Efficiency of a Tetracycline-Adjuvant Combination Against Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Tunisian Clinical Isolates
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Synthesis of Compound 3
2.2. Bacterial Strains
2.3. Susceptibility Testing
2.4. Detection of Efflux Pump Activity
2.5. MIC Determination of Doxycycline, Minocycline, and Compound 3
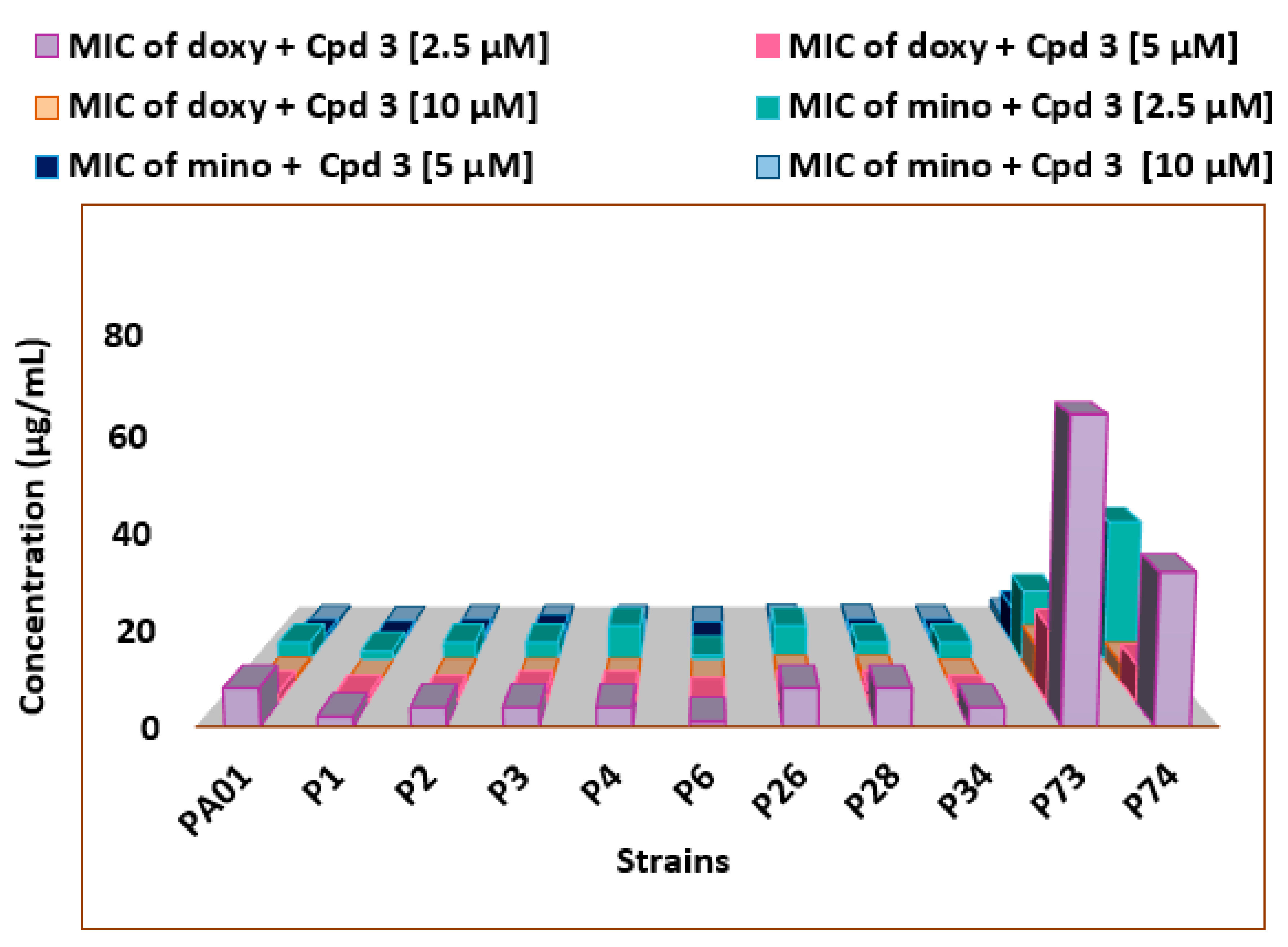
2.6. Drug–Drug Interaction Assay
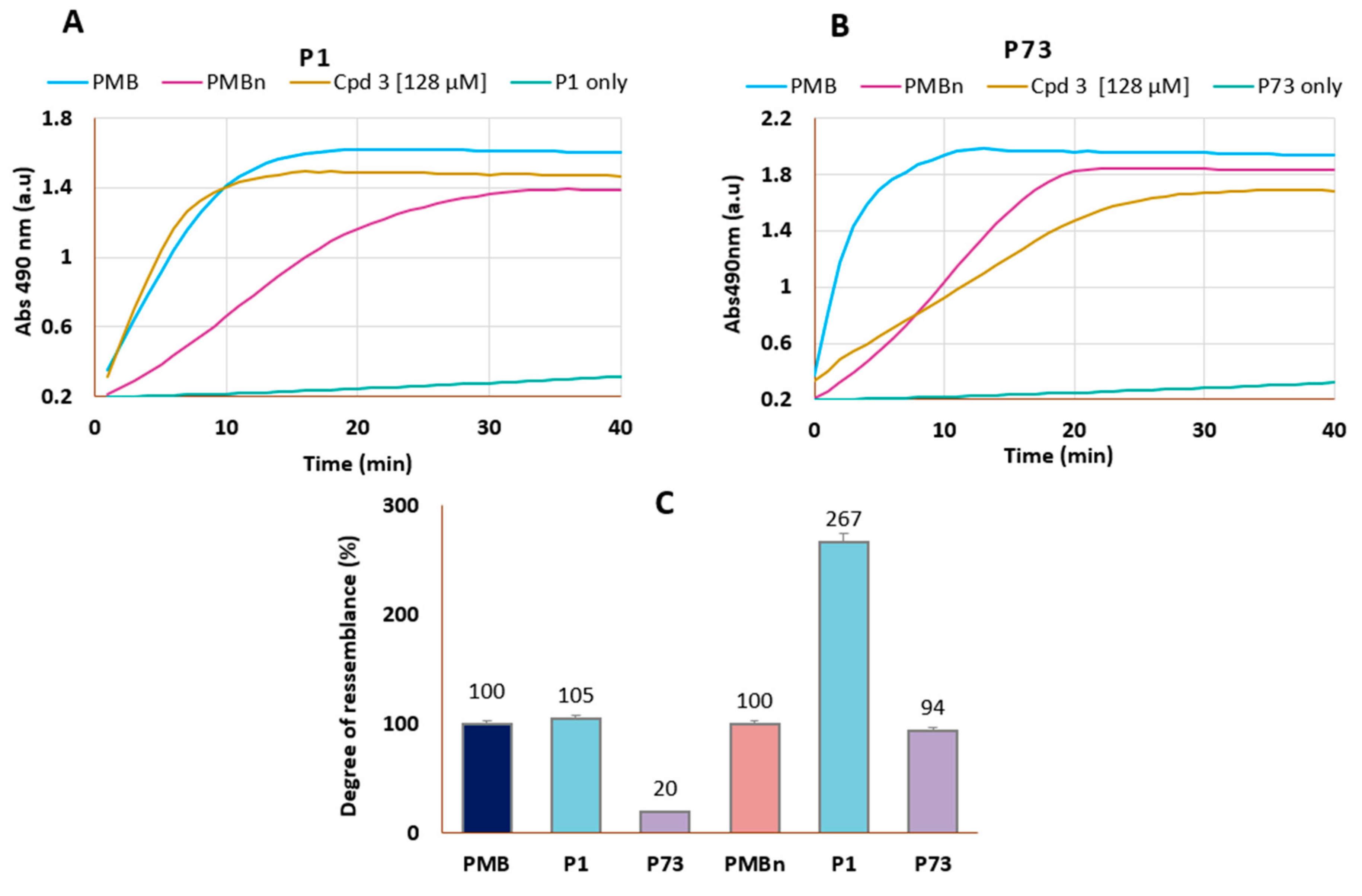
2.7. Outer Membrane Permeabilization Assay
2.8. Membrane Depolarization
2.9. Glucose-Triggered 1,2′-diNA Efflux Assays
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Synthesis of Polyaminofarnesyl Derivative 3
3.2. Characteristics of the Bacterial Strains and MIC Determination
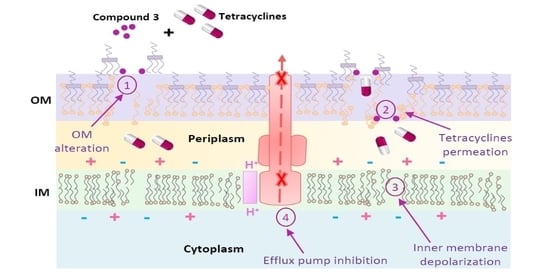
3.3. Mechanism of Action
3.3.1. Outer Membrane Permeabilization
3.3.2. Membrane Depolarization Assay
3.3.3. Glucose-Triggered 1,2′-diNA Efflux Assays
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Martínez, J.L.; Baquero, F. Emergence and spread of antibiotic resistance: Setting a parameter space. Ups. J. Med. Sci. 2014, 119, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dodds, D.R. Antibiotic resistance: A current epilogue. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 134, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aminov, R.I. The role of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance in nature. Environ. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 2970–2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saleem, M.; Nazir, M.; Ali, M.S.; Hussain, H.; Lee, Y.S.; Riaz, N.; Jabbar, A. Antimicrobial natural products: An update on future antibiotic drug candidates. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2010, 27, 238–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, S.; Hayes, D.; Wozniak, D.J. Cystic fibrosis and Pseudomonas aeruginosa: The host-microbe interface. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00138-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez, M.R.; Fleuchot, B.; Lauciello, L.; Jafari, P.; Applegate, L.A.; Raffoul, W.; Que, Y.