Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
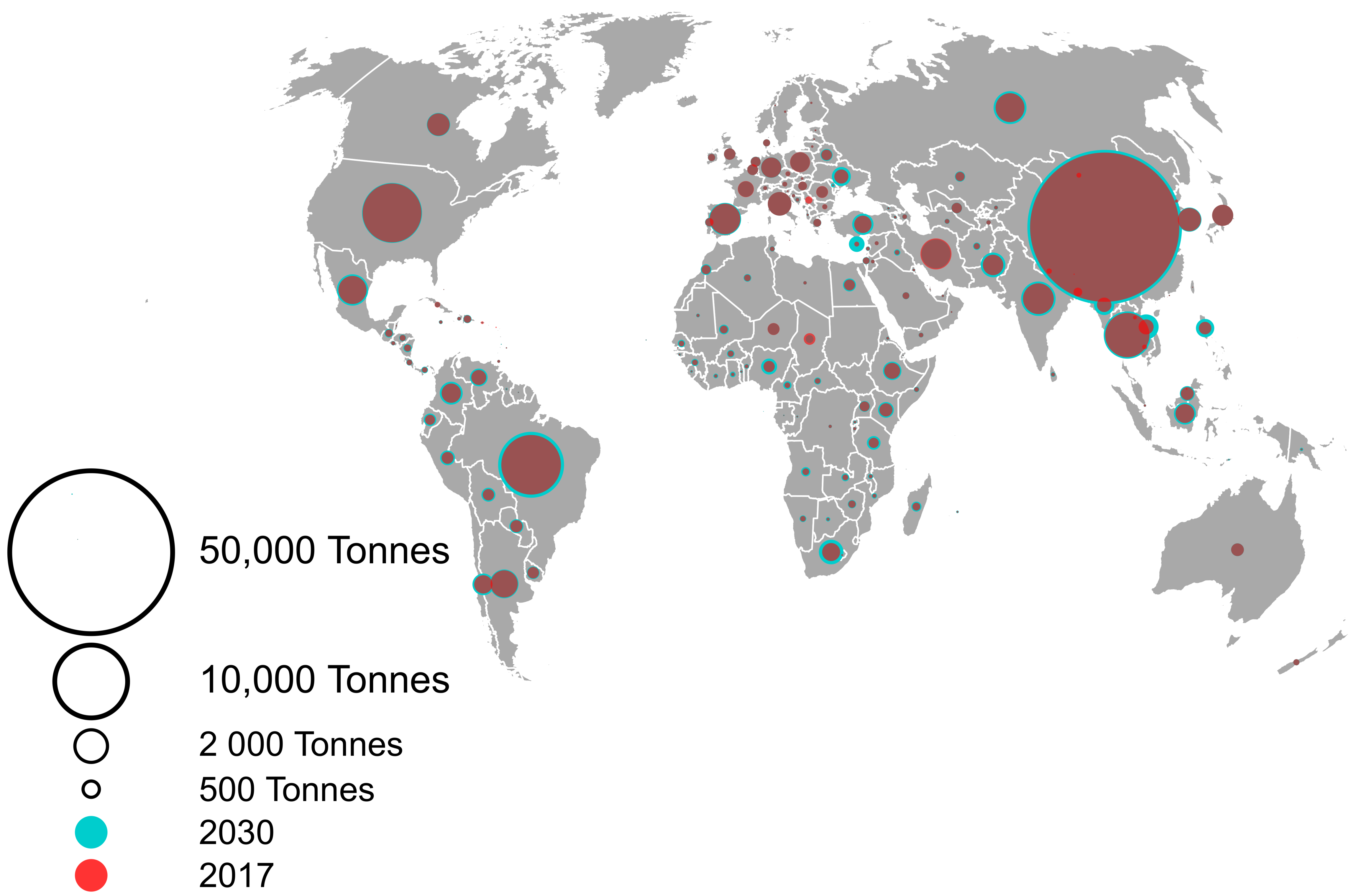
2.1. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use
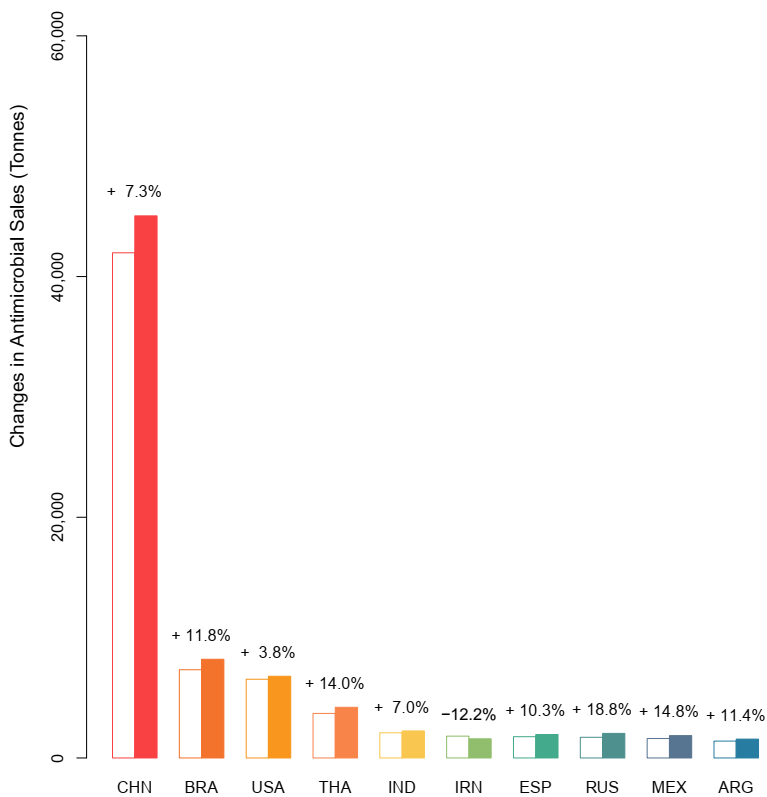
2.2. Projected Consumption Increase by Country
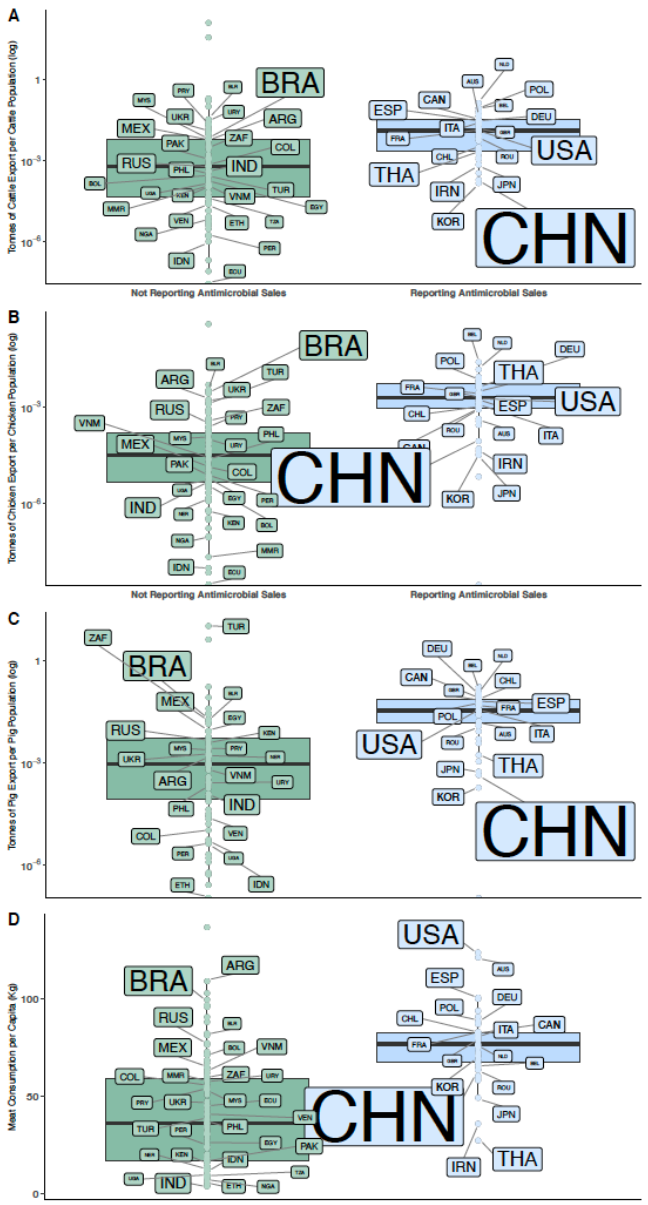
2.3. Antimicrobial Sales vs. Meat Exports
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Antimicrobial Sales Data
4.2. Food Animal Census
4.3. Extrapolation of Consumption
4.4. Projections for 2017 and 2030
4.5. Meat Consumption and Exports
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- FAO’s Animal Production and Health Division: Meat & Meat Products. Available online: http://www.fao.org/ag/againfo/themes/en/meat/backgr_sources.html (accessed on 15 September 2020).
- Delgado, C.L. Rising Consumption of Meat and Milk in Developing Countries Has Created a New Food Revolution. J. Nutr. 2003, 133, 3907S–3910S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henchion, M.; McCarthy, M.; Resconi, V.C.; Troy, D. Meat consumption: Trends and quality matters. Meat Sci. 2014, 98, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Boeckel, T.P.; Brower, C.; Gilbert, M.