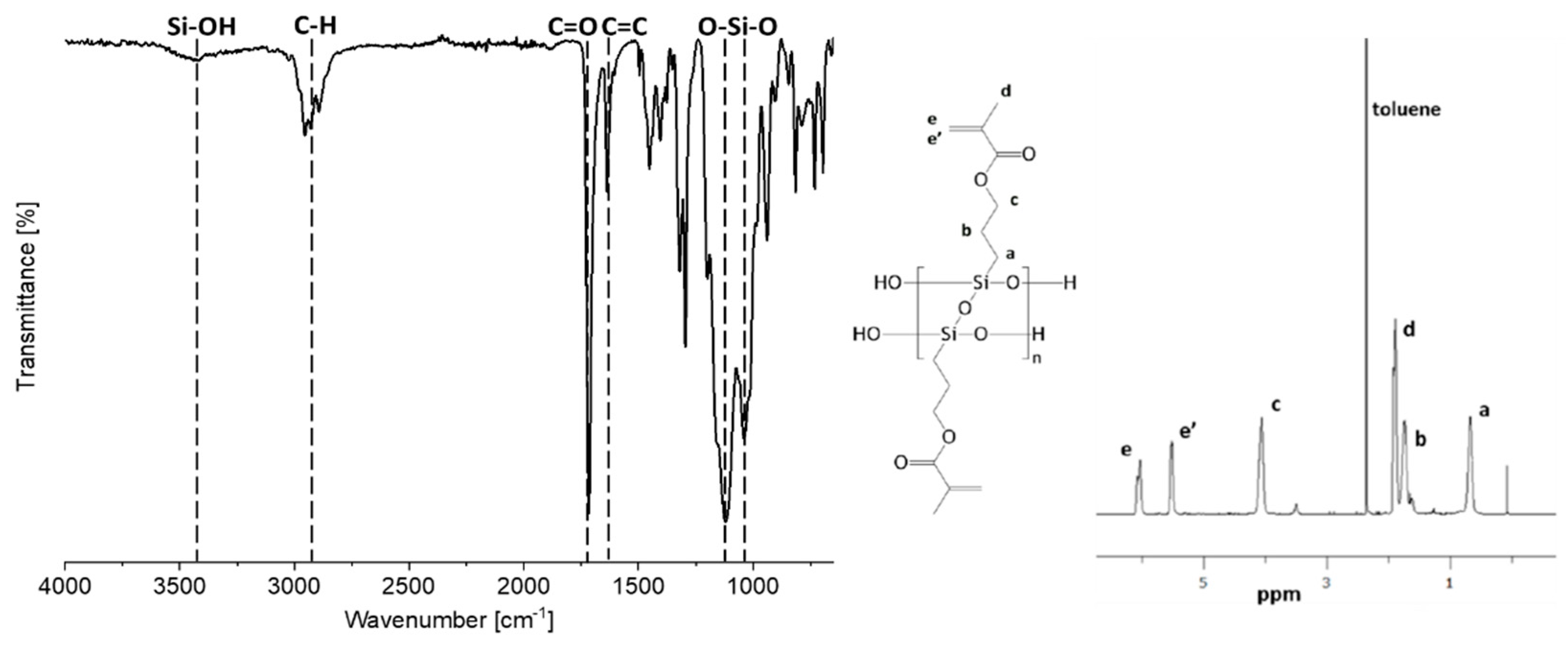
2.2. Synthesis of LPMASQ
2.3. Synthesis of Naked Silica NPs
2.4. Synthesis of TMMS Functionalized Silica NPs
2.5. Preparation of LPMASQ Nanocomposites
2.6. Characterizations
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of Pristine LPMASQ
3.2. Pristine SiO2 and SiO2@TMMS NPs Characterization
3.3. Characterization of LPMASQ Nanocomposites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Available online: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20190419005029/en/ (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Kalyani, T.N.; Dhoble, S.J. Novel materials for fabrication and encapsulation of OLEDs. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 319–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannouli, M.; Drakonakis, V.M.; Savva, A.; Eleftheriou, P.; Florides, G.; Choulis, S.A. Methods for improving the lifetime performance of organic photovoltaics with low-costing encapsulation. ChemPhysChem 2015, 16, 1134–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrows, P.E.; Bulovic, V.; Forrest, S.R.; Sapochak, L.S.; Mccarty, D.M.; Thompson, M.E. Reliability and degradation of organic light emitting devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1994, 65, 2922–2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yüce, M.Y.; Demirel, A.L.; Menzel, F. Tuning the surface hydrophobicity of polymer/nanoparticle composite films in the wenzel regime by composition. Langmuir 2005, 21, 5073–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessler, D.; Theato, P. Reactive surface coatings based on polysilsesquioxanes: Defined adjustment of surface wettability. Langmuir 2009, 25, 14200–14206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saber, I.; Maha, S. Superhydrophobic coating polymer/silica nanocomposites: Part I synthesis and characterization as eco-friendly coating. Silicon 2020, 12, 805–811. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed, N.; Fan, H.; Dubois, P.; Zhang, X.; Fahad, S.; Aziz, T.; Wan, J.J. Nano-engineering and micromolecular science of polysilsesquioxane materials and their emerging applications. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 21577–21604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahlteich, J.; Fahland, M.; Schönberger, W.; Schiller, N. Permeation barrier properties of thin oxide films on flexible polymer substrates. Thin Solid Films 2009, 517, 3075–3080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charton, C.; Schiller, N.; Fahland, M.; Holla, A. Development of high barrier films on flexible polymer substrates. Thin Solid Films 2006, 502, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shi, F.; Niu, J.; Jiang, Y.G.; Wang, Z.Q. Superhydrophobic surfaces: From structural control to functional application. J. Mater. Chem. 2008, 18, 621–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.L.; Feng, L.; Gao, X.F.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired Surfaces with Special wettability. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Callies, M.; Quere, D. On water repellency. Soft Matter 2005, 1, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirtcliffe, N.J.; McHale, G.; Newton, M.I. The superhydrophobicity of polymer surfaces: Recent developments. J. Polym. Sci. Part. B Polym. Phys. 2011, 49, 1203–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arkles, B.; Pan, Y.; Kim, Y.M. The Role of Polarity in the Structure of Silanes Employed in Surface Modification. In Silanes and Other Coupling Agents; Mittal, K.I., Ed.; VSP: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 51–65. [Google Scholar]
- Parale, V.G.; Mahadik, D.B.; Mahadik, S.A. OTES modified transparent dip coated silica coatings. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 835–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouvet-Marchand, A.; Graillot, A.; Abel, M.; Koudia, M.; Boutevin, G.; Loubat, C.; Grosso, D. Distribution of fluoroalkylsilanes in hydrophobic hybrid sol–gel coatings obtained by co-condensation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 24899–24910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, K.S.; Dhinojwala, A. Molecular Structure of Hydrophobic Al kyl Side Chains at Comb Polymer-Air Interface. Macromolecules 2001, 34, 1137–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagliaro, M.; Ciriminna, R.J. New fluorinated functional materials. Mater. Chem. 2005, 15, 4981–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brendel, S.; Fetter, E.; Staude, C.; Vierke, L.; Biegel-Engler, A. Short-chain perfluoroalkyl acids: Environmental concerns and a regulatory strategy under REACH. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2018, 30, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://echa.europa.eu/de/-/five-european-states-call-for-evidence-on-broad-pfas-restriction (accessed on 20 May 2020).