-A.; Perron, K. Effect of human burn wound exudate on Pseudomonas aeruginosa virulence. mSphere 2016, 1, e00111–e00115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migiyama, Y.; Yanagihara, K.; Kaku, N.; Harada, Y.; Yamada, K.; Nagaoka, K.; Morinaga, Y.; Akamatsu, N.; Matsuda, J.; Izumikawa, K.; et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa bacteremia among immunocompetent and immunocompromised patients: Relation to initial antibiotic therapy and survival. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 69, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedfi, M.; Khouni, H.; Massoudi, Y.; Abdelhedi, C.; Sassi, K.; Chouchen, A. Epidemiology of nosocomial infections: About 70 cases. La Tunis. Med. 2016, 94, 401–406. [Google Scholar]
- Strateva, T.; Yordanov, D. Pseudomonas aeruginosa—A phenomenon of bacterial resistance. J. Med. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventola, C.L. The Antibiotic Resistance Crisis. Pharm. Ther. 2015, 40, 277–283. [Google Scholar]
- Davies, J.; Davies, D. Origins and Evolution of Antibiotic Resistance. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2010, 74, 417–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, K.G.; Snelling, A.M. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: A formidable and ever-present adversary. J. Hosp. Infect. 2009, 73, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chairat, S.; Ben Yahia, H.; Rojo-Bezares, B.; Sáenz, Y.; Torres, C.; Ben Slama, K. High prevalence of imipenem-resistant and metallo-beta-lactamase-producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa in the Burns Hospital in Tunisia: Detection of a novel class 1 integron. J. Chemother. 2019, 31, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reboud, E.; Basso, P.; Maillard, A.P.; Huber, P.; Attrée, I. Exolysin shapes the virulence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa clonal outliers. Toxins 2017, 9, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, P.H.; Tetu, S.G.; Larouche, A.; Elbourne, L.; Tremblay, S.; Ren, Q.; Dodson, R.; Harkins, D.; Shay, R.; Watkins, K. Complete genome sequence of the multiresistant taxonomic outlier Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA7. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojo-Bezares, B.; Cavalié, L.; Dubois, D.; Oswald, E.; Torres, C.; Sáenz, Y. Characterization of carbapenem resistance mechanisms and integrons in Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains from blood samples in a French hospital. J. Med. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee, S.A. Comité de l’Antibiogramme de la Société Française de Microbiologie report 2003. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2003, 21, 364–391. [Google Scholar]
- Andrews, J.M. Determination of minimum inhibitory concentrations. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2001, 48, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, M.; Borselli, D.; Rodallec, A.; Peiretti, F.; Vidal, N.; Bolla, J.-M.; Digiorgio, C.; Morrison, K.; Wuest, W.; Brunel, J.M. Claramines: A new class of broad-spectrum antimicrobial agents with bimodal activity. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 1018–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghavami, A.; Labbé, G.; Brem, J.; Goodfellow, V.J.; Marrone, L.; Tanner, C.A.; King, D.T.; Lam, M.; Strynadka, N.C.J.; Pillai, D.R.; et al. Assay for drug discovery: Synthesis and testing of nitrocefin analogues for use as β-lactamase substrates. Anal. Biochem. 2015, 486, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shannon, K.; Phillips, I. β-Lactamase detection by three simple methods: Intralactam, nitrocefin and acidimetric. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 1980, 6, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azeez, Q.; Sajjad-ur-Rahman, U.W.; Ismail, M.; Ali, R.; Ali, T. Application of Nitrocefin Test for the Direct Detection of Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus aureus from Bovine Mastitis Milk Samples. Life 2012, 11, 96–101. [Google Scholar]
- Lakaye, B.; Dubus, A.; Joris, B.; Frère, J.-M. Method for estimation of low outer membrane permeability to β-lactam antibiotics. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2002, 46, 2901–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Holmes-Davis, R.; Rafinski, Z.; Jedrzejewska, B.; Choi, K.; Zwick, M.; Bupp, C.; Izmailov, A.; Paczkowski, J.; Warner, B. Accelerated photobleaching of a cyanine dye in the presence of a ternary target DNA, PNA probe, dye catalytic complex: A molecular diagnostic. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 2043–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borselli, D.; Lieutaud, A.; Thefenne, H.; Garnotel, E.; Pagès, J.-M.; Brunel, J.M.; Bolla, J.-M. Polyamino-isoprenic derivatives block intrinsic resistance of P. aeruginosa to doxycycline and chloramphenicol in vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, A.; Mulet, X.; López-Causapé, C.; Juan, C. The increasing threat of Pseudomonas aeruginosa high-risk clones. Drug Resist. Updates 2015, 21, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maatallah, M.; Cheriaa, J.; Backhrouf, A.; Iversen, A.; Grundmann, H.; Do, T.; Lanotte, P.; Mastouri, M.; Elghmati, M.S.; Rojo, F. Population structure of Pseudomonas aeruginosa from five Mediterranean countries: Evidence for frequent recombination and epidemic occurrence of CC235. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e25617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieutaud, A.; Guinoiseau, E.; Lorenzi, V.; Giuliani, M.; Lome, V.; Brunel, J.; Luciani, A.; Casanova, J.; Berti, L.; Bolla, J. Inhibitors of antibiotic efflux by AcrAB-TolC in Enterobacter aerogenes. Anti-Infect. Agents 2013, 11, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borselli, D.; Brunel, J.M.; Gorgé, O.; Bolla, J.M. Polyamino-isoprenyl derivatives as antibiotic adjuvants and motility inhibitors for Bordetella bronchiseptica porcine pulmonary infection treatment. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lôme, V.; Brunel, J.-M.; Bolla, J.-M. Multiparametric profiling for identification of chemosensitizers against Gram-negative bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchet, M.; Borselli, D.; Brunel, J.M. Polyamine derivatives: A revival of an old neglected scaffold to fight resistant Gram-negative bacteria? Future Med. Chem. 2016, 8, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevalier, J.; Bredin, J.; Mahamoud, A.; Malléa, M.; Barbe, J.; Pagès, J.-M. Inhibitors of antibiotic efflux in resistant Enterobacter aerogenes and Klebsiella pneumoniae strains. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1043–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lieutaud, A.; Pieri, C.; Bolla, J.M.; Brunel, J.M. New Polyaminoisoprenyl Antibiotics Enhancers against Two Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria from Enterobacter and Salmonella Species. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 10496–10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