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Robinson, T.P.; Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial use in food animals. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 5649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, S.W.; Gautier, P. Use of antimicrobial agents in livestock. Rev. Sci. Tech. Int. Off. Epizoot. 2012, 31, 145–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.who.int/westernpacific/health-topics/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Lhermie, G.; Tauer, L.W.; Gröhn, Y.T. The farm cost of decreasing antimicrobial use in dairy production. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0194832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prescott, J.F. Antimicrobial use in food and companion animals. Anim. Health Res. Rev. 2008, 9, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeckel, T.P.V.; Glennon, E.E.; Chen, D.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Grenfell, B.T.; Levin, S.A.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Reducing antimicrobial use in food animals. Science 2017, 357, 1350–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, T.C.; Gebreyes, W.A.; Abley, M.J.; Harper, A.L.; Forshey, B.M.; Male, M.J.; Martin, H.W.; Molla, B.Z.; Sreevatsan, S.; Thakur, S.; et al. Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus in Pigs and Farm Workers on Conventional and Antibiotic-Free Swine Farms in the USA. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, J.A.; Curriero, F.C.; Cosgrove, S.E.; Nachman, K.E.; Schwartz, B.S. High-Density Livestock Operations, Crop Field Application of Manure, and Risk of Community-Associated Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus Infection in Pennsylvania. JAMA Intern. Med. 2013, 173, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manges, A.R.; Smith, S.P.; Lau, B.J.; Nuval, C.J.; Eisenberg, J.N.S.; Dietrich, P.S.; Riley, L.W. Retail Meat Consumption and the Acquisition of Antimicrobial Resistant Escherichia coli Causing Urinary Tract Infections: A Case–Control Study. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2007, 4, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, A.R.; Collignon, P.; Aarestrup, F.M.; McEwen, S.A.; Hendriksen, R.S.; Hald, T.; Wegener, H.C. Association between Antimicrobial Resistance in Escherichia coli Isolates from Food Animals and Blood Stream Isolates from Humans in Europe: An Ecological Study. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21883007/ (accessed on 2 December 2020).
