Genomic Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to a New Hybrid aEPEC/ExPEC Pathotype O153:H10-A-ST10 eae-beta1 Occurred in Meat, Poultry, Wildlife and Human Diarrheagenic Samples
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Conventional Typing
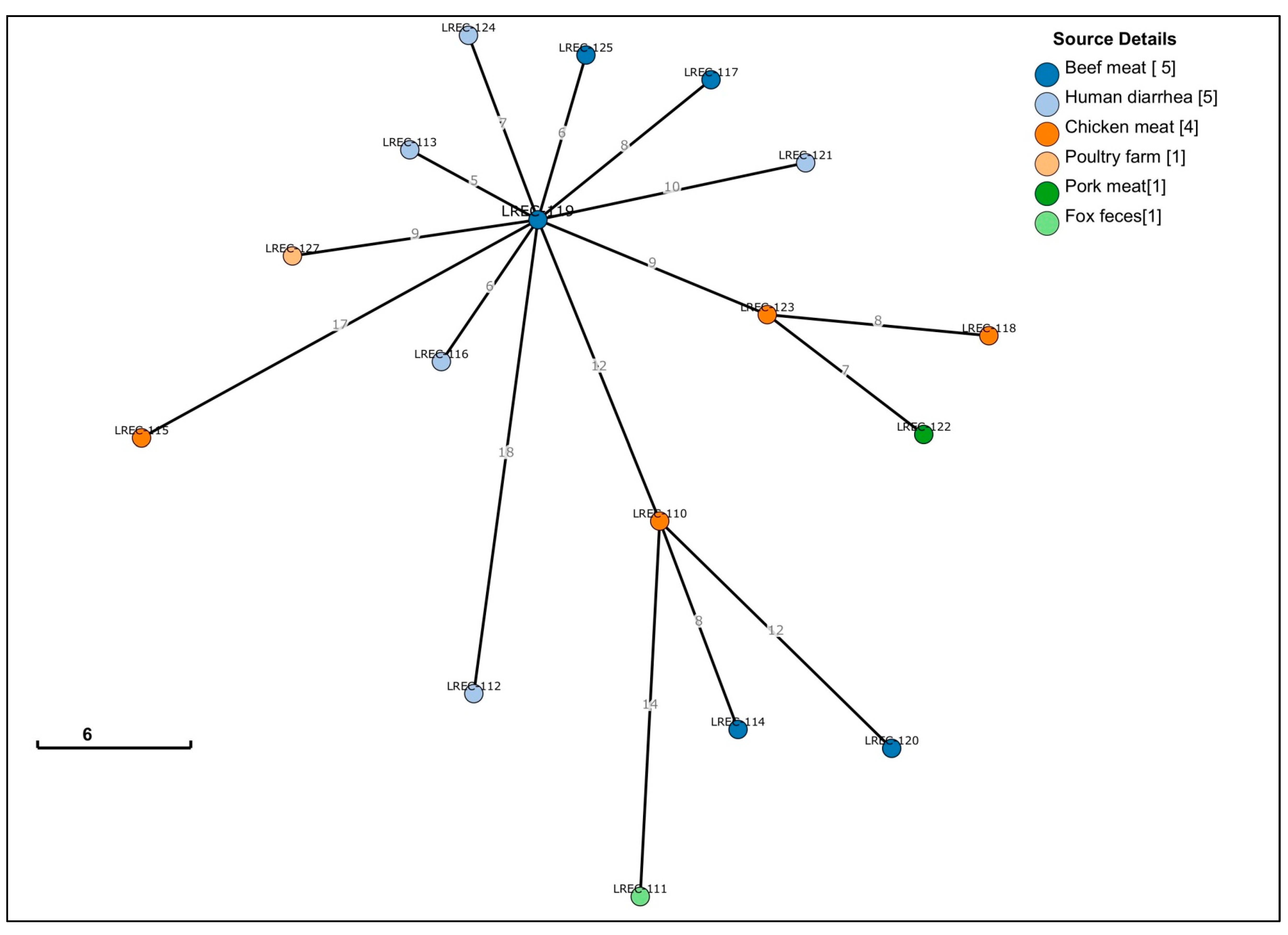
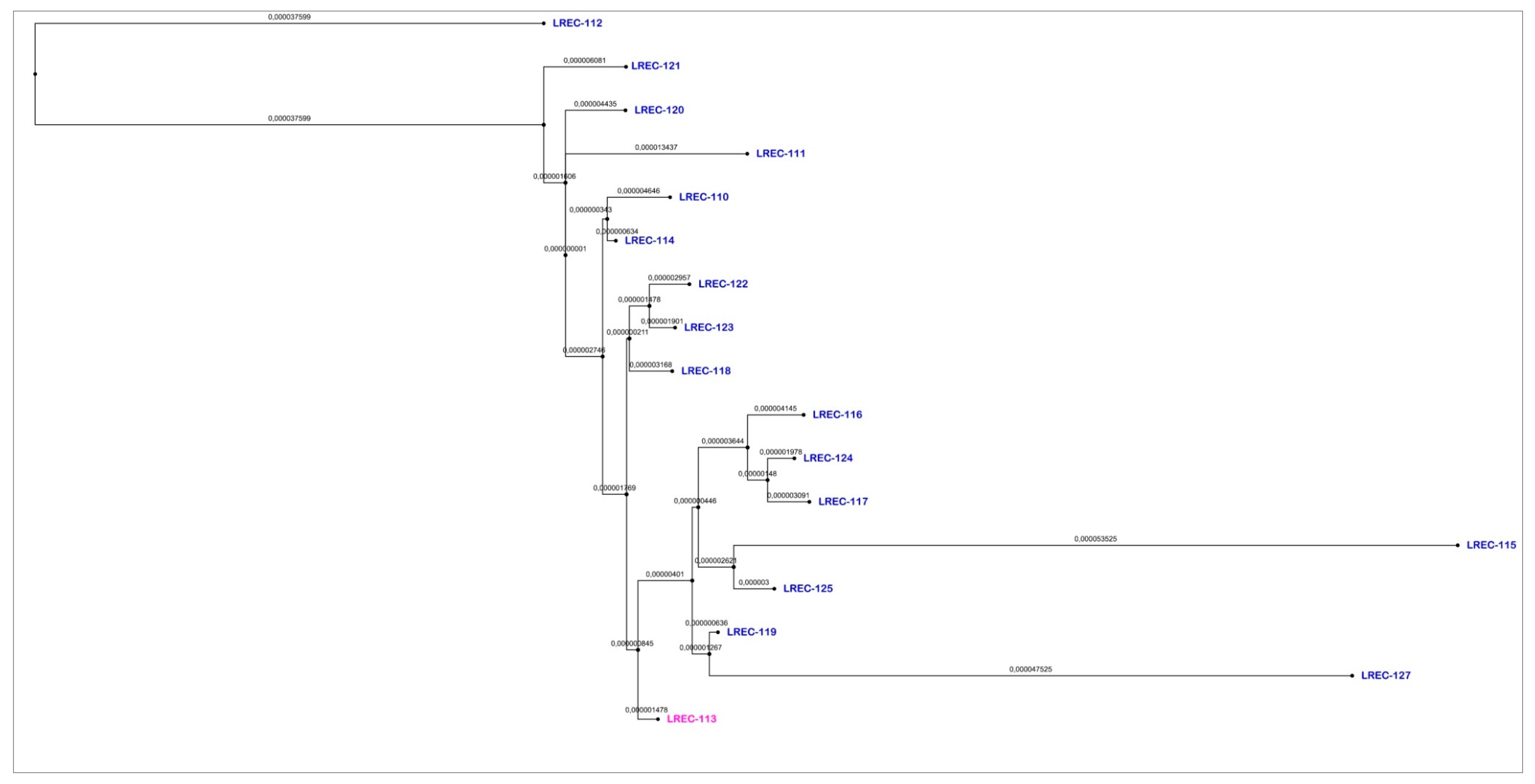
2.2. Whole Genome Sequencing (WGS)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. E. coli Collection
4.2. Antimicrobial Susceptibility and ESBL Typing
4.3. Phylogenetic Assignment and PFGE Comparison
4.4. Genome Sequencing, Assembly and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Data Availability
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaper, J.B.; Nataro, J.P.; Mobley, H.L. Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 123–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riley, L.W. Pandemic lineages of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 380–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caron, E.; Crepin, V.F.; Simpson, N.; Knutton, S.; Garmendia, J.; Frankel, G. Subversion of actin dynamics by EPEC and EHEC. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, A.; Blanco, M.; Yamamoto, D.; Dahbi, G.; Blanco, J.E.; Lopez, C.; Alonso, M.P.; Vieira, M.A.; Hernandes, R.T.; Abe, C.M.; et al. HeLa-cell adherence patterns and actin aggregation of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) and Shiga-toxin-producing E. coli (STEC) strains carrying different eae and tir alleles. Int. Microbiol. 2009, 12, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.E.; Mora, A.; Dahbi, G.; Alonso, M.P.; Gonzalez, E.A.; Bernardez, M.I.; Blanco, J. Serotypes, virulence genes, and intimin types of Shiga toxin (verotoxin)-producing Escherichia coli isolates from cattle in Spain and identification of a new intimin variant gene (eae-xi). J. Clin. Microbiol. 2004, 42, 645–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandes, R.T.; Elias, W.P.; Vieira, M.A.M.; Gomes, T.A.T. An overview of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2009, 297, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, V.; Rodríguez-Calleja, J.M.; Otero, A.; García-López, M.L.; Santos, J.A. Genetic characterization of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolates from ewes’ milk, sheep farm environments, and humans by multilocus sequence typing and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 79, 5864–5869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso, C.A.; Mora, A.; Diaz, D.; Blanco, M.; Gonzalez-Barrio, D.; Ruiz-Fons, F.; Simon, C.; Blanco, J.; Torres, C. Occurrence and characterization of stx and/or eae-positive Escherichia coli isolated from wildlife, including a typical EPEC strain from a wild boar. Vet. Microbiol. 2017, 207, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, J.R.; Murray, A.C.; Gajewski, A.; Sullivan, M.; Snippes, P.; Kuskowski, M.A.; Smith, K.E. Isolation and molecular characterization of nalidixic acid-resistant extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli from retail chicken products. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2003, 47, 2161–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurbeck, R.R.; Dinh, P.C., Jr.; Walk, S.T.; Stapleton, A.E.; Hooton, T.M.; Nolan, L.K.; Kim, K.S.; Johnson, J.R.; Mobley, H.L. Escherichia coli isolates that carry vat, fyuA, chuA, and yfcV efficiently colonize the urinary tract. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 4115–4122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, C.D.; Dobrindt, U. What defines extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli? Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2011, 301, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, A.; Stephan, R.; Nüesch-Inderbinen, M. Distribution of virulence factors in ESBL-producing Escherichia coli isolated from the environment, livestock, food and humans. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 667–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hindermann, D.; Gopinath, G.; Chase, H.; Negrete, F.; Althaus, D.; Zurfluh, K.; Tall, B.D.; Stephan, R.; Nuesch-Inderbinen, M. Salmonella enterica serovar Infantis from Food and Human Infections, Switzerland, 2010–2015: Poultry-Related Multidrug Resistant Clones and an Emerging ESBL Producing Clonal Lineage. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora, A.; Herrera, A.; Mamani, R.; Lopez, C.; Alonso, M.P.; Blanco, J.E.; Blanco, M.; Dahbi, G.; Garcia-Garrote, F.; Pita, J.M.; et al. Recent emergence of clonal group O25b:K1:H4-B2-ST131 ibeA strains among Escherichia coli poultry isolates, including CTX-M-9-producing strains, and comparison with clinical human isolates. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 6991–6997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokes, H.W.; Gillings, M.R. Gene flow, mobile genetic elements and the recruitment of antibiotic resistance genes into Gram-negative pathogens. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 790–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins-Browne, R.M.; Holt, K.E.; Ingle, D.J.; Hocking, D.M.; Yang, J.; Tauschek, M. Are Escherichia coli Pathotypes Still Relevant in the Era of Whole-Genome Sequencing? Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2016, 6, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Herrrera, A.; Lopez, C.; Dahbi, G.; Mamani, R.; Pita, J.M.; Alonso, M.P.; Llovo, J.; Bernardez, M.I.; Blanco, J.E.; et al. Characteristics of the Shiga-toxin-producing enteroaggregative Escherichia coli O104:H4 German outbreak strain and of STEC strains isolated in Spain. Int. Microbiol. 2011, 14, 121–141. [Google Scholar]
- Scheutz, F. Taxonomy Meets Public Health: The Case of Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Spectr. 2014, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marc, D.; Dho-Moulin, M. Analysis of the fim cluster of an avian O2 strain of Escherichia coli: Serogroup-specific sites within fimA and nucleotide sequence of fimI. J. Med. Microbiol. 1996, 44, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Johnson, J.R.; Stell, A.L. Extended virulence genotypes of Escherichia coli strains from patients with urosepsis in relation to phylogeny and host compromise. J. Infect. Dis. 2000, 181, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, T.J.; Wannemuehler, Y.M.; Nolan, L.K. Evolution of the iss gene in Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2360–2369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Jimenez, D.; Zhou, Z.; Herrera, A.; Viso, S.; Blanco, M.; Costoya, L.; Mora, A. Genomic evidence of the close relatedness of food, poultry, wildlife and human clincal isolates of ESBL-producing Escherichia coli O153:H10-A-ST10 eae-beta1. In Proceedings of the 7th Congress of European Microbiologists FEMS, Valencia, Spain, 9–13 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Torres, A.G. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: Foe or innocent bystander? Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 729–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco, M.; Blanco, J.E.; Dahbi, G.; Alonso, M.P.; Mora, A.; Coira, M.A.; Madrid, C.; Juarez, A.; Bernardez, M.I.; Gonzalez, E.A.; et al. Identification of two new intimin types in atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Int. Microbiol. 2006, 9, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mora, A.; Garcia-Pena, F.J.; Alonso, M.P.; Pedraza-Diaz, S.; Ortega-Mora, L.M.; Garcia-Parraga, D.; Lopez, C.; Viso, S.; Dahbi, G.; Marzoa, J.; et al. Impact of human-associated Escherichia coli clonal groups in Antarctic pinnipeds: Presence of ST73, ST95, ST141 and ST131. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Bai, X.; Jin, Y.; Hu, B.; Wang, H.; Sun, H.; Fan, R.; Fu, S.; Xiong, Y. High prevalence of virulence genes in specific genotypes of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robins-Browne, R.M.; Bordun, A.M.; Tauschek, M.; Bennett-Wood, V.R.; Russell, J.; Oppedisano, F.; Lister, N.A.; Bettelheim, K.A.; Fairley, C.K.; Sinclair, M.I.; et al. Atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli: A leading cause of community-acquired gastroenteritis, Melbourne, Australia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2004, 10, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abe, C.M.; Trabulsi, L.R.; Blanco, J.; Blanco, M.; Dahbi, G.; Blanco, J.E.; Mora, A.; Franzolin, M.R.; Taddei, C.R.; Martinez, M.B.; et al. Virulence features of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli identified by the eae(+) EAF-negative stx(-) genetic profile. Diagn. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2009, 64, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, M.A.; Dos Santos, L.F.; Dias, R.C.B.; Camargo, C.H.; Pinheiro, S.R.S.; Gomes, T.A.T.; Hernandes, R.T. Atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli as aetiologic agents of sporadic and outbreakassociated diarrhoea in Brazil. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 998–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contreras, C.A.; Ochoa, T.J.; Lacher, D.W.; DebRoy, C.; Navarro, A.; Talledo, M.; Donnenberg, M.S.; Ecker, L.; Gil, A.I.; Lanata, C.F.; et al. Allelic variability of critical virulence genes (eae, bfpA and perA) in typical and atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in Peruvian children. J. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 59, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Bai, X.; Zhao, A.; Zhang, W.; Ba, P.; Liu, K.; Jin, Y.; Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; Sun, H.; et al. Genetic diversity of intimin gene of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from human, animals and raw meats in China. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Yang, G.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cui, L.; Wu, Q. Prevalence and characterization of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from retail foods in China. J. Food Prot. 2018, 81, 1761–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balière, C.; Rincé, A.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Gourmelon, M. Molecular profiling of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and enteropathogenic E. coli strains isolated from French coastal environments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 3913–3927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciesielczuk, H.; Doumith, M.; Hope, R.; Woodford, N.; Wareham, D.W. Characterization of the extra-intestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli ST131 clone among isolates recovered from urinary and bloodstream infections in the United Kingdom. J. Med. Microbiol. 2015, 64, 1496–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Kennedy, C.A.; Walsh, C.; Karczmarczyk, M.; O’Brien, S.; Akasheh, N.; Quirke, M.; Farrell-Ward, S.; Buckley, T.; Fogherty, U.; Kavanagh, K.; et al. Multi-drug resistant Escherichia coli in diarrhoeagenic foals: Pulsotyping, phylotyping, serotyping, antibiotic resistance and virulence profiling. Vet. Microbiol. 2018, 223, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konishi, N.; Obata, H.; Kai, A.; Ohtsuka, K.; Nishikawa, Y.; Terajima, J.; Hara-Kudo, Y. Major vehicles and o-serogroups in foodborne enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli outbreaks in Japan, and effective detection methods of the pathogen in food associated with an outbreak. J. Food Hyg. Soc. Japan 2018, 59, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schremmer, C.; Lohr, J.E.; Wastlhuber, U.; Kosters, J.; Ravelshofer, K.; Steinruck, H.; Wieler, L.H. Enteropathogenic Escherichia coli in Psittaciformes. Avian Pathol. 