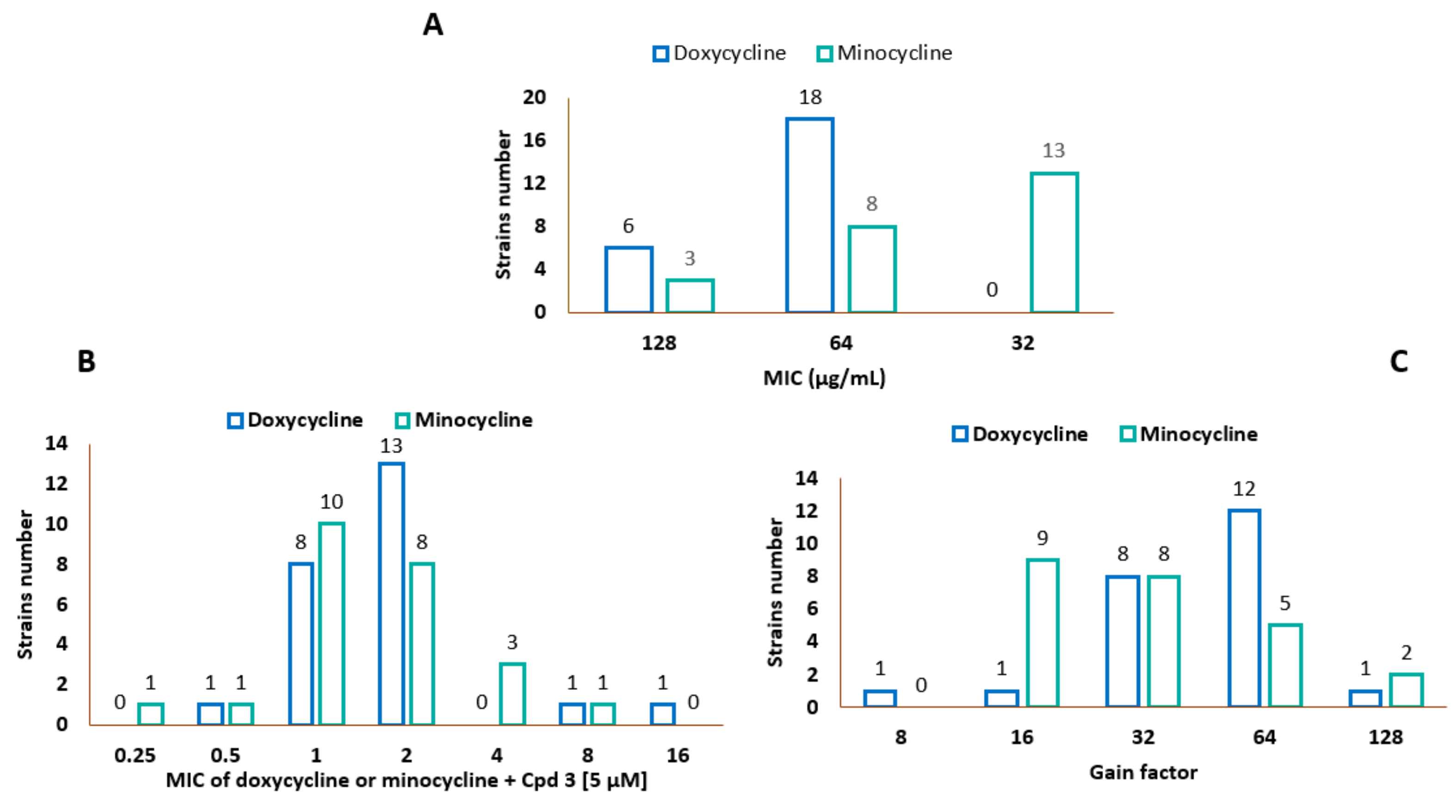


| Entry | Strains | MIC of Doxycycline (μg/mL) | MIC of Minocycline (μg/mL) | MIC of Compound 3 (µg/mL) (μM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PA01 | 64 | 32 | 10 (25) |
| 2 | P1 | 64 | 32 | 10 (25) |
| 3 | P2 | 64 | 32 | 10 (25) |
| 4 | P3 | 64 | 32 | 10 (25) |
| 5 | P4 | 64 | 32 | 10 (25) |
| 6 | P6 | 64 | 32 | 5 (12.5) |
| 7 | P26 | 128 | 128 | 10 (25) |
| 8 | P28 | 64 | 64 | 10 (25) |
| 9 | P29 | 64 | 64 | 10 (25) |
| 10 | P34 | 64 | 64 | 10 (25) |
| 11 | P73 | 128 | 128 | 10 (25) |
| 12 | P74 | 128 | 64 | 20 (50) |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Troudi, A.; Fethi, M.; Selim El Asli, M.; Bolla, J.M.; Klibi, N.; Brunel, J.M. Efficiency of a Tetracycline-Adjuvant Combination Against Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Tunisian Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120919
Troudi A, Fethi M, Selim El Asli M, Bolla JM, Klibi N, Brunel JM. Efficiency of a Tetracycline-Adjuvant Combination Against Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Tunisian Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics. 2020; 9(12):919. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120919
Chicago/Turabian StyleTroudi, Azza, Meha Fethi, Mohamed Selim El Asli, Jean Michel Bolla, Naouel Klibi, and Jean Michel Brunel. 2020. "Efficiency of a Tetracycline-Adjuvant Combination Against Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Tunisian Clinical Isolates" Antibiotics 9, no. 12: 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120919
APA StyleTroudi, A., Fethi, M., Selim El Asli, M., Bolla, J. M., Klibi, N., & Brunel, J. M. (2020). Efficiency of a Tetracycline-Adjuvant Combination Against Multidrug Resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa Tunisian Clinical Isolates. Antibiotics, 9(12), 919. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics9120919