- Muloi, D.; Ward, M.J.; Pedersen, A.B.; Fèvre, E.M.; Woolhouse, M.E.J.; Van Bunnik, B.A.D. Are Food Animals Responsible for Transfer of Antimicrobial-Resistant Escherichia coli or Their Resistance Determinants to Human Populations? A Systematic Review. Foodborne Pathog. Dis. 2018, 15, 467–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrique-Mas, J.; Van, N.T.B.; Cuong, N.V.; Truong, B.D.; Kiet, B.T.; Thanh, P.T.H.; Lon, N.N.; Giao, V.T.Q.; Hien, V.B.; Padungtod, P.; et al. Mortality, disease and associated antimicrobial use in commercial small-scale chicken flocks in the Mekong Delta of Vietnam. Prev. Vet. Med. 2019, 165, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freivogel, C.; Visschers, V.H.M. Understanding the Underlying Psychosocial Determinants of Safe Food Handling among Consumers to Mitigate the Transmission Risk of Antimicrobial-Resistant Bacteria. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2020, 17, 2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, T.P.; Bu, D.P.; Carrique-Mas, J.; Fèvre, E.M.; Gilbert, M.; Grace, D.; Hay, S.I.; Jiwakanon, J.; Kakkar, M.; Kariuki, S.; et al. Antibiotic resistance is the quintessential One Health issue. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 110, 377–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DANMAP—The Danish Integrated Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring and Research Programme. Consumption of Antimicrobial Agents and Occurrence of Antimicrobial Resistance in Bacteria from Food Animals, Food, and Humans in Denmark. 1997. Available online: http://www.danmap.org/pdffiles/danmap_1996_uk.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Trends in the Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in Nine European Countries (2005–2009); EMA/238630; European Medicines Agency. 2011. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/trends-sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-nine-european-countries_en.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 31 European Countries in 2017; EMA/294674/2019; European Medicines Agency, European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption. 2019. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-31-european-countries-2017_en.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (CIPARS): Annual Report 2008; Government of Canada, Public Health Agency of Canada: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2011; Available online: https://www.canada.ca/en/public-health/services/surveillance/canadian-integrated-program-antimicrobial-resistance-surveillance-cipars/cipars-2008-annual-report.html (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- National Veterinary Assay Laboratory, Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries. A Report on the Japanese Veterinary Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System (2000–2007). 2009. Available online: https://www.maff.go.jp/nval/english/pdf/jvarm2000_2007_final_201005.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Teillant, A.; Laxminarayan, R. Choices: The Magazine of Food, Farm, and Resource Issues. A Publication of the Agricultural and Applied Economics Association; Quarter. 2015. Available online: https://www.choicesmagazine.org/choices-magazine/theme-articles/theme-overview/economics-of-antibiotic-use-in-us-swine-and-poultry-production (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- McKendree, M.G.S.; Widmar, N.O.; Ortega, D.L.; Foster, K.A. Consumer Preferences for Verified Pork-Rearing Practices in the Production of Ham Products. J. Agric. Resour. Econ. 2013, 38, 397–417. [Google Scholar]
- Asante-Addo, C.; Weible, D. Is there hope for domestically produced poultry meat? A choice experiment of consumers in Ghana. Agribusiness 2020, 36, 281–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maron, D.F.; Smith, T.J.; Nachman, K.E. Restrictions on antimicrobial use in food animal production: An international regulatory and economic survey. Glob. Health 2013, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China. Official Veterinary Bulletin; Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2019; Volume 21, p. 61. Available online: http://english.agri.gov.cn (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Zhang, Q.-Q.; Ying, G.-G.; Pan, C.-G.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhao, J.-L. Comprehensive Evaluation of Antibiotics Emission and Fate in the River Basins of China: Source Analysis, Multimedia Modeling, and Linkage to Bacterial Resistance. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 6772–6782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, E.Y.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Martinez, E.M.; Pant, S.; Gandra, S.; Levin, S.A.; Goossens, H.; Laxminarayan, R. Global increase and geographic convergence in antibiotic consumption between 2000 and 2015. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E3463–E3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speksnijder, D.C.; Mevius, D.J.; Bruschke, C.J.M.; Wagenaar, J.A. Reduction of Veterinary Antimicrobial Use in the Netherlands. The Dutch Success Model. Zoonoses Public Health 2015, 62, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 26 EU/EEA Countries in 2012; European Medicines Agency, European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption. 2014, Volume 4, p. 128. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/veterinary-regulatory/overview/antimicrobial-resistance/european-surveillance-veterinary-antimicrobial-consumption-esvac (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Xiao, Y.; Li, L. China’s national plan to combat antimicrobial resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 1216–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- China Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs. National Action Plan to Combat Animal Resources Antimicrobial Resistance (2017–2020); China Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs: Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 29 European Countries in 2014; European Medicines Agency, European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption. 2016, Volume 6, p. 175. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/sixth-esvac-report-sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-29-european-countries-2014_en.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 26 EU/EEA Countries in 2013; European Medicines Agency, European Surveillance of Veterinary Antimicrobial Consumption: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 5, p. 162. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/fifth-esvac-report-sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-26-european-union/european-economic-area-countries-2013_en.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Declaración de Venta de Antimicrobianos. Available online: http://www.sag.cl/ambitos-de-accion/declaracion-de-venta-de-antimicrobianos (accessed on 2 September 2020).