- Nguyen-Tri, P.; Tran, H.N.; Plamondon, C.O.; Tuduri, L.; Vo, D.-V.N.; Nanda, S.; Mishra, A.; Chao, H.-P.; Bajpai, A.K. Recent progress in the preparation, properties and applications of superhydrophobic nano-based coatings and surfaces: A review. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 132, 235–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Tri, P.; Nguyen, T.A.; Carriere, P.; Ngo Xuan, C. Nanocomposite coatings: Preparation, characterization, properties, and applications. Int. J. Corros. 2018, 2018, 4749501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brink, G.H.; Foley, N.; Zwaan, D.; Kooi, B.J.; Palasantzas, G. Roughness controlled superhydrophobicity on single nanometer length scale with metal nanoparticles. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 28696–28702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Milionis, A.; Martiradonna, L.; Anyfantis, G.C.; Cozzoli, P.D.; Bayer, I.S.; Fragouli, D.; Athanassiou, A. Control of the water adhesion on hydrophobic micropillars by spray coating technique. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, N.; Yan, Y. Characterisation of surface wettability based on nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 2202–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, X.; Mi, C.; Zong, L.; Wang, X. Preparation and characterization of perfluorine-SiO2 nanoparticles and superhydrophobic fluorosilicone/silica hybrid composite coating. Appl. Phys. A 2019, 125, 250–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Yea, Q.; Xu, J. Polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane-based hybrid materials and their applications. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 212–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayandele, E.; Sarkar, B.; Alexandridis, P. Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane (POSS)-Containing Polymer Nanocomposites. Nanomaterial 2012, 2, 445–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raftopoulos, K.N.; Pielichowski, K. Segmental dynamics in hybrid polymer/POSS nanomaterials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 52, 136–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W. Building Blocks Precisely from Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Nanoparticles. ACS Cent. Sci. 2016, 2, 62–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- D’Arienzo, M.; Diré, S.; Redaelli, M.; Borovin, E.; Callone, E.; Di Credico, B.; Morazzoni, F.; Pegoretti, A.; Scotti, R.J. Unveiling the hybrid interface in polymer nanocomposites enclosing silsesquioxanes with tunable molecular structure: Spectroscopic, thermal and mechanical properties. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 512, 609–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.W.; Chang, F.C. POSS related polymer nanocomposites. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2011, 36, 1649–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fina, A.; Monticelli, O.; Camino, G.J. POSS-based hybrids by melt/reactive blending. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 9297–9305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Chujo, Y.J. Advanced functional materials based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS). Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 1733–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arienzo, M.; Redaelli, M.; Callone, E.; Conzatti, L.; Di Credico, B.; Dirè, S.; Giannini, L.; Polizzi, S.; Schizzi, I.; Scotti, R.; et al. Hybrid SiO2@POSS nanofiller: A promising reinforcing system for rubber nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Front. 