1999, 28, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lindstedt, B.-A.; Finton, M.D.; Porcellato, D.; Brandal, L.T. High frequency of hybrid Escherichia coli strains with combined Intestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (IPEC) and Extraintestinal Pathogenic Escherichia coli (ExPEC) virulence factors isolated from human faecal samples. BMC Infect. Dis. 2018, 18, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyholm, O.; Heinikainen, S.; Pelkonen, S.; Hallanvuo, S.; Haukka, K.; Siitonen, A. Hybrids of Shigatoxigenic and Enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli (STEC/ETEC) Among Human and Animal Isolates in Finland. Zoonoses Public Health. 2015, 62, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michelacci, V.; Maugliani, A.; Tozzoli, R.; Corteselli, G.; Chiani, P.; Minelli, F.; Gigliucci, F.; Arancia, S.; Conedera, G.; Targhetta, C.; et al. Characterization of a novel plasmid encoding F4-like fimbriae present in a Shiga-toxin producing enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli isolated during the investigation on a case of hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Int. J. Med. Microbiol. 2018, 308, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cointe, A.; Birgy, A.; Bridier-Nahmias, A.; Mariani-Kurkdjian, P.; Walewski, V.; Lévy, C.; Cohen, R.; Fach, P.; Delannoy, S.; Bidet, P.; et al. Escherichia coli O80 hybrid pathotype strains producing Shiga toxin and ESBL: Molecular characterization and potential therapeutic options. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2020, 75, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cointe, A.; Birgy, A.; Mariani-Kurkdjian, P.; Liguori, S.; Courroux, C.; Blanco, J.; Delannoy, S.; Fach, P.; Loukiadis, E.; Bidet, P.; et al. Emerging multidrug-resistant hybrid pathotype shiga toxin–producing Escherichia coli O80 and related strains of clonal complex 165, Europe. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2018, 24, 2262–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cartelle, M.; Del Mar Tomas, M.; Molina, F.; Moure, R.; Villanueva, R.; Bou, G. High-level resistance to ceftazidime conferred by a novel enzyme, CTX-M-32, derived from CTX-M-1 through a single Asp240-Gly substitution. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 2308–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamani, R.; Camille Flament-Simon, S.; García Menéndez, V.; Mora, A.; Pilar Alonso, M.; López, C.; García-Meniño, I.; Díaz-Jiménez, D.; Blanco, J.; Blanco, M.; et al. Sequence Types, Clonotypes, Serotypes, and Virotypes of Extended-Spectrum β-Lactamase-Producing Escherichia coli Causing Bacteraemia in a Spanish Hospital Over a 12-Year Period (2000 to 2011). Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Meniño, I.; Diaz-Jimenez, D.; Garcia, V.; de Toro, M.; Flament-Simon, S.C.; Blanco, J.; Mora, A. Genomic Characterization of Prevalent mcr-1, mcr-4, and mcr-5 Escherichia coli Within Swine Enteric Colibacillosis in Spain. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wick, R.R.; Judd, L.M.; Gorrie, C.L.; Holt, K.E. Completing bacterial genome assemblies with multiplex MinION sequencing. Microb. Genomics. 2017, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Scheutz, F.; Lund, O.; Hasman, H.; Kaas, R.S.; Nielsen, E.M.; Aarestrup, F.M. Real-time whole-genome sequencing for routine typing, surveillance, and outbreak detection of verotoxigenic Escherichia coli. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2014, 52, 1501–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Toro, M.; Fernandez, J.; Garcia, V.; Mora, A.; Blanco, J.; de la Cruz, F.; Rodicio, M.R. Whole genome sequencing, molecular typing and in vivo virulence of OXA-48-producing Escherichia coli isolates including ST131 H30-Rx, H22 and H41 subclones. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Millan, A.; MacLean, R.C. Fitness Costs of Plasmids: A Limit to Plasmid Transmission. Microbiol. Spectr. 2017, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionisio, F.; Zilhão, R.; Gama, J.A. Interactions between plasmids and other mobile genetic elements affect their transmission and persistence. Plasmid 2019, 102, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mora, A.; Viso, S.; Lopez, C.; Alonso, M.P.; Garcia-Garrote, F.; Dabhi, G.; Mamani, R.; Herrera, A.; Marzoa, J.; Blanco, M.; et al. Poultry as reservoir for extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli O45:K1:H7-B2-ST95 in humans. Vet. Microbiol. 2013, 167, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinée, P.A.M.; Jansen, W.H.; Wadström, T.; Sellwood, R. Escherichia coli associated with neonatal diarrhoea in piglets and calves. In Laboratory Diagnosis in Neonatal Calf and Pig Diarrhoea: Current Topics in Veterinary and Animal Science, 13; Leeww, P.W., Guinée, P.A.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Germany, 1981; pp. 126–162. [Google Scholar]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute. Performance Standars for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing; Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute: Wayne, PA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Clermont, O.; Christenson, J.K.; Denamur, E.; Gordon, D.M. The Clermont Escherichia coli phylo-typing method revisited: Improvement of specificity and detection of new phylo-groups. Env. Microbiol. Rep. 2013, 5, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wirth, T.; Falush, D.; Lan, R.; Colles, F.; Mensa, P.; Wieler, L.H.; Karch, H.; Reeves, P.R.; Maiden, M.C.; Ochman, H.; et al. Sex and virulence in Escherichia coli: An evolutionary perspective. Mol. Microbiol. 2006, 60, 1136–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weissman, S.J.; Johnson, J.R.; Tchesnokova, V.; Billig, M.; Dykhuizen, D.; Riddell, K.; Rogers, P.; Qin, X.; Butler-Wu, S.; Cookson, B.T.; et al. High-resolution two-locus clonal typing of extraintestinal pathogenic Escherichia coli. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alikhan, N.F.; Zhou, Z.; Sergeant, M.J.; Achtman, M. A genomic overview of the population structure of Salmonella. PLoS Genet 2018, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joensen, K.G.; Tetzschner, A.M.M.M.; Iguchi, A.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Scheutz, F. Rapid and easy in silico serotyping of Escherichia coli isolates by use of Whole-Genome Sequencing data. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2015, 53, 2410–2426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsen, M.V.; Cosentino, S.; Rasmussen, S.; Friis, C.; Hasman, H.; Marvig, R.L.; Jelsbak, L.; Sicheritz-Ponten, T.; Ussery, D.W.; Aarestrup, F.M.; et al. Multilocus sequence typing of total-genome-sequenced bacteria. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2012, 50, 1355–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camacho, C.; Coulouris, G.; Avagyan, V.; Ma, N.; Papadopoulos, J.; Bealer, K.; Madden, T.L. BLAST+: Architecture and applications. BMC Bioinf. 2009, 10, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carattoli, A.; Zankari, E.; Garcia-Fernandez, A.; Voldby Larsen, M.; Lund, O.; Villa, L.; Moller Aarestrup, F.; Hasman, H. In silico detection and typing of plasmids using PlasmidFinder and plasmid multilocus sequence typing. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 3895–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zankari, E.; Hasman, H.; Cosentino, S.; Vestergaard, M.; Rasmussen, S.; Lund, O.; Aarestrup, F.M.; Larsen, M.V. Identification of acquired antimicrobial resistance genes. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2012, 67, 2640–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Alikhan, N.-F.; Sergeant, M.; Luhmann, N.; Vaz, C.; Francisco, A.; Carriço, J.A.; Achtman, M. GrapeTree: Visualization of core genomic relationships among 100,000 bacterial pathogens. bioRxiv 2017. bioRxiv:216788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamada, M.; Yamada, K.; Sato, K.; Frith, M.C.; Asai, K. CentroidHomfold-LAST: Accurate prediction of RNA secondary structure using automatically collected homologous sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W100–W106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benson, G. Tandem repeats finder: A program to analyze DNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1999, 27, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edgar, R.C. PILER-CR: Fast and accurate identification of CRISPR repeats. BMC Bioinf. 2007, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
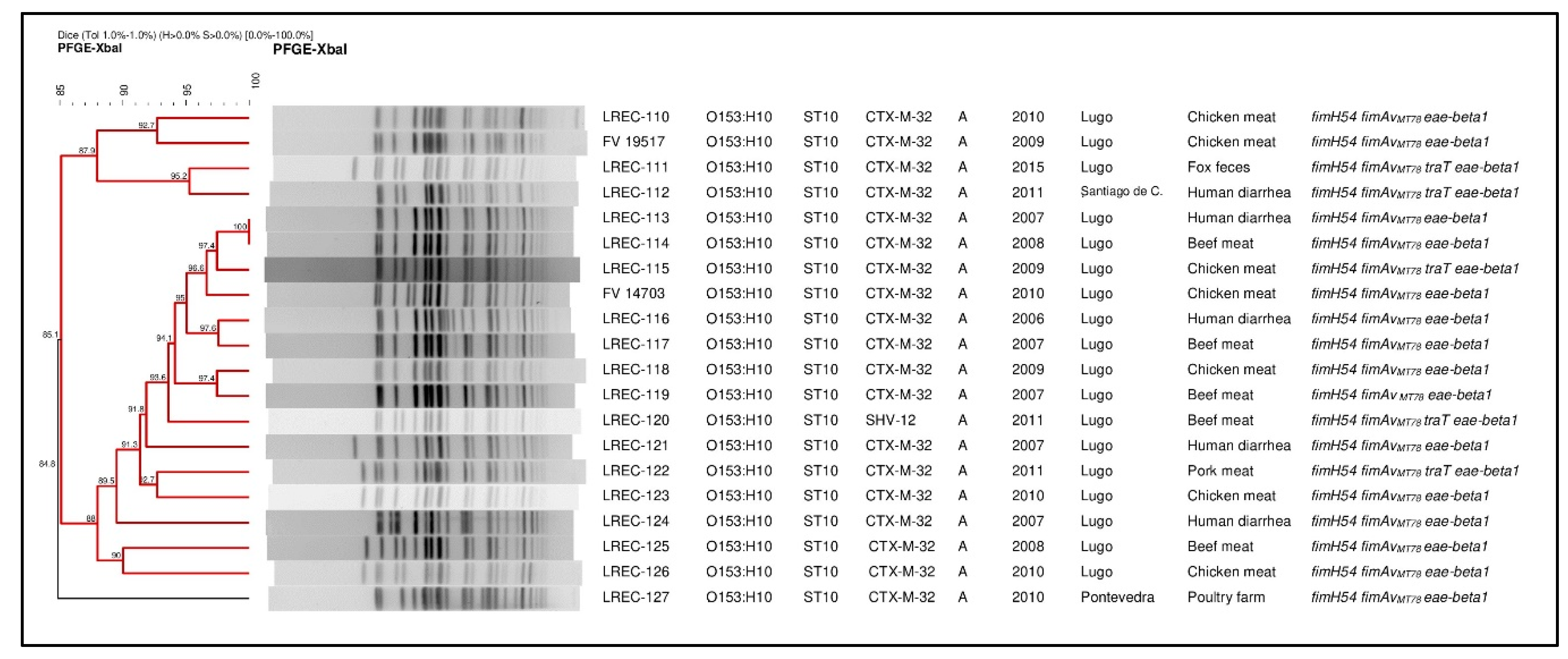
| Sample Origin | Code a | Year | Geographic Origin | Virulence Gene Profile | Resistance Profile b | blaESBL Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pork meat | *LREC-122 | 2011 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN | CTX-M-32 |
| Chicken meat | *LREC-115 | 2009 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB | CTX-M-32 |
| Chicken meat | FV 19517 | 2009 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN | CTX-M-32 |
| Chicken meat | *LREC-118 | 2009 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN | CTX-M-32 |
| Chicken meat | *LREC-110 | 2010 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN | CTX-M-32 |
| Chicken meat | FV 14703 | 2010 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB, FOF | CTX-M-32 |
| Chicken meat | LREC-126 | 2010 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB | CTX-M-32 |
| Chicken meat | *LREC-123 | 2010 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB | CTX-M-32 |
| Beef meat | *LREC-119 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN | CTX-M-32 |
| Beef meat | * LREC-117 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN | CTX-M-32 |
| Beef meat | 4-3a | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ | SHV-12 |
| Beef meat | 85-5a | 2008 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | AMP, GEN | − |
| Beef meat | *LREC-125 | 2008 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, FEP | CTX-M-32 |
| Beef meat | *LREC-114 | 2008 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB | CTX-M-32 |
| Beef meat | 65-6a | 2009 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | − | − |
| Beef meat | *LREC-120 | 2011 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP | SHV-12 |
| Wildlife (Fox) | *LREC-111 | 2015 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB | CTX-M-32 |
| Poultry farm | *LREC-127 | 2010 | Pontevedra | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN | CTX-M-32 |
| Human | *LREC-116 | 2006 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB | CTX-M-32 |
| Human | *LREC-113 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB | CTX-M-32 |
| Human | *LREC-121 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB | CTX-M-32 |
| Human | *LREC-124 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, GEN, TOB | CTX-M-32 |
| Human | 31952. 07 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | − | − |
| Human | 32651. 07 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | NAL, CIP | − |
| Human | 32884. 07 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CAZ, AMC, SXT | − |