- International Health Policy Program. Thai Working Group on Health Policy and Systems Research on Antimicrobial Resistance (HPSR-AMR) Consumption of Antimicrobial Agents in Thailand in 2017. 2018. Available online: http://ihppthaigov.net/DB/publication/attachresearch/421/chapter2.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- European Medicines Agency. Sales of Veterinary Antimicrobial Agents in 30 European Countries in 2015. Eur. Surveill. Vet. Antimicrob. Consum. 2017, 7, 178. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/report/seventh-esvac-report-sales-veterinary-antimicrobial-agents-30-european-countries-2015_en.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Government of Canada. Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (CIPARS) 2015 Annual Report; Public Health Agency of Canada: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Government of Canada. Canadian Integrated Program for Antimicrobial Resistance Surveillance (CIPARS) 2017: Figures and Tables; Public Health Agency of Canada: Guelph, ON, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- 2015 Summary Report on Antimicrobials Sold or Distrubuted for Use in Food-Producing Animals; Food and Drug Administration Center for Veterinary Medicine, Department of Health and Human Services. 2016; p. 49. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/files/about%20fda/published/2015-Summary-Report-on-Antimicrobials-Sold-or-Distributed-for-Use-in-Food-Producing-Animals.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- 2017 Summary Report on Antimicrobials Sold or Distributed for Use in Food-Producing Animals; Food and Drug Administration Center for Veterinary Medicine, Department of Health and Human Services. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/119332/download (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- UK Five Year Antimicrobial Resistance Strategy (2013 to 2018); UK Department of Health and Department for Environment, Food, & Rural Affairs. 2013. Available online: https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/uk-5-year-antimicrobial-resistance-strategy-2013-to-2018 (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Center for Veterinary Medicine CVM GFI #209 The Judicious Use of Medically Important Antimicrobial Drugs in Food-Producing Animals. 2012. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/regulatory-information/search-fda-guidance-documents/cvm-gfi-209-judicious-use-medically-important-antimicrobial-drugs-food-producing-animals (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- 2018 Summary Report On Antimicrobials Sold or Distributed for Use in Food-Producing Animals; Food and Drug Administration Center for Veterinary Medicine, Department of Health and Human Services. 2019. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/133411/download (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- The Antimicrobial Use Reduction Strategy|Chicken Farmers of Canada. Available online: https://www.chickenfarmers.ca/the-antimicrobial-use-reduction-strategy/ (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Kavallari, A.; Conforti, P.; Van der Mensbrugghe, D. The Global Agriculture Perspectives System (GAPS) Version 1.0; ESA Working Papers; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Agricultural Development Economics Division (ESA). 2016. Available online: http://www.fao.org/policy-support/tools-and-publications/resources-details/fr/c/470673/ (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- FAO. The Future of Food and Agriculture—Alternative Pathways to 2050. 2018, p. 224. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/I8429EN/i8429en.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Alexandratos, N.; Bruinsma, J. World Agriculture towards 2030/2050: The 2012 Revision; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. 2012, p. 160. Available online: http://www.fao.org/3/a-ap106e.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- OECD; FAO. OECD-FAO Agricultrual Outlook 2018–2027; OECD Publishing, Paris/Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 2018; ISBN 978-92-64-29721-0. [Google Scholar]
- Global Trends in Antimicrobial Resistance in Animals in Low- and Middle-Income Countries|Science. Available online: https://science.sciencemag.org/content/365/6459/eaaw1944 (accessed on 12 October 2020).