2017, 1, 212–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Redaelli, M.; D’Arienzo, M.; Brus, J.; Di Credico, B.; Geppi, M.; Giannini, L.; Matejka, L.; Martini, F.; Panattoni, F.; Spirkova, M.; et al. On the key role of SiO2@POSS hybrid filler in tailoring networking and interfaces in rubber nanocomposites. Polym. Test. 2018, 65, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cordes, D.B.; Lickiss, P.D.; Rataboul, F. Recent Developments in the Chemistry of Cubic Polyhedral Oligosilsesquioxanes. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 2081–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirè, S.; Borovin, E.; Ribot, F. Architecture of Silsesquioxanes. In Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology; Klein, L., Aparicio, M., Jitianu, A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Lee, A.S.; Hwang, S.S.; Baek, K. Structural Control of Fully Condensed Polysilsesquioxanes: Ladderlike vs Cage Structured Polyphenylsilsesquioxanes. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 6063–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huoa, L.; Dub, P.; Zhoua, H.; Zhanga, K.; Liu, P. Fabrication and tribological properties of self-assembled monolayer of n-alkyltrimethoxysilane on silicon: Effect of SAM alkyl chain length. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 396, 865–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabry, J.M.; Vij, A.; Iacono, S.T. Fluorinated Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxanes (F-POSS). Angew. Chem. 2008, 120, 4205–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Zhang, X.; Wang, D.; Cheng, J.; Pang, X.; Qu, W.; Li, C.; Li, S. Facile Fabrication of Superhydrophobic Surface from Fluorinated POSS Acrylate Copolymer via One-Step Breath Figure Method and Its Anti-Corrosion Property. Polymers 2019, 11, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Lichtenhan, J.D.; Otaigbe, J.U. Facile route to nature inspired hydrophobic surface modification of phosphate glass using polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane with improved properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 470, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcinkowska, A.; Przadka, D.; Andrzejewska, E.J. POSS functionalized with mixed fluoroalkyl and methacryloxy substituents as modifiers for UV-curable coatings. Coat. Technol. Res. 2019, 16, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Meuler, A.J.; Chhatre, S.S.; Nieves, A.R.; Mabry, J.M.; Cohen, R.E.; McKinley, G.H. Examination of wettability and surface energy in fluorodecyl POSS/polymer blends. Soft Matter 2011, 7, 10122–10134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dodiuk, H.; Rios, P.F.; Dotan, A.; Kenig, S. Hydrophobic and self-cleaning coatings. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2007, 18, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foorginezhad, S.; Zerafat, M.M. Fabrication of superhydrophobic coatings with self-cleaning properties on cotton fabric based on Octa vinyl polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane/polydimethylsiloxane (OV-POSS/PDMS) nanocomposite. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 540, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, K.; Kawaguchi, D.; Abe, T.; Komino, T.; Mamada, M.; Kabe, T.; Adachi, C.; Naka, K.; Tanaka, K. Surface Segregation of a Star-Shaped Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane in a Polymer Matrix. Langmuir 2020, 36, 9960–9966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.S.; Lee, A.S.; Lee, H.S.; Jeon, H.Y.; Baek, K.Y.; Choi, D.H.; Hwang, S.S. Synthesis and characterization of UV-curable ladder-like polysilsesquioxane. J. Polym. Sci. Part. A Polym. Chem. 2011, 49, 5012–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.S.; Choi, S.S.; Lee, H.S.; Jeon, H.Y.; Baek, K.Y.; Hwang, S.S. Synthesis and characterization of organic–inorganic hybrid block copolymers containing a fully condensed ladder-like polyphenylsilsesquioxane. J. Polym. Sci. Part A Polym. Chem. 2012, 50, 4563–4570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, A.S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.; Hong, S.M.; Hwang, S.M.; Min Koo, C.J. Novel polysilsesquioxane hybrid polymer electrolytes for lithium ion batteries. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 1277–1283. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.X.; Hao, J.; Xie, P.; Zhang, X.; Han, C.C.; Zhang, R. A Well-Defined Ladder Polyphenylsilsesquioxane (Ph-LPSQ) Synthesized via a New Three-Step Approach: Monomer Self-Organization−Lyophilization—Surface-Confined Polycondensation. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 1322–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prado, L.A.S.D.A.; Radovanovic, E.; Pastore, H.O.; Yoshida, I.V.P.; Torriani, I.L. Poly(phenylsilsesquioxane)s: Structural and morphological characterization. J. Polym. Sci. Part. A Polym. Chem. 2000, 38, 1580–1589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.H.; Choi, G.M.; Bae, J.G.; Kim, Y.H. High-Performance and Simply-Synthesized Ladder-Like Structured Methacrylate Siloxane Hybrid Material for Flexible Hard Coating. Polymers 2018, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.S.; Jo, Y.Y.; Jeon, H.; Choi, S.-S.; Baek, K.-Y.; Hwang, S.S. Mechanical properties of thiol-ene UV-curable thermoplastic polysilsesquioxanes. Polymer 2015, 68, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, A.S.; Do, Y.S.; Kim, J.F.; Hwang, S.S.; Lee, Y.M.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.S. Side-chain engineering of ladder-structured polysilsesquioxane membranes for gas separations. J. Membr. Sci. 2016, 516, 202–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhang, C.; Ding, R.; Cui, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, Y. New Water Vapor Barrier Film Based on Lamellar Aliphatic-Monoamine-Bridged Polysilsesquioxane. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 14766–14775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, C.I.; Ko, J.U.; Yin, Z.X.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S. Solvent-Free and Highly Transparent SiO2 Nanoparticle–Polymer Composite with an Enhanced Moisture Barrier Property. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 9433–9439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopanati, G.N.; Seethamraju, S.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Madras, G. A Surlyn/magnesium oxide nanocomposite as an effective water vapor barrier for organic device encapsulation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 32580–32587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saravanan, S.; Gupta, S.; Ramamurthy, P.C.; Madras, G. Effect of silane functionalized alumina on poly(vinyl butyral) nanocomposite films: Thermal, mechanical, and moisture barrier studies. Polym. Compos. 2014, 35, 1426–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scotti, R.; Conzatti, L.; D’Arienzo, M.; Di Credico, B.; Giannini, L.; Hanel, T.; Stagnaro, P.; Susanna, A.; Tadiello, L.; Morazzoni, F. Shape controlled spherical (0D) and rod-like (1D) silica nanoparticles in silica/styrene butadiene rubber nanocomposites: Role of the particle morphology on the filler reinforcing effect. Polymer 2014, 55, 1497–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; McCarthy, T.J. Teflon is Hydrophilic. Comments on Definitions of Hydrophobic, Shear versus Tensile Hydrophobicity, and Wettability Characterization. Langmuir 2008, 24, 9183–9188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McHale, G. All Solids, Including Teflon, Are Hydrophilic (To Some Extent), But Some Have Roughness Induced Hydrophobic Tendencies. Langmuir 2009, 25, 7185–7187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.B.; Dos Santos, S.; Antonini, C. Water Touch-and-Bounce from a Soft Viscoelastic Substrate: Wetting, Dewetting, and Rebound on Bitumen. Langmuir 2016, 32, 8245–8254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borovin, E.; Callone, E.; Ceccato, R.; Quaranta, A.; Dirè, S. Adsorptive properties of sol–gel derived hybrid organic/inorganic coatings. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 147, 954–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arienzo, M.; Diré, S.; Masneri, V.; Rovera, D.; Di Credico, B.; Callone, E.; Mascotto, S.; Pegoretti, A.; Ziarelli, F.; Scotti, R. Tailoring the Dielectric and Mechanical Properties of Polybutadiene Nanocomposites by Using Designed Ladder-like Polysilsesquioxanes. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 3817–3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Maggio, R.; Callone, E.; Girardi, F.; Diré, S.J. Structure-related behavior of hybrid organic–inorganic materials prepared in different synthesis conditions from Zr-based NBBs and 3-methacryloxypropyl trimethoxysilane. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2012, 125, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, H.; Kajiwara, T.; Abe, Y.; Gunji, T.J. Synthesis and structure of ladder polymethylsilsesquioxanes from sila-functionalized cyclotetrasiloxanes. Organomet. Chem. 2010, 695, 1363–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmo, J.P.; Kroll, P.J. First-Principles Calculations and Analysis of 29Si Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Chemical Shifts in Silicon Oxycarbide Ceramics. Phys. Chem. C 2014, 118, 29952–29961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, W.; An, G.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, D.Y.; Kim, H.; Cho, J.H. Ladder-Type Silsesquioxane Copolymer Gate Dielectrics for High-Performance Organic Transistors and Inverters. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 3501–3508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.J.; Heo, Y.M.; Cho, J.H. Ladder-type silsesquioxane copolymer gate dielectrics for gating solution-processed IGZO field-effect transistors. Org. Electron. 2017, 43, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turri, S.; Levi, M. Wettability of Polyhedral Oligomeric Silsesquioxane Nanostructured Polymer Surfaces. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2005, 26, 1233–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, A.W.; Good, R.J. Thermodynamics of contact angles. I. Heterogeneous solid surfaces. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1972, 38, 341–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, R.D.; Possart, W.; Kamusewitz, H.; Bischof, C.J. Young’s equilibrium contact angle on rough solid surfaces. Part I. An empirical determination. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 1989, 3, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Sample | Conversion η Air Side% | Conversion η Substrate Side% | Polymer/Unreacted Monomer(η/1 − η) |
|---|---|---|---|
| h-LPMASQ | 87 | 55 | 2.5 |
| SiO2/LPMASQ | 75 | 51 | 1.7 |
| SiO2@TMMS/LPMASQ | 68 | 63 | 1.9 |
| Sample | Diffraction Peak (2θ) | d-Spacing (Å) |
|---|---|---|
| h-LPMASQ | 5.94 | 14.9 |
| SiO2/LPMASQ | 5.94 | 14.9 |
| SiO2@TMMS/LPMASQ | 6.74 | 13.1 |
| all | 20.08 | 4.4 |
| Sample | d’/d |
|---|---|
| h-LPMASQ | 67.2/32.8 = 2.1 |
| SiO2/LPMASQ | 61.2/38.8 = 1.6 |
| SiO2@TMMS/LPMASQ | 61.3/38.7 = 1.6 |
| Sample | Signal at −64,0 ppm | Signal at −66,9 ppm | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % | LW/2* | % | LW/2* | |
| h-LPMASQ | 25.8 | 132.8 | 74.2 | 161.6 |
| SiO2/LPMASQ | 24.2 | 129.3 | 75.8 | 156.8 |
| SiO2@TMMS/LPMASQ | 22.3 | 127.8 | 77.7 | 150.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
D’Arienzo, M.; Dirè, S.; Cobani, E.; Orsini, S.; Di Credico, B.; Antonini, C.; Callone, E.; Parrino, F.; Dalle Vacche, S.; Trusiano, G.; et al. SiO2/Ladder-Like Polysilsesquioxanes Nanocomposite Coatings: Playing with the Hybrid Interface for Tuning Thermal Properties and Wettability. Coatings 2020, 10, 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10100913
D’Arienzo M, Dirè S, Cobani E, Orsini S, Di Credico B, Antonini C, Callone E, Parrino F, Dalle Vacche S, Trusiano G, et al. SiO2/Ladder-Like Polysilsesquioxanes Nanocomposite Coatings: Playing with the Hybrid Interface for Tuning Thermal Properties and Wettability. Coatings. 2020; 10(10):913. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10100913
Chicago/Turabian StyleD’Arienzo, Massimiliano, Sandra Dirè, Elkid Cobani, Sara Orsini, Barbara Di Credico, Carlo Antonini, Emanuela Callone, Francesco Parrino, Sara Dalle Vacche, Giuseppe Trusiano, and et al. 2020. "SiO2/Ladder-Like Polysilsesquioxanes Nanocomposite Coatings: Playing with the Hybrid Interface for Tuning Thermal Properties and Wettability" Coatings 10, no. 10: 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10100913
APA StyleD’Arienzo, M., Dirè, S., Cobani, E., Orsini, S., Di Credico, B., Antonini, C., Callone, E., Parrino, F., Dalle Vacche, S., Trusiano, G., Bongiovanni, R., & Scotti, R. (2020). SiO2/Ladder-Like Polysilsesquioxanes Nanocomposite Coatings: Playing with the Hybrid Interface for Tuning Thermal Properties and Wettability. Coatings, 10(10), 913. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings10100913