| Human | 34535. 07 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | NAL, CIP | − |
| Human | 39044. 07 | 2007 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | − | − |
| Human | 21011. 08 | 2008 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | − | − |
| Human | 38506. 08 | 2008 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | CIP | − |
| Human | 40237. 08 | 2008 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | NAL, CIP | − |
| Human | *LREC-112 | 2011 | Santiago de Compostela | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | AMP, CXM, CTX, CAZ, FEP, NAL | CTX-M-32 |
| Human | 55515.12 | 2012 | Lugo | fimH54, fimAvMT78, traT, eae-beta1 | AMP, GEN | − |
| Code | Serotype 1 | Phylo Group 2 | CHType 3 | ST 4 | Plasmid Content Inc Group (pMLST) 5 | Acquired Resistances (black) and Point Mutations (blue) 6 | Virulence Genes 7,8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LREC-110 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, espF, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-111 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 Col (MG828) | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-112 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncX1 Col156 Col (MG828) | blaCTX-M-32;aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A); gyrA S83L | astA, eae, espA, espB, espF, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP |
| LREC-113 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, espF, gad, iss, mchF, tir |
| LREC-114 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 Col (MG828) | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, espF, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tir |
| LREC-115 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, espF, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-116 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, gad, iss, mchF, tccP, tir |
| LREC-117 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 | blaCTX-M-32; aadA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, gad, iss, mchF, tccP, tir |
| LREC-118 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 Col(MG828) | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, espF, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-119 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | Col156 | blaCTX-M-32, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, gad, iss, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-120 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncI1 (ST22-CC2) IncQ1 IncX1 Col156 Col (MG828) | blaSHV-12; aadA1, aadA2; catA1, cmlA1; mdf(A); sul3; tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-121 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-122 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 Col (MG828) | blaCTX-M-32; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-123 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 Col (MG828) | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-124 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 IncY Col156 | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, espF, gad, iss, mchF, tccP, tir |
| LREC-125 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 | blaCTX-M-32; aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, espF, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| LREC-127 | O153:H10 | A | 11-54 | 10 | IncF (F2:A-:B-) IncI1 (STunknown) IncX1 Col156 Col (MG828) | blaCTX-M-32, blaTEM-1A; aac(3)-IIa, aadA1; catA1; mdf(A); tet(A) | astA, eae, espA, espB, espF, gad, iss, mchF, nleA, tccP, tir |