- FAOSTAT. Available online: http://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#data/FBS (accessed on 31 August 2020).
- Johnson, R. The U.S.-EU Beef Hormone Dispute; Congressional Research Service. 2017. Available online: https://fas.org/sgp/crs/row/R40449.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Meat Companies Go Antibiotics-Free as More Consumers Demand It—WSJ. Available online: https://www.wsj.com/articles/meat-companies-go-antibiotics-free-as-more-consumers-demand-it-1415071802 (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Gould, D. Survey Reveals Growing Consumer Demand For Antibiotic-Free Meat [Video]. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/daniellegould/2012/06/26/survey-reveals-growing-consumer-demand-for-antibiotic-free-meat/ (accessed on 5 November 2020).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Get Smart for Healthcare—Know When Antibiotics Work. Available online: www.cdc.gov/Features/GetSmart (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Food and Drug Administration FDA Task Force on Antimicrobial Resistance: Key Recommendations and Report. Available online: http://fda.gov/downloads/ForConsumers/ConsumerUpdates/UCM143458.pdf (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Boeckel, T.P.V.; Pires, J.; Silvester, R.; Zhao, C.; Song, J.; Criscuolo, N.G.; Gilbert, M.; Bonhoeffer, S.; Laxminarayan, R. Global trends in antimicrobial resistance in animals in low- and middle-income countries. Science 2019, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, R.S.; Finch, R.; Wegener, H.C.; Bywater, R.; Walters, J.; Lipsitch, M. Antibiotic resistance—The interplay between antibiotic use in animals and human beings. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2003, 3, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Q.; Wang, W.; Regev-Yochay, G.; Lipsitch, M.; Hanage, W.P. Antibiotics in agriculture and the risk to human health: How worried should we be? Evol. Appl. 2015, 8, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stichele, R.H.V.; Elseviers, M.M.; Ferech, M.; Blot, S.; Goossens, H. Undefined European surveillance of antimicrobial consumption (ESAC): Data collection performance and methodological approach. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2004, 58, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuong, N.V.; Padungtod, P.; Thwaites, G.; Carrique-Mas, J.J. Antimicrobial Usage in Animal Production: A Review of the Literature with a Focus on Low- and Middle-Income Countries. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewulf, J.; Van Immerseel, F. Biosecurity in Animal Production and Veterinary Medicine: From Principles to Practice; Centre for Agriculture and Bioscience International: Wallingford, UK, 2020; ISBN 978-1-78924-568-4. [Google Scholar]
- Gjedrem, T.; Robinson, N.; Rye, M. The importance of selective breeding in aquaculture to meet future demands for animal protein: A review. Aquaculture 2012, 350–353, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schar, D.; Klein, E.Y.; Laxminarayan, R.; Gilbert, M.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Aquaculture. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 21878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabello, F.C.; Godfrey, H.P.; Tomova, A.; Ivanova, L.; Dölz, H.; Millanao, A.; Buschmann, A.H. Antimicrobial use in aquaculture re-examined: Its relevance to antimicrobial resistance and to animal and human health. Environ. Microbiol. 2013, 15, 1917–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.; Conchedda, G.; Boeckel, T.P.V.; Cinardi, G.; Linard, C.; Nicolas, G.; Thanapongtharm, W.; D’Aietti, L.; Wint, W.; Newman, S.H.; et al. Income Disparities and the Global Distribution of Intensively Farmed Chicken and Pigs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorne, J.L.C.M.; Fernández-Cruz, M.L.; Bertelsen, U.; Renshaw, D.W.; Peltonen, K.; Anadon, A.; Feil, A.; Sanders, P.; Wester, P.; Fink-Gremmels, J. Risk assessment of coccidostatics during feed cross-contamination: Animal and human health aspects. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2013, 270, 196–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO. Advisory Group on Integrated Surveillance of Antimicrobial Resistance (AGISAR) Critically Important Antimicrobials for Human Medicine, 6th ed.; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Warriss, P.D. Meat Science: An Introductory Text; CABI; ISBN 978-1-84593-593-1. 2010. Available online: https://www.cabi.org/bookshop/book/9781845935931/ (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Robinson, T.P.; Wint, G.R.W.; Conchedda, G.; Boeckel, T.P.V.; Ercoli, V.; Palamara, E.; Cinardi, G.; D’Aietti, L.; Hay, S.I.; Gilbert, M. Mapping the Global Distribution of Livestock. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e96084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wickham, H.; François, R.; Henry, L.; Müller, K. Dplyr: A Grammar of Data Manipulation. 2020. Available online: https://dplyr.tidyverse.org (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Müller, K.; Wickham, H. Tibble: Simple Data Frames. 2020. Available online: https://tibble.tidyverse.org (accessed on 30 November 2020).
- Gilbert, M.; Nicolas, G.; Cinardi, G.; Van Boeckel, T.P.; Vanwambeke, S.O.; Wint, G.R.W.; Robinson, T.P. Global distribution data for cattle, buffaloes, horses, sheep, goats, pigs, chickens and ducks in 2010. Sci. Data 2018, 5, 180227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Country | 2015 Sales | 2017 Sales (% Decrease) 1 |
|---|---|---|
| Spain | 3028.62 | 1761.68 (−41.83) |
| United States | 10,836.36 | 6538.52 (−39.66) |
| The United Kingdom | 408.2 | 248.2 (−39.2) |
| Slovakia | 12.15 | 8.44 (−30.54) |
| Croatia | 27.87 | 21.14 (−24.15) |
| Switzerland | 41.34 | 32.02 (−22.54) |
| Estonia | 8.02 | 6.27 (−21.82) |
| Canada | 1201.26 | 948.62 (−21.03) |
| Italy | 1300.24 | 1057.52 (−18.67) |
| Hungary | 176.18 | 146.39 (−16.91) |
| Belgium | 258.2 | 220.99 (−14.41) |
| Latvia | 6.78 | 5.87 (−13.42) |
| The Netherlands | 214.14 | 188.42 (−12.01) |
| Germany | 852.49 | 767.91 (−9.92) |
| Denmark | 102.22 | 94.08 (−7.96) |
| Austria | 48.47 | 44.69 (−7.8) |
| Finland | 10.54 | 9.82 (−6.83) |
| Czech Republic | 47.43 | 44.23 (−6.75) |
| France | 501.72 | 483.69 (−3.59) |
| Cyprus | 46.88 | 45.43 (−3.1) |
| Lithuania | 11.9 | 11.59 (−2.61) |
| Iceland | 0.58 | 0.57 (−1.72) |
| Sweden | 10.47 | 10.31 (−1.53) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tiseo, K.; Huber, L.; Gilbert, M.; Robinson, T.P.; Van Boeckel, T.P. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120918
Tiseo K, Huber L, Gilbert M, Robinson TP, Van Boeckel TP. Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(12):918. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120918
Chicago/Turabian StyleTiseo, Katie, Laura Huber, Marius Gilbert, Timothy P. Robinson, and Thomas P. Van Boeckel. 2020. "Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030" Antibiotics 9, no. 12: 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120918
APA StyleTiseo, K., Huber, L., Gilbert, M., Robinson, T. P., & Van Boeckel, T. P. (2020). Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food Animals from 2017 to 2030. Antibiotics, 9(12), 918. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120918