| Genome Code/ cgMLST | LREC- 110 | LREC- 111 | LREC- 127 | LREC- 112 | LREC- 113 | LREC- 120 | LREC- 117 | LREC- 121 | LREC- 119 | LREC- 116 | LREC- 115 | LREC- 114 | LREC- 123 | LREC- 122 | LREC- 124 | LREC- 125 | LREC- 118 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37600 | 37601 | 37602 | 37605 | 37606 | 37607 | 37609 | 37610 | 37611 | 37612 | 37613 | 37614 | 37615 | 37616 | 37617 | 37618 | 38299 | ||
| LREC-110 | 37600 | 0 | 14 | 17 | 19 | 13 | 12 | 18 | 19 | 12 | 15 | 27 | 8 | 15 | 15 | 18 | 16 | 14 |
| LREC-111 | 37601 | 14 | 0 | 21 | 23 | 16 | 20 | 22 | 23 | 16 | 19 | 30 | 11 | 19 | 18 | 22 | 20 | 17 |
| LREC-127 | 37602 | 17 | 21 | 0 | 24 | 9 | 22 | 14 | 16 | 9 | 11 | 24 | 15 | 13 | 13 | 15 | 13 | 13 |
| LREC-112 | 37605 | 19 | 23 | 24 | 0 | 19 | 25 | 24 | 25 | 18 | 21 | 33 | 17 | 22 | 22 | 24 | 23 | 21 |
| LREC-113 | 37606 | 13 | 16 | 9 | 19 | 0 | 18 | 9 | 11 | 5 | 6 | 18 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 11 | 9 | 8 |
| LREC-120 | 37607 | 12 | 20 | 22 | 25 | 18 | 0 | 23 | 23 | 18 | 20 | 33 | 14 | 20 | 20 | 24 | 22 | 19 |
| LREC-117 | 37609 | 18 | 22 | 14 | 24 | 9 | 23 | 0 | 17 | 8 | 12 | 22 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 14 | 12 | 13 |
| LREC-121 | 37610 | 19 | 23 | 16 | 25 | 11 | 23 | 17 | 0 | 10 | 13 | 25 | 15 | 16 | 16 | 16 | 14 | 14 |
| LREC-119 | 37611 | 12 | 16 | 9 | 18 | 5 | 18 | 8 | 10 | 0 | 6 | 17 | 10 | 9 | 9 | 7 | 6 | 8 |
| LREC-116 | 37612 | 15 | 19 | 11 | 21 | 6 | 20 | 12 | 13 | 6 | 0 | 22 | 12 | 11 | 11 | 13 | 11 | 10 |
| LREC-115 | 37613 | 27 | 30 | 24 | 33 | 18 | 33 | 22 | 25 | 17 | 22 | 0 | 22 | 24 | 23 | 23 | 15 | 20 |
| LREC-114 | 37614 | 8 | 11 | 15 | 17 | 10 | 14 | 15 | 15 | 10 | 12 | 22 | 0 | 13 | 12 | 15 | 14 | 11 |
| LREC-123 | 37615 | 15 | 19 | 13 | 22 | 9 | 20 | 14 | 16 | 9 | 11 | 24 | 13 | 0 | 7 | 15 | 13 | 8 |
| LREC-122 | 37616 | 15 | 18 | 13 | 22 | 8 | 20 | 13 | 16 | 9 | 11 | 23 | 12 | 7 | 0 | 15 | 13 | 9 |
| LREC-124 | 37617 | 18 | 22 | 15 | 24 | 11 | 24 | 14 | 16 | 7 | 13 | 23 | 15 | 15 | 15 | 0 | 12 | 14 |
| LREC-125 | 37618 | 16 | 20 | 13 | 23 | 9 | 22 | 12 | 14 | 6 | 11 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 13 | 12 | 0 | 12 |
| LREC-118 | 38299 | 14 | 17 | 13 | 21 | 8 | 19 | 13 | 14 | 8 | 10 | 20 | 11 | 8 | 9 | 14 | 12 | 0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Díaz-Jiménez, D.; García-Meniño, I.; Herrera, A.; García, V.; López-Beceiro, A.M.; Alonso, M.P.; Blanco, J.; Mora, A. Genomic Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to a New Hybrid aEPEC/ExPEC Pathotype O153:H10-A-ST10 eae-beta1 Occurred in Meat, Poultry, Wildlife and Human Diarrheagenic Samples. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040192
Díaz-Jiménez D, García-Meniño I, Herrera A, García V, López-Beceiro AM, Alonso MP, Blanco J, Mora A. Genomic Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to a New Hybrid aEPEC/ExPEC Pathotype O153:H10-A-ST10 eae-beta1 Occurred in Meat, Poultry, Wildlife and Human Diarrheagenic Samples. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(4):192. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040192
Chicago/Turabian StyleDíaz-Jiménez, Dafne, Isidro García-Meniño, Alexandra Herrera, Vanesa García, Ana María López-Beceiro, María Pilar Alonso, Jorge Blanco, and Azucena Mora. 2020. "Genomic Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to a New Hybrid aEPEC/ExPEC Pathotype O153:H10-A-ST10 eae-beta1 Occurred in Meat, Poultry, Wildlife and Human Diarrheagenic Samples" Antibiotics 9, no. 4: 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040192
APA StyleDíaz-Jiménez, D., García-Meniño, I., Herrera, A., García, V., López-Beceiro, A. M., Alonso, M. P., Blanco, J., & Mora, A. (2020). Genomic Characterization of Escherichia coli Isolates Belonging to a New Hybrid aEPEC/ExPEC Pathotype O153:H10-A-ST10 eae-beta1 Occurred in Meat, Poultry, Wildlife and Human Diarrheagenic Samples. Antibiotics, 9(4), 192. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9040192






